
An Ontology based Task Oriented Dialogue
Jo
˜
ao Quirino Silva
1
, Dora Melo
1,3 a
, Irene Pimenta Rodrigues
1,2 b
, Jo
˜
ao Costa Seco
1 c
,
Carla Ferreira
1
and Joana Parreira
1
1
NOVA Laboratory for Computer Science and Informatics, NOVA LINCS, Portugal
2
Department of Informatics, University of
´
Evora, Portugal
3
Coimbra Business School—ISCAC, Polytechnic of Coimbra, Portugal
jb.parreira@campus.fct.unl.pt
Keywords:
OWL2 Ontologies, Natural Language Processing, Dialogue Systems, Semantic Web.
Abstract:
An ontology based task oriented dialogue as an interface to an user developing applications using natural lan-
guage instructions is presented. The dialogue system represents the domain knowledge in an OWL2 ontology
that is consulted and updated in the interpretation of the user utterances. The utterances are processed using
an Universal Dependencies parser whose output is then interpreted to obtain a partial semantic representation.
The pragmatic interpretation computes a set of possible interpretations by matching the partial representation
with the ontology information, classes, properties, instances and data properties values, such as names. The
dialogue manager is able to use soft constraints to choose the set of best interpretations. A set of preliminary
experimental cases with promising results is also presented.
1 INTRODUCTION
This work was done in the context of GOLEM (Auto-
mated Programming to Revolutionize App Develop-
ment)
1
, a most ambitious collaboration effort OutSys-
tems has pursued with academic communities. The
R&D project involves the collaboration of OutSys-
tems with Carnegie Mellon, NOVA Laboratory for
Computer Science and Informatics at Universidade
Nova de Lisboa, and INESC-ID. The main goals of
the three-year program are to automate programming
and revolutionize the application development expe-
rience. GOLEM is one of a few select large-scale
collaborative research projects funded by Carnegie-
Mellon Portugal partnership.
One of the modules of this project is a natural lan-
guage interface, a task oriented dialogue, that must be
able to interpret the user natural language instructions
in order to represent them in a predefined owl2 on-
tology that will be executed by a program synthesis
module. Natural language utterances are interpreted
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3744-2980
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2370-3019
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2840-3966
1
https://nova-lincs.di.fct.unl.pt/project/277,
https://nova-lincs.di.fct.unl.pt/news-single/97
in the context of the user dialogue and in the context
of the instructions ontology that represents the previ-
ous user instructions and domain knowledge.
The goal of this paper is to present the strategies
performed to semantically represent a natural lan-
guage utterance into an instruction ontology, an ori-
ented data-centric application model.
A follow up set of experimental case examples are
presented in this paper and the domain knowledge
considered consists of databases content (tables and
attributes, attributes types, etc), display operations on
tables and columns such as searchable, orderable, etc.
The remainder of this paper is divided into the fol-
lowing sections. In Section 2, the main concepts and
related work are presented, as well as the main ideas
followed in this work. The proposed approach is de-
tailed in Section 3 and for better understanding an il-
lustrative example is presented. Section 4 describes
a set of experimental examples including the results
obtained. An evaluation discussion of the proposed
approach regarding the experimental examples is pre-
sented in Section 5. Finally, in Section 6, conclusions
and future work are drawn.
96
Silva, J., Melo, D., Rodrigues, I., Seco, J., Ferreira, C. and Parreira, J.
An Ontology based Task Oriented Dialogue.
DOI: 10.5220/0010711900003064
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2021) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 96-107
ISBN: 978-989-758-533-3; ISSN: 2184-3228
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Figure 1: Architecture of the Proposed Approach.
2 RELATED WORK
Task-oriented dialogue systems are natural language
interfaces for a system that executes the user ins-
tructions. Examples of spoken or written dialogue
systems can be found in domains such as human-
robot interaction (Fong et al., 2003), technical support
(Acomb et al., 2007), natural language code specifi-
cation (Atzeni and Atzori, 2018), information search
in several domains (Asiaee et al., 2015; Melo et al.,
2016; Abdi et al., 2018; Devi and Dua, 2017), and
automatic booking (Wei et al., 2018),
The interpretation of user’s utterances is a chal-
lenging task in dialogue systems and many techniques
are used.
