
Effect of Working Capital Management on Profitability of
Manufacturing Companies Listed on the IDX
Septriyani and Seto Sulaksono Adi Wibowo
Managerial Accounting Study Program, Politeknik Negeri Batam, Indonesia
Keywords: Working Capital Management, Profitability, Gross Operating Income.
Abstract: This study aims to determine the effect of WCM on the profitability of Indonesia’s listed manufacturing firms
for 2015-2019. This study has one dependent variable, namely profitability which is measured by GOI and
has an independent variable, namely WCM, which is measured by ICP, RCP, APP, and CCC. This study also
has two control variables, firm size and leverage. The sampling technique used the purposive sampling
method. Data is obtained from the annual reports of 86 companies. The data analysis technique is panel data
regression analysis with the E-views 9 software. The results of the study found that ICP, RCP, APP, and CCC
have a significant effect on profitability.
1 INTRODUCTION
Along with the times and technological
developments, every year, manufacturing companies
also experience effects and improvements. One of the
things that make economic growth also increases is
caused by the role of the manufacturing company
itself (Syafitri & Adi Wibowo, 2016). Along with the
increase in company growth, competition between
companies is also getting tighter.
Every company certainly needs funds, to be able to
finance all the company's needs, both for operational
activities or for long-term investment. This fund is
known as working capital. If you run out of working
capital, the company will certainly not be able to run
well. Setyanto & Permatasari (2014), in their
research, states that Working Capital Management
(WCM) includes Inventory, Accounts Receivables,
Accounts Payables, and Cash Conversion Cycle.
WCM needs to be appropiately managed, because
WCM is a financial component required to carry out
company activities or operations based on plans and
policies that have been set by it. Mistakes in
managing WCM can slow down the company's
performance and even cause the company to stop
operating and make its business fail.
CCC is defined as the cash flow starting from cash
disbursement to cashback (receivables paid) and can
be calculated by adding the RCP and ICP then
deducting the APP (Mamduh, 2008). Inventory
Conversion Period (ICP) is the time for a company to
process the inventory until the products can be sold.
This ICP needs to be considered because to determine
how long it takes the company to spend stock in its
production process.
Receivables Conversion Period (RCP) is the time for
the company to collect its receivables into cash.
Receivables occur when the sale is made, but the
company has not yet received it as cash. Thus, the use
of accounts receivable is expected to increase profits
and sales.
Accounts Payable Period (APP) is the time for the
company to purchase the inventories, labor, and
payments (Brigham & Houston, 2006). If debt
payments are delayed, the additional capital owned
can be used for other purposes. The level of debt,
which is an element of liability for the company, is
also an important thing that must be considered in
financing and managing working capital. Apart from
managing working capital properly, there are other
important things that companies must do, namely
maintaining and increasing profitability.
Profitability is the primary goal of every business, a
service, trading, or manufacturing company. Every
company must maintain its profitability properly so
that investors are interested in investing because
investors will usually see and analyze the company’s
profitability first before deciding to invest. In
Indonesia, the contribution of the manufacturing
sector plays a significant role in its economic growth.
Researchers hope that analyzing the effect of WCM
126
Septriyani, . and Sulaksono Adi Wibowo, S.
Effect of Working Capital Management on Profitability of Manufacturing Companies Listed on the IDX.
DOI: 10.5220/0010861700003255
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science (ICAESS 2021), pages 126-131
ISBN: 978-989-758-605-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

will provide an overview and suggestions for the
company to managing working capital.
2 THEORETICAL STUDY
2.1 Pecking Order Theory
Mayers & Majluf (1984) explained that in this theory,
companies tend to use minimal risk funding sources.
This theory also suggests that in managing to fund,
companies will tend to choose internal financing first.
The use of external funds determined if internal
financing is insufficient.
2.2 Agency Theory
Jensen & Meckling (1976) explained that agency
theory is an agreement in which a principal gives
orders to the agent and is entrusted with making the
right decision for the principal. If both of them have
the same goals in increasing the firm valuation, then
it is believed that the agent has acted in the principal’s
interests.
2.3 Cash Conversion Cycle Theory
Richards & Laughlin (1980) explain how firms can
ensure short CCC to reduce the implications of poor
working capital management. Thus, it measures the
time between purchasing a company's inventory and
receiving cash from its accounts receivable.
