
Bio-cord as an Ecotechnological Wastewater Treatment for
Productive and Attractive Urban Open Spaces
Ferlina Sugata
1a
, Nathalia Yunita Sugiharto
1b
, Nina Nurviana
2c
, Seriwati Ginting
2d
,
Isabella Isthipraya Andreas
3e
, Shirly Nathania Suhanjoyo
3f
, Andi A. Hamzah
4g
and Heddy Heryadi
5h
1
Architecture Department, Universitas Kristen Maranatha, Bandung, Indonesia
2
Visual Communication Design Department, Universitas Kristen Maranatha, Bandung, Indonesia
3
Interior Design Department, Universitas Kristen Maranatha, Bandung, Indonesia
4
Three-Year Diploma Program in Arts and Design, Universitas Kristen Maranatha, Bandung, Indonesia
5
Visual Communication Design Department, Universitas Kristen Maranatha, Bandung, Indonesia
seriwati.ginting@maranatha.edu, isabella.ia@art.maranatha.edu, shirly.ns@art.maranatha.edu,
andi.ah@art.maranatha.edu, heddy.heryadi@art.maranatha.edu
Keywords: Bio-cord, Urban Open Space, Wastewater Technology, Sustainable Architecture.
Abstract: Bandung, has a great variety urban spaces within the city as urban fabric. Rapid urban population leads to a
rapid destruction. Therefore, there is an urgent need to optimize the utilization of existing open spaces become
more productive and attractive. This study attempts to examine and identify the potential and capability of
open space along Babakan Irigasi stream zones to optimize the spatial around neighbourhood. The hypothesis
is that by using Bio-Cord as wastewater treatment will develop sustainable characteristics and reshaping urban
spaces, it will help to be productive and liveable spaces. The paper presents the field data contains all open
spaces along Babakan Irigasi, and the variable aspects that optimize open spaces that consists of quality,
functional, and ecological-environmental aspects. Then, analyse the design strategies as the impact of the
wastewater treatment along the stream with Bio-Cord technology to achieve sustainable urban development,
and find values of productive and attractive urban open spaces. The Bio-Cord as an ecotechnological treatment
play a key role in the environmental design and sustainable development of the urban structure. This study
showed that productive and attractive open spaces are great importance for urban spatial structure that can
support sustainability.
1 INTRODUCTION
Bandung, the capital city of West Java province has a
great variety urban space. One of the typical urban
open spaces is Babakan Irigasi area. Babakan Irigasi
is located in two districts Astana Anyar and
Bojongloa Kaler. It is uniques because open spaces
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0570-2787
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2294-8674
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9158-4520
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9377-0722
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8577-2576
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8252-1843
g
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4157-935X
h
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6429-7489
along Babakan Irigasi area flowed by two rivers,
Citepus River and Ciroyom River. The specific area
of Babakan Irigasi that was studied is the segment
between Pagarasih road and Terusan Pasir Koja road.
Those rivers across along the research object area
approximately 400 meters in length. Like other
riverside settlements area, all building orientation is
following the stream’s shape characteristics.
Sugata, F., Sugiharto, N., Nurviana, N., Ginting, S., Andreas, I., Suhanjoyo, S., Hamzah, A. and Heryadi, H.
Bio-cord as an Ecotechnological Wastewater Treatment for Productive and Attractive Urban Open Spaces.
DOI: 10.5220/0010748500003113
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering and Science (ICE-TES 2021), pages 233-244
ISBN: 978-989-758-601-9
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
233

Figure 1: Urban Fabric Pattern Along Babakan Irigasi
Segment Pagarsih-Terusan Pasir Koja.
The utilization, protection, creation, and
development of urban open spaces is one of the key
elements to achieve sustainable urban development.
But the rapid urban population and the socio-cultural
of the communities sometimes lead to a rapid
destruction, also has caused a decreased number of
the quality of open spaces. Therefore, there is an
urgent need to optimize the utilization of existing
open spaces become more productive and attractive.
Figure 2: Open Space an Circulation Along Babakan Irigasi
Stream.
Could the urban open spaces at Babakan Irigasi be
optimize to become a productive and attractive open
space within the city of Bandung to help it become
sustainable? This study attempts to examine and
identify the potential and capability of open space
along Babakan Irigasi stream zone to make use the
spatial around their neighbourhood. What are the
functions of space created and activities that can be
created as urban open spaces with the characteristic
of riverside area.