Some of the recent dialogue systems are develo-
ped using deep learning techniques. Deep learning
can require a large amount of data to learn represen-
tations in dialogue systems. Different types of dialo-
gues, task-oriented or non-task-oriented models, may
benefit from different deep learning techniques (Chen
et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2021). Reinforcement learning
techniques for training dialogue agents (Wei et al.,
2018) is another technique used in the development
of a dialogue system. In (Stoyanchev et al., 2021),
deep learning for task oriented dialogues is used in a
dialogue module, for action state updates.
In task-oriented-dialogues, another actual ap-
proach is the use of ontologies to represent the dia-
logue domain information (Wessel et al., 2019; Mil-
ward and Beveridge, 2003; Meditskos et al., 2020;
Stoilos et al., 2019; Atzeni and Atzori, 2018). This
approach is the one followed in this work. A proces-
sing pipeline with a module for the natural language
understanding and an ontology for domain specific
knowledge enabling the development of generic di-
alogue system components.
The natural language processing module uses a
state of the art statistical English parser, Universal
dependencies parser - stanza and the semantic repre-
sentation of the sentences is a simplified form of a
discourse representation structure (Kamp and Reyle,
1993; Geurts et al., 2020).
In (Liu et al., 2021), an Universal Discourse Rep-
resentation Structure Parsing based on a Transformer
architecture, is proposed. However this neural net-
works based tool is not available. In related literature
it is possible to find other promising semantic parsers
(
ˇ
Zabokrtsk
´
y et al., 2020; Gotham and Haug, 2018;
Reddy et al., 2016).
An important issue in the development of a Dia-
logue System is the evaluation (Deriu et al., 2020).
Generally, a task-oriented dialogue system has to re-
cognize and execute a clearly defined task. The tasks
involve finding information within a knowledge base
and performing an action. The evaluation of the di-
alogue performance can be done trough a qualitative
analysis modelling the user satisfaction or by a more
quantitative analysis measuring the task-success rate.
The task success rate can be calculated by taking into
account the set of constraints and the set of requests
correctly represented from the user utterance.
3 PROPOSED APPROACH
The strategy followed in the implementation of a task-
oriented-dialogue system includes a pipeline for the
natural language utterances processing that associates
to each user utterance, a discourse representation
structure, see Figure 1. The next module, called Prag-
matic Interpretation, rewrites the utterance semantic
An Ontology based Task Oriented Dialogue
97

representation, into a set of utterances meaning in the
context of the ontology. Finally, the Discourse Ma-
nager module infers the ’discourse acts’ and the ’user
intention’, as well as the the set of constraints of the
’discourse acts’. This module has to choose the most
plausible meaning, from the set of the possible mea-
nings, and if needed, it can introduce questions to
clarify the intended meaning of the user utterance. To
choose the most plausible interpretation, the dialogue
manager uses strategies to select the interpretations,
such as to select those with the less number of new
ontology instances, or those that has the set of the dis-
course act restrictions more complete.
The use of an ontology to represent domain spe-
cific knowledge enables the development of generic
dialogue system components that may be used in dif-
ferent domains.
3.1 An Instructions Ontology
The ontology associated with the dialogue system
must model the discourse acts and its constraints. It
should also model the specific domain knowledge.
The scenario for which this ontology was develo-
ped is a written natural language interface for building
applications for displaying a database content. In this
scenario, the discourse acts are instructions for build-
ing the components of the application’s display. The
following instructions were considered:
Show Display a set of the columns, from a table, in a
screen.
Input example: ”Show name, price and stock, of
the Products, on a page Analysis.”
The result of the execution of this instruction
should be an application with a window, named
”Analysis”, where the attributes ”name”, ”price”
and ”stock” of the table, named ”Products”, are
displayed.
DisplayValue Display column values operated by a
value.
Input example: ”Show the price, with VAT.”
The price should be displayed with its values mul-
tiplied by 1+VAT.
Filter Put a filter on a column for searching or order-
ing the values.
Input example: ”Show Products, with filter
name.”
The display of column ”name” must have a
searchable attribute.
The instructions (discourse acts) are subclasses of
the Class Action. The other classes considered are:
Action - with subclasses: Show, Display Filter,
Display Value, ...
Object - with subclasses: Multiple Value and
Single Value. Multiple value may represent a
table or an entity set; Single value may represent
a column or an attribute.
Page - represents the window where the objects are
displayed.
