
Development of Accounting Application for MSMEs based
on Cloud Computing
Supardianto, Nelmiawati, Maidel Fani and Hamdani Arif
a
Informatics Engineering Department, Batam State Polytechnic, Jl. Ahmad Yani No 1 Batam Centre, Batam, Indonesia
Keywords: information technology, accounting application, cloud computing, rapid application development
Abstract: A good accounting or financial governance is the most important factor in development of Micro, Small and
Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). Ability to create a good transaction record produces a strong financial report
which is one way of good governance examples done by MSMEs. A good quality financial report contains
information that is trustworthy, straightforward, appropriate, reliable, relational, and understandable. They
are essential since they will be utilized in making a decision to determine direction of MSMEs development.
An efficient accounting application is necessary to assist MSMEs in creating essential financial reports such
as accounting journal, general ledger report, balanced list, income statement, and statement of capital changes.
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is an application design approach used to build the application.
System analysis began with a literature review, followed by creation of designs, prototypes, and collected
user input requirements. The application was tested using a Black-Box testing approach and have been
developed with Cloud Computing technology. There is a Software-as-a-Service in Cloud Computing
technology that has the benefit of being able to be run by multiple customers and without requiring them to
purchase extra infrastructure. This is due to features of start-up in the early stage, thus there is no need to
invest in an extra infrastructure. Therefore, cloud application development by utilizing Software-as-a-Service
technology is the right solution.
1 INTRODUCTION
A good accounting or financial governance is the
most important factor in development of Micro,
Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). A strong
financial governance produces a good quality of
financial report based on good transaction records.
A good quality of financial report offers
information that is trustworthy, straightforward,
appropriate, reliable, relational, and understandable.
It is important since it will be used as a basis for
decision-making of MSMEs development (Fiesgrald
Wungow et al., 2016).
Many MSMEs lack of strong accounting and
financial literacy (Supardianto et al., 2019), creating
a financial report preparation was challenging. A
numerous forms of financial reports that must be
produced impede the development of MSMEs.
The use of technology in all MSMEs financial
management activities also play a role in their success
and growth. Accounting software is one of example
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4925-9465
on how technology can be used to accomplish many
activities. The usage of this software may be a
solution towards freshly created MSMEs that do not
have an accountant or could not afford for engaging
one (Vanessa Dawson, 2016).
Financial statements are data records of an
industry in an accounting period that describe the
industry's performance. Bankers, creditors, owners,
and other interested parties can utilize financial
reports to analyze and evaluate financial performance
and industry circumstances.
Financial statements are the result of an
accounting process that provides financial data of an
industry that is useful for interested parties in making
economic decisions. The financial statement consists
of five various, namely accounting journal, general
ledger report, balanced list, income statement, and
statement of capital changes.
Supardianto, ., Nelmiawati, ., Fani, M. and Arif, H.
Development of Accounting Application for MSMEs based on Cloud Computing.
DOI: 10.5220/0010935600003255
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science (ICAESS 2021), pages 435-443
ISBN: 978-989-758-605-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
435

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Financial Statement
Financial statements are a report of transaction
records that occur in a business, such as purchase
transactions or sales transactions. Financial reports
are records of information about a company's
performance during accounting period. Financial
statements allow banks, creditors, business owners,
and other interested parties to analyse and interpret
company's financial performance and condition
(Anggraini & Putri, 2021). Financial reports depict
company's current economic state over a specific time
period. The goal of financial statements is to show
current conditions of company's financial situation at
a specific date (on the balance sheet) and time period
(on the income statement). Balance sheets, income
statements, changes in equity, and cash flow reports
are examples of financial statements (Ismail &
Suhami, 2021)
Figure 1: Service on Cloud Computing (T. Chou, 2010)
2.2 Cloud Computing
An application of technology in accounting
administration aims to increase number of tax payers
and tax income. The usage of this technology allows
for improved on automation and data collection
(Cotton & Dark, 2017). Cloud Computing technology
may be the greatest choice for developing systems that
may solve these challenges.
In terms of computer technology, Cloud
Computing has a potential to alter the view on
infrastructure investment. Previously, investment in
computer technology was seen as an asset; now, Cloud
Computing may be regarded as an investment in
computing as a service provider (De Paula & De
Figueiredo Carneiro, 2016). Cloud Computing
technology is a synthesis of technology and business,
and it has emerged as a potential commercial
computing paradigm. The goal is to make
infrastructure administration less complicated for
users.
