
Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells-secreted IDO as Candidate
of Anti-inflammation Therapy
Wahyu Widowati
1,* a
, Teresa Liliana Wargasetia
1b
, Fanny Rahardja
1c
,
Rimonta F. Gunanegara
1d
, Hanna Sari Widya Kusuma
2e
, Seila Arumwardana
2f
,
Cintani Dewi Wahyuni
1g
, Cahyaning Riski Wijayanti
2h
, Tri Handayani
2i
and Rizal Rizal
2,3 j
1
Faculty of Medicine, Maranatha Christian University, Jl. Surya Sumantri No. 65, Bandung 40164, West Java, Indonesia
2
Biomolecular and Biomedical Research Center, Aretha Medika Utama, Jl Babakan Jeruk II No. 9, Bandung 40163,
West Java, Indonesia
3
Biomedical Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Indonesia,
Depok 16426, West Java, Indonesia
hannasariw@amubbrc.co.id, seila.wardana91@gmail.com, cintanidewi@gmail.com, cahyaningwidodo@gmail.com,
mbaktrihandayani@gmail.com, rizal_biotek@yahoo.com
Keywords: Covid-19, Cytokine Storm, Indoleamine 2,3 Dioxygenase, Secretome, Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem
Cells.
Abstract: Local inflammation in lung can induce by viral pneumonia which causes acute respiratory distress
syndrome (ARDS). ARDS also caused by COVID-19 SARS-COV-2 infection. hWJMSCs will release anti-
inflammatory signals such as indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO) as tissue homeostasis between MSCs and
resident macrophages as anti-inflammatory signals. This led to the idea of investigating potential of
hWJMSCs-Secreted IDO as candidate of anti-inflammation therapy. The hWJMSCs have been isolated
from the human umbilical cord using an explant method and characterized using a flow cytometer to detect
the cell surface markers CD105, CD73, CD44, CD90, and negative lineage expression of hWJMSCs. The
hWJMSCs secretome was characterized by measuring the level of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) in
various starving cells. The isolated umbilical cord hWJMSCs showed positive expression of CD105, CD73,
CD44, CD90, and negative lineage expression from 5, 10, and 15 passage. The hWJMSCs IDO secretion
level was 5.86 ng/mL for non-starving cells, 6.84 ng/mL for 24 h starving cells, 9.59 ng/mL for 48 h
starving cells, and 13.32 ng/mL for 72 h starving cells. The early, medium, and old passage of hWJMSCs
have the same characteristics. Longer starvation periods up to regulate the IDO level in hWJMSCs
secretome which indicate as anti-inflammation therapy.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5401-7794
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9990-4741
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2982-8437
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3053-1120
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7422-0036
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0422-7379
g
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7764-0482
h
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3397-099X
i
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9186-9841
j
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2783-0672
*
Corresponding author
1
INTRODUCTION
Inflammation is a critical biological reaction to
damage that is linked to a variety of disorder such as
acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). ARDS
is caused by viral pneumonia as the virus infects the
respiratory tract, it induces local inflammation, which
results in the production of pro- inflammatory
Widowati, W., Wargasetia, T., Rahardja, F., Gunanegara, R., Kusuma, H., Arumwardana, S., Wahyuni, C., Wijayanti, C., Handayani, T. and Rizal, R.
Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells-secreted IDO as Candidate of Anti-inflammation Therapy.
DOI: 10.5220/0010749700003113
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering and Science (ICE-TES 2021), pages 271-278
ISBN: 978-989-758-601-9
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
271

cytokines and chemokines. T cells and monocytes
from the blood are drawn to the infectious site as a
result (Tay et al., 2020; Canham et al., 2020).
Excessive release of proteases and reactive oxygen
species (ROS) is caused by the uncontrolled invasion
of inflammatory cells into the lungs (Abraham &
Krasnodembskaya; 2020). Cytokine Storm Syndrome
(CSS) or Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) is a
condition in which the body produces excessive
amounts of cytokines (Ye et al., 2020; Azmi et al.,
2020). SARS-CoV-2 binds to the angiotensin-
converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor on the surface
of human cells for cell entry (Azmi et al., 2020),
Increased serum cytokines such as Interleukin-1 (IL-
1), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-, peripheral
lymphopenia, elevated ferritin level, lactate
dehydrogenase (LDH), d-dimer, C-reactive protein
(CRP), and coagulation factors are all part of the
host's immune response to COVID-19 (Zhou et al.,
2020; Chen et al., 2019; Acosta, 2020). Infection
with SARS-CoV-2 causes an increase in IL-1
Receptor Antagonist (IL- 1RA), IL-2, IL-6, IL-7, IL-
9, IL-10, Interferon Gamma (IFN), Interferon
Gamma Inducible Protein-10 (IP-10), Monocyte
Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP1), Granulocyte-
Colony Stimulating Factor (GCSF), Basic Fibroblast
Growth Factor (FGF), Platelet-Derived Growth
Factor (PDGF), and Inflammatory Protein 1- Alpha
(MIP1-α), MIP-1β (Durand et al., 2020, Huang et al
2020; Canham et al., 2020). There are also high
levels of chemokines (CCL2, CCL3, CCL5, CXCL8,
CXCL9 and CXCL10) (Huang et al., 2019; Williams
& Chambers, 2014; Cetin & Topcul; 2020), edema in
the alveoli, reduced efficiency of gas exchange,
ARDS, and acute cardiac injury (ACI), which can
result in hypoxemia, secondary infection (Huang et al
2020; Canham et al., 2020), and death (Huang et al.,
2020).ARDS caused by COVID-19 is due to
respiratory failure (53%), respiratory failure coupled
with cardiac failure (33%), myocardial damage and
circulatory impairment (7%), or death by unknown
cause (Gibson et al., 2020). CSS refers to a group of
disorders that result in a violent immune system
assault on the host body, such as systemic
inflammation, multiorgan failure, and
hyperferritinemia, and, if left untreated, death.
