
E-Learning Critical Success Factors in Moroccan Universities
during the Covid-19 Pandemic: Case Moulay Ismail University
Azeddine Zriba, Said Amali
Faculty of Sciences, Moulay Ismail University, Meknes, Morocco
Keywords: E-learning, COVID-19, pandemic, CSF, AHP, TOPSIS
Abstract: The pandemic COVID-19 has significantly disrupted the world, higher Education is among the most
impacted activities when schools and universities remained closed all over the world. In response to the
state of health emergency implemented by Moroccan authorities to minimize the spread of the coronavirus,
the Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research and Professional Training have decided to suspend
classroom courses in all educational institutions from 16 March 2020 until further notice.
This paper proposes to identify the critical success factors (CSFs) for the remote learning mode adopted by
the Moroccan universities during the COVID-19 pandemic by using two techniques, the first one is the
multi-criteria Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), and the second is Technique for Order Preference by
Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS). This study was carried out on a sample of 244 teachers and 3877
students who participated in the surveys established by Moulay Ismail University.
1 INTRODUCTION
The pandemic COVID-19 has significantly disrupted
the world, higher Education is among the most
impacted activities when education institutions
remained closed all over the world. As a result of
this situation, Moroccan authorities declared a state
of emergency on 16 March 2020
1
, and many
precautionary measures have been taken to ensure a
pedagogical continuity, including suspension of the
classroom courses in all public and private schools
and universities, and adopting distance learning
mode, to avoid the spread of the coronavirus
2
.
In this pandemic context of the coronavirus
Covid-19, Moulay Ismail University has deployed a
pedagogical continuity plan to continue the training
of its more than 70,000 students through distance
learning.
In this study, we determinate the critical success
factors (CSFs) during the COVID-19 pandemic from
1
News, Morocco World (19 March 2020). "COVID-19:
Morocco Declares State of Emergency". Morocco
World News. Retrieved 19 March 2020
2
Courses Suspended in Morocco from March 16 Until
Further Notice". Maghreb Arabe Press. 13 March
2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
the perspectives of teachers and students by
evaluating the E-learning experience during the
spring session using multi-criteria decision-making
methods.
This research can help decision-makers in
Moroccan universities to determine the best strategy
to adopt during a crisis by improving the most
critical factors to be taken into consideration when
implementing any remote learning process.
2 RESEARCH CONTEXT:
E-LEARNING IN MOROCCO
Over the last few years, higher Education knows a
new dynamic aimed at improving the quality of
higher Education and modernize its practices by
putting the learner in the center of educational
action, and integrating ICT (Information and
Communication Technology) into Education, as part
of the national strategy. “Maroc Numeric 2013”
3
To improve performance, quality and
productivity, and harmonize with standards
3
https://lematin.ma/journal/2012/NTI_Strategie-de-Maroc-
Numeric-2013--un-premier-bilan-globalement-
positif/170317.html
Zriba, A. and Amali, S.
E-Learning Critical Success Factors in Moroccan Universities during the COVID-19 Pandemic : Case Moulay Ismail University.
DOI: 10.5220/0010732300003101
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Big Data, Modelling and Machine Learning (BML 2021), pages 267-273
ISBN: 978-989-758-559-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
267

international organizations and to make it a vector of
development, the Moroccan education system has
been the subject of numerous reforms and upgrading
programs (Alem , 2012):
The Education Reform (Law 0100), initiated
in 2002/2003, consists of establishing the
LMD (Bachelor's-Master's-Doctorate) system
(Bologna process 1999). The significant
contribution of this new reform was the
reference to ICT both as an object and as a
learning and governance tool for all
disciplines and higher education institutions.
The Emergency Program (2009-2012) aims to
increase the reception capacity of universities,
improve the quality of training and promote
scientific and technical research. This program
emphasizes the continuing Education of
teachers and requires the university to acquire
a Digital Work Environment (ENT) and a
strategy for integrating educational
technologies in university-wide training.
Maroc Numeric 2013 is a national strategy,
aiming to position Morocco as a regional
technological hub and to insert it into the
global knowledge economy through its
companies and universities. At the university
level, it consists of supporting them in
equipment and teacher training.
