
Application of Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) Method and
Decision Table in Decision Support System Determines the Level of
Problem Student Punishment Levels
Riyadi Purwanto
a
, Dwi Novia P., Ratih Hafsarah Maharrani
b
and Lutfi Syafirullah
Informatic Engginering Departement, Politeknik Negeri Cilacap, Dr. Soetomo Street, Cilacap, Indonesia
Keywords: Decision Support System, Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) Method, Decision Table, Punishment Rate,
Problematic Students.
Abstract: The teaching and learning process that runs cannot be separated from the various problems of students who
violate school rules. Giving punishments or sanctions to problematic students using a point system where the
value of points and sanctions vary according to the type of violation. Some of the problems that arise are that
the instrument is conventional, the calculation of violations is still in the form of paper based which is prone
to errors (human error) and the sanctions given are sometimes due to likes and dislikes. So that the decision
taken is not correct. Based on the problem, an application is made that can support decision making using the
Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) method and the Decision Table. the weighting of the violation points is
based on 3 (three) violations criteria, namely academic violations, aesthetic violations, and ethical violations.
Each criterion will be reduced to several sub-criteria. The SAW method is a problem solving method using a
weighted addition method based on certain criteria, while the Decision Table is a table that is used as a medium
for solving logic in a program. In this research.
1 INTRODUCTION
Information Technology plays an important role asa
medium of communication in supporting various
fields of business, government, and education.
Information technology can function as a media
support system in decision making (Purwanto, 2018).
One of the factors that influence the comfort of
teaching and learning in a school environment is
problematic students who violate school rules. The
role of the Guidance Counseling teacher as the front
guard must be fast and responsive in dealing with
problem students. Therefore, the Decision Support
System (DSS) can be implemented as a decision
support system in determining what actions schools
must take to these students, so that the decisions made
are potential and can be justified.
SMK N 1 Kawunganten is a public school located
in Cilacap Regency. The number of students currently
reaches ± 1,235 students who are distributed in 35
classes in various majors. The learning process that
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7066-2905
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4960-8944
runs at the school certainly cannot be separated from
the various problems of the students caused by the
indiscipline of compliance with school rules.
Various violations that are often committed by
students in schools include disciplined learning time,
disrespectful attitude and harming others, fighting,
smoking, consuming alcohol and drugs, watching
porn videos, promiscuity, and other forms of
violations. Therefore, the handling of problem
students is the responsibility of all schools, both
teachers and school leaders. Educational goals can be
optimally achieved if the school has school rules and
regulations (Utomo and Nursalim, 2019).
Policy at SMK N 1 Kawunganten in dealing with
problem students using a point system. Each violation
has a point value and sanctions that vary according to
the type of violation. At a certain point limit, the
school will determine the level and type of
punishment in the form of warning letters, parent
summons, suspension, and Drop Out (DO).
But now the instruments used are still
conventional. Calculation of the point of violation is
1194
Purwanto, R., P., D., Maharrani, R. and Syafirullah, L.
Application of Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) Method and Decision Table in Decision Support System Determines the Level of Problem Student Punishment Levels.
DOI: 10.5220/0010962300003260
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2021), pages 1194-1202
ISBN: 978-989-758-615-6; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

still in the form of paper based that is prone to errors
(human error). Engineering punishment is very likely
to occur due to factors like and dislike. Thus the
decision taken becomes inappropriate. This causes
frequent complaints by students and parents to the
school.
Noting the problems that occur, it is necessary to
make an application that can help decision making.
To that end, researchers intend to create a Decision
Support System to Determine the Problematic
Punishment Rate for Students. Application
development uses the Simple Additive Weighting
(SAW) method and Decision Table. The SAW
method is a method of solving problems using a
weighted sum method based on certain criteria (Putra,
Aryanti and Hartati, 2018), while the Decision Table
is a table used as a medium for solving logic in a
program so that it is effectively used when the
conditions selected in the program are numerous
(Kristianto, 2017).
