
Improving the Quality of Fishery Products by Maintaining Ideal
Composition of Seaweed Caragenan: Kappaphycus Alvarezii
Siti Hajar
1
and Herlina
2
1
Fishery Technology Politeknik Negeri Nunukan, Nunukan, Indonesia
2
Business Administration Politeknik Negeri Nunukan, Nunukan, Indonesia
Keywords: Carrageenan, Mackerel, Meatball.
Abstract
:
This study aim is to determine the ideal composition of good carrageenan as a natural preservative for
improving the quality of fishery products. Other aim is to analyze the quality of fishery products by
maintaining of seaweed carrageenan (Kappaphycus alvarezii). This research was conducted for 4 (four)
months at the Laboratory of the Fishery Products Processing Technology Study Program Nunukan, Indonesia.
Nunukan. Data were collected based on observations of organoleptic tests which consist of color, taste, texture,
and aroma. The method used is an experiment with treatment A0 (meatballs without the
addition of
carrageenan) as a control, treatment A1 (meatballs with the addition of carrageenan 2.5%), treatment A2
(meatballs with the addition of carrageenan 5%), treatment A3 (meatballs with the addition of carrageenan 7,
5%). The composition ideal of carrageenan flour with a concentration of 2.5% could led the
best effect on the
elasticity quality of mackerel fish balls. The organoleptic value with the hedonic test of mackerel fish balls
with the extra of carrageenan flour of 2.5% has an appearance parameter value IS 3.76 (neutral to like). The
color parameter value is3.87 (neutral to like), and aroma parameter value is 3.87 (neutral to like). The taste
parameter is 4.69 (like to very like) and the value of the texture parameter is 4.34 (like). Other material such
water content is 66.04%, and protein content is 11.87%, while fat content is
1.13%. The essential material
such as carbohydrate content is 8.59%, crude fiber content is 9.61%, and ash content is 1.53%.
1 INTRODUCTION
Most of Indonesia's territory is waters that have
the
potential to produce quite large marine products.
One
of them is seaweed which has high economic
value
because it can produce carrageenan (Dewi, et
al,
2015).
Carrageenan is a polysaccharide extracted from
several species of seaweed or red algae
(rhodophyceae). Carrageenan is a hydrophilic linear
sulfated galactan. These polymers are repeating
disaccharide units. These sulfated galactans are
classified according to the presence of the 3,6-
anhydro galactose (DA) unit and the position of the
sulfate group (Distantina, et al, 2010). Carrageenan
functions as a thickener, emulsifier, suspending
agent, preservative and stabilizing factor.
Carrageenan is also used in the food industry to
improve the appearance of coffee products,
meatballs, sausages, nuggets, salads, ice cream,
condensed milk, chocolate and jelly. (Ega, et al,
2016).
Fishery products have different durability and it
depending on the nature of the food itself. Its usually
handling during processing and storage. One of the
main causes of damage to fishery products is
contamination by microbes from outside or naturally
present in these foodstuffs. To extend the shelf life of
foodstuffs can be done in various ways, one of which
is the extra of chemicals as preservatives.
Preservatives in fishery products have become an
inseparable part, especially since the times they have
demanded products that are practical, durable, and it
also have an attractive appearance. The solution
should be taken by the industry is to add preservatives
for increasing product quality and make it last longer.
One of the preservatives that often used is chemicals,
but if it used in excess, so it can cause endanger
health. It can be stated that carrageenan is an
alternative as a natural food preservative and is safe
to use to improve the quality and quality of processed
fishery products, especially seaweed. So the author
took the title Improving the Quality and Quality of
Fishery Products by Adding the Ideal Composition of
Hajar, S. and Herlina, .
Improving the Quality of Fishery Products by Maintaining Ideal Composition of Seaweed Caragenan: Kappaphycus Alvarezii.
DOI: 10.5220/0010961200003260
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2021), pages 1153-1157
ISBN: 978-989-758-615-6; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
1153

Seaweed Carrageenan (Kappapychus Alvarezii).
