
Natural Frequencies and Mode Shapes of Human Tympanic
Membrane in Myringoplasty
Hidayat
1
, Sudarsono
2
, Ruspita Sihombing
1
, Rozaini Othman
3
and Minir
1
1
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Politeknik Negeri Samarinda, Jl. Ciptomangunkusumo, Samarinda, Indonesia
2
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Universitas Halu Oleo, Kampus Hijau, Kendari, Indonesia
3
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Pematang Sauh, Malaysia
minirpolnes@gmail.com
Keywords:
Tympanic Membrane, Natural Frequency, Finite Element Method, Eigenvalue Analysis.
Abstract:
The tympanic membrane of the human ear, sometimes called the eardrum, is a thin membrane that separates
the outer and middle ears. Perforation of the tympanic membrane might result in longer-lasting hearing loss.
This research aims to determine the natural frequencies and mode shape of the tympanic membrane by using
the finite element method. The geometric model of the human tympanic membrane was created using CAD
software (Solidworks) based on previously published physical parameters reported by other researchers. Then,
Hypermesh was used to carry out eigenvalue analysis by imported the geometrical model. Two analysis
models were used to compare the dynamic behavior, namely normal tympanic membrane and reconstruction
of the membrane, using sliced cartilage myringoplasty. The thickness of the sliced cartilage was varied from
0.05 to 0.5 mm. Finally, the natural frequency and mode shape of reconstruction of the tympanic membrane
is the same as normal tympanic membrane when cartilage thickness is 0.4 mm.
1
INTRODUCTION
Hearing loss is one of the most severe issues that
people face in their daily lives. Numerous examples
of conductive hearing loss have occurred due to
issues with the tympanic membrane or ossicles. A
perforated tympanic membrane or perforated
eardrum, such as a holed tympanic membrane, is
associated with liquid discharge from the middle ear
through the ear canal. Tympanic membrane
perforation refers to a hole in the thin membrane that
divides the outer and middle ears.
Many researchers studying the human middle ear
system used finite element analysis to replicate the
tympanic membrane's dynamic behavior. The human
hearing system's sensitivity to these qualities is
determined. The characteristics that dictate the
membrane's bending stiffness properties have been
investigated, mainly two critical parameters: the
tympanic membrane's Young's modulus and the
eardrum thickness (Caminos, Garcia-Manrique,
Lima-Rodriguez, & Gonzalez-Herrera, 2018).
Another study calculates the viscous damping within
the tympanic membrane, which may assist in
smoothing the wideband response of a possibly
highly resonant TM and Examine the role of an
unusual element of human middle-ear anatomy: the
narrow mucosal epithelial fold that connects the
manubrium's midsection to the TM (De Greef et al.,
2014). The next study calculates Young's modulus of
a thin-shell model of the eardrum with subject-
specific geometry that is numerically adjusted to
match measured pressured forms (Ghadarghadar,
Agrawal, Samani, & Ladak, 2013). Simulation of the
dynamic behavior of tympanic membrane perforation
had been done using the finite element method
(Hidayat, Sudarsono, & Othman, 2020). The
frequency responses of the human middle ear system
with eardrum perforation using the finite element
method were investigated by researchers (Hidayat,
Sudarsono, Aviva, & Othman, 2019). The best graft
thickness for cartilage myringoplasty was determined
using finite element analysis in patients with varying
diameters of tympanic membrane (TM) holes (Lee et
al., 2007). A study predicted the conductive hearing
loss would increase with increasing perforation size
(Mehta, Rosowski, Voss, O'Neil, & Merchant, 2006).
The simulation of the effect of perforation on the
pressure difference across the TM by including a
channel for sound coupling from the ear canal to the
Hidayat, ., Sudarsono, ., Sihombing, R., Othman, R. and Minir, .
Natural Frequencies and Mode Shapes of Human Tympanic Membrane in Myringoplasty.