(Behrens EM, Koretzky, 2017; Cetin & Topcul;
2020).
Because of the COVID-19's serious respiratory
effects as a result of CSS, infection prevention,
surveillance, and supportive care, such as
supplementary oxygen and mechanical ventilation,
are now needed in the clinical management of
critically ill patients (Baruah & Bose, 2020; Golchin
et al., 2020). Since there is currently no specific cure
for COVID-19 it is critical to develop new treatment
approaches that are more innovative, safe, and
promising in the treatment of ARDS. Cell-based
therapy, especially stem cell therapy, is currently
viewed as a promising therapy for curing incurable
diseases (Golchin & Farahany, 2019; Golchin et al.,
2020). Adult stem cells derived from mesenchymal
stem cells (MSCs) is a promising source for cell
therapy and tissue engineering (Widowati et al.,
2015). MSCs are a more superior care than the
others, and they've gotten a lot of coverage because
of: i). source potential, easily accessible, and can be
isolated from a variety of tissues including bone
marrow (BM), adipose tissues (AT) (such as
infrapatellar fat pad, abdominal fat, and buccal fat
pad), neonatal birth-associated tissues such as
placenta (PL), amniotic fluid (AF), Wharton jelly
(WJ), umbilical cord (UC), and cord blood (CB),
dental pulp, menstrual blood, buccal fat pad, fetal
liver; ii). high proliferation rate; iii). multipotent
stem cells with high proliferation rate; iv). simple
culture and harvesting procedures; v). easy ex vivo
expansion to clinical volume; vi). can be processed
for repeated therapeutic use; vii). trophic paracrine
secretion, producing a large amount of therapeutic
growth factor and cytokines; and viii). autologous
and allogenic clinical therapy (Golchin et al., 2018;
Golchin et al., 2020). MSCs have low major
histocompatibility complex (MHC) type 1
expression and no MHC type 2 expression, making
them non-immunogenic and suitable for allogeneic
therapy (Berglund et al., 2017; Canham et al., 2020).
MSCs have ability to restore the balancing
immunological response at inflammation sites and in
the surrounding environment by communicating with
different immune system components. MSCs have
the ability to interact with adaptive immune and
innate immune systems by sensing the inflammatory
state and detecting the presence of microbes through
stimulation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) on their
surface. In the presence of an inflammatory
microenvironment, such as high levels of Interferon-γ
(INF-γ) and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) or
TLR3 receptor stimulation by viral RNA, MSCs will
release anti-inflammatory signals such as
indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO), Tumor Growth
Factor- β (TGF-β), and prostaglandin E-2 (PGE-2),
as tissue homeostasis between MSCs and resident
macrophages as anti-inflammatory signals that cause
the emergence of both regulatory T and dendritic
cells (Bernardo & Fibbe, 2013; Glenn & Whartenby,
2014; Canham et al., 2020). When MSCs interact
directly with immune cells, they perform paracrine
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
272

modulation as a result of the immune response by
releasing cytokines such as IDO, IL-10, TGF- β, and
IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL- 1RA), and nitric oxide
(NO) (van Buul et al., 2012). Several studies have
shown that tryptophan catabolism occurs
predominantly at areas of tissue inflammation and
that IDO expression might well be involved in
inhibiting the inflammatory reaction and therefore
decreasing tissue injury (Wolf et al, 2004; Nikolaus,
et al., 2017). IDO is a rate-limiting enzyme of
tryptophan catabolism along the kynurenine (Kyn)
pathway. The immunosuppressive mechanism of
IDO is mediated by depletion of tryptophan,
accumulation of kynurenines (Lee et al., 2016).
Several soluble factors either produced
constitutively by MSCs or as a result of cross-talk
with target immune cells have been attributed to
immunomodulatory property of MSCs, including
PGE2, IDO, NO, IL-10, and hepatocyte growth
factor (HGF) (Meesuk et al., 2016). MSCs exhibit as
anti- inflammatory several factors, including IDO
and TNF- stimulated gene 6 (TSG-6). IDO controls
the TSG-6 mediated anti-inflammatory therapeutic
potent of MSCs (Wang et al., 2018). TSG-6-
knockdown (TSG- 6-KD) MSCs have less
therapeutic effect on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-
induced Acute Lung Injury (ALI) model mice
compared to MSCs control. This data demonstrates
that IDO expression by MSCs has capability to
alleviates ALI by regulating the TSG-6. Expression
(Wang et al., 2018).
