
Case Study: Integrating SMART Decision Making Attributes to
Improve the Selecting Subcontractor Strategy
Theofilus Purnama Putra and Sudarso Kaderi Wiryono
School of Business and Management, Institut Teknologi Bandung, Bandung, Indonesia
Keywords: Subcontractor, Construction Value Chain, Financial Ratio, Capacity Planning, Project Funding, Strategic
Improvement, Subcontract Performance.
Abstract: PT McDermott Indonesia is subsidiary of McDermott International Incorporated. In its working practice,
McDermott cooperate with other contractors so called subcontractors to complete specific work on a project.
This research was conducted using lessons learned from the non-conformance made by one of the
subcontractor on the project of Qatar Gas North Field. The objective of this business research is to ascertain
the elements where this problematic subcontractor error occurs. An integrated framework is developed
incorporate attributes of : construction value chain, financial ratio, capacity planning and project funding. The
study uses analysis methods to identify the potential problem, interviews among related parties and simulation
methods to formulate an improvement plan. This research concludes that the analysed attributes have an
important role and should be included in the key for subcontractor selection by using the proposed SMART
decision making method. This new strategy expected can help PT McDermott Indonesia to improve the
assessment of each subcontractor competency prior to contract awards.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Subcontractor
According to Eccles (1981) and Costantino et al.,
(2001) the contractor will not carry out all the works
but sublet specialist works, such as building
services works, to subcontractors specialized in the
respective work disciplines. Hughes et al. (1997)
and Yik et al. (2006) describes specialist work as
those that involve the use of special methods,
delivery of proprietary products, or works that can
only be performed by registered or licensed
companies or persons.
PT McDermott Indonesia divides the rules in
this subcontracting into four parts, the purpose of
this division is to maintain the effectiveness of the
process, consisting of Pre-Subcontract Planning,
Sourcing, Management and Vessels (see flowchart
on Figure 1).
The process of subcontracting itself are divided
by (a) Identification of the work scope to be
subcontracted (b) Preparation of the relevant
package for the identified scope of work to be
subcontracted (c) Selection of qualified
subcontractor from whom quotes/bids are to be
obtained for the specified work and (d) Evaluation
of the respective bids from the Subcontractor(s) and
subsequent selection of the Subcontractor based on
technical capability, cost, quality and schedule for
the execution of the specific scope of work.
Figure 1: Subcontracting.
1.2 Problem Statement
PT McDermott Indonesia was started the
fabrication of Qatar Gas North Field project since
2019. One part of the fabrication scope of work for
the piping contract of this project is to fabricate
cladded pipes which is subcontracted.
184
Purnama Putra, T. and Kaderi Wiryono, S.
Case Study: Integrating SMART Decision Making Attributes to Improve the Selecting Subcontractor Strategy.
DOI: 10.5220/0010861300003255
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science (ICAESS 2021), pages 184-189
ISBN: 978-989-758-605-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

The subcontractor was considered having a
product delivery problem. This case almost causes
delays in the delivery of the whole project module
plan which can cause a loss of reputation of PT
McDermott Indonesia. The management assumed
that: (a) This problem was caused by
subcontractor's financial problems with the
possibility of non-smooth cash flow conditions. (2)
On the other hand, there may also be problems
related to production aspects, insufficient
machinery and equipment as well as the supply of
raw materials. (3) Other possibilities also arise such
as technical skills, procedures for financing the
projects or constraints in the administrative area.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 SMART Analysis Method
The Simple Multi Attribute Rating Technique
(SMART) decision-making technique has been
used to explore how decision analysis can be used
to support decision makers who have multiple
objectives. According to Paul Goodwin and
George Wright (2004) when decision problems
involve a number of objectives unaided decision
makers tend to avoid making trade-offs between
these objectives. This can lead to the selection of
options that perform well on only one objective, or
the rejection of relatively attractive options
because their good performance on several
objectives is not allowed to compensate for poor
performance elsewhere.
So this is the based to use SMART method on
this research, this method also based on a linear
additive model. This means that an overall value of
a given alternative is calculated as the total sum of
the performance score (value) of each criterion
(attribute) multiplied with the weight of that
criterion.
