
Factors Influencing User’s Satisfaction with Information Systems
Laila Zeroual and Ouafae Zerouali Ouariti
Ibn Zohr University, ENCG-A Rue Hachtouka Hay Salam, BP: 37/S Agadir- Morocco
Keywords: User Satisfaction, Information System, Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM)
Abstract: User satisfaction is considered to be one of the most important main dependent variables used to measure
the success of the information system, this vision initiated Cyert and March in 1963 since they propose that
if an information system meets the needs of the user, the satisfaction of that user will be enhanced while if
not, the user will be dissatisfied and look for another source or another system. This is also confirmed by
several authors indicating that user satisfaction is directly linked to the use of the system. Also the most
frequent measures of success in the literature are user satisfaction, use of the information system and their
influence on performance. In this article we have first presented the main models of user satisfaction as well
as some definitions. Secondly the methodology adopted. And finally we will present the results of the
empirical study using the partial least square structural equation modeling (SEM).
1 INTRODUCTION
User satisfaction is one of the mechanisms to be
taken into account in setting up an information
system. User satisfaction is defined as the extent to
which users believe that the information system
available to them meets their information needs. For
its part, Bailey and Pearson (1983) defined it as the
set of feelings and attitudes of users of a technology
in relation to the characteristics of information and
user involvement.
For Raymond (1995) user satisfactions is “a
multidimensional attitude towards various aspects of
IS management, such as the quality of results, the
man-machine interface, personnel and IT services,
and various related constructs to the user, such as
feelings of participation and understanding”. Yet for
Spreng and MacKoy (1996), it is “an affective state
reflecting an emotional reaction to a product or
service”. In addition, user satisfaction is an overall
emotional and cognitive assessment of the user of the
level of achievement related to their experience with
the IS.
In this sense, user satisfaction is one of the key
factors for the success of information systems. Note
that a good system perceived by its users as being
poor is a poor system (Thong and Yap, 1996). This
concept was also present in the work of Shao, Z. and
al, (2020) who suggest that an information system
that perfectly meets the needs of the user will
strengthen their satisfaction with this system, and if it
does not provide the necessary the user will become
dissatisfied. These authors were the first to propose
the concept of user satisfaction as a proxy measure
for IS success, so several other studies have shown
this direct link between satisfaction and usage
behavior.
We can therefore understand that user satisfaction
is a subjective measure; it measures how users
perceive the information system they are using, either
through a feeling of pleasure and satisfaction or a
feeling of dissatisfaction. Usually, the systems that
best meet user information requirements are used the
most. The main models for measuring employee
satisfaction users, namely the Bailey and Pearson
(1983) model which was reassessed by Ives et al,
(1983) and the Doll and Torkzadeh (1988) model and
the Delone and Mclean information system access
model (2003). These models are considered the most
important and form the basis of any study aimed at
measuring user satisfaction.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 User Satisfaction Measurement
Models
2.1.1 Bailey and Pearson Model (1983)
Bailey and Pearson (1983) consider user satisfaction
as a basic criterion for measuring the success or
552
Zeroual, L. and Zerouali Ouariti, O.
Factors Influencing User’s Satisfaction with Information Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0010743500003101
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Big Data, Modelling and Machine Learning (BML 2021), pages 552-557
ISBN: 978-989-758-559-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

failure of information systems. The researchers put
in a tool to measure user satisfaction with 39 items.
This analysis included many factors such as the
quality of information, the performance of systems,
personal relationships and management
involvement. However this study presents a set of
limitations namely the sample which was small, 29
responses which were retrieved with difficulty in
applying and testing the questionnaire in different
contexts.
Ives et al, (1983) re-evaluated the model of
Bailey and Pearson and proposed a more developed
version focusing on the satisfaction of information
users (UIS), it is therefore a question of measuring
the general satisfaction of users vis- with respect to
the information provided. The goal of the
researchers was to strengthen the validity and
reliability of the Bailey and Pearson instrument
through a larger sample of about 200 users.
