
A Comparative Study of Back-propagation Algorithms:
Levenberg-Marquardt and BFGS for the Formation of Multilayer
Neural Networks for Estimation of Fluoride
R. El Chaal
a
, M. O. Aboutafail
Engineering Sciences Laboratory. Data Analysis, Mathematical Modeling, and Optimization Team,
Department of Computer Science, Logistics and Mathematics, Ibn Tofail University.
National School of Applied Sciences ENSA, Kenitra 14 000 Morocco
Keywords:
back-propagation algorithm, multilayer perceptron, prediction, optimization, statistical indicators
Abstract: This work describes a comparative approach between the two back-propagation algorithms: the Levenberg-
Marquardt (LM) and the Broyden Fletcher Goldfarb Shanno (BFGS); For the prediction of Fluoride in the
Inaouène basin, using artificial neural networks (ANN) of the multilayer perceptron type (MLP), from the
concentrations of sixteen physicochemical parameters. We have developed several models based on the
evolution of combinations of activation functions and neurons number in the hidden layer. The performance
of the different ANN model training algorithms was evaluated using the mean square error (MSE) and the
correlation coefficient (R). The evaluation shows that the LM training algorithms perform better than the
BFGS training algorithm. The results obtained demonstrate the efficiency of the LM algorithm for the
prediction of Fluoride compared to the BFGS algorithm by MLP type neural networks, as shown by the
statistical indicators ({R = 0.99 and MSE = 0.135 for LM} and {R = 0.95 and MSE = 41.22 for BFGS}).
1 INTRODUCTION
The most popular learning algorithm is Back-
propagation (BP) (Rumelhart et al., 1986), and it is
the most common and widely used supervised
training algorithm for solving approximation
problems, recognition of shapes, classifying and
discovering patterns, and making predictions from
data, and other well-known issues. Based on
statistics, data mining, pattern recognition, and
predictive analyzes. The BP algorithm(BPA) is the
most widely used example of supervised learning
because of the media coverage of some spectacular
applications, such as the demonstration of Sejnowski
and Rosenberg (1987) and Adamson and
Damper(1996), in which BPA is used in a system that
learns to pronounce a text in English(Adamson &
Damper, 1996; Sejnowski & Rosenberg, 1987).
Another success was the prediction of stock market
prices (Refenes & Azema-Barac, 1994) and, the
Comparative study of different artificial neural
network (ANN) training algorithms for atmospheric
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4705-2006
temperature forecasting in Tabuk, Saudi Arabia
(Perera et al., 2020) and, more recently, a study on
cumulative hazards evaluation for the water
environment(Shi et al., 2021).
The gradient BP technique is a method that
calculates the error gradient for each Neuron in the
network, from the last layer to the first. The
publication history shows that BPA has been
discovered independently by different authors but
under different names. The principle of BP can be
described in three basic steps: routing information
through the network; BP of sensitivities and
calculation of the gradient; and adjust the parameters
by the approximate gradient rule. It is important to
note that BPA suffers from the inherent limitations of
the gradient technique because of the risk of being
trapped in a local minimum. If the gradients or their
derivatives are zero, the network is trapped in a local
minimum. Add to this the slowness of convergence,
especially when dealing with large networks
(Govindaraju, R. S., Rao, 2000) (i.e., for which the
number of connection weights to be determined is
558
El Chaal, R. and Aboutafail, M.
A Comparative Study of Back-propagation Algorithms: Levenberg-Marquardt and BFGS for the Formation of Multilayer Neural Networks for Estimation of Fluoride.
DOI: 10.5220/0010746300003101
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Big Data, Modelling and Machine Learning (BML 2021), pages 558-565
ISBN: 978-989-758-559-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

essential). To make the optimization more efficient,
we can use second-order methods such as the so-
called Quasi-Newton or modified Newton methods.