All these initiatives and efforts have made ICT
a vital component as an object and a learning
tool in the education system.
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
3.1 Definition of e-Learning
E-learning, also referred to as distance learning,
online learning (Sangra, 2011), virtual learning
(VL)( Bezhovski et al, 2016), Computer-Based
Learning (CBL) (Fenouillet et al, 2006) “is a
conjunction of information and telecommunication
technology (ICT) with educational world” (Grubisic
et al, 2009). (Sun et al, 2008) stated that e-learning is
delivering and transferring educational learning
information through information and communication
technology (ICT). The most essential advantages of
e-learning are increasing teacher/student interactions
and relations between students without location and
time limitations via synchronous and asynchronous
educational network models (Hameed et al, 2008).
According to (Beningo et al, 2000), e-learning is
conducted on the internet, where students can access
lectures online at any place and time as needed, and
allows them the possibility to review the information
many times.
E-learning has two aspects: The first aspect is
related to structural issues (technology, learning
process, learning design), and the other aspect is
related to communicational issues (trainees habits,
skills and communication patterns (Beningo et al,
2000).
3.2 Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)
In 1980 Saaty developed the Analytic Hierarchy
Process (AHP) (Saaty, 1988). This technique is used
to manage qualitative and quantitative multi-criteria
elements involving in decision-making behavior.
AHP is one of the most inclusive systems, which
is considered to make decisions with multiple
criteria because this method gives to formulate the
problem as a hierarchical and believe a mixture of
quantitative and qualitative criteria as well
(Taherdoost, 2017).
3.3 Technique for Order Preference by
Similarity to Ideal Solution
(TOPSIS)
The (TOPSIS) method has been developed by
Hwang and Yoon in 1981 (Hwang et al, 1981).
This method is used to choose the best
alternative among a group of alternatives
(Backmann et al, 1981), also, it allows knowing the
distance of both the positive and the negative
alternatives of the ideal solution (Prakash et al,
2015).
3.4 CSF and Types of e-Learning
Systems
The critical success factors are referred to as
“characteristics, conditions, or variables that, when
properly sustained, maintained, or managed, can
have a significant impact on the success of a firm
competing in a particular industry” 16 (Alhabeeb et
al, 2018). The three types of e-learning systems used
in this study are defined in Table 1, to determine the
best type of e-learning system associated with AHP
and the TOPSIS technique during COVID-19. In
Table 2, we defined the factors that were considered
in this paper. Fig1 explain the critical success factor
hierarchy problem discussed in this study based on
the multiple-criteria decision analysis problem
representation.
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
268

Table 1: Types of E-learning systems
T
yp
e Definition
Face to face
learning
Traditional learning where the course
content and learning material are
taught from teacher to student. This
allows for live interaction between a
learner and an instructor.
(Thai et al 2017) (Young et al, 2014)
Blended
Learning
A mix of traditional and online classes.
(Graham et al, 2013)
(Young et al, 2014)
Synchronou
s Learning
A real-time interaction distance
learning.
(
Rowe, 2019
)
Table 2: definitions and studies related to CSF of e-
learning
Facto
r
Criteria
Learner’s
dimension
Motivation, learning speed, computer
skill, commitment.
(Bhuasiri et al, 2012)(Anggrainingsih
et al, 2018)
Instructor’s
dimension
Teaching style, instructor attitude to
the student, knowledge of learning
technology.
(Bhuasiri et al, 2012)(Anggrainingsih
et al, 2018
)
Learning
Environment
dimension
Learning management system,
technical infrastructure, design of user
interface, network security.
(Bhuasiri et al, 2012)
(
An
gg
rainin
g
sih et al, 2018
)
Course
dimension
Sufficient, updated and understandable
content.
(Bhuasiri et al, 2012)
(
An
gg
rainin
g
sih et al, 2018
)
Support
dimension
Providing financial support,
communication tools, help disk
availability, and training.
(Bhuasiri et al, 2012)
(
An
gg
rainin
g
sih et al, 2018
)
Figure 1: Hierarchical structure for dimensions and CSFs
of E-learning system.
4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The methodology used in this paper is based on
three parts, a survey, the AHP method, and the
TOPSIS method, a detailed description of each part
will be presented in the next sections.