2.1.2 Ives and al, Model (1983)
Ives, and al, (1983) confirmed the validity of the
user satisfaction measurement tool developed by
Bailey and Pearson (1983). Indeed, the services
offered and the relationship with the personnel are
reflected in the relationships with the personnel of
the IT department; the quality of the information
produced is reflected, for example, by the reliability
and precision of the information; and the knowledge
and the implication are also translated for example
by the training carried out to the users on the use of
the SI ... let us know that the results of the work of
Ives, and al, (1983) inspired Doll and Torkzadeh
(1988) in the implementation of another model to
measure the satisfaction of users of information
systems.
2.1.3 Doll and Torkzadeh Model (1988)
Doll and Torkzadeh (1988) proposed another model
which takes into account the environment of the use
of the information system, and propose to integrate
variables linked to the conditions of interaction
between users and information systems. . A model
considered as complete since they went through a
review of previous work on user satisfaction,
moreover they presented in the bibliography of their
study an exhaustive list of articles dealing with this
link.
Indeed, a new instrument has been put in place
by these authors to measure user satisfaction with
specific applications, and was carried out using a
survey of 340 end users on their satisfaction /
dissatisfaction with regard to web portals.
2.1.4 Mahmoud and al, Model (2000)
The researchers produced a synthesis of the
literature on the main variables that affect user
satisfaction. The work of Mahmood and al, (2000) is
based on the results of empirical research between
the year 1986 and 1998, their model is composed of
three main factors (perceived benefits, user training
and organizational support), and each factor is
linked to three variables.
2.1.5 DeLone and Mclean Model (2003)
Management Information Systems researchers
DeLone and McLean have developed a model for
evaluating information systems and its effect on
performance. Their model is generally referred to as
the Information Systems Success Model. The
researchers identified five main dimensions of the
success of an information system namely: the quality
of the information, the quality of the system, the
quality of the service, the use, the satisfaction of the
users and the net benefits.
2.2 User Satisfaction
User satisfaction is determined by positive attitudes
towards the information system and by the response
of the user to the use of the output, thus constituting
the level of satisfaction of the user when he uses an
IS (Y.K. Dwivedi et al, 2012). Also it reflects the
user's feeling about the overall system experience,
i.e. the system itself, the end result, then to the
services provided by the system (Petter, Set al,
2008).
Indeed, several researchers have suggested
models to measure user satisfaction mainly we cite
(Bailey and Pearson, Ives et al, Doll and Torkzadeh
and Delone and Mclean their models are considered
the most important to measure user satisfaction. Two
other authors Seddon and Kiewont worked on a
satisfaction model rather than an evaluation of the
success of the IS covering a technological dimension
rather than an organizational one, the authors
proposed to use the user satisfaction variable as a
measure of perception of the success of the system.
User satisfaction is supposed to be a substitute
for the contribution of information systems to
performance, better performance will automatically
follow if the system meets users' information needs
Petter and al (2013). We keep this principle with the
definition of satisfaction as the degree of
correspondence between the characteristics of the
task and the functionality of the information system.
In addition, the quality of the information system, in
Factors Influencing User’s Satisfaction with Information Systems
553

terms of response time and availability of
information is the variable that most affects user
satisfaction.
3 HYPOTHESIS OF STUDY
H1: The quality of training is positively
associated with user satisfaction;
H2: The quality of service is positively
associated with user satisfaction;
H3: The quality of the information system is
positively associated with user satisfaction;
H4: The quality of information is positively
associated with user satisfaction;
4 METHODOLOGY
Our method of investigation is based on a
questionnaire made up of closed logical questions,
and with a Likert attitude scale evaluating the
different aspects questioned. The idea is to help the
interviewee to answer as well as possible the
different questions answered.
We have adopted convenience sampling for
practical reasons of accessibility, the population we
want to study is all IS users with different profiles.
We were able to distribute our questionnaire online
and face-to-face to 480 people with the
questionnaire link (www.) And with a message
inviting respondents to give it some time. Only
volunteers responded with 256 responses.