2.2 Construction Value Chain
According to Porter (1985: 12). The idea of the
value chain is based on the process view of
organizations, the idea of seeing a manufacturing
(or service) organization as a system, made up of
subsystems each with inputs, transformation
processes and outputs. Inputs, transformation
processes, and outputs involve the acquisition and
consumption of resources – money, labour,
materials, equipment, buildings, land,
administration and management. How value chain
activities are carried out determines costs and
affects profits. The Inbound Logistics, Operations,
Outbound Logistics, Marketing and Sales, and
Service are categorized as primary activities, while
the other included on secondary activities (see
Figure 2).
Figure.2. Construction Value Chain
2.3
Financial Ratio Analysis
According to Gropelli (2000: 433) a financial ratio
or accounting ratio is a relative magnitude of two
selected numerical values taken from an
enterprise's financial statements. Often used in
accounting, there are many standard ratios used to
try to evaluate the overall financial condition of a
corporation or other organization. Financial ratios
may be used by managers within a firm, by current
and potential shareholders (owners) of a firm, and
by a firm's creditors. Financial analysts use
financial ratios to compare the strengths and
weaknesses in various companies. In this research,
the financial ratios of the problematic
subcontractor are detailed and checked.
2.4 Capacity Planning
According The North Carolina State University on
the book "Terms and Definitions - Supply Chain
Management", Capacity planning describes as the
process of determining the production capacity
needed by an organization to meet changing
demands for its products. The strategy which is
broadly used worldwide are:
Lead strategy, it is the strategy by adding
capacity in anticipation of an increase in demand.
Lead strategy is an aggressive strategy with the
goal of luring customers away from the company's
competitors by improving the service level and
reducing lead time. It is also a strategy aimed at
reducing stock out costs. A large capacity does not
necessarily imply high inventory levels, but it can
Case Study: Integrating SMART Decision Making Attributes to Improve the Selecting Subcontractor Strategy
185

imply higher cycle stock costs. Excess capacity can
also be rented to other companies.
Lag strategy describe as the strategy by adding
capacity only after the organization is running at
full capacity or beyond due to increase in demand
(North Carolina State University, 2006). This is a
more conservative strategy and opposite of a lead
capacity strategy. It decreases the risk of waste, but
it may result in the loss of possible customers either
by stock out or low service levels. Three clear
advantages of this strategy are a reduced risk of
overbuilding, greater productivity due to higher
utilization levels, and the ability to put off large
investments as long as possible. Organization that
follow this strategy often provide mature, cost-
sensitive products or services.
Match strategy, It is by adding capacity in small
amounts in response to changing demand in the
market. This is a more moderate strategy.
Adjustment strategy, with method of adding or
reducing capacity in small or large amounts due to
consumer's demand, or, due to major changes to
product or system architecture.
2.5 Project Funding
Funding is the act of providing resources to finance
a need, program, or project. While this is usually in
the form of money, it can also take the form of
effort or time from an organization or company.
Generally, this word is used when a firm uses
its internal reserves to satisfy its necessity for cash,
while the term financing is used when the firm
acquires capital from external sources. Sources of
funding include credit, venture capital, donations,
grants, savings, subsidies, and taxes.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Methodology Flowchart
Figure.3: ADDIE Methodology.
This research used ADDIE model which consists of
five stages: Analysis, Design, Development ,
Implementation and Evaluation (see Figure 3). Stage
Evaluate in this methodology is iteration process which
aims to review again, add improvements if there are still
deficiencies, as well as the process of sharpening the
process results.
4 ANALYSIS
4.1 Analysis 1, the Construction Value
Chain of the Subcontractor
The Porter’s Value Chain describe the importance
of each activities, both activities are involved and
support each other. First step is checking five
Primary Activities (see Appendix.1), these are
essential in adding value and creating a competitive
advantage of the subcontractor.
From the first analysis, it was found that there
were no issues related to five primary activities at
the subcontractor area, but subcontractor could
harness a competitive advantage at any one of
activities in the value chain. For example, by
creating inbound logistics that are highly efficient
or by reducing a company's operation costs, it
allows to either realize more profits or pass the
savings to the consumer by way of lower prices.
The Support Activities is using to helps make
primary activities more effective. Increasing any of
the four support activities helps at least one
primary activity to work more efficiently (see
Appendix.2).
