
Organizational Development at Human Resources Department of
Export-oriented Semiconductor Manufacturing Company
Wanda Abubakar
1
and Yudo Anggoro
2
1
Human Resource Department, PT. Infineon Technologies Batam, Indonesia
2
School of Business and Management, Institut Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia
Keywords: Organizational development, Sustainable performing organization, Human Resources, Decision making,
Alternative Solutions.
Abstract: 2020 was a challenging business year. Pandemic was unprecedented situations required speedy and well-
thought actions in managing business with upholding health and safety of the employees as company’s utmost
priority. The Human Resources (HR) Department plays critical role to sustain employees’ safety and health
as well as their motivation. Despite many achievements, to stay relevant in the future, HR must continuously
evolve. This paper will firstly identify categories of high-performing HR organization which enable
organization to achieve sustainable performance. In addition, this paper will also propose and select best-fit
solutions from identified organizational alternatives. The author elaborates conceptual framework of 5-Star
model from Jay Galbraith as reference in Organizational Development (OD) initiatives. The author combines
the framework with the 7-steps approach to systematically develop the framework. The author initiates OD
with business analysis conducted during the departmental review. The result of workshop is presented in the
SWOT analysis format. To confirm the SWOT, author conducts quantitative and qualitative survey to internal
and external organizational stakeholders. Once the focus category is clarified, the organization alternatives
are developed and selected. Lastly, after confirming the best-fit solution, work-packages on how to improve
each category are developed and prioritized as executable actions.
1 INTRODUCTION
The semiconductor manufacturing company in
Batam Island produces outputs with export-oriented
market. The operation is subjected to global supply
and demand curves. When world economy slow-
down due to trade-war between USA and China
followed by COVID-19 pandemic in the late 2019 to
2020, the company experienced significant
contraction which hindering its further growth.
Challenges were multiplied when prolonged
pandemic created new-ways of doing things, then
followed by emergence of regulatory restrictions
which impacted everyone personally and
professionally. However, things were rapidly
changing in 2021 as endorsed by Semiconductor
Industry Association (SIA) on World Semiconductor
Trade Statistics (WSTS) in Spring 2021 global
semiconductor sales forecast, which projects the
industry’s worldwide sales will be $527.2 billion in
2021, a 19.7% increase from the 2020 sales total of
$440.4 billion (Dan, R., 2021).
It is important to note that high performing
companies are putting their people first as the key
success factors to strive in the business competition.
While the business leaders are working feverishly to
manage companies’ profitability, however, pandemic
situation creates critical needs for leaders to invest in
protection of their employees as prerequisite of
organization's long-term survival (Gabsa, R., &
Rastogi, S., 2020). It is also found that an
organization whose mission combines revenue
growth with the need to respect and support its
environment and stakeholder network including its
employees will be successful (Deloitte, 2020).
Therefore, Human Resource (HR) organization
played pivotal role in the company during such
challenging and unprecedented period. The tasks
include enabling company to adapt with situations
through proactively policies review on safe
workplace and ensuring both operations and
employees’ services platforms updated to meet latest
requirements. The platform adjustment was expected
to contribute to company’s performance and
Abubakar, W. and Anggoro, Y.
Organizational Development at Human Resources Department of Export-oriented Semiconductor Manufacturing Company.
DOI: 10.5220/0010935900003255
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science (ICAESS 2021), pages 213-221
ISBN: 978-989-758-605-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
213

operational sustainability by fostering more flexible
and agile workforce during and post-pandemic period.
The digitalization was also introduced in many areas
including performance management and learning.
These were clear example of achievements of HR
Department in this tough period.
Despite many achievements, there were still
business expectations unable to fulfil by HR
organization. Reflection was made on those gaps
revealed 3 (three) main area of concerns from the
business leaders which were mainly deduced from the
following areas: availability of right-fit product
needed by business, effective & efficient functions
and transparent processes & structures. All those
dimensions are typical topics to be addressed in
Organizational Development.