The microenvironment of cells, such as food
deprivation and low oxygen stress, has an effect on
their characteristics (Ferro et al., 2019). Many
studies show that starving MSCs in vitro to mimic in
vivo post- transplantation improves MSC survival
and therapeutic efficacy (Ferro et al., 2019). Human
MSCs are protected from a rapid transition from in
vitro culture to a harsh environment in vivo by using
fetal bovine serum (FBS) and glucose deprivation
before transplantation (Moya et al., 2015; Ferro et
al., 2019). COVID-19 therapy using stem cells,
especially WJMSCs, has several advantages,
including a high capability for regeneration and
differentiation, as well as the ability to rapidly
expand (Garzon et al., 2020). WJMSCs are a non-
controversial stem cell source (Yang et al., 2012;
Bongso et al., 2013). WJMSCs are more useful and
straightforward in terms of donor entry, expansion,
proliferative ability, and banking; they can also be
used in clinical and experimental therapy (Tamura et
al., 2011). Between the amniotic epithelium and the
umbilical vessels is the WJ, which is embryonic
mucous connective tissue. Adult tissue- derived
MSCs have a lower proliferation rate and self-
renewal capability than WJ derived MSCs or
WJMSCs (Marino et al., 2019; Widowati et al.,
2014). This study looked at the immunophenotyping
of human WJMSCs (hWJMSCs) at different
passages, including positive CD105, CD73, CD44,
CD90, and negative lineage expression, as well as
the IDO secretion of hWJMSCs.
2
MATERIAL AND METHOD
2.1 hWJMSCs Isolation
Human umbilical cords (UC) were collected from
normal delivery women aged 25 to 40 who signed an
informed consent document that was accepted by the
Institutional Ethics Committee of Maranatha
Christian University, Bandung, Indonesia, and
Immanuel Hospital Bandung, Bandung, Indonesia
(Widowati et al., 2017). Phosphate Buffer Saline
(PBS) (Biowest, X0515500) was used to wash UC's
blood, which was then supplemented with antibiotics
and transported to the laboratory using transport
medium (Widowati et al., 2019a; Widowati et al.,
2019b).
The vessel was extracted from the UC after being
transferred and washed in PBS (1x). Wharton jelly
tissue explants were dissected into 1-2 mm
3
pieces
and plated on 6 well plates in Minimum Essential
Medium (MEM- α) (Biowest, L0475-500)
supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS)
(Biowest, S1810-500), 1% ABAM, 0.1%
Gentamicin (Gibco, 15750060), 1% Amphotericin B
(Amp B) (Biowest, L0009-100), and 1%
Nanomycopulitin (Biowest, LX16-100). After 3
weeks of incubation at 37
o
C in a humidified
atmosphere with 5% CO2, adherent cells and tissue
fragments were detached using Trypsin-EDTA
solution (Biowest, L0931-500) and washed with
basal medium. The cells were harvested and re-
plated at a density 8 x 10
3
cells/cm
2
when cells
reached 80-90% confluence (Widowati et al., 2014;
Widowati et al., 2017; Widowati et al., 2019a;
Widowati et al., 2019b).
2.2 Markers Detection of hWJMSCs
using Fluorescence Activated Cell
Sorting
The hWJMSCs surface marker was observed in
Passage 5 (P5), 10, and 15 cell cultures. The cells
culture that had reached 80-90% confluence were
Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells-secreted IDO as Candidate of Anti-inflammation Therapy
273

harvested and analyzed for surface marker using
flow cytometry (MACSQuant Analyzer 10, Miltenyi
Biotec). The cells were stained with specific
antibodies (CD90 FITC, CD73 APC, CD105 PerCP-
Cy5, CD44 PE, negative lineage:
CD34/CD45/CD11b/CD19/HLA-DR PE) according
to manufacturer’s protocol (BD stem flow
TM
kit,
562245). The surface marker of hWJMSCs were
conducted in triplicate for each passage (Widowati
et al., 2014; Widowati et al., 2019a; Widowati et al.,
2019b).
2.3 Preparation of Conditioned
Medium From hWJMSCs
The medium was collected and centrifuged at 3000
rpm for 4 minutes at room temperature, and the
supernatant was filtered by a 0.22-mm MillexeGV
Filter Unit with Durapore (Millipore Corporation,
SLGV 033 RS) and used as hWJMSCs secretome
(Widowati et al., 2015).
2.4 IDO level of hWJMSCs Secretome
The hWJMSCs P5 cell culture was used for
experiments. The cells were seeded 8x10
3
cells/cm
2
in complete medium. After the cells reached 80-90%
confluence, the cells were grown in starving medium
(MEM-α no- phenol red, 1% ABAM, 0.1%
Gentamicin, 1% Amphotericin B and 1%
Nanomycopulitin) for 24, 48 and 72 hours.
