
Bioactivity of Soybean Tempeh against Diarrhea Associated Pathogen
Is More Correlated with the Number of Total Bacteria than Specific
Major Bacterial Phylum
T. E. Pramudito
a
, E. G. A. Putri, E. Paluphi, G. Florencia, M. R. Gunawan, M. P. Pratiwi
and Y. Yogiara
b
Faculty of Biotechnology, Atma Jaya Catholic University of Indonesia, Jl. Raya Cisauk Lapan No.70,
Tangerang, Banten 15345, Indonesia
monarispania@gmail.com, melatipratiwi9@gmail.com, yogiara@atmajaya.ac.id
Keywords: Soybean Tempeh, ETEC, Anti-diarrhea, RT-PCR, Yeast Agglutination Assay.
Abstract: Soybean tempeh can reduce the severity of diarrhoea through the inhibition of enterotoxigenic Escherichia
coli (ETEC) adhesion to intestinal cells. This bioactivity is due to the presence of bioactive oligosaccharides
derived from degradation of soybean matrix by fungi. Tempeh also contains other microorganisms such as
bacteria and there has been no report whether bacteria can also influence the anti-adhesion bioactivity of
tempeh extract against ETEC. In this research, we quantified bacterial population in tempeh samples using
real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method and measured the anti-adhesion bioactivity against
ETEC of the extract using yeast agglutination assay. Data from both analyses were compared to see if there
is any correlation between the two variables. Bacterial quantification with RT-PCR was focused on the
enumeration of total bacteria and two specific major bacterial phyla in tempeh: Firmicutes and γ-
Proteobacteria. There was a significantly strong positive correlation (R = 0.733) between total number of
bacteria with anti-adhesion bioactivity of tempeh. However, there was no strong correlation between the
number of Firmicutes and γ-Proteobacteria with anti-adhesion bioactivity. Our finding indicates that the anti-
adhesion bioactivity of tempeh tends to increase following the abundance of bacteria but is not significantly
affected by specific major bacterial phylum.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tempeh is a traditional Indonesian food made from
the fermentation of legumes, most commonly
soybeans, by the mold Rhizopus oligosporus (Nout &
Kiers, 2005). At the end of fermentation process,
fungal mycelia will bind the soybeans together
resulting in a firm and compact cake. The firm texture
of the end product is due to the activity of various
fungal enzymes that break down the soy matrix thus
increasing the digestibility and nutritional value of the
substrate (Nout & Kiers, 2005). One of the products
derived from the fungal enzymatic activity during
fermentation is bioactive oligosaccharides that have
been reported to have anti-diarrheal bioactivity (Kiers
et al., 2002). This bioactivity is due to the capability
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8547-267X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4725-3614
of bioactive oligosaccharides in binding with the
fimbriae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC)
thus inhibiting adhesion of the pathogenic bacteria to
intestinal cells (Roubos-van den Hil et al., 2010). This
results in the lower incidence of diarrhea since the
pathogenicity of ETEC is determined by its capability
of adhering to the intestines to produce enterotoxins
(Nataro & Kaper, 1998).
Other microorganisms other than fungi, such as
bacteria, are also present in tempeh (Seumahu et al.,
2013). Bacteria in particular plays an important role
in tempeh production for the acidification of soybeans
to inhibit the growth of spoilage microorganism
(Nurdini et al., 2015). Characteristics and nutritional
content of tempeh can also be influenced by bacteria
such as bitterness in tempeh that is correlated with
320
Pramudito, T., Putri, E., Paluphi, E., Florencia, G., Gunawan, M., Pratiwi, M. and Yogiara, Y.
Bioactivity of Soybean Tempeh against Diarrhea Associated Pathogen Is More Correlated with the Number of Total Bacteria than Specific Major Bacterial Phylum.