2 SECOND-DEGREE
OPTIMIZATION METHOD
(QUASI-NEWTONIAN
METHODS)
2.1 Levenberg-Marquardt
Back-Propagation Method (LM)
The LM algorithm is a variation of Newton's method
(Basterrech et al., 2011), which was designed for
minimizing functions that are sums of squares of non-
linear functions (Bishop, 2006; Dreyfus, 2005). This
is very well suited to artificial neural network (ANN)
training; this is known to be very efficient when
applied to ANN (Ampazis & Perantonis, 2000; Hagan
& Menhaj, 1994), where the root mean square error is
the performance index. Newton's; update for
optimizing a performance index F(x) is
1
1kkkk
x
xAg
where
2
()
k
k
x
x
AFx
and
()
k
k
x
x
gFx
supposing that F(X) is a sum of the square function
(1)
therefore the j th element of the gradient is
(2)
The gradient is written in matrix form
(3)
where(Chen & Zhang, 2012)
(4)
it is the Jacobian matrix. to determine the Hesse
matrix, the element k, j of this matrix would be
(5)
The Hessian matrix can then be expressed in matrix
form
(6)
Where: (7)
If S(x) it is assumed to be minor, the Hessian matrix
can be approximated as
(8)
Substituting (8) and (3) into
1
1
kkkk
x
xAg
, the
Gauss-Newton method is obtained(Scales, 1985)
(9)
From this, the advantage of the Gauss-Newton
method over Newton's standard method is that it does
not require the calculation of second-order
derivatives. A problem with the Gauss-Newton
method is that the matrix
T
H
JJ
may not be
invertible. This can be overcome by using the
following modification to the approximate Hessian
matrix:
GH I
To make this matrix invertible, we first assumed that
the eigenvalues and the eigenvectors of H are
respectively the following:
12
, ,...,
n
and
12
, ,...,
n
zz z
.
Then
𝑮𝒛
𝑯𝜇𝑰
𝒛
𝑯𝒖
𝜇𝒛
𝜆
𝒛
𝜇𝒛
𝜆
𝜇
𝒛
(10)
herefore, the eigenvectors of G are the same as the
eigenvectors of H, and the eigenvalues of G are
().
j
G
can be made positive definite by
increasing
until
()0
j
for all is,
(11)
or
(12)
1
() ()()
N
T
i
Fvv
xxx
1
()
()
[()] 2 ()
N
i
ji
i
jj
v
F
Fv
x
x
x
x
xx
() 2 ()()
T
FxJxvx
11 1
2
22 2
2
2
1
1
1
() () ()
() () ()
() () ()
n
n
NN N
n
vv v
xx x
vv v
xx x
vv v
xx x
xx x
xx x
xx x
2
() 2 ()() 2()
T
F xJxJxSx
2
1
() () ()
N
ii
i
vv
Sx x x
2
() 2 ()()
T
FxJxJx
1
1
1
22
TT
kk kk k k
TT
kkk kk
x x JxJx Jxvx
xJxJx Jxvx
1
1
TT
kk kkk kk
xxJxJx IJxvx
1
TT
kkkkkk
xJxJxIJxvx
2
2
2
,
1
() () ()
()
() 2 ()
N
ii i
i
kj
i
kj k j kj
vv v
F
Fv
x
xxxxx
xx x
x
xx
A Comparative Study of Back-propagation Algorithms: Levenberg-Marquardt and BFGS for the Formation of Multilayer Neural Networks
for Estimation of Fluoride
559

This algorithm has a helpful feature that as
k
is
increased, it approaches the steepest descent
algorithm with a small learning rate.
(13)
for large
k
and if
k
is decreased to zero, the
algorithm becomes Gauss-Newton.
The algorithm begins with
k
a set to some small
value (e.g.,
0.01
k
). If a step does not yield a
smaller value for F(x) then the step is repeated with
k
multiplied by some factor
1( . . 10)eg
.
Eventually; F(x) should decrease, as a small step is
taken in the direction of the steepest descent. If the
step does produce a smaller value for F(x) then
k
is
divided by
for the next step, so that the algorithm
will approach Gauss-Newton, which should provide
faster convergence.
