
Exploratory Factor Analysis of the Indonesian Version of Student
Engagement Scale
Mario Pratama and Anindra Guspa
Department of Psychology, Faculty of Education, Universitas Negeri Padang, Indonesia
Keywords: Student Engagement, Factor Analysis.
Abstract: Student engagement is one of the factors that influence student academic achievement. However, there is
much debate about the operational definition and dimensionality of this construct. For this reason, this study
intends to examine dimensionality of this construct. A total of 596 students in Indonesia participated in this
study consisting of junior high school students, high school students, and undergraduate students. Data was
collected online using a student engagement scale (SES), the Indonesian version of the adaptation of the SES
by Reeve & Tseng, which contains 22 items. The results of this scale found that the Cronbach alpha reliability
coefficient was 0.927. Content validity analysis by Forward-Backward translation by linguists and by expert
judgment. Analysis of construct validity with exploratory factor analysis found that the SES version of the
Indonesian language consisted of three 3 factors accounting 57.986% of total variance explained, but it also
consisted 4 factors accounting 62.078% of total variance explained. So, based on these results, the Indonesian
version of the student engagement scale can be applied using three or four dimensions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Adolescence is a crucial development period where
adolescents experience a phase of self-identity
formation, social integration, and commitment to
learning (Skinner et al., 2009). In this phase,
adolescents are busy with activities at school,
especially in the learning process. Therefore, in this
learning process, adolescents as students should be
able to participate actively. Active student
participation which is marked by interest, investment
and student effort in school assignments and activities
both inside and outside the classroom is known as
student engagement (Wang & Holcombe, 2010).
Student engagement leads to the totality of
students to be actively and proactively involved in
learning activities in a behavioral, cognitive, and
emotional manner (Fredricks & McColskey, 2012).
According to Wang and Holcombe (2010)
adolescents who have student engagement will be
involved in their school, take the time to develop their
academic potential, channel their energies to positive
activities and mobilize their motivation to be actively
involved in classroom and outside activities. Student
engagement is also a predictor that shows the level of
attention, effort, persistence, positive emotions, and
commitment of a student in the learning process
(Handelsman et al., 2005).
Student engagement is important for students,
because this behavior supports the learning process so
that it can take place well. Klem & Connell (2004)
stated, students who are engaged in learning
activities, especially in class, are much more likely to
have good performance than those who are not
involved in these activities. Low student engagement
among students is a contributing factor to low
achievement, boredom, feelings of alienation, and
even causes students to drop out of school (Fredricks
& McColskey, 2012).
The importance of student engagement is one of
the most interesting and widely researched studies
today, including in Indonesia. It's just that researchers
have limitations in data collection instruments. Not
many studies have been found on psychometric
property testing regarding student engagement
measurement tools, so it is often the cause of
weaknesses in research on student engagement.
Based on this, the researcher is interested in
conducting research on testing psychometric
properties of dimensionality and reliability of the
Indonesian version of the student engagement
measurement tool.
Research on the psychometric properties of student
Pratama, M. and Guspa, A.
Exploratory Factor Analysis of the Indonesian Version of Student Engagement Scale.
DOI: 10.5220/0011095600003368
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Mental Health (Icometh 2021), pages 73-76
ISBN: 978-989-758-586-9
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
73

engagement has been conducted by Fredriks &
McColskey (2012). In his research, it was found that
student engagement is a multidimensional construct
consisting of three dimensions. These dimensions are
cognitive engagement, emotional engagement, and
behavioral engagement. In this study, 21 items were
valid and reliable for measuring student engagement.
Another study conducted by Reeve & Tseng (2011)
found that student engagement is a multidimensional
construct consisting of four dimensions, namely
cognitive engagement, emotional engagement,
behavioral engagement, and agentic engagement. The
results of research conducted by Veiga (Veiga, 2016)
found that student engagement consists of cognitive
engagement, emotional engagement, behavioral
engagement, and agentic engagement. Meanwhile,
research conducted by Appleton, Cristenson, Kim, &
Reschly (2006) found that student engagement
consists of two dimensions, namely cognitive
engagement and psychological engagement.
In this study, the student engagement scale (SES)
being tested is a scale adapted from the SES made by
Reeve and Tseng (2011) which states that student
engagement consists of four dimensions, namely:
Agentic engagement (AE) is student involvement in
a form that deliberately acts proactively about what
will be learned and prepare for the lesson, Behavior
engagement (BE) is the involvement of students in
the form of concentration, attention, and effort during
the learning process, Emotional engagement (EE) is
student involvement in the form of interest in learning
and the absence of emotional resistance (stress) on
lessons, and Cognitive Engagement (CE) is the
involvement of students in the form of using
strategies in learning activities.
2 METHOD
This study uses a quantitative research design. The
validity of the measuring instrument in this study was
obtained in two ways: first, through content validity
carried out through an assessment by a panel of
experts and secondly through the obtained construct
validity through exploratory factor analysis, namely to
test the dimensional properties of the construct this
student engagement. The reliability of the measuring
instrument was obtained using the alpha Cronbach
analysis.
A total of 596 students in Indonesia participated in
this study consisting of junior high school students,
high school students, and undergraduate students.
Data was collected online using a student engagement
scale (SES), the Indonesian version of the adaptation
of the SES by Reeve & Tseng (2011), which contains
22 items.
3 RESULTS
The student engagement scale used is an adaptation
of the student engagement scale made by Reeve &
Tseng (2011). The adaptation process refers to the
way described by Beaton et al., (2000) in which the
processes include: 1) Translating the original
language measuring instrument into Indonesian. In
this case the researcher translates with the help of a
licensed translator and another translator who is
proficient in psychology. 2) Synthesis of translation.
