
Innovative Development of Regions under the Modern Conditions
I. U. Shahgiraev
1a
, A. K. Dikinov
2b
and R. B. Khapsaeva
3c
1
Chechen State University, Grozny, Russia
2
Kabardino-Balkarian State University named after H.M. Berbekov, Nalchik, Russia
3
North Ossetian State University named after Kosta Levanovich Khetagurov Vladikavkaz, Russia
Keywords: Region, Sustainable Development, Innovative Potential, Economic Growth, Modern Society.
Abstract: The problem of sustainable growth of the country is one of the major tasks under modern conditions. Studying
the results and trends in the socio-economic development of Russia and its regions allows tracing the
efficiency of the state management programs, planning the measures for putting the economy on a growth
path, and developing further solutions for effective management. Identification of patterns and trends in
development encourages the increase of the probability of further development prediction and allows making
timely adjustments to the strategic plans of the state and regions. This, in turn, contributes to more accurate
resources planning, the organization of clear institutional interaction in the economic space of the country.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the modern economy, the role of regions as
subjects of economic activity is increasing, since the
problems, the solution of which will allow the
transition to the sustainable development of the entire
country, are solved exactly at the regional level.
The ability of regions to withstand external threats
depends directly on the achieved level of socio-
economic development of the territory. The key
problem is that the development of the regions of
Russia today is characterized by a rather strong
differentiation of the territories in terms of economic
development, which forms the presence of additional
threats to stability.
To ensure the sustainable development of modern
society, a transition to an innovative model of
economic growth is necessary. This will require an
annual increase in investment in the innovation
sphere, significant costs for fundamental and applied
research and the development of new technologies.
All this causes the creation of an effective mechanism
for financial support of innovative activities based on
the attraction of public and private financial
resources.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6644-9519
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7560-0340
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0245-4992
2 METHODOLOGY
For many decades, the problem of sustainable
development has remained relevant for the world
community. The most important factor ensuring the
sustainable development of the world economy is
innovation. In the developed countries of the world
the results of innovative activities make up a
significant part of the gross domestic product (GDP)
growth, and the volume of investments in the
innovation sphere is increasing annually. Innovation
is one of the main national priorities for the leading
economies of the modern world.
The development of the innovative activity, both
in Russia and in any other country, is determined by
the forms of its organization and depends directly on
the level of funding. The transition of the domestic
economy to an innovative model of economic
development is impossible without an increase of
investment in the innovation sector, costs for research
and development, as well as making an effective
national system for new technologies financing,
which ensures large private capital raising to this
sector.
This problem is especially relevant for Russian
regions with a scarce natural resource base, limited
186
Shahgiraev, I., Dikinov, A. and Khapsaeva, R.
Innovative Development of Regions under the Modern Conditions.
DOI: 10.5220/0010665900003223
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Forum on Sustainable Development of Socio-economic Systems (WFSDS 2021), pages 186-190
ISBN: 978-989-758-597-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

export potential and relatively low investment
attractiveness. One of the options for solving the
problem of transition to a new quality of economic
growth for the regions can be scientific knowledge,
an increase in fundamental and applied research, the
efficiency of practical implementation of innovations
in production and the social sphere. This requires the
creation of an effective mechanism for financial
support of innovative activities, which would allow
accumulating the requisite capital for the
implementation of regional programs of scientific and
innovative development based on cooperation of the
potential of territorial authorities, research
organizations, business and financial structures under
the conditions of limited financial resources in the
region.
The development of innovative infrastructure
ensures the growth of innovative activity of economic
entities of the regional economy.
Most of the country's technological, innovative,
intellectual and production potential is concentrated
in the regions. Therefore, it is extremely important to
pursue a policy aimed at ensuring national
modernization and sustainable development of the
regions for the effective functioning of the economic
activity of the country.
The increase in the rates of economic
development will facilitate the increase in the
innovation activity of the region, an improvement in
the situation with its financial support, since it is the
gross regional product growth that will expand the
potential for attracting additional budgetary and
extra-budgetary sources to the innovation process.