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The high value of Indonesia's wealth, especially
the
fisheries sector which is supported by the vastness
of
Indonesia's oceans. It also provides its own points
for
increasing people's income.
A. Types of Processed Fishery Products
To meet the need for animal protein, it can be
obtained through the use of non-economical fish
bycatch products into products that have added some
values. One of the efforts to increase the
diversification of processed fishery products is by
developing fishery product processing technology
that can increase the selling value of these products
(Juminda, F, 2015).
Surimi is a semi-finished material made from
white meat, tasteless and odorless and it has high
gelling ability. The advantages of using surimi such
as (1) surimi can be used directly for processing food
products such as meatballs, sausages, nuggets,
kamaboko, burgers and others. (2) Surimi is odorless,
free of bones and thorns so that the processed product
is easier to consume by people of all ages. (3) The
supply and price are relatively stable because surimi
can be stored and this facilitates are the planning of
processed production. (4) The cost of storage,
distribution and transportation is cheaper because
surimi can be stored for a long time. (5) Save time and
labor because the handling is cheaper. (6) The
problems that arise due to waste disposal are smaller
(Peranginangin, et al, 1999).
The manufacture of surimi-based processed
products uses a variety of fillers and binders. These
fillers and binders can be distinguished according to
their protein and carbohydrate content. The filler is
usually a material that has a high carbohydrate
content and has little effect on the properties of the
emulsion. The binder is usually in the form of
vegetable or animal protein, with higher protein
content, and it can improve the properties of the
emulsion. Some of the processed surimi-based
products that use fillers and binders are as follows:
B. Fish Sausages (Sosis Ikan)
Sausage is meat or a mixture of several meats that
are
mashed and mixed with spices or herbs. The thing
that
needs to be considered in processed sausages is
the
binder. To get good quality sausage, so flour is
needed as a binder of good quality. The binder in
sausages serves to attract water, and it gives a
distinctive color, with form a dense texture, also it
improve the emulsion stability, and to reduce cooking
time shrinkage, improve taste and slice properties.
The binder will bind with water to form a mass,
strengthening the emulsifier ability of the meat. It
leads the emulsion more stable. Sausages on the
market are made from a mixture of meat, flour, and
STPP (sodium tripolyphosphat) as a binding material.
STPP is an inorganic compound in the form of white
crystals which is usually used for food preservatives
and texturizers, but it is currently the use of chemicals
in limited. For this reason, that why a natural STPP
substitute is still needed. The natural STPP is namely
carrageenan. Carrageenan is obtained from seaweed
extraction and it is an alternative to STPP.
C. Fish Meatball (Bakso Ikan)
Meatballs are foods that are favored by various
groups of people of all ages in all corners of
Indonesia. Fish ball is a processed fish product that is
round in shape, highly nutritious, tastes delicious. It
can be eaten under any circumstances and it is also
very easily accepted by anyone. Fish balls are made
by adding spices, salt, garlic, pepper, ice 20% and
flour 10-30% (Ministry of Fisheries and Marine
Affairs RI Agency for Research and Human
Resources for Marine and Fisheries. Fisheries
Training and Extension Center, 2016).
D. Fish Nugget (Nugget Ikan)
Fish nuggets are a food favored by the
community,
especially children. According to
Lukman et al
(2009), Evanuarini and Purnomo
(2011) in the
Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Affairs
RI Agency
for Research and Human Resources for
Marine and
Fisheries and Fisheries Training and
Extension
Center (2016) noticed that Nuggets are
restructured
meat products with dough and coating to
maintain
quality. In the manufacture of nuggets, the
filler and
basic ingredients determine the
characteristics of the
nuggets produced. It is usually
used as the main
ingredient in the form of fish as the main ingredient,
while the filler is in the form of
wheat flour, tapioca
and cornstarch.
3
RESEARCH METHODS
The design used in this study was a completely
randomized design (CRD) with 4 treatments and 3
replications. Variations in addition of carrageenan
concentration to the weight of the mackerel used are:
A.
