
Transaction Application Management through Wireless LAN for
Small and Medium Enterprises
I Made Ari Dwi Suta Atmaja
1a
, I Nyoman Gede Arya Astawa
1b
, Ni Wayan Wisswani
1c
,
I Made Riyan Adi Nugroho
1d
and Putu Wijaya Sunu
2e
1
Department of Electrical Engineering, Bali State Politechnic, Badung, Indonesia
2
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bali State Politechnic, Badung, Indonesia
Keyword: Management Order, Wireless LAN, Waitress App, Tablet, SME.
Abstract: In the current condition, business actors, especially Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) are increasingly
showing a tendency to utilize information technology by conducting business operational transactions using
local applications as needed. In general, transactions carried out in the SME business model are data input
directly through the PC device used. This causes the infrastructure model used for these applications to tend
to be fixed and inflexible and cannot be operated on a mobile basis or move from one place to another in the
business area. The solution to these problems is to build a transaction management system that utilizes
Wireless LAN network infrastructure modeling so that it can facilitate operational activities where employees
can serve transactions not only in one place. But by moving from one place to another around the business
area. With this application, the process of printing order notes is separated between food and beverage orders.
Benefits This application can be accessed using smaller devices such as smartphones or tablets, making it
easier to carry around mobile in the business area
1 INTRODUCTION
Today's information technology is growing very
rapidly along with the development of human needs
for flexibility and efficiency of time and thought
energy in various aspects of life. Information
technology is useful as a means to communicate,
disseminate, search for data, and the most widespread
nowadays is to use it to conduct business transactions
(Ana Rita Sampaio, Rhodri Thomas, Xavier Font,
2012). It is undeniable that information technology
has changed the behavior of economic actors in
conducting business transactions, from conventional
paper-based business to modern electronic and
digital-based business (J. Srikanth and S. Mohanavel,
2018).
Business actors, especially Small and Medium
Enterprises (SMEs) are increasingly showing a
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1103-528X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1472-896X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0318-4178
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3448-3405
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6915-0475
tendency to utilize information technology by
conducting business operational transactions using
local applications as needed (V Prajová, M
Homokyová, M Horvátová, 2019). One of the
specific SMEs is the food outlet business. In a food
outlet business like this, the applications used are
generally operated on a standalone basis with PC
devices and must be connected directly to the
application provider server (Irving Reascos Paredes,
João Alvaro Carvalho, 2017). In general, transactions
carried out in the application model are inputting data
directly through the PC device used (Linus Udoh,
Ibrahim Inuwa, 2016). This causes the infrastructure
model used for these applications to tend to be fixed
and inflexible and cannot be operated on a mobile
basis or move from place to place within the business
area. As with transaction applications in general, this
modeling does not provide flexibility for business
470
Atmaja, I., Astawa, I., Wisswani, N., Nugroho, I. and Sunu, P.
Transaction Application Management through Wireless LAN for Small and Medium Enterprises.
DOI: 10.5220/0010947700003260
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2021), pages 470-476
ISBN: 978-989-758-615-6; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

actors who have limited employees and a fairly large
business area (Umar Bin Qushem, Akram M. Zeki,
Adamu Abubakar, 2017). The customer order process
must be recorded by the waitress then inputted
manually through the PC device used as Order Taking
(Maia A.W. and Farias P.P.M., 2019). Another
problem that arises in the SME business of food
outlets is that generally the printing of food and
beverage orders is not separated so that if there are
quite a lot of orders, it will cause difficulty in
managing the time in completing orders between food
and drinks (Holzinger A., Treitler P. and Slany W.,
2012). And one of the most importantly are the
security of transaction data via wireless lan must also
be well protected, because transaction data is
important data for a company (N. C. Kiran and G. N.
Kumar, 2011).
From the problems faced by SME business actors,
especially food outlets, this research will build a
system for transaction management that utilizes
Wireless LAN network infrastructure modeling so
that it hoped that the construction of this system can
facilitate operational activities where employees can
serve transactions not only in one place but also in
one place. By moving from place to place according
to the customer's location. As well as in the process
of printing the order note, it is possible to separate
food and beverage orders. This application can be
accessed using smaller devices such as smartphones
or tablets, making it easier to carry on mobile in the
business area.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
The development of this application can be applied to
SME businesses anywhere. The flow of the
application system that was built as shown in Figure
1 below:
Figure 1: Application System Flow.
