
Moodle Platform as a Key to the Effectiveness of Sustainable
Development of Higher Education
K. A. Melnikova
a
and L. A. Tyukina
b
Yaroslavl State Technical University, Yaroslavl, Russia
Keywords: Moodle, Grammar Trainer, Blended Learning, Sustainable Learning.
Abstract: In the modern world, it is very important to constantly develop the skills of a specialist. From this point of
view, the sustainable development of educational technologies is a fundamental factor in the educational
process. The objective of the research is to assess the impact of online courses using Moodle platform on the
effectiveness of learning a foreign language. The research participants were 1st and 2nd year students of
Yaroslavl State Technical University (YSTU), Yaroslavl, Russia. The research period was 2019/2020 and
2020/2021 academic years. The importance of this research is determined by the use of different approaches
to grammar learning from the traditional ones. The course is designed in such a way that a student, having
understood the grammatical model (formula), trains practical skills. The research results, namely: the students'
scores, course completion time, the number of test passes on each topic were collected and analyzed using
quantitative and qualitative analysis methods. Students' reviews of the course show not only their interest in
this type of educational activity, but also an increase in educational indicators, and, as a result, an increase in
cognitive knowledge by 9 %.
1 INTRODUCTION
The sustainable use of digital technologies in teaching
a foreign language in universities is due to the steady
need to train competitive staff (Saltzberg, and
Polyson, 1995).
The COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic has
accelerated the transition of universities to mixed and
online education. Although earlier models of mixed
teaching in universities were actively discussed by
scientists of the world community, Russian
universities did not strive to turn to such a teaching
mode (Collis, 2003).
The so-called Grem model is the most widely used
in YSTU. The advantages of this model are: an
unlimited number of educational materials of
different complexity levels, process cost-
effectiveness, 24/7 availability of educational
materials, social interaction between the teacher and
the student, automation of checking test results
process, no need to perform tasks at a strictly defined
time, which is the key to the student's personal
freedom in choosing the time/ place/ method of
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1998-7963
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5676-2325
learning a foreign language (Garrison and Kanuka,
2004). Moreover, the digital educational environment
allows students to choose the most appropriate
materials and courses for their educational goals and
independently assess their progress.
The Moodle platform is a software tool that
provides a unified framework within which students
can access a wide range of online resources. It also
allows teachers and students to interact at any time.
Various assessment tools, such as self-assessment
tests, provide instant feedback to students and give
both parties of the process an understanding of the
knowledge and skills acquired during the course.
The use of Moodle platform in the general
(traditional) course of education has been repeatedly
described by both Russian (Tyukina, Babayan and
Lazović, 2020) and foreign scientists. Moreover, the
vast majority of authors noted an improvement in
academic performance and an increase in motivation
for students to learn a foreign language (Vician and
Charlesworth, 2003).
According to the "Law on Education in the
Russian Federation", e-learning means "the
492
Melnikova, K. and Tyukina, L.
Moodle Platform as a Key to the Effectiveness of Sustainable Development of Higher Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0010670800003223
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Forum on Sustainable Development of Socio-economic Systems (WFSDS 2021), pages 492-497
ISBN: 978-989-758-597-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

organization of educational activities with the use of
information contained in databases and providing its
processing of information technologies, technical
means, as well as information and
telecommunications networks that ensure the
transmission of this information over communication
lines, the interaction of students and teachers."
Distance learning technologies are understood as
educational technologies implemented mainly with
the use of information and telecommunications
networks in the indirect interaction of students and
teachers. Organizations engaged in educational
activities have the right to apply these types of
teaching in the implementation of educational
programs in accordance with the procedure
established by the federal executive authority (Vician
and Charlesworth, 2003).
Effective learning of a foreign language with the
help of Moodle began in the 2018/2019 academic
year at YSTU. At first, these were just control lexico-
grammatical tests. Now the trainer effectively
functions in the system of the mixed mode of training,
allowing students to eliminate gaps in knowledge of
grammar.