In recent years, innovations have had a great
influence on the development of the socio-economic
sphere of the region. Their introduction into all
spheres of human activity provides the regions with
the formation of sustainable development, which is
based on innovative technologies and the innovative
potential of the territory. Innovation is, first of all, a
factor of economic development, since the
development of innovative technologies, their
introduction into production, the release of previously
unknown types of products determine the prospects
for long-term economic growth, and are also a
solution to many socio-economic problems. The
factors of innovative development are the structural
elements of the regional economy.
The innovative potential of the region is a
combination of financial, material, scientific and
technical resources that are used in the realization of
activities in economic development. To implement
competently the innovation policy and form the
sustainable development of the region, the country
needs to assess the effectiveness of the use of
innovative potential. It consists of the following
elements: infrastructure, financial, labor, information,
technological resources, and their practical
application. The Kaluga Region is characterized by
the implementation of innovative potential through
the production of high-tech goods and services,
improving the quality of education, up-grading the
qualifications of researchers and creating new jobs for
them, increasing the share of innovative investment
and financing in the region not only from investors
but also from the country.
Realization of the concept of sustainable
development, in particular, at the regional level, is an
important condition for the progress of territories,
countries and all of humanity, which is confirmed by
the serious attention of authoritative international
organizations, subjects of public authorities and
administration, scientists and practitioners.
Under modern conditions, the development of
industry and the national economy as a whole largely
depends on the inflow of foreign capital. Therefore, it
is necessary to create favorable conditions for foreign
investments, but at the same time, of course, to ensure
constant government control over their quality and
reliability.
To solve the mentioned strategic tasks, the top-
priority tactical goals are as follows: reducing the tax
burden imposed on innovative enterprises,
implementing a policy of protectionism in the field of
new technologies, developing innovative
infrastructure, supporting venture capital funding of
innovative projects, supporting the export of high-
tech products abroad, defining the list and
implementation mechanism of the main innovative
state projects for the next few years, the formation of
favorable conditions for the development of small
innovative business activity, comprehensive support
for innovation-oriented enterprises, facilitation of the
procedure for official registration of enterprises and
organizations engaged in scientific and technical
innovation. The implementation of these and other
measures should sharply increase the stability and
competitiveness of the regional economy as a whole
and ensure the dynamic social development of the
region and the economic security of the country.
The development of a regional strategy is largely
based on the analysis of factors of the external and
internal environment, in particular, resource
potential, territorial geographic, geopolitical,
economic and socio-cultural features, competitive
advantages, risks, bottlenecks and restrictions. The
restrictions that need to be considered in its formation
and assessment can be very diverse and include, in
Innovative Development of Regions under the Modern Conditions
187

particular, limiting factors of a natural-geographical
and geopolitical nature as well as resource,
infrastructural, institutional, financial-economic,
demographic nature. They affect the potential and
opportunities for the development of the territory
mainly negatively, although in some cases, there is a
reverse effect due to the compensatory policy when
the limitations of some factors stimulate additional
opportunities for return from other ones.
3 RESULTS
According to the forecast of the Ministry of
Economic Development of the Russian Federation for
2019-2020, economic growth was predicted only
from 2021 up to 3.1-3.3% (Shardan et al., 2020),
considering the implementation of economic
digitalization programs, improving the business
climate in the country, reducing administrative
business barriers, etc. According to the Concept, real
GDP growth was planned in 2020 by 64-66%
compared to 2012. In reality, this did not happen: for
the period from 2013 to 2019 it grew only by 5.8%.
The same situation has arisen in actual revenues:
according to the forecast an increase of 64-72% was
expected; actually, starting from 2014 to the 3rd
quarter of 2019, household incomes began to decline
and the overall decrease was 5%. At the same time,
according to other economic indicators, the dynamics
was negative. In 2019, GDP growth amounted to
1.3% with positive dynamics in the industrial sector,
construction, and retail trading. The volume of
investments in fixed assets has also grown. But in
2019, the growth rate of the economy in these sectors
was below the level of 2018. At the end of 2019, the
Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian
Federation predicted the growth of the domestic
economy in 2020 by 1.7%; in fact, it decreased by
3.1% ($ 226 billion).