DOI: 10.5220/0010753500003113
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering and Science (ICE-TES 2021), pages 320-327
ISBN: 978-989-758-601-9
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
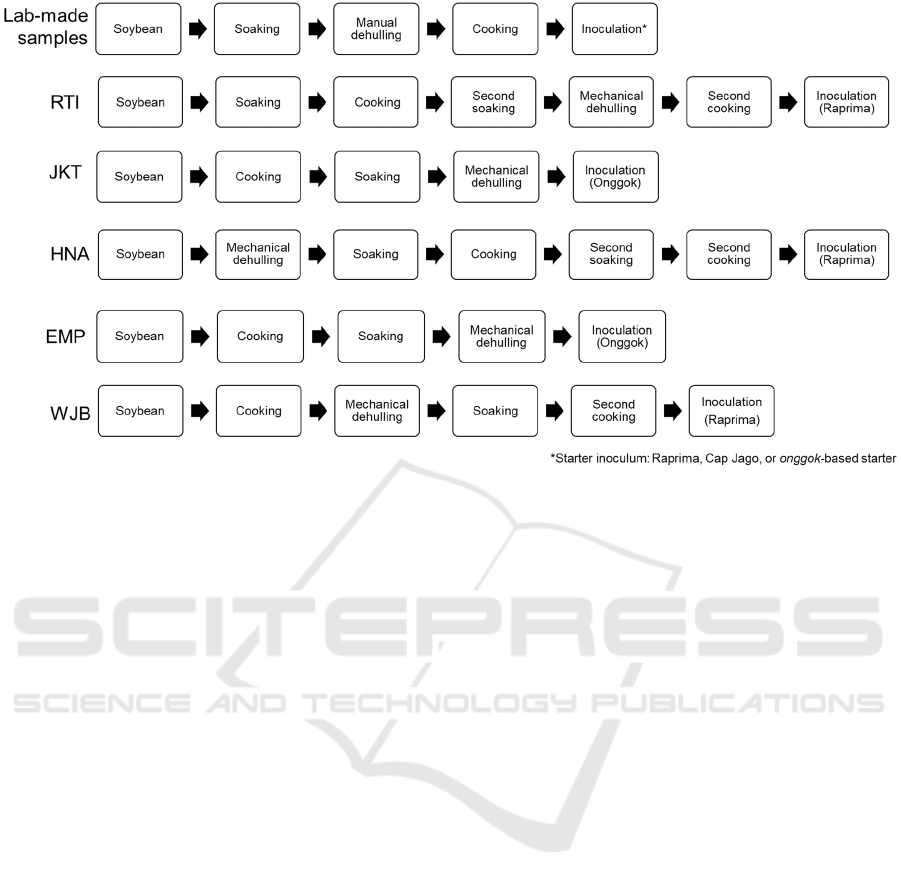
Figure 1: Major steps involved in the production process of the samples used in this experiment.
proteolytic bacteria and vitamin B12 in the product
that is produced by bacteria from the genus of
Klebsiella (Keuth & Bisping, 1994). Considering the
abundance of bacteria in tempeh, a question arises
whether or not these bacteria can influence the anti-
diarrheal potential in tempeh.
The bacterial population in tempeh is dominated
by the phylum Firmicutes (Radita et al., 2018).
Roubos-van den Hil et al. (2010) demonstrated that
fermentation of soybeans by Bacillus sp. can also
result in anti-adhesion bioactivity against ETEC but
the same activity was not observed in soybeans
inoculate with Lactobacillus sp.. However, most
reported experiments so far are focused on the
fermentation of soybean by single bacterial or fungal
culture. It is possible that in real life tempeh
fermentation, these microorganisms might support or
hinder one another during the breakdown of soy
matrix polysaccharides thus influencing the level of
anti-adhesion bioactivity. For example, bacteria could
produce a polysaccharide-degrading enzyme
allowing the substrate to be more accessible for
further degradation by fungi. The opposite could also
take place, that bacteria might consume the bioactive
oligosaccharides thus decreasing bioactivity.
In this research, we focused on the correlation
between anti-adhesion bioactivity against ETEC from
tempeh extract with the population of all bacteria and
two specific phyla: Firmicutes and γ-Proteobacteria.
We decided to focus on those two phyla because both
are reported to be the two major phyla found in
tempeh (Radita et al., 2017). Firmicutes in particular
can produce bacterial exopolysaccharides (EPS) that
can bind to ETEC fimbriae (Wang et al., 2010). We
measured the anti-adhesion bioactivity of tempeh
extract using yeast agglutination assay, which
Saccharomyces cerevisiae act as a model organism
for eukaryotic cells. Real-time polymerase chain
reaction (RT-PCR) was used as a method for bacterial
quantification. Data from both experiments were
statistically analyzed to determine the possibility of
correlation between anti-adhesion bioactivity with the
abundance of all bacteria or certain specific phylum.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials
Tempeh samples used in this experiment consisted of
five commercial tempeh and three tempeh made in
laboratory condition with a variation of starter
culture. All tempeh samples were made from the
same type of yellow-seeded soybeans. Commercial
samples were purchased from tempeh producers in
Bogor (EMP, WJB, and RTI), Jakarta (JKT) and
Surabaya (HNA). EMP, WJB, and JKT were
produced by home-scale industries with the
uncontrolled condition during the production process
while RTI and HNA were produced by standardized
industry with proper environmental control. Tempeh
samples made in the laboratory were prepared with
three different starters: the commercial starters
Bioactivity of Soybean Tempeh against Diarrhea Associated Pathogen Is More Correlated with the Number of Total Bacteria than Specific
Major Bacterial Phylum
321

Raprima (RP; PT. Aneka Fermentasi Industri,
Bandung, Indonesia), Cap Jago (JG; UD. Jaya Mulya,
Kediri, Indonesia) and cassava-based onggok starter
(OG; acquired from a traditional producer in Cisauk,
Banten, Indonesia). Full-fat yellow-seeded elongated
soybeans for tempeh fermentation were purchased
from Pasar Modern Intermoda BSD (Tangerang,
West Java). All tempeh samples were transported and
kept at 4
o
C prior to analysis. Figure 1 details the
production steps of each sample.
