
The Role of Affective Commitment in Mediating the Relationship
between Authentic Leadership and Organizational Learning at
Chicken-based Food Processing Company in Indonesia
Henilia Yulita
1
a
, Vincencius Farrel Jonathan
1
b
, Yustinus Yuniarto
1
c
, Michael Christian
1
d
,
Eko Retno Indriyarti
2
e
and Suryo Wibowo
3
f
1
Faculty of Social and Humanities, Universitas Bunda Mulia, Jl. Lodan Raya No. 2 Ancol, Jakarta, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Trisakti, Jl. Kyai Tapa No. 1 Grogol, Jakarta, Indonesia
3
Psychological Science Doctoral Program, Universitas Persada Indonesia YAI,
Jl. Pangeran Diponegoro No. 74 Senen, Jakarta, Indonesia
ekoretno@trisakti.ac.id, suryowibowojkt@yahoo.com
Keywords: Affective Commitment, Leadership, Organizational Learning.
Abstract: The phenomenon of closing many retail outlets in Indonesia recently has one of the impacts of decreasing the
processed food distribution network. Anticipating this, an organization must adjust its capabilities through the
support of the leaders and continuous organizational learning (OL). Studies explain the importance of
authentic leadership (AL) styles in OL. However, the role of affective commitment (AC) is still slightly
involved. Therefore, this study aims to measure the role of AC in mediating the relationship between AL and
OL. This study is an empirical-quantitative study on company X based in Jakarta, one of the largest chicken-
based food processing companies in Indonesia. Using the probability sampling technique, 78 employees at
the head office were sampled in this study. The questionnaire and the SMART PLS complement the analysis.
This study states that the role of AC successfully mediates the relationship between AL and OL. Furthermore,
this study also explains that AL affects AC and OL. In addition, AC also affects the OL. Surviving, competing,
and even winning are inseparable from the role of the leader, team, and organizational learning. Trust from
stakeholders (strengthen or even weaken) is considered necessary to be involved in the next research.
1 INTRODUCTION
The integration of aspects of human resources,
technology and market tastes in today's times is a
challenge for organizations. The ability of the
organization in carrying out organizational functions
and the aspects of existing resources needs to be
continuously adjusted to the business competition and
economy of a country. Thus, the organization is
expected to have a strong commitment to continue to
adapt to existing conditions and should continue to
learn so that it can survive and develop during
existing competition. To support this, the role of
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3782-2273
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8858-735X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0904-8302
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8892-5400
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5966-327X
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7460-0250
organizational management, especially leadership in
an organization, is an important forming factor.
Support from organizational leaders can facilitate and
maintain the direction of organizational learning.
Concerning leadership styles in an organization,
authentic leadership styles are seen to shape learning
for workers (Oh & Han, 2017). In this leadership
style, the behavior of workers is to make the leader of
the organization a role model. This is also
corroborated by the views of Delić, Slåtten, Milić,
Marjanović, & Vulanović (2017) which explain that
authentic leadership is related to workers' mindsets
and perceptions of organizational learning and
Yulita, H., Jonathan, V., Yuniarto, Y., Christian, M., Indriyarti, E. and Wibowo, S.
The Role of Affective Commitment in Mediating the Relationship between Authentic Leadership and Organizational Learning at Chicken-based Food Processing Company in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0010753700003112
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Emerging Issues in Humanity Studies and Social Sciences (ICE-HUMS 2021), pages 453-457
ISBN: 978-989-758-604-0
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
453

affective commitment at work. It is further explained
that organizations need continuous learning to
respond to changes in existing conditions, be it a
competition, developments in information
technology, market tastes, or the regulations that
apply in an organization or company. Furthermore, to
be able to survive in the existing business
competition, Christian et al. (2021) explain these
aspects with market orientation and marketing
capabilities factors..
One company that is closely related to the
organizational learning process, affective
commitment, and authentic leadership is a company
that has a complex business process. This can be
indicated by looking at the company's business
process distribution network. In addition, the use of
complex resources can also support the need for the
strength of company learning and the commitment of
all stakeholders to continue to survive and develop in
all existing competitive conditions. To accommodate
this need, this study conducted observations on
companies that met the criteria. In the end, the
researcher decided to use company X which is
engaged in processing chicken-based food in Jakarta.
As part of the largest chicken-based processed food
subsidiary in Indonesia, company X has an extensive
distribution network complexity with international
standards. On the other hand, with the data and
observations made there are still inconsistencies in
the commitment to carry out forms of organizational
learning such as training in the past 3 years (2017-
2019). Even though as is well known, training is one
of the important media to be able to transfer learning
within an organization.
In addition, the authentic leadership of this
company is considered interesting to be studied in
line with the many human resources owned by the
company which until now have proven that the role
of company leaders can maintain, maintain, and
develop the company to this extent. During this
prolonged pandemic, the company’s vision and
mission must be maintained to survive and develop.
