
Demographic Issues as a Condition for the Regions Sustainable
Development (on the Example of the Irkutsk Region)
O. B. Istomina
1a
, Yu. R. Gerasimova
2b
and M. K. Gaiday
3c
1
Irkut State University, Irkutsk, Russia
2
Irkut National Research Technical University, Irkutsk, Russia
3
East Siberian Institute of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, Irkutsk, Russia
Keywords: Russian Region, Demographic Structure, Migration, Population Movement, Quality of Life, Life Expectancy,
Sustainable Development.
Abstract: The authors analyze the state, forms, demographic structure dynamics factors and their role in the regions
sustainable development program. The article justifies the viewpoint on the demographic indicators and the
region socio-economic situation interdependence. The data from statistical agencies on the natural and
migration decline of the population are analyzed. As determinants of transformations of the Irkutsk region
quantitative and qualitative population characteristics, the authors identify destructive changes in the quality
of life of the population in the region, a decrease in the human development index, a steady decline in
population real incomes and, in this regard, the persistence of trends in subsidizing the poor, an increase in
the volume of this stratum in the social structure, the entrenchment of negative trends in short life expectancy
and problems with providing medical services, as well as environmental threats. In the article, the authors
substantiate the demand for serious long-term socially-oriented measures for the peripheral northern territories
development, the population preservation and multiplication, improving the quality of life to ensure the
effectiveness of sustainable development programs measures, as well as the integrity of the state borders and
the elimination of socio-economic and stratification disunity of the Russian regions.
1 INTRODUCTION
The choice of the research topic is caused by the
significant changes in the demographic structure in
many regions of modern Russian society. The Irkutsk
region is a prime example of the transformations that
are typical for the entire Siberian Federal District. The
dynamic state is characterized by a number of
polyvariant forms and social expressions from mass
migration to the central part of the country and the
northern territories "emptying" to changes in the
ethno-national structure in the studied region,
changes in the gender and age pyramid and a decrease
in the total birth rate. The situation with the
population composition negative dynamics caused by
both natural causes (the health level, the population
life expectancy, an emergency situation for a number
of diseases, including cancer and HIV) and unnatural
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4060-6106
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1816-173Х
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1428-7319
factors in a socio-economic nature (economic
unattractiveness, a decrease in real incomes, an
increase in labor migration to the central and southern
regions of Russia) raises concerns. The destructive
nature of stable trends in the region demographic
indicators transformation significantly actualizes the
designated topic, which determined the object,
purpose and methods of this study.
The object of the study is the state, forms, factors
of the demographic structure transformation and its
role in the modern region development (based on the
materials from the Irkutsk region).
The purpose of the study is to determine the
Irkutsk region demographic structure current state, to
identify its transformation factors, to analyze the
demographic characteristics of 2000-2021, to identify
the dynamics forms and social forecasts in relation to
Istomina, O., Gerasimova, Y. and Gaiday, M.
Demographic Issues as a Condition for the Regions Sustainable Development (on the Example of the Irkutsk Region).
DOI: 10.5220/0010667400003223
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Forum on Sustainable Development of Socio-economic Systems (WFSDS 2021), pages 287-292
ISBN: 978-989-758-597-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
287
changes in the demographic indicators of the region
typical for the Siberian Federal District.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In the paper the authors conducted a secondary
analysis of the results of surveys conducted by the
All-Russian Center for Public Opinion Research, the
Federal State Statistics Service statistical data, the
Federal State Statistics Service for the Irkutsk Region
territorial body, as well as the research materials of
Irkutsk public organizations aimed at determining the
population quality of life and at solving the Baikal
Region demographic structure dynamics problems.
The Russian regions demographic analysis are
characterized components are characterized
according to the data from the National Demographic
Report - 2020 (Ryazancev, Arhangel'skij and
Vorob'eva, 2020) and the census periods of 2002-
2010 results.