2.2 Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno
Back- Propagation Method (BFGS)
Newton's method is based on a quadratic
approximation instead of a linear approximation of
the function F(x). The following approximate
solution is obtained at a point that minimizes the
quadratic function:
(14)
The sequence obtained is
1
1kkkk
x
xAg
The main advantage of Newton's method is that it has
a quadratic convergence rate, while the steepest
descent has a much slower, linear convergence rate.
However, each step of Newton's method requires a
large amount of computation. Assuming that the
problem’s dimensionality is N an
3
()ON
the
floating-point operation is needed to compute the
search direction
k
d
. A method that uses an
approximate (Goldfarb, 1970) Hessian matrix in
computing the search direction is the quasi-Newton
method. Let
k
H
, be an N*N symmetric matrix that
approximates the Hessian matrix
k
A
; Then the
search direction for the quasi-Newton method is
obtained by minimizing the quadratic function:
(15)
If
k
H
it is invertible, a descent direction can be
obtained from the solution of the quadratic program:
(16)
As the matrix,
k
H
is to approximate the Hessian of
the function F(x) at
k
x
x
it needs to be updated
from iteration to iteration by incorporating the most
recent gradient information.
The matrix
k
H
is updated according to the
following equation(Battiti, 1992; Battiti & Masulli,
1990):
1
k k kkk k
kk
kk k kk
yy HssH
HH
ys sHs
••
••
(17)
Where
11
;
kk kk k k
s
xx
yg g
(18).
2.3 Collection of Data
TAZA is a city located in the northeast of Morocco in
the Taza corridor, a pass where the Rif and Middle
Atlas Mountains meet. Apart from the "corridor"
formed by the valley of the Wadi Inaouen and the
plain of Guercif, the rest of the province is dominated
by mountains. Indeed, the province occupies the area
which connects the Rif to the Middle Atlas, the two
mountain ranges narrowing at the level of the
Touaher pass (559 m above sea level). The Inaouen is
a Moroccan river, that forms near the city of TAZA,
by the confluence of the Boulejraf and Larbaâ wadis,
and borrows from east to west the breach of Taza,
which marks the limit between the Rif and the Middle
Atlas.
Our database consists of 100 surface water
samples (notes) taken in the governorate of Taza (The
Inaouen watershed), between the periods 2014 to
2015, and the collection, transport, and storage of
water samples refer to the protocol and procedures, it
was required by the National Bureau of Drinking
Water. Part of the analysis was carried out on-site
(temperature, dissolved oxygen, etc.). The rest was
done in the Regional University Interface Center
(CURI), backed by the Sidi Mohamed Ben Abdellah
University (USMBA) in Fez.
1
1
1
()
2
T
kk kkk
kk
F
xx Jxvxx x
1
1
2
TT
kkkkkkkkk
FF F
xxxxgAxxAx
1
1
2
TT
kkkkkkkkk
FF F
xxxxgΔxxHx
1
d()
k
kT
kk
F
xx
xx H x
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
560

2.4 Reduction and Preprocessing of
Data
2.4.1 Selection of Inputs
Use The independent (explanatory) variables are the
physical-chemical characteristics determined in these
samples, which are sixteen: Temperature (T ° C), pH,
dissolved oxygen (DO), Conductivity (Cond), total
dissolved solids (TDS) ), Bicarbonate (HCO3), Total
Alkalinity (as CaCO3), Magnesium (Mg), Sodium
(Na), Potassium (K), Chlorides (Cl), Calcium (Ca),
Sulfates (SO4), Nitrate (NO3), Phosphorus (P) and
Ammoniacal nitrogen (NH4),
The dependent variable (to be predicted), it is
Fluoride (F).
The distribution of the database is as follows: 70%
of the samples, chosen at random, from the totality of
the samples, for the learning phase of a predictive
model of the dependent variable. The remaining 30%
samples were used to verify network performance and
to avoid over-learning. This is to test the validity and
performance of the prediction of these models (15%
for the test and 15% for the validation).
2.4.2 Data Formatting
Normalization is a method of preprocessing data that
helps reduce the complexity of models. The input data
(16 independent variables) are raw, untransformed
values. They have very different orders of magnitude.