Operator - Constants that can be represented as sub-
classes and identifies an operator of an operation,
such as the subclasse VAT.
This ontology represents the discourse acts ena-
bling the inference of the user intentions. Figure 2
presents the instructions ontology with more detail re-
garding the classes and the relations between them.
The instructions ontology is still under development.
3.2 Partial Semantic Representation
The user utterance representation results from apply-
ing an Universal Dependencies Parser to obtain the
syntactic dependency representation of the utterance,
that contains the utterance terms properly classified
and the existing relations between them. And, after,
an algorithm is applied to build the discourse repre-
sentation structure. This algorithm is based on the
Discourse Representation Theory (Kamp and Reyle,
1993) but it only takes into account some discourse
phenomena, such as variables are always existentially
quantified, conditional are not considered, and events
and time are not represented. In the future, the algo-
rithm defined can be extended or replaced by a new
tool such as a semantic parser.
Stanza library
2
is used to perform the syntactic
analysis. Stanza is a Python natural language analysis
package, containing a collection of accurate and effi-
cient tools for the linguistic analysis of many human
languages, in particular the English natural language.
The Stanza tools can be used in a pipeline to convert
raw text into lists of sentences and words to generate
base forms of those words, their parts of speech and
morphological features, to give a syntactic structure
dependency parse, and to recognize named entities.
Starting from raw text and by applying a
Stanza pipeline, including tokenization, part-of-
speech, lemmatization and dependency parsing, a
syntactic structure dependency of the raw text is ob-
tained.
For better understanding, consider the following
natural language utterance example:
2
https://stanfordnlp.github.io/stanza/
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
98

Figure 2: Instructions Ontology.
Figure 3: Universal Dependencies Parse.
”Show name, price and stock, of the Products,
on a page Analysis.”
Figure 3 shows the universal dependency parse of
the utterance example. The dependency tags are used
to construct the utterance partial semantic represen-
tation, a simplified discourse representation structure
(Kamp and Reyle, 1993), where:
• Each noun phrase gives rise to a corresponding
discourse variable, a discourse entity.
• Each action verb also gives rise to a corresponding
discourse variable, a discourse entity.
• Each subject, object and indirect object of a verb,
modifiers such as propositional phrases, adjec-
tives and adverbs, define the relations between
discourse entities.
Considering the illustrative example, the utterance
partial semantic representation is shown in Figure 4
as a direct graph, where the nodes represent the dis-
course entities and the edges represent the relations
between the variables. For instance, the action verb
token, ’Show’, defines a discourse entity and each
noun token linked to the verb through the relation
obj, direct object, or obl, indirect object, also defines