The article summarizes the experience of foreign
and domestic researchers to determine the conceptual
positions, among them are: J. Olaguibe, D. López-
Hernández, A.Yu. Chang, V.F. Skirbekk, S.
Tirovoras, S. Kassebaum, Dzh. L. Dil'man, V.N.
Barsukov, O.N. Kalachikova, N.А. Khvylya-Olinter,
O.V. Arakcheeva, I.Yu. Krivdina, S.V. Ryazantsev,
V.N. Arkhangel'sky, O.D. Vorob'eva, O.L.
Rybakovsky, O.A. Tayunova, V.G. Dobrokhleb etc.
(Olaguibe; and López-Hernández, 2021; Chang,
Skirbekk, Tirovoras, Kassebaum and Dil'man Dzh,
2019 Arakcheeva and Krivdina, 2020; Ryazancev,
Arhangel'skij and Vorob'eva, 2020; Dobrohleb, 2020;
Vinokurov and Suhodolov, 2009).
3 RESEARCH RESULTS
The natural and migration decrease of the population
in Eastern Siberia is accompanied by a number of
destructive socio-economic processes, including an
increase in the demographic burden, an aging
population, an increase in the decile coefficient and a
decrease in the quality of life, an increase in ammount
of depressed people against the background of a
decrease in the population real incomes and an
increase in social disadvantage in the region, a
decrease in the human development index. So,
according to the regional Statistics Committee, in the
third quarter of 2020, 92,478 people lived in families
receiving subsidies, which is 7% of the total number
of families. The share of the population with
monetary incomes below the subsistence minimum is
still significant. Today, 17.6% of the total population
receives subsidies to meet the vital order minimum
needs.
These processes indicate the expected objectivity
and the regularity of destructive changes in the
demographic structure of Eastern Siberia in general
and the Irkutsk Region in particular. The negative
processes that have emerged since the late 1990s have
taken root and are showing expansion tendencies. So,
for example, the region population since 1995 has
decreased by 373,052 people (from 2,748,073 people
in 1995 to 2,375,021 people on 01/01/2021). The
current population figures are comparable to those of
the 1970. The natural population decrease in January-
March 2021 was 2,819 people (9,259 deaths for 6,440
births were registered) (Demograficheskie pokazateli
Irkutskoj oblasti, 2020). Due to the new infectious
disease Covid-19, 2,280 deaths were recorded with
66,843 cases of infection as at 05/05/2021. The
number of migrants arriving today does not
compensate the population natural loss. Since the
beginning of this year, the population decrease has
amounted to 647 people (11,691 arrivals account for
12,338 departures) (Ryazancev, Arhangel'skij and
Vorob'eva, 2020) It should be noted that the decrease
in the population in the region is correlated with
losses within the whole state.
The types of migration and its balance in the
Irkutsk Region have been stable since the late 1990s.
There is a negative balance of both interregional and
international migration types (Table 1).