This study also beneficial to safeguard the future
of sustainable architecture in the city, to improve the
quality of urban areas especially the neighbourhoods
along Babakan Irigasi, to make urban areas more
attractive, productive and to enhance the well-being
of local people. The hypothesis is that by using Bio-
Cord technology as wastewater treatement will
optimize the sustainable characteristics on existing or
reshaping urban open spaces, it will help it to be
productive and liveable.
2 METHODS (AND MATERIALS)
The structure of the paper presents the data about the
concept and typology of sustainable urban open
spaces, field data of the research object, that is open
spaces along Babakan Irigasi stream, and the variable
aspect that optimize urban open spaces that consists
of quality aspects, functional aspects, and ecological-
environmental aspects. The second part, to analyze
the design strategies of the utilization, protection,
creation, and development of the areas as the impact
of the waterwaste treatment along the stream with
Bio-Cord technology. Whether this technology is an
innovative solution for effective design urban spaces
to achieve sustainable urban development. And the
last part of this paper is to find productive value and
attractive value of urban open spaces which link
social, cultural, environmental and economic
dimensions of sustainability.
2.1 Urban Open Space
Urban open space is one of important element that
included in eight elements of urban designs (Shirvani,
1985, p. 5-49). Open space has so many benefits for
human and environment because it can be used as an
alternative for social interaction place and as rain
absorption land besides its beauty.
There are two types of open space which are space
that has fixed function such as swimming pool,
basketball court, etc. and space that has adaptive
function like a court with public seating area and
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
234

vegetation so people can do sports, playing with
children or picnic. Furthermore, open space has its
qualification based on Urban Open Space (Francis,
2003, p. 6-7)
Table 1: Typology of Urban Open Spaces.
T
yp
e Subt
yp
e
Public Parks: the
subtypes are based on its
size and location
Central parks
Downtown parks
Neighbourhood parks
Mini
p
arks
S
q
uares and Plazas Central s
q
uare
Markets Farmers markets
Atrium
Downtown shopping
centre
Streets Pedestrian sidewalks
Bicycle path
Traffic restricted street
Playground Pla
yg
roun
d
School
p
la
yg
roun
d
Waterfront Riverfront
Lakefront
Piers
An open space can be created by placing building
mass or objects that surround it. It also called as
positive space because it has contribution for human
and environment.
Figure 3: Open Space and Buildings Type 1.
Figure 4: Open Space and Buildings Type 2.
As an architect, we have to aware of negative
spaces that occur when there are spaces that don’t
have specific function and scattered among building
mass or objects.
2.2 Sustainable Urban Development
Sustainable urban development is meant to enrich the
lives of the society, that’s why planners have to know
how to engage with the complexity of community
life. Sustainable development is something that
comes from within communities. Development is a
process, it needs to be defined in terms of social
change and what is changing that brings about a
significant and patterned shift in the technologies,
techniques, infrastructure, and/or associated life-
forms of a place or people. Significant changes
include the changing forms of urbanization such as
urban sprawl and the decentralization of non-
residential functions, for example retail parks,
massively increased levels of commuting between
urban and rural areas, the development of
communication and transport technologies.
Sustainability is usually defined in terms of being
able to carry on, endure, or have a future. (James,
2015, p. 21).
Sustainable urban development is a multi-layered
concept. It synthesizes land development and nature
preservation. It also refers to the capacity of nature to
support its activities, the vitality of a city as a complex
system, and the quality of life of its inhabitants.
Sustainable urban development covers many fields of
activity such as environmental protection, human
development, and inhabitant wellbeing. (Tang and
Lee, 2016, p. 10)
Figure 5: Three Aspects Sustainable Urban Development.
Bio-cord as an Ecotechnological Wastewater Treatment for Productive and Attractive Urban Open Spaces
235

Furthermore, related with human settlements context,
there are some aspects in developing a sustainable
community such as:
• Sustainable land use
• Social development
• Population
• Environmentally sustainable, healthy and liveable
• Sustainable energy use
• Sustainable transport and communication systems
• Conservation and rehabilitation of the historical
and cultural heritage
• Improving urban economies
• Balance development in rural regions
• Disaster prevention, mitigation and preparedness,
and post-disaster rehabilitation capabilities
(Lundqvist, 2007, p. 11-12)
Succinctly, public space design aims sustainibilty
in 5 aspects, there are :
1. CommunityWelfare
Community welfare as basic motivation in creating
and developing public space. Community provides
movement path or circulation, communication centre
and a place to feel free and relax.