Standard curves for RT-PCR were generated
using pure cultures of Escherichia coli,
Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella enterica
ATCC 51741 grown overnight in Luria broth at 37
o
C. S. cerevisiae and ETEC cultures were used for
yeast agglutination assay and obtained from the
Faculty of Biotechnology, Atma Jaya Catholic
University of Indonesia (Cisauk, Indonesia). D-(+)-
mannose (Sigma Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) was
used as a positive control for yeast agglutination
assay.
2.2 Tempeh Fermentation
Lab-made tempeh with starter culture variation were
prepared in the Laboratory of Microbiology, Atma
Jaya Catholic University of Indonesia following the
protocol detailed by Nout and Kiers (2005) with
modifications. Full-fat yellow-seeded elongated
soybeans were soaked overnight in distilled water at
room temperature. Following overnight soaking, the
soybeans were boiled and dehulled. The soybeans
were cooled, dried, and divided to three experimental
groups, each group weighing the same amount. Each
group was mixed thoroughly with a tempeh starter
(0.2 % (w/w) of soybeans) and packed in a perforated
plastic bag followed with incubated at 30
o
C for 48 h.
The final products were immediately used for the
bioactive oligosaccharide and bacterial DNA
extraction.
2.3 Extraction of Bioactive
Oligosaccharides
Extraction of bioactive oligosaccharides from tempeh
was based on the method described by Roubos-van
den Hil et al. (2010) with modifications. Tempeh
samples were lyophilized for 96 h and homogenized
to obtain tempeh powder. About 1 L of distilled water
was added to 75 g tempeh powder and the suspension
was stirred 1 h at room temperature. The pH of the
suspension was kept at 8.0 through the addition of
NaOH 2 M for every 30 min. The suspension was
centrifuged (30 min, 10000× g, 20
o
C) and filtered to
obtain crude extract. Following lyophilization for 96
h, the extract was stored at 4
o
C before analysis.
2.4 Extraction of Bacterial DNA
Total bacterial DNAs from tempeh samples were
extracted based on the method described by Seumahu
et al. (2013) with modifications. Phosphate buffer
saline (PBS) pH 7.4 (150 mL) was added to 50 g of
diced tempeh. The mixture was homogenized and the
suspension was centrifuged at 1000× g for 10 min.
The collected supernatant was centrifuged again at
10000× g for 10 min. The pellets were collected for
bacterial DNA extraction using ZymoBIOMICS™
DNA Miniprep Kit (Zymo Research, Orange, CA,
USA) and the DNA isolate was kept at -20
o
C.
2.5 Measurement of Anti-adhesion
Bioactivity against ETEC
Anti-adhesion bioactivity of tempeh extract against
ETEC adhesion to eukaryotic cells was measured
using yeast agglutination assay based on the method
described by Mirelman et al. (1980). S. cerevisiae was
grown in potato dextrose broth (HiMedia, India) at 37
o
C for overnight with shaking. ETEC was grown
overnight without shaking in Luria Bertani broth
(HiMedia) at 37
o
C. Both cell cultures were
centrifuged at 3000× g for 5 min at 4
o
C and the
collected pellets were suspended in an equal volume
of PBS pH 7.4. The cells were washed twice in PBS
pH 7.4 and the densities of yeast and ETEC
suspensions were adjusted to OD
600
of 1.0 and 0.5,
respectively.
Tempeh extract was suspended in PBS pH 7.4 to
the concentration of 2 % (w/v) and the suspension
was vortexed for 30 min. The suspension was
centrifuged at 10000× g for 10 min and the
supernatant was collected. Mannose 2 % (w/v) in PBS
pH 7.4 was used as a positive control. Tempeh extract
was mixed with ETEC suspension with the ratio of
1:1 in a 96-wells microtiter plate. The mixture was
incubated at room temperature with orbital shaking
for 10 min. Afterwards, yeast suspension at the same
volume was added into the mixture and followed with
incubation for 30 min with orbital shaking. A mixture
of an equal volume of yeast, ETEC, and PBS pH 7.4
was used as a negative control. The suspension was
transferred onto concave object glass and covered
with cover glass. Cell agglutinates were observed
using a light microscope (Nikon Eclipse E100;
Tokyo, Japan) at 100× magnification. The number of
yeast agglutinates was enumerated using the program
DinoCapture 2.0 (Dino-Lite, Torrance, CA, USA).