With strong mandate to sustain and enable
employees for company’s further growth, HR
Department in the semiconductor manufacturing
company in Batam, has critical role to shape the
future of the company. The Organizational
Development at HR Department will ensure
sustainable performing organization in both present
and future especially when business is ramping up.
This paper has 2 (two) objectives. Firstly, it aims
to analyse which category of organizational model
need further intervention to make HR Department as
high-performing organization. This analysis is
important so that the author could make further
refinement in the existing setup to achieve sustainable
performing organization. Secondly, the paper aims to
identify best possible organizational alternatives for
HR Department to continuously deliver results.
2 THEORETICAL
FRAMEWORKS
Organization Development (OD) approaches
developed continuously with many theories behind
contributed to this field since 1950s when Kurt Lewin
came with the ideas of group dynamics and action
research which underpin the basic of OD process.
Several theories have been identified to explain the
basis on which the OD was developed. These theories
have been presented in three major categories: the
individual approach, T-group approach and the total
system approach (Gallos, 2006). In principle, OD
involves ongoing, systematic process of
implementing effective organizational change. In
other word, the changes through OD are properly
planned, incremental and participative where
outcomes are focused on the improved effectiveness
of the organization.
Organizational Development’s focus is within the
workplace where primary implementation of
humanistic ideals at work emphasizing values
including personal development, interpersonal
competency, participation, commitment, satisfaction,
and work democracy (Austin & Bartunek, 2003). The
improvement is designed based on action research,
long-term focus and emphasis on changing the
attitudes and behaviour of the people. In OD, change
should benefit not just only the organization but the
people who are in the organization. It is clear that OD
is aligning organization with its business objectives
striving to improve overall organizational
effectiveness.
Star model is adopted in this paper as
methodological basis for conducting standardized
OD initiative in the company. The model which is
referred as structured mental model on key
dimensions of OD, interlinked all elements in
organizational building blocks and form a star-like
formation. Originally developed in the 1960s, the
“Star Model” from Galbraith has been regularly
updated with latest findings from academic research
and lessons learned from practical use at various
organizations.
Star model includes five categories, each
representing one point of the star: strategy, structure,
people, rewards, and processes. Culture is not
included amongst the factors of the Star Model since
the managers usually are not in direct control to the
culture. However, managers could change culture
through the other categories (Galbraith, 2014). In
Galbraith’s model, strategy refers to the mission or
overall goals of the organization, while structure
pertains to placement of people, authority and
functions within the organization. Processes address
the way in which information flows across the
organization and the formal and informal means of
decision-making and interaction. Rewards or
incentives deal with reward structures, and people
include the policies and cultural aspects of the
organization that stimulates the way in which people
within the organization perform. Galbraith asserted
that depending on the specific goals of an
organization, the five points of the star could be
manipulated to minimize the shortcomings and
maximize the strengths of any one organizational
design.
The Galbraith’s Star Model was adopted as
methodological basis for OD in the company with
addition on culture category. The company believes
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
214

that the Culture forms the centre of the supporting
building categories. The culture concerns on the
common values and behaviour acceptable to the
organization for example the quality mindset,
compliance or agile culture. As such, OD framework
in the company offers both “hard” and “soft”
categories of an organization. As depicted in the
following Figure 1, Organizational Development
requires a strategy which is already defined and needs
to be deployed in the organization.
Figure 1: Company’s adaptation to Star Model with their
Interdependencies
3 METHOD
In order for OD initiatives are properly executed,
structured approach would be adopted. The Figure 2
describes 7-steps process which give guidance along
the full OD initiatives’ lifecycle. The strategy to be
deployed should be defined and clarified. Next, the
specific context and situation (“As-is”) including
certain boundary conditions need to be recognized
thoroughly. Using an analogy of designing a house,
the first step is to decide what the purpose of the
house is (e.g. to have single or multi-storey house,
how much is the budget, will there be any specific
requirement such as earth-quake resistance etc.); then
the architect can design and the builders and
carpenters can deliver it which fit to the specific
purpose. Therefore, iterative refinement between
defining objective and understanding “As-Is”
analysis are important steps. Once finalized, design
criteria will be selected as in step 3. It is important to
note that each organizational design includes certain
trade-offs which need to be considered and decided
during designing criteria phase.