2. Visual Enhancement
A public space in a city will increase its visual quality
by being more human, harmony and good looking.
3. Environmental Enhancement
Greenery in open public space can give a boost in
aesthetic value and provides better air quality in the
middle of air pollution.
4. Economic Development
Economic development as a general purpose in
creating and developing an open public space.
5. Image Enhancement
Image enhancement is an abstract goal that isn’t
clearly stated in creating an open public space but it
has to be achieved.
(Carr, S,Et All., 1992, p.420)
2.3 Urban Farming as Productive
Urban Open Space
Massive development in urban areas has led to the
displacement of green open spaces. The loss of green
open space affects the stability of environmental
ecosystems. It also increases pollution, which is bad
for the health of urban communities. The concept of
urban farming then offers a solution by creating green
open land in the midst of dense urban buildings.
Urban farming can manage polluted urban areas into
a comfortable and healthy environment to live in
(cybex.pertanian.go.id).
What can become urban farming land is: a.
Private land, such as home yards, terraces, walls,
fences, gutters, and rooftop. b. Common land, such as
abandoned land, walls of alleys, riverbanks or over
rivers. Limited land, which is often seen as an
obstacle, can be overcome by applying various
cultivation technologies. From the simplest things
such as pots and polybags, also using waste materials
such as noodle containers, paint containers, and used
buckets. The vertical planting is called the
verticulture system. Containers used waste mineral
bottles, or from pipes (www.dekoruma.com.) In the
market, there is also a media that resembles a pocket
that can be hung on the wall.
(www.tokopedia.com/find/wall-planter-bag).
Difficult techniques are called hydroponic
techniques and aquaponics techniques (Pudjiastuti,
2017, p. iii). Cultivation consists of vegetables, herbs,
fruit, and ornamental plants. The type of plant is
adapted to the container. Small pots, verticulture, and
hydroponics are usually applied to light, short-rooted,
and short-lived plants (Pudjiastuti, p 3). Combined
cultivation is called the aquaponic technique, for
example, cultivating vegetables with fish or fruit with
fish (Pudjiastuti, p. 99). Law Number 26 of 2007
concerning Spatial Planning Article 29 states that the
proportion of Green Open Space in urban areas is at
least 30% of the total area (Nurmala, 2019, p. 1) The
city of Bandung has a composition and proportion of
green open space area of only 12.20% (Nurmala, p.
3). The city of Bandung supplies 98% of its foodstuffs
from other cities. The limited land and food
availability are anticipated by the Bandung City
Government with the SAE (Healthy, Natural and
Economical Yard and Kangpisman (Reduce, Separate
and Utilize) Waste Program
(buruansae.bandung.go.id). It takes creative thinking
from the community and universities to enrich urban
programs. farming in the fields of economics,
environmental aesthetics, creative activities, and
citizen recreation.
2.4 Bio-cord Technology
As cities continue to grow, they also generate lots
amount of solid and liquid waste. In some developing
countries, the waste is being disposed to the river that
cause river water pollution. Since 2017, Indonesia
adopted a technology called bio-cord in its
wastewater treatment. This technology help to
increase water quality up to 50% depending on the
pollution (Sugara, 2017:17).