From this Value Chain analysis result, found
several areas need to have improvement:
Operations, Human Resources Management and
Technological Development. From those three
activities that need improvement, only one is the
primary activity, the finding which is also a minor
finding in the form of improving dimensional
inspection forms, training matrix and one more
finding which has not been resolved. In this case it
can be concluded that in general the condition of
the construction value chain of subcontractor is in
good condition.
There are four red dots which are finding in the
construction value check above, the finding part is
then used as a basic measure of risk checking,
which is called the Key Risk Indicator (KRI) and
transformed to ranking table (see Appendix.3)
The table shows that technological
development shall give first attention, the use of
tools and materials without a certificate is very
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
186

risky, especially when testing pipes in a shop is in
progress. The next critical item is in both the
operations and human resources areas, this also
shows that the technical work in operations is also
influenced by the completeness of tools possessed
by the human resources department.
4.2 Analysis 2, the Financial Ratio of
the Subcontractor
Financial Ratio will determine the Company
performance. Company performance showing the
company capability to generate profit. In
connection with the selection of a subcontractor,
company performance will make it easier for
McDermott to choose a subcontractor from one of
the important considerations, called Financial
Health.
Financial performance is measured from three
important aspects: Liquidity Ratio, Solvability
Ratio and Profitability ratio from the Statement of
Financial Position report from subcontractor for
2018 and 2019 (see Appendix.4).
The table conclude that from the twelve ratios
that were checked in relation to the financial
performance of subcontractor, eleven are dropping
from year 2018 to 2019.
4.3 Analysis 3, Project Funding of the
Subcontractor
A company will be said to be an unhealthy
company not only from the quality of its human
resources or from the value of its sales. However,
it can be measured from an internal financial
perspective. One way to do this is by measuring the
Debt to Equity Ratio (DER).
Debt to Equity Ratio or DER is the ratio of debt
to equity or financial ratio that compares the amount
of debt to equity. Equity and the amount of debt is
used for the operational needs of the company,
which must be proportional to the amount. In
addition, this Debt to Equity Ratio is also
commonly called the leverage ratio, where this ratio
is used to measure an investment in the company.
The formula for calculating DER is as follows:
From the financial report of subcontractor, in
2018 the total long-term liabilities is IDR
36,074,010,000,000 with total owner's equity is
IDR 3,975,872,000,000, from the two data
obtained DER = 9.07, while in 2019 the total long
term liabilities is IDR 34,478,745,000,000 with
total owner's equity is IDR 6,071,641,000,000,
DER is obtained from both data is = 5.68
According to Finance Minister Regulation No.
PER-25/PJ/2017 (article 2), the reference for DER
is that a company can be said to be healthy with a
maximum ratio of : 4 liabilities and 1 equity. So the
smaller this ratio, the better the company.
Subcontractor's DER in 2018 is 9.07 And in the
year 2019 is 5.68, This higher DER indicates that
more creditor financing is used than equity
financing. Movement of DER ratio tends to
decrease from 9.07 to 5.68 and it indicates that
company moving to better condition.
4.4 Analysis 4, Capacity Planning of
the Subcontractor
This research uses project data carried out by
subcontractor from January 2019 to March 2021.
Data obtained from the Project Reference List
consists of two weld overlay (WOL) activities,
pipes is measured in length (meters) and fittings is
measured by quantity.
From the Project reference list data, it is found
that the accumulated changes in load are
summarized from the each month load on
Appendix.5 (a) and (b).
The existing monthly capacity of Subcontractor
is 650 meters for pipe welding overlay (WOL) and
650 ea. for fittings per month. This calculation is
an average calculation because the capacity will
depend on the diameter and thickness of the pipes
and fittings, for example a material with a size of
16 inches and above will require 2 times the
processing time than the small material. Besides
that, it also depends on the requirements of the
client regarding the overlay material and the
thickness it requires, each overlay material has its
own difficulties in the process.
Capacity utilization rate used to measure of
how close the firm is to its best possible operating
level, the formula for calculating the Capacity
Utilization rate is:
From the Subcontractor data, the best operating
level is 650 meters and 650 ea. There are several
monthly loads that exceed the capacity, it is shown
on Appendix.5 (c).