Figure 2: 7-steps approaches in OD
Step 4 and 5 are developing and detailing future
organization concept based on the elements of the
“Star Model”. In the step 6 explains details required
to implement the future organization including sizing
estimating how many staffs and particular
competencies required (sizing) and recruiting
activities (filling) to close potential gaps and
reconfigure the essential elements accordingly. Long
term implementation of future organization concept
in a sustainable way is at the core of Organizational
Development and would be achieved after
completion of step 7. In the company, change
management as well as project management are
essential throughout the whole OD process.
3.1 SWOT Analysis
The author conducted departmental review through
virtual workshop in October 2020 involving all HR
leaders to review organizational performances,
contributions and areas for improvement. The team
assessed internal and external challenges compared to
today baseline. Through author’s facilitation and
dialogues, the team summarized factors of Strengths,
Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats as described
in Figure 3.
Figure 3: SWOT matrix of HR Department
3.2 Organizational Design Criteria
Alignment on what are the required criteria to shape
future of HR Department organizational set-up was
made. In principle, design criteria are established
based on contribution to the strategy-driven change
needs. Design criteria are statements that simplify the
process on how the target model will be shaped and
provide sufficient clarity to shape the design.
However, they are not an attempt to articulate the
solution. These represent the principles applied when
considering design decisions where once choice has
been made there is no possibility of resorting to any
other option.
Organizational Development at Human Resources Department of Export-oriented Semiconductor Manufacturing Company
215

The identified criteria were derived from SWOT
analysis mainly from “Weaknesses” quadrant of the
SWOT. The “Strengths” were purposely not included
as team assessed that “Strengths” are inherent value
of the organization now. The criteria are then group
into three OD pillars.
Table 1: Design criteria of future organization.
3.3 Assessment to Design Criteria
In February 2021, in order to gauge perception of HR
Department members and company’s business
leaders towards HR organizations, to obtain pulse
check for any HR initiatives and to identify areas of
improvements linked to Organization Development
initiatives, a survey was conducted.
In this survey, the author used quantitative and
qualitative methodologies to assess condition of
future organizational Design Criteria and define the
basis of Organizational Development efforts in
Department. The quantitative method questionnaires
to both internal and external respondents consisted of
24 multiple-answer statements with 5 rating-scales:
“Strongly disagree”, “Disagree”, “Neutral”, “Agree”,
“Strongly agree”. Those statements were derived
from OD pillars of Design criteria.
The survey’s target groups were external
(represented by Head of Departments with total 14
respondents) and internal (all HR employees with
also 14 respondents) stakeholders with target
minimum 70% participation rate from each party. The
survey was conducted between 21st to 25th February
2021. Participation rate for both internal and external
stakeholders were 90% and 72% respectively, hence,
the author concluded the survey results were valid.
The quantitative method’s rating utilized share of
positive evaluations in percentage to determine level
of acceptance from respondents. The survey was only
accepting respondents’ selection “Agree” and
“Strongly-agree” when respondents were evaluating
certain statement. For example, if 8 out of 10
respondents checked the selection “Agree” or
“Strongly-agree”, the ratio of positive evaluations is
80%. This is to ensure the feedbacks received is free
of inherent noises generated from “neutral” answers.
The list of statements asked to all target participants
are listed in the following Table.
Table 2: List of indexed statements during HR Surve
y.
In addition, through qualitative method, 3 open-
ended questions to both internal and external
respondents on what HR Department should start
doing, stop doing and continue doing were asked.