4.1 Data Collection
This study is based on data collected from two
surveys released by Moulay Ismail University, the
first was for teachers
4
, and the second was for
students
5
. Table 3 summarizes the teachers who
participated in the study regarding seniority,
disciplinary field, degrees concerned by E-learning,
and table 4 summarizes the students who
participated regarding gender, place of residence,
faculty, and cycles of studies.
Table 3: Teachers demographic data
Frequency Percentage
Seniority Less than 5 years 54 22%
From 5 to 10
years
48 20%
From 11 to 20
years
32 13%
More to 20 years 110 45%
disciplinary
field
Sciences and
techniques
83
34%
Legal sciences 17 7%
Economic
Science and
Business
Administration
23
9%
Letters and
human sciences
73
30%
Engineering
Sciences
39
16%
Educational
Sciences
9
4%
degrees
concerned
by E-
learning
Technological
University
Degree
22
6%
Bachelor 187
54%
Master 105
30%
Engineering
degree
33
9%
ENCG degree 2
1%
4
https://questionnaire.umi.ac.ma/index.php/179221
5
https://questionnaire.umi.ac.ma/index.php/747239
E-Learning Critical Success Factors in Moroccan Universities during the COVID-19 Pandemic : Case Moulay Ismail University
269

Table 4: Students demographic data
Frequency Percentage
Gender
Male
1898 49%
Female
1979 51%
Place of
residence
Rural area
1060 27%
Urban area
2817 73%
Faculty /
school
FLSH
412 11%
FSJES
611 16%
FS
624 16%
FST
476 12%
FP
233 6%
ENSAM
744 19%
ENS
132 3%
EST
217 6%
ENCG
2 0%
No response
426 11%
Cycle of
studies
Bac + 2
299 8%
Bac + 3
1813 47%
Bac + 5
1258 32%
Other
457 12%
No response
50 1%
4.2 The Analytic Hierarchy Process
To use the AHP method, the following steps are
applied (Saaty, 1988) (Alqahtani, 2020):
1. Completing the pairwise comparison matrix
Table 5 using the ratings in the table 6, by
evaluating every two criteria at a time in terms
of their relative importance. The diagonal of
the matrix contains only values of 1.
Table 5: Pairwise comparison matrix
Students
dimension
Instructors
dimension
Learning
Environment
dimension
Instructional
Design
dimension
Support
dimension
Students
dimension
1 1/2 1 1 1
Instructors
dimension
2 1 3 2 2
Learning
Environment
dimension
1 1/3 1 1/2 1/3
Course
dimension
1 1/2 2 1 1/3
Support
dimension
1 1/2 3 3 1
Table 6: Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) ratings
Verbal Judgment of
Preference
Numerical Rating
3 Extremel
y
p
referre
d
2 Stron
g
l
y
p
referre
d
1 E
q
uall
y
p
referre
d
2. Calculating the criteria weight, by creating a
normalized comparison matrix where each
value in the matrix is divided by the sum of
its column table 7.
Table 7: Normalized matrix
Students
dimension
Instructors
dimension
Learning
Environment
dimension
Instructional
Design
dimension
Support
dimension
Students
dimensio
n
0,166 0,166 0,100 0,142 0,217
Instructors
dimensio
n
0,330 0,357 0,300 0,285 0,434
Learning
dimensio
n
0,166 0,119 0,100 0,070 0,070
Course
dimensio
n
0,166 0,166 0,200 0,142 0,070
Support
dimensio
n
0,166 0,166 0,300 0,428 0,217
3. Determine the average priority vector by
averaging across the rows, the sum of all
elements in priority vector is 1. The priority
vector shows relative weights among the
things that we compare, as shown in table 8.
Table 8: priority vectors
Students
dimension
Instructors
dimension
Learning
Environment
dimension
Instructional
Design
dimension
Support
dimension
0,158 0,341 0,105 0,141 0,255
4.3 The Technique for Order
Preference by Similarity to Ideal
Solution
The TOPSIS process is carried out by applying the
following steps as defined on (Alqahtani, 2020)
(Sunardi, 2019):
1. Form the matrix expressed as follows:
D =
mnmmm
n
n
n
XXXA
XXXA
XXXA
XXXA
21
222213
112112
211
......