Cloud Computing is a computer technique that uses
dynamic and scalable resources that can be shared
electronically and accessed over the internet (Wu et
al., 2010). Cloud Computing is a computer approach
in which the Internet plays primary role. The cloud
may be seen as a shared resource in which programs
and information are made available to users on
demand. In general, Cloud Computing technology is
used to run on Internet application. Since the program
is already available on the Internet, common user does
not require to install it. Services in Cloud Computing
can be seen at Figure 1.
Cloud Computing has three services offered, i.e
Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service
(PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) (Zhang
et al., 2010). SaaS is a service that delivers
applications so that customers do not need to install
and access them over the Internet; consumers also do
not need to consider how data is kept or how
applications are managed. PaaS is a platform-as-a-
service that allows developers to build applications on
a customizable platform. IaaS seeks to offer virtual
hardware technology to customers, so that they do not
need to physically install their gear at workplace, but
may be accessed or remotely over the Internet.
SaaS is a service in which software and
applications are developed on a platform supplied by
the PaaS layer. It is concerned with end-users since
end-users may access and employ cloud provider-
created applications (E & R, 2013; Katyal & Mishra,
2013). It also enables customer to access applications
through cloud infrastructure using thin/thick client
interfaces such as Mozilla Firefox and Internet
Explorer.
Users do not actively manage or control cloud
infrastructure, such as networks, servers, operating
systems, and storage media, with the potential of
exceptions from restricted circuits of users with
particular application settings. This paradigm has a
potential to deliver significant benefits to both
consumers and providers of Cloud Computing
services (Youseff et al., 2008). SaaS services have
several advantages, among others (Kulkarni et al.,
2012; Mather et al., 2009; Thakral & Singh, 2014):
Reducing the cost of application software
licenses.
Enables several customers to use the same
program at the same time.
The application provider is in charge of
controlling and restricting the application's use.
SaaS consumers do not need to purchase
infrastructure since it provides by the cloud
service provider.
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
436

3 RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Research Tools and Materials
The tools used to support this research are as follows:
Microsoft Visio 2016 is a program for creating
UML system models.
PHP and HTML are computer languages that
are used to create web-based applications.
MySQL is a database management system
(DBMS) that is used to manage databases.
3.2 Research Approach
The research was conducted by created an application
system with a goal of designed and developed of
cloud-based accounting application that has been
utilized by MSMEs to easily create financial
statements reports.
3.3 Application System Development
A MSMEs accounting application system takes the
advantage of Cloud Computing and Software-as-a-
Service. The program has been hosted on the cloud
for users to access on the Internet through a browser.
The program was used to create financial
statements such as an accounting journal, general
ledger report, balanced list, income statement, and
statement of capital changes. Software Development
Life Cycle (SDLC) was used in system development,
such as Rapid Application Development (RAD)
paradigm. The process includes analysis and rapid
design, prototype cycles, testing, and
implementation. There were three processes in the
prototype cycle stage: construct, showcase, and
refine. Flow diagram of the application system
development can be seen in Figure 2.
Figure 2: The Flow Diagram of the Application System
Development
3.3.1 Analysis and Quick Design Phase
RAD was started through project requirement
identification process. At this point, the team must
identify which requirements to be satisfied by a
project. This preliminary stage is excellent for
presenting a high-level overview of the project.
The process continues to design a cloud-based
taxation application, among others. Making UML
diagrams that consist of use case diagrams, activity
diagrams, making database schemes, and designing
the interface design of the application that will
developed.
3.3.2 Prototyping Cycles Phase
At this stage, developer designs an application
prototype with various features and functions. The
goal is to evaluate whether the prototype that is
produced is consistent with the original concept. This
procedure allows for an investigation of any mistakes
that may arise later. It is important for error reduction
and debugging.
The development of application program has been
done by using IDE Visual Studio Code software with
PHP programming language, Zilla, Putty File
software to put the application in the Cloud.
3.3.5 Testing Phase
The application that was developed in the prototype
stage has been tested at this step-in order to obtain
feedback from users. The procedure has been
repeated until the final step, which is the product's
implementation and finalization.
