
Design of Concepts Sustainable Development of Flagship University
in the Digital Economy
Sergey Sazonov
a
, Ekaterina Kharlamova
b
and Vera Tsygankova
c
Volgograd State Technical University, av. Lenina 28, Volgograd, Russia
Keywords: Flagship University, Sustainable Development, Smart University, Socially-Oriented (Civic) University,
MOOC, Digital Economy.
Abstract: The concepts of sustainable development were initially developed in the framework of environmental theories,
but were later applied in socio-economic systems (including educational ones), since they have similar laws
of development, the balance of the rates of development and resource consumption, and the interaction of
complex systems. The development programs of the main universities within the framework of the concept
of sustainable development are aimed at increasing the competitiveness of the regions, stimulating innovative,
technological and social processes in interaction with applicants, employers, entrepreneurs, regional
authorities, but at the same time the universities compete with each other, develop development strategies,
analyze strengths and weaknesses, resource opportunities and limitations. This article analyzes the
possibilities of transformation of universities in the digital economy, taking into account regional and
university competition, nowadays it is necessary to apply development programs that consider the conditions
of the growing requirements for all participants of the system.
1 INTRODUCTION
The activities of modern universities are carried out
within the framework of national and international
initiatives and programs that are aimed at
strengthening stability in the region and developing
their national contribution to solving global
problems, such as sustainable development. The role
of universities is the scientific support and diffusion
of the ideas of sustainable development through y
networks, professional societies, mass media and
other resources.
The concept of “the triple helix’ of (Etzkowitz and
Leydesdorff, 1995) is widely used for exploration
systems of factors that form the rules of work in the
conditions of the innovation economy, the extension
in the rate of updating knowledge, the growth in
employers ' requirements for the quality of graduate
training, the construction of network structures that
unite universities, regions, public administration and
business structures. As a result, universities become
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3485-8390
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8803-0970
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0133-7946
the core of cluster structures, ensuring their
development.
An important direction of implementation of the
concept of sustainable development in the activities
of the reference university is cooperation with local
or regional authorities in the implementation of
specific programs for the sustainable development of
the industry, region or territory.
Cooperation with local enterprises and support for
entrepreneurial initiatives aimed at sustainable
development are beneficial both for small and
medium-sized enterprises that receive new ideas and
approaches to doing business from university
specialists, and for universities that accumulate
specific experience to train future specialists and
business leaders.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
The general research methodology is the philosophy
of sustainable development at the stage of transition
Sazonov, S., Kharlamova, E. and Tsygankova, V.
Design of Concepts Sustainable Development of Flagship University in the Digital Economy.
DOI: 10.5220/0010672100003223
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Forum on Sustainable Development of Socio-economic Systems (WFSDS 2021), pages 575-579
ISBN: 978-989-758-597-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
575

to a post-industrial society, the increasing role of
higher education in the world and the leading trends
in its development in the digital economy. In
accordance with the logic of the research, a set of
complementary theoretical, empirical, statistical
methods, adequate to the subject of the research, was
used to solve the set tasks, including: theoretical
analysis, generalization, classification, modeling,
sociological methods, generalization of best practices
in the field of sustainable development of flagship
universities in Russia.
The history of the creation and the features of the
sustainable development of reference universities in
Russia are discussed in detail in the works of Berestov
A.V. (Berestov et al., 2020), Krakovetskaya I. V.
(Krakovetskaya et al., 2020), Saginova O.V.(
Saginova, 2012), Gubar L.N.( Gubar, 2016), Arnaut
M.N. (Arnaut, 2014) and Sazonov S .P. and
Kharlamova E. E. (Sazonov et al.).
Figure 1 shows the main five principles on which
the concept of sustainable development of the
university is based.
Figure 1. Basic principles of sustainable development of the
University (Saginova, 2012)
The sustainability of the university's development
is achieved as a result of the development of a number
of interrelated concepts described in table 1.
Table 1: Concepts of sustainable development of the
University (Krakovetskaya et al., 2020).
