
Design and Implementation of Smart Village Application
Sri Andriati Asri
1
, I Nyoman Gede Arya Astawa
1
, I Gusti Agung Made Sunaya
2
,
I Made Riyan Adi Nugroho
1
, I Nyoman Eddy Indrayana
1
and Widyadi Setiawan
2
1
Electrical Department, Politeknik Negeri Bali, Jimbaran, Indonesia
2
Electrical Department, Universitas Udayana, Jimbaran, Indonesia
widyadi@unud.ac.id
Keywords: Smart Village Application, Tourism Village, Design, Implementation.
Abstract: In 2019, according to TripAdvisor Bali is the top 5 favorite destinations in the world. Bali offers cultural and
natural tourism attraction as a unique characteristic. Many traditional villages tried to provide cultural and
unique tourism attractions to attract tourists to visit. The dorp with those characters is called a tourism village.
Many tourism villages in Bali do not have an application or information system to promote or even to manage
their resources yet. This research aims to develop a smart village application to help tourism village to manage
and promote their tourism resources. The smart village application development begins with requirements
analysis to gathering customer needs and the system specifications. Design the system architecture, the use
case diagram, and the database. The main features of the application are tourism attraction, art shop, culinary,
lodging, and event. Users of the application are the admin village, the owners of tourism resources, and guests.
This web-based application can provide the ability to manage and promote its tourism products. Information
about the tourism village included the location also prepared before the tourists visiting the dorp.
1 INTRODUCTION
In 2019, according to TripAdvisor Bali is the top 5
popular destinations in the world. Bali offers cultural
and natural tourism attraction as a unique
characteristic. The provincial government of Bali has
taken steps to maintain Bali as a favorite tourism
destination. One of the steps is by developing
Tourism Village. Since 2013, the government has
targeted the development of a hundred new tourism
villages. Tourism Village is a form of integration
between attractions, accommodations, and supporting
facilities that provided in the community structure
that integrates with the prevailing traditional
procedures. Like other areas in Indonesia, there is a
gap between well-developed tourism villages and the
poor one. Well developed tourism villages in Bali are
using Information and Communication Technology
(ICT) to promote their tourism potentials. The usage
of ICT so far just for promotion needs. It does not
include the management aspect yet. Empowering
tourism villages and promoting tourism potentials as
well, the use of ICT is necessary. The utilization of
ICT is needing to empowering tourism village is also
spelled out by Purnomo. He stated by taking
advantage of the ICT utilization the tourists can get
sufficient information about object tourism before
visiting.
The ICT utilization in the tourism villages
development field was also described by Choirunnisa,
in the case of tourism villages in Yogyakarta. This
research aims to design the architecture system, user
interface, use case diagram, and activity diagram of a
smart village application for tourism village. The
application is design to manage and also promote
tourism objects and accessible by computers and
smartphones.
2 RELATED WORKS
There are many studies and interpretations of the
smart village. According to Shukla, a smart village
should be interactive and multifunctional. It needs the
active participation of people in various activities. A
smart village is an integration of several modules
stored in a database that can access via smartphone or
tablet. Another definition of a smart village is an
innovation of sustainable planning approach at the
village level that promotes knowledge-based
Asri, S., Astawa, I., Sunaya, I., Nugroho, I., Indrayana, I. and Setiawan, W.
Design and Implementation of Smart Village Application.
DOI: 10.5220/0010965900003260
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2021), pages 1387-1391
ISBN: 978-989-758-615-6; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
1387

development through the continuous learning of
human resources as an integrative part of village
resource development, especially in encouraging
rural areas development as a part of the regional
system in the context of national development
planning system. The objective of rural development
in Indonesia is to encourage rural development in
smartness manner known as the smart village with
respecting the existing diversity values of each village
One of the characteristics of a smart village is the
usage of ICT to manage and promote the village
resources. The development of smart village
application has been carried out by many researchers.
Marlintha had designed and implemented a smart
village mapping Geographic Information System of
the Cinunuk village. GIS has been used extensively
in developing a smart village application. Afnarius
has developed GIS for buildings in the customary
village of the Minangkabau Koto Gadang West
Sumatera Indonesia. Information Technology is one
important factor to support and promote the potential
of village tourism. An application of geoinformatics
for smart village creation has been conducted by
Prakash R, a case study of Vishnupuri village in
eastern Maharashtra, India.
