
The Development of Dance Movement in Humanoid Robot Dancing
ERISA
Novian Fajar Satria, Eko Henfri Binugroho, Ridhan Hafizh Chairussy, Dwi Kurnia Basuki
and Bianca Surya Nobelia
Politeknik Elektronika Negeri Surabayaa, Jl. Raya ITS, Kampus PENS, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: ERISA, Humanoid Robot Dancing, Blender Software.
Abstract: Robots have become an important part of human life today, especially with today's rapid and modern
technological developments. One of them is a type of humanoid robot that has been developed from time to
time with various types, shapes and sizes. ERISA is the name of a humanoid robot that has the ability to
perform dance moves and can also follow the accompaniment of music. In making the desired dance
movement takes a long time, this is because the process in making it is still manual for each desired movement,
namely trial and error. In this research using Blender software to answer these problems, where the Blender
software displays a 3D design model of the humanoid robot ERISA which was made first using Autodesk
Inventor Professional CAD software and then converted to Blender software. The parameters used in this
Blender software are the joints in the 3D design of the ERISA robot model which is a representation of the
servo motor actuator. By adjusting the position of each joint and the resulting angle value in the Blender
software, the desired movement can be carried out. The process mechanism is the result of the angle data
obtained at each joint in the Blender software and then converted into a pwm value which is entered into the
servo motor to drive it. The results obtained in this research test are that there is an error of 3.25% from the
accuracy of the angle value issued in the Blender software with the angle value on the ERISA robot when
performing the same dance movement.
1 INTRODUCTION
At this time, robots are not stranger anymore and have
been used by developers to complete a profession.
Various types of robots have been developed, such as
mobile robots, drones, humanoid robots, manipulator
robots, et cetera. In this research, the topic of
humanoid robots is taken as a discussion. The
development of humanoid robots has become the
spotlight for researchers in the field of robotics.
Proven by educational institutions and technology
companies that have competed to show the results of
research on humanoid robots such as robots ASIMO
by Honda (Sakagami, 2002), T-HR3 by Toyota
(Toyota, 2017). One of the discussions in humanoid
robot research is related to the balancing control
system. The implementation of current balance
control aims to make ERISA robot able to walk on
sloped field surface in balance and not easy to fall.
The test results show the addition of the balance
control system gives ERISA robot capability of
walking on the sloped surface up to 10° (A.H.
Alasiry, 2018). The IMU (Measurement Inertia Unit)
is used as a tilt detection sensor and there are
accelerometer sensor and gyroscopic sensor that is
used in sensor fusion algorithm of the humanoid
robot. The test results show the addition of the sensor
fusion algorithm in reading data, gives the robot
capability of walking on the slope with maximum tilt
12° (Dian Alarmi, 2020).
Even in Indonesia, the discussion of humanoid
robots is still ongoing developing. The discussion is
supported by the Ministry of Education and Culture,
with The Indonesian Robot Contest (KRI) is held
every year. Humanoid The robot is in the Indonesian
Dance Robot Contest (KRSTI) division against
several robot teams from several colleges in
Indonesia. Every year the theme of the dance
constantly changes with the level of difficulty in the
dance moves, and the competition arena changes in
size and placement of start and stop zones robot. The
robot is programmed in such a way that it can dance
to follow a rhythm that matches the theme. To make
a motion, you need trial and errors that take a long
626
Satria, N., Binugroho, E., Chairussy, R., Basuki, D. and Nobelia, B.
The Development of Dance Movement in Humanoid Robot Dancing ERISA.
DOI: 10.5220/0010950100003260
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2021), pages 626-632
ISBN: 978-989-758-615-6; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
time because it only estimates the angle of the servo.
If it does not match the expected then, you need to try
again, and it has an impact on the longevity of the
servo motor and the time it takes quite a while.