Concept
name
Concept essence
The concept
of a green
university
(green
campus)
This concept involves the formation of a
"green", environmentally sound
education, the introduction of
environmental practices in the
university, increasing the level of
environmental behavior of students and
employees, monitoring the environment
and assessing the quality of the
environment, describing possible
environmental risks and ways to reduce
them
The concept
of a Smart
University
(Smart
Campus)
The concept involves the formation of a
university that effectively uses all types
of resources and implements modern
information technologies to manage its
key processes, working "ahead of the
curve", developing promising areas
based on the results of foresight research
in the di
g
ital econom
y
.
The concept
of a
socially-
oriented
(civic)
University
This concept is aimed at creating
conditions that ensure a decent life and
free development of the individual.
Social demand and social responsibility
of the university are formed on the basis
of public expectations. It’s implemented
through various projects: training of
highly qualified specialists, retraining of
regional personnel, social assistance and
social support of students and
em
p
lo
y
ees, etc.
The concept
of the
University
as a
stakeholder
organization
The concept is aimed at building long-
term and mutually beneficial
relationships with stakeholders:
applicants, students, graduates,
employees, potential employers,
authorities and management, etc. The
concept is aimed at coordinating the
goals and criteria for measuring the
effectiveness of the university's
activities to the goals of key groups of
stakeholders , as well as organizing
monitoring of stakeholders ' satisfaction
with the university's activities
The concept
of the
"Third
mission" of
the
University
This concept is aimed at active
interaction of the university with the
society as an organization producing
knowledge and technology, as well as a
complex of social, legal, and financial
institutions that can ensure effective
cooperation of regional authorities,
scientific and educational organizations,
industrial enterprises and the business
community, non-profit organizations in
all spheres of socio-economic and public
life
Growth of sustainable
development issues in the
university's curriculum.
Growth of sustainable
development issues in the
university's research topics.
Building the current
activities of the university
on the principles of
sustainable development.
Creating opportunities for
students and university staff
to acquire skills of behavior
aimed at sustainable
develo
p
ment.
Development of cooperation
and partnership programs
with other organizations for
the sustainable development
goals.
The concept of
sustainable
development of the
University
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
576
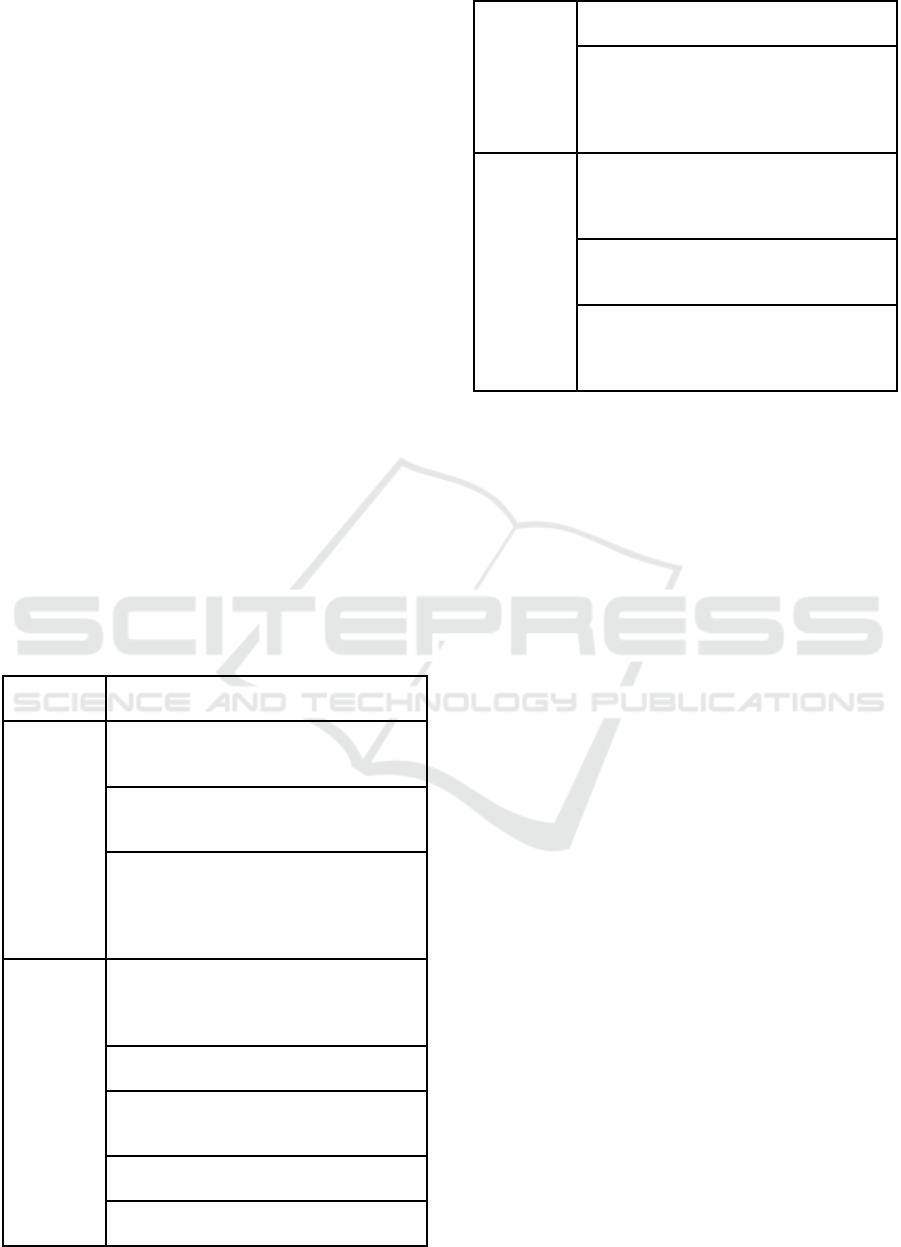
Each of the presented concepts contributes to
achieving the sustainability of the University and
therefore should be taken into account when forming
the overall concept of sustainable development of the
university.
The sustainability of the development of a
regional reference university lies in the possibility of