3 METHODOLOGY
According to the Bali Government Tourism Office,
there are 155 tourism villages in Bali. Less than fifty
percent of those villages had an application or
information system to manage and promote the
village resources.
This research aims to design an able application
used widely by tourism villages. The methodology of
this research consists of requirements analysis,
design, implementation, and testing.
3.1 Requirements Analysis
To meet the user needs, we need to communicate the
basic need of the user. Good communication can give
sufficient information to develop an application that
can meet customer objectives. Requirement analysis
took place at the very beginning of the development
process. There are three types of requirements:
customer requirements, functional requirements, and
performance requirements.
1. Customer requirements: Define system
expectations based on certainty facts, and
assumptions. Table 1 shows the business processes of
the tourism village.
Table 1: Business processes of tourism village.
Business
Bussiness Processes
Main Processes Products Owner
Culinary Selling, ordering
Food &
Bevera
g
e
Villager
Artshop Selling, ordering
Handycraft,
painting,
clothes
Villager
Lodging/
guest host
Renting,
b
ooking roo
m
Room, services
Villager,
village
Tourist
Attraction
Promoting,
ticketin
g
Attraction
Villager,
villa
g
e
Village
Event
Promoting
Cultural
attraction
Village
Understanding the customer wants it done by
conduct a survey of several tourism villages in Bali.
In this research, there are several certainty facts can
be concluded during the communication with the user
and observation during the requirements gathering
process. Table 1 shows the business processes of a
tourism village. The data as gathered in, the business
process, and the characteristic of villagers in a
tourism village. The villager characteristics are also
important things to define user requirements. The
villagers of the tourism village have various
educational backgrounds and ages. As we observed in
the survey area, most of them can communicate in
English. They also have a strong will to encourage
themselves to achieve a better income.
Several assumptions are made to make the
application constraints. Based on the survey’s result,
several parties are directly involved with the
application. We named it as a potential user. We
defined three users, which are the village’s
government (admin village), villagers (owners of
tourism potencies), and guests (tourists). The system
design for computers and Android smartphones or
tablets use.
2. Functional requirements: is used to describes
inputs, outputs, and system behaviors. Based on
Table 1, the system functionality is created. The
system functionality has to be able to manage
culinary, art shop, guest house/ homestay, tourism
attraction, and to manage the village’s events as well.
3. Performance requirements: are the degree to
which missions or functions are required. The
performance requirements of an application are
determined by the speed of data entry, data
transferring, and processing. When we develop a
smart village application, we must define which
features of the application that needs speedy
transferring and processing. The application is
designed to be able to provide information to the
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1388
tourist quickly. The database must be made
effectively and efficiently to provide information
faster.
3.2 Design
1. System Architecture: The smart village application
provides services to users. The services must be
accessible to all users using various devices, such as
computers or laptops, smartphones, and tablets. The
system architecture is described in Figure 1.
Figure 1: System architecture.