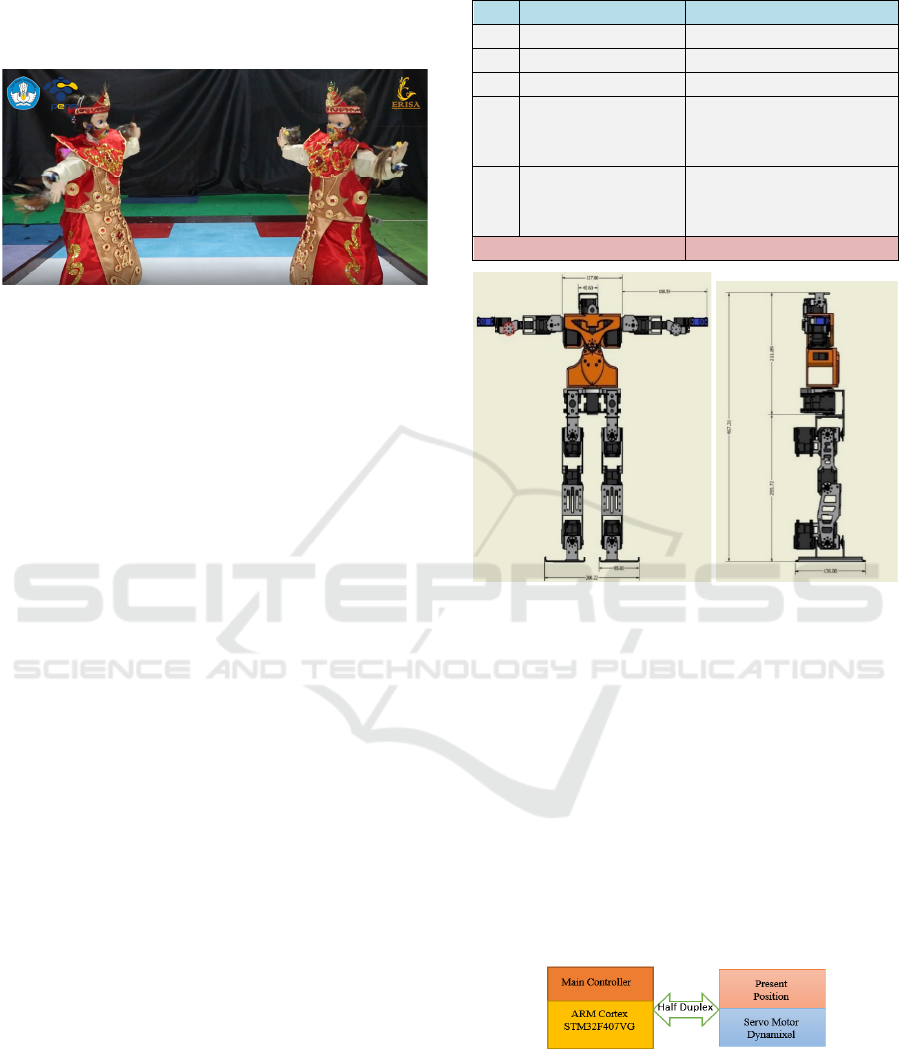
Figure 1: ERISA robot in action.
In connection with this problem, it is motion
control for choreography using the powerful Blender
software was to make a 3D design of the robot then it
is given 2. Bones and the frames on each servo horn
will be moved to get the value from the servo, then
enter the value from the resulting choreography in
Blender software for creating motion, namely the
KEIL Microcontroller Development Kit (MDK-
ARM). This software itself is the software used on
Cortex-M, Cortex-R4, ARM7, and ARM9
processors. MDK Version 5 consists of MDK Core
and Software Packs. Both are central to the processor
(Integrated Development Environment) KEIL IDE
Vision 5 using C/C++ language or assemblies.
1.1 ERISA Robot Construction
The ERISA robot is designed with 29 DoF servo
motors arranged on an aluminum frame, PLA +, and
using an ARM type microcontroller as the main
control system. The details will be explained below.
1.1.1 Mechanical Design
The ERISA robot design has 29 DoF consisting of the
head, body, hands, and feet, as shown in table 1.
Figure 2 shows the front and side view of the robot
design. The design is made using software Inventor,
and the manufacturing process uses CNC machines
for aluminium and 3D machines print for PLA+, and
most robot joints use motor servo with the type is
Dynamixel MX-28.
Table 1: DoF Part Detail on ERISA Robot.
N
o Body of Part Amount DoF
1 Head 3 (
N
ec
k
)
2 Stomach 1 (Stomach)
3 Waist 1 (Wais
t
)
4 Hand
6 (Shoulder)
2 (Elbow)
4 (Wris
t
)
5 Feet
6 (Waist)
2 (Knee)
4 (Ankles)
Total Number of DoF 29 DoF
(a) (b)
Figure 2: (a) Front View Robot Design, (b) Side View.