In this study 3 (three) criteria for violations will
be made, namely: Academic Violation, Aesthetic
Violation, and Ethical Violation. Each criterion will
be reduced to several sub criteria. For this reason, this
study will use a Decision Table model that functions
to identify the multilevel decisions which will then be
normalized using the SAW method.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Related Research
Research related to the development of Decision
Support System applications has been conducted by
several researchers before with different methods,
objects, and scope of problems.
Previous research with the title Decision Support
System for Student Achievement Selection in SMK
PGRI 3 Malang Using Weighted Product (WP)
Method. The study was conducted with the aim of
building the Achievement Student Selection Decision
Support System with WP Method. The output of this
system is in the form of ranking information for high
achieving students based on criteria data and weight
data (Faisal, 2017).
Previous research with the title Support System
for Decision of Acceptance of New Students with the
SAW Method at SMK Kusuma Bangsa. The
parameters used are NEM, academic achievement,
non-academic achievement, and test results. This
decision support system is designed by ranking
method using SAW by finding the weight value of
each attribute, then an alternative ranking process is
carried out, namely prospective students who pass the
selection (Dzulhaq, Sutarman and Wulandari, 2017).
Previous research with the title Best Student
Selection Decision Support System with Analytical
Hierarchy Process Method. The developed system
can help objective decision making in determining the
best students based on five criteria, including report
card grades, attendance lists, spiritual attitudes, social
attitudes, and skills (Zaki, Setiyadi and Khasanah,
2018).
Different from previous studies. In this study,
researchers made DSS to determine the type and level
of punishment of problem students by using the SAW
method and the Decision Table. Information obtained
from this system is in the form of punishment
recommendations, namely verbal reprimands, written
reprimands (warning letters), parent summons,
suspension, and Drop Out (DO). Punishment is given
based on the total score point for each type of
violation committed by the student. In this study 3
(three) criteria for violations will be made, namely:
Academic Violation, Aesthetic Violation, and Ethical
Violation. Each criterion will be reduced to several
sub criteria. For this reason, this study will use a
Decision Table model that functions to identify the
multilevel decisions which will then be normalized
using the SAW method.
2.2 Basic Theory
2.2.1 Decision Support System
Decision Support System is part of a computer-based
information system that is included in the knowledge
management based system that can be used to support
decision making in an organization or company
(Nawir and Manda, 2018). Decision Support System
is also a system that provides the ability to solve
problems and communication for semi-structured
problems (Sugiyarti et al., 2018).
Decision making always correlates with the
uncertainty of the results of decisions taken.
Therefore, to reduce the uncertainty factor, the
decision requires valid information about the
conditions that occur, then processes the information
into several alternative problem solving as
consideration for deciding the steps to be carried out,
so that the decision taken is expected to provide
benefits (Siregar et al., 2018).
2.2.2 Simple Additive Weighting (SAW)
Method
SAW method is a method of solving problems known
as weighting sum method based on certain criteria
Application of Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) Method and Decision Table in Decision Support System Determines the Level of Problem
Student Punishment Levels
1195
(Putra, Aryanti and Hartati, 2018). The concept of the
SAW method is to find the weighted sum of each
alternative on all attributes(Kusumawardani et al.,
2019).
The SAW method only performs the
normalization process by having a matrix where
viewed from the columns and rows the highest value
is drawn or called the maximum value and the lowest
value is pulled in a row called the minimum value,
normalizing the value if the value of benefits or
including the criteria of benefits is done every row
value divided by the highest value owned by the row,
and if it is a criterion value in the form of the lowest
cost value of the row divided by row value
(Hutahaean and Badaruddin, 2020).
2.2.3 Decision Tables
Decision tables are tables that are used as a tool to
solve logic in a program. Decision tables are also
known as cause-and-effect tables that will be used to
obtain decision tables (Joosten, Permanasari and
Adji, 2020). Algorithms containing multilevel
decisions are difficult to draw directly with
pseudocode can be made in advance using the
Decision Table. This method is effectively used if the
conditions selected in the program are
numerous(Kristianto, 2017).