To test and confirm the causal relationships, we
used Partial least square structural equation
modeling (SEM), using the SmartPLS3 software,
this procedure consists of two main parts which are
the measurement and the structure model.
5 RESULTS
5.1 Measurement Model
This model is made up of all the relationships
between the indicators (Id) and the latent variables
or constructs that they help to measure (V).
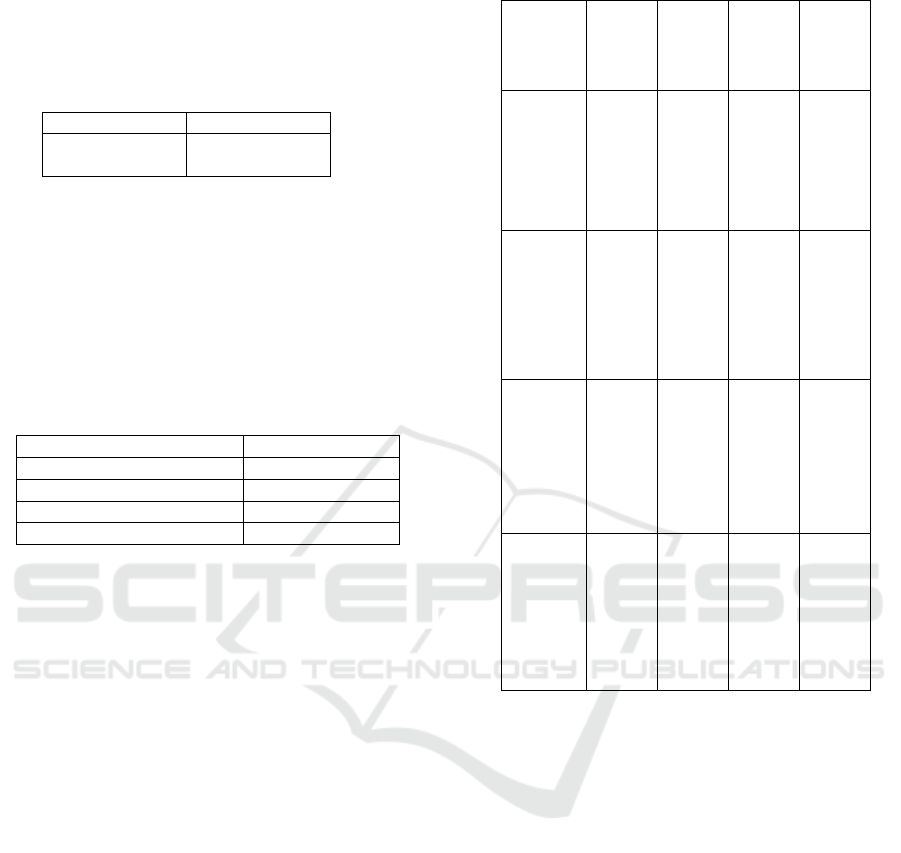
Table 1: Results of Evaluation the Measurement Model
Latent variable
indicators
Factor Loading
Composite
Reliability
AVE
Cronbach’ s
alpha
User
Satisfaction
US1 0.868
0.895
0.77
5
0.903
US2 0.840
US3 0.886
US4 0.926
Training
Quality
TQ1 0.838
0.869
0.68
8
0.771
TQ2 0.812
TQ3 0.838
Service
Quality
SQ1 0.782
0.881
0.65
0
0.821
SQ2 0.772
SQ3 0.874
SQ4 0.794
Information
System Quality
ISQ1 0.840
0.920
0.69
8
0.891
ISQ2 0.875
ISQ3 0.716
ISQ4 0.879
ISQ5 0.857
Information
Quality
INQ1 0.864
0.887
0.61
2
0. 840
INQ2 0.808
INQ3 0.788
INQ4 0.719
INQ5 0.722
This table lists the survey scales and their internal
consistency reliability, for the responses provided all
of the composite reliability measures were well
above the recommended level of 0.70. The C.Rs
found vary between (0.8 and 0.9) values greater than
the suggested threshold, indicating good internal
consistency (Nunnally, J.C, 1978).