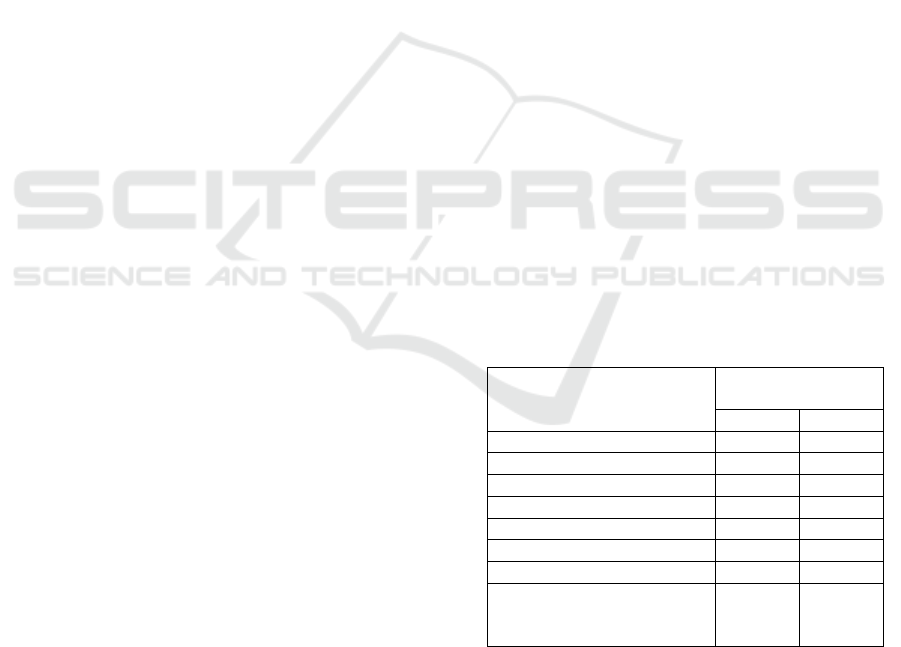
Table 1: The Irkutsk region population migration types.
Migration growth
(decrease)
2019 2020
Mi
g
ration as a whole -3,250 -7,069
Within Russia -7,426 6,753
Intrare
g
ional 0 0
Interregional -5,614 -6,753
International migration 4,151 -316
With the CIS countries 1,990 672
With other forei
g
n countries 2,161 -988
Out of the total volume –
the region external
mi
g
ration
-3,275 -7,069
These changes cause the greatest concern in the
situation with accounting the population average age
(Table 2). On his basis it is not possible to predict
natural population growth in the coming decades in
the region. The transition of the female stratum to the
age group over 40 years causes low expectations for
an increase in childbirth in the region.
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
288
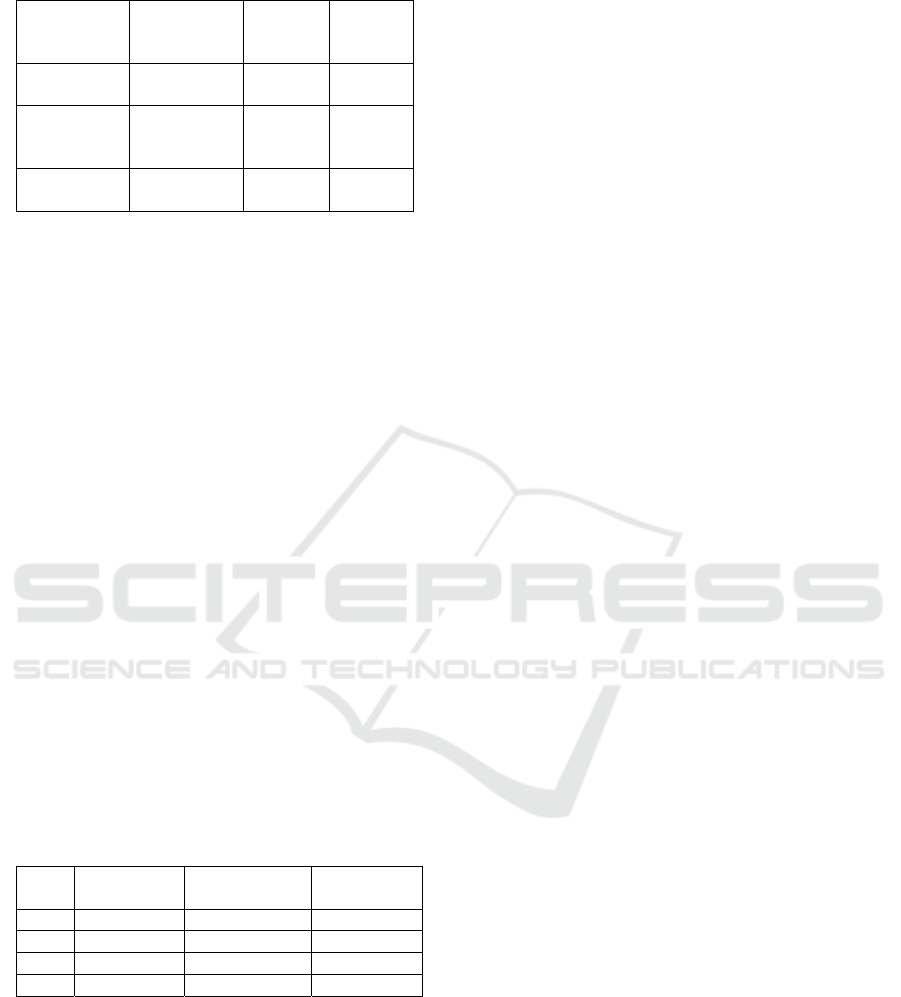
Table 2: Average population age (at the beginning of 2020).