2.2.4 School Rules
School rules are provisions that govern life at school
and contain sanctions against violators. Violations of
school rules can be grouped into four categories,
namely academic violations, administrative
violations, aesthetic violations, and ethical violations
(Utomo and Nursalim, 2019)
3 RESEARCH METHODS
The method used in the development of the Decision
Support System to determine the level of punishment
of problematic students is grouped into four main
components, namely research materials, research
tools, research paths, and system design.
3.1 Research Materials
Research materials include:
1) Data obtained from analysis studies at SMK
Negeri 1 Kawunganten through interviews.
2) Data obtained from study literature or scientific
references.
3) Analysis of data or documents from research
objects to find out how the system works to be
built.
4) Information regarding the development of a
Decision Support System that was previously
carried out.
3.1.1 Research Tool
In this study, research tools are needed, namely
computer devices with sufficient specifications and
internet access devices.
3.1.2 Research Path
Application development in this study uses the
waterfall method which consists of several phases /
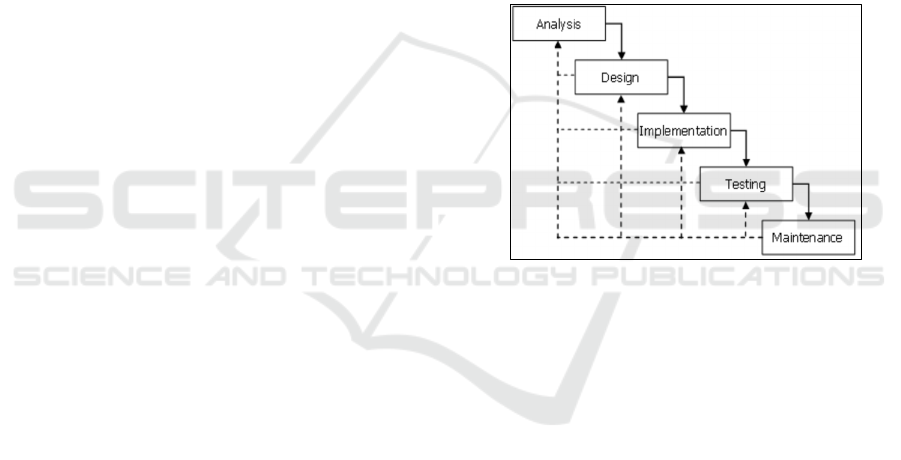
stages (Bassil, 2012), as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Waterfall Model (Bassil, 2012).
Figure 1. shows the phases / stages that can be
explained as follows:
1) Analysis Phase
There are several analysis activities, including:
a. Analysis of the problem (existing condition)
b. Analysis of information about the types of
student violations, point weight violations as
well as the mechanisms and procedures for
punishment of problematic student students at
SMK N 1 Kawunganten. In the process of
information analysis, data collection is also
needed for research activities, either by
interviewing or copying the data needed.
c. User analysis is to determine user needs.
d. Technology analysis is to determine the
system requirements both software and
hardware.
2) The design stage
This stage will make the design of the system
design include:
a. Flowchart flow system,
b. Systems analyst modeling
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1196

c. Relationship table
d. Database system design
e. Make up design (system display)
3) Implementation Phase
The system design that has been made will be
implemented in the coding program so that a
Decision Support System application is
created.
4) Testing Phase
After the application is made the next stage is
the system testing phase.
5) Maintenance Phase
At this stage improvements will be made if the
application does not function (error).
3.1.3 System Design
The system to be developed can be shown in the
flowchart as follows:
Figure 2: Flowchart System.
Figure 2 explains the flow of the decision support
system that will be developed. In the figure, there are
two users who use the application, namely the
counseling teacher and the head master. The
counseling teacher can input the types of violations
and the weight of each of these violations.
