
Metallization Development of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
(MWCNTs) with Copper by an Electroless Plating
Dewa Made Pancarana and I Nyoman Budiartana
Mechanical Engineering Department, Bali State Polytechnic, Bukit Jimbaran, Indonesia
Keywords: Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes, Metallization, Colloidal Tin-Palladium, Activation, Acceleration, Copper,
Electroless.
Abstract: In this study, Multi Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) were coated with copper by an electroless plating
process. The aim is to form a strong bond between the MWCNTs and the Aluminum matrix. Aluminum in
liquid form has a high surface tension compared to the surface tension of MWCNTs, resulting in very poor
wettability. The surface of MWCNTs coated with metal (copper) will increase the dispersion and wettability
between MWCNTs and the Aluminum matrix. The research was conducted at the mechanical engineering
laboratory, Bali State Polytechnic. Coating MWCNTs with copper is carried out in three steps, namely:
activation, acceleration, and electroless. MWCNTs were activated using a Pd-Sn colloidal solution adapted
from the Plating on Plastics (POP) industry. The ingredients used in the activation process were a mixture of
37.5 ml of Pd-Sn colloid solution, 37.5 ml of HCl (37%), and 175 ml of DI water. In the acceleration process,
fluoride acid (HF 55%) is used as an accelerator. The last process is the electroless plating process, in which
the surface of the MWCNTs that has been catalyzed is inserted into the Copper-Cobalt (Cu-Co) electrolyte
solution. Copper-coated MWCNTs were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM-EDX)
analysis using (JEOL-JSM 6510 A) at the Mechanical Engineering Materials Laboratory, Udayana
University. The results of the SEM-EDX test showed that the copper content was 84.1%, carbon 12.08%, and
the rest were other elements, such as: O, Na, K, Co, Pd, Sn. The increasing size of MWCNTs indicates the
presence of copper on the surface of MWCNTs. The average diameter of the 85 nm copper-clad MWCNTs
increased compared to the average diameter of the initial MWCNTs (10–20 nm).
1 INTRODUCTION
Multi-walled Carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) have
been widely used in the manufacture of composites
with aluminum matrices because MWCNTs have a
high strength-to-weight ratio. Several previous
studies have shown that the use of MWCNTs to
strengthen the aluminum matrix is very effective.
Most of these studies report using powder
metallurgical techniques such as high energy ball
milling followed by conventional and unconventional
compaction and sintering techniques for sample
preparation (Esawi, 2010, 2009). Of course, the Al-
MWCNTs composite manufacturing process using
powder metallurgy techniques, requires relatively
expensive costs.
In the metal industry, casting is one of the
techniques that can be used for the manufacture of
metal matrix composites. The use of MWCNTs in the
fabrication of aluminum-MWCNTs composites by
casting process faces several obstacles. The main
constraints are poor wetting which limits the
dispersion of MWCNTs in molten aluminum as well
as the problem of oxidation of MWCNTs at high
temperatures which destroys the structure of
MWCNTs (So, 2011). Recently, electroless coating
has offered many advantages that enable it to work
in harmony with MWCNTs in foundry engineering.
Applying a metallic layer
on the surface of MWCNTs
can increase their
wettability in molten metal and also
helps in increasing their dispersion (So, 2011). In
addition, it protects MWCNTs from oxidation at high
temperatures.
In general, electrolytic plating has two main
reactions occurring simultaneously, the oxidation of
the reducing agent to generate electrons representing
the anodic partial reaction and the reduction reaction
of the metal ions present in the solution without
electricity by the resulting electrons representing the
cathodic partial reaction. Since electroplating occurs
only on catalytic surfaces, the surface of MWCNTs
1086
Pancarana, D. and Budiartana, I.
Metallization Development of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) with Copper by an Electroless Plating.