1.1.2 Electrical Design
To control all the performance, the ERISA robot uses
an STM32F407VGT microcontroller with a clock
frequency of up to 168MHz. This primary control is
used starting from kinematic calculations, sensor
access and communication. To be able to drive all
these servos, a microcontroller is needed as a logic
controller. Microcontroller acts like a human brain
because it can give commands to the servo to rotate.
In its use, the microcontroller will process the
commands given by the programmer and then execute
them into servo movements.
Figure 3: Electrical System Diagram of ERISA.
1.1.3 Block Diagram Process
In figure 4 is a process about the process of making
movement on the robot, in the Autodesk Inventor
software a design is made from the robot, then the
The Development of Dance Movement in Humanoid Robot Dancing ERISA
627
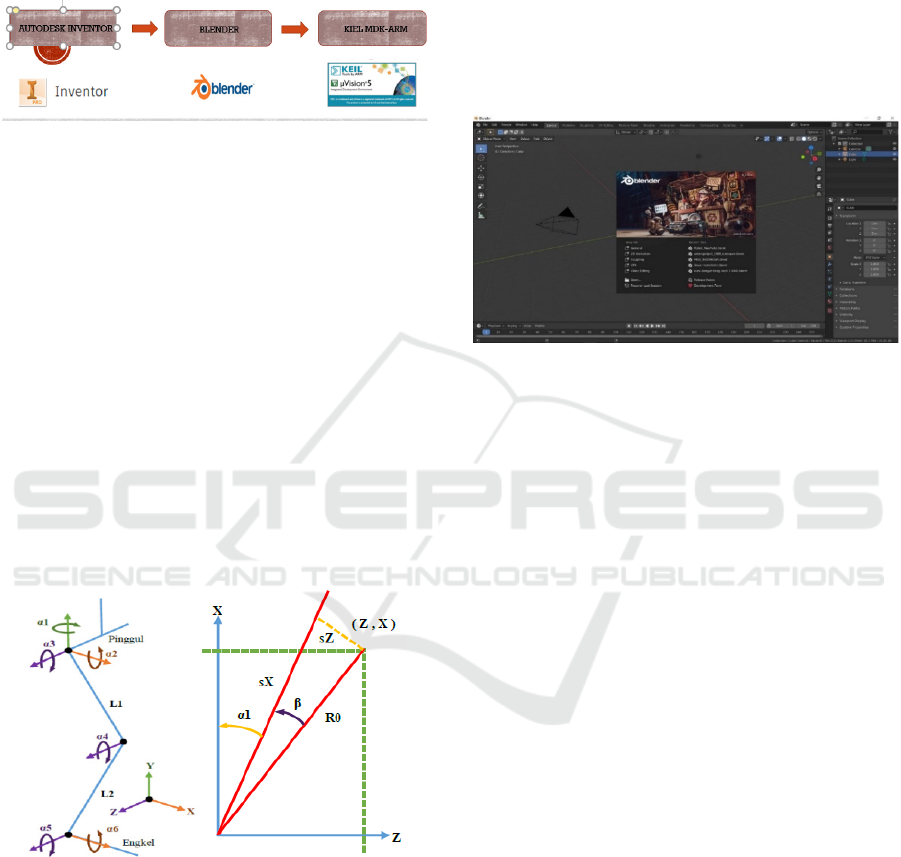
design results from the Autodesk Inventor are
imported into the Blender software to make a robot
motion simulation by giving bones in each joint, then
the value from the servo is taken to be entered into
Keil software.
Figure 4: Block Diagram Process.
2 CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN
2.1 Kinematic
There are two types of kinematics applied to the
ERISA robotic motion system: forward kinematics
and reverse kinematics. This advanced kinematics is
used to control the movement of the hand servo. In
comparison, inverse kinematics is used to control the
movement of the legs. This inverse kinematic system
is modelled on each robot's leg, where the hip is used
as the base and the ankle as the end effector. This
inverse kinematic uses 6 DoF in this inverse
kinematic, input conditions from the ankle, X, Y, Z,
and Heading Coordinates.
(a) (b)
Figure 5: (a) Isometric Visible Kinematic Model, (b)
Kinematic Model Top View [3].