Application system testing were done by
functional testing of each module section of the
program, whether it was running following the
functions of system design. Testing using Black-Box
testing focuses on logic, functionality, and minimize
errors as well as ensure the resulting output is as
expected.
3.3.6 Implementation Phase
At this step, developer was verified any flaws
discovered throughout program development process
who have been resolved. This work includes
enhancing the application's steadiness, refining the
interface, doing maintenance, and produced
documentation.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 System Overview
System overview design is shown in Figure 3.
Development of Accounting Application for MSMEs based on Cloud Computing
437

Figure 3: System Overview
Note:
1. A user will enter data transaction process. Data
transaction process consists of debit and credit
transactions. The data will be sent to the
application and stored in the database.
2. The application will provide an output report
according to data transaction that has been input
by user. The application will automatically
generate and display a report.
There are two main processes contained in the
accounting application i.e.:
The process of recording transactions.
The first step taken by the application user is to
record the transactions that occur in the business
activities. This transaction recording process
requires user to provide a number for each
transaction that occurs. This number intends to
make each transaction have an identity.
The process of creating a report.
After calculation has been done and the
application calculates per transaction, the
application displays financial report such as an
accounting journal, general ledger report,
balanced list, income statement, and statement
of capital changes.
4.2 System Requirements Analysis
4.2.1 Functional Requirements Analysis
Functional requirements analysis identifies the
processes that will be carried out by the system. The
functional requirements of accounting applications
for MSMEs based on cloud-based i.e.:
1. Add transactions.
2. View accounting journal.
3. View ledger report.
4. View balanced list.
5. View income statement.
6. View statement of capital changes.
4.2.1 Non-functional Requirements Analysis
Analysis of non-functional requirements identify
behaviour property owned by the system. The needs
of non-functional accounting applications for
MSMEs were as follows:
Availability
System availability is a capacity to offer
services to users. Except for system
maintenance or system upgrades, the system can
function continuously for 24 hours.
Availability guarantees that users may obtain
information and utilize the program at any time.
Ergonomic
Ergonomic refers to the interaction of system or
application users. The program that is created
must be efficient or user friendly. This is due to
the fact that application users are ordinary users
who are not all familiar with computers.
Portability
The applications can be accessed on any
platform or operating system capable of running
web-based applications. It is designed for
consumers to be able to access apps from any
devices.
Security
To maintain data security, the user's browser
must be able to obtain an SSL certificate from
the system. It is restricted to the Internet, and
trials for offline access are not available.
4.3 Design System
4.3.1 Use Case Diagram
The accounting application use-case diagram for
cloud-based start-ups can be seen in Figure 4:
User
Add Transactions
View accounting journal
View ledger report
View balanced list
View income s tatement
Registration
Login
<<in clude>>
<<in clud e>>
<<i nclud e>>
<<i nclud e>>
<<i nclud e>>
View statement o f capital changes
<<in clud e>>
Figure 4: Use Case Diagram
4.3.2 Design Table
Database used in development of accounting
applications for cloud-based is a MySQL database
that consists of several tables as follow:
TB_User
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
438
Table 1 contains user data (MSMEs) that
register to be able to use the application.
Table 1: TB_Business_Identity
No. Field
Data
Type
Note
1 id_user int(11)
An auto-
increment that use
as the id of the
user
2
nama_usa
ha
Varchar
(50)
The name of the
user’s business
3 email
Varchar
(50)
Full email from
user
4 password
Varchar
(50)
The password
used by the user
5
tahun_ber
diri
Int (4)
Years of the
user’s business
stood
6
status_usa
ha
Varchar
(20)
The legal status of
the business of the
user
7
deskripsi_
usaha
text
Description of the
user’s business
TB_Faktur
Table 2 contains invoice data recorded by user
in the form of transaction activities of the
ongoing business.
Table 2: TB_Transaction
No. Field
Data
Type
Note
1
id_fak
tur
int(11)
An auto-increment
that use as the id of
a transaction
invoice
2
id_use
r
int(11)
Foreign key from
table TB_business_
identity
3
descri
ption
Varchar
(50)
Invoice number
used on each
invoice
4
tgl_fa
ktur
Date
The date the invoice
transaction occurred
5 file
Varchar
(50)
The name of the
buyer of the
transaction that
occurred
TB_Detail_Transaction
Table 3 contains detail data from transaction
which have been made by users be recorded into
the application.