In order to standardize the measurement scales, these
data are converted into standardized variables.
Indeed, the values of each independent variable (i)
have been normalized with respect to its means and
its standard deviation according to the relation:𝑋𝑣
(Abdallaoui et al., 2015; Bayatzadeh Fard et al., 2017;
Patro et al., 2015)
X
𝑣
(19)
With:
X
𝑣
: Standardized value relating to the variable i.
X𝑣
: Observed value relating to variable i.
𝑋
𝑣
: Average value relating to variable i.
𝑋
𝑣
∑
𝑋
𝑣
(20)
σ𝑣
: standard deviation relating to the variable i.
σ𝑣
∑
𝑋
𝑣
𝑋
𝑣
(21)
The purpose of normalizing the values for all
variables is to avoid very large or minimal
exponential calculations and to limit the increase in
variance with the mean.
The values corresponding to the dependent variables
were also normalized in the interval [0;1] to fit the
requirements of the transfer function used by neural
networks. This normalization was carried out
according to the relation:
𝐘
(22)
With:
Y
: Standardized value;
Y : Original value;
Y
: Minimum value;
Y
: Maximum value.
2.4.3 Neural Network Implementation with
MATLAB
The multilayer perceptron (MLP) type networks are
much more potent than simple single-layer networks.
The network used in this study consists of three
layers: an input layer, a hidden layer, and an output
layer. The number of neurons in the hidden layer is
not fixed a priori. This is determined during learning.
The neural network simulations were performed
using MATLAB 2018 software.
The implementation of multilayer neural
networks has two parts of the design: determining the
architecture of the network, and an optimization
numerical calculation part. This calculation is the
determination of the synaptic coefficients and the
updating of these coefficients by a supervised
learning algorithm. The algorithm chosen for our
study is the LM and BFGS algorithm. These two
algorithms seek to minimize, by non-linear
optimization methods, a cost function (the mean
squared error (MSE)) which constitutes a measure of
the difference between the actual responses of the
network and its desired responses. This optimization
is done iteratively by modifying the weights as a
function of the gradient of the cost function: the
gradient is estimated by a specific method to neural
networks, called the BP method. It is used by the
algorithm optimization. The weights initialize
randomly before learning.
2.4.4 Evaluation of Performances
For the evaluation of the quality of our predictive
model, and the judgment of these performances,
MATLAB 2018 uses the function of cost, which is
most often used in statistics, and called the least-
squares criterion, and consists of minimizing the sum
of the squares of the residuals, in this case, the
network will learn a discriminant function. The mean
squared error (MSE) is simply given by the sum of
the differences between the target values and the
expected outputs defined for the training set. The
result of the evaluation is expressed in two ways: by
1......16i
A Comparative Study of Back-propagation Algorithms: Levenberg-Marquardt and BFGS for the Formation of Multilayer Neural Networks
for Estimation of Fluoride
561

statistical indicators and by examining graphs. The
indicators used in this study are the correlation
coefficient (R) and the mean squared error (MSE),
which are defined as follows:
The correlation coefficient:
(23)
The mean squared error (MSE)
(24)
With
obs
i
Y
is the observed (actual) value of the
studied metal,
predi
i
Y
is the estimated value of the
metal by the model at observation i,
Y
is the mean
value. The best prediction is when
R
on the one
hand and SSE, on the other hand, tends towards 1 and
0, respectively.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Tests have shown us that to improve the performance
of a model established by MLP (Multilayer
Perceptron) type neural networks, we must modify
the architecture of the network, we change the
number of hidden layers, or the number of hidden
neurons and, or the number of training cycles
(number of iterations). For this, we successively
modified the number of hidden neurons (NHN = 1, 2,
3, ..., 15). In this study, we used two learning
algorithms, called high-performance algorithms LM
and BFGS. For each learning algorithm, we changed
the number of neurons in the hidden layer and the
pairs of transfer functions. Performance was assessed
using the mean square error (MSE) and the
correlation coefficient (R). The algorithms are
implemented and developed in a computer with the
MATLAB 2018 platform. The processor of the
computer is an Intel Core i5-7200U CPU 2.50GHZ
processor, 4 GB RAM.
