
Investment Gallery: Improving Students’ Interests
through Activities and Knowledge
Albert Ignatius Saragih
and Dwi Kartikasari
Department of Business Administration, Politeknik Negeri Batam, Jl A Yani, Batam, Indonesia
Keywords: Investment Gallery, Activities, Knowledge, Interests, Capital Market, Stock Exchange, Students
Abstract: The literacy level regarding the capital market is generally low in Indonesia; thus investment galleries are set
up to increase public awareness, interests, and participation since the early stage of student investors. This
study aims to prove whether activities done by the investment gallery and the knowledge about the capital
market impact students’ interests in learning and investing in the Indonesian Stock Exchange. Socialization,
training, and competition operate as proxies for activities. Knowledge about the capital market, the investment
gallery, and education serve as proxies for knowledge. While desire, awareness, and taking time to study
investing function as proxies for students’ interests summing up to nine indicators of three variables. The
research uses a quantitative approach by implementing multiple linear regression analysis using IBM SPSS
Statistics 22. The sample totaled 213 students of Politeknik Negeri Batam who attended any activity attributed
to the investment gallery selected using a proportionate sampling technique. The authors verified that the test
was valid and reliable. They also confirmed that the relationship between variables met the classical
assumption tests, including multicollinearity, heteroscedasticity, and normality. The results of this study
indicate that both the activities variable and the knowledge factor have a significant positive effect on
investment interest, either partially or simultaneously. Therefore, investment galleries are proven to improve
student investors’ interests in participating in the capital market through their activities and knowledge sharing.
1 INTRODUCTION
The level of literacy regarding the capital market is
generally low in Indonesia. There is less than thirty
percent of Indonesia’s population who understand
financial products and services. Furthermore, those
who understand the capital market are less than five
percent, and those who invest in it are even more
shockingly low at just around 0.4 percent. When the
last number compared to that of neighboring
countries, it is 12.8 percent in Malaysia, 30 percent in
Singapore, and 13.7 percent in China (Thamrin,
2019). Thus, investment galleries are set up to
increase public awareness, interests, and participation
since the early stage of student investors at campuses
across Indonesia.
People work not only to make money but also to
be rich. Some said that the rich get richer because of
her mindset. The rich always have the principle that
money works for her so that she does not need to work
to make money anymore. Take one of the most
expensive stocks in Indonesia, namely BCA Bank
(BBCA), whose shares are owned by the wealthiest
persons in Indonesia. They have been rich for a long
time that was why they could afford to buy the stocks.
Still, they kept on being the wealthiest by maintaining
their investment in the capital market where their
secured and profitable stocks and mutual funds return
their investment.
According to Kamus Besar Bahasa Indonesia
(Indonesian Dictionary), stocks indicate our shares in
a company. Indonesia, as a developing country and
the fourth most populous country in the world, has a
myriad of potential investments like those offered by
the capital market. The latter is no longer a strange
thing to hear, but the distrust and unawareness make
it secluded. Mr. Joko Widodo, as the President of the
Republic of Indonesia, always promoted investment
and stock exchange in previous years through
newspapers and media so that people feel more secure
in investing.
Investment galleries around the country are
obliged to promote the capital market in their settings.
The investment gallery (IG) of Politeknik Negeri
Batam (Polibatam – Batam State Polytechnic) is no
exception. The IG constantly promotes and
250
Ignatius Saragih, A. and Kartikasari, D.
Investment Gallery: Improving Students’ Interests through Activities and Knowledge.
DOI: 10.5220/0010862200003255
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science (ICAESS 2021), pages 250-255
ISBN: 978-989-758-605-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

introduces the basic to stocks 101 to Polibatam
students via its activities to ignite interest in investing
in the capital market. Students’ participation in the IG
programs is voluntary. Various financial products and
services are offered by the capital market for
investors to choose and make profits, either short or
long-term investment, depending on the style of the
investor.
Although students are not interested in investing
in the capital market, the IG still serve its purposes to
improve the financial literacy of students by
introducing them to the stock market trading
simulations and games that are proven to improve
their overall grades substantially (Harter & Harter,
2010; Smith & Gibbs, 2019). The IG holds many
education programs to make sure the student
investors are ready to invest in the capital market
reasonably once they want to get in. Studies have
shown that student investors are at risk of being
unreasonable as well as irrational to some extent
(Ray, 2009; Sairafi et al., 2008). That is why the IG
comes into play.