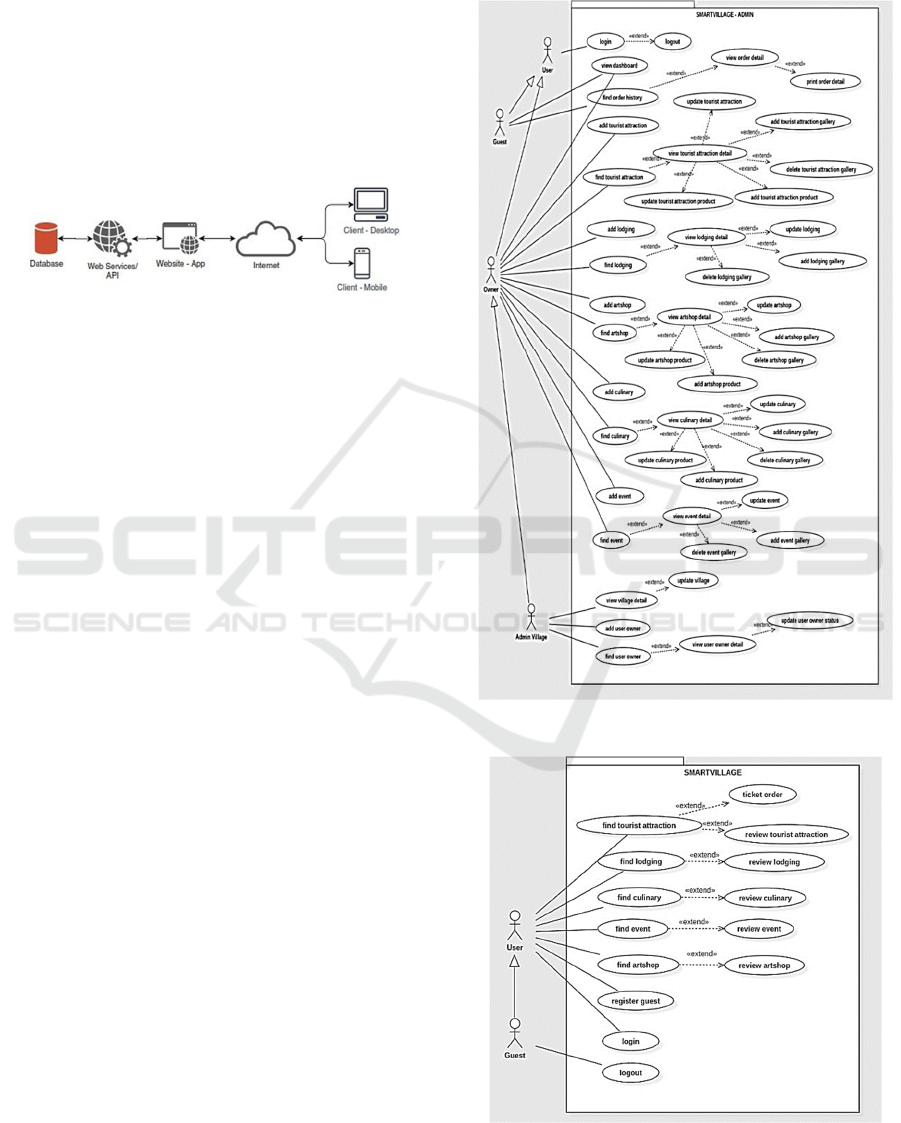
2. Use Case Diagram: To model the system
requirements we used use case diagrams. The steps to
build a use case diagram are identify the actors and
the relationship of each actor, identify use cases, and
the relationship between use cases. The actors from
the result of requirement analysis are village admin,
owners dan guests. The uses cases of the system are
derived based on Table 1. The system functionality
spelled out into use cases. There are five business
processes will be developed. They are culinary, art
shop, Lodging/guest host, tourist attraction, and
village event. The culinary, art shop and tourist
attractions have similar main processes. The basic
idea of the village event is to promote the cultural
event, which is they need no ticket to watch the event.
The lodging has different main processes, which are
renting and booking rooms. Therefore we designed
the use cases are the same for similar business
processes. Figure 2 describes the use case diagram of
the application. The main business process is broken
down into several use cases using extend relations.
Two main use cases of each business process are
"add" and "find" functions. Users can add and find the
data or information they need.
Figure 3 shows the guest use case diagram of the
smart village application. The sub-use cases are
review and ticket order. The guest needs to register
first before reviewing the products to avoid
unappropriated reviews from anonyms. The users’
review can give much information to the owners and
admin village to improve the services.
3. The Database: A good design of the database can
enhance the ability of the application to run fastly. Fig
4 shows the relational tables of the database of the
application. Each main process of Table 1 is mapped
in tables in the database. Lodging, art shop, culinary,
tour, and event, and other tables are created to
accommodate the data.
Figure 2: Use case diagram of smart village application
Figure 3: Guest use case diagram of smart village
application.