The level of IDO in the cell-free supernatant of
hWJMSCs was measured using human IDO
(Indoleamine-2,3- Dioxygenase) ELISA Kit
(Elabsci, E-EL-H2162). Regarding the manual 50
µL of stop solution was applied to each well, and the
absorbance was read at 450 nm microplate reader
(Multiskan Go, Thermos Fisher Scientific)
(Widowati et al., 2017).
3
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 The Effect of Different Passages on
hWJMSC Markers
The result of evaluating the effect of different
passages (P5, P10, P15) on hWJMSC surface
markers. The hWJMSCs were positive for CD90,
CD44, CD105, CD73 and negative for CD11b,
CD19, CD34, CD45, and HLA-II. The effect of
different passages on the surface marker of
hWJMSCs are given in Table 1. Positive and
Table 1: Effects of different passages on the percentage of
hWJMSCs with positive and negative surface marker
lineages.
Passage
CD44
(%)
CD73
(%)
CD90
(%)
CD10 5
(%)
negative-
lineage
(%)
P5 99.44±0.01 96.97±0.24 99.44±0.03 99.56±0.03 0.23±0.02
P10 98.77±0.26 97.68±0.09 98.79±0.13 98.86±0.27 0.71±0.05
P15 99.75±0.06 99.36±0.20 99.71±0.03 99.78±0.05 0.43±0.04
*
Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation from 3
replications; CD90, CD44, CD105, CD73 are positive
lineage- markers; CD14, CD19, CD34, CD45, HLA-II are
negative lineage- markers.
negative surface marker expression of hWJMSCs
P5, P10, and P15 were not significantly different
(p>0.05). MSCs should have CD44, CD73, CD90,
and CD105 positive lineage markers and CD11b,
CD19, CD34, CD45, and HLA-DR negative lineage
markers (Figure 1). Propyl etidium (PE), fluorescein
isothiocyanate (FITC), and peridinin chlorophyll
protein-5 (PerCP-Cy5) staining were used to detect
the surface markers of hWJMMSCs. The MSC
characteristics were visible in different passages,
including early (P5), medium (P10), and old passage
(P15) (Table 1).
This finding is also in line with another previous
study that human adipose tissue-derived MSCs
(hATMSCs) exhibited positive lineage markers
(CD44, CD73, CD90, CD105) and negative lineage
markers (CD11b, CD19, CD34, CD45, HLA-DR)
from passage 4 to 15 (Widowati et al., 2014;
Widowati et al., 2019a; Widowati et al., 2019b). The
passaging from P4-P15 affects the cells proliferation
but not affects the cells morphology and cells
characteristic (Widowati et al., 2019b). Our previous
research that passage 3 and passage 8 of hWJMSCs
isolated by explant and enzymatic method exhibited
un-significantly differences between P3 and P8,
between explant and enzymatic isolation (Widowati
et al., 2019a). Our previous research exhibited that
passage P4 and P8 of hWJMSCs cultured in
normoxic and hypoxic condition showed hWJMSCs
un-significantly differences between P4 and P8,
between normoxic and hypoxic condition (Widowati
et al., 2014). The flow cytometric analysis showed
that oxygen level, isolation method and passage did
not affect the MSC’s character. The hWJMSCs from
P5, P10, P15 showed a very little expression (0.23-
0.71%) of negative lineage (CD11b, CD19, CD34,
CD45, HLA-DR).
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
274

3.2 Effect Starvation on hWJMSCs-
secretome IDO Levels
The secretome (conditioned medium) and P5 of
hWJMSCs that had been starved (fee FBS) for 24,
48, and 72 hours were harvested, and the IDO levels
of the hWJMSCs-secretome was calculated. The
IDO level was measured using enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit assay. The IDO
levels of hWJMSCs- secretome are shown Figure 1.
The results indicate that hWJMSCs secrete IDO at
concentrations ranging from 5.86 ng/mL to 13.12
ng/mL or 39.39 ng/mg protein to 82.05 ng/mg (Figure
1). This data was supported with previous study that
MSCs release TGF-β, IL-10, IL-1RA, NO, IDO (van
Buul et al., 2012). MSCs change inflammation from
releasing pro- inflammatory cytokines including IL-1,
IL-6, IL-12, IL- 17, MCP-1, MIP-2, CXCL-1, CXCL-
2, TNF-α, IFN-γ, proteases like MMP-2, MMP-9 and
MMP-12 to an anti- inflammatory status with
releasing anti-inflammatory TGF-β, CCL18, IL-4, IL-
10, PGE2, IDO, NO, inflammation resolving lipoxin
A4 (LXA4) which enable reduce inflammation and
improve tissue repair (Zheng et al., 2015; Mao et al.,
2015). MSCs control excessive inflammation,
improve the microenvironment for tissue repairing
LPS-induced ALI model mice but MSCs of IDO
knockdown (IDO- KD) didn’t increase the
inflammation compared to control group, indicating
that IDO is important in mediating the inflammation
therapeutic role of MSCs (Wang et al., 2018).
