
Tuning Convolutional Neural Networks Hyperparameters
for Offline Handwriting Recognition
Ahmed Remaida
a
, Aniss Moumen
b
, Younes El Bouzekri El Idrissi
c
and Benyoussef Abdellaoui
d
Laboratory of Engineering Sciences, National School of Applied Sciences,
Ibn Tofaïl University, Kenitra, Morocco
Keywords: EMNIST, Deep Learning, Convolutional Neural Networks, Handwriting Letters Recognition.
Abstract: Deep Learning Artificial Neural Networks has pushed forward researches in the field of image recognition,
furthermore in handwriting recognition. In writing or writer identification, segmentation, or features
extraction applications, many ANNs models are applied in the process. This paper presents a comparative
study of one of the most widely used ANNs for offline handwriting recognition, known as Deep
Convolutional Neural Networks. We describe the challenging benchmark Dataset entitled EMNIST
introduced in 2017 as an extended version of the well-known MNIST to fill the gap of handwritten letters
characters. The accuracies obtained in this work for the letters dataset compares favourably with many other
approaches in the literature. The effect of the choice of hyperparameters related to our network architecture
and capabilities are explored and detailed, like the number of layers, neurons, optimizers, learning rates and
other parameters.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2981-8936
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5330-0136
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4018-437X
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5950-0187
1 INTRODUCTION
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have
proven their incredible ability for feature extraction
leading to outstanding classification performances in
several application areas, such as object detection,
language processing, image recognition, and many
more. Nevertheless, their performance is affected by
small changes in the network hyperparameters like
the number of convolutional layers, dense layers,
activation functions, optimizers, learning rates… etc.
For the last decade, researchers have made great
efforts to automatically tune hyperparameters
seeking to enhance the CNNs performances for
different applications. Although these methods
exceeded most of the manually generated
architectures, the searching process requires greater
computational resources and implies time to train all
possibilities during the search for the best
architecture. Here in this paper, we intend to
compare different CNNs performances based on
hyperparameters changes when applied for EMNIST
letters recognition. It is structured as the following:
Section two where we give a non-exhaustive
description of the benchmarked handwriting
datasets. After that, in section 3 where we describe a
comprehensive explanation of the Convolutional
Neural Networks architecture. Finally, in section 4
where we present our results and findings.
2 HANDWRITING DATASETS
BENCHMARK
Many handwritten datasets have been developed
across the years, building a solid background for
evaluating numerous recognition tasks. These
datasets could be classified based on different
dimensions: Online or Offline data acquisition
method, script, size, and types of supported tasks
(Hussain et al., 2015). This section highlights some
Remaida, A., Moumen, A., El Bouzekri El Idrissi, Y. and Abdellaoui, B.
Tuning Convolutional Neural Networks Hyperparameters for Offline Handwriting Recognition.
DOI: 10.5220/0010728600003101
In Proceedings of the 2nd Inter national Conference on Big Data, Modelling and Machine Learning (BML 2021), pages 71-76
ISBN: 978-989-758-559-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
71
of the Benchmarks used in offline handwriting
recognition for validating novel techniques and
algorithms.
2.1 NIST SD 19
Since the beginning of the 90s, the National Institute
of Standards and Technology (NIST) developed a
series of image databases intended for handprint
document processing and OCR research. In 1995
they introduced the Special Database 19 (Grother,
1995), composed of handwriting samples forms of
3600 writers and 810,000 isolated character images
in addition to ground-truth information. Even if it
was available since 1995, it remained mostly unused
because of difficulties in both accessing and using
for modern computers, due to the way it was stored.
2.2 MNIST
The Mixed National Institute of Standards and
Technology dataset, or simply (MNIST) was
introduced in 1998 by LeCun et al., it is a
handwriting digit database derived from a small
subset of the numerical digits contained within the
larger database NIST (Le Cun et al., 1989). It is
constructed based on two different sources: The
NIST SD 1 collected among high-school students
and the NIST SD 3 retrieved from Census Bureau
employees. We could describe the MNIST as a
labelled images database that contains handwritten
digits, with a separate training dataset (60,000
samples) and test dataset (10,000 samples), making
it easy to use and allows a fast comparison between
different techniques. Initially, black and white
images from NIST were sized to fit in a 20*20
pixels box with aspect ratio preservation and then
normalized to grey-scale with anti-aliasing
technique. As a final result, images were centred in a
28*28 image by computing the pixel’s centre of
mass. The MNIST dataset remained the most known
and used dataset in the computer vision and neural
networks community and was widely used as the
“hello-world” of machine and deep learning
tutorials.