its existence in the market of educational services and
demonstrating high achievements in its work. It may
by characterized by a number of necessary and
sufficient conditions, the most significant of which
are:
the positive dynamics of the given contingent
of students;
qualification of scientific personnel;
structure of the services provided by the
university;
overall positive trend in financial resources;
increased R & D funding;
growing share of modern equipment;
the insignificant deviation of the planned
indicators of the university's activities from
the actual ones, etc.
Based on these factors, the researchers distinguish
the following indicators for assessing the
sustainability of the university's development.
Table 2: Indicators for assessing the sustainability of
university development (Arnaut, 2014).
Group of
indicators
Characteristics of indicators
1: Highly
scientific
staff
Growth of the share of persons with a
Doctor of science degree in the total number
of university teaching staff, %.
Growth of the share of persons with a PhD
degree in the total number of university
teachin
g
staff, %.
Growth of the share of teaching staff
awarded state and world-class prizes, as
well as full members and corresponding
members of the state academies of Russia,
%
2: Innovative
scientific
and
educational
complex
Growth of the number of research,
innovation and implementation structures,
including technology parks, business
incubators, etc.,%.
Growth of the number of interactive
trainin
g
materials, %
Growth of the number of scientific journals,
including electronic ones, published by an
educational organization, %
Growth of the book value of machinery and
e
q
ui
p
ment, %.
Growth of the number of personal
com
p
uters with Internet access, %
Growth of the total area of educational and
scientific
p
remises, %
Growth of the share of the cost of modern
(not older than 5 years) machinery and
equipment in an educational organization in
the total cost of machinery and equipment,
%
3: Extra-
budgetary
financial
base
Growth of the share of the educational
organization's income from income-
generating activities in the total amount of
the universit
y
's funds, %
Growth in the income of an educational
organization from funds from income-
generating activities, %
The growth of the educational
organization's income from the funds from
income-generating activities aimed at the
implementation of R & D, %
Berestov A. V. studied in detail the evolution of
the main universities during the period of the program
of their development. Although the period 2016-2020
was accompanied by depression in the economic
situation, universities managed to improve business
activity, expand the list of programs, and conclude
agreements for conducting commercial research
(Berestov et al.,2020),.
Nowadays, Russian universities participate in
numerous rating systems that allow them to compare
their achievements at the national and global levels
(National University Rankings).
Participation in the world educational rankings
motivates Russian universities to create their own
strategies based on the principles of sustainable
development, for international recognition and
creating a positive image of Russian education and
research.