The applications that are built are customized
according to the needs of the ongoing business
operations For details of the application system that
was built, it is shown in Figure 2 below:
Figure 2: Detail Flowchart of Wireless LAN-based
Transaction System.
The process flow system according to the flow chart
Figure 1 and Figure 2 is described as follows:
1. Waitress accesses the system via a browser.
Where the device used is a device such as a
smartphone or a tablet that can be carried
anywhere in the business area. The device
accesses the application through a Wireless LAN
Network that has been built and is intended for
applications.
2. The waitress will make an order (login required),
the waitress will access the order page and enter
the table information from the customer, then the
waitress will input the customer order list and
process the order.
3. When the order is processed by the waitress, the
order data will be saved to the database, and the
system will print the order customer in the
waitress printer, a food order note printed in the
kitchen, and a drink order note printed the bar by
direct and parallel print.
4. After the waitress makes an order, the cashier can
make payments on orders that have been inputted
by the waitress, where the cashier will access the
system via a browser and log into the system, then
the cashier will make payments according to the
Transaction Application Management through Wireless LAN for Small and Medium Enterprises
471
order information listed, and save it to the
database.
5. When payment information is saved to the
database by the cashier, the order data will be
saved to the database, and the system will print a
transaction note for the cashier.
6. In the system admin has access to manage master
data, be it product data, package data, promo data,
and user data. To manage master data the admin
will access the system via a browser (login
required) then manage the required master data
and save changes to the system.
Then for the design of the Wireless LAN Network
Framework for the application is described in Figure
3 below
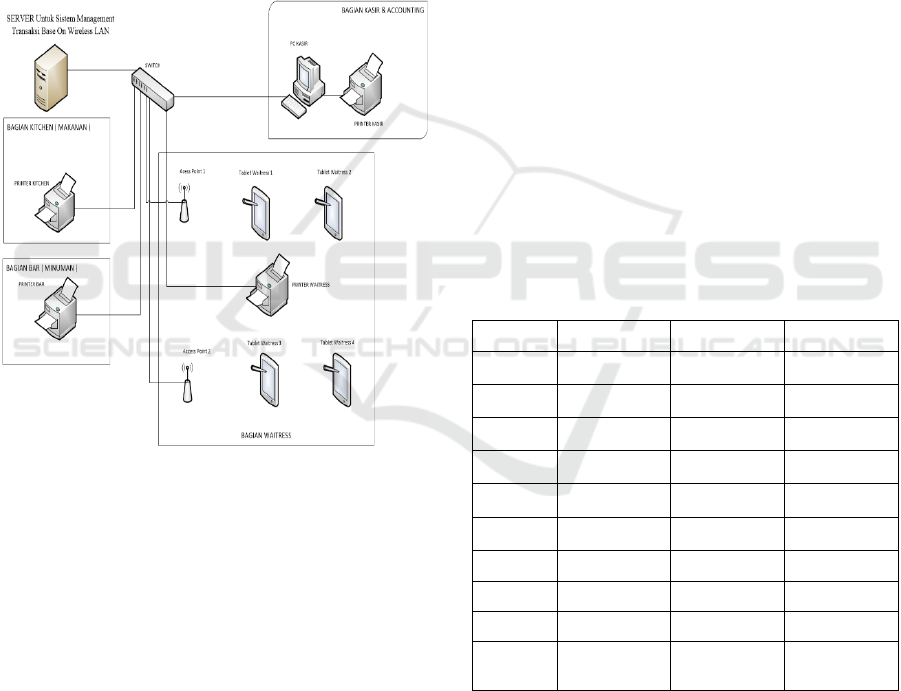
Figure 3: Wireless LAN Network Design.
The network design flow process according to
Figure 3 is explained as follows
1. The application is installed on the Server device
where all transaction data is stored.
2. There is one printer in each section which used in
printing order notes and transactions.