The reasons for the drop in the GDP in 2020 are
not only a pandemic, the introduction of quarantine
restrictions, a decrease in employment, business
economic and consumer activity, a decrease in the
labor force and demand for labor, but also a
significant decline in demand for oil, a reduction was
3.1% at the end of the year. The nominal volume of
GDP in this year amounted to 106.6 trillion rubles.
The government took large-scale and targeted
measures to adapt the business to the new working
conditions, anti-crisis management, employment
restoration, increase of unemployment payment
(from 4.5 to 12.1 thousand rubles), incomes of the
population, and direct targeted payments to the
population, the creation of a social treasury for social
support for the population, which made it possible in
a certain way to soften the “blows” to the economy.
Economic growth in the future is planned to be
ensured through accelerated technological
development, growth in labor productivity and
digitalization.
Failure of the strategic goals outlined in the
Concept is not the result of adopting an optimistic
forecast but is caused by the influence of the world
economic and internal problems of the country. At the
same time, some goals were retained for a longer
period, but adjusted to consider new scientific and
statistical studies, real events. So, a sustainable
increase of the income of the population and the
reduction of unemployment (no more than 5%) is
planned already for 2021.
Medium-term trends in the socio-economic
development of Russia are forecasted on the
assumption that a decrease in the rate of world
economic growth, the persistence of international
trade contradictions, a slowdown in aggregate
demand, a decrease in business activity, and a
deterioration of the global investment climate are
expected.
It is predicted that the measures of a unified plan
to achieve the national development goals of Russia
until 2024, which was approved by the Chairman of
the Government of the Russian Federation dated
07.05.2019 No. 4043p-P13, should ensure the growth
of the production potential of the domestic economy,
its orientation towards the investment model of
development, sustainable balanced growth, which, in
turn, will lead to an increase in investment in fixed
assets, an increase in the competitiveness of the
domestic economy, the efficiency of the public sector,
the development of science and research activities, an
increase in labor productivity, an increase in real cash
earnings and a decline in unemployment. The growth
of industrial production, construction, agro-industrial
complex and manufacturing industry is forecasted for
this period.
Prospective tasks of the country's socio-economic
development in the medium-term are to ensure the
sustainable balanced economic growth, transition to
an innovative development model and in the
formation of an appropriate infrastructure and a new
social policy.
In the context of the geopolitical situation of the
recent years, an increasingly prominent place among
the restrictions is taken by international restrictive
measures, associated, in particular, with political
confrontations, trade wars, global competition and
attempts to redistribute markets and create a
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
188
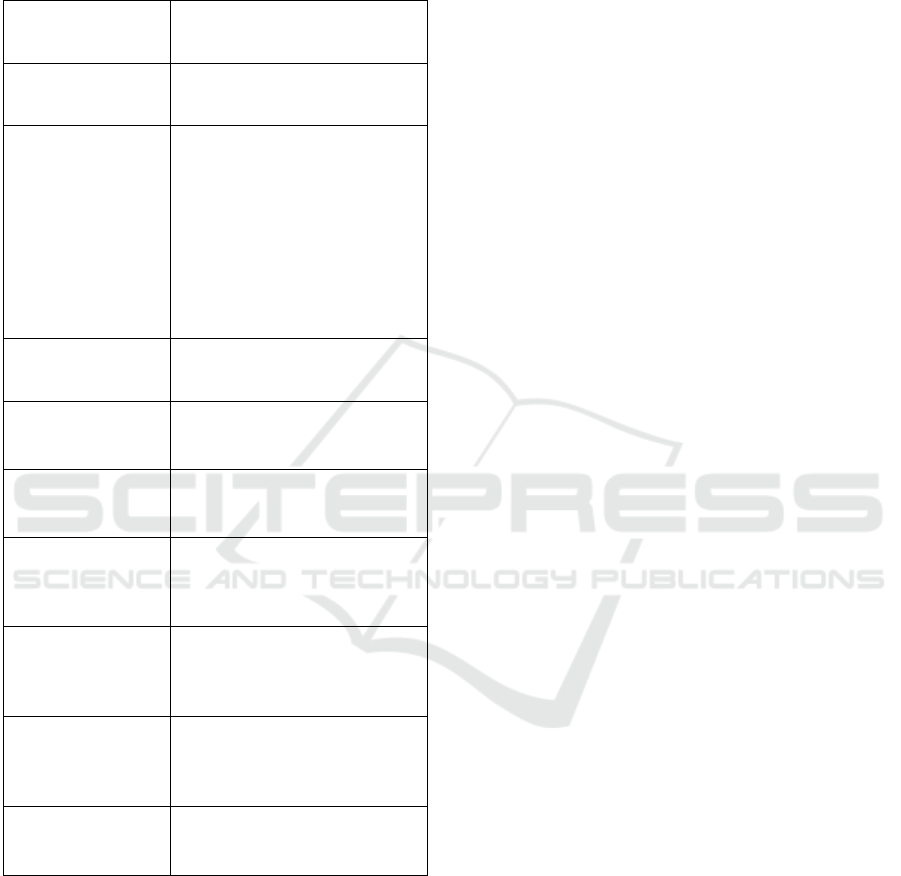
multipolar economic world order. Table 1 gives a
classification of limiting factors.