2.2 Choreography Making
Blender is a 3-dimensional (3D) processing software
for creating 3D animations, which can be run on
Windows, Macintosh and Linux. Blender is also the
same as 3D software in general, such as 3DS Max,
Autodesk Maya and Lightwave. Their fundamental
differences include work projects in Blender that can
be done in almost all other commercial 3D software.
The appearance can be adjusted at will, has the
rigidify feature that makes it easy to make motions in
3D designs (James Chronister, Edition 4).
The armature is a framework used to change the
shape of the mesh. It can be used to create characters,
suspensions on cars and much more. In making the
choreography, to make bones and skeletons in the
ERISA robot design, which uses the Blender
software.
Figure 6: Blender Software Version 2.82.
3 RESULT
In this section is the result of making motion robot
motion in Blender software.
3.1 Simulation Information
Figure 7 below is a condition where the robot is first
turned on (SetPos). It is assumed that all values are
zero with the SetPos. The robot above has 29 DoF,
which for convenience is labelled on each servo joint
to make it easier to operate.
The Image below in figure 8 is a label to make it
easier to make a choreography.
Information:
1. Right Hand Servo 1 (T.KN-1)
If you want to move the joint (T.KN-1) outward
away from the robot body, then the value entered
is positive.
2. Right Hand Servo 2 (T.KN-2)
If you want to move the joint (T.KN-2) outward
away from the robot body, then the value entered
is positive.
3. Right Hand Servo 3 (T.KN-3)
If you want to move the joint (T.KN-3) outward
away from the robot body, then the value entered
is positive.
4. Right Hand Servo 4 (T.KN-4)
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
628
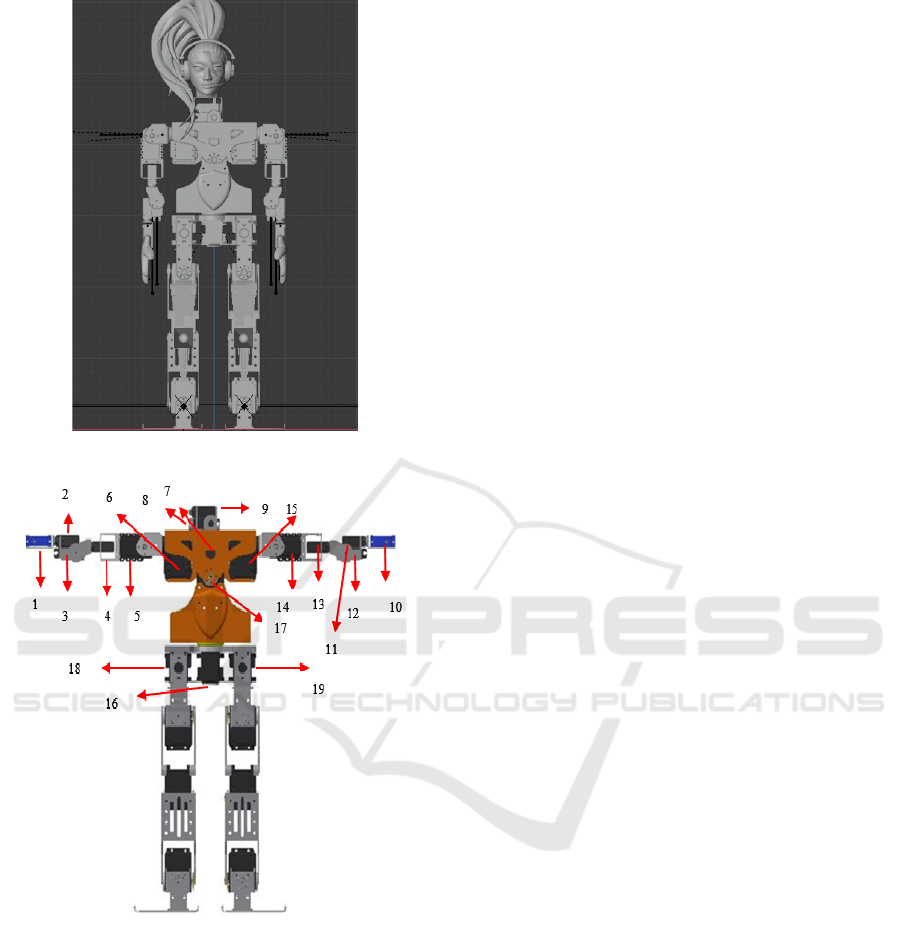
Figure 7: Robot Initial Position Front View.