The IG, in cooperation with students in a study
group of capital market (Kelompok Studi Pasar
Modal - KSPM), organizes many webinars to
socialize and educate the public especially fellow
students about the advantages of the capital market.
This study did not target KSPM members only but
also students who took Finance course and used the
IG services to complete their course. This kind of
event gave students knowledge and stimulated
students to open investments account and start
becoming investor (Badriatin et al., 2021). However,
this study was not backed up empirically in a
quantitative approach; thus the finding of this study is
not applicable and not be generalized to other
contexts. Therefore, the study about an investment
gallery in our paper attempts to fill this gap.
Activities conducted by an investment gallery are
confirmed to provoke the students’ interest in
investing in the capital market (Purboyo et al., 2019).
Nonetheless, this paper only speaks about sharia
investments. Hence, our paper seeks to extend
previous research by expanding the scope of
investments to not only sharia but also conventional
stocks.
The knowledge that students have about the
capital market and the investment gallery is validated
to drive the students’ interests (Supriyanto et al.,
2019). But the latter study talks about students on its
campus only. Thus, our research makes an effort to
broaden the applicability and transferability of
previous research across different settings.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
2.1 Research Design
This paper uses a quantitative method with an
explanatory approach. The authors seek for a causal
relationship between activities and knowledge
variables to students’ interests in the investment
gallery of Politeknik Negeri Batam. A questionnaire
is distributed to samples, and data collected are
analyzed by implementing multiple linear regression
analysis using IBM SPSS Statistics 22.
2.2 Population and Samples
In this study, the population is the students of faculty
of Management and Business at Batam State
Polytechnic who attended any activity attributed to
the investment gallery by 2019, totaling 978 students.
The authors picked samples using a proportionate
sampling technique, where samples are taken from
each study program proportionately according to
population distribution. Sample number is
determined according to Isaac dan Michael formula
using a table for known population (N) up to 1000 and
confidence level of 10 percent leading to 213 samples
(Sugiyono, 2017).
2.3 Hypotheses and Framework
Activities conducted by an investment gallery
provoke the students’ interest in investing in the
capital market (Purboyo et al., 2019). Theoretically,
the AIDA model states that awareness and or
attention leads to interests (Hadiyati, 2016). The aim
of marketing is always to raise awareness and or
attract attention, then increase the consumer’s interest
and desire to act (purchase). When students
understand more deeply about the capital market
through activities held by the investment gallery, they
feel more interested in investing. Thus, the following
hypothesis is set:
H1: Activities done by the investment gallery affect
students’ interests in investing in the capital market.
The knowledge that students have drives the
students’ interests (Supriyanto et al., 2019). In
modern marketing theory, the AIDA model claims
that awareness leads to interests (Hadiyati, 2016).
When students know more broadly about the capital
market, they are more interested in investing. Thus,
the following hypothesis is set:
H2: Knowledge owned by students affects students’
interests in investing in the capital market.