a discourse entity. Therefore, in the partial semantic
representation the action verb token establishes a re-
lation between those entities. The coordination of the
direct object nouns is taken into account by imposing
the same relation between the action and the entities
representing the nouns. The prepositional phrase re-
presentation ’of Products’ is also imposed to each of
the coordinated nouns representation.
Figure 4: Partial Semantic Representation.
3.3 Pragmatic Interpretation
The pragmatic representation module consists of de-
termining a set of possible ontology semantic repre-
An Ontology based Task Oriented Dialogue
99
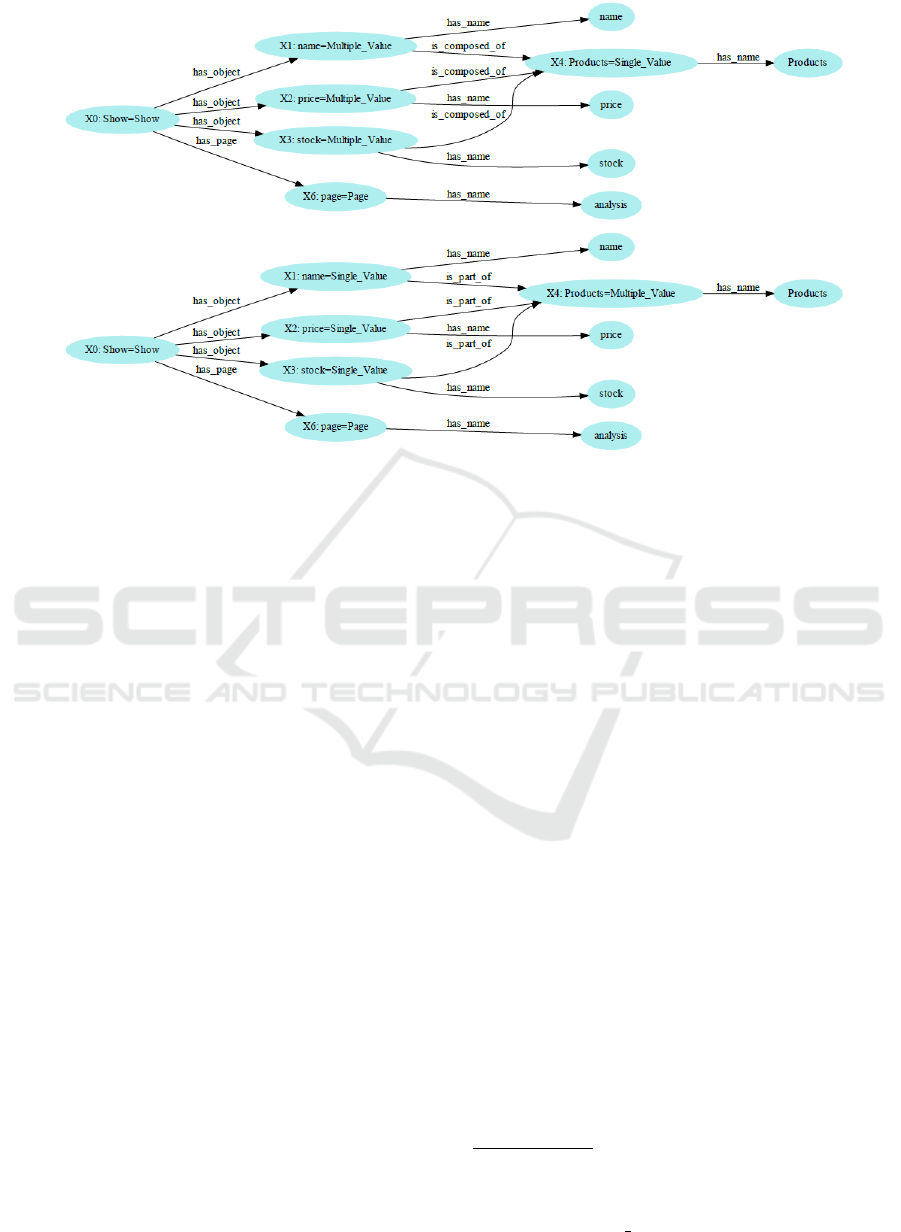
Figure 5: Solutions Semantic Representation.
sentations, based on the utterance partial semantic
representation and the ontology content matching.
Starting with the utterance partial semantic repre-
sentation obtained in the previous step, the problem
that must be solved is to choose: for each discourse
variable an instance of a class, and for each edge an
object property.
The first step to solve this problem is done by ap-
plying a constraint satisfaction problem (CSP) solver.
Where each variable has as domain the ontology
classes and the variables are constrained by the rela-
tions in the partial representation and the object prop-
erties in the ontology.
The second step involves the constraints intro-
duced by utterance word lemmas. For each lemma
there are three possibilities: first, the lemma of the
entity is the name of an existing individual in the on-
tology; second, the lemma of the entity is the name
of a class of the ontology; or third, the lemma is the
name of the new individual.
In this step the possible matches are obtained
by determining the similarities between the lemmas
and the ontology names, whether they are individ-
ual names or class names. A similarity method is
used for this task, this method uses state of the art
techniques such as Levenshtein, Jaccard and Cosine
distance combined values together with a local dic-
tionary and Wordnet (Fellbaum, 1998).
The third step consists of the matching process be-
tween the partial representation relations and the on-
tology properties, see Figure 5 where two possible so-
lutions are represented.
Finally, for each solution the set of class instances
and properties instances is calculated, this informa-
tion is attached to each solution enabling a future
choice of the best solution by taking into account the
completeness of the user utterance.
The Python package Owlready2
3
is used to load,
manage, reason and update the OWL2 Instructions
Ontology. Additionally, the Python tool CP-SAT
Solver
4
is used to solve the constraint satisfaction
problem.
Back to the illustrative example, since the onto-
logy is not yet populated, each variable has as its do-
main the possibility of being the name of an indivi-
dual belonging to any class, and also the possibility
of representing any class name. Then, solving the
corresponding CPS problem consists of determine all
the possible combinations of the variable classes, ta-
king into account the entities relations and the onto-
logy object properties. For the example, there are 165
solutions of the problem.