Table 3: TB_Detail_Transaction
No Field
Data
Type
Note
1 id_detail int(11)
An auto-increment
that use as the id
of a tax deposit
2 Id_faktur int(11)
Foreign key the id
of a transaction
3 id_user int(11)
Foreign key from
table
TB_business_
identity
3
account_
name
Varchar
(50)
Account name
4 amount
Varchar
(20)
Amount
5
descriptio
n
Int (11)
Description
transaction
6
State_acc
ount
Enum
(debit,
kredit)
State transaction
account
4.4 Implementation System
4.4.1 Register
Figure 5 displays a registration form that allows users
to register to be able to use the application.
Figure 5: Register
4.4.2 Login
Figure 6 displays a login form that users can use to
enter the application. On the login page, the user will
be validated whether the user is registered or not.
Development of Accounting Application for MSMEs based on Cloud Computing
439

Figure 6: Login
4.4.3 Add Transactions
Figure 7 displays an added transaction form. It was
used for those who want to record transactions and
will be stored in database.
Figure 7: Add Transactions
4.4.6 Accounting Journal Report
Figure 8 displays an accounting journal report. This
page display data transaction per date when user add
transactions.
Figure 8: Accounting Journal
4.4.7 Ledger Report
Figure 9 contains information about ledger report.
This page display data per account name and status
account where is debit or credit.
Figure 9: Ledger Report
4.4.8 Balance Book Report
Figure 10 is a page for view balance book. Balance
book is a list containing the balances (difference
between total debits and total credits) of each account
in the general ledger on a certain date. The purpose of
making a balance list is to find out the balance of each
account and check that the balance of the accounting
equation is maintained.
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
440
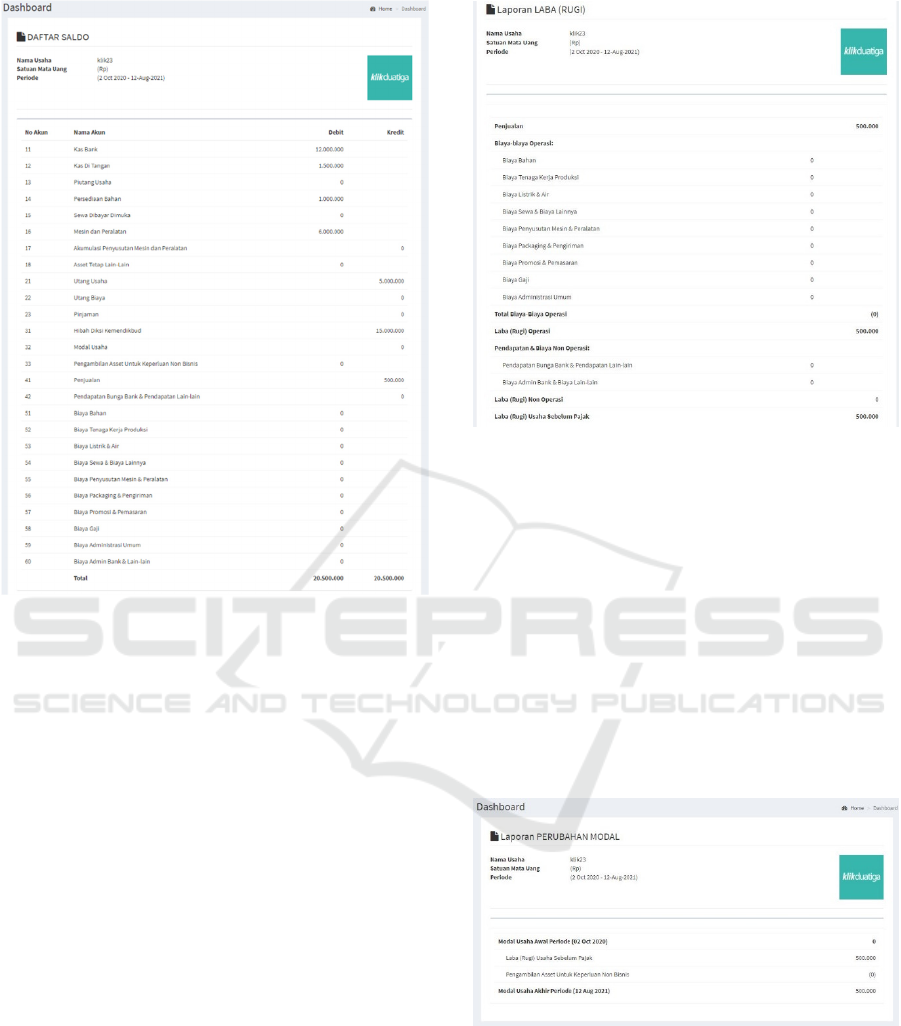
Figure 10: Balance List
4.4.9 Income Statement
Figure 11 displays income statement. Income
statements that a company must have after the
balance sheet and cash flow. From the report, we can
see how much income and expenses are borne by the
company in a certain period of time.