Control without the addition of carrageenan
(sausage, nuggets and mackerel fish meatballs)
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1154
B.
Sausage, Nuggets and Mackerel Fish Meatballs
with the addition of 2.5% Carageenan flour
C.
Sausage, Nuggets and Mackerel Fish Meatballs
with the addition of 5% Carrageenan flour
Sausage, Nuggets and Mackerel Fish Meatballs
with the addition of 7.5% Carrageenan flour
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
A. Physical Characteristics of Mackerel Fish
Meatballs with the Addition of Carrageenan
The physical properties of a product greatly
determine the level of consumer acceptance of the
product. The physical properties of a product also
affect the quality of the product and the price of the
product. Making mackerel fish balls with various
variations of the addition of carrageenan flour may
cause changes in the physical properties of the
mackerel fish balls producing.
B. Gel Strength
Testing the hardness level of mackerel fish balls was
carried out with the Llyoid Instrument. The testing
technique is carried out by determining the maximum
force required to break (share force) the cooked
mackerel fish ball product. The maximum force (N)
here is the maximum force required to give the
formation of the meatball. This means that the higher
the force required to break with the same level of
damage.
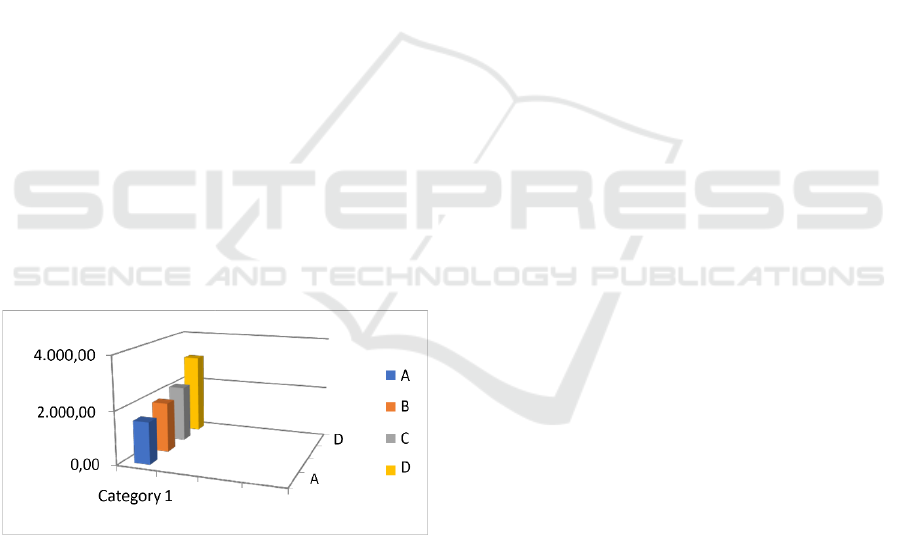
Figure 1: Gel Strength of Mackerel Meatballs with the
Extra
of Different Carrageenan Flour.
In Figure 1 it can be seen that the gel strength of
the mackerel fish ball increased with the increase in
the concentration of the addition of carrageenan flour.
The gel strength of the mackerel fish balls produced
ranged from 1,673.17 Blooms (A treatment) to
3,090.61 Blooms in D treatment.
The results of statistical analysis ANOVA test
showed that the addition of carrageenan flour had a
significant effect (α < 0.05) on the real gel strength (α:
0.05) with the extra of carrageenan flour as much as
7.5%. This shows that the extra of carrageenan flour
is directly proportional to the increasing in gel
strength of mackerel fish balls. The difference in gel
strength of the mackerel balls produced for each
treatment was caused by the extra of carrageenan
flour from the mackerel fish balls. The results showed
that the extra of carrageenan flour as much as 0%,
2.5% and 5% had a different effect on the addition of
carrageenan flour as much as 7.5%. This shows that
the addition of carrageenan flour is directly
proportional to the increasing in gel strength of
mackerel fish balls. The difference in gel strength of
the mackerel fish ball produced for each treatment
was caused by the extra of carrageenan flour.