2.4 Literature Review
Based on previous research, Jin-Yap (2017)
examined the effect of WCM on profitability in
companies in Vietnam. Independent variables use
WCM, which is proxied by ICP, RCP, APP, and
CCC. FS, sales growth, and debt were used as control
variables. Meanwhile, profitability is proxied through
GOI (Gross Operating Income). The results show that
ICP, ARP, APP, and CCC have a significant effect on
profitability.
Ng, Ye, Ong, & Teh (2017) examined the effect of
WCM. Independent variables use WCM, which is
proxied by ICP, RCP, APP, and CCC. GOI is used as
the dependent variable. The results show that ICP,
ARP, APP, and CCC have a significant effect on
profitability.
Le (2018) examines the effect of WCM on firm value,
profitability, and risk. It uses NWC and CCC as
independent variables. ROI is used as the dependent
variable. As a result, there is a negative relationship
between NWC and firm value, profitability, and risk.
The results of this study suggest that in managing
working capital, managers must make objective
considerations for profitability and risk control.
Kwatiah & Asiamah (2020) examined the effect of
WCM on manufacturing companies in Ghana. WCM
is proxied through ICP, RCP, APP, and CCC as
independent variables. The control variables are
Current Ratio, Current Assets, Firm Size, and
Leverage. Meanwhile, the dependent variables are
ROA and ROE. The results show that ICP, ARP,
APP, CCC, Current Ratio, Current Assets, and Firm
Size have a positive effect on ROA and ROE.
Meanwhile, leverage has a negative impact on ROA
and ROE.
2.5 Hypothesis Development
2.5.1 Effect of Inventory Conversion Period
on Profitability
ICP is the period used to process raw material until
the product is finished and can be sold. The longer the
ICP, the costs will be increase the company's
operational costs. If the company's operating costs are
high, it will reduce profitability. Therefore, to reduce
costs arising from excess inventory, a low ICP level
is needed (Brigham & Houston, 2006).
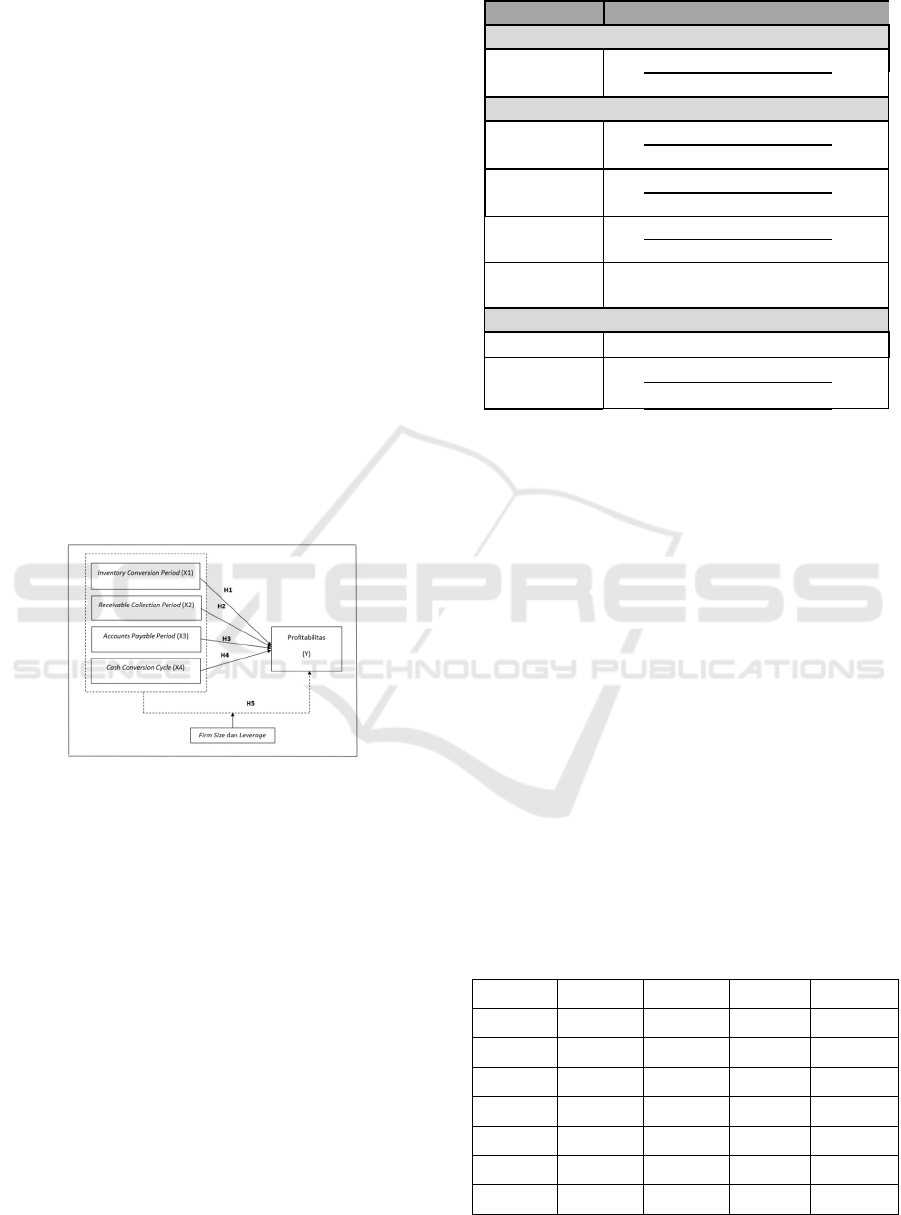
H1: Inventory Conversion Period has a significant
effect on profitability
2.5.2 Effect of Receivable Collection Period
on Profitability
RCP is the time a company takes to convert
receivables into cash. Receivables arise because of a
sale, but the company has not yet received it as cash.
So that the use of receivables is expected to increase
profits, but there are other risks arise in the form of
unpaid receivables. RCP is calculated by dividing the
number of receivables by the number of sales and
then multiplying by 365 days (Deloof, 2003).
H2: Receivable Collection Period has a significant
effect on profitability
2.5.3 Effect of Accounts Payable Period on