2.3 EMNIST
Considering that MNIST dataset has becomes a non-
challenging benchmark, Cohen et al. introduced in
April 2017 the extended version of the MNIST
(EMNIST) consisting of both handwritten letters and
digits with the same structure as the MNIST database
(Cohen et al., 2017), offering new challenges for
researchers on computer vision. The EMNIST was
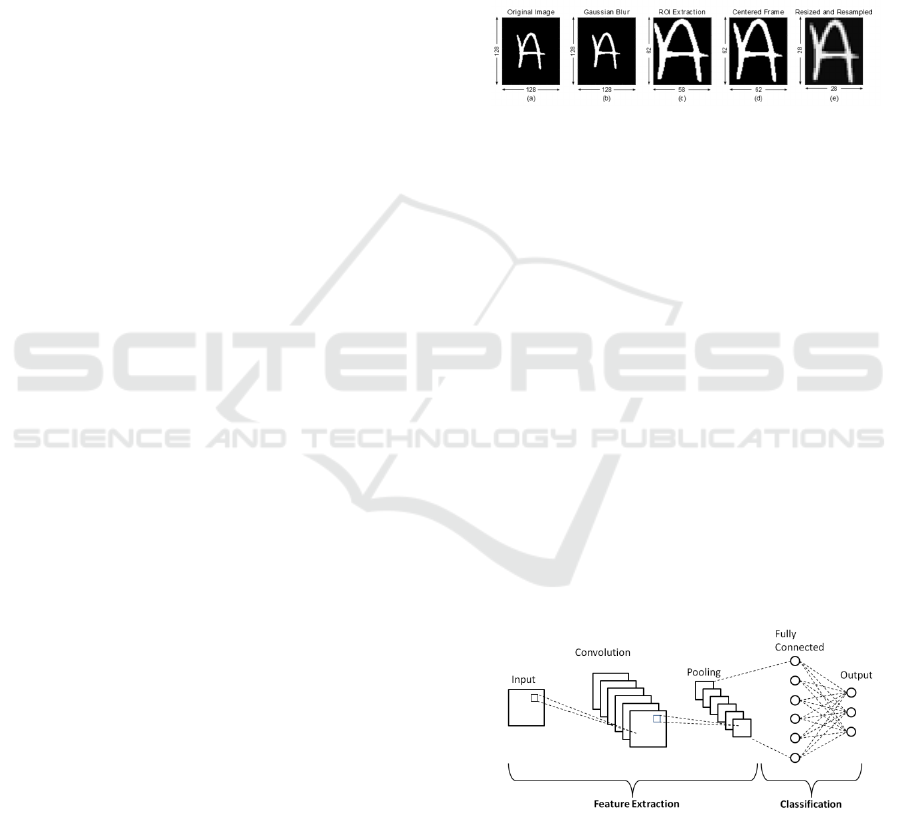
constructed with the NIST Special Database 19
(NIST SD 19), where original images were stored as
28*28-pixel binary images and with using the bi-
cubic interpolation with a Gaussian filter to soften
the edges with aspect ratio preservation. In the Figure
below, the process of transforming NIST SD 19
images into the EMNIST. The EMNIST database is
growing more interest among researchers in the
Neural Networks community. Like the MNIST it is
now known as the “hello-world 2” of machine and
deep learning tutorials.
Figure 1: Diagram of the conversion process used to
convert the NIST dataset into EMNIST
(Cohen et al., 2017)
3 CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL
NETWORKS
In general, CNN's architecture comprises two parts:
the first one is composed of alternate layers of
convolution and pooling that extract features from
imputed data. The second one is composed of one or
more fully connected layers leading to classification.