The ability of meatballs to form a compact
structure is basically due to the ability of the meat to
bind together. This bonding process is caused by
heating. Carrageenan in fresh meat does not show a
tendency to bind to each other (Peranginangin, 1987
in Dwi, Wiwin. 2008).
Fish meat protein, especially myosin, is
responsible for the good or bad formation of gels and
emulsions in soft meat products. Small myosin
aggregates are thought to play a role in the formation
of fat emulsions. In addition, these aggregates have
the ability to expand when heated and bind all
components including water. It is determining the
consistency of the meatball product (Schut, 1976 in
Dwi, Wiwin. 2008).
The addition of salt also serves to increase the
ionic strength of the meat and dissolve the
actomyosin of the meat into cell forms which it if
heated for a certain time will form an elastic gel.
Starching can be viewed as a simple filler or binding
agent for protein gels. Gel formation is also
influenced by the addition of a thickening agent
added to the meatball which will react with starch to
form a structure.
C.
Test
1)
Bite Test
Elasticity affects a person's palatability to a
product.
The elasticity is based on the ease of
chewing time
without losing the proper tissue
properties.
Elasticity involves the easy initial
penetration of the
teeth into the meatball, the ease of
chewing into
smaller pieces and the amount of
residue left during
mastication (Lawrie, 2003 in
Sudrajat, G. 2007).
The results of the bite test on
mackerel fish balls
with the addition of different
carrageenan flours are
compact and sturdy, so the
texture of the meatballs
formed becomes chewy
(Fitrial et.al. 2005, in Dwi,
Wiwin. 2008). The bite
test of the mackerel fish balls
Improving the Quality of Fishery Products by Maintaining Ideal Composition of Seaweed Caragenan: Kappaphycus Alvarezii
1155

produced ranged from 2.69 (weak) to 5.79 (chewy
and acceptable).
Mackerel fish balls which have
chewy and acceptable
properties are the addition of
2.5% carrageenan flour.
(treatment B).
The results of the ANOVA test showed that the
addition of carrageenan flour had a significant effect
(α < 0.05) on the results of the bite test (elasticity) of
the mackerel fish balls produced. The results of
further tests with Duncan's DMRT as shown showed
that the addition of carrageenan flour had a
significantly different effect for all treatments on the
value of the bite test.
The addition of carrageenan flour can help the
formation of gels that can improve the elasticity
properties. The consistency of carrageenan gel
formation can be influenced by several factors,
including the type and concentration of carrageenan
and the presence of ions. Carrageenan can bind well
with water and protein and the meatballs also have the
strength to withstand external pressure and return to
their original shape after the pressure is removed.
This property is called ductility.
2)
Folding Test
The folding test is one of the tests on the quality
of
the meatball gel. The quality level used is on a scale of
1 to 9 (1 = completely cracked/cracked into pieces
when pressed with both fingers, up to 9 = not cracked
when folded in four). The value of the folding test
results obtained is 2.78 (cracked but still united when
folded in half) to 5.70 (slightly cracked when folded
in half to slightly cracked when folded in four).
The results of the folding test on mackerel fish
balls with the addition of different carrageenan flour
were directly related to the gel texture, especially the
gel strength. The higher folding test value, the better
the gel strength of the product. The higher
concentration of carrageenan flour is in the mackerel
fish ball product or it is higher the gel strength. The
results of the ANOVA test showed that the addition
of carrageenan flour had a significant effect (α < 0.05)
on the value of the folding test of mackerel fish balls
produced and the results of further tests with
Duncan's DMRT showed that the treatment of adding
carrageenan flour of 0% gave a significantly different
effect with treatment 2, 5%, 5% and 7.5%. The extra
of carrageenan flour treatment of 2.5% gave a
significantly different effect with the treatment of 5%
and 7.5%. However, the extra of carrageenan flour by
5% did not give a significantly different effect from
the 7.5% treatment.