Profitability
APP calculates the number of days it will take to pay
its suppliers. It is calculated by dividing the accounts
payable by the cost of sales, and then multiplying by
Effect of Working Capital Management on Profitability of Manufacturing Companies Listed on the IDX
127
365 days (Deloof, 2003). The results of previous
research (Chowdhury, Alam, Sultana, & Hamid,
2018) explain that APP has a significant effect on
profitability.
H3: Accounts Payable Period has a significant
effect on profitability
2.5.4 Effect of Cash Conversion Cycle on
Profitability
CCC is a calculation to determine the period when the
company makes payments and receives cash.
Increased profit can be obtained if the company
shortens the conversion cycle.
H4: Cash Conversion Cycle has a significant effect
on profitability
H5: Inventory Conversion Period, Receivable
Collection Period, Accounts Payable Period, and
Cash Conversion Cycle is having a simultan
impact on profitability
The research model can be seen in Figure 1:
Figure 1: Research Model.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study uses a quantitative approach which is a
type of structured, systematic, and planned research
aimed at proving how the influence between the
dependent variable and the independent variable is.
The independent variable used is the working capital
management is represented by the ICP, RCP, APP,
and CCC. The dependent variable used is profitability
which is measured by GOI. The operational variables
and indicators can be seen in table 1:
Table 1: Operational variables and indicator.
Variable Indicator
Dependent Variable
GOI =
Sales-Cost of Sales
Total Assets
Independent Variable
ICP =
Inventory
X
365
Cost of Sales
RCP =
Accounts Receivable
X
365
Sales
APP =
Accounts Payable
X
365
Cost of Sales
CCC = ICP+RCP-APP
Control Variables
FS = Ln Total Sales
LEV =
Long Term Debt
Total Assets
The object in this study is the financial statements of
manufacturing companies for 2015-2019 listed on the
IDX. The data analysis technique used panel data
regression analysis using E-Views 9 software.
Descriptive statistical analysis will be used in this
study. Determination of the estimation model using
the Chow test and Hausman test. The classical
assumption test were used in this study is the
multicollinearity and heteroscedasticity test.
4 RESULT
The population data used in this study are
manufacturing companies listed on the IDX from
2015 to 2019, with 86 companies. This amount is
reduced by the criteria of the research sample. The
total sample for 2015-2019 that meets the
requirements is 86 companies or 430 data samples.
4.1 Descriptive Statistical Analysis
Table 2: Descriptive statistical table.