Design and Implementation of Smart Village Application
1389
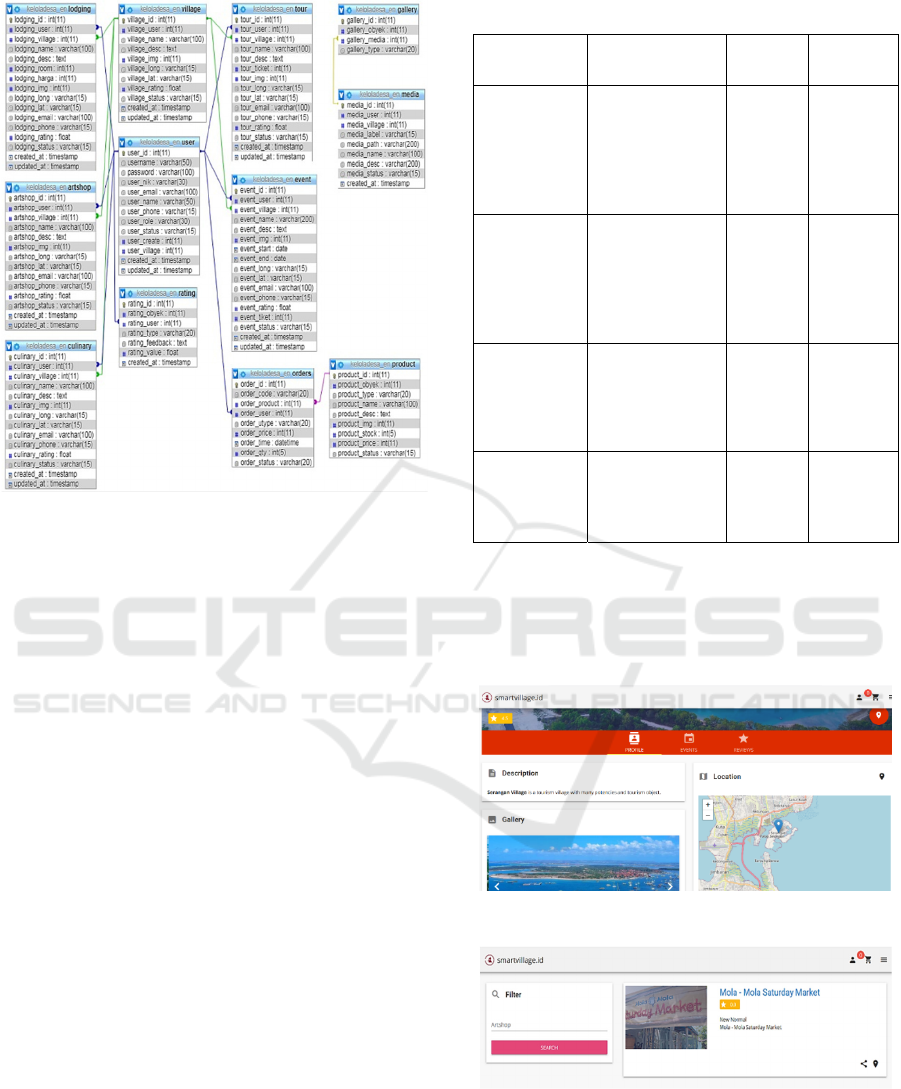
Figure 4: Relational tables design.
3.3 Implementation and Testing
The design that had conducted in the previous
becomes a reference and guidance to develop the
application. The development of the application using
the following programming languages:
• Front end web using HTML, CSS, and
Javascript with vue.js framework.
• Web services using PHP with SLIM
framework
• Database using MySQL version 5.0.12
Application testing we used black-box testing.
The tester only knows the input and the required
output of the testing. Black-box testing is focused on
the testing of functionality of the software
application. We ran testing for more than 48 testing
units. Each testing unit can consist of more than one
scenario. Table 2 shows the result of black-box
testing of the login unit the application. Table 2 shows
the test result of black-box testing of the login unit of
the application.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The smart village application to manage and promote
the potencies of tourist village consists of several
main menu or features. Each potential business
process is made the form application feature.
Table 2: Black-Box Testing Result Of The Login Unit.
Scenario Required Result Result Conclution
Username:
(empty)
Password:
(empty)
The system will
reject, and it’s
displaying
message:
username is
required
As
required
valid
Username:
(empty)
Password:
admin
The system will
reject, and it’s
displaying
message:
username is
required
As
required
valid
Username:
email address
Password:
(empty)
The system will
reject, and it’s
displaying
message: invalid
data
As
required
valid
Username:
email address
Password:
text
The system will
accept the input
and proceed.
As
required
valid
The application has six features: village profile,
tourism object, lodging, art shop, culinary, and
events. Each feature has geotagging to give directions
to the guests. Figure 5 shows the homepage of the
application.