DOI: 10.5220/0010961600003260
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2021), pages 1169-1172
ISBN: 978-989-758-615-6; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
1169
middle-ear cavity through the perforation (Voss,
Rosowski, Merchant, & Peake, 2001). A study to
determine the acoustic transmission properties of
cartilage with various thicknesses and its mechanical
deformation in response to air pressure changes
(Zahnert, Hüttenbrink, Mürbe, & Bornitz, 2000).
However, there is no report on the tympanic
membrane reconstruction using sliced cartilage
performing eigenvalue analysis to determine the
dynamic behavior. In the present study, the natural
frequencies and mode shapes were determined to find
out the proper thickness of sliced cartilage used for
the reconstruction of tympanic membrane
perforation. The three-dimensional model of the
human tympanic membrane was created using CAD
software. The human tympanic
membrane was
considered a flat elliptical shape.
Then, the
Hypermesh was used to generate the finite
element
model of the tympanic membrane. Two types
of
finite element model, namely model I and model
II. Model I has the same material properties as the
material used to close the hole at the center of the
membrane then the model II used sliced cartilage
myringoplasty. Finally, eigenvalue analysis was
performed to determine the proper thickness of
cartilage myringoplasty by comparing the natural
frequencies and mode shapes of the model I and II.
2
MATERIALS AND METHOD
2.1 Finite Element Model of Human
Tympanic Membrane
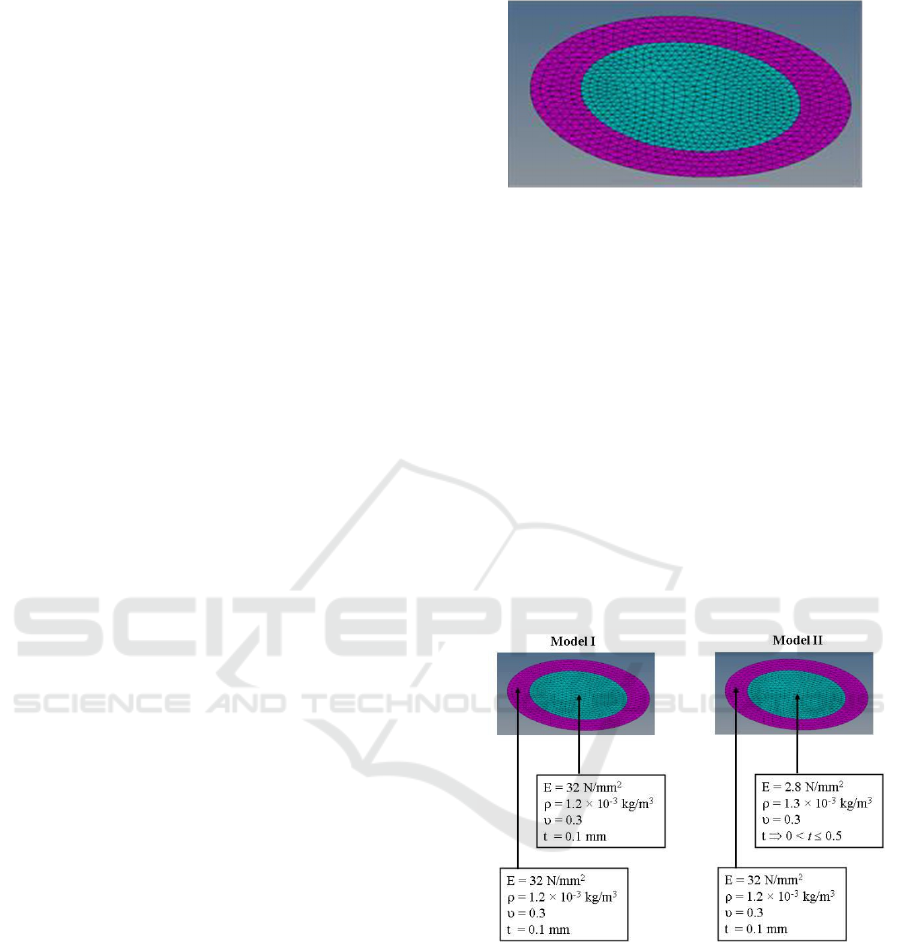
Figure 1 shows the finite element model of the
human tympanic membrane. The human tympanic
membrane shown in Fig. 1 was considered a flat
elliptic shape. The dimensions of flat elliptic shape
are 10 mm and 9 mm for major and minor axis,
respectively. This research used a tympanic
membrane repaired by sliced cartilage at the center of
the membrane. The value of 0.1 mm was used as the
thickness of the membrane. Then, the thickness of
cartilage was varied from 0.02 to 0.5 mm. In this
study, two types of material properties were used to
compare the natural frequencies and mode shapes of
the human tympanic membrane, considered as Model
I and Model II.