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
322

The number of agglutinates was determined as the
sum of agglutinates observed from seven location
points and the measurement was done in triplicates.
Anti-adhesion bioactivity of tempeh extract against
ETEC adhesion to yeast cells was expressed as the
percent of adhesion inhibition which was calculated
with the following formula (1).
% 𝑎𝑑ℎ𝑒𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑖𝑛ℎ𝑖𝑏𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 = 100% −
× 100% … (1)
Whereas:
X
̄
N = average number of agglutinates in sample
X
̄
C = average number of agglutinates in negative
control
2.6 Bacterial Quantification with
RT-PCR
Quantification of total bacteria, Firmicutes, and γ-
Proteobacteria was carried out using RT-PCR based
on 16s rDNA that are specific to each targeted
bacterial group. Bacterial genomes of E. coli, S.
aureus, and S. enterica ATCC 51741 were extracted
using Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit
(Promega, Madison, WI, USA) to generate standard
curves for total bacteria, Firmicutes, and γ-
Proteobacteria, respectively. DNA isolates from pure
bacterial culture were amplified based on the method
described by Soka et al. (2014) and the amplified
products were diluted tenfold to seven standard
concentrations between 10
2
– 10
10
DNA copy/mL.
Samples and standards were each added into PCR
mix comprised of 10 µL Solg™ Real-Time PCR
Smart Mix (SolGent, Daejeon, South Korea), 1 µL
DNA template, 1 µL of each primer (10 pmol.µL
-1
)
(Table 1) and NFW for the total volume of 20 µL. The
primers were designed specifically to amplify the
regions of 16s rDNA that are specific to each of the
bacterial groups used in this experiment. The PCR
reaction conditions were as follow: 94
o
C for 5 min;
40 cycles of 94
o
C for 20 sec, 55 – 57
o
C (Table 1) for
20 sec and 72
o
C for 50 sec; and 72
o
C for 15 sec.
Each sample was amplified in triplicate. RT-PCR
reading of the standards showed linearity between C
t
value and log of DNA copy number (R
2
> 0.99). The
concentration of a certain bacterial group in a sample
was determined based on the C
t
value and regression
equation generated from the standard curve. All of the
measurements were done in triplicates.
2.7 Statistical Analysis
The data were statistically analyzed using SPSS
Statistics (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
The correlation between bacterial numbers based on
RT-PCR and anti-adhesion bioactivity of tempeh
extract was determined by calculating the P-value and
Pearson correlation coefficient (R-value) of the two
variables. Correlation was considered significant at P
< 0.01 and strong at R > 0.70.
Table 1. Primers for the amplification of group-specific 16s rRNA gene.
Target bacterial
group
Primer Sequence (5’-3’) Size (bp) Annealing
temperature
(°C)
Citation
Universal bacteria Eub338F ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG 220 57 (Soka et al.,
2014)
Eub518R ATTACCGCGGCTGCTGG
Firmicutes Firm934F GGAGTATGTGGTTTAATTCGAAGCA 126 56.5 (Guo et al.,
2008)
Firm1060R AGCTGACGACAACCATGCAC
γ-Proteobacteria 1080γF TCGTCAGCTCGTGTYGTGA 122 55 (Karamipour
et al., 2016)
γ1202R CGTAAGGGCCATGATG
Bioactivity of Soybean Tempeh against Diarrhea Associated Pathogen Is More Correlated with the Number of Total Bacteria than Specific