Furthermore, each student's violation will be input
through the application and the number of violation
scores will be calculated to determine the level of
punishment. If, the violation score exceeds the
stipulated limit, head master will give punishment in
accordance with the stipulated provisions. However,
if the student's violation score is less than the
maximum limit, the student will not give punishment.
To explain in more detail about the interaction
between users and the system, a use case is made as
shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Use Case System.
Figure 3 describes the use case of the system to be
developed. Use Case describes the interaction of
actors with the existing system.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Decision Table Making
In this research discusses the level of punishment of
problematic students where an assessment of
violations will be carried out by students using a
combination of decision tables and SAW.
Punishment is given based on the total accumulated
total score of each point for each type of violation
committed by the student in one semester. As a first
step, a decision table will be made which will be used
as a tool to solve the logic in the program. In making
decision tables, references and actions will be given
to students if they commit violations. The
Application of Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) Method and Decision Table in Decision Support System Determines the Level of Problem
Student Punishment Levels
1197
classification of violations that are often carried out
by students up to the actions to be taken by the school
in handling these violations can be summarized in the
table below :
Table 1: Violation Points.
No.
Clasificati
on
Criteria Point
Punishment
and Action
1. Academic
Violation
Late for
school
2 Reprimand
and
Counselin
g
Not present
without a
certificate
5 Reprimand
and
Counselin
g
Leave
school
during class
time
5 Reprimand
and
Counseling
Not
following
the flag
ceremon
y
10 coaching
and
Counseling
Activate the
handphone
while
learning is in
p
ro
g
ress
5 Reprimand
and
Counseling
2. Aesthetics
Violation
Not dressed
in uniform
or school
attributes in
accordance
with the
p
rovisions
2 Reprimand
and
Counseling
Does not
carry out
cleanliness
2 Reprimand
and
Counseling
Long-haired
/ long-haired
male
students or
hair dyes
3 Reprimand
and
Counseling
Damaging
or crossing
out school
facilities
5 Reprimand
and
Counseling
Princess
students
wear jewelry
or dress up
excessivel
y
2 Reprimand
and
Counseling
Using
tattoos or
body
piercings
that are not
a
pp
ro
p
riate
50 Warning
Letter II,
coaching
and calling
parents
3. Ethics
Violation
Harrasing
teacher in
the school
50 Warning
Letter II,
coaching
and calling
p
arents
Carrying
and smoking
in the school
environment
15 Warning
Letter I
Drinking
alcohol and
dru
g
abuse
100 Drop Out
Committing
or engaging
in criminal
actions
against
others
Carry sharp
weapons
that can
endanger
and threaten
the safety of
others
100 Drop Out
Students
proven to
steal
Bringing,
showing and
distributing
p
orno
g
ra
p
h
y
30 Warning
Letter II,
coaching
and calling
parents
Students
become
pregnant or
impregnate
other
students
80 Warning
Letter I and
Skorsing
Based on the table, a decision table can be made using
the help of a table that contains the relationship
between several attributes that affect certain attributes
with the following steps:
1. Determination of the conditions to be selected, in
the condition of giving punishment to students
who are in trouble there are 3 pieces of conditions
to be selected namely:
a) Academic Violations
b) Aesthetic Violations
c) Ethics Violations
Referrals given by the school include loud
reprimands, regular reprimands, sanctions,
guidance and dispensation
2. Based on the number of conditions selected, it can
be determined the number of possible events that
occur, in this case as many as: N = 23 = 8 possible
events
3. Then it is formulated that there are 5 (five) actions
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1198

to be taken along with the maximum point limit:
1) No violation occurs if the total accumulated
number of violations <= 10
2) Warning Letter I (counseling & coaching) if
the total accumulated number of violations <=
30
3) Warning Letter II (summons of parents) if the
total accumulated number of violations <= 50
4) Warning Letter III (suspension) if total
accumulated violations <100
5) Drop Out if total accumulated violations >=
100
4. Fill in the condition entry
5. Fill in the action entry
Table 2: Action Entry.