Figure 11: Income Statement
4.4.10 Statement of Changes in Capital
Figure 12 displays statement of changes in capital.
Statement of Changes in Capital is a financial report
of a service company that shows the causes of
changes in capital, from initial capital to end of period
capital.
In the report on changes in capital, it shows that
by calculating the owner's capital at the beginning of
the period, adding to the net profit as stated in the
profit/loss statement, then subtracting it from the
owner's personal take (private), so that the owner's
capital at the end of the period is obtained.
Figure 12: Statement of Changes in Capital
Development of Accounting Application for MSMEs based on Cloud Computing
441
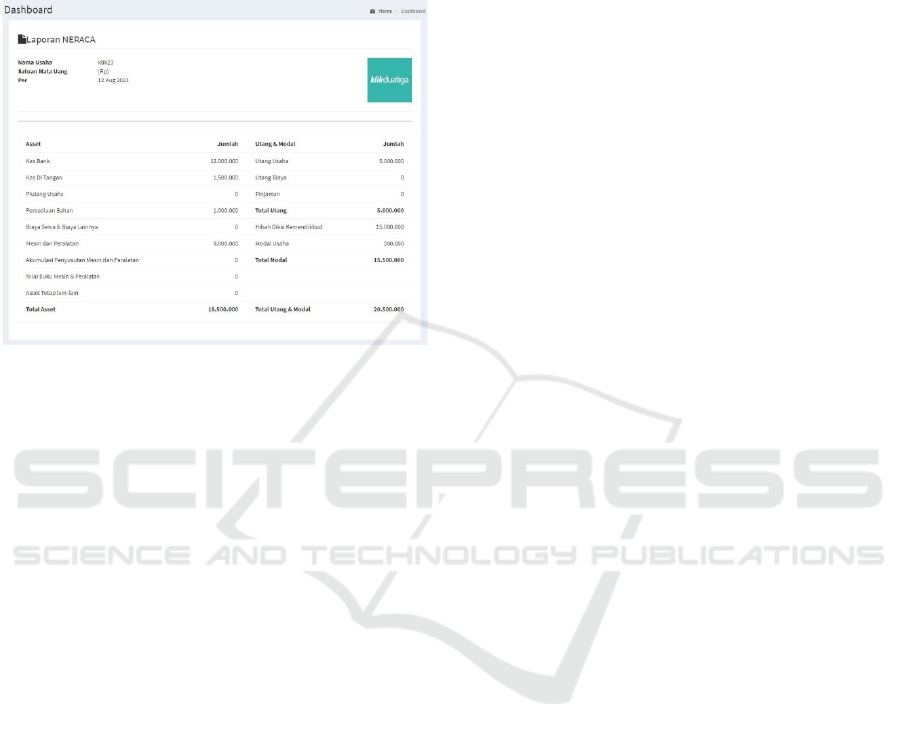
4.4.11 Balance Sheet
Figure 13 displays a balance sheet. Balance sheet is a
financial statement that presents the total assets,
liabilities (debt), and equity (capital) of the company
at a certain time period.
Figure 13: Balance Sheet
4.5 System Testing
Functional testing for Accounting Application Cloud
Computing-based were performed by using Black-
Box testing methods, which involves outcome
execution by using data test and evaluated the
functionality of the application. Findings on
functionality testing demonstrated that the
application provides relevant functionality.
4.6 Discussions
Development of accounting application helps
MSMEs to record sales transactions. This application
also helps MSMEs to generate financial report such
as accounting journal, ledger report, balanced list,
income statement, and statement of capital changes.