The summary table explained that there are six
months overloaded for pipe cladding project and
eight months for the fittings. Some of the load gap
Case Study: Integrating SMART Decision Making Attributes to Improve the Selecting Subcontractor Strategy
187

even too big, especially on the piping part, while
on fitting part, there are extravagant gap found on
March 2020, in this condition Subcontractor gets
support for the requirement of project fabrication
machine from the facility branches in Rio De
Janeiro, Brazil and Dammam Saudi Arabia. In this
case, actually the capacity of Subcontractor Batam
still has limitations which can be increased by
adding new machines and experts. However, this
will require a fairly long consideration given the
continuity of projects and loads that vary widely.
4.5 Proposed Improvement for
Subcontractor
From the four analysis that have been carried out,
in general we can see better regarding the condition
of subcontractor, the results of this research can be
used as a basis for proposals to subcontractor and
also as input for improvement in the subcontractor
selection method at McDermott.
In the Construction Value Chain analysis, from
the Deployment Table for Target and Profile Risk,
there are twelve key risk indicators which are a
combination of the risk of their primary and
supporting activities. The unique thing is that the
risks between these parts are interconnected, for
example: risk in the area of supporting activities,
called Technological Development, which is all
included in Extreme Risk, if it is not immediately
followed up, it will affect risk in the Operations
area. Risk in the Technological Development area
which includes material, tools and instrument
certification is critical, so it must be handled
quickly, and after the problem is resolved,
monitoring tools must be created immediately to
avoid the same case occurring in the future.
In the Financial Ratio analysis, with exception
of DER analysis, from the 2018 and 2019 financial
reports, there was a declining trend for almost all
of the ratios studied, Liquidity Ratio, Solvability
Ratio and Profitability ratio. This indicates that the
company is in a state of decline or can be said to be
unhealthy.
In the Project Funding area, using the same data
from Financial Ratio data, DER which is the
determinant of project funding for the two (2) years
of data studied, 2018 and 2019, got a value of 9.07
for 2018 and 5.68 for 2019. These two conditions
are not good enough seen from the minimum
standard of DER which should be below the
number 4, however there is a tendency that
improvements are taking place within the
company's financial institutions.
Analysis for the Capacity Planning resulting
subcontractor's line of business is classified as a
business whose load cannot be planned, in other
words, the load varies greatly, for example: there
are circumstances where in one month the
company only gets orders for only four pcs of
fittings to work on, but there are times within one
month it get orders of 8635 pcs of fittings, a very
unequal number. By looking at this situation,
Capacity Planning can only be predicted in general
terms, mitigation at the time of overload has also
been made, i.e. by borrowing fabrication machines
from subcontractor headquarters or branches.
Table on Appendix.6 showing the improvement
proposals that can be used by Subcontractor to
improve the health of its company.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSSION
5.1 Integrating SMART Decision
Making Attributes to Improve the
Selecting Subcontractor Strategy
The default for the subcontractor selection method
is from two main parts: Cost and Operations, the
cost in this case is represented by fabrication and
transport, while in the operation area it only
focuses on checking the capacity of the
subcontractor, even this checking is not done in
detail.
Figure 4: Subcontract Attributes.
From the research that has been done, it was
found three items which turned out to be important
to check as well and have an overall effect on
company performance, they are Financial Ratio and
Project Funding plan, as well as checking the
Construction value chain. These three items must
be registered into attributes which will be used as
the basis for the next decision making process (see
Figure.4).