After the set of possible solutions is determined,
the corresponding set of possible solutions semantic
representations, the agenda, is constructed, i.e., for
each possible solution:
• the corresponding ontology properties semantic
representation are established;
• the ontology individuals are created and linked to-
3
https://owlready2.readthedocs.io/en/v0.32/
4
https://developers.google.com/optimization/cp,
https://developers.google.com/optimization/reference/
python/sat/python/cp model
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
100

gether with the ontology properties belonging to
the solution;
• and the missing properties and individuals are de-
termined, taking into account the ontology rules
such as the mapping cardinality.
The agenda, set of possible solutions semantic
representations, obtained is the input of the next step,
the dialogue manager.
3.4 Dialogue Manager
The dialogue manager consists of selecting the se-
mantic representations, according to a set of rules that
allows to restrict the agenda, and then update the dis-
course structure and the ontology.
When the agenda contains more than one semantic
representation solution, it means that there are several
ontology interpretations for the utterance representa-
tion. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce those in-
terpretations in order to achieve the correct one. Be-
fore questioning the user about his meaning and in-
tentions, the following weighting rules are applied:
• first, preference is given to solutions that consider
the utterance token near the name of an ontology
class;
• second, preference is given to solutions that mini-
mize the creation of new individuals;
• and finally, preference is given to solutions that
minimize the missing properties and individuals,
i.e., with a minor solution agenda.
Considering again the example, after applying the
weighting rules to the agenda, it is possible to reduce
substantially its size to only two solutions. Figure 5
illustrates the two solutions filtered. The correct so-
lution is the second one, where the entities ”name”,
”price” and ”stock” are considered instances of the
class ”Single value”, with the corresponding names
(has name property), and are part of (is part of
property) the entity ”Products”, an instance of the
class ”Multiple value”.
At this point, if the agenda contains more than one
solution and it is not possible to naturally reduce it,
then a question is posed to the user in order to clari-
fy the possible ambiguities. The user can clarify and
also add new information to be interpreted and repre-
sented in the ontology. So each time the user post an
utterance, a new iteration of the process is performed,
that could add new semantic interpretation entities to
the ontology or work with the already existing onto-
logy population.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
In this section, a set of experimental cases and the
results obtained are presented.
Case 1. The first experimental case is the one pre-
sented above as an illustrative example, in Section 3.
As previously presented, the utterance considered is
”Show name, price and stock, of the Products, on a
page Analysis.” and its partial semantic representation
is shown in Figure 4. In this experiment, the starting
instructions ontology is not yet populated and, due to
the fact that the similarity method is not applied, all
the variables’ domain is maximum. A set of 165 so-
lutions is obtained from the corresponding constraint
satisfaction problem, which means that there are 165
combinations of ontologies classes and properties that
match with the partial semantic representation of the
utterance. The goal is to determine which of these
solutions is the correct one. As explained before in
Subsection 3.4, the weighting rules are applied and it
is possible to reduce to only two semantic representa-
tion solutions, see Figure 5. At this step, a question
is posed to the user in order to clarify if, for instance,
the utterance token ”Products” refers to a single value
or a multiple value.
Case 2. The second experimental case is similar to
the first one, except that the ontology is already po-
pulated with the individuals for the multiple value
”Products”, and the single values ”name”, ”price” and
”stock”. When applying the weighting rule, where
preference is given to solutions that minimize the cre-
ation of new individuals, the set of semantic repre-
sentation solutions is reduced to just one, the correct
one, see Figure 6. In this case, no question is posed to
the user and the ontology is populated with the miss-
ing individuals and corresponding properties that link
them together.
Case 3. This experimental case is a variant of the
second case, where the token ”Show” is replaced by
the token ”Put”, i.e., the utterance considered is ”Put
name, price and stock, of the Products, on a page
Analysis.” The test goal is to evaluate the performance
of the overall approach, even when the token ”Put”
it is not known from the ontology side. The partial
semantic interpretation of this utterance is similar to
the second experimental case and the resulting set of
semantic representation solutions has 137 solutions,
considering the ontology already populated. After ap-
plying the weighting rules, the set of semantic rep-
resentation solutions is reduced to just one solution,
again the correct one. The utterance partial semantic
An Ontology based Task Oriented Dialogue
101

Figure 6: Caso 2 - Solution Semantic Representation.