3.1 Training ANN with LM
Algorithm
Table 1 represents the best performance found for the
different combinations of transfer function pairs for
the LM algorithm; they converge quickly and result in
low values of the mean square error MSE and high
values of the correlation coefficient R in a time of no
more than a few seconds.
Table1: Recap of the best architectures offered by Matlab
for prediction fluoride with algorithm LM.
Hidden
layer
Output
layer
R
MSE Architecture
Number of
iterations
Tansig Tansig 0,980 33.96 [16-3-1]
11
Tansig Logsig 0,994 26.14 [16-4-1]
15
Tansig Purelin 0,910 95.12 [16-5-1]
9
Logsig Logsig 0,911 92.31 [16-6-1]
12
Logsig Purelin 0,970 41.4 [16-7-1]
18
Logsig Purelin 0,999 0.135 [16-8-1]
22
From this table, we note that:
* The [16-8-1] architecture, with a Logsig function for
the input layer and a Purelin function for the output
layer, gave the best performance for the LM
algorithm: R=0.99 and MSE=0.135.
* The LM algorithm converges with the minimum
number of iterations (22iterations) for all
combinations of transfer functions; this algorithm is
reputed to be very efficient in the approximation of
functions, mainly when the network contains less than
a hundredweight to be updated, which is the case here.
The network reached overtraining after 22 iterations;
it is interesting to keep learning until this stage for the
test to reduce the gradient and improve our network
(Figure.3). From the obtained results in Figure.2; 3,
and 4, we note the different values of training
parameters found in this study:
• Maximum number of iterations (Epochs) = 22
• coefficients of determination = 0.99
• Mean square error (MSE) = 0.135
• Rate of learning (Mu) = 0.0001
• Gradient minimum = 0.875
100
1
100
22
1
obs obs predi
i
i
obs obs p
predi
i
redi
i
predi
i
i
YY Y
YY
Y
YY
R
100
2
1
1
MSE
100
obs predi
ii
i
YY
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
562
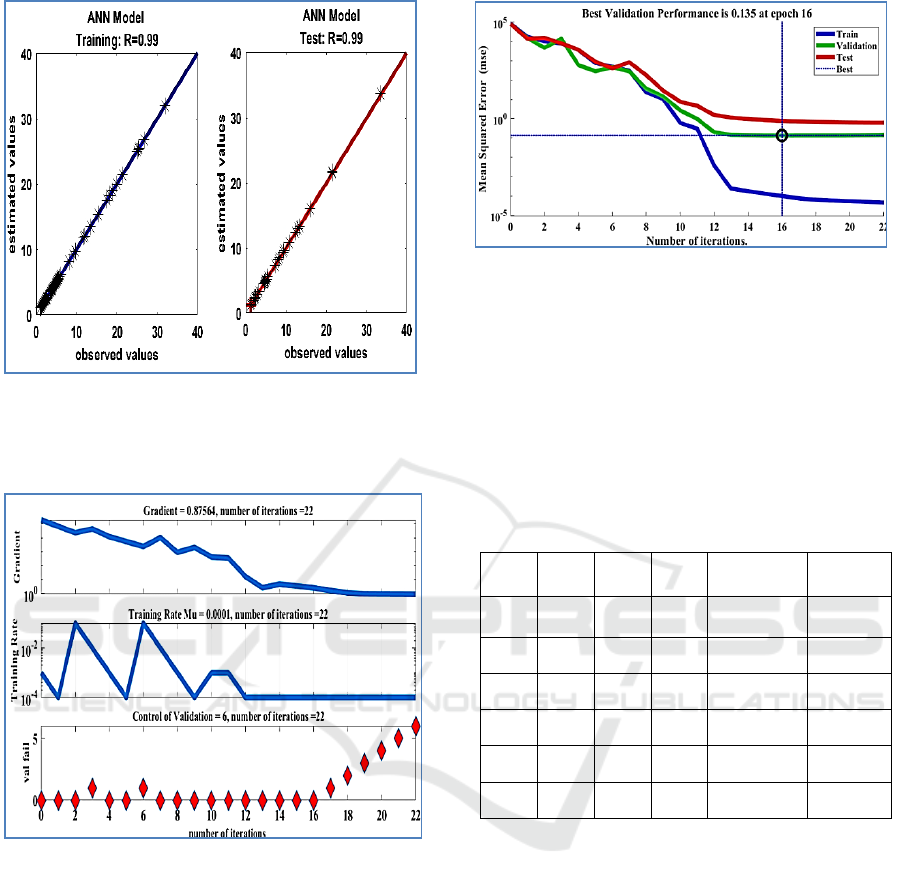
Figure 1: Trend line showing the relationship between the
observed values and values estimated by the MLP model
with algorithm ML for fluoride for the training and test
phase
Figure 2: evolution of the error gradient, the learning rate
and the validation error (for fluoride) as a function of the
number of iterations.