Major Bacterial Phylum
323
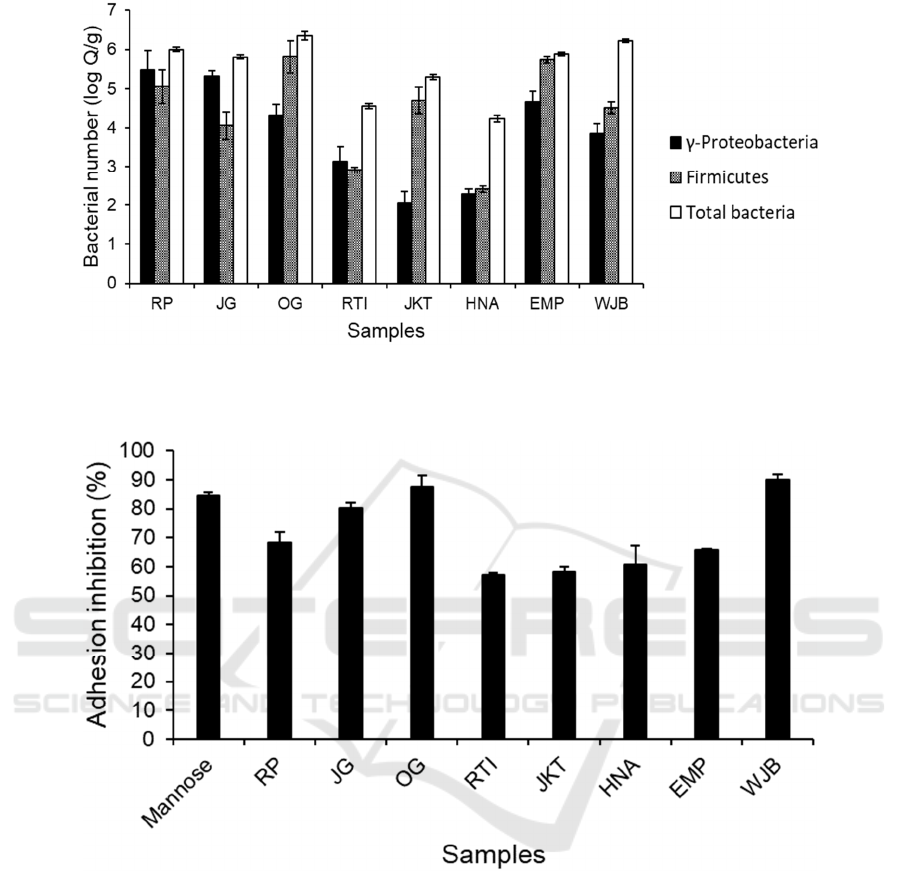
Figure 2: Anti-adhesion bioactivity of 2 % (w/v) tempeh extract against ETEC adhesion to S. cerevisiae. Mannose (2 % (w/v))
was used as a positive control. Bars represent the mean of % adhesion inhibition based on triplicates. Error bars represent
standard errors.
Figure 3: Bacterial amount in tempeh samples based on RT-PCR analysis with primers that amplified regions of 16s rDNA
that are specific to γ-Proteobacteria, Firmicutes and total bacteria. Bars represent mean values, expressed as log copy number
per gram total weight of sample (log Q/g), from three replicates of measurement. Error bars represent the standard error of
mean.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Tempeh Samples Showed a
Varying Level of Bacterial
Abundance and Anti-adhesion
Bioactivity
Yeast agglutination assay was used to determine the
bioactivity of tempeh extract in inhibiting ETEC
adhesion to eukaryotic cells. The yeast S. cerevisiae
acted as a model organism for eukaryotic cells which
will form agglutinates in the presence of ETEC. We
quantified the number of agglutinates under a
microscope with 100× magnification and compared
the number of agglutinates between yeast and ETEC
suspension with and without the addition of tempeh
extract. Mannose was used as a positive control due
to its capability to bind to ETEC fimbriae thus
inhibiting yeast agglutination. Yeast and ETEC
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
324

suspension treated with mannose 2% (w/v) resulted in
84.66 ± 1.14 % reduction of agglutinates compared to
untreated suspension. Figure 2 showed that tempeh
samples resulted in varying levels of adhesion
inhibition ranging from 57 to almost 90 %. Tempeh
fermented in laboratory condition (RP, JG, and OG)
tended to have anti-adhesion bioactivity compared to
commercial tempeh (RTI, JKT, HNA, and EMP)
except for WJB. Both extracts from OG and WJB
showed anti-adhesion bioactivity higher than
mannose control at 87.52 ± 4.04 % and 89.95 ± 1.84
% respectively. Overall, this varying level of anti-
adhesion bioactivity was ideal for this experiment as
it allowed us to plot the data against bacterial number
from the next part of this experiment.
Bacterial number in tempeh samples was
determined using RT-PCR to measure the number of
total bacteria and the specific phyla of Firmicutes and
γ-Proteobacteria. Figure 3 showed that the bacterial
numbers in tempeh were also varied from one sample
to another. There was less variation of total bacteria
between tempeh made in the laboratory with different
starter culture indicating that starter culture did not
play a major role in affecting total bacterial number.
Despite the lack of significant variation of total
bacterial number in lab-made tempeh, there was a
variation of bacterial profile composition with RP and
JG containing more γ-Proteobacteria compared to
OG. The bacterial profile in most samples was
dominated by the phylum Firmicutes with the
exception of RP, JG, and JKT that were dominated by
γ-Proteobacteria. RTI and HNA contained the fewest
number of bacteria at 4.55 ± 0.06 and 4.23 ± 0.08 log
Q/g respectively. Both RTI and HNA are commercial
samples that were produced using a standardized
industrial method in a hygienic condition.