The basic principle of Bio-Cord technology is
using synthetic fibre (Bio-Cord) that become a host
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
236
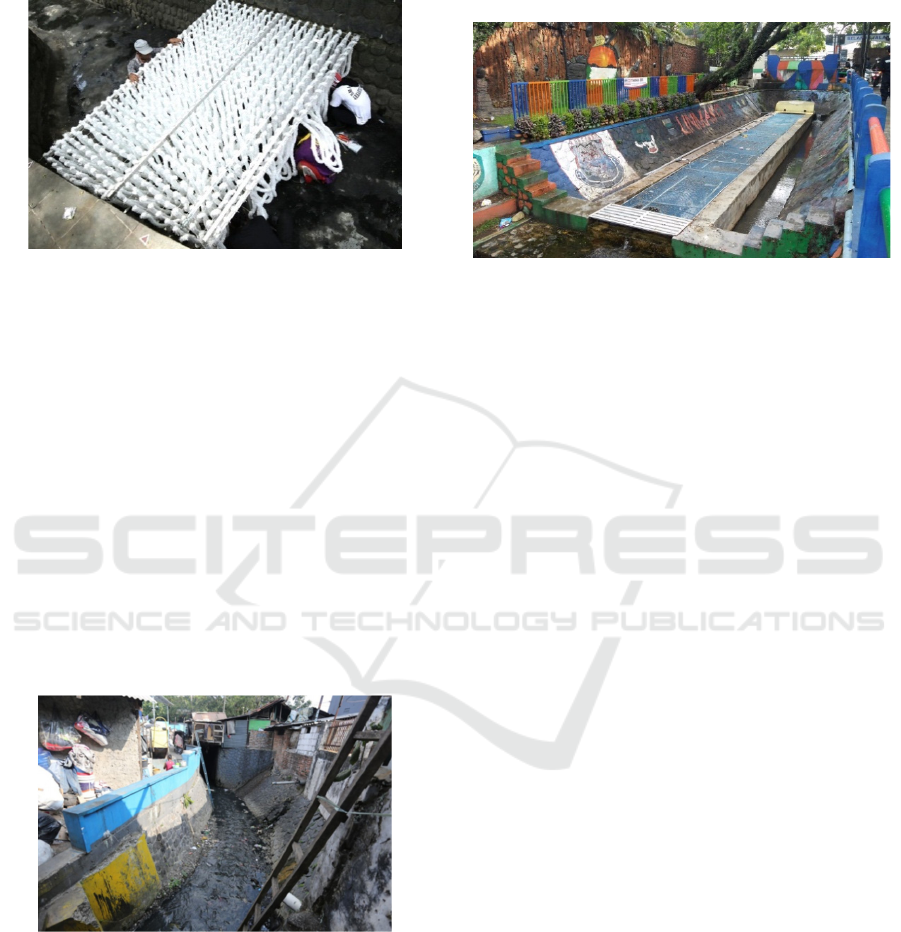

for microbial. This microbial can break down the
polluted substance inside the water and change it into
a better water.
Figure 6: Bio-Cord Installation at Cikapayang River.
About the installation, there are several
requirements, such as:
1. Water body length: 100 metre
2. Water body width: 2 metre
3. Number of Bio-Cord lines: 20
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Before the installation of Bio-Cord technology on
Babakan Irigasi stream is negative urban spaces,
which non-productive and not atrractive area. Urban
settlement around the riverside settlement looks slum
with black water as waste water. The condition of
surrounding is also passive, no public activities that
creates livable spaces and places.
Figure 7: The Condition of Babakan Irigasi before Bio-
Cord Installation.
Poorly maintained environmental conditions
along Babakan Irigasi caused unpleasant odors and
bad views. Wastewater treatment with Bio-cord
technology aims to process water purification, so that
the river water becomes clear and odorless. This This
condition will make benefit for all, both local
government and local residents where the riverside
conservation where this kind of efforts will have the
potential power to become a productive and attractive
open spaces that increase the economy of the local
community.
Figure 8: Bio-Cord Installation at Babakan Irigasi.
In 2020 The Bandung city government get
PEMERINTAH Kota (Pemkot) Bandung obtain
financial assistance from PT Bank Rakyat Indonesia
Persero Tbk for riverside conservation program at
RW 04 Babakan Irigasi. Since that time of Bio-Cord
technology was installed at Babakan irigasi area. This
program brings the potential and capability of urban
open space to become productive and attractive area.
Below is some functions of spaces and some
activities that can be created as urban open spaces
with the characteristic of riverside area.
3.1 Productive Public Open Spaces
Since the supply of clean water from the river due to
installation of Bio-Cord technology, local community
creates various productive spaces to their activities. It
is said to be productive because these activity spaces
facilitate activities that can have positive impacts in
terms of quality aspects, functional aspect, and
ecological-environmental aspects. Moreover, it is
also improving socio-economic welfare for local
community.
The quality aspects of urban open spaces deal
mostly with:
- The suitability and quality of site structure
- Design of urban green spaces with regard to their
importance and functions
- Site condition quality
- Quality aspects associated with natural and
landscape features, historic and cultural values and
qualities that should be preserved or emphasised.
The functional aspects of urban open spaces are
linked with:
- Accessibility and use of open spaces
- Connectivity of public spaces
Bio-cord as an Ecotechnological Wastewater Treatment for Productive and Attractive Urban Open Spaces
237

Ecological and environmental aspects deal with:
- Biodiversity and ecological value
- Natural corridors
- Urban climate; and
- Other environmental aspects that are important for
human well-being and health.
As for the spaces created are vegetables garden,
hydroponic garden, vertical flower garden, fish pond,
compost plant, clean water reservoir (ground tank and
upper tank), cafeteria, retail, vertical garden along the
circulation area both edible and aesthetic plants, etc.