DOI: 10.5220/0010959500003260
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2021), pages 1086-1090
ISBN: 978-989-758-615-6; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

must be catalytically made to be ready for
electrocoating. The general scheme for surface
catalyzing is the conventional two-step technique of
sensitization and activation through aqueous
solutions of Tin(II) chloride (SnCl2) and Palladium
(II) chloride (PdCl) (Feng, 2004). This approach
helps in depositing catalytic palladium particles on
top of the MWCNTs. However, the optimization
process of such catalyst deposition on MWCNTs is
difficult due to the need to control the four
main
factors represented by SnCl
2
concentration PdCl
2
concentration,
PH level for both solutions, and the
resulting catalytic particle size. Such a process would
be difficult to optimize when it comes to coating
MWCNTs supplied from different sources due to the
different surface area and volume ratios for different
MWCNTs. However, electroless nickel and copper
phosphorus have been reported in decorating
MWCNTs following the previously mentioned
catalyst system. After that, the coated MWCNTs were
placed in molten aluminum which reported a
promising improvement in the mechanical properties
of the resulting composite (So, 2011).
One of the problems reported in this study for the
previous zero-electric approach was the absence of a
reaction stop mechanism to stop further copper
deposition on top of the MWCNTs once the required
copper layer was reached. This appears to be
particularly important during the final filtration in the
absence of sonication and stirring. Further copper
deposits may lead to the formation of Cu-coated
MWCNTs aggregates. The presence of electrolytes
with low deposition rates makes it difficult to achieve
a precise reaction stop mechanism. For electroplating
copper, the key factor to increase the deposition rate
is to increase the anodic partial reaction kinetics. By
oxidizing more formaldehyde (reducing agent), more
electrons will be generated and more copper ions will
be reduced in the cathodic partial reaction.
The key parameter of formaldehyde oxidation is
the pH value which is controlled by NaOH. As the pH
value increases, the deposition rate increases.
However, the pH reaches a threshold where it starts
to fall when it reaches a value of 12.5. Conventional
copper electrolytes rely on pH values and heating to
control the reaction kinetics (Feng, 2004) and
(Mishra, 1996). In this work, a room temperature
copper-cobalt electrolyte having a high deposition
rate was used. A new catalytic strategy using
palladium-tin colloids was explored.
2 MATERIALS AND
EXPERIMENTAL
PROCEDURES
2.1 Materials
The multi-walled carbon nanotubes are widely
supplied by Chengdu Organic Chemicals Co. Ltd.,
China (OD: 10 - 20 nm, length: 10 - 30 m and purity
>98%) was used in this study. Colloidal palladium-
tin drive was prepared with a composition of 0.5 g of
palladium chloride (PdCl2), 50 ml of 37%
hydrochloric acid (HCl), 200 ml of deionized water,
25 g of stannous chloride. Cupric Sulphate
Pentahydrate (98.5% Assay) and Sodium Carbonate
Anhydrous (99.5% Assay) were supplied by Bofa
Laboratotium. Sodium Hydroxide (99% Assay) was
supplied by Bofa Laboratotium. Potassium Sodium
Tartrate Tetrahydrate otherwise known as Rochelle
salt (99% Assay) is supplied by Bofa Laboratotium.
Cobalt(II) Chloride Hexahydrate (99% Assay) was
supplied by Bofa Laboratotium. Formaldehyde 37%
in aqueous solution was supplied by Bofa
Laboratotium.
2.2 Experimental Procedures
The process of coating the surface of MWCNTs with
copper is carried out in three steps. Starting with the
surface activation process of MWCNTs using Pd-Sn
colloidal particles. The next step is the acceleration
process to remove stanno hydroxide deposits on the
surface of the activated MWCNTs. The last process,
electroplating of Cu-Co on the surface of the
catalyzed MWCNTs. The above procedure globally
is shown in Figure 1
Figure 1: General Scheme of cu-co Electroless Plating on
MWCNTs.
Metallization Development of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) with Copper by an Electroless Plating
1087

2.3 Activation of MWCNT’s in Pd-Sn
Colloidal Solution
The amount of MWCNTs used in this process was set
to 0.1 gram MWCNTs. MWCNTs is used when
received without any function. MWCNTs were
activated using a Pd-Sn colloidal solution adapted
from the Plating on Plastics (POP) industry. The
activation process was carried out in a mixture of 37.5
ml of Pd-Sn colloid solution, 37.5 ml of HCl (37%),
and 175 ml of DI water. When using, mix 15%
palladium-tin colloidal catalyst solution and 15%
hydrochloric acid (37%) together, and balance with
deionized water, then heated to 50 - 60 °C to get a
better catalytic effect.