Figure 8: Joint Robot Description.
If you want to move the joint (T.KN-4) outward
away from the robot body, then the value entered
is positive.
5. Right Hand Servo 5 (T.KN-5)
If you want to move the joint (T.KN-5) outward
away from the robot body, the value entered is
positive.
6. Right Hand Servo 6 (T.KN-6)
If you want to move the joint (T.KN-6) forward,
the value entered is positive.
7. Servo Head 1 (Kpl-1)
If you want to move the joint (Kpl-1) to the right,
the value entered is positive.
8. Servo Head 2 (Kpl-2)
If you want to move the joint (Kpl-2) to the right,
the value entered is positive.
9. Servo Head 3 (Kpl-3)
If you want to move the joint (Kpl-3) downwards,
the value entered is positive.
10. Left Hand Servo 1 ( T.KR-1)
If you want to move the joint (T.KR-1) outward
away from the robot body, then the value entered
is positive.
11. Left Hand Servo 2 ( T.KR-2)
If you want to move the joint (T.KR-2) outward
away from the robot body, the value entered is
positive.
12. Left Hand Servo 3 ( T.KR-3)
If you want to move the joint (T.KR-3) outward
away from the robot body, then the value entered
is positive.
13. Left Hand Servo 4 ( T.KR-4)
If you want to move the joint (T.KR-4) outward
away from the robot body, the value entered is
positive.
14. Left Hand Servo 5 ( T.KR-5)
If you want to move the joint (T.KR-5) outward
away from the robot body, the value entered is
positive.
15. Left Hand Servo 6 ( T.KR-6)
If you want to move the joint (T.KR-6) forward,
the value entered is positive.
16. Body 1
If you want to move the Body 1 joint to the right,
then the value entered is positive.
17. Body 2
If you want to move the Body 2 joint to the right,
then the value entered is positive.
18. Heading 1