In the first semester of the first year of all the
specialties at YSTU, the number of learning hours for
practical classes is 34-36 hours per semester. The
number of students in the group is 12-15 people. A
large number of students in a group and a small
number of training hours make it difficult for students
to effectively perceive information, and significantly
reduce the educational process effectiveness.
Moreover, the heterogeneity of knowledge, skills and
abilities of students coming from different
educational institutions leads to the same
heterogeneous motivation to learn a foreign language
and is a significant problem for a teacher (Universitet
sht. Pensel'vanii, 2004).
In the Russian system of compulsory full
secondary education (grades 1-11), a foreign
language begins to be studied in schools from the 5th
grade. Thus, at the time of entering the higher
education system, students have been learning a
foreign language for 8 years. In some schools, a
foreign language is a mandatory subject for learning
from the 2nd grade. And such students learn the
language for 10 years. But the analysis of students'
knowledge at the entrance, intermediate and final
lexical and grammatical tests over the past 7 years
(2012-2020) shows that, although students learn a
foreign language for more than one year, their
knowledge is poor and unsystematic, and the results
of the entrance tests for about 60-70% of students are
depressingly low.
Since learning a foreign language is a complex
and complicated process, we decided to introduce an
additional online course "English Trainer. Level 1” in
order to fill in the gaps in grammar knowledge,
increase the motivation of students to learn a foreign
language and provide them with the opportunity to
successfully pass the intermediate and final tests. The
online course "Grammar Trainer. Basic level"
considered hereto is designed for 72 academic hours
and consists of 5 modules containing 14 grammar
sections: noun, adjective, etc. Each topic contains
some lecture material and a final test. A final test is
provided at the end of the section. Each test on the
topic consists of 140 multiple-choice questions. The
questions in the test fall out randomly. Thus, the
probability of repeating the questions in the final test
is very small. In the 2019/2020 academic year, the
course was first introduced and tested in the
educational process. In the 2020/2021 academic year,
the course was recommended by the University's
management as mandatory for English-language
students of the 1st year of all areas of learning. Since
during the 2020/2021 academic year, YSTU took a
mixed version of training, the online course was used
along with the traditional teaching methods, in order
to:
systematize students' knowledge;
increase the effectiveness of the educational
process;
increase the motivation of students to learn.
Although our main goal was to improve student
achievement in terms of passing the test successfully,
the research also revealed additional, accompanying
educational goals. Additional educational objectives
are:
developing educational skills in a mixed
training mode;
self-selection of the most appropriate training
mode;
developing time management skills;
development of self-assessment skills.
To achieve these goals, we have chosen a mixed
educational approach, where e-learning is integrated
into teaching, learning, evaluation, and feedback in
real time. When creating a course on Moodle
platform, we used the experience of foreign scientists
(Universitet sht. Pensel'vanii, 2004).
By integrating the experience of foreign
colleagues in an innovative way, we developed a
course in the virtual educational environment of
Moodle, which not only provided the necessary
content of the theoretical rules of English grammar
for successfully passing the intermediate certification
Moodle Platform as a Key to the Effectiveness of Sustainable Development of Higher Education
493

test, but also allowed students to work out their skills
to absolute automatism.
Starting from the 2018/2019 academic year, the
online course of training was structured into 5
modules, developed, prepared and uploaded to the
YSTU Moodle platform. First-year students of the
Institute of Chemistry and Chemical Technology and
the Institute of Digital Systems practiced these
modules for two academic years (2019/2020 and
2020/2021) as preparation for the intermediate test in
English. The full course of education includes two
intermediate tests in a foreign language and a final
test. The score for the final test is presented in the
certificate of bachelor's degree.
This article discusses the design, content of the
online course and the results of these two years to
assess the impact of online courses on the
effectiveness of learning a foreign language using the
Moodle platform in terms of improving the
performance of the intermediate test and the degree
of student satisfaction with the mixed learning
approach.
Assessment of students' use of the online course
"English Grammar Trainer. Level 1” was performed
using a specially designed questionnaire, which
included the following questions:
1 Will students use Moodle online resources, and
if so, how?
2. Do students with the access to online materials
have better overall academic performance and
intermediate assessment test results?