.
Where:
Ai = ith alternative project and Xij= the
numerical outcome of the ith alternative project
compared to the jth criterion.
Table 9 is the result of the TOPSIS matrix.
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
270
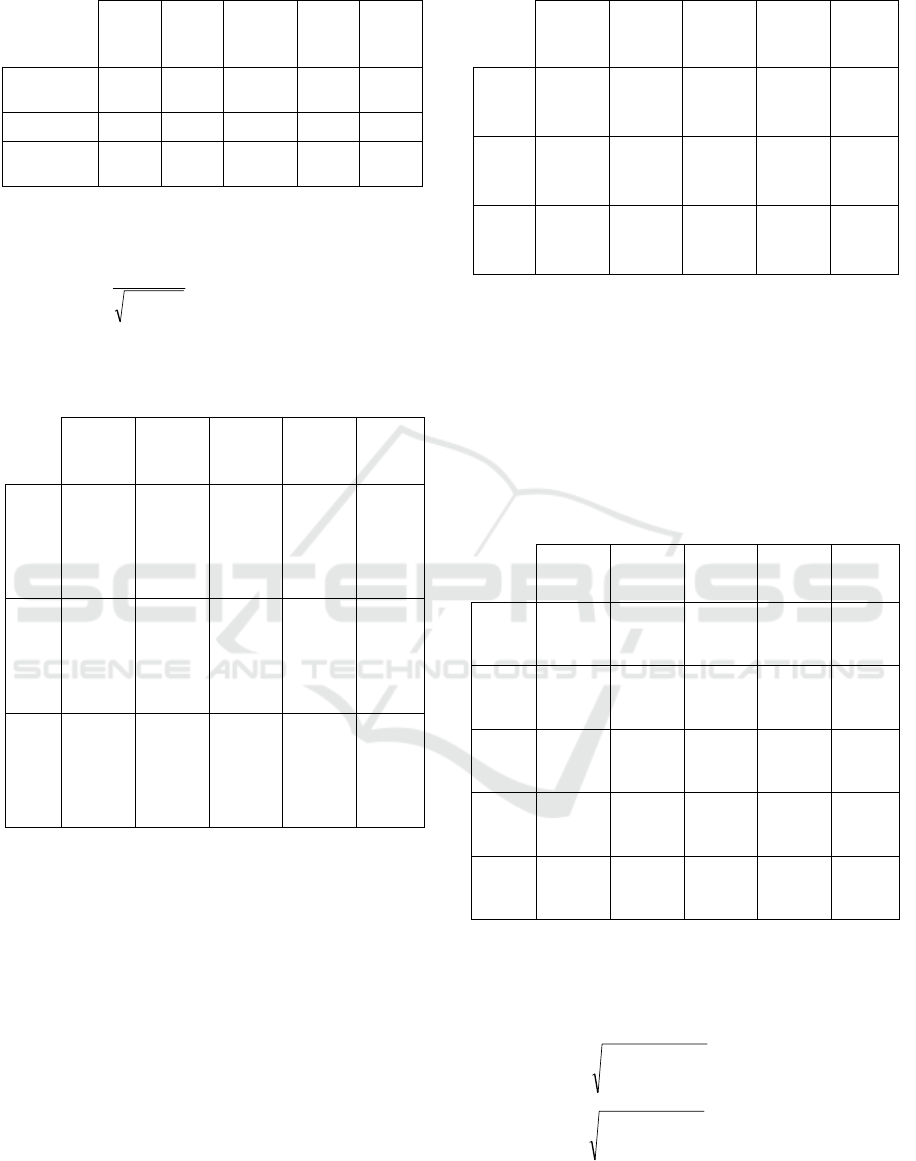
n
i
ij
ij
X
r
X
ij
1
2
Table 9: TOPSIS matrix
Students
dimension
Instructors
dimension
Learning
Environment
dimension
Course
dimension
Support
dimension
Face to Face
Learning
3 3 1 3 1
Blended Learning
2 3 3 2 2
Synchronous
Learning
2 2 1 2 2
2. The normalized matrix is obtained by
applying the following formula :
Table 10 shows the TOPSIS normalize matrix.