3.2 Tempeh Samples Showed a
Varying Level of Bacterial
Abundance and Anti-adhesion
Bioactivity
We plotted the anti-adhesion bioactivity against
ETEC measured using yeast agglutination assay with
the bacterial number in tempeh determined by RT-
PCR. Figure 4A showed that there was a strong
correlation between anti-adhesion bioactivity with a
total bacterial number in tempeh with the R-value of
0.733. The correlation was very significant at P <
0.01. This indicated that the anti-adhesion bioactivity
of tempeh against ETEC tends to increase following
an increase in the number of total bacteria in the
product. The correlation between anti-adhesion
bioactivity and the quantity of both Firmicutes and γ-
Proteobacteria was also significant at P < 0.05.
However, the correlation of both phyla with anti-
adhesion bioactivity was weak with the R-value of
0.446 and 0.488 for Firmicutes and γ-Proteobacteria
respectively (Figure 4B and 4C). Our finding
indicated that the influence of major bacterial phyla
in tempeh on its anti-adhesion bioactivity against
ETEC was minimal compared to the influence from
bacterial community as a whole.
3.3 General Discussion
The anti-adhesion bioactivity of tempeh extract
against ETEC adhesion to eukaryotic cells arises from
the degradation of soy matrix polysaccharide into
bioactive oligosaccharides (Roubos-van den Hil et
al., 2010). This bioactivity is not exclusive to soybean
fermentation by fungal culture (Roubos-van den Hil
et al., 2010). Bacterial fermentation of soybeans
resulted in similar anti-adhesion bioactivity against
ETEC. We found the indication that bacterial role in
the release of bioactive oligosaccharides is also
present in tempeh fermentation by fungal inoculum.
In this experiment, we focused on two specific
phyla: Firmicutes and γ-Proteobacteria. Both phyla
are the major bacterial groups reported in commercial
tempeh that are available in Indonesia (Radita et al.,
2017). We hypothesized there could be two
mechanisms on how the bacterial population can
contribute to the increase of anti-adhesion bioactivity
in tempeh. First, bacteria could break down soy
matrix polysaccharide thus making it more accessible
for further breakdown by fungi or vice versa. Second,
the bacteria produce bacterial exopolysaccharides
(EPS) that can bind to ETEC cells.
It has been reported that most lactic acid bacteria
(LAB) are capable of producing bioactive EPS
(Welman & Maddox, 2003) and these LAB are also
known to be present in tempeh (Radita et al., 2018).
If the latter assumption was true, there should be a
correlation between the Firmicutes population with
anti-adhesion bioactivity. However, the absence of
correlation seemed to indicate that bacterial role on
anti-adhesion bioactivity was more likely due to the
breakdown of soy matrix polysaccharide. We would
like to mention that our finding did not negate the
possibility of EPS or other bacterial secondary
metabolites playing a role on anti-adhesion
bioactivity in tempeh. This research was only focused
on the two major phyla in tempeh and it is possible
that other minor phyla could be more strongly
correlated to anti-adhesion bioactivity. Extraction and
quantification of EPS could also provide more
definitive information on its bioactive potential.
Bioactivity of Soybean Tempeh against Diarrhea Associated Pathogen Is More Correlated with the Number of Total Bacteria than Specific
Major Bacterial Phylum
325
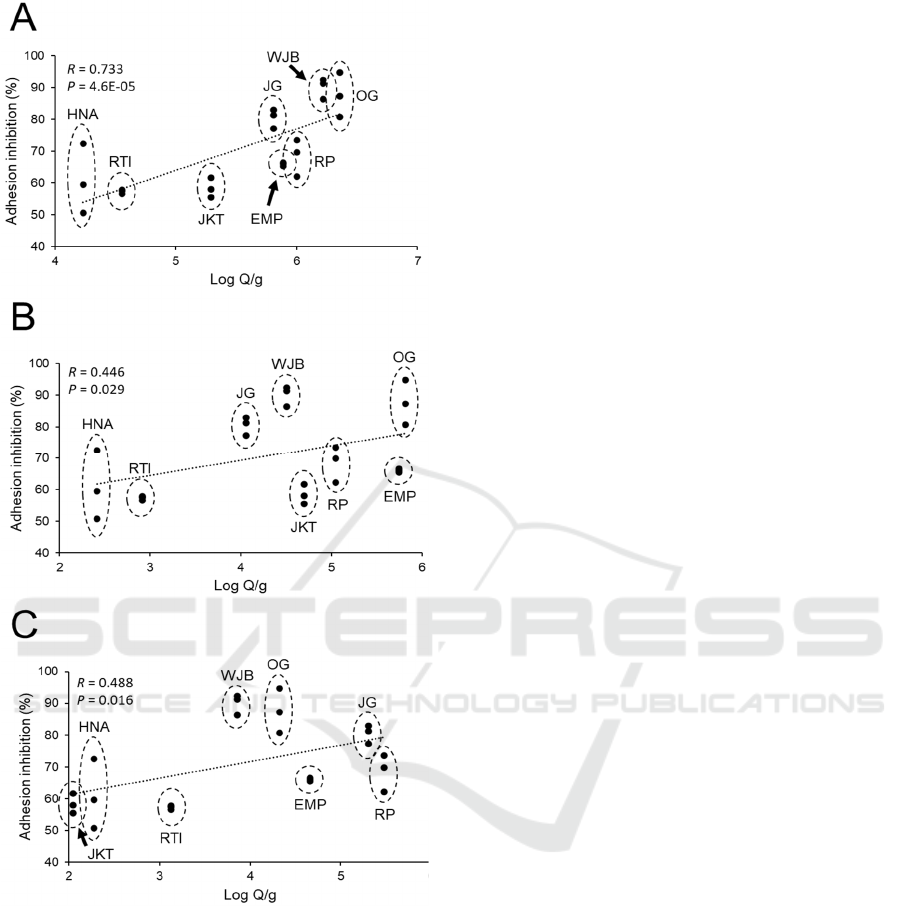
Figure 4: Correlation between anti-adhesion bioactivity of
tempeh extract at 2 % (w/v) (expressed as % adhesion
inhibition) and bacterial number in tempeh based RT-PCR
analysis with primers that amplified regions of 16s rDNA