For activation, MWCNTs were dispersed with a
magnetic stirrer in a colloidal solution for 30 minutes.
After the stirring was completed, the treated
MWCNTs were filtered using a 0.22 lm PTFE filter
membrane on the microfiltration kit. The filtered
MWCNTs were re-dispersed in DI water and filtered
again to remove excess colloidal particles and
residual colloid solution from activated MWCNTs.
After filtration, MWCNTs were collected from the
membrane using tweezers.
2.4 Acceleration of MWCNTs in a
Mixture of Acids
The activated MWCNTs are then introduced into a
mixed acid solution known as an accelerator.
The
accelerator serves to remove excess tin hydroxide
on
the surface of the catalytic particles in the MWCNTs
allowing the palladium surface to be exposed. The
acceleration process will not remove lead from the
core of colloidal particles (Cohen, 1976). The
acceleration process uses 55% (50 mL) HF acid in
500 mL DI water.
After acceleration, the MWCNTs were re-
dispersed in water and filtered again to remove traces
of the previous solution. Following the previous step,
the MWCNTs surface becomes catalytic.
2.5 Electroless Cu-Co Plating of
MWCNTs
The catalyzed MWCNTs were put into a 1 liter
solution of Cu-Co electrolyte with concentrations as
shown in Table I.
Table 1: Typical Concentrations of Cu-Co electrolyte.
Copper-Cobalt electrolyte
Concentrations
CuSO
4
.6H
2
O
6.99 g/L
Na₂CO₃
CoCl
2
2 g/L
CoCl
2.
6H
2
O
1.09 g/L
KNaC
4
H
4
O
6
·4H
2
O (Rochelle
Salt)
22.57 g/L
NaOH 4.5 g/L
Formaldehyde 37% 6 ml/L
All precursor powders were dissolved in DI
water under magnetic stirrer for 5 min. After making
sure all the powder is dissolved in the solution,
formaldehyde is added to the solution. Subsequently,
the activated MWCNTs were placed in an electroless
bath under a magnetic stirrer for 10 min and the
reaction started on the catalytic surface of the Pd-
coated MWCNTs. Air bubbles began to emerge from
the solution after the MWCNTs were added. This
occurs due to the dissolution of hydrogen from the
surface of the palladium and the oxidation of
formaldehyde which produces hydrogen. Then the
solution in a glass beaker was stirred using a magnetic
stirrer for 30 minutes. When the air bubbles stop, it
gives a good indication that the copper has
completely covered the entire surface of the catalyst.
In this case the copper surface became auto-catalyzed
and the solution turned dark brown indicating the
coverage of MWCNTs by copper. After stirring is
complete, the copper-coated MWCNTs begin to
accumulate on the bottom of the glass due to their
increased density. Then the solution was filtered
using a 0.22 nm PTFE filter membrane. The color of
the filtered solution appears to be a light pink color
indicating the consumption of all copper ions in the
solution prior to filtration. The color of the copper-
coated MWCNTs powder obtained, is shown in
Figure 2.
The characterization of copper-clad MWCNTs
was carried out at the Mechanical Engineering
Materials Laboratory of Udayana University using
scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis using
(JEOL-JSM 6510 A).
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1088

Figure 2: Copper Coated MWCNT’s of a Brown Color.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The addition of cobalt(II) chloride to an electroless
copper solution helps in the autocatalytic reduction of
copper ions in an electroless solution increasing the
deposition rate tremendously. The use of colloidal
Pd-Sn nanoparticle catalytic system limits the
catalyst optimization process to two factors (colloidal
particle concentration and solution volume relative to
the number of MWCNTs) rather than four factors in
the predecessor system. In addition, the new system
provides a fixed average size of the colloidal
nanoparticles for better coating fit over MWCNTs.
The optimized catalyst concentration and volume
required to cover the surface area of a fixed number
of MWCNTs helps in controlling the catalyst
concentration-dependent initial copper deposition
rate.