Investment Gallery: Improving Students’ Interests through Activities and Knowledge
251
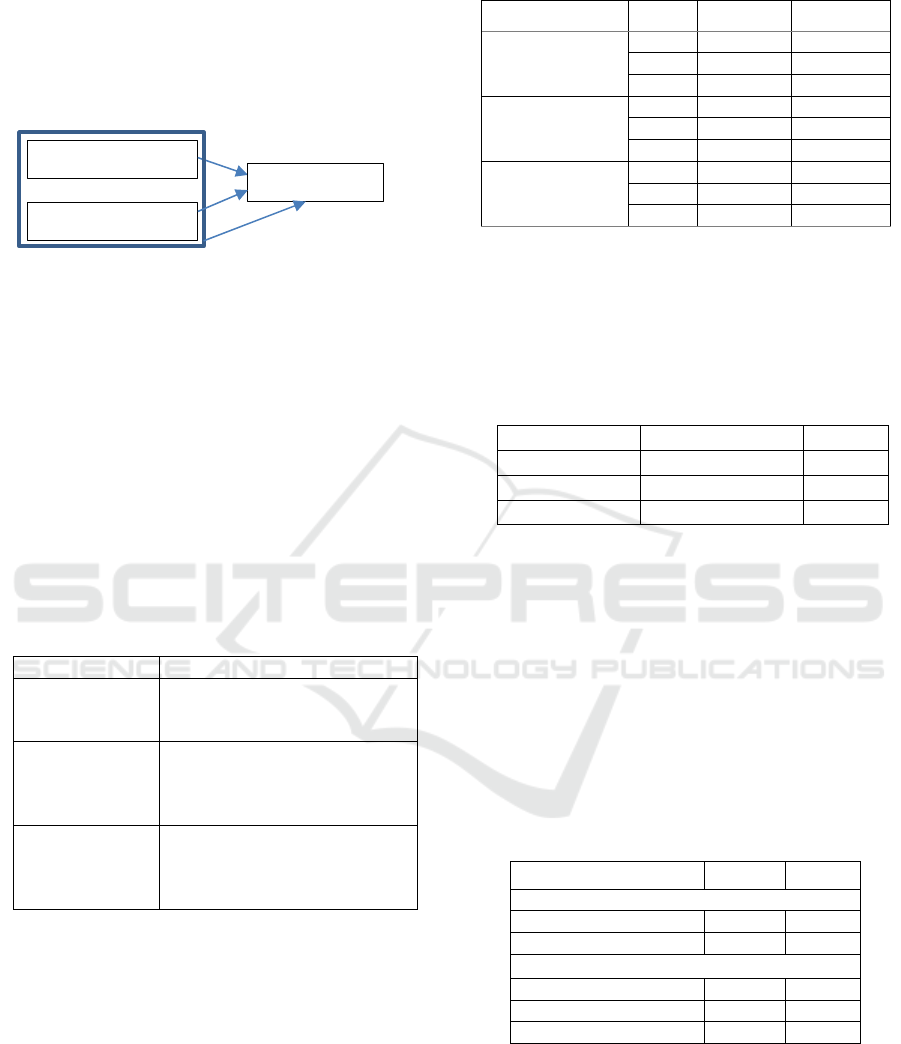
Simultaneously, both variables influence
students’ interests in investing (Hadiyati, 2016;
Purboyo et al., 2019; Supriyanto et al., 2019) as set
by the following hypothesis:
H3: Activities and knowledge affect students’
interests in investing in the capital market.
Figure 1: Research Framework
Figure 1 depicts the framework of this research
where the three hypotheses are related to one another.
2.4 Research Instrument
The authors use a questionnaire to collect data by
giving a written statement or set of questions to
respondents to be answered (Sugiyono, 2014). In this
paper, the authors use several closed statements
where the respondents answer whether they strongly
agree (4 scores), agree (3 scores), disagree (2 scores),
or strongly disagree (1 score), also known as the
Likert scale.
Table 1: Operationalization
Variable Dimension
Activity
(Purboyo et al.,
2019
)
X1.1 Socialization
X1.2 Training
X1.3 Com
p
etition
Knowledge
(Supriyanto et
al., 2019)
Knowledge about:
X2.1 The capital market
X2.2 The investment gallery
X2.3 Education progra
m
Interests
(Purboyo et al.,
2019; Supriyanto
et al., 2019)
X3.1 Desire
X3.2 Awareness
X3.3 Taking time to study
investing
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
3.1 Validity and Reliability
The authors verified that the test was valid and
reliable, as shown in table 2 and table 3 below.
Table 2: Validity Test Results
Variable Item Pearson r Remarks
Activity (X1) X1.1 0.796 Vali
d
X1.2 0.729 Vali
d
X1.3 0.784 Vali
d
Knowledge (X2) X2.1 0.801 Vali
d
X2.2 0.780 Vali
d
X2.3 0.771 Vali
d
Interests (Y) Y.1 0.786 Vali
d
Y.2 0.805 Vali
d
Y.3 0.787 Vali
d
The value of Pearson r of all items or indicators is
greater than the r table of 0.1345; thus we can claim
that all statements are valid to be used as a measuring
instrument. While the reliability test results are
demonstrated in table 3 below.
Table 3: Reliability Test Results
Variable Alpha Cronbach Remarks
Activity (X1) 0.656 Reliable
Knowledge (X2) 0.684 Reliable
Interests (Y) 0.704 Reliable
Table 3 shows that all variables have Alpha
Cronbach values greater than 0.600 so that all
variables are declared reliable.