Figure 9: Community Vegetables Garden.
Figure 10: Community Hydroponic Garden.
Figure 11: Community Fish Pond.
Figure 12: Café Walungan.
Figure 13: Food Counter at The Bridge.
Figure 14: Community Compost Plant.
Figure 15: Clean Water Ground Tank Reservoir.
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
238

Figure 16: Clean Water Upper Tank Reservoir.
3.2 Attractive Public Open Spaces
Besides the productive spaces that was created.
Installation of Bio-Cord technology also creates
various attractive spaces. As for the attractive spaces
referred to in the context of architectural design,
includes facade design, composition of open space
and building mass, outdoor materials, street furniture,
and new attractive functions of space.
As for the spaces created at Babakan Irigasi area
are natural swimming pool, relaxing garden, children
playground, colourful bulding façade, semi-
amphitheatre, selfie spot, etc.
Figure 17: Children are Playing and Swimming.
Figure 18: Public Relaxing Garden.
Figure 19: Community Children Playground.
Figure 20: Public Relaxing Garden with Roof.
Figure 21: Attractive House Fasade.
Figure 22: Mini Semi-Amphitheatre
Bio-cord as an Ecotechnological Wastewater Treatment for Productive and Attractive Urban Open Spaces
239
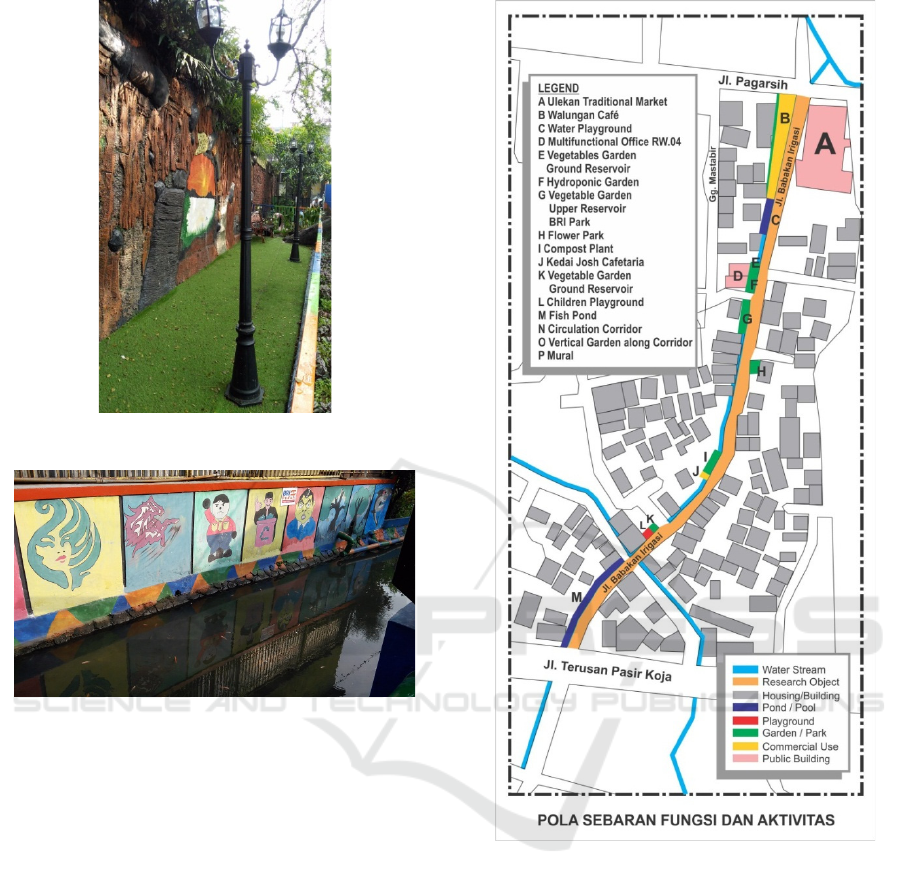
Figure 23: Selfie Spot.
Figure 24: Attractive Spaces Retaining Wall with Mural
Wall.
3.3 Productive Value and Attractive
Value of Urban Open Spaces as
Dimensions of Sustainibilty
We measure productive value and attractive value of
urban open spaces which link to public space design
that aims sustainibilty consists of these variable
aspects : Community Welfare, Visual Enhancement,,
Environmental Enhancement, Economic
Development, Economic Development and Image
Enhancement.