Figure 7: Case 3 - (a) Partial Semantic Representation. (b) Solution Semantic Representation.
representation and the corresponding correct solution
are shown in Figure 7. As in experimental case two, it
is not needed to pose a question to the user and the on-
tology is populated with the missing individuals and
corresponding properties that link them together.
Case 4. At this experimental case, it is considered
the previous utterance and the token ”page” was ex-
changed by the token ”screen”, i.e., the utterance is
”Put name, price and stock, of the Products, on a
screen Analysis.” As in the previous experiment, even
when the token ”screen” is not known in the ontology,
it is possible to obtain a set of 232 semantic represen-
tation solutions and, by applying the weighting rules,
reduce it to just two solutions. The utterance partial
semantic representation is similar to the previous ones
and is presented in Figure 8.
Case 5. This experimental case is a variant of the
fourth case, where the token ”Put” is replaced by the
token ”Show”, i.e., the utterance considered is ”Show
name, price and stock, of the Products, on a page
Analysis.”. The utterance partial semantic represen-
tation is similar to the previous ones and when apply-
ing the constraint satisfaction problem solver results a
set of 144 semantic solutions, with the ontology free
from individuals. After applying the weighting rules,
a set of only two solutions, the same from the previous
experimental cases, is obtained, see Figure 9.
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
102

Figure 8: Case 4 - (a) Partial Semantic Representation. (b) Solutions Semantic Representation.
Figure 9: Case 5 - (a) Partial Semantic Representation. (b) Solutions Semantic Representation.
An Ontology based Task Oriented Dialogue
103

Figure 10: Case 6 - (a) Partial Semantic Representation. (b) Solution Semantic Representation.
Figure 11: Case 7 - (a) Partial Semantic Representation. (b) Solution Semantic Representation.
Case 6. The sixth experience consists of a second
iteration of the dialogue, i.e., starting with the first ut-
terance and after its semantic interpretation and the
corresponding update of the ontology population are
performed, the user posts a new utterance, for in-
stance ”Show the price, with VAT.” The semantic in-
terpretation must take into account the existing in-
formation, obtained in previous iterations of the di-
alogue, and generates solutions according to the con-
text of it. The fact that the token ”price” is already
known and represented in the ontology, the seman-
tic interpretation must take it into account and use
that knowledge to generate the solutions. The partial
semantic interpretation provides the variables entities
and their relations, as shown is Figure 10. The starting
ontology population has now 8 individuals, including
one individual of the class VAT. The set of semantic in-
terpretation solutions has now 81 possibilities for the
utterance ontology representation and after applying
the weighting rules, those possibilities were reduced
to only two. Figure 10 shows the correct one obtained
after a question clarification.
Case 7. The last experience is similar to the previ-
ous. The utterance ”Show Products, with filter name.”
is posed after the semantic interpretation and the cor-
responding update of the ontology population of ut-
terances 1 and 6 are concluded. Similarly to the pre-
vious one, the tokens ”Product” and ”name” are al-
ready known and represented in the ontology. The
semantic interpretation must take it into account and
use that knowledge to generate the solutions. The
partial semantic interpretation provides the utterance
variables entities and their relations, as shown is Fig-
ure 11. Starting the ontology population with 8 in-
dividuals, the set of semantic interpretation solutions
has now 130 possibilities for the utterance ontology
representation and after applying the weighting rules,
those possibilities were reduced to only three. Figure
11 shows the correct one obtained after a clarification
question.
Table 1 presents a summary of the results obtained
for each experimental case and Figure 12 presents
the Ontology Population considering the experimen-
tal cases 1, 6 and 7.
5 EVALUATION DISCUSSION
The evaluation of the dialogue system can be done by
verifying the correctness of the recognition of the user
dialogue acts.
Consider the dialogue examples detailed in the
previous Sections:
User utterance 1: ”Show name, price and
stock, of the Products, on a page Analysis.”
User utterance 2: ”Show the price, with VAT.”
User utterance 3: ”Show Products, with filter
name.”
Taking into account that the dialogue manager was
able to choose the right interpretation for each utter-
ance, the individuals existing in the ontology, after all
the 3 utterances were interpreted, are represented in
Figure 12. To evaluate the correctness of the inter-
pretation, the SPARQL query below was lunched in
Proteg
´
e and the query answer is presented in Figure
13. The SPARQL query selects all the actions ins-
tances and their arguments names, showing that there
are three actions to specify the content of the screen
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
104

Figure 12: Individuals of the dialogue example (3 utterences).