IFN-γ, IL-12, and IL-18 are powerful inducers of
IDO expression. However, IDO acts as a negative
feedback loop that can inhibit pro-inflammatory
activation (IFN-γ, IL-12, and IL-18). Thus Wolf et al
(2004) hypothesized that IDO has an anti-
inflammatory role characterized by Th1
overexpression (Wolf et al., 2004; Nikolaus et al.,
2017). This study was supported by previous
research, it has shown that indoleamine 2,3-
dioxygenase (IDO) plays a critical role in the
immunomodulatory ability of human MSCs. This
enzyme catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step of
tryptophan catabolism along the kynurenine
pathway, and IDO and several of its downstream
Figure 1: Dot plot of immunophenotype representative hWJ-MSCs from P5, P10, P15.
Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells-secreted IDO as Candidate of Anti-inflammation Therapy
275
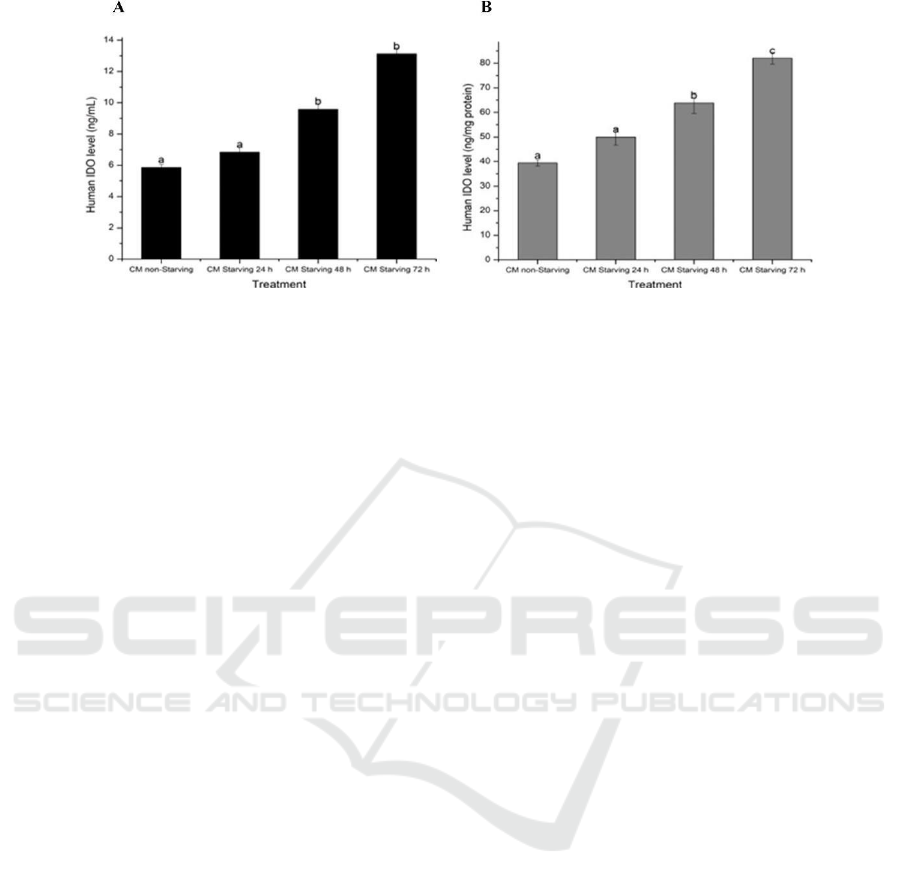
Figure 2: Effect starving time on hWJMSCs IDO levels (A) IDO level (ng/mL); (B) IDO level (ng/mg protein). The data
was presented as mean + standard deviation. Different letters (a,b) show a significant different between different starving
time for IDO level in ng/mL (Figure A). Different letters (a,b,c) show a significant different between different starving time
for IDO level in ng/mg protein (Figure B) based on Dunnett T3 post hoc test (p<0.05).
metabolites, such as kynurenine (KYN) and 3-
hydroxyanthranilic acid, not only inhibit effector T-
cell proliferation but also induce regulatory T-cell
differentiation (Treg). Notably, IDO has been found
to influence inflammation-associated gene
expression, either directly as a signaling factor or
indirectly through the production of bioactive
intermediates such as kynurenic acid via the
kynurenine pathway. MSC has a metabolite of IDO
that controls the TSG-6-mediated anti-inflammatory
therapeutic effects (Wang et al., 2018). The other
study reported that MSCs can improve inflammation
and repair tissue from chronic inflammation
(Rubtsov et al., 2017).
Figure 1 shows that longer deprivation increased
IDO levels, with the longest deprivation resulting in
the highest level of IDO. This data was confirmed
by a previous study, which found that deprivation
did not cause an obvious apoptotic response in
immortalized human MSC (ihMSCs) until~120 h of
deprivation (Nuschke et al., 2016). In response to
starvation stress, cells cause adaptive responses such
as angiogenesis, which promote tissue
reorganization and repair, as well as up-regulation of
multiple cytokines and chemokines, including IL-6
and IL-8 (Püschel et al., 2020).