3. In network modeling, there are two access points
that use as Wireless LAN infrastructure that
serves as a medium for communicating order data
entered by the waitress.
4. The smartphone or tablet device will be carried by
each waitress on a mobile basis or move from
place to place around the business area.
5. The ordering process is carried out through a
device brought by the waitress where the device is
connected to the Server via Wireless LAN.
6. After the order input is made by the waitress, later
the order will be printed directly in the kitchen
section for food and the Bar section for drinks.
Likewise, the waitress printer will also print all
the orders that have been inputted earlier.
7. Once there is a note printed on the Kitchen or Bar,
depending on the order. Then the Kitchen or Bar
will immediately process the order without having
to be manually informed by the waitress that there
is an incoming order.
8. For printing notes on the waitress printer, it is used
by the waitress to cross-check which orders have
been completed and brought to the customer. Thus
minimizing the order process errors.
9. When the customer wants to make a payment, he
or she is immediately invited to the cashier to
make a payment there either in cash or using a
debit/credit card. And the payment receipt will be
directly printed on the cashier's printer.
10. All transactions will be stored and recorded in the
application on the Server. If you want to print
transaction reports, the admin can do it directly
through the server or through the cashier's PC by
first logging in as Admin
For the IP Address scheme of the device used, it is
explained in table 1 below:
Table 1: IP address device configuration mapping.
DEVICE LOCATION IP ADDRESS INFORMATION
PC Server 3
rd
Floor 192.168.0.1 /28 Application
Serve
r
PC Cashier 1
st
Floor 192.168.0.2 /28 PC Cashier and
Accountin
g
Tablet 1 1
st
Floor 192.168.0.6 /28 Device Waitress
1
Tablet 2 1
st
Floor 192.168.0.7 /28 Device Waitress
2
Tablet 3 2
nd
Floor 192.168.0.8 /28 Device Waitress
3
Tablet 4 2
nd
Floor 192.168.0.9 /28 Device Waitress
4
Printer 1 1
st
Floor 192.168.0.10 /28 Waitress Printer
Printer 2 1
st
Floor 192.168.0.11 /28 Kitchen Printer
Printer 3 1
st
Floor 192.168.0.12 /28 Bar Printer
Printer 4 1
st
Floor 192.168.0.13 /28 Cashier and
Accounting
Printe
r
System testing will be carried out directly through the
tablet waitress device so that the orders entered will be
directly printed through the cashier printer in each
section, making it easier to manage customer orders.
This transaction management application's goal is to
process orders through wireless LAN so that the
waitress can move around the business area to adjust
the customer's position. Then for order management
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
472

and output notes can be arranged according to the type
of order made, such as food orders will be directly
printed in the kitchen section as well as for drink
orders will be directly printed on the bar.
3 RESULT AND EVALUATION
The results obtained from this study are transaction
management applications that can be accessed through
a wireless network from the waitress device without
any problems. This application was built using the
programming language commonly used to build an
information system is PHP with a responsive display
so that it is easy to access via web browsers on smaller
devices, such as Tablets and Mobile Phones. And for
the database using MySQL. The results of the study
are as follows:
3.1 Result
The results of this application have been implemented
at Hungrypedia Food Outlets. The figure below is the
business logo of the food outlet where this application
is used.
Figure 4: Business logo of the food outlet.
Applications are divided into 2 important parts,
that is Server Applications and Client Applications.
Server applications are placed on a PC Server located
in the office and client applications are accessed
directly via tablet devices brought directly by the
Waitress around the business area. The following is
the user interface display if the user (waitress)
accesses the system via a tablet device via a Wireless
Lan network
Figure 5: Display applications via tablet devices.
And Figure 5 below show the system interface
when accessed via a desktop computer.
Figure 6: Display the application via a desktop computer
In Figure 6 below, we can see a list of menus and
pages available on the system if accessed with an
admin account. For the administrator menu and pages,
users with cashier and waitress roles cannot have
access rights.
Figure 7: Display list of main menu admin user.
In access the system, 2 application shortcuts were
created, namely through the cashier's desktop PC and
Transaction Application Management through Wireless LAN for Small and Medium Enterprises
473

via the waitress tablet device. This application runs
on a local network so that to access the application the
localhost system used as shown in Figure 7 below :
Figure 8: Application Shortcut via Desktop PC.