However, it needs to be adjusted according to the
conditions of business competition that occur. The
phenomenon of closing retail outlets in Indonesia
during the pandemic also had an impact on company
X. With the closure of many retail outlets in Indonesia
has hampered the sales of processed chicken food
products made by this company. The distribution
network and sales of the company's products have
been reduced or even stopped. According to the
Indonesian Retail Entrepreneurs Association
(APRINDO), 1,200 retail stores were closed from
April to December 2020 (Kontan, 2021).
Complementing this phenomenon, studies of
previous studies have succeeded in explaining the
relationship between organizational commitment,
leadership style, and organizational learning. Okmen,
Elçi, Murat, & Yılmaz (2018) in their research
explain that the learning capacity of an organization
is affected by authentic leadership styles. Other
studies have even added that affective commitment
from workers can reduce the desire to change jobs
(Lau, McLean, Lien, & Hsu, 2016). At least, this is
also reinforced by research by Javaid, Luqman, Amir,
& Umair, (2015) which explains that authentic
leadership affects workers' affective commitment.
Furthermore, organizational commitment can
mediate between leadership and organizational
learning, as explained by the research results
(Mercurio, 2015).
The importance of the commitment variable as a
mediator between authentic leadership and
organizational learning in companies engaged in the
processing of chicken-based food during the
challenges of the many closures of sales networks
during this pandemic has become the focus as well as
the originality of this research. Therefore, by adopting
the organizational learning research model from
Delić et al. (2017), this study will specifically analyse
whether affective commitment can mediate authentic
leadership styles and organizational learning in types
of processed food production companies with
extensive distribution and sales networks in
Indonesia.
2 METHODS
This research is an empirical quantitative study at
company X which is engaged in the processing of
chicken-based food. This company is in Jakarta. By
using the probability sampling method, 78 employees
at the head office were sampled in this study. This
study used a survey with a questionnaire instrument.
The questionnaire was designed using items and a
Likert scale of 1 (strongly disagree) and 5 (strongly
agree). This study focuses on the formulation of the
problem, namely whether organizational
commitment mediates authentic leadership on
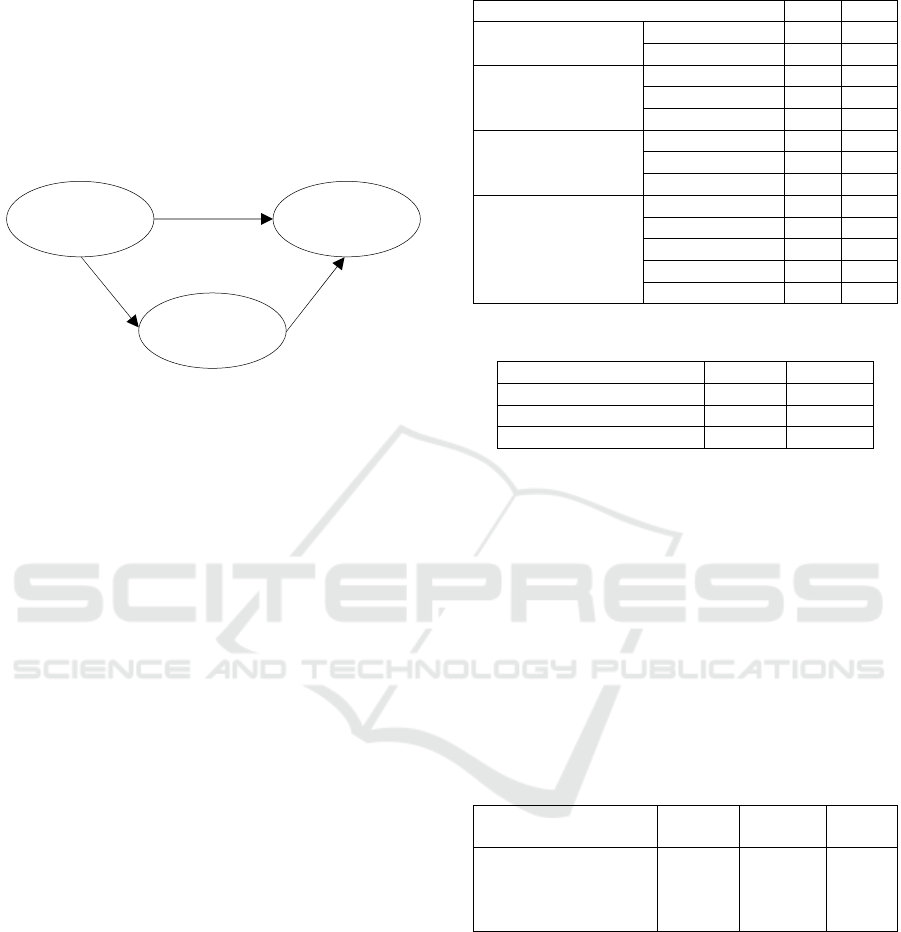
organizational learning. Thus, as shown in Figure 1,
the hypothesis (H) in this study is that Authentic
Leadership affects Organizational Learning mediated
by Affective Commitment. For research
measurement, the variables of authentic leadership,
affective commitment, and organizational learning
each consisted of 8 items. The items are adapted from
Delić et al., (2017). To analyse the research data, this
ICE-HUMS 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Humanity Studies and Social Sciences
454
study used a Partial Least Square-Structural Equation
Modeling (PLS-SEM) approach with SMART PLS as
an analysis tool. In addition, SEM-PLS is used to
analyse a structural model with causal relationships.