If you want to move the joint heading one
outwards, the value entered is positive.
19. Heading 2
If you want to move the joint heading two
outwards, the value entered is positive.
Meanwhile, for the legs, using inverse kinematic to
make the legs of robot moving. The x-axis is for
forwarding, the y-axis is for upwards, and the z-axis
is for the robot's tilt. To make a simulation using
Blender software, one of the features in the Blender
software is used with the name timeline, which
contains a keyframe where we move or rotate the
robot joint and then lock it in the desired position.
The Development of Dance Movement in Humanoid Robot Dancing ERISA
629
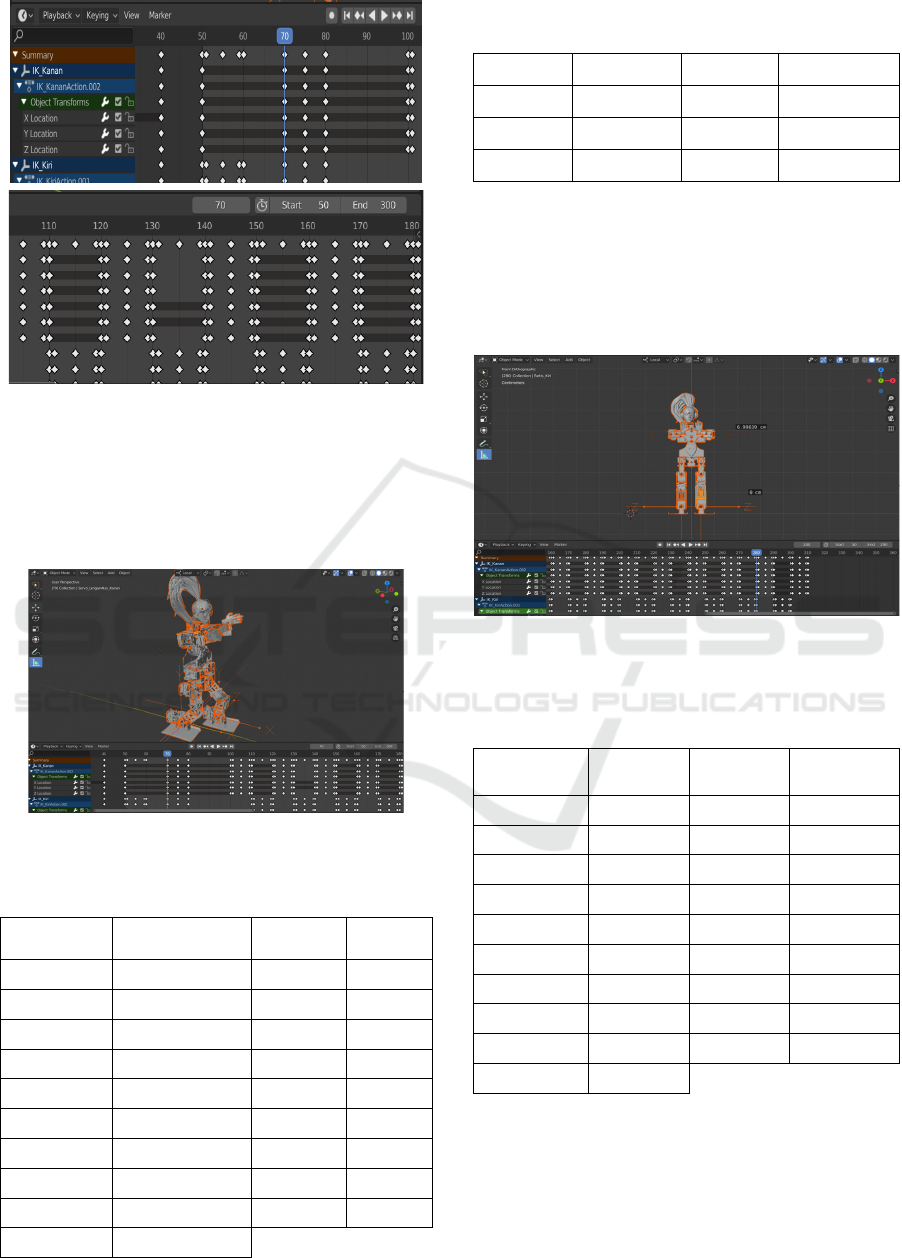
Figure 9: Timeline in software Blender.
3.2 Opening Prayer Movement
The opening prayer movement is a respectful gesture
to start a dance. In this opening prayer, it starts from
frames 50 to 70
Figure 10: Opening Prayer Movement.
Table 2: Prayer Movement Opening the body, hands and
head on a 70 Frame.
Joint Value (Deegre) Joint
Value
(
Dee
g
re
)
T.KN-1 45 T.KR-1 45
T.KN-2 -10 T.KR-2 -10
T.KN-3 -45 T.KR-3 -45
T.KN-4 0 T.KR4 0
T.KN-5 -10 T.KR-5 -10
T.KN-6 100 T.KR-6 100
Heading 1 0 Kpl-1 0
Heading 2 0 Kpl-2 0
Body 1 0 Kpl-3 20
Body 2 0
Table 3: Opening Prayer Movement on the leg 50
th
to 70
th
legs of the frame.
Axis Value (cm) Axis Value (cm)
X Ri
g
h
t
0X Lef
t
11.5
Y Ri
g
h
t
0Y Lef
t
3.3
Z Ri
g
h
t
3.5 Z Lef
t
0
3.3 Closing Prayer Movement
The closing prayers is a respectful gesture to end a
dance. This movement is the last movement of the
simulation in the Blender software, it starts from
frames 280 to 290
Figure 11: The Closing Prayer Movement on the 280
Frame.
Table 4: Closing Prayer Movement Data on Body, Hands
and Head Frame to 280.