Table 10: TOPSIS normalize matrix
Students
dimension
Instructors
dimension
Learning
Environment
dimension
Course
dimension
Support
dimension
Face to
Face
Learning
0,727606875 0,639602149 0,301511345 0,727606875 0,33333333
Blended
Learning
0,48507125 0,639602149 0,904534034 0,48507125 0,66666667
Synchron
ous
Learning
0,48507125 0,426401433 0,301511345 0,48507125 0,66666667
3. During this step, we construct the weighted
normalize decision matrix by multiplying the
normalized decision matrix by its relative
weights, the result is shown in table 11. The
following formula is applied to calculate the
weighted normalized value V
ij
V
ij
= W
ij
R
ij
Table 11: weighted normalize decision matrix
Students
dimension
Instructors
dimension
Learning
Environment
dimension
Course
dimension
Support
dimension
Face to
Face
Learning
0,115107408 0,218232253 0,031658691 0,108267903 0,08513333
Blended
Learning
0,076738272 0,218232253 0,094976074 0,072178602 0,17026667
Synchrono
us
Learning
0,076738272 0,145488169 0,031658691 0,072178602 0,17026667
4. Define both the ideal best and ideal worst
value
V
+
= (max v
ij
)
V
-
= (min v
ij
)
Table 12 shows the TOPSIS positive and
negative ideal solutions.
Table 12: the ideal best and worst values
Students
dimension
Instructors
dimension
Learning
Environment
dimension
Course
dimension
Support
dimension
Face to
Face
Learning
0,115107408 0,218232253 0,031658691 0,108267903 0,08513333
Blended
Learning
0,076738272 0,218232253 0,094976074 0,072178602 0,17026667
Synchrono
us
Learning
0,076738272 0,145488169 0,031658691 0,072178602 0,17026667
V
+
(best
value)
0,115107408 0,218232253 0,094976074 0,108267903 0,17026667
V
-
(worst
value)
0,076738272 0,145488169 0,031658691 0,072178602 0,08513333
5. Calculating the Euclidean distance from
ideal best and worst value Table 13, by
applying the following formula :
(5)
(6)
(2)
(3)
(4)
n
j
i
VV
S
jij
1
2
n
j
i
VV
S
jij
1
2
(1)
E-Learning Critical Success Factors in Moroccan Universities during the COVID-19 Pandemic : Case Moulay Ismail University
271
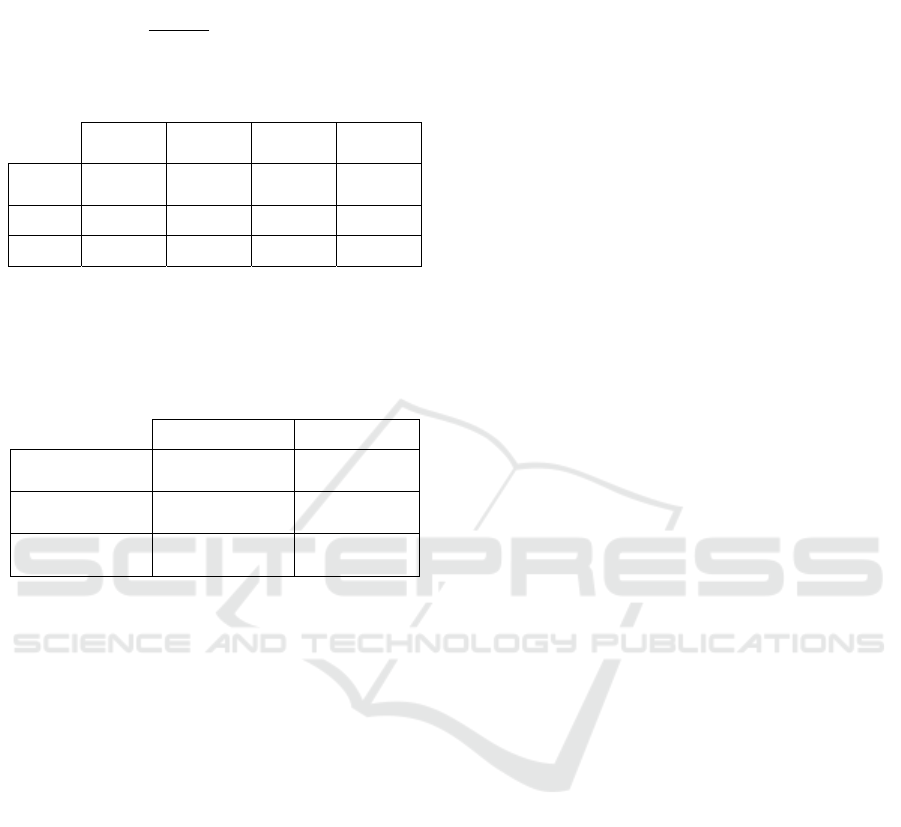
6. Calculating the performance score P table
13, by using the following formula :
Table 13: Euclidean distance from best and worst value
and performance score
S
+
S
-
S
+
+ S
-
P
Face to
Face
Learning
0,106097952 0,08981275 0,195910702 0,458437182
Blended
Learning
0,05267474 0,128640885 0,181315625 0,70948593
Synchronou
s Learning
0,10988822 0,085133333 0,195021554 0,436532946
7. The last step is ranking the order of
preference alternatives. Table 14 shows the
result of the ranking of alternatives.
Table 14: ranking the alternatives
P Rank
Blended
Learning
0,70948593 1
Face to Face
Learnin
g
0,458437182 2
Synchronous
Learnin
g
0,436532946 3
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The principal goal of this paper is to identify and
analyze the critical success factors of the E-learning
system deployed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
We used the AHP and TOPSIS methods to analyze
the data collected from two surveys. The findings