Figure.3 describes network training. It shows that at
the end of the sixteenth iterations, the desired result is
achieved. With eight hidden neurons, the three curves
relating to the evolution of the mean square error of
the three phases converge correctly to the minimum
mean square error (MSE)
Figure 3: the representative graph concerning the
development of the mean square error for a network
architecture [16-8-1].
3.2 Training ANN with BFGS
Algorithm
Table 2 represents the best architecture found for the
different combinations of transfer function pairs for
the BFGS algorithm.
Table 2: Recap of the best architectures offered by Matlab
for prediction Fluoride with algorithm BFGS.
Hidden
layer
Output
layer
R
MSE Architecture
Number of
iterations
Tansig Tansig 0,920 82.16 [16-3-1]
180
Tansig Logsig 0,916 100.85 [16-4-1]
215
Tansig Purelin 0,901 111.12 [16-5-1]
149
Logsig Logsig 0,953 41.22 [16-6-1]
222
Logsig Purelin 0,932 63.12 [16-7-1]
482
Logsig Purelin 0,945 48.45 [16-8-1]
237
From this table, we note that:
- The [16-6-1] architecture, with a Logsig function for
the input layer and a Purelin function for the output
layer, gave the best performance for the Broyden-
Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno algorithm and her indicator
statistical (R=0.95 and MSE=41.22)
The network reached overtraining after 222
iterations; it is interesting to keep learning until this
stage for the test, to minimize the gradient and
improve our network (Figure 6). According to the
results obtained in Figures 5; 6 and 7, we note the
different values of the training parameters found in
this study:
• Maximum number of iterations (Epochs) = 222
• coefficients of determination = 0.95
• Mean square error (MSE) = 41.22
A Comparative Study of Back-propagation Algorithms: Levenberg-Marquardt and BFGS for the Formation of Multilayer Neural Networks
for Estimation of Fluoride
563
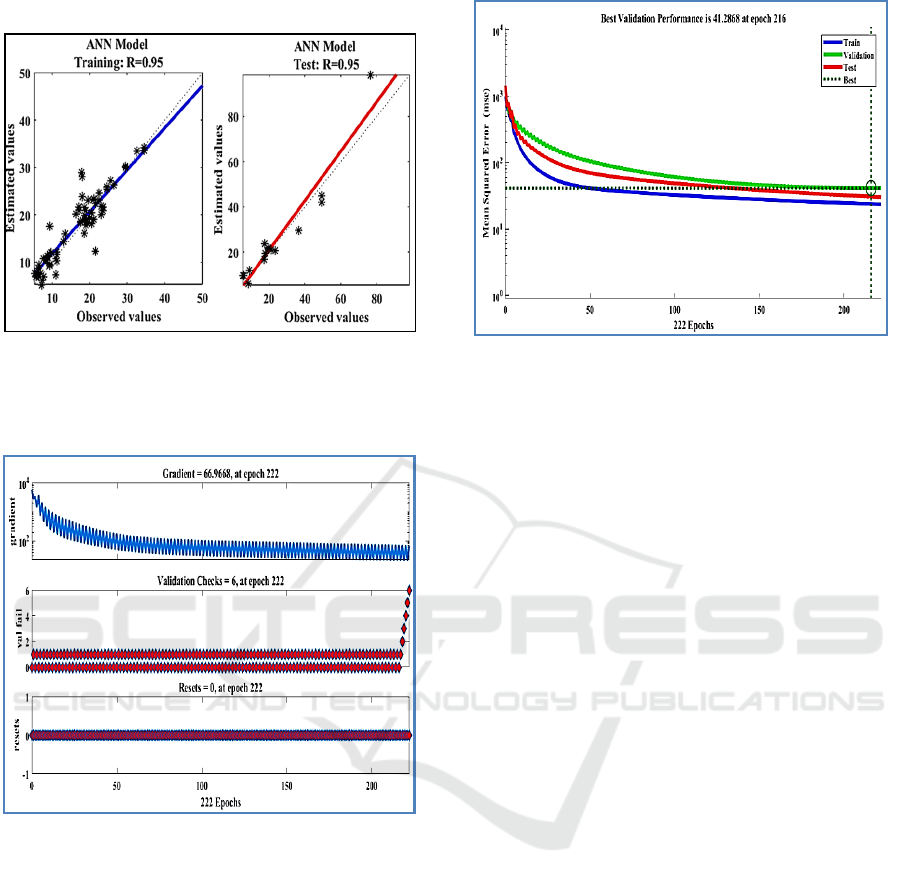
• Gradient minimum = 66.96
Figure 4: Trend line showing the relationship between the
observed values and values estimated by the MLP model
with algorithm BFGS for fluoride for the training and test
phase.
Figure 5: evolution of the error gradient, the learning rate
and the validation error (for fluoride) as a function of the
number of iterations.
Fig.6 describes network training. It shows that at the
end of the 216 iterations, the desired result is achieved.
With six hidden neurons, the three curves relating to
the evolution of the mean square error of the three
phases converge correctly to the minimum mean