Then for system access via tablets, application
shortcuts have been created and configured to the
Transaction Management Application which remains
connected to the application server. Figure 8 below is
an application shortcut display via a tablet device
Figure 9: Application Shortcut via Tablet Waitress.
Furthermore, figure 9 shown the login display on the
application. The login option in the application
adjusts the floor position of the waitress working so
that it can do tracing if an input error occurs
Figure 10: Waitress Login Form display.
After login, the Transaction Management Application
can be used properly
3.2 Evaluation
The tests carried out were testing the connection test
from the tablet device waitress then testing the order
input according to the type of food until an order note
was printed in each section. To test the connection
from the tablet device waitress equipment to the
application server, it is shown in Figure 10 below:
Figure 11: Test the tablet waitress connection.
The results connection test evaluation shown that the
tablet device waitress connected well to the
application server, as well as testing connections to
other devices that used in this application
Furthermore, evaluation of the application itself is
carried out to ensure that the order input process can
run properly, both order input from the tablet waitress
or order input from the cashier's PC. Order input from
the cashier's PC is still needed to be an alternative to
input orders other than the tablet waitress. For order
input, it is shown in Figure 11 below:
Figure 12: Input Order PC cashier.
After inputting the order through the application,
an evaluation of the notes printed on each section is
carried out. Where for food orders the order note is
printed on the kitchen and for drink orders, the order
note is printed on the bar. Order notes that are input
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
474
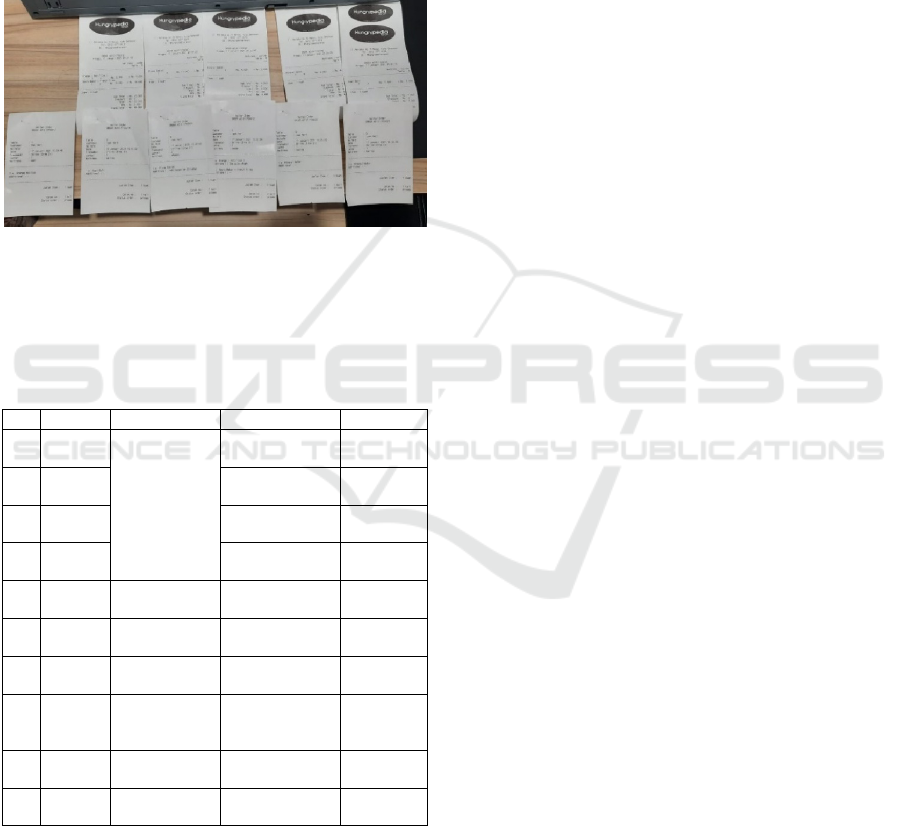
are also printed on the waitress printer, where the
notes are used for controlling the order input by the
waitress. And for the overall order note accompanied
by the total price printed on the cashier, where the
customer will make payment after the order is
completed. The payment process is still carried out at
the cashier's PC where the payment process can be
done in cash or using a debit card through the provided
EDC machine.