3.2 Respondent Profile
The sample in this study is dominated by female and
managerial accounting study program. This
distribution seems reflective of the actual proportion
of students in business and management that are
primarily women and majoring in accounting, as
detailed in table 4 below.
Table 4: Respondent Profile
Cate
g
or
y
Numbe
r
Percent
Stud
y
p
ro
g
ra
m
Managerial accounting 116 54
Business administration 97 46
Gende
r
Male 35 16
Female 178 84
Total 213 100
3.3 Classical Assumptions
The author confirmed that the relationship between
variables met the classical assumption tests, including
multicollinearity and normality as exposed in table 5,
as well as heteroscedasticity as in Figure 1 below.
Activities (X1)
H1
Interests (Y)
H2
Knowledge (X2)
H3
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
252
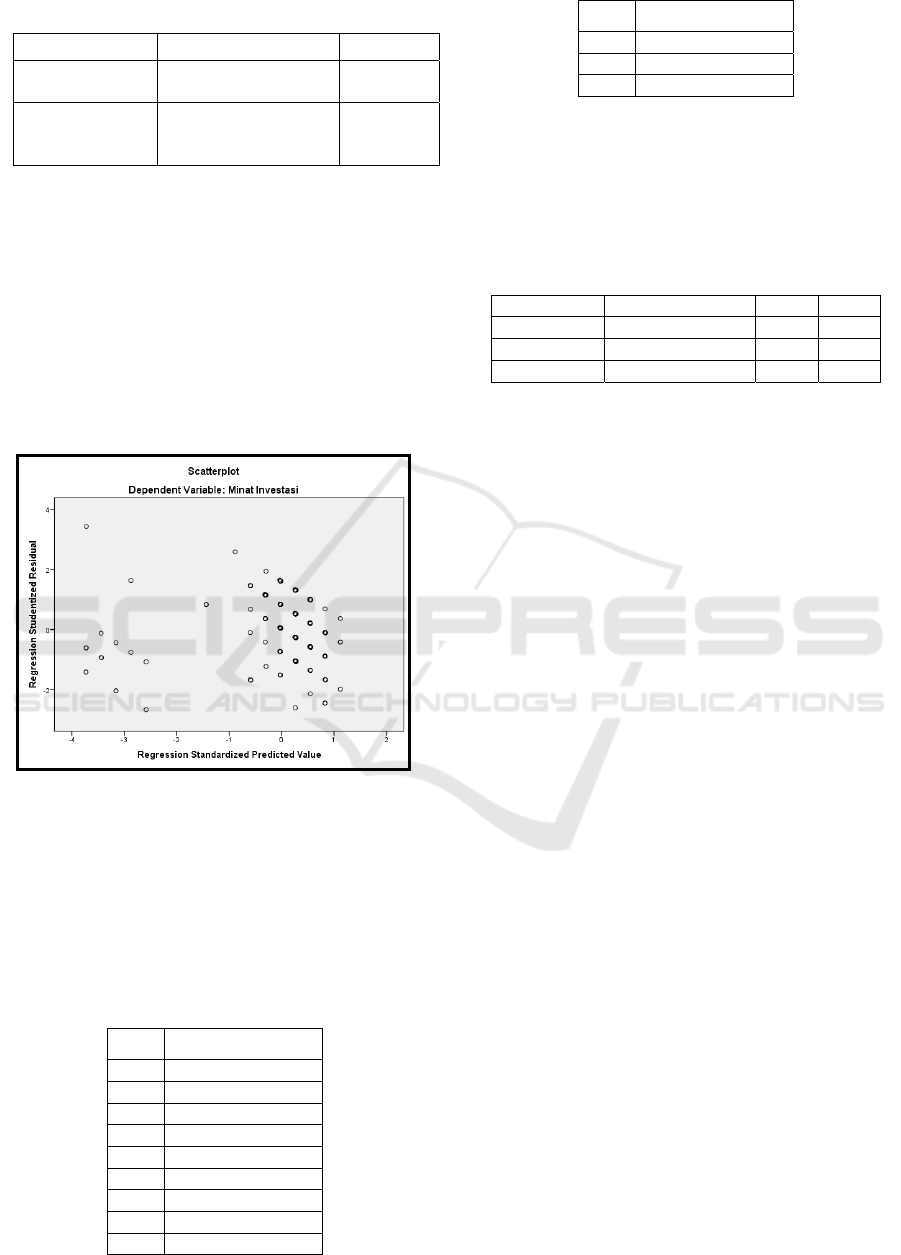
Table 5: Classical Assumptions Test Results
Test Indicator Remarks
Multicollinearity Tolerance 0.488, VIF
2.050
Not
detecte
d
Normality Kolmogorov-Smirnov
Asymp. Sig. (2-
tailed) 0.232
Not
detected
Based on the table above, it can be seen that since
tolerance values > 0.1 and VIF <10, then no
symptoms of multicollinearity problems are detected
in the regression model in this study. Likewise, the
data is claimed as normally distributed because the
significance value of the data is 0.232, which is
greater than 0.05. Meanwhile, figure 1 below reveals
that there are no specific patterns in the scatterplot
graph, so it can be said that no symptoms of
heteroscedasticity problems in the regression model
in this study.