a modeling tool for analyzing structural models (Al
Idrus, Ahmar, & Abdussakir, 2018). Meanwhile,
SMART-PLS was used with a small sample size
(Wong, 2013).
Figure 1: Research model.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Table 1 shows the profile of 78 respondents, which is
divided into three parts, including gender, educational
background, length of work, and age. In this study,
the sex of men was 35 people or 45%, while women
were 43 people or 55%. This research indicates that
most respondents are women. Furthermore, the latest
high school education is 18 people or 23% and S1 as
many as 57 people or 73% and S2 as many as 3 people
or 4%. Thus, this study indicates that most of the
respondents' last education was S1. In this study, it is
known that PT X has employees with 1-3 years of
work by 40% and 32% for 4-6 years and 28% of those
who have worked> 6 years. Furthermore, the age of
respondents <20 years is 1 person or 1%, 20-29 years
is 42 people or 54%, 30-39 years is 21 people or 27%
and 40-49 years 12 people or 15% while age> 50
years amounted to 2 people or 3%. This indicates that
most respondents are 20-29 years old with a
percentage of 54%.
Based on the results of validity and reliability in
Table 2, Average Variance Extracted (AVE) shows
results of more than 0.5 and Cronbach's Alpha (CA)
shows results of more than 0.7. Thus, the variables in
this study are valid and reliable.
Table 1: Respondent’s profile.
Profile N %
Gender
Male 35 45%
Female 43 55%
Education
SMA 18 23%
S1 57 73%
S2 3 4%
Long Experience
Working
1-3
y
ears 31 40%
4-6
y
ears 25 32%
>6
y
ears 22 28%
Age
<20 years ol
d
1 1%
20-29 years ol
d
42 54%
30-39
y
ears ol
d
21 27%
40-49
y
ears ol
d
12 15%
≥50
y
ears ol
d
2 3%
Table 2: Validity and reliability tests.
Variable AVE CA
Authentic leadership 0.604 0.888
Affective Commitment 0.508 0.842
Or
g
anizational Learnin
g
0.529 0.851
The output parameter test of significance is seen
from the total effect, not the coefficient table because
the mediation effect is not only tested for the direct
effect of the independent variable on the dependent
variable, but also the interaction between the
independent variable and the mediating variable on
the dependent variable. Therefore, the total effect is
used to see the total effect of the prediction. If the
results of the bootstrapping iteration obtained a T-
Statistical value of ≥ 1,96 then there is an effect, and
if the P-Values value is below ≤ 0,5, it can be said that
the effect is significant.
Table 3: Test of significance.
Profile Original
Sample
T
Statistics
P
Values
Authentic leadership
Affective Commitment
Organizational
Learnin
g
0.180 3.385 0.001
It can be seen in Table 3 that there is an affective
commitment that will mediate authentic leadership
and learning organizations with a T-statistic value of
more than 1,96 (3,385>1,96) The hypothesis is
accepted with the original sample 0.180 (positive)
and P values less than 0,05 (0,001<0,05) so it can be
explained that affective commitment mediates the
relationship between authentic leadership and
organizational learning. This research is in line with
several previous research results such as Mercurio
(2015), Walumbwa, Christensen, & Hailey, (2011),
Authentic
leadership
Organizational
Learning
Affective
Commitment
The Role of Affective Commitment in Mediating the Relationship between Authentic Leadership and Organizational Learning at
Chicken-based Food Processing Company in Indonesia
455

Leroy, Palanski, & Simons (2012), which also
explains the role of affective commitment in
mediating authentic leadership with organizational
learning. Complementing these results, this study also
explains that authentic leadership has a positive and
significant relationship with the learning organization
with a T-statistic value of more than 1,96, namely
(3,783>1,96). Furthermore, affective commitment
has a positive and significant relationship with the
learning organization, namely with a T-statistic value
of more than 1,96 (5,339>1,96) and authentic
leadership has a positive and significant effect on
affective commitment, namely with a T-statistic value
of more than 1,96 (4,022>1,96).