In addition, convergent validity is adequate when
constructs have an extracted mean variance (AVE)
of at least 0.5 (Fornell, C. et al, 1981), and as shown
in the table all AVE values are greater than at the
limit value of 0.5 varies between (0.5 and 0.7).
Finally for the scales, the loading of the items is
greater than or equal to (0.7).
5.2 Structural Model
This system of structural relations refers to the
determination of the causal relations between the
latent variables (V), which makes it possible to trace
the direction of the hypotheses to be tested by taking
into account the measurement errors of the estimate.
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
554
5.2.1 R-squard
The validity of the structural model is assessed using
the coefficient of determination (R²).
Table 2: Result of the R² test
Variable R²
User
Satisfaction
0.658
We obtained a coefficient R² = 0.658> 0.30, this
value of 66% corresponds to a good coefficient of
determination, that is to say a good prediction.
5.2.2 F-squard
Effect size f² allows analyzing the contribution of
each independent variable on the dependent variable.
Table 3: Result of the f² test
User Satisfaction
Training Qualit
y
0.212
Service Qualit
y
0.051
Information S
y
stem Qualit
y
0.210
Information Qualit
y
0.552
For the size effect f² of the quality of information on
the dependent variable "user satisfaction", the value
obtained from our calculations shows a very high
size effect f². This effect can be interpreted by the
role that information plays in the success of any
organization, and its importance in this changing
field. Other than the quality of the information, the
training and the quality of the information system
have an effect considered to be moderate, playing a
role as well in the satisfaction of the actors. Finally
service quality with low effect.
5.2.3 Hypothesis Testing
The result of hypothesizes testing showed significant
support for all of hypothesis in this study.
Table 4: Summary of Hypothesis Testing
β
t-
value
p-
value
Suppo
rt
H1: Training
Quality User
satisfaction
0,377 6,780 0,000 Yes
H2:Service
Quality user
satisfaction
0,174 3,060 0,002 Yes
H3:Information
System Quality
user satisfaction
0,237 4,273 0,000 Yes
H4:Information
Quality user
satisfaction
0,377 6,780 0,000 Yes
6 DISCUSSION
It emerges from these causal coefficients that:
The quality of information has a positive and
significant effect on user satisfaction. For the safety
of organizations, information becomes a strategic
stake, it is considered in several works as the raw
material of the economic world allowing being
efficient. Any organization will be better than its
competitors especially if it has precise and correct
information, making it easier to control unexpected
variations. In other words, it makes it possible to
control the present and to foresee the future, by
meeting the requirements which all rely on
information.
The quality of information seems to be the
quality most expected of users, determining their
satisfaction. ((In terms of information that meets
their needs, allowing them to make better
decisions)).
Factors Influencing User’s Satisfaction with Information Systems
555

The quality of the information system has a
significant effect on user satisfaction; it is a variable
that represents the user's perception of the
interaction with the functionalities of the
information system used. Indeed, this is where the
dimension "speed of the information system used"
takes place given the constraints of the economic
environment which is characterized by volatile
demand. Users consider that the better the quality of
the IS, the higher their satisfaction.
The quality of training has a positive and
significant effect on the quality of service, user
satisfaction, quality of logistics and user information
system, which shows that training or precisely its
perceived quality plays an important role in the
acceptance of new technologies leading to a certain
satisfaction with the service and the IS used.
Training therefore provides the tools necessary to
apply practical solutions to problems encountered in
the workplace. IS users consider that the better the
quality of the training they receive, the higher their
satisfaction, by offering them functional ease.
Finally, the quality of service has also a positive
and significant effect on the quality of the logistics
information system and on user satisfaction. This
result reflects the effort that IT staff must provide to
meet user expectations and listen to them. . So that
this significance was confirmed through the
assurance, empathy, reliability and responsiveness of
the service to respond to the problems encountered.