3)
pH
The pH measurement aims to determine the
acidity
level of mackerel fish balls caused by
hydrogen
ions (H+). The final product that undergoes
cooking
and salting depends on the pH of the meat.
High temperatures increase the rate of pH
decrease while low temperatures inhibit the rate of pH
decrease (Suparno, 1998 in Sudrajat, G. 2007). The
average pH value of mackerel fish balls with the extra
of carrageenan flour is different. The pH of mackerel
fish balls ranged between 7.15 and 7.17, which means
that the acidity level of the mackerel fish balls which
produced in a neutral range. Based on the results of
the ANOVA test, it showed that the extra of
carrageenan flour had no significant effect (α > 0.05)
on the pH value of mackerel fish balls.
D.
Organoleptic Quality of Mackerel Fish Meatballs
with the Addition of Carrageenan
Sensory test conducted in this study is a preference
test which includes appearance, color, aroma, taste
and texture. In Table 1 it can be seen that the results
of the calculation of the average organoleptic value
could be done by the preference test (hedonic test) of
mackerel fish balls with the addition of carrageenan
flour.
Table 1: Results of the Hedonic Organoleptic Test on
mackerel fish balls with the addition of different
carrageenan flour.
No Parameter Treatment
AB C D
1. Visibilit
y
3.06 3.76 3.78 3.40
2. Colo
r
3.64 3.87 3.96 3.56
3. Aroma 3.77 3.87 4.48 3.76
4. Taste 3.96 4.69 4.56 3.76
5. Texture 3.27 4.34 4.15 3.48
Total 17.58 20.28 20.65 17.78
Average 3.58 4.09 4.17 3.59
Note: From 15 Panelis
The physical test results obtained were very
significant where the addition of carrageenan had a
significant effect (α < 0.05) on gel strength, fold-test
and bite-test values, but had no significant effect (α>
0.05) on the pH of mackerel fish balls. The hedonic
test results showed that the addition of carrageenan
flour had a significant effect (α < 0.05) on the
appearance, taste and texture parameters, but had no
significant effect (α > 0.05) on the color and aroma
parameters on consumer preferences for mackerel
fish balls.
The extra of carrageenan flour with a
concentration
of 2.5% gave the best effect on the
elasticity quality
of mackerel fish balls. The chemical
characteristics of
mackerel fish balls with the
addition of carrageenan
flour of 2.5% which has a
water content of 66.04%,
protein content of
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1156

11.87%, fat content of 1.13%,
carbohydrate content
of 8.59%, crude fiber content of
9.61%, ash content
of 1.53%,. The physical
characteristics of mackerel
fish balls with the addition
of carrageenan flour as
much as 2.5% are having a gel
strength of 3,090.61
Bloom, a pH of 7.17, a bite test
value of 5.79
(acceptable, slightly chewy), and a
folding test
value of 2. 78 (slightly cracked when
folded in
half). The organoleptic value with the
hedonic test
of mackerel fish balls with the addition
of
carrageenan flour of 2.5% and it has an appearance
parameter value of 3.76 (neutral to like), while the
color parameter value is 3.87 (neutral to like), and the
aroma parameter value is 3.87 ( neutral to like). Based
Table 1 result can be identified that the value of
the
taste parameter is 4.69 (like to very like) and the
value
of the texture parameter is 4.34 (like).
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the tes t which already done in previous, it
can be concluded that treatment A1 (meatballs with
the addition of carrageenan 2.5%), treatment A2
(meatballs with the addition of carrageenan 5%),
treatment A3 (meatballs with the addition of
carrageenan 7, 5%). The composition ideal of
carrageenan flour with a concentration of 2.5%
could
led the best effect on the elasticity quality of
mackerel
fish balls. The organoleptic value with the
hedonic
test of mackerel fish balls with the extra of
carrageenan flour of 2.5% has an appearance
parameter value IS 3.76 (neutral to like). The color
parameter value is3.87 (neutral to like), and aroma
parameter value is 3.87 (neutral to like). The taste
parameter is 4.69 (like to very like) and the value of
the texture parameter is 4.34 (like). Other material
such water content is 66.04%, and protein content is
11.87%, while fat content is 1.13%. The essential
material such as carbohydrate content is 8.59%,
crude
fiber content is 9.61%, and ash content is
1.53%.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
There were many barriers in doing this research
both
essential matters and non-essential matters. For
fulfill
this research requirements, there are several
figures
need to be appreciated as follows:
1.