The analysis of the rating allows you to identify
the leading universities, change priorities in certain
areas, but there are also gaps in the rankings between
individual categories of universities.
One of the main directions is the digitalization of
education, which received a significant impetus
during the forced format of distance learning.
Although traditional education remains basic, an
alternative has appeared on the educational services
market-EdTech and MOOCs, which allows achieving
a higher speed of information exchange, integration
of work programs, benchmarking of educational
processes, and reducing the cost of training.
MOOCs fit well into the students' requests for
new learning formats, increasing the variability of
disciplines, forming an individual educational
trajectory, and reducing the duration of training. 2020
was even called the year of MOOCs (Shah, 2020), as
Design of Concepts Sustainable Development of Flagship University in the Digital Economy
577

it showed the demand for these courses and their real
possibility to replace traditional education.
MOOCs transform teaching methods, the market
for educational services, and the requirements for
both teachers and students. Nowadays there are
changes in the development strategies of the
education market, its globalization, and the removal
of geographical and linguistic restrictions. There is a
gradual diffusion of MOOCs. This field of activity
has become attractive for startups that attract millions
of dollars, covering the fields of education, business,
and communications. Aggregate platforms offer a
wide choice to users, promoting their advertising (for
example, Class Central), with which you can quickly
and in a single format get information about old and
new MOOCs, about their start dates and access
conditions, about the growth of MOOC platforms,
and many other information.
The global market shows growth, in 2021, it is
possible to reach $ 241 billion. the number of students
is increasing, for example, the number of registered
users on Coursera has reached 76 million, edX-35
million, Future Learn-15 million (Shah,2020).
There are 4 main characteristics of MOOC that are
well consistent with the concept of sustainable
development of the university (Yuan & Powell,
2013):
1) Open schedule: students combine educational
resources, classes and / or training complexes in
different disciplines in order to meet their needs.
2) Open learning: teachers, experts and/or other
students will generate ideas through various activities
and share them in the learning process. This provides
students with opportunities for independent, self-
directed learning based on personal interests.
3) Open assessment: the assessment of what
students have learned is made by their teachers and
other students in the course of training, that is, the
assessment of students by each other or in a group
with "accreditation" on request.
4) Open Platform: Supports a dynamic and
interactive open education community by creating
and maintaining an attractive, intuitive and stable user
interface for teachers and students. Computer
software based on the information cloud principle and
the use of open standards facilitates the exchange of
data for different platforms and services.
MOOC may be considered as a social innovation
that uses technological capabilities, and as a variant
of social entrepreneurship aimed at expanding the
field of education and its diversification, minimizing
(in the long term) the costs of organizing the
educational process, teaching thousands of students
(Tsygankova, 2019). The number of completely free
courses is decreasing there is a orientation to the
corporate consumer, who is interested in both new
knowledge and career advancement, or obtaining a
full higher education in the MOOC format. There is
also a regionalization of MOOCs-the Spanish,
Chinese, and Russian sectors are actively developing,
covering new demographic groups (restrictions on
age, health status, and tuition fees are removed),
while there is a drop in interest in conventional forms.
MOOC provide new opportunities for the
sustainable development of the university in the
digital economy, but their creation and application
depend on some factors:
ability to create own courses;
human factor (the desire to learn, the
motivation of students);
using platforms (using existing ones or
creating new ones);
the ability to use the achievements of
digitalization;
financing of digitalization projects;
active monitoring of the requirements of
employers and students, expanding the scope
of activities.
3 RESULTS
Thus, MOOCs and digitalization can have a dual
impact on supporting universities:
Stimulating – If universities can change their
infrastructure, develop new courses in the format of
mixed learning, attract applicants, expand the range
of research.
Depressing - If there is no change in the principles
of work, ignoring the requirements of the
environment, the transition of applicants to virtual
platforms or to central universities.
The implementation of the concept of sustainable
development based on digitalization, it will allow the
reference universities to become the technological,
innovative and cultural core of the regional socio-
economic system; to ensure the development of
scientific and educational opportunities of the
university; to train more in-demand specialists with
the requirements of the digital economy.