Starvation for 3 days (see Figure 2) on umbilical
cord MSCs (UCMSCs) increase L-Kynurenine
(correlated IDO activity) 6 µM compared to untreated
UCMSCs 2 µM. IFN-γ, IFN-β, TGF- β increase IDO
activity 27 µM, 10 µM, 3 µM (de Witte et al., 2017).
IDO level increase in human adipose stem cells
(hASCs) in the presence of activated peripheral blood
mononuclear cells (PBMCs) (Rubtsov et al., 2017).
The amnion-derived MSCs (AM- MSCs) and BM-
MSCs induced by Phytohemagglutinin (PHA) and
IFN-γ exhibit that the IDO gene expression increase
compared negative control (AMMSCs, BMMSCs)
(Meesuk et al., 2016).
The AD-MSCs secrete IDO 52.82 IU/mL, IFN-γ
induction on AD-MSCs increase IDO level 81.25-
94.79 IU/mL, higher IFN-γ increase IDO level
(Laksmitawati et al., 2011). hWJMSCs secretes IDO
as an anti- inflammatory (Zheng et al., 2015; Mao et
al., 2015), indicating that hWJMSCs secretion is a
promising therapy candidate for enhancing cytokine
storm in COVID-19.
4
CONCLUSIONS
The hWJMSCs have distinct MSCs until passage 15
that differ in a non-significant way in both positive
and negative lineage surface markers. The IDO is
secreted by hWJMSCs, and longer deprivation
increases IDO levels. However, the longer starvation
periods up to regulate the IDO level in hWJMSCs
secretome are one of method as an alternative
Covid- 19 therapy.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was funded by the Ministry of Research,
Technology and Higher Education of the Republic
of Indonesia and research grant 2021 (Penelitian
Terapan Unggulan Perguruan Tinggi). This research
was also supported by Aretha Medika Utama
Biomolecular and Biomedical Research Center,
Bandung, Indonesia. We also acknowledge the
technical support of Ervi Afifah from Aretha Medika
Utama-Biomolecular and Biomedical Research
Center, Bandung, Indonesia.
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
276

REFERENCES
Abraham, A., Krasnodembskaya, A., 2020. ‘Mesenchymal
stem cell‐derived extracellular vesicles for the
treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome’. Stem
Cells Transl. Med. 9(1), 28-38.
Acosta, M.A.T., Singer, B.D. 2020. ‘Pathogenesis of
COVID-19- induced ARDS: implications for an
ageing population’. Eur. Respir. J. 56(3), 2002049.
Azmi, N.U., Puteri, M.U., Lukmanto, D. 2020. ‘Cytokine
storm in COVID-19: an overview, mechanism,
treatment strategies, and stem cell therapy
perspective’. Pharm. Sci. Res. 7(4), 1- 11.
Baruah, V., & Bose, S. 2020. ‘Immunoinformatics‐aided
identification of T cell and B cell epitopes in the
surface glycoprotein of 2019‐nCoV’. Journal of
medical virology, 92(5), 495-500.
Behrens, E.M., Koretzky, G.A. 2017. ‘Review: Cytokine
storm syndrome: Looking toward the precision
medicine era’. Arthritis Rheumatol. 69(6), 1135-1143.
Berglund, A.K., Fisher, M.B., Cameron, K.A., Poole, E.J.,
Schnabel, L.V. 2017. ‘Transforming growth factor-β2
downregulates major histocompatibility complex
(MHC) I and MHC II surface expression on equine
bone marrow- derived mesenchymal stem cells
without altering other phenotypic cell surface
markers’. Front. Vet. Sci. 4, 84.
Bernardo, M.E., Fibbe, W.E. (2013). ‘Mesenchymal
stromal cells: sensors and switchers of inflammation’.
Cell Stem Cell. 13(4), 392-402.
Bongso, A., Fong, C.Y. 2013. ‘The therapeutic potential,
challenges and future clinical directions of stem cells
from the Wharton’s jelly of the human umbilical
cord’. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 9(2), 226-240.
Canham, M.A., Campbell, J.D., Mountford, J.C. 2020.
T’he use of mesenchymal stromal cells in the
treatment of coronavirus disease 2019’. J. Transl.
Med. 18(1), 1-15.
Çetı̇ n, I., Topçul, M. 2020. ‘Can mesenchymal stem cells
be used to treat COVID-19-induced pneumonia?’.
Biomed. Rep. 13(6), 1-1.
Chen, G., Wu, D.I., Guo, W., Cao, Y., Huang, D., Wang,
H. 2020. ‘Clinical and immunological features of
severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019’. J.
Clin. Invest. 130(5), 2620-2629.
De Witte, S.F.H., Merino, A.M., Franquesa, M., Strini, T.,
van Zoggel, J.A.A., Korevaar, S.S. 2017. ‘Cytokine
treatment optimises the immunotherapeutic effects of
umbilical cord- derived MSC for treatment of
inflammatory liver disease’. Stem Cell Res. Ther.
8(140), 1- 12.