that are specific to A) total bacteria, B) Firmicutes and C)
γ-Proteobacteria. Regression line is represented by a dotted
line. Correlation between anti-adhesion bioactivity and the
number of each bacterial group was expressed as P-value to
indicate correlation strength and R-value to indicate
correlation significance.
Although we found that total bacterial number is
more strongly correlated to anti-adhesion bioactivity,
the role of the bacterial profile could still not be
crossed out. Figure 2 showed that there was a stark
difference in the anti-adhesion bioactivity of tempeh
extract from three lab-made tempeh against ETEC.
The three samples were produced from the same
batch of soybeans and through the same line of
preparation with the only difference was after they
were inoculated with different starter and incubated
separately at the same temperature. It has been
reported that variation in starter culture does not
affect the total bacterial number in tempeh
(Pramudito et al., 2021; Radita et al., 2017). Figure 3
showed that the number of total bacteria based on RT-
PCR was not too varied especially in the case of RP
and JG.
The contrast between the variation of anti-
adhesion bioactivity and total bacterial number
among the three lab-made samples could imply that
bacterial composition might still play a role in anti-
adhesion bioactivity. A previous report mentioned
that although variation in tempeh starter did not affect
the total bacterial population, it could still influence
bacterial composition in the final product (Pramudito
et al., 2021). JG was made with the commercial starter
‘Cap Jago’ that has been reported to result in a lower
rate of fungal mycelium growth thus allowing
spoilage bacteria, mainly from the phylum γ-
Proteobacteria, to grow uninhibited in the early stage
of fermentation (Pramudito et al., 2021). The rapid
growth of γ-Proteobacteria during the fermentation
process could lead to more degradation of soy matrix
polysaccharides. Bacteria from the phylum γ-
Proteobacteria such as the genus Pseudomonas is
known to be capable of producing polysaccharide-
degrading enzymes such as glycoside hydrolase
(Edwards et al., 2010; Kurakata et al., 2008). More
research is needed to see the role of specific bacterial
growth dynamic on the formation of bioactive
oligosaccharides in tempeh.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The amount of total bacteria in tempeh is strongly
correlated to the anti-adhesion bioactivity of tempeh
extract against ETEC adhesion to eukaryotic cells.
However, there was only a weak correlation between
anti-adhesion bioactivity with the amount of two
major bacterial phyla in tempeh, Firmicutes, and γ-
Proteobacteria. Our finding did not rule out the
possibility that a specific bacterial phylum could still
influence anti-adhesion bioactive in tempeh through
bacterial growth dynamic during the fermentation
process. Results from this experiment could provide
new insight on the development of tempeh into a
functional food product for diarrhea prevention. The
ICE-TES 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering, and Science
326

bacterial amount and profile present during tempeh
fermentation process need to be considered to
produce tempeh with optimum bioactive potential
against ETEC adhesion.
REFERENCES
Edwards, J. L., Smith, D. L., Connolly, J., McDonald, J. E.,
Cox, M. J., Joint, I., Edwards, C., & McCarthy, A. J.
(2010). Identification of Carbohydrate Metabolism
Genes in the Metagenome of a Marine Biofilm
Community Shown to Be Dominated by
Gammaproteobacteria and Bacteroidetes. Genes, 1(3),
371–384. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes1030371
Guo, X., Xia, X., Tang, R., Zhou, J., Zhao, H., & Wang, K.