revealed, after calculating every factor’s weight, that
instructor dimension (0,341), support dimension
(0,225), student’s dimension (0,158), course
dimension (0,141), and learning environment
dimension (0,105) table 8 were the most critical
success factors influenced the E-learning process
during the COVID-19 pandemic.
According to the ranking obtained the most
important factors that influencing the remote
learning success are:
The instructor’s knowledge of technology:
given the importance of this factor, it is
necessary to implement a training program
for teachers allowing them to integrate
educational technologies into their teaching
practices.
Learning environment: This includes the
learning management system, networking,
technical infrastructure, and other facilities.
Decision-makers have to ensure the quality
of this infrastructure by allocating an
adequate amount of financial and human
resources.
On the other hand, and as a result of applying the
TOPSIS method, we find that Blended Learning
appears to be the best decision alternative for the
universities when adopting a distance learning mode
during the COVID-19 pandemic with a total weight
of 0,709. In the second position, we find face to face
learning mode with a total weight of 0,458, and
Synchronous learning mode, which was considered
to be the third position with a total weight of 0,436
as showing in table 14.
6 CONCLUSION
The universal pandemic Covid-19 in 2020 has
helped propel the remote teaching practices of
Moroccan universities as in other countries to an
unprecedented level. Indeed, the university’s
pedagogical continuity has been ensured in record
time thanks to an up-to-date technological
infrastructure of the various university components.
Distance Education has proven to be effective in
meeting the needs of learners in terms of knowledge
acquisition and further study in confinement periods.
This study makes a helpful contribution to better
understanding the factors that might impact the
adoption and success of e-Learning, and the results
found to provide useful information to the decisions
makers in the universities in their process of
implementing and adopting e-Learning mode in
Education.
REFERENCES
Alem N, (2012), numéro 5,Plates-formes d’enseignement
à distance dans l’enseignement supérieur, modes
d’appropriation et standardisation des usages,
frantice.net.
Alqahtani, Y., Rajkhan, A., (2020) E-Learning Critical
Success Factors during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A
Comprehensive Analysis of E-Learning Managerial
Perspectives, Educ. Sci
A Grubisic, S. Stankov, M. Rosic, B. Zitko, (2009),
Controlled experimentreplication in evaluation of e-
learning system s educational influence, Computer &
Education, vo1.53, pp.591-602.
(7)
S
S
P
ii
i
S
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
272

Sun, P.,Tsai, R., Finger, G., Chen, Y., (2008), What
drives a successful elearning? An empirical
investigation of the critical factors influencing learner
satisfaction,
Computers & Education, pp. 1183-1202,
vo1.50.