We identified various type of public spaces along
Babakan Irigasi and analysed all the supporting
variables to find how does the Bio-Cord Technology
optimize urban open spaces along Babakan Irigasi.
Figure 25: Productive and Attractive Spaces at Babakan
Irigasi Riverside Settlement.
1. Analysis of Community Welfare Aspect
This table shows how community welfare as basic
motivation in creating and developing public space.
Community provides movement paths or circulation,
communication centre and a place to feel free and
relax.
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
240

Table 2: Aspects of Community Welfare in Dimensions of
Sustainibility.
Productive Public
Spaces at Babakan
Irigasi
LE
GE
ND
Community Welfare
Move
ment/
Circul
ation
Comm
unicati
on
Relax
&Free
Circulation Corridor N √ - -
Vegetables Garden E - - -
Hydroponic Garden F - - -
Vertical Garden
along the
Circulation Corridor
O √ - √
Fish Pond M - √ √
Compost Plant I - - -
Clean Water
Reservoir
(ground tank)
E - - -
Clean Water
Reservoir
(upper tank)
G - - -
Cafeteria B - √ √
Retail Kiosk J - √ √
Flower Park H - - √
Attractive Public
Spaces at Babakan
Irigasi
LE
GE
ND
Move
ment/
Circul
ation
Comm
unicati
on
Relax
&Free
Water Playground C √ √ √
Colourful building
façade with Mural
P √ - √
Outdoor Semi-
Amphitheatre
B - √ √
Selfie Spot B - √ √
Relaxing Garden G - √ √
Children
Playground
L - √ √
Vegetables Garden, Hydroponic Garden,
Compost Plant, Clean Water Reservoir are urban
public open spaces that are not fulfilled in community
welfare aspects.
2. Analysis of Visual Enhancement Aspect
A public space in a city will increase its visual quality
by being more human, harmony and good looking.
Table 3: Aspects of Visual Enhancement in Dimensions of
Sustainibility.
Productive Public
Spaces at Babakan
Irigasi
LE
GE
ND
Visual Enhancement
Huma
nist
Harmo
ny
Good
Lookin
g
Circulation Corridor N √ √ √
Vegetables Garden E √ √ √
Hydroponic Garden F √ √ √
Vertical Garden
along the
Circulation Corridor
O √ √ √
Fish Pond M √ √ √
Compost Plant I - - -
Clean Water
Reservoir
(ground tank)
E - - -
Clean Water
Reservoir
(upper tank)
G - - -
Cafeteria B √ √ √
Retail Kiosk J √ - -
Flower Park H √ √ √
Attractive Public
Spaces at Babakan
Irigasi
LE
GE
ND
Huma
nist
Harmo
ny
Good
Lookin
g
Water Playground C √ √ √
Colourful building
façade with Mural
P √ √ √
Outdoor Semi-
Amphitheatre
B √ √ √
Selfie Spot B √ √ √
Relaxing Garden G √ √ √
Children Playground L √ √ √
There are only two open spaces that are not
fulfilled according to visual enhancement variables.
They are Compost Plant and Clean Water Reservoir.
3. Analysis of Environmental Enhancement Aspect
Greenery in open public space can give a boost in
aesthetic value and provides better air quality in the
middle of air pollution.