In company X, according to the results of this
study, it explains that affective commitment has a
relationship between authentic leadership and
organizational learning. As there is no sense of
commitment then the leader cannot run well. The
desire to learn new things in a learning organization
will be difficult if there is no commitment from all
employees. So affective commitment as a mediator
between authentic leadership and organizational
learning becomes important. Affective commitment
to mediate the relationship between authentic
leadership and learning organizations with existing
learning organization indicators (Even though I have
different opinions, I still accept joint decisions with
them in learning organizations even though joint
decisions are the most important even though there
are different opinions). Every employee can develop
himself with a learning organization within the
company in the form of any activity, employee
knowledge is always updated and not out of date.
Next in Table 4 shows that authentic leadership
affects affective commitment by 15.2%, while 84.8%
is explained by other latent variables outside of this
study. And affective commitment affects the learning
organization by 49.7%, while 50.3% is explained by
other latent variables outside of this study.
Table 4: R-square.
Variable R-s
q
uare score
Affective Commitment 0,152
Or
g
anizational Learnin
g
0.4.97
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of research that has been carried
out with due regard to various things, it can be
concluded that the affective commitment variable
mediates the relationship between authentic
leadership and learning organizations. A good
leadership style can encourage employees to continue
to upgrade themselves in the learning organization
within the company as well. Furthermore, affective
commitment is important for learning organizations
because employee commitment will shape the
employee's own motivation to develop. Other related
implications are the role of the leader also has an
impact on the employee's sense of commitment, if the
leader is not good, what about the employee's sense
of affective commitment in the company. In the end,
this study states that the role of leader in company X
is closely related to a sense of affective commitment
to shaping organizational learning.
REFERENCES
Al Idrus, S., Ahmar, A. S., & Abdussakir, A. (2018). The
effect of organizational learning on market orientation
moderated by job satisfaction. Cogent Business &
Management, 5(1475048), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1
080/23311975.2018.1475048
Christian, M., Dewi, D., Rembulan, G. D., Indriyarti, E. R.,
Wibowo, S., & Yuniarto, Y. (2021). Business
performance determinants of salted fish distribution in
Kapuk during the COVID-19. Journal of Distribution
Science, 19(6), 29–39. https://doi.org/10.15722/jds.
19.6.202106.29
Delić, M., Slåtten, T., Milić, B., Marjanović, U., &
Vulanović, S. (2017). Fostering learning organisation in
transitional economy – the role of authentic leadership
and employee affective commitment. International
Journal of Quality and Service Sciences, 9(3/4), 441–
455. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJQSS-02-2017-0012
Javaid, M. F., Luqman, K., Amir, H., & Umair, T. (2015).
Authentic leadership affects employee’s attitudes
(Affective Commitment) through the mediation role of
Personal Identification and Organizational
Identification. International Journal of Academic
Research in Business and Social Sciences, 5(12), 215–
231. https://doi.org/10.6007/IJARBSS/v5-i12/1945
Kontan. (2021). Wabah Covid-19 pukul daya beli
masyarakat, banyak gerai ritel terpaksa tutup.
Lau, P. Y. Y., McLean, G. N., Lien, B. Y.-H., & Hsu, Y.-
C. (2016). Self-rated and peer-rated organizational
citizenship behavior, affective commitment, and
intention to leave in a Malaysian context. Personnel
Review, 45(3), 569–592. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-
04-2014-0083
Leroy, H., Palanski, M. ., & Simons, T. (2012). Authentic
leadership and behavioral integrity as drivers of
follower commitment and performance. Journal of
Business Ethics, 107(3), 255–264.
Mercurio, Z. A. (2015). Affective commitment as a core
essence of organizational commitment: An integrative
literature review. Human Resource Development
ICE-HUMS 2021 - International Conference on Emerging Issues in Humanity Studies and Social Sciences
456

Review, 14(4), 389–414. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534
484315603612
Oh, J., & Han, S. J. (2017). A new research direction of
authentic leadership in the field of adult education.
Adult Education Research Conference, 1–7. Norman:
New Prairie Press.
Okmen, S., Elçi, M., Murat, G., & Yılmaz, Y. (2018). The
impact of authentic leadership on organizational
learning capacity. Journal of Global Strategic
Management, 12(1), 057–066. https://doi.org/10.
20460/JGSM.2018.261
Walumbwa, F. ., Christensen, A. L., & Hailey, F. (2011).
Authentic leadership and the knowledge economy:
sustaining motivation and trust among knowledge
workers. Organisational Dynamics, 40(2), 110–118.
Wong, K. K.-K. (2013). Partial Least Squares Structural
Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) techniques using
SmartPLS. Marketing Bulletin, 24(1), 1–32.
The Role of Affective Commitment in Mediating the Relationship between Authentic Leadership and Organizational Learning at
Chicken-based Food Processing Company in Indonesia
457