To determine the weight of attributes, a
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
188
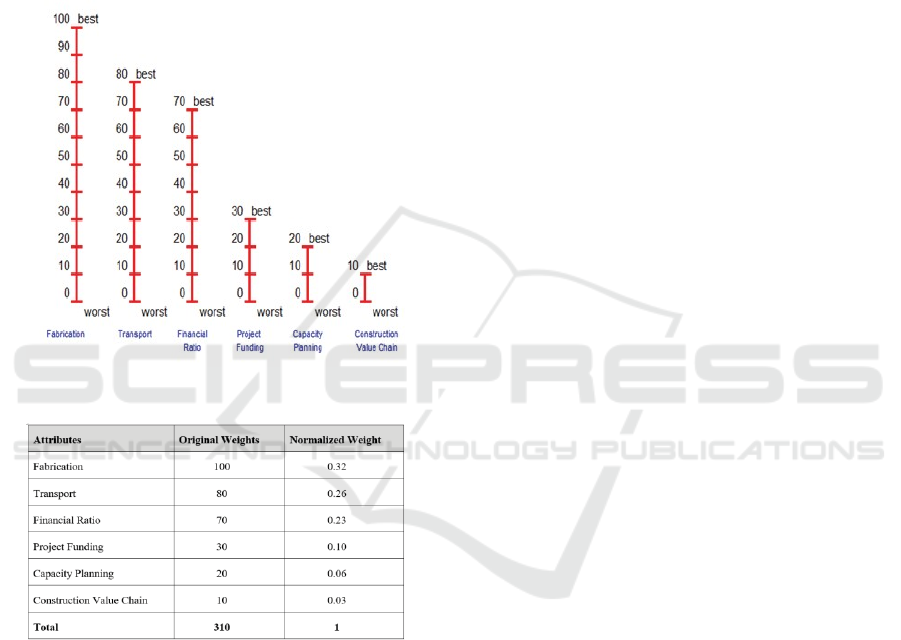
discussion of three parties who is involved with
this activity, including: Project Engineer,
Subcontracting Coor- dinator and Completion
Coordinator. From the discussion, the results
showed that cost still gets the highest ranking,
followed by finance and operations (see Figure.5
and Table.1).
This normalized weight then can be used for
calculating of aggregate of weighted value for each
subcontractor with the purpose to make the
calculation more details.
Figure 5: Attributes Weight.
Figure 6: Original and Normalized Weight.
6 CONCLUSION
As assumed earlier, the problem that occurs is due
to the method of selecting subcontractors which
seems to ignore several important items. As
evidenced by the four analyses: Construction
Value Chain, Financial Ratio Analysis, Project
Funding and Capacity Planning in subcontractor
area, found deficiencies that indicate the company
is not healthy.
In Construction Value Chain area, the
Technological Development area which includes
material, tools and instrument certification is
critical, so it must be handled quickly, and after the
problem is resolved, monitoring tools must be
created immediately to avoid the same case
occurring in the future. In Financial Area,
improvement need to be done as the company is in
a state of decline or can be said to be unhealthy. In
Project Funding plan, even there is a tendency that
improvements are taking place within the
company's financial institutions, improvement still
need to be done. In Capacity Planning area,
improvement need to be done to make the load
uniform so will be easier to make capacity
planning.
Seeing from these results, we can conclude that
the attributes studied are items that are important in
relation to the decision making in selecting the
subcontractor, therefore it needs to be included in
the existing attributes.
REFERENCES
Eccles, R.G., 1981. Bureaucratic versus Craft
Administration: The Relationship of Market
Structure to the Construction Firm, Administrative
Science Quarterly, Vol.26, pp.449-469.
Constantino, N., Pietroforte, R. and Hamill, P., 2001,
Subcontracting in commercial and residential
construction: an empirical investigation,
Construction Management and Economics, Vol. 19,
pp. 439-447.
Goodwin, P and Wright, G. 2004. Decision Analysis for
Management Judgment, Third Edition, John Wiley
& Sons Ltd, West Sussex, England. pp. 27
Porter, Michael E., 1985. Competitive Advantage:
Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. New
York.: Simon and Schuster. ISBN 9781416595847.
Retrieved 9 September 2013. pp. 12, 37.
Gropelli, A. A., & Ehsan, N., 2000, Finance (4th Edn.).
New York: Baron’s Educational Series, Inc. pp. 433
North Carolina State University., 2006, Terms &
Definitions - Supply Chain Management. Retrieved
2008-10-26.
Greener, Sue. & Martelli, J. 2015, An Introduction to
Business Research Methods. bookboon.com
Direktorat Jenderal Pajak. 2017, Peraturan Direktur
Jenderal Pajak Nomor: PER-25/PJ/2017. Jakarta
Management Team, 2015, Management System Manual
- Global. LinQ, McDermott.
Management Team. (2006) Subcontract Procedure for
Subcontract Bid Solicitation, Evaluation and Award.
LinQ, McDermott.
Management Team. (2020) Pre-Subcontract Planning.
Unifi, McDermott
Management Team. (2020) Supply Chain Management
Policy. Unifi, McDermott
Case Study: Integrating SMART Decision Making Attributes to Improve the Selecting Subcontractor Strategy
189