Variable Mean Max Min Std.Dev
GOI
24.98030 94.40000 -4.71000 17.50968
ICP 114.5353 387.8100 12.12000 71.07829
RCP 67.93681 300.3500 9.200000 4470.256
APP 47.80144 182.2100 -4.71000 28.65895
CCC 134.6705 520.3600 12.12000 91.93375
FS 14.43579 18.49000 9.200000 1.479053
LEV 15.41570 212.8600 0. 66000 18.08306
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
128
4.2 Classic Assumption Test
4.2.1 Multicollinearity Test
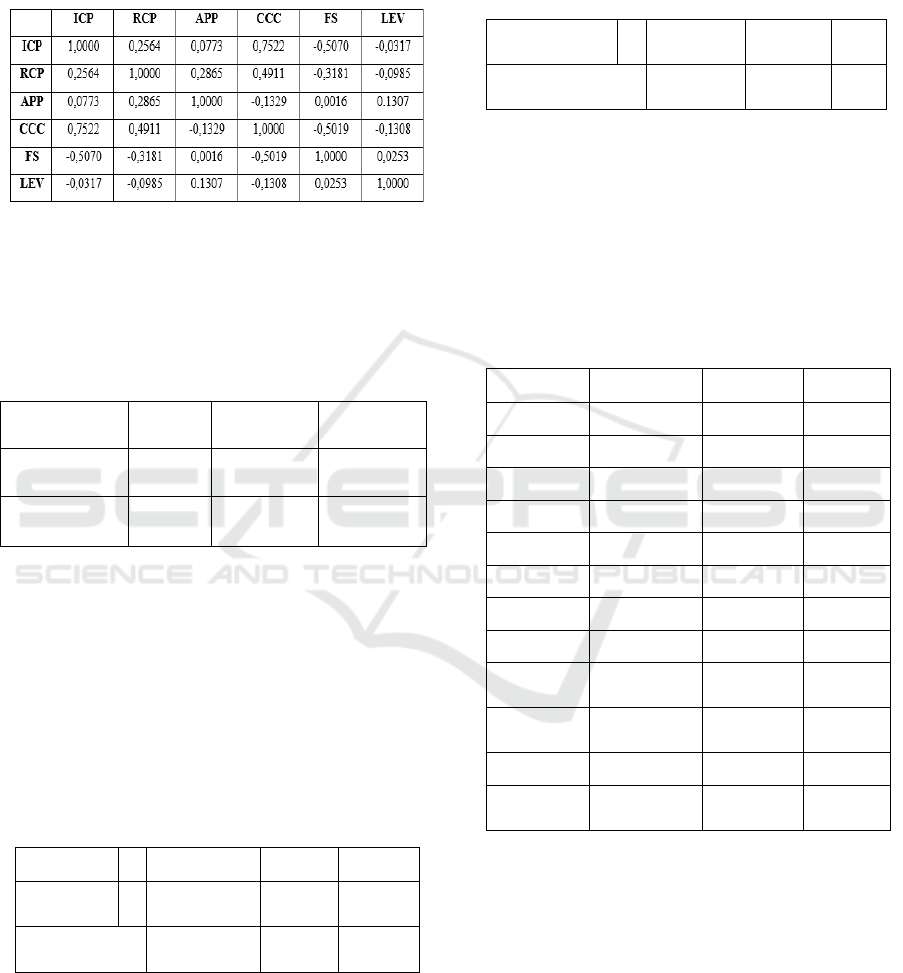
Table 3: Multicollinearity test.
The value of the correlation coefficient between
variables has a value below 0.8. This shows that the
data in this study does not have multicollinearity
problems.
4.2.2 Heteroscedasticity Test
Table 4: Heteroscedasticity test.
Heteroscedasticity test in this study using the Glejser
test. Obs *R-Squared is 10.1664, and the probability
is 0.1178, which is > of (5%). This indicates that the
data does not have heteroscedasticity problems.
4.3 Model Selection
4.3.1 Chow Test
This test aims to see whether the FEM or CEM.
Table 5: Chow Test.
Effect Test Statistic d.f. Prob
Cross-
section F
37.84328 (85,338
)
0.00000
Cross-Section
Chi-Square
1011.7788 85 0.00000
Prob. Cross-section F is greater than 5% alpha (0.000
> 0.05), which means that the best estimation model
is Fix Effect Model.
4.3.2 Hausman Test
This test aims to determine the suitable model
between FEM or REM.
Table 6: Hausman Test.
Test Summary Chi-Sq.
Statistic
Chi-Sq.
d.f.
Pro
b.