Territory All
population
(
both sexes
)
Men
Women
Russian
Federation
40.23 37.47 42.63
Siberian
Federal
District
39.12 36.38 41.49
Irkutsk
region
37.88 34.96 40.4
Moreover, the average age indicators (only at the
initial view) can generate optimistic estimates and
forecasts, while a detailed analysis of the region
population reveals negative trends in short life
expectancy in the region, especially in the male
stratum. Life expectancy in 2021, according to the
Regional Statistics Committee information
references, will be 70.58 years (64.86 years for men,
76.3 years for women). In terms of these indicators,
the Irkutsk Region is significantly behind the average
indicators not only for Russia, the Siberian Federal
District, but also for some regions with traditionally
high life expectancy. Thus, the average population
life expectancy in the subjects of the Russian
Federation was noted at the level of 66.8 years (60.5
years for men; 73.3 years for women), on the 80th
position out of 83 subjects of the Russian Federation.
The Irkutsk Region outpaces only the Republic of
Tyva, the Chukotka Autonomous District, the Jewish
Autonomous Region (the data are given on
01/01/2016). Unfortunately, these trends persist in the
current environment. With the expected decline in the
total birth rate, the destructive vector in the dynamics
of the region demographic structure is objectively
difficult to change (Table 3).
Table 3: Total birth rate (number of children per woman).
Year Total
p
opulation
Urban
p
opulation
Rural
p
opulation
2020 1.697 1.561 2.337
2025 1.581 1.454 2.177
2030 1.641 1.509 2.260
2035 1.693 1.557 2.331
It is important to understand that the demographic
structure state is at the same time the population
quality of life indicator, the region social well-being
indicator and a factor of a region social stability and
territories preservation. With the current population
density of the region (3.07 people per km2 with an
area of 774.8 thousand km2), the Irkutsk region
occupies the 6th place out of 20 regions of Siberia,
which is 150 times less than in the Moscow region.
The settlement unevenness determines not only the
sparsely populated area, but also the weak
development of the northern regions, where
population density differs significantly (more than
100 times from the national indicators) (Vinokurov
and Suhodolov, 2009). This information is important
not only from the state internal geopolitics viewpoint,
from ensuring socio-economic balance and social
justice in different regions of the country, but also in
relation to foreign policy in the context of Western
aggression increasing and the growth in the territorial
interests of Eastern neighbors. Moreover, it is
difficult to overestimate the importance of the number
and territorial location of the population for
preserving the integrity of the state borders.
In modern realities, it is obvious that the expected
birth rate depends not only on the physiological
characteristics of the population in birth age, but to a
greater extent it depends on the region socio-
economic indicators, the quality of life level, the
social well-being indicator and the nature of the
population social expectations.