Condition / Action Rules
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Academic Violations >
maximum violations Y Y Y N N Y N N
Aesthetic Violations >
maximum violations Y Y N Y N N Y N
Ethics Violations >
maximum violations Y N Y Y Y N N N
No violations X
Warning Letter I X X X
Warning Letter II X X
Warnin
g
Letter III X
Dro
p
Out X
4.2 Calculation Process in the SAW
Method
After making a decision table, the next step is to
perform calculations using the SAW method, where
this method is known as the weighted sum method.
For example here a sample of 10 students will be
taken to calculate the steps as follows:
a) There are 3 basic criteria that become a reference
in making decisions, namely:
1) C1 = Academic violation
2) C2 = Aesthetic violation
3) C3 = Ethical violation
b) Determination of criteria weights
Weights for each criterion are: C1 = 30%, C2 =
20%, and C3 = 50%. Determination of this weight
by looking at which criteria will be given a
maximum and minimum value based on
consideration of the existing point factors
c) Table of alternative values of students (candidates)
will be taken as a random sample 1 class of 30
people, there are :
Table 3: Value Alternative.
Alternative Name
Criteria
C1 C2 C3
A1
Maulana Alif
Anugerah
17 4 0
A2 Peter Sulaeman 10 9 80
A3
Nandya Saphira
Esfandian
7 24 15
A4 Arya Mahardika 5 14 0
A5
Lucky Wiratama
Su
g
anda
22 53 50
A6 Gracia Vini 12 7 0
A7 Ckasinta Winda Santi 27 22 30
A8
Yolanda Novitra
Setiawan
2 8 50
A9 Hazana Delfani 30 7 15
A10
Rosyanda Sastie
La
g
attri
15 17 18
A11 Afinda Andi Pra
y
u
g
o 10 2 0
A12
Akhmad Rofiq
Mustofa
15 4 0
A13 Azis Satria Putra 2 5 15
A14 Cah
y
a Romadhon 5 7 15
A15 Dendi Fajar Efendi 2 2 0
A16 Farid Al A'rof 2 9 0
A17
Azka Raihan Tahta
Aunillah
2 10 0
A18 Bara Bima Hestya 17 15 0
A19 Dafi' Al Khayyan 5 5 15
A20
Juan Dwi Bhakti
Nugroho
5 5 15
A21 Aan Wili Krisyanto 15 10 0
A22 Abdul Khalim 20 17 0
A23 Achmad Fuad
y
25 12 0
A24 Andi Wah
y
u Perdana 5 4 0
A25 Atha S
y
arif Pri
y
anto 5 4 0
A26 Bagas Artha Jati 25 22 15
A27 Bagas Prayogo 0 7 0
A28 Banu Muarif 2 9 0
A29
Bayu Mangun
Kusumo
2 12 0
A30 Beni Setiawan 12 12 0
d) Determine the value of each weight
Table 4: Weighted Value.
Total points
of violation
The weight value is based on the
total number of subscribers of the
total violation
p
oints
0
–
20 1
21
–
45 2
46
–
75 3
76
–
99 4
>100 5
e) Based on the data suitability value between the
Application of Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) Method and Decision Table in Decision Support System Determines the Level of Problem
Student Punishment Levels
1199
alternatives with the criteria in the table above,
and with the weight of the existing values, a
decision matrix (X) can be made and a
normalization calculation is carried out to obtain
a normalized value matrix of each existing value.
The values are shown in tabular form as follows:
Table 5: Normalization Calculation.
Alternative
Decision matrix
value
Normalized value
matrix
C1 C2 C3 C1 C2 C3
A1 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A2 1 1 4 0,5 1 1
A3 1 2 1 0,5 0,50,25
A4 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A5 2 3 3 1 0,330,75
A6 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A7 2 2 2 1 0,5 0,5
A8 1 1 3 0,5 1 0,75
A9 2 1 1 1 1 0,25
A10 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A11 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A12 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A13 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A14 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A15 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A16 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A17 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A18 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A19 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A20 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A21 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A22 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A23 2 1 1 1 1 0,25
A24 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A25 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A26 2 2 1 1 0,5 0,25
A27 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A28 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A29 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
A30 1 1 1 0,5 1 0,25
f) To simplify the action to be performed, a range
of values is determined from the sum of each
criteria.