Cross-section
random
12.595621 6 0.04
99
Based on table 6, the cross-section value is smaller
than alpha 5% (0.0499 < 0.05), which means that the
best estimation model is the FEM, because the results
of the test both show that the correct model is FEM,
so it is no need to do the next test, that is the Lagrange
multiplier test.
4.4 Panel Data Regression Analysis
Table 7: Fixed Effect Model.
Variable Coefficient t-statistic Prob.
C -15,15280 -0,642977 0,5207
ICP -119,7704 -2,097767 0,0367
RCP -119,7177 -2,096778 0,0368
APP 119,6675 2,095988 0,0368
CCC 119,6884 2,096265 0,0368
FS 3,627146 2,250003 0,0251
LEV 0,011572 0,384364 0,7010
R-Squared
0.907
Adjusted
R-Squared
0.8822
Prob (F-
Statistic)
0.00000
N 75
Model
Result
Fixed
The following equation can be obtained:
GOIt = -15,1528 – 119,7704ICPt –
119,7177RCPt + 119,6675APPt + 119,6884CCCt +
3,6271FSt + 0,0115LEVt
4.5 Coefficient of Determination
The Adjusted R-squared value in table 7 shows a
value of 0.8822. The meaning of the dependent
variable in the form of GOI is influenced by
independent variables and control variables (ICP,
RCP, APP, CCC, FS, and LEV) by 88% (0.8822).
F-Statistic 1.7072 Prob F.
(3.71)
0.1177
Obs*R-
squared
10.1664 Prob. Chi-
Square(3)
0.1178
Scaled
explained SS
14.0872 Prob. Chi-
Square(3)
0.0287
Effect of Working Capital Management on Profitability of Manufacturing Companies Listed on the IDX
129

4.6 F Test
Results of the F test with the dependent variable GOI
can be shown in table 7. The probability value (F-
statistic) is 0.000003. The value is smaller than the
alpha level (5%). It means that ICP, RCP, APP, and
CCC simultaneously affect on GOI.
4.7 Data Analysis
The following is a summary table of test results from
this study:
Table 8: Summary of test result
Hypothesis Result
H1: Inventory Conversion Period
has a significant effect on
profitability
Supported
H2: Receivable Collection Period
has a significant effect on
profitability
Supported
H3: Accounts Payable Period has
a significant effect on
profitability
Supported
H4: Cash Conversion Cycle has a
significant effect on profitability
Supported
H5: Inventory Conversion Period,
Receivable Collection Period,
Accounts Payable Period, dan
Cash Conversion Cycle has
simultaneously effect on
profitability
Supported
4.7.1 Effect of Inventory Conversion Period
on Profitability
The statistical tests show that the ICP has a significant
effect on firm’s profit. The coefficient is -119.7704,
which means that the ICP negatively affects
profitability. Jin-Yap (2017) and Berg (2016)
supported these studies. This indicates that the longer
the ICP, the company's profitability will decrease,
because the longer the period required to convert
inventory to cash, the longer the company receives
money which will be used as working capital funds.
Where if the ICP is low, it will increase profitability.
A low ICP indicates that the company carries out the
process of producing and selling goods for a short
period so that there are no idle items in the warehouse.
4.7.2 Effect of Receivable Collection Period
on Profitability
The statistical tests show that RCP has a significant
affects profitability. The coefficient is -119.7177,
which means that RCP negatively effect the
profitability. Jin-Yap (2017) and Berg (2016) explain
that improving the efficiency of RCP can increase a
firm’s profit. Berg (2016) examines the effect of
WCM on companies in Norway. The independent
variable uses RCP. That shows the longer the period
for receiving accounts receivable, the company's
profitability will decrease. The longer it takes to
convert receivables into cash, it means that the more
likely the supplier company will not pay its accounts
payable.
4.7.3 Effect of Accounts Payable Period on
Profitability
The statistical tests show that APP has a significant
effect on profitability. The coefficient value is
119.6675. The results of this study are supported by
research by Ng, Ye, Ong, & Teh, (2017) and Afrifa,
Tauringana, & Tingbani (2015). Therefore, the
company is expected to know the effective WCM,
especially determining the debt deferral period. If the
debt deferral period can be appropriately managed,
then the company can maximize the profit earned.
However, the deferral period is relative, depending on
the type of industry of each company.