Risk factors in the region are social indicators that
determine the duration and quality of life, which
prevent the establishment of health-saving behavior
and the active longevity extension. Still some
difficulties remain in providing timely, high-quality
medical care and recreational activities. For several
decades the region has maintained a high mortality
rate from the cardiovascular system diseases,
tuberculosis (it exceeds the all-Russian indicators
twice), HIV (according to the Federal Register of
Patients, as at 01/01/2019, 28,808 people with the
immunodeficiency virus are registered in the Irkutsk
region, 82.6% of the infected people are registered,
60.4% of the dispensary group receive the therapy),
cancer (500 cases per 100,000 people, in the Baikal
region cancer is diagnosed by a thousand more cases
every year). There are still high statistics of primary
drug use and the drug addiction formation (23.7 new
cases of drug use are registered per 100,000 children
and adolescents in the region). The situation is
significantly complicated by the high level of
alcoholization among the population (despite low
incomes, the population spends significant amounts
to meet the needs of alcohol addiction, for example,
according to 2016 data, an adult resident spent 15,724
rubles on alcohol, without taking into account the
alcohol self-production and the technical alcohol-
containing liquids consumption) (Massovoe
otravlenie v Irkutske) and the growth of mass non-
communicable diseases (the morbidity threshold is
1.8 times higher than the all-Russian one due to the
Demographic Issues as a Condition for the Regions Sustainable Development (on the Example of the Irkutsk Region)
289

environmental factors harmful effects) (Press-vypusk
VCIOM). The accumulation of these destructive
processes has been exacerbated by the ill-considered
regional policy of the regional Ministry of Health
since 2018, when a massive reduction in medical
personnel (by 6,000 staff units) was carried out.
According to the experts, today the shortage in the
full-time number of medical staff is approximately
equal to 30,000 employees. The regional medical
institutions are staffed by less than 50%. Moreover,
the data need to be clarified, since during the
pandemic there were even greater losses in the
number of medical staff because of natural losses due
to infection, as well as due to migration from the
profession due to the growth of already high labor
intensity. It is obvious that these listed circumstances
significantly complicate the planned demographic
indicators implementation in the region, objectively
jeopardize the achievement of the total life
expectancy (by 2035, according to the plan in the
region – 76.78 years, 72.13 years for men, 81.23 years
for women). These processes generally have a
negative impact on the social well-being and social
reality perception, which, from an objective and
subjective points of view, contributes to the growth of
depressive moods among the region population.
4 DISCUSSION OF RESULTS
There is no doubt that the regional demographic
structure dynamics is a social phenomenon with a
complex nature, determined by the influence of a
composite of objective economic and subjective
socio-psychological factors.
The objective side of the issue traditionally
includes the population nominal and real income, life
expectancy, availability of high-quality medical care
and recreational activities, stable working conditions,
housing conditions that meet sanitary standards, the
amount of vital and cultural goods consumed, and the
safety of life and health.
The subjective, but also relevant side, are social
affiliation, full participation in public life, social well-
being, life satisfaction index, the level of population
inclusion in social relations and cultural
environments.
Despite the current socio-economic situation
disappointing statistics of the region, its territories
today are characterized by social processes of a dual
nature, including not only destruction, but also some
advantages over other Russian regions.
These advantages include the geolocation
features, the natural resources presence and diversity,
the landscape and minerals richness. But at the same
time, there are still real threats to the environmental
situation in the region. There are still unresolved
issues assessed by the modern scientific community
as eco-disasters that pose threats not only to the
region, but also to the territories of neighboring
regions and the entire State, including (these are, first
of all, man-made "traces" in Usolye-Sibirskoye,
Baikal, etc.), "frightening" indicators of the air, water,
and land pollution. The region has an extensive
production, which simultaneously "feeds" the
territory, finances an extensive structure of
educational, cultural and leisure institutions, but also
lays new environmental risks.