Figure 5: Homepage smart village application.
Figure 6: The artshop feature.
Figure 6 shows the art shop feature. The smart village
application that developed in this research is not only
used GIS to give location information about the
tourism objects that conducted by others researcher in
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1390

the related works, but it also can manage and promote
the tourism objects. The application can
accommodate the basic need to manage many tourism
objects owned by villagers.
5 CONCLUSION
The smart village application design begins with
requirements analysis to gathering customer needs
and system specifications. The design process
consists of designing system architecture, making the
use case diagram and relational table also conducted
in the design process. Implementation of the
application is using HTML, CSS, and Javascript for
front end web, PHP for web services, and MySQL for
the application database. Users of the application are
owner, village admin, and guest (tourist). The
application can manage and promote the tourism
potential of the village as well. The application is a
web-based application only. A mobile smart village
application can be developed with a payment gateway
feature for future works.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was support by the Directorate of
Research and Community Service, Director General
of Development and Research Enhancement,
Ministry of Research, Technology, and Higher
Education.
REFERENCES
Indonesian Minisry of Culture and Tourism regulation no.
KM.18/HM.001/MKP/2011 about National
Community Empowerment Program. (2011). p. 6,
S. Purnomo, E. Siti Rahayu, A. Laksmi Riani, and Suminah.
( 2019). Tourism village managementbased on
information technology with destination management
system. 1
st
International Conference of Health, Science
& Techonolgy (ICOHETEC), pp. 229 – 233.
U. Choirunnisa and R Rachmawati. (2020). ICT usage in
Yogyakarta’stouirst village management. Journal of
Indonesia Tourist and Development Studies, vol.8 no.2,
pp. 112 – 118.
Dr P. Y. Shukla. (2016). The Indian smart village:
fondation for growing India. International Jurnal of
Applied Research, vol. 2(3), pp. 72 – 74.
M. R. Hegade, S. C. Kuber, P. P. Sathe, R. R. Mote, and R.
R. Bhosale. (2016). Smart village system. International
Jurnal of Science Technology & Engineering, vol. 3
issue 4, pp. 163-166.
R Sutriadi. (2018). Defining smart city, smart region, smart
village, and technopolis as an innovative concept in
indoensia’s urban and regional development themes to
reach sustainability. Earth and Enviromental Science
Conf. Series, IOP Publishing, vol 202, p.012047.
A.Bella Marlintha, B. Irawan, and R. Latuconsina. (2017).
Design and implementation of smart village mapping
Geographic Information System based web in the
Cinunuk village,” The 2017 IEEE Asia Pacific
Conference on Wireless and Mobile (APWiMob).
S. Afnarius, M. Syukur, E. G. Eaputra, Y. Parawita, and R
Darman. (2020). Development of GIS for buildings in
the customary village of Minagkabau Koto Gadang,
West Sumatra, Indonesia. International Jurnal of Geo-
Information, p. 365.
A. Herawati, A. Purwaningsih, and Y. D. Handharko.
(2018). Promoting village tourism through the
development of information system. Review of
Integrates Business and Economics Research, vol. 7
supplementary issue 1, pp. 221- 236.
S. Prakash, P.V. Poul, and D. Nilesh. (2017). Application
of geoinformatics for smart village creation.”
International Journal of Computational Intelligence
Research, vol. 13 no. 5, pp. 1073 - 1081.
L. K. P. D. Gunawardhana. (2019) Process of requirement
analysis link to software development. Juornal of
Software Engineering and Application, vol. 12, pp.
406-422.
S. A. Asri, I. N. G. A. Astawa, I. G. A. M. Sunaya, K. A.
Yasa, I. N. E. Indrayana, and W. Setiawan. (2019).
Implementation of prototyping method on smart village
application. Jurnal of Physics: Conference Series, IOP
Publishing, vol.1569, p.032094.
M. I. Muhairat, and R. E. Al-Qutaish. (2009). An approach
to derive a use case diagram form an event table.
Proceeding of the 8th WSEAS Int. Conference on
Software Enggineering, Parallel and Distributed
Systems, pp 33-38.
M. E. Khan. (2011). Different approaches to black box
testing technique for finding error. International Journal
of Software Engineering and Applications, vol 2 no.4.
Design and Implementation of Smart Village Application
1391