Bio-cord as an Ecotechnological Wastewater Treatment for Productive and Attractive Urban Open Spaces
241
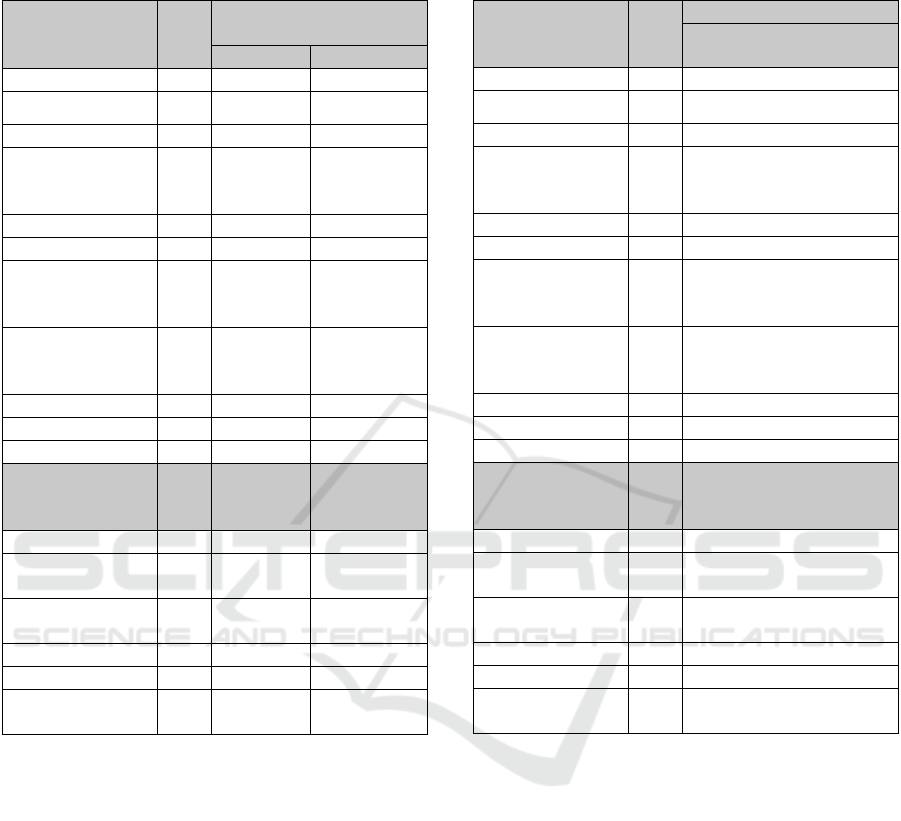
Table 4: Aspects of Environmental Enhancement in
Dimensions of Sustainibility.
Productive Public
Spaces at Babakan
Irigasi
LE
GE
ND
Environmental
Enhancement
City Lungs Greenery
Circulation Corridor N √ -
Vegetables Garden E √ √
Hydroponic Garden F √ √
Vertical Garden
along the
Circulation Corridor
O √ √
Fish Pond M - √
Compost Plant I - √
Clean Water
Reservoir
(ground tank)
E - √
Clean Water
Reservoir
(upper tank)
G - √
Cafeteria B - -
Retail Kiosk J - -
Flower Park H - √
Attractive Public
Spaces at Babakan
Irigasi
LE
GE
ND
City Lungs Greenery
Water Playground C - √
Colourful building
façade with Mural
P - -
Outdoor Semi-
Amphitheatre
B - -
Selfie Spot B - -
Relaxing Garden G √ √
Children
Playground
L - -
There are some public spaces that are not
fulfilled to these variables : Cafeteria, Retail Kiosk,
Colourful Building with Mural Facade, Outdoor
Semi-Amphitheatre, Selfie Spot, and Children
Playground.
4. Analysis of Economic Development Aspect
Economic development as a general purpose in
creating and developing an open public space.
Table 5: Aspects of Economic Development in Dimensions
of Sustainibility.
Productive Public
Spaces at Babakan
Irigasi
LE
GE
ND
Economic Development
Economic Value
Circulation Corridor N -
Vegetables Garden
E √
Hydroponic Garden F √
Vertical Garden
along the
Circulation Corridor
O -
Fish Pond M -
Compost Plant I -
Clean Water
Reservoir
(ground tank)
E -
Clean Water
Reservoir
(upper tank)
G -
Cafeteria B √
Retail Kiosk J √
Flower Park H -
Attractive Public
Spaces at Babakan
Irigasi
LE
GE
ND
Economic Value
Water Playground C -
Colourful building
façade with Mural
P -
Outdoor Semi-
Amphitheatre
B √
Selfie Spot B -
Relaxing Garden G -
Children
Playground
L -
According to Economic Development Aspect
there are five public spaces have the economical
value that increasing economy of the community,
following Circulation Corridor, Hydroponic Garden,
Cafeteria, Retail Kiosk, Outdoor Semi-Amphitheatre.
5. Analysis of Image Enhancement Aspect
Image enhancement is an abstract goal that isn’t
clearly stated in creating an open public space but it
has to be achieved.
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
242

Table 6: Aspects of Image Enhancement in Dimensions of
Sustainibility.