Joint
Value
(Dee
g
re)
Joint
Value
(Dee
g
re)
T.KN-1 90 T.KR-1 10
T.KN-2 0 T.KR-2 0
T.KN-3 0 T.KR-3 0
T.KN-4 90 T.KR-4 90
T.KN-5 10 T.KR-5 10
T.KN-6 60 T.KR-6 90
Heading 1 0 Kpl-1 0
Heading 2 0 Kpl-2 0
Body 1 0 Kpl-3 0
Body 2
0
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
630
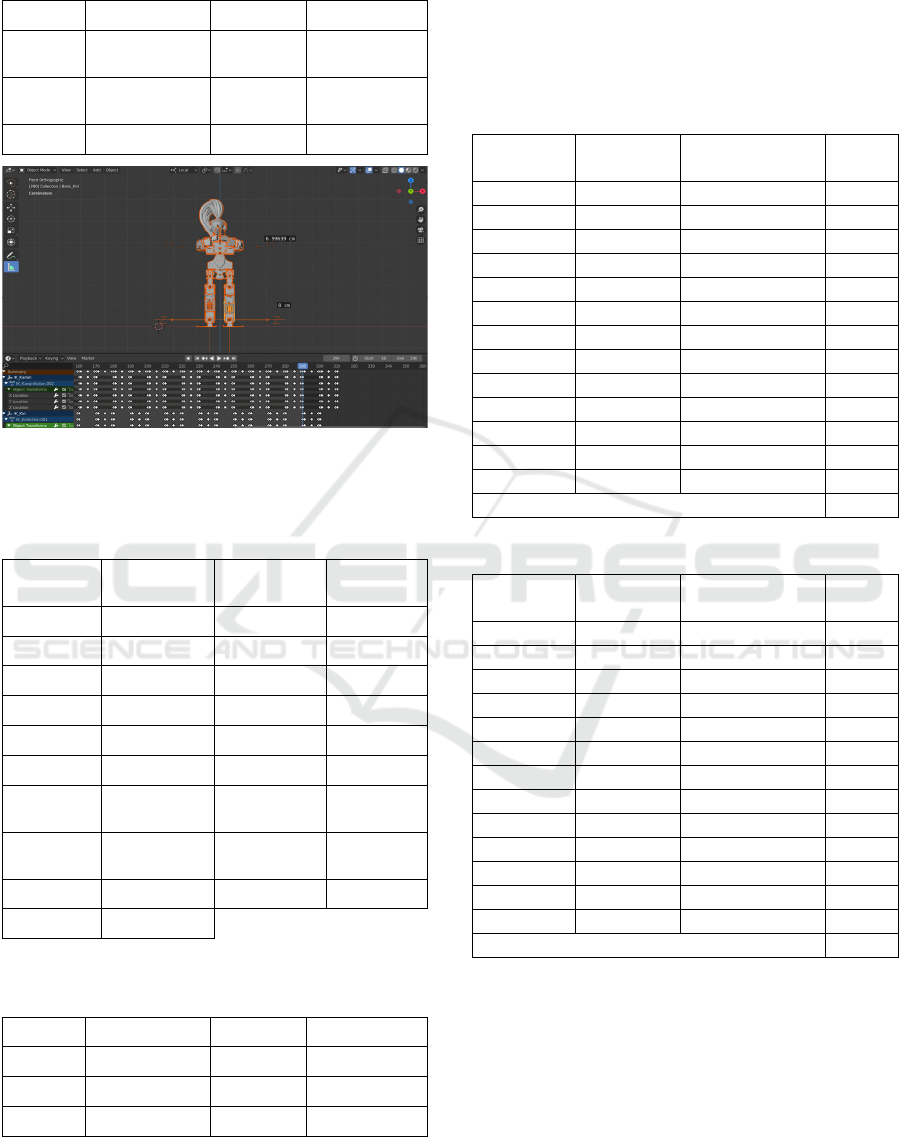
Table 5: Closing Prayer Movemnt Data at the Foot of
Frames 270 to 280.
Axis Value (cm) Axis Value (cm)
X
Ri
g
h
t
0 X Lef
t
8
Y
Ri
g
h
t
0 Y Lef
t
3.3
Z Ri
g
h
t
3.5 Z Lef
t
0
Figure 12: The Closing Prayer Movement on the 290
Frame.
Table 6: Closing Prayer Movement Data on Body, Hands
and Head Frame to 290.
Joint
Value
(Dee
g
re)
Joint
Value
(Dee
g
re)
T.KN-1 45 T.KR-1 45
T.KN-2 -10 T.KR-2 -10
T.KN-3 -45 T.KR-3 -45
T.KN-4 0 T.KR4 0
T.KN-5 -10 T.KR-5 -10
T.KN-6 100 T.KR-6 100
Heading
1
0 Kpl-1 0
Heading
2
0 Kpl-2 0
Body 1 0 Kpl-3 20
Body 2 0
Table 7: Closing Prayer Movement Data at the Foot of
Frames 280 to 290.
Axis Value(cm) Axis Value(cm)
X Ri
g
h
t
8 X Lef
t
0
Y Ri
g
h
t
3.3 Y Lef
t
0
Z Ri
g
h
t
0 Z Lef
t
3.5
The following is a summary comparison of the
values entered on the Keil MDK ARM and the direct
values taken one of the variation movement is
executed on the robot. To calculate the error in the
table below use the formula:
Error = |(input value– output value) / input value
)|*100%
Table 8: Servo Error Value in Variation Movement 1.