Different regulating units like batch normalization or
dropout can be incorporated with the different
mapping functions in order to optimize CNN
performances. Therefore, the arrangement of
components in a CNN is considered fundamental to
designing new architectures for enhancing
performances. Here in the following, we describe
each one of those components:
Figure 2: A Typical Convolutional Neural Networks
Architecture
3.1 Convolutional Layer
The existing neurons in the convolutional layer act
as filters that aim to divide the image into small
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
72

parts known as kernels or receptive fields. By sliding
those filters over the inputted image, we calculate
the product between the parts of the input image and
the filter respecting the size of the filter (M*M). As
a result, we get a feature map that provides the
classification part of the network with relevant
information about the image, such as edges and
corners, leading to enhancing the features extraction
process and classification performances.
3.2 Pooling Layer
Pooling, also referred to as down-sampling, is a
great local operation that allows summing a number
of similar information in the neighbourhood of the
kernels leading to output the dominant response
within this local region. It also reduces the size of
resulted feature maps from the convolutional layer
which regulates the network complexity. Different
formulas of pooling exist such as max, average,
overlapping, spatial pyramid, L2… etc. When using
a max-pooling layer the resulted map would contain
the most prominent features in the previous feature
map generated in the convolutional layer.
3.3 Fully Connected Layer
The fully connected layer represents the
classification part at the end of the Convolutional
Neural Network. It takes the pooled feature maps as
inputs and performs non-linear combinations in
order to classify the data. In some cases, we replace
the fully connected layer with a global-average-
pooling layer.
3.4 Dropout Layer
Dropout is a technique that introduces regularization
within the network by skipping some of the units or
connections (randomly) with a predefined
probability. In a CNN, multiple connections that
learn a non-linear relation are sometimes co-adapted,
which causes over-fitting (Srivastava et al., 2014).
Randomly dropping some connections or units
produces several thinned network architectures, and
as a result, the one representative network with small
weights is selected to be considered as an
approximation of all proposed networks.
3.5 Activation Functions Layer
The Activation function is one of the main
hyperparameters of the CNNs model. It adds the
non-linearity aspect to the model, allowing it to
decide which information is fired in the forward
direction and which ones are not at the network's
end. Several activation functions are commonly
used, such as tanH, Sigmoid, ReLU, Softmax, and
most recently Mish (Misra, 2019). Each of these
functions has a specific usage: Sigmoid and Softmax
are more used in a binary classification, ReLU is
generally used in multi-class classification.
3.6 Normalization Layer
Data normalization ensures similar data distribution
for each input parameter. It is a process that makes
convergence faster while the network is training.
Many normalization layers types have been used in
CNNs architectures like Batch Normalization,
Weight Normalization, Layer Normalization and
Group Normalization.
3.7 Optimizers Algorithms
Optimizers are algorithms used to change a CNN’s
attributes like the weights and learning rate with the
purpose of reducing the losses. Changing the
optimizers and learning rates reduces the losses, so
they are a key factor for reducing the losses and
providing the most accurate results possible. There
are various choices of optimizers such as Adam
(Kingma & Ba, 2017), RMSprop (Hinton, 2012),
GD and SGD (Ruder, 2017).
4 EXPERIMENT
METHODOLOGY
There is an important number of hyperparameters in
a Convolutional Neural Network. Changing all those
parameters would result in a more significant
number of cases. Thus, we only chose
hyperparameters like the number of layers,
activation functions, optimizers, learning rates,
dropout rates and the number of neurones.
Combining nine possible architectures with three
different optimizers and four learning rates, we
generated 108 CNNs architecture. We trained and
tested all of them on the EMNIST Letter dataset
after grouping existing samples and splitting them
randomly into training and testing sets with a ratio of
80% to 20%. The training was for 50 epochs with a
fixed batch size equal to 512 batches and took nearly
three and a half-hour. We have automated
implementing, training and testing all the possible
models in Python 3.7 using Keras, a well-known
high-level neural networks API that runs on top of
the TensorFlow Framework. We carried out our
Tuning Convolutional Neural Networks Hyperparameters for Offline Handwriting Recognition
73

experiments on the Kaggle, a cloud-based
workbench for Data Science and Deep Machine
Learning. It offers a free virtual notebook powered
by a 2-core of Intel Xeon CPU @ 2.30GHz, 16GB
of RAM, 16GB of the NVidia K80 GPUs and 73 GB
of Storage access. Here below in Table 1, we give a
detailed description of all the hyperparameters
choices:
Table 1: Hyperparameters choice description.