Durand, N., Mallea, J., Zubair, A.C. (2020). ‘Insights into
the use of mesenchymal stem cells in COVID-19
mediated acute respiratory failure’. NPJ Regen. Med.
5(1), 1-9.
Engin, A.B., Engin, E.D., Engin, A. 2020. ‘The effect of
environmental pollution on immune evasion
checkpoints of SARS-CoV- 2’. Environ. Toxicol.
Pharmacol. 81(2020), 103520.
Ferro, F., Spelat, R., Shaw, G., Duffy, N., Islam, M. N.,
O'Shea, P.M., et al. 2019. ‘Survival/adaptation of bone
marrow‐derived mesenchymal stem cells after long‐
term starvation through selective processes’. Stem
Cells. 37(6), 813-827.
Garzon, I., Chato-Astrain, J., Campos, F., Fernandez-
Valades, R., Sanchez-Montesinos, I., Campos, A., et
al. 2020. ‘Expanded differentiation capability of
human Wharton's jelly stem cells toward pluripotency:
a systematic review’. Tissue Eng. Part B: Rev. 26(4),
301- 312.
Gibson, P.G., Qin, L., Puah, S. 2020. ‘COVID-19 ARDS:
clinical features and differences to ‘usual’ pre COVID
ARDS’. Med. J. Australia. 213(2), 54-56.
Glenn, JD., Whartenby, K.A. 2014. ‘Mesenchymal stem
cells: Emerging mechanisms of immunomodulation
and therapy’. World J. Stem Cells. 6(5), 526–539.
Golchin, A., Seyedjafari, E., Ardeshirylajimi, A. 2020.
‘Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for COVID-19:
present or future’. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 16(3), 427-433.
Golchin, A., Farahany, T.Z. 2019. ‘Biological products:
cellular therapy and FDA approved products’. Stem
Cell Rev. Rep. 15(2), 166- 175.
Golchin, A., Farahany, T.Z., Khojasteh, A., Soleimanifar,
F., Ardeshirylajimi, A. 2019. ‘The clinical trials of
mesenchymal stem cell therapy in skin diseases: an
update and concise review’. Curr. Stem Cell Res.
Ther. 14(1), 22- 33.
Huang, C., Wang, Y., Li, X., Ren, L., Zhao, J., Hu, Y., et
al. 2020. ‘Clinical features of patients infected with
2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China’. Lancet.
395(10223), 497-506.
Laksmitawati, D.E., Sardjono, C.T., Pawitan, J.A. Sadikin,
M., Sandra, F. 2010. ‘Secretion of Indoleamine 2,3-
dioxygenase, an immunomodulatory substance, by
adipose- derived mesenchymal stem cell’. IJCC. 1(2),
92- 98.
Lee, S.M., Park, H.Y., Suh, Y-S., Yoon, E.H., Kim, J.,
Jang, W.H. 2017. ‘Inhibition of acute lethal pulmonary
inflammation by the IDO–AhR pathway’. Proc. Natl.
Acad. Sci. USA. 144(29), E5881–E5890.
Mao, Y.X., Xu, J.F., Seeley, EJ., Tang, X. D., Xu, L.L.,
Zhu, Y.G., et al. 2015. ‘Adipose tissue‐ derived
mesenchymal stem cells attenuate pulmonary infection
caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa via inhibiting
overproduction of prostaglandin E2’. Stem Cells.
33(7), 2331-2342.
Marino, L., Castaldi, M.A., Rosamilio, R., Ragni, E.,
Vitolo, R., Fulgione, C., et al. 2019. ‘Mesenchymal
stem cells from the Wharton’s jelly of the human
umbilical cord: biological properties and therapeutic
potential’. Int. J. Stem Cells. 12(2), 218-226.
Moya, A., Larochette, N., Paquet, J., Deschepper, M.,
Bensidhoum, M., Izzo, V., et al. 2017. ‘Quiescence
preconditioned human multipotent stromal cells adopt
a metabolic profile favorable for enhanced survival
under ischemia’. Stem Cells. 35(1), 181-196.
Meesuk, L., Tantrawatpan, C., Kheolamai, P.,
Manochantr, S. 2016. ‘The immunosuppressive
Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells-secreted IDO as Candidate of Anti-inflammation Therapy
277

capacity of human mesenchymal stromal cells’.
Biochem. Biophy. Rep. 8(2016), 34–40.
Nikolaus, S., Schulte, B., Al-Massad, N., Thieme, F.,
Schulte, DM., Bethge, J., et al. 2017. Increased
Tryptophan Metabolism Is Associated With Activity
of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterology,
153(6): 1504-1516.
Nuschke, A., Rodrigues, M., Wells, A.W., Sylakowski, K.,
Wells, A. 2016. ‘Mesenchymal stem cells/multipotent
stromal cells (MSCs) are glycolytic and thus glucoseis
a limiting factor of in vitro models of MSC
starvation’. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 7(1), 1-9.
Püschel, F., Favaro, F., Redondo-Pedraza, J., Lucendo, E.,
Iurlaro, R., Marchetti, S., et al. 2020. ‘Starvation and
antimetabolic therapy promote cytokine release and
recruitment of immune cells’. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
USA. 117(18), 9932-9941.