SEM image in Fig. 3 shows MWCNTs after being
coated with copper. The increase in the thickness of
the MWCNTs indicates the presence of copper on the
surface of the MWCNTs. The mean diameter of the
copper-clad MWCNTs was found to be 85 nm
compared to the diameter of the initial MWCNTs,
averaging 10-20 nm. The SEM images show a
uniform layer that completely covers all the surfaces
of the MWCNTs.
Figure 3: SEM Image of The Copper Coated MWCNT’s.
To determine the percentage of the elements
present, chemical analysis was carried out using
energy dispersive X-ray (EDX). The spectrum
obtained is shown in Figure 4.
The results of the analysis showed that the
weight of copper was 84.10 % and 12.08 % C . Other
elements such as Na, K, Co and Sn were found in
minimal percentages as listed in Table 2.
Figure 4: EDX Spectrum of Copper Coated MWCNTs.
Metallization Development of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) with Copper by an Electroless Plating
1089
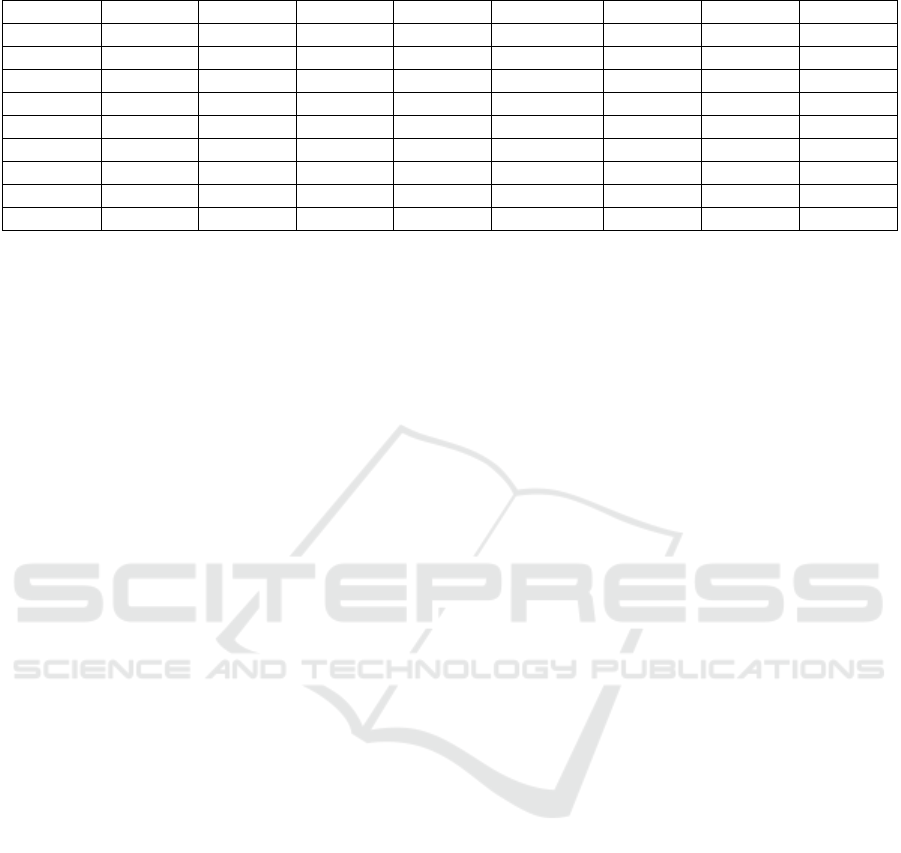
Table 2: Edx Elemental Analysis of Copper Coated Mwcnt’s.
Element (keV) Mass% Sigma Mol% Compound Mass% Cation K
C K 0.277 12.08 0.24 47.47 C 12.08 0.00 2.9938
O 17.81
Na K 1.041 1.30 0.12 1.34 Na
z
O 1.76 1.22 0.6077
K K 3.312 0.05 0.03 0.03 K
2
O 0.07 0.03 0.0754
Co K 6.924 1.53 0.09 1.23 CoO 1.95 0.56 2.7533
Cu K 8.040 67.19 0.71 49.92 CuO 84.10 22.80 93.5240
Pd L
Sn L 3.442 0.04 0.07 001 SnO 0.05 001 0.0458
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 24.62
ZAF Method Standardless Quantitative Analysis (Oxide)
Fitting Coefficient : 0.0326
Total Oxide : 24.0
The process of coating MWCNTs with copper
produces different amounts of elements, compared to
the results of previous studies (Elsharkawi, 2018).