H
yp
er
p
arameters Value
Number of convolution la
y
ers 1-3
Number of filters respectivel
y
32-64-128
Kernel sizes 3x3
Pool size in MaxPooling laye
r
2x2
Dropout rates
0.2-0.5
(0.05 steps)
Number of dense layers 1-3
Number of neurons per dense
512-1024
(
2 ste
p
s
)
Activation function for all
convolutional and dense la
y
ers
Mish
Optimizer
Adam , SGD,
RMSprop
Number of E
p
ochs 50
Batch size 512
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
We have noticed that the choice of learning rates is
remarkably affecting the efficiency of the
optimizer’s algorithm. We have noticed that with the
SGD optimizer, there is stability using all the
learning rates, it take more time for the network to
learn, and the smaller is the learning rate, the slower
the learning is getting. However, the best
performances were with the bigger learning rates
like 1e-2. As for Adam and RMSprop optimizers, it
seems that they are unstable when used with bigger
learning rates. Nevertheless, all nine CNNs
architectures showed faster learning with accurate
performances when used with the learning rate 1e-4,
whichever optimizer is chosen. The use of three
convolutional layers with one or two dense layers
marked the best results in all cases. A summary of
the results can be found in Tables 2 and 3 below:
Table 2: Top 3 CNN’s Architectures with highest Testing
Accuracy.
CNN Architectures Optimizer (L R) Accuracy
3 Conv, 2 Dense Adam
(
1e-3
)
94.681 %
3 Conv, 2 Dense Adam
(
1e-4
)
94.517 %
3 Conv, 2 Dense RMS
p
ro
p
(
1e-4
)
94.517 %
Table 3: Top 3 CNN’s Architectures with highest Testing
Error rate.
CNN Architectures Optimizer (L R)
Error
Rate
3 Conv, 1 Dense Adam
(
1e-4
)
16.706 %
3 Conv, 1 Dense RMSprop (1e-4) 17.043 %
3 Conv, 2 Dense Adam (1e-4) 17.323%
The highest accuracy was achieved by a CNN model
with three convolutional and two dense layers. A full
description of this model’s architecture is presented
in the following Figure:
Figure 3: Architecture of the best CNN model.
Here in Figures 4 and 5, we give more details
about the best CNN model with the highest accuracy
rates, an illustration of monitoring the training and
validation for the 50 epochs:
Figure 4: Top CNN’s Training and Validation Accuracy
across different learning Epochs
Figure 5: Top CNN’s Training and Validation Loss
across different learning Epochs.
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
74

There is an apparent absence of the phenomena of
neither overfitting nor underfitting across the
training and validation process. The main factor of
such achievement is the choice of the Mish
activation function (Misra, 2019) in addition to the
use of the batch normalization layer (Ioffe &
Szegedy, 2015). We strongly believe that further
training for this model could lead to better results.
Satisfied with what we had achieved, we chose to
present only those results. In the following table, we
compare our best achievement to the existing works
under the same scope:
Table 4: Our best achievement compared to the state of
art.
CNNs for EMNIST Letters Accuracy
(Peng & Yin, 2017) 95.44%
(
Baldominos et al., 2019
)
95.35%
This wor
k
94.68 %
(Sen Sharma et al., 2018) 94.36%
(Cavalin & Oliveira, 2019) 93.63%
(
Ci
r
esan et al., 2011
)
92.42%
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we have described the EMNIST
benchmark dataset alongside Deep Convolutional
Neural Networks architectures and hyperparameters.
By tuning hyperparameters of CNNs, we have
achieved excellent results that compare favourably
with other work under the same scope. We believe
that further tuning would lead to better outcomes.
Thus we intend to evaluate deeper architectures of
the CNNs with larger hyperparameters tuning to
enhance performances even further.