3.3.1 External Assessment
Overall approval rating reflected from overarching
statement, “Overall I am satisfied with the HR
services and support” was 68% sharing positive
evaluation. There was no strong disagreement while
about 32% of respondents were giving strong
agreement to that statement.
Figure 3: HoD’s over-arching statement.
In general, the overall satisfaction result from the
external assessors were positive towards HR
organizational performance.
Deeper analysis to HoD’s responses distribution
revealed that 3 statements were rated 100% positive
evaluation. That means all respondents agreed or
strongly agreed that HR organization delivered these
statements. Those statements are HR continuously
improves its services (2.3), HR has well defined roles
and responsibilities (3.7) and HR follows clear
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
216

policies and processes (3.8). However, the author
captured 3 bottom statements rating which indicated
that effort should be focused in that area, namely HR
has a fast decision-making (3.2), HR actively
addresses megatrends (e.g. demography or
digitalization) (1.3) and different HR functions (e.g.
BP, POE, TAS, CB, ER) are well aligned (3.1).
When author did a closer look into those low
ratings responses, about 40% of respondents of each
low-rated statement selected “neutral” answers as
their perspective to statements about HR. This
uncertain population might have experienced
different level of satisfaction on those specific
statements from what HR delivered in the past. Thus,
one of the topics to be reviewed would be how to have
consistency in the organizational performance.
Figure 4: HoD’s responses distribution
3.3.2 Internal Assessment
The internal group assessment for over-arching
statement, “Overall I believe HR provides satisfying
services and support” was rated 69%. It is in the same
level of external view to overall satisfaction level.
Figure 5: HR members’ over-arching statement
HR members’ response distribution revealed
interesting facts. Firstly, HR members were proud of
statements: we translate the business strategy of
company into our HR topics (1.2) and we are a trusted
partner (1.8). These 2 statements displayed high
confident level that the organization were listening to
customers’ voices, thus, becoming trusted partner.
Secondly, the following statements: We have enough
time for all customer requests (2.2), We are
competent in its respective area of responsibility (2.5)
and the different HR functions (e.g. BP, POE, TAS,
CB, ER) are well aligned (3.1) were among the lowest
rating statements. Lastly, compared to external
respondents, internals were more critical to each
statement as there were numbers of disagreement and
strong disagreements to certain statements.
Figure 6: HR members’ responses distribution
3.3.3 Differential Analysis
In order to make sound decision on which statements
need to be focused, differential analysis was
conducted. In investment term, the differential
analysis is focusing on the future costs and benefits
that differ between the alternatives. In this OD
context, differential analysis was performed to see
what are differing views from both internal and
external perspectives. From each dimension, the
author derived 3 groups of opinions identified,
namely: significant gaps, strongest links and weakest
links.