3. How do students perceive the impact of the
online course "English Grammar Trainer. Level 1" on
the results of the intermediate assessment test in the
discipline "Foreign Language" and understanding of
grammatical material?
4. What is the students' opinion about the online
course "English Grammar Trainer. Level 1”?
A mixed learning model was used to obtain
answers to these questions. The results were
extrapolated from Moodle platform and analyzed in
comparison with the results obtained when the
platform was not used. In addition, the results of the
final tests were analyzed. The main characteristics of
the students who participated in the research are
shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Main characteristics of the research participants.
Academic year Number of
students
M. F. %, Institute of Chemistry
and Chemical Technology
%, Institute of
Digital
S
y
stems
2018-2019 171 54.3 49.7 79.5 20.5
2019-2020 185 44.3 55.7 65.9 34.1
2020-2021 196 38.3 61.7 68.4 31.6
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The research results are based on data extracted from
Moodle platform. The statistical analysis of the
intermediate assessment test conducted for students
and the analysis of the results of the survey of
students' subjective perception of educational
activities using the Moodle platform were carried out.
In particular, we analyzed:
the model of students' use of the Moodle
platform and each module's section;
improving the results of the intermediate
assessment test for students who used the e-
learning course;
percentage of students who have passed the test
in two years 2019/2020; 2020/2021.
As for the model of using the Moodle platform by
students, we also compared the number of requests to
the online course depending on gender and direction
of education. We analyzed the training analytics
extracted from the Moodle platform after the students
completed the course, and organized it in the form of
tables representing the number of requests to various
resources and activities to get information about the
interaction of students with each of them. In terms of
improving the results of the intermediate assessment
test for students, we compared the results of the
intermediate exam obtained by students in 2020/2021
who had access to the training course on the Moodle
platform with the results obtained from students in
2018/2019 who did not have access to the electronic
training course. To do this, we compared the results
of two academic years, presenting them to the
ANOVA statistical analysis (Table 2) The results of
ANOVA statistical analysis show that the results of
students who use an online course in their training
(2020/2021) are higher than the results of students
who do not use an online course in their training
(2018/2019).
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
494

Table 2: Number of students, total score (0-1), average score, deviation value.
Academic year
Number of students
SUM of normalized score
MEAN of
normalized score
Variance,
2018-2019 171 55.4120 0.6641 0.0412
2020-2021 196 56.8652 0.6827 0.0501
3 RESEARCH RESULTS
Do students use the online resources of the Moodle
platform, and if so, how did they use them?
In general, during the fully implemented year of
education using Moodle platform, i.e. 2020/2021,
students used the platform in preparation for the
intermediate test, but they began to use the platform
more actively before the final test (according to the
Moodle log, there is an increase in the number of
requests from students using the platform after the
intermediate test date by 230%). 61.7% of students
successfully completed the intermediate test (121 out
of 196), all of them actively used the platform and
made up 97% (163 out of 196). The fact that 97% of
active students successfully passed the intermediate
test can mean either that learning with the help of the
platform is really more effective, or that they were the
most motivated and conscientious and would still
have passed the intermediate test for positive grades,
even without the help of online resources. In
particular, before the intermediate testing, 121
students used the Moodle platform system and gained
access to its resources (hereinafter referred to as
"active students"), while after the intermediate testing
and before the final testing, the number of such
students increased to 163. Compared to 2019/2020,
the number of active students on the platform has
increased (+35.3%). The percentage of active women
in 2019/2020 was 55.7%; and in 2020/2021 – 61.7%
and was slightly higher than that of men (2019/2020,
44,3%; 2020/2021, 38,3%). The share of Institute of
Chemistry and Chemical Technology participants
was 65.9% in 2019/2020 and 68.4% in 2020/2021
academic years. While the share of Institute of Digital
Systems students in the same time frame was 34.1%
and 31.6 %, respectively.
3.1 Moodle Platform Usage Models
Here we analyzed the data of the online course for
2019/2020. The total usage indicator can be obtained
according to the Moodle content access log data, it
shows the level of students' interaction with each
module of the course (Table 2), despite the fact that
the student can access the information and tests of the
modules countless times. Based on data from the
Moodle online platform, students did not use forums
at all, preferring the traditional face-to-face
explanation in class.