The program was used to create financial statements
such as an accounting journal, ledger report, balanced
list, income statement, and statement of capital
changes. This application produces a simple financial
report for those MSMEs who do not have an
accounting.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of development and evaluation
of applications that have been carried out,
conclusions are as follows:
1. Application can record and stored data
transactions to database.
2. Accounting applications that have been built for
MSMEs can create financial statement such as
accounting journal, ledger report, balanced list,
income statement, and statement of capital
changes automatically.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is fully funded and supported by Politeknik
Negeri Batam under “Penelitian Internal P2M”.
REFERENCES
Anggraini, L. D., & Putri, A. U. (2021). Implementation of
SAK-EMKM Towards Controlling Financial
Statements on Msmes in Palembang City. Ijisrt.Com,
6(2), 437–441.
https://ijisrt.com/assets/upload/files/IJISRT21FEB372.
pdf
Cotton, M., & Dark, G. (2017). Use of Technology in Tax
Administrations 2 : Core Information Technology
Systems In Tax Administrations. IMF Technical Notes
and Manuals.
De Paula, A. C. M., & De Figueiredo Carneiro, G. (2016).
Cloud Computing adoption, cost-benefit relationship
and strategies for selecting providers: A systematic
review. ENASE 2016 - Proceedings of the 11th
International Conference on Evaluation of Novel
Software Approaches to Software Engineering, Enase,
27–39. https://doi.org/10.5220/0005872700270039
E, E., & R, G. (2013). Cyber Security and Reliability in a
Digital Cloud. US Dep. Def. Sci. Board Study, January.
Fiesgrald Wungow, J., Lambey, L., & Pontoh, W. (2016).
Pengaruh tingkat pendidikan, masa kerja, pelatihan dan
jabatan terhadap kualitas laporan keuangan pemerintah
Kabupaten Minahasa Selatan. JURNAL RISET
AKUNTANSI DAN AUDITING “GOODWILL,” 7,
174–188.
Ismail, B., & Suhami, H. (2021). Making Guidance of
Financial Reports Using the Application and Improving
Company Profile for B2b Promotion on Indonesia
Leather Shoes MSMEs. 1st ICEMAC 2020:
International Conference on Economics, Management,
and Accounting, 2021, 71–80.
Katyal, M., & Mishra, A. (2013). A Comparative Study of
Load Balancing Algorithms in Cloud Computing
Environment. Int. J. Distrib. Cloud Computing, 1 no. 2.
Kulkarni, G., Chavan, P., Bankar, H., Koli, K., & Waykule,
V. (2012). A new approach to software as service cloud.
2012 7th International Conference on
Telecommunication Systems, Services, and
Applications, 196–199.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TSSA.2012.6366050
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
442

Mather, T., Kumaraswamy, S., & Latif, S. (2009). Cloud
Security and Privacy (First Edit). O’Reilly Media, Inc.
https://doi.org/978-0596802769
Supardianto, Ferdiana, R., & Sulistyo, S. (2019). The role
of information technology usage on startup financial
management and taxation. Procedia Computer Science,
161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.11.246
T. Chou. (2010). Introduction to Cloud Computing. Cloud
Book.
Thakral, D., & Singh, M. (2014). Virtualization in Cloud
Computing. Journal of Information Technology &
Software Engineering, 04(02), 1262–1273.
https://doi.org/10.4172/2165-7866.1000136
Vanessa Dawson. (2016). How To Manage Your Startup’s
Finances From Day One.
https://www.forbes.com/sites/vinettaproject/2016/09/2
7/how-to-manage-your-startups-finances-from-day-
one/#2b6e379d271e
Wu, J., Ping, L., Ge, X., Ya, W., & Fu, J. (2010). Cloud
storage as the infrastructure of Cloud Computing.
Proceedings - 2010 International Conference on
Intelligent Computing and Cognitive Informatics,
ICICCI 2010, 380–383.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICCI.2010.119
Youseff, L., Butrico, M., & Da Silva, D. (2008). Toward a
Unified Ontology of Cloud Computing. 2008 Grid
Computing Environments Workshop, 1–10.
https://doi.org/10.1109/GCE.2008.4738443
Zhang, Q., Cheng, L., & Boutaba, R. (2010). Cloud
Computing State of the art and research.pdf. Journal of
Internet Services and Applications, 7–18.
Development of Accounting Application for MSMEs based on Cloud Computing
443