Productive Public
Spaces at Babakan
Irigasi
LE
GE
ND
Image Enhancement
In Order Cleanliness
Circulation Corridor N √ √
Vegetables Garden
E √ √
Hydroponic garden F √ √
Vertical Garden
along the
Circulation Corridor
O √ √
Fish Pond M √ √
Compost Plant I √ √
Clean Water
Reservoir (ground
tank)
E √ √
Clean Water
Reservoir (upper
tank)
G √ √
Cafeteria B √ √
Retail Kiosk J √ √
Aesthetic Plants
Garden
H √ √
Attractive Public
Spaces at Babakan
Irigasi
LE
GE
ND
In Order Cleanliness
Water Playground C √ √
Colourful building
façade with Mural
P √ √
Outdoor Semi-
Amphitheatre
B √ √
Selfie Spot B √ √
Relaxing Garden G √ √
Children Playground L √ √
This table shows how effective Bio-Cord
Technology as the trigger which creating urban open
spaces that all the functions of urban open spaces
became tidy, in order and clean. These image is
totally different like other urban open spaces along
the stream or river we used to see.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The Bio-Cord Technology that installed at Babakan
Irigasi area as an ecotechnological treatment play a
key role in the environmental design and sustainable
development of the urban structure of the city
settlement. This study showed that productive and
attractive open spaces are of great importance for
urban spatial structure that can support sustainability.
Table 7: Aspects of Economic Development in Dimensions
of Sustainibility.
Dimension of Sustainibility Fulfilled
Not
Fulfilled
Community Welfare 70,6% 29,4%
Visual Enhancement 82,3% 17,7%
Environmental Enhancement 64,7% 35,3%
Economic Development 29,4% 70,6%
Image Enhancement 100% 0%
This table shows that the result of functional
mapping of urban open spaces that created as the
impact of Bio-Cord Technology analyze by five
aspects as dimensions of sustainibilty,
Image Enhancement is the most fulfilled aspect
where all public spaces that created were fulfilled
100%. Visual Enhancement is also fulfilled 82,3%
that means urban open spaces that were created are
humanist, harmony and good looking. While the
community welfare aspects show that urban public
were fulfilled 70,6% that contains of movement,
communication, relaxing&free activity as the
variables. The environmental enhancement aspects
show the number of 64,7% where urban public open
spaces enabled as the city lung and greenery elements
which means environmental friendly. Meanwhile
economical development aspects only shows 29,4%
that are fulfilled, where only a few spaces have the
economical value.
This kind transformation of waste land to a
productive and open space is one of the city urban
renewal plan
.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper is part of our devotion to the riverside
urban community which which requires spatial
planning and visual design that can make productive
and attractive to increase community welfare. All the
authors also express the gratitude to the community at
RW 04 Babakan Irigasi Bandung for the filed data to
complete this paper.
REFERENCES
Carr, S., Et All. (1992), Public Space, Cambridge
University Press, Cambridge.
Francis, Mark. (2003), Urban Open Space: Designing for
User Needs, Island Press. Washington DC.
Haqi, Ibnul Faruq (2016) ‘Sustainable Urban Development
and Social Sustainability in the Urban Context’
Bio-cord as an Ecotechnological Wastewater Treatment for Productive and Attractive Urban Open Spaces
243

.EMARA Indonesian Journal of Architecture Vol 2 No
1.
James, P. (2015), Urban Sustainability for Theory and
Practice, Routledge. Newyork.
Lundqvist, M. (2007), Sustainable Cities in Theory and
Practice, Karlstad Universitet, Sweden.
Pudjiastuti, E. (2017). 29 Teknik Urban Farming. PT
Trubus Swadaya. Jakarta.
Shirvani, Hamid. (1985). The Urban Design Process, Van
Nostrand Reinhold Company, Inc. New York.
Sugara, Asep. (2017). ‘Implementasi Kebijakan
Pengelolaan Kualitas Air dan Pengendalian
Pencemaran Air Kali Sabi di Kota Tangerang’. Jurnal
Mozaik Vol. IX Edisi 1, 10-18.
Tang , Hui-Ting and Lee , Yuh-Ming (2016) ‘The Making
of Sustainable Urban Development: A
Synthesis Framework’. www.mdpi.com/journal/
sustainability id (Accessed: 4 May 2021)
Yuditia, N. (2019). Evaluasi Pemanfaatan Ruang Terbuka
Hijau sebagai Sarana Rekreasi Masyarakat Kota
Bandung. “Taman Tematik Kota Bandung”.
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia repository.upi..edu.
Bandung
buruansae.bandung.go.id (Accessed: 5 May 2021)
cybex.pertanian.go.id (Accessed: 14 May 2021)
www.dekoruma.com/artikel (Accessed: 14 May 2021)
www.tokopedia.com/find/wall-planter-bag (Accessed: 14
May 2021)
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
244