Table 1: Experimental Results.
Example Case #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 #7
Starting Ontology Population 0 5 5 5 0 8 8
Total of Semantic Interpretation Solutions 165 165 137 232 144 81 130
Final Agenda 2 1 1 2 2 2 3
Figure 13: Query’s Answer.
”analysis”, exactly as the user intended with its utte-
rances.
PREFIX io: <http://www.semanticweb.org/id/2021/5/onto#>
SELECT *
{{SELECT ?action ?page ?object ?singleValue ?operator
WHERE {
?action io:has_page ?y .
?action io:has_object ?z .
?z io:is_composed_of ?w .
?y io:has_name ?page.
?z io:has_name ?object.
?w io:has_name ?singleValue}}
UNION
{SELECT?action ?page ?object ?singleValue ?operator
WHERE {
?action io:has_page ?y .
?action io:has_operand ?z .
?action io:has_operator ?operator .
?y io:has_name ?page .
?z io:has_name ?singleValue }}
UNION
{SELECT ?action ?page ?object ?singleValue ?operator
WHERE {
?action io:has_page ?y .
?action io:has_singlevalue ?z .
?action io:has_multivalue ?w .
?y io:has_name ?page .
?z io:has_name ?singleValue .
?w io:has_name ?object}}}
The verification of the correctness of a dialogue
representation has to be done by a human, but a
dataset could be built to evaluate the correctness of
the dialogue acts recognition.
Another evaluation for this system would be to
have users evaluating qualitatively the system’s ac-
tions. This can be done when the project modules,
dialogue system and action execution, are connected.
An Ontology based Task Oriented Dialogue
105

6 CONCLUSIONS
An ontology based task oriented dialogue, considered
as the natural language interface to an intelligent ap-
plication for helping unskilled users to build apps to
display databases contents, was developed in the con-
text of an undergoing project.
The dialogue architecture uses a domain depen-
dent ontology to model the specific discourse acts,
instructions, and the domain knowledge. The natu-
ral language module is a domain independent modu-
le that represents the user utterances in a partial dis-
course representation structure, which will be used
to match the ontology terms in order to obtain a set
of possible semantic representations of the user utter-
ance. The module responsible for managing the di-
alogue is able to use general concepts to prefer se-
mantic representation using general criteria, such as
to minimize the number of instances introduced by
the user, to minimize the number of missing instances
that are missing in the dialogue act, or to ask a ques-
tion to the user to clarify the meaning of its sentence.
The last module is still under development but the
preliminary results are promising as were presented.
The dialogue evaluation is still rudimentary and made
by the developers. It will be further developed when
the other project tasks are integrated and real users are
used.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is funded by FEDER, POR Lisboa 2020,
ANI - Ag
ˆ
encia Nacional de Inovac¸
˜
ao and Fundac¸
˜
ao
para a Ci
ˆ
encia e a Tecnologia, I.P. and Carnegie-
Mellon Portugal partnership, within the scope of the
GOLEM an International R&D project - GOLEM
Lisboa-01-0247-Feder-045917.
REFERENCES
Abdi, A., Idris, N., and Ahmad, Z. (2018). Qapd:
an ontology-based question answering system in the
physics domain. Soft Computing, 22(1):213–230.
ˇ
Zabokrtsk
´
y, Z., Zeman, D., and
ˇ
Sev
ˇ
c
´
ıkov
´
a, M. (2020). Sen-
tence Meaning Representations Across Languages:
What Can We Learn from Existing Frameworks?
Computational Linguistics, 46(3):605–665.
Acomb, K., Bloom, J., Dayanidhi, K., Hunter, P., Krogh, P.,
Levin, E., and Pieraccini, R. (2007). Technical sup-
port dialog systems:issues, problems, and solutions.
In Proceedings of the Workshop on Bridging the Gap:
Academic and Industrial Research in Dialog Tech-
nologies, pages 25–31, Rochester, NY. Association
for Computational Linguistics.
Asiaee, A. H., Minning, T., Doshi, P., and Tarleton, R. L.
(2015). A framework for ontology-based question
answering with application to parasite immunology.