Servo Input
value
Output
value
Error
T.KN-1 90 86 4.4%
T.KN-2 60 57 5%
T.KN-3 -70 - 67 4.2 %
T.KN-4 5 5 0%
T.KN-5 -30 -31 3%
T.KN-6 95 93 2.1%
T.KR-1 -90 -88 2.2%
T.KR-2 -70 -67 4.2%
T.KR-3 55 57 3.6%
T.KR-4 -5 -5 0%
T.KR-5 -30 -28 6.6%
T.KR-6 85 80 5.8%
Kpl-3 -30 -32 1.5%
Avera
g
e Erro
r
3.2 %
Table 9: Servo Error Value in Variation Movement 2.
Servo Input
value
Output
value
Error
T.KN-1 70 73 4.2%
T.KN-2 55 56 1.8%
T.KN-3 -90 - 87 3.3%
T.KN-4 25 24 4%
T.KN-5 -50 -51 2%
T.KN-6 85 84 1.1%
T.KR-1 -75 -78 4%
T.KR-2 -62 -63 1.6%
T.KR-3 90 88 2.2%
T.KR-4 -35 -37 5.7%
T.KR-5 -50 -52 4%
T.KR-6 79 77 2.5%
Kpl-3 -45 -42 6.7%
Avera
g
e Erro
r
3.3%
In the table above from table 8 and table 9, it can be
seen that the error values for each servo on the robot
are mostly not in accordance with the input values,
and the test results of the 2 variations of the
movement, an average error of 3.25% is generated.
Several factors causing the discrepancy of the output
value on the robot, one of which is the servo's age
which is quite long and can also be due to human error
when measuring the output value of the robot's servo.
The other factor can be in terms of mechanics and can
The Development of Dance Movement in Humanoid Robot Dancing ERISA
631

also be in terms of hardware, for example too tight or
too loose the bolts installed on the robot can affect the
movement of the servo
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the results of the experiment both in
simulation using the Blender software in determining
and making dance movements with the output in the
form of degrees of each joint which is then
implemented and proven by entering the data after
being converted into pwm data to drive the servo
motor, there are differences that have either a slight
or a slight difference large with an average error of
3.25%. Using Blender software can reduce the time
in making dance moves and can immediately see the
results and forms of movements made.
REFERENCES
Y. Sakagami, R. Watanabe, C. Aoyama, S. Matsunaga, N.
Higaki, dan K. Fujimura, 2002, "The intelligent Asimo:
System overview andintegration," in Intelligent Robots
and Systems (IROS), IEEE/RSJ International
Conference on, vol. 3, pp. 2478.2483.J. Clerk Maxwell,
A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism, 3rd ed., vol.
2. Oxford: Clarendon, 1892, pp.68–73.
Toyota Global Newsroom. (2017, Nov) Toyota Unveils
ThirdGeneration Humanoid robot T-HR3. [Online].
Available: https://newsroom.toyota.co.jp/en/download/
20110424K. Elissa, “Title of paper if known,”
unpublished.
James Chronister. Blender Basics Classroom Tutorial
Book. Edition 4
A. H. Alasiry, N. F. Satria and A. Sugiarto, "Balance
Control of Humanoid Dancing Robot ERISA while
Walking on Sloped Surface using PID," 2018
International Seminar on Research of Information
Technology and Intelligent Systems (ISRITI), 2018, pp.
577-581, doi: 10.1109/ISRITI.2018.8864447.
R. Dian Alarmi, A. Husein Alasiry, N. Fajar Satria and B.
Sumantri, "A Sensor Fusion Algorithm in Humanoid
Robot PD Balancing Control for Walking on Slope,"
2020 International Electronics Symposium (IES), 2020,
pp. 289-296, doi: 10.1109/IES50839.2020.9231674.
R. Dimas Pristovani. 2017. Walking Optimization
Algorithm for Robot Humanoid Soccer On Artificial
Grass. PENS.
A. Sugiarto, Kontrol Keseimbangan Robot humanoid
Dancing ERISA Menggunakan Feedback Tilt Sensor.
Surabaya, 2018
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
632