The Director of Politeknik Negeri Nunukan, who
already guided us for improving the essential
matters for this research.
2.
Vice Director 1 of Politeknik Negeri Nunukan,
who already motivated us in achieving the
research performance.
The Head Branch Office of Nunukan BNI, who
allowed us to make this research and also allowed
their customers to be our respondents.
REFERENCES
Anggadireja,et all. (2006). Rumput Laut (Pembudidayaan,
Pengolahan dan pemasaran) Komoditas
Perikanan
Potensial. Jakarta: Penebar
Swadaya.
Dewi Wulan, et all. (2015). Analisis Pengendalian Kualitas
Menggunakan Statistical Quality Control (SQC)
Produk Sepatu Pria Untuk Meminimumkan Produk
Cacat (Studi Kasus pada CV. Kabupaten Bandung:
Valentino Shoes, ISSN:2460-6545.
Distantina, S., Fadhilah, Rochmadi, Moh. Fahrurrozi, dan
Wiratni.(2010). Proses Ekstraksi Karagenan Dari Eu-
chema Cottonii. Seminar Rekayasa Kimia dan Proses.
Ega, L., C. G. C. Lopulalan, dan F. Meiyasa.(2016). Artikel
Penelitian Kajian Mutu Karaginan Rumput Laut
Euchema Cottonii Berdasarkan Sifat Fisiko- Kimia
pada Tingkat Konsentrasi Kalium Hidroksida (KOH)
yang Berbeda. Jurnal Teknologi Aplikasi Pangan. 5(2)
:38-44.
Erick, Satryo. (2016). Cara Mudah Mengenali Bakso Yang
Menggunakan Boraks.
http://www.kaskus.co.id.
Inglett, G. E. (Ed). (1974). Wheat: Production and
Utilization. Wesport, Connecticut: The AVI Publishing
Company, Inc.
Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Affairs RI Agency (2016).
Research and Human Resources for Marine and
Fisheries. Fisheries Training and Extension Center.
Ismanto, A dan Sumarna, D. (2016). Pengaruh Penambahan
Karagenan dengan Level Yang Berbeda Tehadap
Komposisi Kimia, Kualitas Fisik, Sensoris dan
Mikrostruktur Sosis Ayam. Buletin Peternakan. Vo.
40(1):58-65.
Juminda, Fitra (2015, Juni). Aneka Olahan Ikan. http//
www.slabance.blogspot.com./2015/aneka-olahan-ikan-
sektor-perikanan.html.
Kementerian Perikanan dan Kelautan RI Badan Riset dan
SumberDaya Manusia Kelautan dan Perikanan. (2016).
Balai Pelatihan dan Penyuluhan Perikanan. Bahan
Pengisi dan Bahan Pengikat Produk Olahan Berbahan
Surimi.
Parlina, Iin. (2009). Karagenan, produk olahan rumput laut
merah Indonesia yang sangat bermanfaat.
Peranginangin, R. S., Wibowo, dan Y. N. Easy. (1999).
Teknik Pengolahan Surimi, Balai Penyuluhan
Perikanan
Laut, Jakarta: Puslitbang Perikanan,
Rasyid,W M. (2015). Potensi Ekonomi Ikan Dan Produk
Perikanan Indonesia Dalam Lingkup
Masyarakat
Ekonomi ASEAN. Proceeding
SENDI_U.
R
etrieved
from
http://www.unisbank.ac.id/ojs/index .php/sendi_u/
article/view/3286.
Improving the Quality of Fishery Products by Maintaining Ideal Composition of Seaweed Caragenan: Kappaphycus Alvarezii
1157