Figure 1: Finite Element Model of Human Tympanic
Membrane.
Then, the fixed boundary condition was used around
the shape of the tympanic membrane. The six-node
triangular element was used to divide the tympanic
membrane into 1155 pieces of finite elements.
2.2 Material Properties
Figure 2 shows the material properties of model I
and model II. Firstly, the cartilage used in
myringoplasty at the center of the tympanic
membrane in the model I was defined the same as the
material properties of the human tympanic
membrane. Secondly, the sliced cartilage with the
value of 2.8 N/mm
2
was used as Young's modulus at
the center of the human tympanic membrane.
Figure 2: Material Properties of Model I and Model II.
As for the mass density, the value of 1.2 × 10
-3
kg/mm
3
was used, which is the same value as the
human tympanic membrane. Then, the mass density of
sliced cartilage myringoplasty is 1.2 × 10
-3
kg/mm
3
.
Both models used the value of 0.3 for Poisson's ratio.
Finally, the Optistruct of Hypermesh was used to
carry out eigenvalue analysis of the model I and II.
Eigenvalue analysis was used to obtain the natural
frequencies and mode shapes of both models of the
human tympanic membrane. In this research, the 1
st
and 2
nd
natural frequencies and mode shapes will be
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1170

compared to each other in order to show the dynamic
behavior of models I and II.
3
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Result
Figure 3 shows the mode shape of the 1
st
natural
frequency of the human tympanic membrane. The 1
st
natural frequency was obtained at 440 Hz. The model
I and II have similar mode shapes for all-natural
frequencies, which shows the fundamental shape for
a vibrating circular membrane. The mode number is
(0,1) due to the absence of nodal diameters but the
presence of a circular node (the outside edge).
Figure 3: The Mode Shape of the 1
st
Natural Frequency.
Figure 4 shows the 1
st
natural frequency of the
human tympanic membrane. In the eigenvalue
analysis, the thickness of sliced cartilage was varied
from 0.02 mm to 0.5 mm. Furthermore, the natural
frequencies of model II were increased due to the
effect of thickness of sliced cartilage. Thus, model I
and model II have the same natural frequency when
the thickness of sliced cartilage is 0.42 mm.
Figure 4: The 1
st
Natural Frequency of Tym
Membrane.
Figure 5 shows the mode shape of the 2nd natural
frequency.
The
mode
shape
of
model
I
and
II
are
similar
mode
for
the
2
nd
natural
frequency
at
the
809
Hz.
In
this
case,
the
mode
shape
of
the
tympanic
membrane
is
(1,1),
which
has
a
single
nodal
diameter
and a single circular node (the outside edge).
Figure 5: The Mode Shape of the 2
nd
Natural Frequency.
Figure 6 shows the 2
nd
natural frequency of the
tympanic membrane. The 2
nd
natural frequency of
model II was increased when the thickness of the
cartilage myringoplasty become larger. Finally, the
2
nd
natural frequency for both models has the same
value when the thickness of cartilage myringoplasty
is 0.398 mm.
Figure 6: The 2
nd
Natural Frequency of Tympanic
Membrane.