Figure 2: Heteroscedasticity Test (scatterplot) Results
3.4 Descriptive Statistics
Table 6 below shows that the activity variable (X1)
captures the most awareness to students at 3.41, with
socialization activity (X1.1) being the highest value
at 3.46.
Table 6: Descriptive Statistics
Item Mean (out of 4.00)
X1.1 3.46
X1.2 3.41
X1.3 3.36
X1 3.41
X2.1 3.31
X2.2 3.27
X2.3 3.28
X2 3.28
Y.1 3.32
Item Mean (out of 4.00)
Y.2 3.34
Y.3 3.30
Y 3.32
3.5 Hypotheses Testing
Table 7 below shows that partially activity variable
(X1) or knowledge variable (X2) affect students’
interests in a statistically significantly manner.
Table 7: Partial Regression Results
Model Unstandardized B t Sig
Constant 1.960 3.835 0.000
Activit
y
* 0.394 6.053 0.000
Knowled
g
e* 0.404 5.931 0.000
* Statistically significant
The t threshold value of 1.971 is found in the
table for df (degree of freedom) equals (213-2) =
(211) with a significance level of α = 5%. Table 7
indicates that activity (X1) amounted to 6.053> t
tabel
1.97 and sig value of 0.00 <0.05; hence H1 is
confirmed, and it can be stated that the activity (X1)
has a partially positive effect on the investment
interest variable. While the value of t
knowledge
(X2) is 5.931 > t
tabel
1.97 and sig value of 0.00 < 0.05
hence H2 is confirmed and it can be stated that the
knowledge (X2) has a partially positive effect on the
investment interest variable.
Based on the simultaneous F test, SPSS results in
the value F at 126.259 with a sig value of 0.000 while
the F threshold with 5% significance
was 3.04.
Because the value of F 126,259 > 3.04 and sig value
of 0.00 < 0.05 hence H3 is confirmed and it can be
stated that both variables of the activity (X1) and the
knowledge (X2) have a simultaneously significant
positive effect on the investment interest variable.
3.6 Discussions
This research affirms previous studies (Hadiyati,
2016; Purboyo et al., 2019; Supriyanto et al., 2019),
proving that awareness that stimulated by variables
of activity and knowledge significantly influences
students’ interests. However, this study extends the
context from a previously sharia environment to a
more generalized setting. Furthermore, this study
enriches literature in a way that it finds the
simultaneous significant positive effect of these two
factors (H3) on students’ interests especially given
the fact that the two reference studies did not test this
hypothesis and only tested separate effects.
Investment Gallery: Improving Students’ Interests through Activities and Knowledge
253

Provided the consistency of this finding with
previous researches, this study implies that it is
imperative for managers of investment galleries
across Indonesia to pay great attention to plan
successful activities to stimulate students’ interests
and further sales in the capital market’s products and
services. It is evident that students appreciate
updated and relevant socialization about the products
and services. The student investors tend to accept
services from the capital market once they are
introduced by their fellow in the investment gallery;
hence the capital market and Indonesia Stock
Exchange should collaborate strongly with the
investment gallery in each campus. All institutions
should work hand in hand to build a good reputation
and respectable opinions of the capital market’s
products and services among potential investors.
Future studies might find disparities of outcome
where they might be caused by differences in the
respondents’ culture that result in distinct behavior.
Activities vary in different campuses and regions.