The significant gaps contrasted statements from
external and internal perspectives with more than
30% gaps. These gaps might be created due to
different understanding and expectations from of
statements, expectation on statements. Next,
strongest links were identified when both external and
internal perspectives agreed the statements with
rating more than 80%. Lastly, the weakest link
Organizational Development at Human Resources Department of Export-oriented Semiconductor Manufacturing Company
217
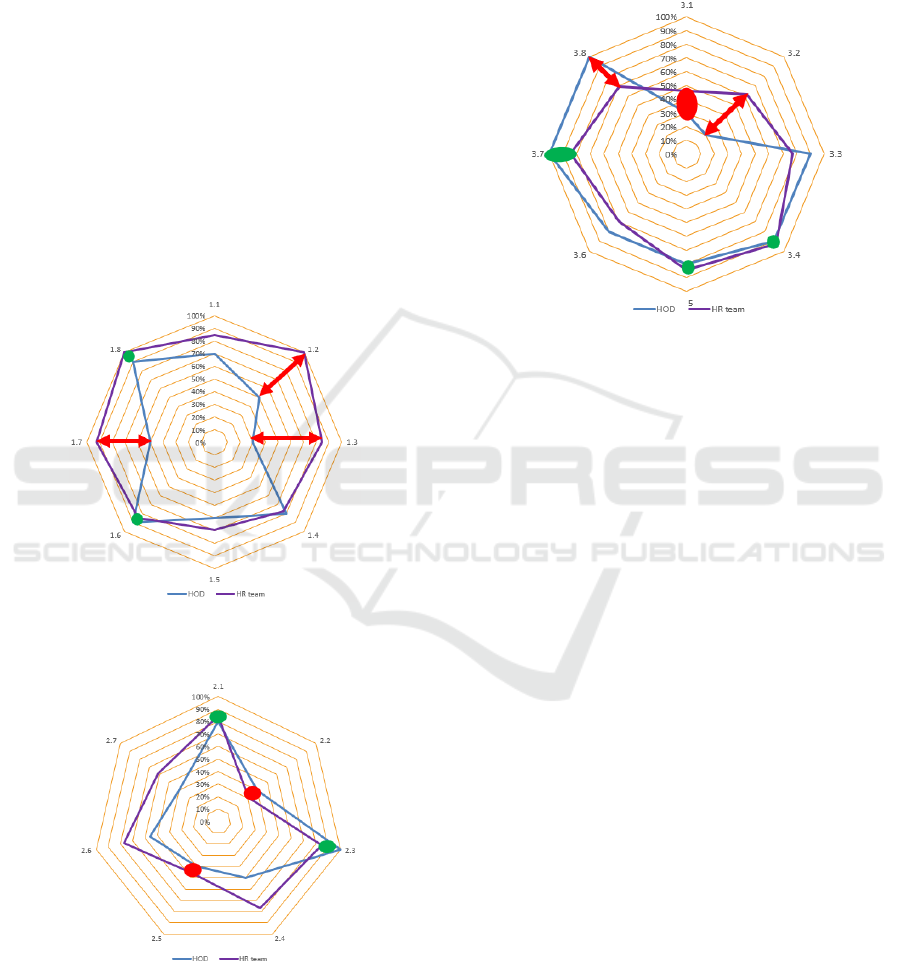
occurred when both perspectives gave statements
rating below 50%.
Using share of positive evaluation, data was
plotted into spider-web charts according to respective
OD pillars identified in the design criteria. From the
first dimension, author identified 3 significant gaps
and 2 strongest links. The following statements: HR
translates the business strategy of company and our
department into HR topics (1.2), HR actively
addresses megatrends (e.g. demography or
digitalization) (1.3) and HR actively shapes the
company culture (1.7) were rated high by HR
members, however, rated low with gaps more than
50% by HoDs. In addition, both parties have similar
positive views on statements HR provides user-
friendly IT solutions (e.g. STEPS, ATS, Career
Projections, eLeave, DHS, eKiosks, LinkedIn
Learning, PAF etc) (1.6) and HR is a trusted partner
(1.8).
Figure 7: 1st dimension’s differential analysis, Customer
centric and business need driven.
Figure 8: 2nd dimension’s differential analysis, Effective
and Efficient IFBT HR functions.
From the second dimension, the author deduced 2
strongest links and 2 weakest links. The strongest
links were HR processing times are reasonable
compared to the complexity of the issues (2.1) and
HR continuously improves its services (2.3).
However, the weakest links were HR has enough time
for all customer requests (2.2) and HR is competent
in its respective area of responsibility (2.5).
Figure 9: 3rd dimension’s differential analysis, Simple,
clear and transparent process and structures
From the third dimension, the author deduced 2
significant gaps, 1 weakest link and 3 strength links.