3.2 Discussion
The use of cartilage in TM restoration has been
established, most notably in situations of chronic
tubal dysfunction, adhesion processes, and complete
or recurrent TM abnormalities. This work uses
eigenvalue analysis to determine the natural
frequency of the human ear system with a healed
tympanic membrane following myringoplasty with
various cartilage thicknesses. The first and second
natural frequencies of the normal tympanic
membrane and different thicknesses of reconstruction
membrane with cartilage myringoplasty were
compared. The study estimated the optimum cartilage
Natural Frequencies and Mode Shapes of Human Tympanic Membrane in Myringoplasty
1171

thickness for myringoplasty using frequency
response analysis but did not include dynamic
behavior, such as natural frequency and mode shape.
In order to clarify this result, the natural frequency
and mode shape of the human tympanic membrane
using the actual shape to define the optimum
thickness of sliced cartilage myringoplasty.
4
CONCLUSIONS
The effect of various thicknesses on the natural
frequency of the human middle ear system during
myringoplasty was examined in this study.
Eigenvalue analysis of the tympanic membrane with
a flat elliptic shape had been carried out to obtain the
natural frequencies and mode shapes. The first and
second natural frequencies and modes shapes for each
model had been compared. The value of around 0.4
mm was defined as the thickness of sliced cartilage in
myringoplasty.
REFERENCES
Caminos, L., Garcia-Manrique, J., Lima-Rodriguez, A., &
Gonzalez-Herrera, A. (2018). Analysis of the
mechanical properties of the human tympanic
membrane and its influence on the dynamic
behaviour of the human hearing system. Applied
Bionics and Biomechanics
,
2018. https://doi.
org/10.1155/2018/1736957
De Greef, D., Aernouts, J., Aerts, J., Cheng, J. T., Horwitz,
R., Rosowski, J. J., & Dirckx, J. J. J. (2014).
Viscoelastic properties of the human tympanic
membrane studied with stroboscopic holography and
finite element modeling. Hearing Research,
312(2014), 69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.
2014.03.002
Ghadarghadar, N., Agrawal, S. K., Samani, A., & Ladak,
H. M. (2013). Estimation of the quasi-static Young’s
modulus of the eardrum using a pressurization
technique. Computer Methods and Programs in
Biomedicine
,
110(3), 231–239.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2012.11.006 Hidayat, H.,
Sudarsono, S., Aviva, D., & Othman, R. (2019).
Frequency response of the human middle ear system
with eardrum perforation. IJSTR, 8(4).
Hidayat, Sudarsono, & Othman, R. (2020). Dynamic
Behavior of Human Tympanic Membrane
Perforation
Using Finite Element Method. IOP Conference
Series: Materials Science and
Engineering
,
797,
12025.https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/797/1/012025
Lee, C. F., Chen, J. H., Chou, Y. F., Hsu, L. P., Chen, P. R.,
& Liu, T. C. (2007). Optimal graft thickness for
different sizes of tympanic membrane perforation in
cartilage myringoplasty: A finite element analysis.
Laryngoscope
,
117
(4),
725–730. https://doi.org/10.
1097/mlg.0b013e318031f0e7
Mehta, R. P., Rosowski, J. J., Voss, S. E., O’Neil, E., &
Merchant, S. N. (2006). Determinants of hearing loss in
perforations of the tympanic membrane. Otology
and
Neurotology
,
27(2), 136–143. https://doi.org/10.1097/
01.mao.0000176177.17636. 53
Voss, S. E., Rosowski, J. J., Merchant, S. N., & Peake, W.
T. (2001). Middle-ear function with tympanic-
membrane perforations. II. A simple model. The
Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 110(3),
1445–1452. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1394196
Zahnert, T., Hüttenbrink, K. B., Mürbe, D., & Bornitz, M.
(2000). Experimental investigations of the use of
cartilage in tympanic membrane reconstruction.
American Journal of Otology, 21(3), 322–328.
https://doi.org/10.1016/s0196-0709(00)80039-3
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1172