Table 6: Range of Criteria.
Action Value Ran
g
e
No Violation 0 - 0,59
Warnin
g
Letter I 0,60 - 0,72
Warning Letter II 0,73 - 0,84
Warning Letter III 0,85 - 0,97
Drop Out >=0,98
g) The last is calculating the value of preference
weights for each alternative, accompanied by a
reference to the action to be taken.
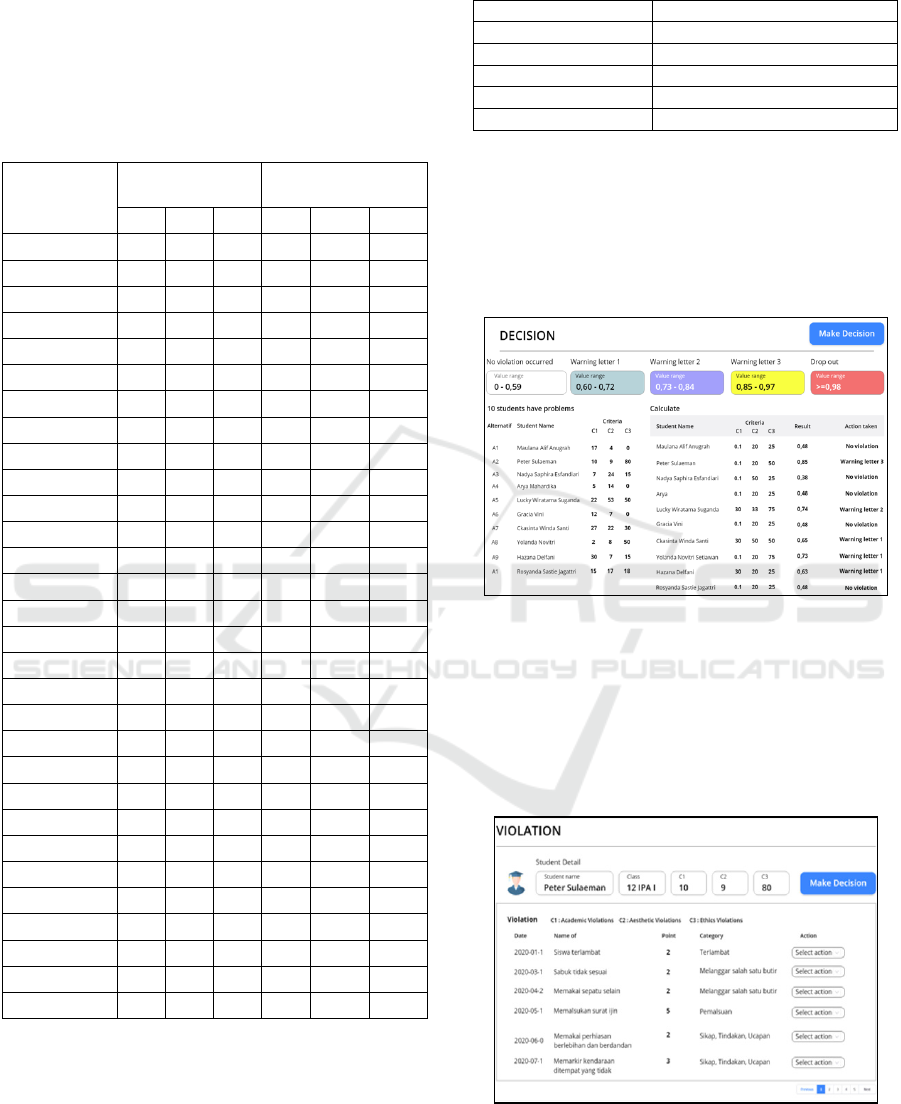
In the system developed, the process of calculating
the violation score of each student can be shown in
Figure 4.