5 CONCLUSION
So, the dynamics of the Irkutsk region demographic
structure are influenced by many trends of the current
time. Among them, in our opinion, the most important
are:
progressing natural population decrease;
low birth rate;
the migration losses that increased during the
pandemic and the maintaining traditional
negative migration balance;
the increase in the decline of the economically
active population migrating to more prosperous
regions, as a rule, to the central part and the
southern territories of Russia;
the increase in the demographic burden and the
growth of the modern pension system financial
needs due to the aging of the region's
population and the older people stratum
expansion;
the preservation of low average life expectancy
trends (80th place out of all subjects of the
Russian Federation);
the unemployment rate, narrowness of labor
spheres in the single-industry cities of the
region (Angarsk, Usolye-Sibirskoye, Baikalsk,
Sayansk, Shelekhov, etc.);
low real incomes, most of which is spent on the
vital goods, especially in the region remote
areas;
the labor crisis and the growth of
unemployment, which led to the shadow
employment expansion in all age groups;
low per capita income;
the infrastructure development disadvantages;
small ammount of quotas for providing
affordable recreation for children and adults;
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
290

"personnel shortage" in the health care system
and the resulting medical care problems.
the insufficient recreational conditions to
ensure active longevity programs, the older
generation active social life development;
some vital environmental issues that require
government intervention and assistance.
The identified social processes have a negative
impact on the social well-being of the population.
There is no doubt that the region is in great demand
for federal support to prevent a decline in
demographic indicators and to develop the quality of
life of the population in the peripheral territories. It
seems, that long-term, logically verified (on the basis
of social forecasts) additional measures are needed on
the part of the state social protection services
(Istomina; 2013). The corrective nature of these
measures is explained by the importance of the
northern territories development. It is obvious that the
population preservation, the improvement of the
residents well-being is an indispensable condition for
the territories and State borders preservation. It also
contributes to the elimination of regional disunity in
the stratification system of modern Russian society
and it is an indispensable condition for the regions
sustainable development.
REFERENCES
A Barsukov V.N., Kalachikova O.N. (2020). The Evolution
of Demographic and Social Construction of the Age of
“Old Age”. Economic and Social Changes: Facts,
Trends, Forecast, vol. 13, 1, pages 34-55.
Olaguibe J., López-Hernández D. (2021). The Challenge of
Demographic Ageing. Contributions from the
Relationship between Work and Family. REVISTA
EMPRESA Y HUMANISMO, VOL XXVI, 1, pages 55-
78.
Arakcheeva O.V., Krivdina I.YU.(2020). Sovremennaya
demograficheskaya situaciya v Rossijskoj Federacii:
regional'nyj aspekt. Uspekhi sovremennogo
estestvoznaniya, 11, pages 39-44.
Vinokurov M. A., Suhodolov A. P. (2009). Ekonomika
Irkutskoj oblasti. Irkutsk.
Demograficheskie pokazateli Irkutskoj oblasti 2020-2021
gg.
http://irkutskstst.gks.ru (data obrashch.: 08.05.2021).
Ryazancev C. V., Arhangel'skij V.N., Vorob'eva O.D.
(2020). Demograficheskoe razvitie Rossii: tendencii,
prognozy, mery, Nacional'nyj demograficheskij doklad.
Moskva.
Dobrohleb V.G. (2020). Demograficheskoe starenie v
aspekte gendernyh problem sovremennoj Rossii.
Narodonaselenie, 2, pages 5-13.
Dolya naseleniya s denezhnymi dohodami nizhe velichiny
prozhitochnogo minimuma. http://irkutskstst.gks.ru
(data obrashch.: 08.05.2021).
CHang A.YU., Skirbekk V.F., Tirovoras S., Kassebaum S.,
Dil'man Dzh. L. (2019). Izmerenie stareniya
naseleniya: analiz issledovaniya global'nogo bremeni
boleznej 2017 goda. Lancet Public Health, 4.
Informaciya o social'no-ekonomicheskom polozhenii
Rossii. YAnvar'-mart (2021) goda. M.: Federal'naya
sluzhba gosudarstvennoj statistiki.