1. The concept of sustainable development is
aimed at a systematic understanding of the role of
universities in the economy, the search for new
resources, development opportunities, but at the same
time, competition for applicants has intensified
2. Qualitative and quantitative changes require
additional funding, one of the sources of which is the
creation of network and cluster structures, the joint
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
578

use of research infrastructure, the creation of
entrepreneurial universities
3. Information interaction plays an important role
in the development of university networks. One of the
forms of this interaction is mass online courses, which
allowed to expand educational opportunities.
4. The development of core universities requires
additional investments in both infrastructure renewal
and professional development, knowledge
management, and access to best practices.
5. The concept of sustainable development can be
implemented in various directions, but digitalization
allows for the integration of educational, financial,
and technological resources.
REFERENCES
Arnaut, M. N. (2014). Organizational and economic
mechanism of management of sustainable development
of the university. Autoref. dis. for the degree of
Candidate of Economic Sciences. Vladivostok, URL:
http://www.uiec.ru/content/files/AvtoreferatArnaut.pdf
Berestov, A.V., Guseva, A.I., Kalashnik, V.M., Kaminsky,
V.I., Kireev, S.V., Sadchikov, S.M. (2020). Project
“National Research University” – Driver of Russian
Higher Education, 29(3): 22-34.
Berestov, A.V., Guseva, A.I., Kalashnik, V.M., Kaminsky,
V.I., Kireev, S.V., Sadchikov, S.M. (2020). Flagship
Universities as Development Potential of Regions and
Industries, 29(8/9): 9-25.
Etzkowitz, H., Leydesdorff L. (1995). The Triple Helix of
University-Industry-Government Relations: A
Laboratory for KnowledgeBased Economic
Development. EASST Review, 14(1).
Gubar, L. N., Ivanova, E. S., Mironov, V. V. (2016).
Modeling and evaluation of sustainable university
development based on IT technologies. IT Arctic, 4: 12-
28.
Krakovetskaya, I.V., Vorobyeva, E.S., & Dalibozhko, A.I.
(2020). Sustainable development of universities:
concepts and approaches to evaluation. Part 1.
Theoretical aspects. Creative Economy, 14(2): 207-
224. DOI: 10.18334/ce.14.2.100555
National University Rankings. URL:
https://academia.interfax.ru/ru/ratings/?status=4&ratin
g=1&year=2020&page=1
Saginova, O. V., Saginov, Yu. L., Grishin, A. I. (2012).
Sustainable development of the University. Bulletin of
the Kazan Technological University, 15:21.
Sazonov, S. P., Ezangina, I. A., Kharlamova, E. E. (2020).
The Role of Russian Flagship Universities of Russia in
the Formation of the Scientific and Human Potential of
the National Centers of Technological Excellence.
Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, 115: 687-695.
DOI 10.1007/978-3-030-40749-0_81.
Sazonov, S.P., Chunakov, A.I., Kharlamova E.E.
Polyanskaya, A.A. and Glebov S.D. (2019). The Role
of the Regional Support of Technical University in the
Training of Professional Personnel for Enterprises of
Volgograd region. IOP Conference Series: Materials
Science and Engineering, 483(7).
Sazonov, S.P., Kharlamova, E.E, Chehovskaya, I.A,
Polyanskaya, A.A. (2015). Evaluating Financial
Sustainability of Higher Education Institutions. Asian
Social Science, 11(20): 34-41.
Sazonov, S.P., Kharlamova, E.E. (2019). Building a
Financial Model for Developing a Flagship Technical
Higher Education Institution. Proceedings of the
International Scientific Conference «Far East Con».
Atlantis Press, 248-252.
Shah, D. (2020). The Second Year of The MOOC: A Review
of MOOC Stats and Trends in 2020. URL:
https://www.classcentral.com/report/the-second-year-
of-the-mooc
Tsygankova, V.N. (2019). The digitalization of educational
process (on the example of mass online courses).
Creative Economy, 13(3): 523-532. DOI:
10.18334/ce.13.3.39958
Yuan, L., Powell, S. (2013). MOOCs and Open Education:
Implications for Higher Education. JISC CETIS.
URL:
http://publications.cetis.ac.uk/2013/667
Design of Concepts Sustainable Development of Flagship University in the Digital Economy
579