(2008). Development of a real-time PCR method for
Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes in faeces and its
application to quantify intestinal population of obese
and lean pigs. Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 47(5), 367–373.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2008.02408.x
Karamipour, N., Mehrabadi, M., & Fathipour, Y. (2016).
Gammaproteobacteria as essential primary symbionts
in the striped shield bug, Graphosoma lineatum
(Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Sci. Rep., 6.
https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33168
Keuth, S., & Bisping, B. (1994). Vitamin B12 production
by Citrobacter freundii or Klebsiella pneumoniae
during tempeh fermentation and proof of enterotoxin
absence by PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 60(5),
1495–1499.
Kiers, J. L., Nout, M. J. R., Rombouts, F. M., Nabuurs, M.
J. A., & Meulen, J. V. D. (2002). Inhibition of adhesion
of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 by soya bean
tempe. Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 35(4), 311–315.
https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1472-765X.2002.011 82.x
Kurakata, Y., Uechi, A., Yoshida, H., Kamitori, S., Sakano,
Y., Nishikawa, A., & Tonozuka, T. (2008). Structural
Insights into the Substrate Specificity and Function of
Escherichia coli K12 YgjK, a Glucosidase Belonging
to the Glycoside Hydrolase Family 63. J Mol. Biol.,
381(1), 116–128.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.05.061
Mirelman, D., Altmann, G., & Eshdat, Y. (1980). Screening
of bacterial isolates for mannose-specific lectin activity
by agglutination of yeasts. J Clin. Microbiol., 11(4),
328–331.
Nataro, J. P., & Kaper, J. B. (1998). Diarrheagenic
Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev., 11(1), 142–201.
https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.11.1.142
Nout, M. J. R., & Kiers, J. L. (2005). Tempe fermentation,
innovation and functionality: Update into the third
millenium. J Appl. Microbiol., 98(4), 789–805.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2004.02471.x
Nurdini, A. L., Nuraida, L., Suwanto, A., & Suliantari.
(2015). Microbial growth dynamics during tempe
fermentation in two different home industries—
ProQuest.
Int. Food Res. J, 22(4), 1668–1674.
Pramudito, T. E., Putri, E. G. A., Paluphi, E., & Yogiara, Y.
(2021). The effect of starter culture on bacterial profile
in soybean tempeh. Food Res., 5(1), 380–389.
https://doi.org/10.26656/fr.2017.5(1).436
Radita, R., Suwanto, A., Kurosawa, N., Wahyudi, A. T., &
Rusmana, I. (2017). Metagenome analysis of tempeh
production: Where did the bacterial community in
tempeh come from? Malay. J Microbiol., 13(4), 280–
288.
Radita, R., Suwanto, A., Wahyudi, A. T., & Rusmana, I.
(2018). Firmicutes is the predominant bacteria in
tempeh. Int. Food Res. J, 25(6), 2313–2320.
Roubos-van den Hil, P. J., Nout, M. J. R., van der Meulen,
J., & Gruppen, H. (2010). Bioactivity of tempe by
inhibiting adhesion of ETEC to intestinal cells, as
influenced by fermentation substrates and starter pure
cultures. Food Microbiol., 27(5), 638–644.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2010.02.008
Roubos-van den Hil, P. J., Schols, H. A., Nout, M. J. R.,
Zwietering, M. H., & Gruppen, H. (2010). First
Characterization of Bioactive Components in Soybean
Tempe That Protect Human and Animal Intestinal Cells
against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC)
Infection. J Agri. Food Chem., 58(13), 7649–7656.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jf101379y
Seumahu, C. A., Suwanto, A., Rusmana, I., & Solihin, D.
D. (2013). Bacterial and Fungal Communities in
Tempeh as Reveal by Amplified Ribosomal Intergenic
Sequence Analysis. HAYATI, 20(2), 65–71.
https://doi.org/10.4308/hjb.20.2.65
Soka, S., Suwanto, A., Sajuthi, D., & Rusmana, I. (2014).
Impact of Tempeh Supplementation on Gut Microbiota
Composition in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Res. J
Microbiol., 9(4), 189–198. https://doi.org/10.3923/
jm.2014.189.198
Wang, Y., Gänzle, M. G., & Schwab, C. (2010).
Exopolysaccharide Synthesized by Lactobacillus
reuteri Decreases the Ability of Enterotoxigenic
Escherichia coli To Bind to Porcine Erythrocytes. Appl.
Environ. Microbiol., 76(14), 4863–4866.
https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03137-09
Welman, A. D., & Maddox, I. S. (2003).
Exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria:
Perspectives and challenges. Trend Biotechnol., 21(6),
269–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7799(03)001
07-0
Bioactivity of Soybean Tempeh against Diarrhea Associated Pathogen Is More Correlated with the Number of Total Bacteria than Specific
Major Bacterial Phylum
327