Irkutskaya oblast' v chisle regionov s samoj nizkoj
prodolzhitel'nost'yu zhizni. Obshchestvennaya zhizn' v
Irkutskoj oblasti (2021).https://i38.ru/obschestvo-
obichnie/irkutskaya-oblast-v-chisle-regionov-s-samoy-
nizkoy-prodolzhitelnostiu-zhizni-v-rossii (data
obrashch.: 08.05.2021).
Irkutskaya oblast' peremestilas' na tret'e mesto po
zabolevaemosti VICH v Sibiri. Obshchestvennaya
zhizn' v Irkutskoj oblasti (2021).
https://i38.ru/obschestvo-pervie/irkutskaya-oblast-
peremestilas-na-trete-mesto-po-zabolevaemosti-vich-
v-sibiri data obrashch.: 08.05.2021).
Istomina O. B. (2013). Sovremennye tendencii razvitiya
pensionnoj cistemy v regione (na primere Irkutskoj
oblasti). Evropejskij zhurnal social'nyh nauk, 12 (2),
pages 432-440.
«Kadrovyj golod» v medicine priobretaet ugrozhayushchij
masshtab v Irkutskoj oblasti.
https://irkutskmedia.ru/news/596056/ (data
obrashcheniya: 12.01.2019).
Massovoe otravlenie v Irkutske.
http://www.ntv.ru/novosti/1736816/ (data obrashch.:
30.01.2017).
Migraciya naseleniya Irkutskoj oblasti po vidam migracii.
http://irkutskstst.gks.ru (data obrashch.: 08.05.2021).
Ozhidaemaya prodolzhitel'nost' zhizni pri rozhdenii.
http://irkutskstst.gks.ru (data obrashch.: 08.05.2021).
Ozhidaemaya prodolzhitel'nost' zhizni. irkutskstat.gks.ru
(data obrashch.: 3.08.2016).
Press-vypusk VCIOM.
http://http://wciom.ru/index.php?id=236&uid=115304
ciom.ru/ ndex.php?id=236&uid=115304 (data
obrashch.: 11.07.2015).
Rybakovskij L.L. (201)5. Koncepciya demograficheskoj
politiki Rossii: opyt razrabotki i puti
sovershenstvovaniya. Sociologicheskie issledovaniya,
9, pages 62-70.
Rybakovskij O.L., Tayunova O.A. (2016). Realizaciya
koncepcii demograficheskoj politiki Rossii v oblasti
postoyannoj migracii naseleniya. Sociologicheskie
issledovaniya, 6, pages 34-41.
Skol'ko chelovek umerlo ot koronavirusa v Irkutskoj oblasti
na dannyj moment (2021). https://gogov.ru/covid-
fatality/irk (data obrashch.: 08.05.2021).
Srednij vozrast naseleniya (na nachalo 2020 g.).
http://irkutskstst.gks.ru (data obrashch.: 08.05.2021).
Srednyaya prodolzhitel'nost' zhizni naseleniya v sub"ektah
RF po sostoyaniyu na 1.01.2016.
http://www.statdata.ru/spg_reg_rf (data obrashch.:
13.06.2016).
Demographic Issues as a Condition for the Regions Sustainable Development (on the Example of the Irkutsk Region)
291

Summarnyj koefficient rozhdaemosti (2020-2035) gg.
http://irkutskstst.gks.ru (data obrashch.: 08.05.2021).
Hvylya-Olinter N.A. (2015). Demograficheskoe sostoyanie
sovremennoj Rossii. Socium i vlast', 4 (54), pages 15-
23.
CHislennost' postoyannogo naseleniya Irkutskoj oblasti
(2021). http://irkutskstst.gks.ru (data obrashch.:
08.05.2021).
CHislo semej, poluchayushchih subsidii, i chislennost' lic,
prozhivayushchih v nih (2021). http://irkutskstst.gks.ru
(data obrashch.: 08.05.2021).
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
292