square error (MSE=41.28).
Figure 6: the representative graph concerning the
development of the mean square error for a network
architecture [16-6-1].
Figures 3 and 6 give the mean square error (MSE)
values for LM algorithm of ANN. The LM algorithms
showed a lowest MSE value at the point of
convergence. However, the BFGS algorithm took
more epochs (216) to converge to the smallest MSE
(41.22). compared to the LM algorithms training.
Nevertheless, the LM algorithm took only 16 epochs
to reach 0.135 MSE
.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Artificial neural networks are potent tools for
prediction. They can deal with non-linear problems.
However, they have a significant drawback in the
choice of network architecture, as this choice often
belongs to the user. In our study, we have developed
several models based on the two learning algorithms
LM and BFGS, which are qualified as high-
performing. The results obtained show that the LM
algorithm has the best performance in terms of
statistical indicators (R=0.99 and MSE=0.135) and
convergence speed (22 iterations). Indeed, the model
established by the ML algorithm allows
improvements of up to 4% in the explanation of the
variance compared to that established by the BFGS
algorithm. The evaluation shows that the LM training
algorithms perform better than the BFGS training
algorithm.
Consequently, the analysis results demonstrate
that the LM algorithm has a more efficient approach
than the BFGS for prediction of the Fluoride in
Inaouen basin. However, the BFGS algorithm can be
viewed as a best substitute method.
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
564

In perspective, we can continue in the
development of this subject through the following
suggestions:
Work on other types of networks such as
recurring networks.
Use other activation function.
The results obtained prompt us to reflect
subsequently on the method which makes it
possible to improve the work accomplished
so far. It would be very interesting for
example to use other algorithms.
Moreover, the models are based on actual
measured data. As a result, they can also be
used to predict future Fluoride
concentrations as a function of
physicochemical parameters.
Test another RNA architecture to see which
architecture provides a better result.
REFERENCES
Abdallaoui, A., & El Badaoui, H. (2015). Comparative
study of two stochastic models using the
physicochemical characteristics of river sediment to
predict the concentration of toxic metals. Journal of
Materials and Environmental Science, 6(2), 445–454.