4.7.4 Effect of Cash Conversion Cycle on
Profitability
The statistical tests show that the CCC has a
significant effect on profitability. The coefficient
value is 119.6675, which means that the CCC has a
positive impact. The results of this study are
supported by Ng, Ye, Ong, & Teh, (2017) and Afrifa,
Tauringana, & Tingbani (2015). The findings
regarding CCC contradict with studies by Jin-Yap
(2017) and Berg (2016). According to Deloof (2003),
this difference is also due to the CCC, which is
influenced by several factors such as the ICP, RCP,
and APP. Thus, there is a difference between the size
of the CCC of each company.
5 CONCLUSION
The study has explored the relationship between
WCM and the profitability of Indonesian
manufacturing firms. It finds that ICP, RCP, APP,
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
130

and CCC have a significant effect on a firm’s profit.
This study suggests that ICP and RCP can increase
firms’ profitability by improving the efficiency of
collecting account receivables and managing the
inventories. This study also suggests that extending
the APP may be regarded as an attractive source of
financing. Firms can reserve working capital by
delaying the payment to suppliers for increased
profitability, but this must be managed properly
because if the company delays debt for too long, it
will generate interest.
REFERENCES
Afrifa, G. A., Tauringana, V., & Tingbani, I. (2015).
Working capital management and performance of listed
SMEs. Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship.
Berg, H. L. (2016). Working capital management: evidence
from Norway. International Journal of Managerial
Finance, Vol. 12 Iss 3.
Brigham, E. F., & Ehrhardt, M. C. (2017). Financial
Management: Theory and Practice 15th Edition.
Boston – United State of America: 20 Channel Center
Street.
Chowdhury, A. Y., Alam, M. Z., Sultana, S., & Hamid, M.
K. (2018). Impact of Working Capital Management on
Profitability: A Case Study on Pharmaceutical
Companies of Bangladesh. Journal of Economics,
Business and Management, Vol. 6, No. 1.
Deloof, M. (2003). Does Working Capital Management
Affect Profitability of Belgian Firms? Journal of
Business Finance & Accounting, Vol. 30(3) & (4),
0306-686X.
Ghozali, I. (2012). Aplikasi Analisis Multivariate Dengan
Program SPSS. Semarang: Badan Penerbit Universitas
Diponegoro.
Jensen, M. C., & Meckling, W. H. (1976). Theory of The
Firm: Managerial Behavior, Agency Costs and
Ownership Structure. Journal of Financial Economics,
Vol. 3 No. 4, pp. 305-360.
Jin-Yap, H. T. (2017). How Does Working Capital
Management Affect the Profitability of Vietnamese
Small and Medium Sized Enterprises? Journal of Small
Business and Enterprise Development, Vol. 24 Iss 1.
Kwatiah, K. A., & Asiamah, M. (2020). Working Capital
Management and Profitability of Listed Manufacturing
Firms in Ghana. International Journal of Productivity
and Peformance Management.
Le, B. (2018). Working capital management and firm’s
valuation, profitability and risk: Evidence from a
developing market . International Journal of
Managerial Finance.
Mamduh, M. H. (2008). Manajemen Keuangan Edisi 1.
Yogyakarta: BPFE.
Mayers, S. C., & Majluf, N. S. (1984). Corporate Financing
and Investment Decisions When Firms Have
Information That Investors Do Not Have. Journal of
Financial Economics 13, 187-221.
Ng, S. H., Ye, C., Ong, T. S., & Teh, B. H. (2017). The
Impact of Working Capital Management on Firm’s
Profitability: Evidence from Malaysian Listed
Manufacturing Firms. International Journal of
Economics and Financial Issues, Vol. 7(3), 662-670.
Richards, V. D., & Laughlin, E. J. (1980). A Cash
Conversion Cycle Approach to Liquidity Analysis.
Financial Management, Vol. 9 No. 1, pp. 32-38.
Setyanto, A. D., & Permatasari, I. (2014). Manajemen
Modal Kerja Dan Dampaknya Terhadap Nilai
Perusahaan Dengan Corporate Governance Sebagai
Variabel Pemoderasi. Akrual: Jurnal Akuntansi, 66-82.
Syafitri, R. A., & Adi Wibowo, S. S. ( 2016). Pengaruh
Komponen Modal Kerja Terhadap Profitabilitas
Perusahaan Manufaktur Yang Terdaftar Di BEI. Jurnal
Akuntansi, Ekonomi dan Manajemen Bisnis, Vol. 4, No.
1.
Effect of Working Capital Management on Profitability of Manufacturing Companies Listed on the IDX
131