Journal of biomedical semantics, 6(1):1–25.
Atzeni, M. and Atzori, M. (2018). Translating natural lan-
guage to code: An unsupervised ontology-based ap-
proach. In 2018 IEEE First International Conference
on Artificial Intelligence and Knowledge Engineering
(AIKE), pages 1–8.
Chen, H., Liu, X., Yin, D., and Tang, J. (2017). A survey on
dialogue systems: Recent advances and new frontiers.
Acm Sigkdd Explorations Newsletter, 19(2):25–35.
Deriu, J., Rodrigo, A., Otegi, A., Echegoyen, G., Rosset,
S., Agirre, E., and Cieliebak, M. (2020). Survey on
evaluation methods for dialogue systems. Artificial
Intelligence Review, page 56p.
Devi, M. and Dua, M. (2017). Adans: An agriculture do-
main question answering system using ontologies. In
2017 International Conference on Computing, Com-
munication and Automation (ICCCA), pages 122–127.
IEEE.
Fellbaum, C. (1998). WordNet: An Electronic Lexical
Database. Bradford Books.
Fong, T., Thorpe, C., and Baur, C. (2003). Collaboration,
dialogue, human-robot interaction. In Jarvis, R. A.
and Zelinsky, A., editors, Robotics Research, pages
255–266, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin Heidel-
berg.
Geurts, B., Beaver, D. I., and Maier, E. (2020). Discourse
Representation Theory. In Zalta, E. N., editor, The
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics
Research Lab, Stanford University, Spring 2020 edi-
tion.
Gotham, M. and Haug, D. (2018). Glue semantics for uni-
versal dependencies. In Proceedings of the LFG’18
Conference University of Vienna, Miriam Butt, Tracy
Holloway King (Editors), CSLI Publications, pages
208–226.
Kamp, H. and Reyle, U. (1993). From Discourse to Logic:
Introduction to Modeltheoretic Semantics of Natural
Language, Formal Logic and Discourse Representa-
tion Theory. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publish-
ers.
Liu, J., Cohen, S. B., Lapata, M., and Bos, J. (2021).
Universal Discourse Representation Structure Pars-
ing. Computational Linguistics, pages 1–32.
Meditskos, G., Kontopoulos, E., Vrochidis, S., and Kom-
patsiaris, I. (2020). Converness: Ontology-driven
conversational awareness and context understanding
in multimodal dialogue systems. Expert Systems,
37(1):e12378.
Melo, D., Rodrigues, I. P., and Nogueira, V. B. (2016).
Using a dialogue manager to improve semantic web
search. International Journal on Semantic Web and
Information Systems (IJSWIS), 12(1).
Milward, D. and Beveridge, M. (2003). Ontology-based
dialogue systems. In Proc. 3rd Workshop on Knowl-
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
106

edge and reasoning in practical dialogue systems (IJ-
CAI03), pages 9–18.
Reddy, S., T
¨
ackstr
¨
om, O., Collins, M., Kwiatkowski, T.,
Das, D., Steedman, M., and Lapata, M. (2016). Trans-
forming dependency structures to logical forms for se-
mantic parsing. Transactions of the Association for
Computational Linguistics, 4:127–140.
Stoilos, G., Wartak, S., Juric, D., Moore, J., and Khodadadi,
M. (2019). An ontology-based interactive system for
understanding user queries. In European Semantic
Web Conference, pages 330–345. Springer.
Stoyanchev, S., Keizer, S., and Doddipatla, R. (2021). Ac-
tion state update approach to dialogue management.
In ICASSP 2021 - 2021 IEEE International Con-
ference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing
(ICASSP), pages 7398–7402.
Wei, W., Le, Q., Dai, A., and Li, J. (2018). AirDialogue:
An environment for goal-oriented dialogue research.
In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empiri-
cal Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages
3844–3854, Brussels, Belgium. Association for Com-
putational Linguistics.
Wessel, M., Acharya, G., Carpenter, J., and Yin, M. (2019).
Ontovpa—an ontology-based dialogue management
system for virtual personal assistants. In Advanced So-
cial Interaction with Agents, pages 219–233. Springer.
Wu, Z., Peng, H., and Smith, N. A. (2021). Infusing Fine-
tuning with Semantic Dependencies. Transactions of
the Association for Computational Linguistics, 9:226–
242.
An Ontology based Task Oriented Dialogue
107