The identified gaps were HR has a fast decision-
making (3.2) and HR follows clear policies and
processes (3.8). The external was more critical on
speed of HR team making the decisions and it had
perception gap with internal respondents. Most likely,
it was due to the impact of speedy decision to the
external’s own processes. On the contrary, internal
was more critical on the clarity of policies and
processes compared to the external as most probably
the internal was the one who lived with those policies
and processes every day. The weakest link identified
was different HR functions (e.g. BP, POE, TAS, CB,
ER) are well aligned (3.1). This statement was
particularly highlighted as lowest in approval rating
statement in both internal and external assessment
results section. Finally, the strongest links identified
were The organizational structure of HR is clear and
understandable (3.4), HR acts globally consistent
(3.5) and HR has well defined roles and
responsibilities (3.7).
3.3.4 Commentary Analysis
To complement quantitative analysis made from
section 3.3.1 to 3.3.3, the commentaries of
respondents were obtained from 3 open-ended
questions as qualitative inputs.
The external respondents’ commentaries to HR
organization were crystalized into 3 areas of concerns
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
218

namely: requirement to be more fast and agile in the
responses, costumer centric solutions and request to
continue clear and transparent processes. On the other
hand, the internal respondents’ commentaries were
mainly on the competency building and improvement
collaboration within HR.
3.3.5 OD Category for Further Intervention
The author with HR leadership team mapped
substance of both quantitative and qualitative analysis
into the Star model in order to understand which area
of organization would be the main concerns in OD
initiatives. The mapping was done and presented in
the following figure.
Figure 10: Mapping of analysis results to blocks of Star
model for OD initiatives.
Therefore, from Star model perspectives, there
were 5 categories contributed as root-causes which
hindering Organizational Development i.e.
“Strategy”, “Structure”, “Process”, “People” and
“Culture”. These categories in HR organization
would be further fine-tuned and intervened to enable
HR Department to sustainably performing with more
dynamics and challenging requirements in the future.
3.4 Solution Alternatives
Having concluded the assessment, first action to do
was to ensure re-alignment of Strategy. The author
discussed the relevance of the Corporate HR Strategy
with local management and found it is still acceptable.
In addition, local management explicitly demanded
deliverables as indicators if HR organization has
achieved its desired maturity level. These
expectations shall be converted into executable action
items during OD implementation.
3.4.1 Define Parameters for Alternatives
To develop new alternatives of organizational setup,
the author established distinct options based on
categories highlighted during the Survey, namely:
“Structure”, “People”, “Process” and “Culture”.
Based on discussion and brainstorming within the
team, there were parameters identified that could be
used as indicators to determine success
implementation of new organization. Index (from -3
to 3) were assigned for each possible scenario from
unfavourable, neutral and favourable outcomes.
Table 3: Parameters for Organizational success.
3.4.2 Develop Alternative Solutions
Alternatives solutions are compared to existing
organization (status-quo) with its brief characteristics
illustrated in the table 4.
Table 4: Characteristics of New organization alternatives.
Subsequently, the author and HR leadership team
continued to do selection of organizational design
alternatives which enable it to meet challenging
requirements in the upcoming future. The team
examined each alternative and arbitrarily assign
numbers based on projected favourability levels of
each alternatives to any parameters. All results from
all parameters from the same categories were made
average. The exercise was documented as follow.
Table 5: Favourability impacts of each Organizational
alternative.
Organizational Development at Human Resources Department of Export-oriented Semiconductor Manufacturing Company
219

3.4.2 Selection of Alternative
Prior selection of most feasible alternative, the author
and the team decided on the level of importance of
each OD category. The company put emphasize on
correct “Structure” and “Process” as most important,
followed by “People” and “Culture”. The weightage
distribution for “Structure”, “People”, “Process” and
“Culture” were assigned 30, 25, 30 and 15
respectively.
Multiplying results of favourability assessment
into weightage of each OD category, the author
obtained the following selection table.
Table 6: Selection matrix of alternative.