Table 1: Classification of limiting factors of the regional
development.
Criterion of
classification
Type of limiting factors
Origin
External
Internal
Character
Natural (geographic,
demographic, environmental)
Sociocultural
Political
Economic (resource,
infrastructural, innovation and
technological, structural and
industrial, production and
technical, foreign economic)
Institutional
Exposure time
Temporary
Permanent
Nature of origin
Immanent
Historically established
Situationall
y
-
b
ehavioural
The degree of
strategizing
measures influence
Controlled
Uncontrolled
The ability of
negative impact
compensation due to
othe
r
factors
Compensable
Non-recompensable
Level of influence
on development
opportunities
High level of influence
Mean level of influence
Low level of influence
Level of potential
risk
High level of risk
Mean level
Low level
The presence of
analogues in the
worl
d
p
ractice
Having analogues
Not having analogues
Economic sanctions include restrictive measures
of the influence of an economic nature introduced by
one state or a group of states concerning a certain
country/territory to force it to change its political
course (Dzobelova and Olisaeva, 2018). Such
sanctions have a long history and can have various
nature, although trade and financial measures are
most often mentioned in the literature. The main
difference between sanctions and trade restrictions of
a protectionist nature is the presence of a political
component as a cause of economic pressure on the
country - the object of influence - for the purpose of
“punishment”, forcing to terminate or prevent certain
actions, including military ones, demonstrations of
resolve and strength, attempts to undermine the
internal political regime, enforcement to change
course. There are many examples of economic
sanctions starting from the ancient world to modern
history; we can mention, for example, such well-
known cases as the United States embargo against
Cuba, the US, EU and G7 sanctions against Iran due
to the Iran-Iraq war and Iran`s nuclear program,
sanctions against the Soviet Union due to restrictions
on the emigration of Soviet citizens imposed since
1974 under the Jackson-Vanik amendment to the US
Trade Law, sanctions against the regimes of Fidel
Castro, Salvador Allende, Saddam Hussein, Josip
Broz (“Tito”) and other politically high-profile
situations of using economic measures of pressure. In
addition to economic sanctions, there are instruments
of political influence that imply non-recognition or
incomplete recognition of countries and territories, as
a result of which they exist as subjects with an
uncertain political status and do not have full rights in
the foreign political arena and the global economic
world order. The examples are the Turkish Republic
of Northern Cyprus, which has existed since 1975 and
has not yet been recognized by any country in the
world, except Turkey, the partially recognized
Republic of Kosovo, the Donetsk People's Republic
and others. In such cases, political isolation brings on
economic measures that impede the full functioning
of the country or region.
Having originally an economic nature of the
influence, sanctions have not only economic but also
social consequences, which affects the quality of life
of the population and significantly hinders the
achievement of those goals of sustainable
development that underlie modern regional
strategizing.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The Russian economy is currently ranked 6
th
in the
world. In terms of GDP, the country takes 11
th
place
in the world ranking, and 50
th
in terms of GDP per
capita. Over the last decade, there have been changes
in the country, but in general, this period is
characterized by the development of the country's
economy. The exception is 2015, the negative results
of which are not only a consequence of the imposition
of sanctions against Russia in connection with the
confrontation with Ukraine but also the consequence
Innovative Development of Regions under the Modern Conditions
189

of the global economic crisis. Today, the most
problematic indicators are inflation, growth in public
debt, demographic development and unemployment.