Figure 4: Calculation of student violation and action.
Figure 4, shows the calculation of the score of
violations committed by each student. In the picture,
the scores of each score are seen and show the actions
given to the problematic students.
The detailed calculation of each student's violation
score is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Calculation of details each student violation score.
Figure 5, shows the calculation of the violation score
of each student in detail.
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1200

Table 7: Final Calculation aPnd Action.
Alter
native
Criteria Total
of each
criteria
Action
C1 C2 C3
A1 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A2 0,15 0,20 0,50 0,85 Warning
Letter III
A3 0,15 0,10 0,13 0,38 No
Violation
A4 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A5 0,30 0,07 0,38 0,74 Warning
Letter II
A6 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A7 0,30 0,10 0,25 0,65 Warning
Letter I
A8 0,15 0,20 0,38 0,73 Warning
Letter I
A9 0,30 0,20 0,13 0,63 Warning
Letter I
A10 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A11 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A12 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A13 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A14 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A15 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A16 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A17 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A18 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A19 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A20 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A21 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A22 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A23 0,30 0,20 0,13 0,63 Warning
Letter I
A24 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A25 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A26 0,30 0,10 0,13 0,53 No
Violation
A27 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A28 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A29 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
A30 0,15 0,20 0,13 0,48 No
Violation
4.3 System Testing
System testing is done by white box testing method.
Tests carried out by 10 respondents with results as
shown in Table 8.
Table 8: System Testing.
No. Assessment
Test Res ult
NA A SA
1. Calculation of point weight
scores for each type of
violation becomes more
p
recise and accurate
0 3 7
2. Can reduce the risk of
miscalculation and
rakapitulation points
violations caused by human
erro
r
0 2 8
3. Can avoid the existence of
engineering punishment
caused by
like and dislike factors
0 2 8
4. The validity of the level of
punishment or sanctions
information that will be given
problematic students are more
guaranteed and in accordance
with the type violations
committed (accurate)
0 5 5
5. Can help the school (elements
of the school leadership) in
making the right decision and
can be accounted fo
r
0 4 6
Amount 0 16 34
Percentage (%) 0 32 68
Notes :
NA = Not Agree
A = Agree
SA = Strongly Agree
Table 8, shows the results of the system testing
conducted by 10 respondents. Based on the results of
testing that has been done, in general the system can
assist leaders in making decisions against students
who have problems and provide penalties in
accordance with the violations that have been
committed.
Application of Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) Method and Decision Table in Decision Support System Determines the Level of Problem
Student Punishment Levels
1201

5 CONCLUSION
Based on research that has been done by developing
a decision support system to determine the
punishment of problem students using the decision
table and the SAW method and testing the system
with 10 respondents, the results show 68% of
respondents strongly agree that with the decision
support system, the calculation of point weight scores
from each type of violation to be more precisely and
accurately, the risk of miscalculation and
rakapitulation points violations caused by human
error can be minimized, punitive engineering caused
by like and dislike factors can be avoided, the validity
of the level of punishment or sanctions that will be
given problematic students are more guaranteed and
in accordance with the type violations committed,
school leaders can make the right decisions and can
be accounted for.
Suggestions that can be made for the development
of the system in further research is the need to develop
an sms gateway function that can provide information
on student violations automatically to parents of
guardians and actions taken by the school against
students with problems. Thus, guardian parents can
find out information on violations committed by their
children.
REFERENCES
Bassil, Y. (2012) ‘A Simulation Model for the Waterfall
Software Development Life Cycle’, International
Journal of Engineering & Technology, 2(5), pp. 2049–
3444. doi: 10.15680/ijircce.2015.0305013.