Table 3: The number of accesses to the modules of the
English Grammar Trainer Level 1 course on Moodle
platform.
Resource References
Module 1 732
(
Total
)
Nouns 315
Personal Pronouns 417
Module 1 Ouiz 306
Module 2 1314 (Total)
Articles 340
Other
p
ronouns 426
Numerals 476
Adjectives 501
Module 2 Quiz 387
Module 3 1582
(
Total
)
Auxiliar
y
Verbs 401
Sim
p
le Tense 523
Modal Verbs 365
Irregular Verbs 296
Module 3 Quiz 523
Module 4 1192
(
Total
)
Word orde
r
235
Sim
p
le Pre
p
ositions 368
There is/are 287
Questions 302
Module 4 Quiz 477
Module 5 561
(
Total
)
Final Test 561
Forum News 0
Forum for interaction 0
After analyzing the statistical data of the platform,
it can be seen that students repeatedly referred to the
course materials, as well as repeatedly performed
tests of modules. The relatively small number of
requests to the Final Test of Module 5 is explained by
Moodle Platform as a Key to the Effectiveness of Sustainable Development of Higher Education
495
the limited number of attempts to pass it (no more
than 3), which is set by the course settings.
An unlimited number of test attempts gave
students the opportunity to improve their test scores,
and, at the same time, increase their self-assessment.
In addition, the ability to evaluate their knowledge
before passing the final test allows to increase the
motivation of students to learn (Lau Gonzalez,
Jauregui, Perez, Farinas and Le, 2014).
Do students who have access to online materials
have better overall academic performance and
intermediate assessment test results?
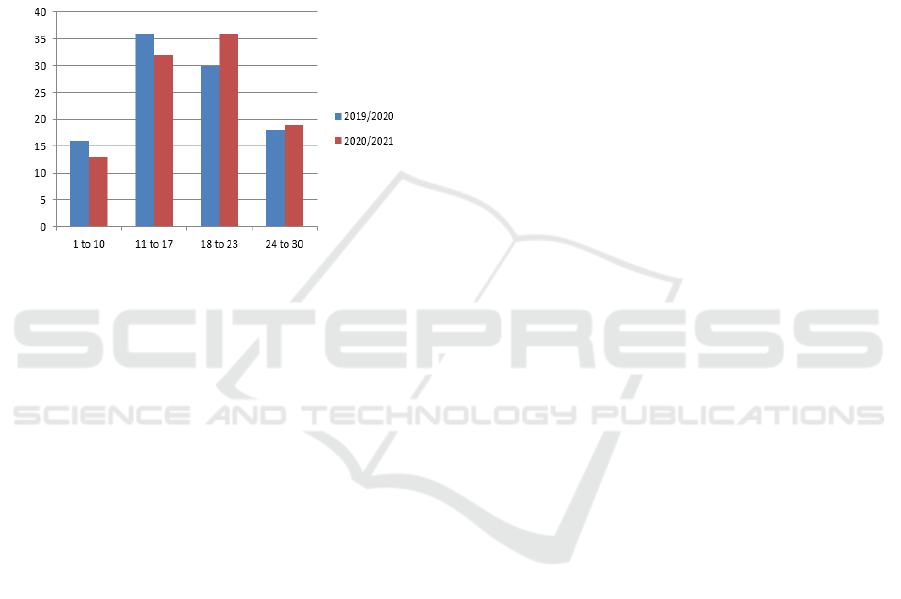
Figure 1: Comparison of the ranges of scores obtained by
students in the 2019/2020 and 2020/2021 academic years.