Rubtsov, Y., Goryunov, K., Romanov, A., Suzdaltseva,
Y., Sharonov, G., Tkachuk, V. 2017. ‘Molecular
Mechanisms of Immunomodulation Properties of
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: A New Insight into the
Role of ICAM-1’. Stem Cells Int. 2017(6516854), 1-
15.
Tamura, M., Kawabata, A., Ohta, N., Uppalapati, L., G
Becker, K., Troyer, D. 2011. Wharton's jelly stem
cells as agents for cancer therapy. Open Tissue Eng
Regen Med J. 4(1), 39-47.
Tay, M.Z., Poh, C.M., Rénia, L., MacAry, P.A., Ng, L.F.
2020. ‘The trinity of COVID-19: immunity,
inflammation and intervention’. Nat Rev Immunol.
20(6), 363- 374.
Van Buul, G.M., Villafuertes, E., Bos, P.K., Waarsing,
J.H., Kops, N., Narcisi, R., et al. 2012. ‘Mesenchymal
stem cells secrete factors that inhibit inflammatory
processes in short-term osteoarthritic synovium and
cartilage explant culture’. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 20(10),
1186-1196.
Wang, G., Cao, K., Liu, K., Xue, Y., Roberts, A.I., Li, F.,
et al. 2018. ‘Kynurenic acid, an IDO metabolite,
controls TSG-6- mediated immunosuppression of
human mesenchymal stem cells’. Cell Death Different.
25(7), 1209–1223.
Widowati, W., Wijaya, L., Bachtiar, I., Gunanegara, R.F.,
Sugeng, S.U., Irawan, Y.A., et al. 2014. ‘Effect of
oxygen tension on proliferation and characteristics of
Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells’.
Biomarkers Genomic Med. 6(1), 43- 48.
Widowati, W., Wijaya, L., Murti, H., Widyastuti, H.,
Agustina, D., Laksmitawati, D. R., et al. 2015.
‘Conditioned medium from normoxia (WJMSCs-
norCM) and hypoxia-treated WJMSCs (WJMSCs-
hypoCM) in inhibiting cancer cell proliferation’.
Biomark. Genom. Med. 7(1), 8-17.
Widowati, W., Gunanegara, R.F., Rizal, R., Widodo,
W.S., Amalia, A., Wibowo, S.H.B., et al. 2019.
‘Comparative analysis of Wharton’s jelly
mesenchymal stem cell (WJ- MSCs) isolated using
explant and enzymatic methods’. J. Phys. Conf. Ser.
1374(1), 012024.
Widowati, W., Noverina, R., Ayuningtyas, W.,
Kurniawan, D., Kusuma, H.S.W., Arumwardana, S., et
al. 2019. ‘Proliferation, characterization and
differentiation potency of adipose tissue- derived
mesenchymal stem cells (AT-MSCs) cultured in fresh
frozen and non-fresh frozen plasma’. Int. J. Mol. Cell
Med. 8(4), 283-293.
Widowati, W., Widyastuti, H., Murti, H., Laksmitawati,
D.R., Kusuma, H.S.W., Rizal, R., et al. 2017.
‘Interleukins and VEGF secretome of human
wharton's Jelly mesenchymal stem cells-conditioned
medium (hWJMSCs-CM) in different passages and
oxygen tensions’. Biosci. Res. 14(4), 776-787.
Williams, A.E., Chambers, R.C. 2014. ‘The mercurial
nature of neutrophils: still an enigma in ARDS?’. Am
J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 306(3), L217-
L230.
Wolf, AM., Wolf, D., Rumpold, H., Moschen, AR., Kaser,
A., Obrist, P., et al. 2004. Overexpression of
indoleamine 2,3- dioxygenase in human inflammatory
bowel disease. J. Clin. Immunol. 113, 47-55.
Xu, Z., Shi, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Huang, L., Zhang, C.,
et al. 2020. ‘Pathological findings of COVID-19
associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome’.
Lancet Respir. Med. 8(4), 420-422.
Ye, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Huang, Z., Song, B. 2020.
‘Chest CT manifestations of new coronavirus disease
2019 (COVID-19): a pictorial review’. Eur. Radiol.
30(8), 4381-4389.
Zheng, G., Ge, M., Qiu, G., Shu, Q., Xu, J. 2015.
‘Mesenchymal stromal cells affect disease outcomes
via macrophage polarization’. Stem Cells Int.
2015(989473), 1-11.
Zhou, F., Yu, T., Du, R., Fan, G., Liu, Y., Liu, Z., et al.
2020. ‘Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of
adult inpatients with COVID- 19 in Wuhan, China: a
retrospective cohort study’. Lancet. 395(10229), 1054-
1062.
Zhu, N., Zhang, D., Wang, W., Li, X., Yang, B., Song, J.,
et al. 2020. ‘A novel coronavirus from patients with
pneumonia in China, 2019’. N. Engl. J. Med.
Massachusetts Med. Soc. 382(8), 727-733.
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
278