Dzulhaq, M. I., Sutarman and Wulandari, S. (2017) ‘Sistem
Pendukung Keputusan Sistem Pendukung Keputusan
Penerimaan Siswa Baru Dengan Metode Simple
Additive Weighting Di SMK Kusuma Bangsa’, Jurnal
Sisfotek Global, 7(2), pp. 50–55.
Faisal, M. (2017) ‘Sistem Pendukung Keputusan Seleksi
Siswa Berprestasi di SMK PGRI 3 Malang
Menggunakan Metode Weighted Product (WP)’,
Journal of Information and technology, 05(01), pp.
119–124.
Hutahaean, J. and Badaruddin, M. (2020) ‘Sistem
Pendukung Keputusan Pemilihan Sekolah SMK Swasta
Penerima Dana Bantuan Menerapkan Metode Simple
Additive Weighting ( SAW )’, Jurnal Media
Informatika Budidarma, 4(April), pp. 466–471. doi:
10.30865/mib.v4i2.2109.
Joosten, J., Permanasari, A. E. and Adji, T. B. (2020) ‘The
use of decision table for reducing complex rules in
software testing’, IOP Conference Series: Materials
Science and Engineering, 732(1). doi: 10.1088/1757-
899X/732/1/012086.
Kristianto, A. (2017) ‘Sistem Pendukung Keputusan
Penentuan Mahasiswa Bermasalah Menggunakan
Metode Ahp’, Jurnal Gaung Informatika, 10(1), pp.
55–66.
Kusumawardani, R. et al. (2019) ‘Implementasi Metode
Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) Pada Sistem
Pendukung Keputusan Untuk Menyeleksi Saham
Prima’, Jurnal Riset Informatika, 1(3), pp. 1–6.
Nawir, S. and Manda, R. (2018) ‘Web Based Application
for Decision Support System with ELECTRE Method
Web Based Application for Decision Support System
with ELECTRE Method’, in 2nd International
Conference on Statistics, Mathematics, Teaching, and
Research. IOP. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1028/1/
012054.
Purwanto, R. (2018) ‘Rancang Bangun Decision Support
System (DSS) Untuk Membantu Menentukan Hasil
Seleksi Pegawai Pada Politeknik Negeri Cilacap
Dengan Menggunakan Metode Perbandingan
Eksponensial (MPE)’, Jurnal Informatika: Jurnal
Pengembangan IT, 3(2), pp. 190–199. doi:
10.30591/jpit.v3i2.861.
Putra, A. S., Aryanti, D. R. and Hartati, I. (2018) ‘Metode
SAW ( Simple Additive Weighting ) sebagai Sistem
Pendukung Keputusan Guru Berprestasi ( Studi Kasus :
SMK Global Surya )’, in Seminar Nasional Teknologi
dan bisnis 2018. Bandar Lampung: IIB Darmajaya, pp.
85–97.
Siregar, D. et al. (2018) ‘Multi-Attribute Decision Making
with VIKOR Method for Any Purpose Decision’,
Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1019(1). doi:
10.1088/1742-6596/1019/1/012034.
Sugiyarti, E. et al. (2018) ‘DECISION SUPPORT
SYSTEM OF SCHOLARSHIP GRANTEE
SELECTION USING DATA MINING’, International
Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, 119(15), pp.
2239–2249.
Utomo, S. B. and Nursalim, M. (2019) ‘Pelanggaran Tata
Tertib Sekolah Siswa Kelas X SMA Negeri 1 Menganti
Serta Penanganannya Oleh Guru Bimbingan Dan
Konseling’, Jurnal Mahasiswa Unesa, p. hlm. 12.
Zaki, A., Setiyadi, D. and Khasanah, F. N. (2018) ‘Sistem
Pendukung Keputusan Pemilihan Siswa Terbaik
Dengan Metode Analytical Hierarchy Process’, Jurnal
Penelitian Ilmu Komputer, System Embedded & Logic,
6(1), pp. 75–84. doi: 10.35141/jvt.v2i1.455.
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1202