For example, socialization, training, and competition
exist in Politeknik Negeri Batam, but might not in
other campuses. Hence this study calls for researches
in diverse settings in the future.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This research affirms previous studies proving that
activities held by the investment gallery, including
socialization, training, and competition positively
associated with students investors’ interests.
Likewise, knowledge owned by student investors
about the capital market, the investment gallery, and
education program positively affect student
investors’ interests. Last but not least, both variables
of activity and knowledge simultaneously impact
students’ interests.
It is important to note that this study extends the
context from the previously sharia setting.
Furthermore, this study enriches literature in a way
that it finds the simultaneous significant positive
effect of these two factors of activity and knowledge
on students’ interest given the fact that past studies
only tested separate effects.
Provided the consistency of this finding with
previous researches, this study implies that it is
imperative for managers of investment galleries
across Indonesia to pay great attention to plan
successful activities to stimulate students’ interests
and further sales in the capital market’s products and
services. It is obvious that students appreciate
updated and relevant socialization about the products
and services. The student investors tend to accept
services from the capital market once they are
introduced by their fellow in the investment gallery;
hence the capital market and Indonesia Stock
Exchange should collaborate strongly with the
investment gallery in each campus. All institutions
should work hand in hand to build a good reputation
and respectable opinions of the capital market’s
products and services among potential investors.
Future studies might find disparities of outcome
where they might be caused by differences in the
respondents’ culture that result in distinct behavior.
Activities vary in different campuses and regions.
For example, socialization, training, and competition
exist in Politeknik Negeri Batam, but might not in
other campuses. Hence this study calls for researches
in diverse settings in the future.
REFERENCES
Badriatin, T., Setiawan, I. A., & Rahayu, S. T. (2021).
Webinar Event about Capital Market Intellectuals in the
Digital Age, as a Form of Socialization, Education and
Scientific Understanding of the Capital Market. Journal
of Character Education Society, 4(2), 514–521.
Hadiyati, E. (2016). Study of Marketing Mix and Aida
Model to Purchasing on Line Product in Indonesia.
British Journal of Marketing Studies, 4(7), 49–62.
http://www.eajournals.org/wp-content/uploads/Study-
of-Marketing-Mix-and-Aida-Model-to-Purchasing-
On-Line-Product-in-Indonesia.pdf
Harter, C., & Harter, J. F. R. (2010). Is Financial Literacy
Improved by Participating in a Stock Market Game?
Journal for Economic Educators, 10(1), 21–32.
Purboyo, Zulfikar, R., & Wicaksono, T. (2019). Pengaruh
Aktivitas Galeri Investasi, Modal Minimal Investasi,
Persepsi Risiko, dan Persepsi Return terhadap Minat
Investasi Saham Syariah. Jurnal Wawasan Manajemen
(Universitas Lambung Mangkurat), 7(2), 136–150.
Ray, K. K. (2009). Investment Behavior and the Indian
Stock Market Crash 2008: An Empirical Study of
Student Investors. IUP Journal of Behavioral Finance,
6(3/4), 41–66.
Sairafi, K., Selleby, K., & Stahl, T. (2008). Behavioral
Finance: The Student Investor. Jonkoping International
Business School, March.
Smith, C. M., & Gibbs, S. C. (2019). Stock market trading
simulations: Assessing the impact on student learning.
Journal of Education for Business, 95(4), 234–241.
https://doi.org/10.1080/08832323.2019.1643279
Sugiyono. (2014). Metode Penelitian Pendidikan
Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif dan R&D. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
Sugiyono. (2017). Metode Penelian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif
dan R&D. Bandung: CV. Alfabeta.
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
254

Supriyanto, R. G. E., Andayani, E., & Arsy, A. F. Al.
(2019). Pengaruh Preferensi Resiko, Literasi Ekonomi,
Pengetahuan Galeri Investasi terhadap Minat Investasi
Mahasiswa Fakultas Ekonomika dan Bisnis. Jurnal
Riset Pendidikan Ekonomi, 4(1), 1–7.
Thamrin, H. (2019). Socialization and Training on
Implementation of Investment Selection Strategies.
ICCD, 2(1), 528–532.
https://doi.org/10.33068/iccd.Vol2.Iss1.261
Investment Gallery: Improving Students’ Interests through Activities and Knowledge
255