This is influenced by the type of catalyst, the type of
accelerator, and the concentration of the solution used
when immersing the MWCNTs. In this study, the
SEM-EDX results showed that there was no Pd in the
copper-coated MWCNTs powder. The use of a
commercial Pd-Sn Colloidal Solution catalyst from
Dupont gave a better effect, obtained elemental
content of Cu 98.56% and Pd 0.43% (Elsharkawi,
2018).
4 CONCLUSIONS
In the electroless plating process of MWCNTs with
Cu, it can be concluded that:
A.
The factors that affect the morphology of the
sample are; the composition of the colloidal
palladium-tin catalyst, the type of catalyst, the
activation temperature, the volume of the HF acid
solution during the acceleration process, and the
volume of the electrolyte solution bath.
B.
The volume of the electrolyte solution bath is more
in electrolytic coating, resulting in better samples.
REFERENCES
Esawi, A.M.K., Morsi, K., Sayed, A., Taher, M. & Lanka,
S. (2010). Effect of carbon nanotube (CNT) content on
the mechanical properties of CNT-reinforced
aluminium composites. Elsevier, Composites Science
and Technology, vol.70, issue 16, pp. 2237-2241,
Esawi, A.M.K., Morsi, K., Sayed, A., Gawad, A.A. & Borah,
P. (2009). Fabrication and properties of dispersed
carbon nanotube–aluminum composites. Elsevier,
Materials Science and Engineering: A, vol. 508, issues
1–2, pp.167– 173.
So, K.P., Lee, I.H., Duong, D.L., Kim, T.H., Lim, S.C.,
An, K.H. & Lee, Y.H. (2011). Improving the wettability
of aluminum on carbon nanotubes. Elsevier, Acta
Materialia, vol.59, pp. 3313–3320.
Mallory, G.O. & Hajdu, J.B. (2009), Electroless plating:
fundamentals and applications. Am Electroplaters Surf
Finish, New York.
Feng, Y. & Yuan, H. (2004). Electroless plating of carbon
nanotubes with silver. Kluwer Academic Publishers,
Journal of Materials Science vol. 39 pp. 3241 – 3243.
Mishra, K.G.(1996). Kinetics and mechanism of electroless
deposition of copper. J Electrochem Soc 143:510.
hpttps://doi.org/10.1149/1.1836473
Cohen, R. & Meek, R. (1976). The chemistry of
palladium—tin colloid sensitizing processes. J Colloid
Interface Sci 55:156–162.
Shacham-Diamand, Y., Sverdlov, Y., Friedberg, S.,
Yaverboim A. (2017). Electroless plating and printing
technologies, in nanomaterials for 2D and 3D printing.
In: S. Magdassi and A. Kamyshny (eds) Wiley-VCH
Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany.
https:// doi.org/10.1002/9783527685790.ch3
Osswald, S., Havel, M. & Gogotsi, Y. (2007). Monitoring
oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by Raman
spectroscopy. J Raman Spectros 38:728–736.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.1686
Mansoor, M. & Shahid, M. (2016). Carbon nanotube-
reinforced aluminum composite produced by induction
melting, Journal of Applied Research and Technology.
Singhal, S.K., Lal, M., Sharma, I. & Mathur, R.B. (2012).
Fabrication of copper matrix composites reinforced with
carbon nanotubes using a combination of molecular-
level-mixing and high energy ball milling. J Compos
Mater 47:613–621.
Agarwal, A., Bakshi, S.R. & Lahiri, D. (2011). Processing
techniques. Carbon nanotubes: reinforced metal matrix
composites. CRC Press- Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton,
Florida, pp 30– 33
Elsharkawi, M. & Esawi, A.M.K.(2018), Development of
an Electroless PlatingProcess for Multi-wall Carbon
Nanotubes to Improve Their Dispersion and Wettability
in Molten Aluminum, The Minerals, Metals &
Materials Society, pp.29-39
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1090