Differentiation and uneven development are
observed across the regions of the country. Among
the positive results of 2019, one can name a gradual
reduction in the gap in the level of socio-economic
development of the leading regions and outsider
regions of the rating.
Fundamental transformations are taking place in
the world economy, global politics, social life,
technology development, which will subsequently
influence the socio-economic situation of the country
and its regions. Constant waves of crises in recent
decades have made it possible to develop certain anti-
crisis management measures. Given that the
government has recently switched to operational
monitoring and management and a quick response to
emerging problems, the undertaken measures are
impossible to be planned precisely. At the same time,
existing and potential threats, positive trends make it
possible to predict the socio-economic situation.
Many trends in the socio-economic development of
the country and regions that have emerged in recent
years have been broken by quarantine restrictions due
to the coronavirus pandemic and economic recession.
The pandemic has intensified the existing problems in
the regions. The old instruments of economic policy
often do not work in the current realities. The way out
for development and economic growth is the growth
of development and implementation of innovative
technologies, digitalization, and the solution of
international problems.
Important components of the strategic
management system for the sustainable development
of the region in the context of sanctions and
restrictions are the following: definition of the
mission and vision of the region in the national and
world system, taking into account geographical,
natural, historical, cultural, ethnic, economic and
socio-humanitarian characteristics, appropriate
positioning and definition of key goals of the
sustainable development of the region; carrying out
of strategic analysis taking into account
environmental factors, including limiting factors and
sanctions, assessment of the degree of their influence,
risk, compensatory measures and corresponding
development drivers; flexible adjustment of goals;
formation of goals and tasks for sustainable
development of the region, considering the restrictive
factors based on a scenario approach and a proactive
management model, selection and coordination of a
system of criteria and indicators that allow
monitoring their achievement; determination of the
target image of the region based on an assessment of
its vision by different groups of stakeholders in the
context of the restrictive measures (the world
community, geopolitical allies, economic partners,
adjacent territories, participants of markets,
population, business, government institutions, civil
society institutions and others); formation of a system
for monitoring indicators of sustainable socio-
economic development, operational research and
control of deviations in order to adjust activities based
on taking into account the responsibility of the
relevant institutions and structures for ensuring the
achievement of target indicators; the formation of an
informational and analytical environment that
ensures the management of the region and the
information transparency of society for all
stakeholders, which is a resource that maintains
reputation capital and “advertises” the territory
through its presence in the global information space
and the formation of trust on the part of society,
business and the political establishment, both outside
and within the region.
REFERENCES
Dzobelova, V.B. (2018). New Ways of Qualified Staff
Training by the Example of the Republic of North
Ossetia-Alania, PTES 2018, pages 23-28.
Dzobelova, V.B. and Olisaeva, A.V. (2018). Staffing Needs
in the Regional Economy under the Modern Conditions
of Labor Market, PTES 2018, pages 185-188.
Dzobelova, V.B. and Olisaeva, A.V. (2018). Analysis of
innovative development of the NCFD regions in
Russia, IDIMT 2018, pages 473-479.
Semenova, L., Dzobelova, V., and Yablochnikov, S.
(2019). Practical application analysis of information
and communication technologies in the socio-economic
sphere, ACM International Conference Proceeding
Series, pages 80-85.
Shardan, S.K., Kolesnik, V.S., Amadaev, A.A., Dzobelova,
V.B., and Bakhova, Ya.S. (2020). Corporate social
responsibility of companies as a factor in sustainable
development of regions, AD ALTA: Journal of
Interdisciplinary Research, 10(2), S12: 31-34.
Sharopatova, A.V., Dzobelova, V.B., Olisaeva, A.V., and
Parshukov, D.V. (2020). Economy of russian regions in
the context of the coronavirus epidemic, III
International Scientific Conference: AGRITECH-III-
2020: 22103.
Yablochnikov, V., Olisaeva, A., Dzobelova, S.,
Cherkasova, O., and Davletbayeva, N. (2019).
Formation and development of the digital economy in
modern conditions - Development within the
framework of industry 4.0, IDIMT 2019, pages 83-88.
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
190