Applying the methodology of qualitative and
quantitative data analysis, we can talk about a
significant difference with a tendency to significantly
improve indicators in favor of a mixed learning
model. To demonstrate this difference, we have
formed four ranges of scores obtained by students,
where from 1 to 10 - unsatisfactory; from 11 to 17 -
satisfactory; from 18 to 23 - good and from 24 to 30 -
excellent. Comparing the indicators of 2019/2020 and
2020/2021 in Figure 1, it is possible to note with
confidence that the use of an online course on the M
platform had almost no impact on the academic
performance of students with low and high scores,
while students with good scores significantly
improved their quality indicators. Therefore,
expanding the possibilities of classical learning
through online resources (mixed method) is not
enough to increase the quality indicators of both
students with very low and very high indicators. But
there is a positive tendency among students with good
indicators.
4 CONCLUSIONS
It is difficult for first-year students to adapt to the new
higher education system. This is due to a complete
change in the learning environment, and due to the
lack of students' training in terms of learning a foreign
language. Since students' knowledge is
heterogeneous, the task of the teacher becomes the
need to help such students improve the efficiency of
their learning process. Therefore, any resource
available to students and which can be used at any
free time and in an unlimited number of times
becomes an opportunity to train and motivate the
training of such students. The use of online courses
provides students with this opportunity. However,
based on the data obtained from the research, it can
be said that students like learning in an online
environment, but they are not ready to fully learn
online and, therefore, prefer to consult with the
teacher in real time. It can also be noted that the online
course on the Moodle platform was not fully used by
students. Students with low scores did not improve
their quality scores, while students with good scores
advanced to a higher level. Based on this, it can be
concluded that more motivated students can
significantly improve their knowledge and test
results, and, accordingly, the course score, using
online learning tools such as the course on Moodle.
Thus, we can note that the Moodle platform is a
useful resource, as it provides students with unlimited
educational content in terms of time and number of
requests; allows students to increase their self-
assessment and adapt more successfully to a new
learning environment; allows the teacher to evaluate
students' knowledge and get data on the difficulties
that students face during the course. Based on this, it
is possible to say with confidence that the use of
online courses on the platform is an integral and
important part of the continuous and sustainable
educational process.
REFERENCES
Saltzberg, S. Polyson, S. (1995). Distributed learning on the
world wide web. Syllabus Journal, 9(1), 10-12.
Collis B., (2003). Course redesign for blended learning:
modern optics for technical professionals, Life. Learn.,
13 (1-2), 22-38.
Garrison, D. R. and Kanuka, H. (2004). Blended learning:
Uncovering its transformative potential in higher
education, Internet High. Educ, 7(2), 95-105.
Graham, C. R. and Robison R. (2007). Realizing the
transformational potential of blended learning:
Comparing cases of transforming blends and enhancing
blends in higher education. in Picciano A.G. and
Dziuban C.D. (Eds), Blended Learning: Research
Perspectives. New York: The Sloan Consortium.
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
496

Tyukina L., Babayan V., M. Lazović M. (2020). SHS Web
of Conferences 88
Melnikova K., Guslyakova A. (2020). SHS Web of
Conferences 88
Vician, C. and Charlesworth P. (2003). Leveraging
technology for chemical sciences education: an early
assessment of WebCT usage in first-year chemistry
courses, J. Chem. Educ., 80 (11):1333-7
Lovatt, J., Finlayson, O. E. and James, P. (2007).
Evaluation of student engagement with two learning
supports in the teaching of 1st year undergraduate
chemistry, Chem. Educ. Res. Pract., 8: 390-402.
Universitet sht. Pensel'vanii. (2004). Otkrytoe i
distancionnoe obuchenie: tendencii, politika i strategii.
SSHA..
Kozielska, M. (2004). Developing creativity of students in
a computer-assisted learning process, Eur. J. Phys., 25
(2), 279-285.
Lau González, M., Jáuregui Haza, U., Pérez Gramagtes, A.,
Fariñas León, G., & Le Bolay, N. (2014). Supporting
students’ learning to learn in general chemistry using
Moodle. J. Chem. Educ, 91(11), 1823-1829
Chiara Schettini, Daniela Amendola, Ido Borsini, Rossana
Galass. (2012). A blended learning approach for
general chemistry modules using a Moodle platform for
first year academic students. Journal of e-learning and
knowledge society Vol 16, 2, pages 61-72.
Moodle Platform as a Key to the Effectiveness of Sustainable Development of Higher Education
497