The printout of the customer's note on the cashier's
PC is shown in Figure 12 below:
Figure 13: Output Bill Customer.
The results of the tests that have been carried out on
the equipment and the transaction management
application are shown in table 2 below:
Table 2: Application Test Results Through the Equipment.
No Device Proses Test Informaton Status
1 Tablet 1
Input, Edit,
Delete Order
Device Waitress
1
Succeed
2 Tablet 2
Device Waitress
2
Succeed
3 Tablet 3
Device Waitress
3
Succeed
4 Tablet 4
Device Waitress
4
Succeed
5 Printer 1
Print Order
Note
Waitress Printer
Succeed
6 Printer 2
Print Food
Orde
r
Kitchen Printer
Succeed
7 Printer 3
Print Drink
Orde
r
Bar Printer
Succeed
8 Printer 4
Print Order
Total Invoice
Cashier and
Accounting
Printe
r
Succeed
9 Server Report Print
Application
Serve
r
Succeed
10
Cashier
PC
Print Daily
Transactions
Cashier and
Accounting PC
Succeed
From the tests that have been carried out, all
transactions, from inputting orders through the tablet
device waitress to printing reports on the application
server, run properly. For network infrastructure as
application support, maintenance must be carried out,
especially Access Point as a key point in order input
wirelessly so that the operational process did not have
any problems
4 CONCLUSION
This study concludes that the Transaction
Management Application has been able to carry out
business operational transactions through wireless
LAN order input and the printing of order notes can
be separated based on the type of order. And cashier
operations have been going well. This application is
implemented into a system that will help digitalize
small and medium businesses in the future.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank the department of
research and community service center of Politeknik
Negeri Bali and the Ministry of Research and
Technology of Higher Education of the Republic of
Indonesia for the financing of this research.
REFERENCES
Ana Rita Sampaio, Rhodri Thomas, Xavier Font. 2012.
Small business management and environmental
engagement. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 20:2,
179-193
J. Srikanth, S. Mohanavel. 2018. Business Analytics
Applications For Small And Medium Enterprises.
International Journal of Advance and Innovative
Research. Vol. 5, 34-35
V Prajová, M Homokyová, M Horvátová. 2019.
Transaction Applications of Enterprise Information
System. IOP Conference Series.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 659
012026.
Irving Reascos Paredes, João Alvaro Carvalho. 2017.
Understanding the process of implantation IT
Enterprise Applications in Small and Medium
Enterprises (SMEs). Conferência da Associação
Portuguesa de Sistemas de Informação (CAPSI’2017),
Guimarães, Portugal. 270-283
Linus Udoh, Ibrahim Inuwa. 2016. Implementation of a
Data Driven Transaction Processing System for the
AUN’s Restaurant, Yola – Nigeria. International
Journal of Computer Applications. Vol 149 No.6, 9-20.
Umar Bin Qushem, Akram M. Zeki, Adamu Abubakar.
2017. Successful Business Intelligence System for
SME: An Analytical Study in Malaysia. IOP
Conference Series: Mater Sci. Eng. 226 012090
Maia A.W., Farias P.P.M. 2019. Transactions as a Service.
Software Engineering Methods in Intelligent
Transaction Application Management through Wireless LAN for Small and Medium Enterprises
475

Algorithms ( CSOC 2019). Advances in Intelligent
Systems and Computing, vol 984. Springer, Cham.
Holzinger A., Treitler P., Slany W. 2012. Making Apps
Useable on Multiple Different Mobile Platforms: On
Interoperability for Business Application Development
on Smartphones. Multidisciplinary Research and
Practice for Information Systems (CD-ARES 2012).
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7465.
Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
N. C. Kiran and G. N. Kumar. 2011. Building robust m-
commerce payment system on offline wireless network.
Fifth IEEE International Conference on Advanced
Telecommunication Systems and Networks (ANTS),
2011, pp. 1-3.
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
476