Hameed, S. Badii, A. Cullen, A.J., 25–26 May (2008),
Effective e-learning integration with traditional
learning in a blended learning environment. In
Proceedings of the European and Mediterranean
Conference on Information Systems
, Al BustanRotana,
Dubai, pp. 25–26.
Benigno. V, Trentin, G., (2000), "The evaluation of
online courses",
Journal of Computer Assisted
Learning
. pp. 259-270,vo1.l6
Saaty, T.L., (1988), What is the analytic hierarchy
process? In Mathematical Models for Decision
Support,
Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, pp.
109–121.
Taherdoost, H., (2017), Decision Making Using the
Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP); A Step by Step
Approach, International Journal of Economics and
Management System, IARAS
.
Hwang, C.L., Yoon, K., (1981), Multiple Attribute
Decision Making: Methods and Applications,
Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany.
Beckmann, M., Künzi, H.P., Hwang, C.L., Yoon, K.,
(1981), Multiple Attribute Decision Making;
Scientific Research Publishing: Southern California,
CA, USA
., volume 186
Prakash, C., Barua, M.K., (2015), Integration of AHP-
TOPSIS method for prioritizing the solutions of
reverse logistics adoption to overcome its barriers
under fuzzy environment, J. Manuf. Syst. 37, 599–615.
Leidecker, J.K., Bruno, A.V, (1984), Identifying and using
critical success factors, Long Range Plan. 17, 23–32.
Alhabeeb, A., Rowley, J., (2018), E-learning critical
success factors: Comparing perspectives from
academic staff and students,
Comput. Educ, 127, 1–12.
Scholkmann, A., (2017), What I learn is what I like. How
do students in ICT-supported problem-based learning
rate the quality of the learning experience, and how
does it relate to the acquisition of competences?,
Educ. Inf. Technol, 22, 2857–2870.
Graham, C.R., Woodfield, W., Harrison, J.B, (2013), A
framework for institutional adoption and
implementation of blended learning in higher
education,
Internet High Educ, 18, 4–14.
Thai, N., De Wever, B., Valcke, M., (2017)
, The impact of
a flipped classroom design on learning performance in
higher education: Looking for the best "blend" of
lectures and guiding questions with feedback,
Comput
Educ,
107, 113–126.
Sunardi, ., Robo, S. and Trisno, (2019), MADM Model for
Evaluation of Non-permanent Teacher Performance
using Fuzzy AHP and TOPSIS Methods
In
Proceedings of the International Conferences on
Information System and Technology (CONRIST 2019)
,
pages 98-104, SCITEPRESS.
Young, T.P., Bailey, C.J., Guptill, M., Thorp, A.W.,
Thomas, T.L., (2014), The flipped classroom: A
modality for mixed asynchronous and synchronous
learning in a residency program,
West. J. Emerg. Med,
15, 938.
Rowe, J.A., (2019), Synchronous and Asynchronous
Learning: How Online Supplemental Instruction
Influences Academic Performance and Predicts
Persistence
. Ph.D. Thesis, Capella University,
Minneapolis, MN, USA
.
Alhabeeb, A., Rowley, J., (2018), E-learning critical
success factors: Comparing perspectives from
academic staff and students,
Comput. Educ, 127, 1–12.
Bhuasiri, W., Xaymoungkhoun, O., Zo, H., Rho, J.J.,
Ciganek, A.P., (2012), Critical success factors for e-
learning indeveloping countries: A comparative
analysis between ICT experts and faculty, Comput
Educ
, 58, 843–855.
Anggrainingsih, R., Umam, M.Z., Setiadi, H., (2018),
Determining e-learning success factor in higher
education based on user perspective using Fuzzy AHP,
MATEC Web Conf, 154, 03011.
Behzadian, M., Otaghsara, S.K., Yazdani, M., Ignatius, J.,
(2012)
, A state-of the-art survey of TOPSIS
applications,
Expert Syst. Appl, 39, 13051–13069.
E-Learning Critical Success Factors in Moroccan Universities during the COVID-19 Pandemic : Case Moulay Ismail University
273