These results are similar to those obtained by J.
Floropoulos et al, (2010); Nunes (2012); Demian
Abrego-Almazán (2017); Solano et al, (2014);
Seddon P, et al, (1996). Although the context of the
studies is different, there is support for our result.
7 CONCLUSION
The results of our study show that the quality of
information is the main determinant of user
satisfaction. The presence of quality qualified
information is an important prerequisite for
management decision making, especially when the
decisions taken can have serious consequences
leading to the loss of customers. Through Therefore,
scrutinizing the information obtained and requiring
that it meet certain characteristics is essential.
REFERENCES
Adam Mahmood, M., Burn, J. M., Gemoets, L. A., &
Jacquez, C. (2000). Variables affecting information
technology end-user satisfaction: a meta-analysis of
the empirical literature. International Journal of
Human-Computer Studies, 52(4), 751–771.
Almazán, D.A., Tovar, Y.S., & Quintero, J. (2017).
Influence of information systems in organizational
performance. Contaduría y Administración, 62, 321-
338.
Bailey, J. E., & Pearson, S. W. (1983). Development of a
Tool for Measuring and Analyzing Computer User
Satisfaction. Management Science, 29(5), 530-545.
Bergeron, F., Raymond, L., Rivard, S., & Gara, M.-F.
(1995). Determinants of EIS use: Testing a behavioral
model. Decision Support Systems, 14(2), 131–146.
DeLone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (2003). The DeLone
and McLean Model of Information Systems Success:
A Ten-Year Update. Journal of Management
Information Systems, 19(4), 9-30.
Doll, W. J., & Torkzadeh, G. (1988). The Measurement of
End-User Computing Satisfaction. MIS Quarterly,
12(2), 259.
Dwivedi, Y. K., Weerakkody, V., & Janssen, M. (2012).
Moving towards maturity. ACM SIGMIS Database,
42(4), 11.
Floropoulos, J., Spathis, C., Halvatzis, D., & Tsipouridou,
M. (2010). Measuring the success of the Greek
Taxation Information System. International Journal of
Information Management, 30(1), 47–56.
G. Nunes. (2012). Estudio de satisfacción del usuario de
sistemas de información en hospitales universitarios
del nordeste. Thèse de doctorat Bresil.
Ives, B., Olson, M. H., & Baroudi, J. J. (1983). The
measurement of user information satisfaction.
Communications of the ACM, 26(10), 785–793.
Petter, S., DeLone, W., & McLean, E. (2008). Measuring
information systems success: models, dimensions,
measures, and interrelationships. European Journal of
Information Systems, 17(3), 236-263.
Seddon, P. B. (1997). A Respecification and Extension of
the DeLone and McLean Model of IS Success.
Information Systems Research, 8(3), 240-253.
Seddon, P., & Kiew, M.-Y. (1996). A Partial Test and
Development of Delone and Mclean‘s Model of IS
Success. Australasian Journal of Information Systems,
4(1).
Shao, Z., Zhang, L., Chen, K. and Zhang, C. (2020),
"Examining user satisfaction and stickiness in social
networking sites from a technology affordance lens:
uncovering the moderating effect of user experience",
Industrial Management & Data Systems, Vol. 120 No.
7, pp. 1331-1360.
Solano Rodriguez, O., García Pérez De Lema, D., &
Bernal García, J. J. (2014). Influence of the
Implementation of Information Systems on
Performance in Small and Mid-sized Enterprises: an
Empirical Study in Colombia. Cuadernos De
Administración, 30(52), 31-43.
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
556

Spreng, R. A., & Mackoy, R. D. (1996). An empirical
examination of a model of perceived service quality
and satisfaction. Journal of Retailing, 72(2), 201–214.
Thong, J. Y. L., & Yap, C.-S. (1996). Information systems
effectiveness: A user satisfaction approach.
Information Processing & Management, 32(5), 601-
610.
Factors Influencing User’s Satisfaction with Information Systems
557