REFERENCES
Baldominos, A., Saez, Y., & Isasi, P. (2019). Hybridizing
Evolutionary Computation and Deep Neural
Networks: An Approach to Handwriting Recognition
Using Committees and Transfer Learning.
Complexity, 2019, 1–16.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2952304
Cavalin, P., & Oliveira, L. (2019). Confusion Matrix-
Based Building of Hierarchical Classification. In R.
Vera-Rodriguez, J. Fierrez, & A. Morales (Eds.),
Progress in Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis,
Computer Vision, and Applications (Vol. 11401, pp.
271–278). Springer International Publishing.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-13469-3_32
Ciresan, D. C., Meier, U., Gambardella, L. M., &
Schmidhuber, J. (2011). Convolutional Neural
Network Committees for Handwritten Character
Classification. 2011 International Conference on
Document Analysis and Recognition, 1135–1139.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDAR.2011.229
Cohen, G., Afshar, S., Tapson, J., & van Schaik, A.
(2017). EMNIST: An extension of MNIST to
handwritten letters. ArXiv:1702.05373 [Cs].
http://arxiv.org/abs/1702.05373
Grother, P. (1995). NIST Special Database 19
Handprinted Forms and Characters Database.
/paper/NIST-Special-Database-19-Handprinted-
Forms-and-
Grother/1ea788f1f4334095d215afd4c137936ff89d7f6
8
Hinton, G. (2012). Lecture Notes On RMSprop.
http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/coursera/lecture6/le
c6.pdf
Hussain, R., Raza, A., Siddiqi, I., Khurshid, K., & Djeddi,
C. (2015). A comprehensive survey of handwritten
document benchmarks: Structure, usage and
evaluation. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video
Processing, 2015(1), 46.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13640-015-0102-5
Ioffe, S., & Szegedy, C. (2015). Batch Normalization:
Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing
Internal Covariate Shift. ArXiv:1502.03167 [Cs].
http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167
Khan, A., Sohail, A., Zahoora, U., & Qureshi, A. S.
(2020). A survey of the recent architectures of deep
convolutional neural networks. Artificial Intelligence
Review, 53(8), 5455–5516.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09825-6
Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2017). Adam: A Method for
Stochastic Optimization. ArXiv:1412.6980 [Cs].
http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980
Le Cun, Y., Jackel, L. D., Boser, B., Denker, J. S., Graf,
H. P., Guyon, I., Henderson, D., Howard, R. E., &
Hubbard, W. (1989). Handwritten digit recognition:
Applications of neural network chips and automatic
learning. IEEE Communications Magazine, 27(11),
41–46. https://doi.org/10.1109/35.41400
Misra, D. (2019). Mish: A Self Regularized Non-
Monotonic Activation Function. ArXiv:1908.08681
[Cs, Stat]. https://doi.org/1908.08681
Peng, Y., & Yin, H. (2017). Markov Random Field Based
Convolutional Neural Networks for Image
Classification. In H. Yin, Y. Gao, S. Chen, Y. Wen, G.
Cai, T. Gu, J. Du, A. J. Tallón-Ballesteros, & M.
Zhang (Eds.), Intelligent Data Engineering and
Automated Learning – IDEAL 2017 (Vol. 10585, pp.
387–396). Springer International Publishing.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68935-7_42
Ruder, S. (2017). An overview of gradient descent
optimization algorithms. ArXiv:1609.04747 [Cs].
http://arxiv.org/abs/1609.04747
Sen Sharma, A., Ahmed Mridul, M., Jannat, M.-E., &
Saiful Islam, M. (2018). A Deep CNN Model for
Student Learning Pedagogy Detection Data Collection
Using OCR. 2018 International Conference on Bangla
Tuning Convolutional Neural Networks Hyperparameters for Offline Handwriting Recognition
75

Speech and Language Processing (ICBSLP), 1–6.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICBSLP.2018.8554701
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2015). Very Deep
Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image
Recognition. ArXiv:1409.1556 [Cs].
http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I.,
& Salakhutdinov, R. (2014). Dropout: A Simple Way
to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. 30.
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
76