Adamson, M. J., & Damper, R. I. (1996). A Recurrent
Network That Learns To Pronounce EnglishText. IEEE
Proceeding of Fourth International Conference on
Spoken Language Processing. ICSLP ’96, 3, 1704–
1707. https://doi.org/10.1109 / ICSLP.1996.607955
Ampazis, N., & Perantonis, S. J. (2000). Levenberg-
Marquardt algorithm with adaptive momentum for the
efficient training of feedforward networks. Proceedings
of the International Joint Conference on Neural
Networks, 1, 126–131.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ijcnn.2000.857825
Basterrech, S., Mohammed, S., Rubino, G., & Soliman, M.
(2011). Levenberg - Marquardt training algorithms for
random neural networks. Computer Journal, 54(1),
125–135. https://doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/bxp101
Battiti, R. (1992). First- and Second-Order Methods for
Learning: Between Steepest Descent and Newton’s
Method. Neural Computation, 4(2), 141–166.
https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1992.4.2.141
Battiti, R., & Masulli, F. (1990). BFGS Optimization for
Faster and Automated Supervised Learning.
International Neural Network Conference, 757–760.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-0643-3_68
Bayatzadeh Fard, Z., Ghadimi, F., & Fattahi, H. (2017). Use
of artificial intelligence techniques to predict
distribution of heavy metals in groundwater of Lakan
lead-zinc mine in Iran. Journal of Mining and
Environment, 8(1), 35–48.
https://doi.org/10.22044/jme.2016.592
Bishop, C. M. (2006). Pattern recognition and machine
learning (Springer (ed.); springer).
Chen, Y., & Zhang, S. (2012). Research on EEG
classification with neural networks based on the
Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm. Communications in
Computer and Information Science, 308 CCIS(PART
2), 195–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34041-
3_29
Dreyfus, G. (2005). Neural Networks Methodology and
Applications. In Springer Science & Business Media.
Goldfarb, D. (1970). A Family of Variable-Metric Methods
Derived by Variational Means. Mathematics of
Computation, 24(109), 23.
https://doi.org/10.2307/2004873
Govindaraju, R. S., Rao, A. R. (2000). Artificial Neural
Networks in Hydrology. In Water Science and
Technology Library: Vol. 10.1007/97.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-9341-0
Hagan, M. T., & Menhaj, M. B. (1994). Training
Feedforward Networks with the Marquardt Algorithm.
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 5
(6), 989–993.
https://doi.org/10.1109/72.329697
Patro, S. G. K., & sahu, K. K. (2015). Normalization: A
Preprocessing Stage. Iarjset, 20–22.
https://doi.org/10.17148/iarjset.2015.2305
Perera, A., Azamathulla, H. M. D., & Rathnayake, U.
(2020). Comparison of different artificial neural
network (ANN) training algorithms to predict the
atmospheric temperature in Tabuk, Saudi Arabia.
Mausam, 71(2).
Refenes, A. N., & Azema-Barac, M. (1994). Neural
network applications in financial asset management.
Neural Computing & Applications, 2(1), 13–39.
https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01423096
Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E., & Williams, R. J. (1986).
Learning representations by back-propagating errors.
Nature, 323(6088), 533–536.
https://doi.org/10.1038/323533a0
Scales, L. E. (1985). Introduction to Non-Linear
Optimization. In Introduction to Non-Linear
Optimization (springer). Macmillan Education UK.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-17741-7
Sejnowski, T. J., & Rosenberg, C. R. (1987). Parallel
systems that learn to pronounce English text. Complex
Systems, 1, 145–168.
Shi, E., Shang, Y., Li, Y., & Zhang, M. (2021). A
cumulative-risk assessment method based on an
artificial neural network model for the water
environment. Environmental Science and Pollution
Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12540-6
A Comparative Study of Back-propagation Algorithms: Levenberg-Marquardt and BFGS for the Formation of Multilayer Neural Networks
for Estimation of Fluoride
565