4 RESULTS
It is now important for the author and team to link
back the new organization with the local
management’s expectations. Work-packages were
derived in consideration of short and long-term
expectations; thus, they are distributed and assigned
to 2 Phases accordingly. The Phase 1 has shorter
duration of time with concrete deliverables while
Phase 2 has longer duration with more intangible
aspects. The following table describes the identified
work-packages to show-case new organization.
Table 7: Work-packages list.
Upon selection of organizational alternative, the
next step would be Detailing of future concept
followed by Sizing and Filing. In detailing of future
concept, any structural implications for
organizational levels, job descriptions, grading, new
or changing interfaces will be reflected and defined.
In addition, the need for associated processes
adaptations, workflows and working relations will
also be considered. Scenario thinking will be drafted
to get precise picture of the future concept through
constructing the future state as close as possible with
all affected aspects and trying to see things from that
new perspective.
In sizing and filling, the number of required staffs
will be finalized. The number could be either the
same, more or less. In addition, filling refers to the
actual filling of vacancies / jobs to implement the
future organization. Therefore, implication towards
workforce planning (quantitative and qualitative)
have to be considered as well. For example,
requirement to hire new employees or start people
development measures to acquire necessary
competencies for crucial position.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper had deliberately explained the
organizational development process in HR
Department of export-oriented semiconductor
manufacturing company and successfully identify
categories for further interventions. The first step was
crystalizing sustainable performing HR organization
as the objective of the organization development
(OD) initiative. It was then followed by workshops,
discussions and alignment for SWOT analysis.
The selection design criteria were summarized
into 3 OD pillars, namely: Costumer centric &
business need driven (Right fit products), Effective
and efficient HR functions (fast and agile) and Simple
clear and transparent processes and structures.
The Star model comes very useful which finally
helps the author through strategy re-alignment and
found that intervention to “Structure”, “Process”,
“People” and “Culture” categories were required. The
level of intervention was designed in future concept
where all parameters and alternatives were examined
carefully. In the last stage before implementation, the
organization detailing, followed by sizing and filling
were included into the overall process and step five
and six accordingly.
The author also identified best option from
organizational alternatives to deliver sustainable
results. The alternative selected was organization
which incorporates certain level of centralization,
continues strengthening processes, enhances
efficiency and clarity, upgrades employees’
competency through development measures and
creates supporting culture. These are the elements of
high-performing organization which author and team
believe will be able to achieve achievements in both
short and long term.
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
220

The implementation of the change where step-by-
step change management process required is not
scope of this paper.
REFERENCES
Austin, J., & Bartunek, J.M., 2003. Handbook of
Psychology, Volume 12 Industrial & Organizational
Psychology: Theories and Practices of Organizational
Development. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Dan, R., “Global Semiconductor Sales Increase 1.9%
Month-to-Month in April; Annual Sales Projected to
Increase 19.7% in 2021, 8.8% in 2022.” Semiconductor
Industry Association, 9 June 2021.
https://www.semiconductors.org/global-
semiconductor-sales-increase-1-9-month-to-month-in-
april-annual-sales-projected-to-increase-19-7-in-2021-
8-8-in-2021/
Deloitte Global Human Capital Trends, 2020, “The social
enterprise at work: Paradox as a path forward.”
https://www2.deloitte.com/cn/en/pages/human-
capital/articles/global-human-capital-trends-2020.html
Gallos, J., 2006. Organization Development: A Jossey Bass
Reader. San Francisco, CA: Jossey Bass.
Galbraith, J., 2014. Designing Organizations - Strategy,
Structure, and Process ate Business Unit and Enterprise
Levels. Third edition. Published by Jossey-Bass
Gabsa, R., & Rastog, S., “Take Care of Your People, and
They'll Take Care of Business.” Gallup, 23 June 2020.
https://www.gallup.com/workplace/312824/care-
people-care-business.aspx
Organizational Development at Human Resources Department of Export-oriented Semiconductor Manufacturing Company
221