The two translations from the translators were
synthesized. 3) Backward transaction. In this case the
researcher is assisted by a translator who speaks
Indonesian and is a native speaker of the original
language. 4) Final translation assessment by expert
judgment.
From the results of data analysis with the
Cronbach Alfha test, the reliability coefficient value
was 0.927. Then to find out the factors / dimensions
that make up SES, it is done by using the EFA test,
by first doing an assumption test analysis with KMO
and Bartlett's test. The assumption test results
obtained a KMO value of 0.939 (>0.05) and a Bartleet
Test of 7000,823 (p=0.000), so it can be concluded
that the assumption test is fulfilled so that it can be
continued to factor analysis. The results were
analyzed by means of the analysis of exploratory
factor analysis (EFA). The results of this analysis
indicated that there were 3 factors that had
eigenvalues above 1, these three factors were able to
explain 57,986% of the total variance of SES. The
results of loading factors from the EFA can be seen in
the following table:
Table 1: SES loading factor results with 3 factors.
No Item
Factors
12 3
i1 .188 .265 .670
i2 .106 .065 .827
i3 .145 .099 .842
i4 .318 .213 .650
i5 .235 .106 .748
i6 .170 .801 .110
i7 .206 .759 .136
i8 .252 .796 .102
i9 .410 .697 .124
I10 .135 .548 .128
i11 .445 .616 .186
Icometh 2021 - International Conference of Mental Health
74
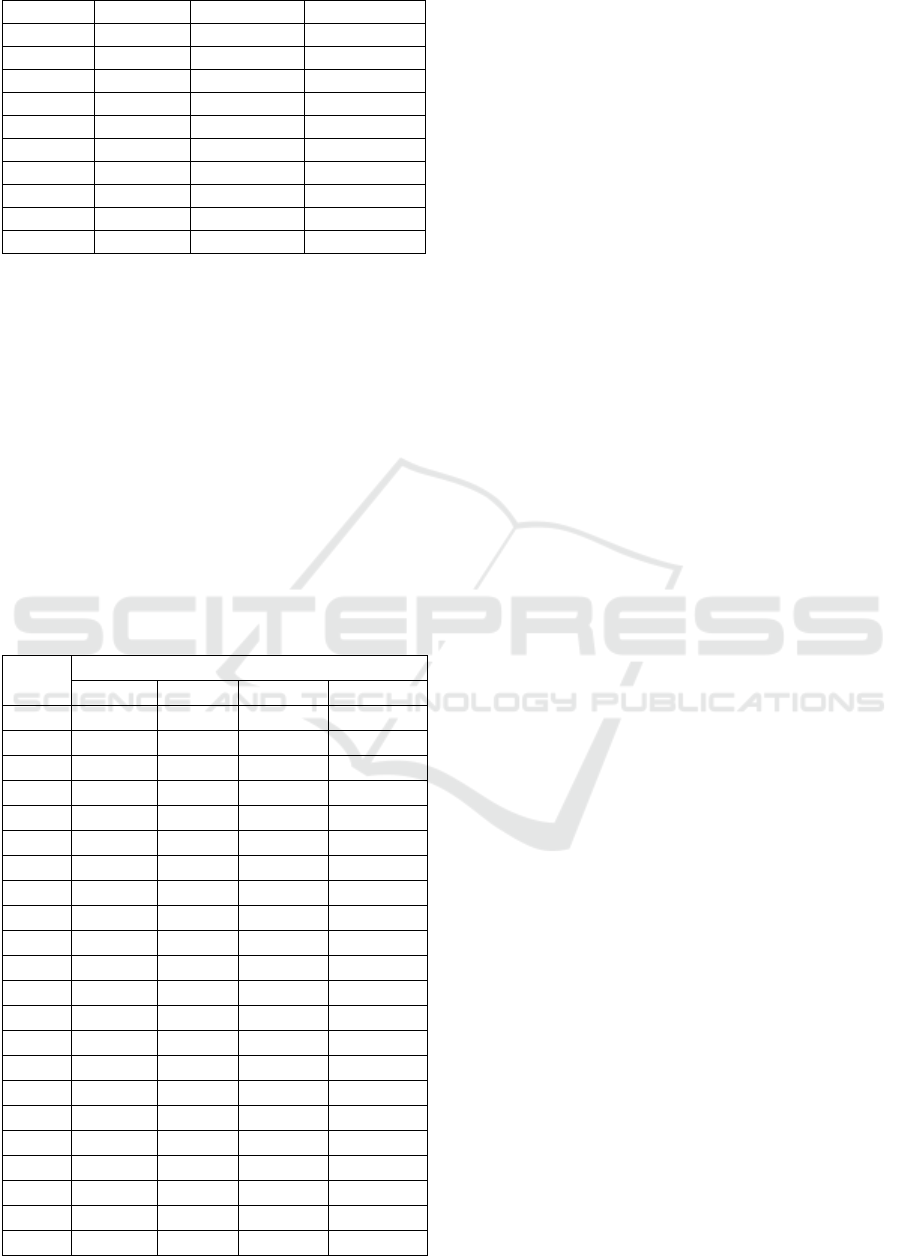
i12 .372 .610 .174
i13 .535 .603 .185
i14 .325 .329 .285
i15 .720 .292 .185
i16 .716 .240 .146
i17 .747 .199 .235
i18 .635 .196 .273
i19 .636 .174 .257
i20 .614 .313 .027
i21 .694 .237 .161
i22 .599 .284 .168
Based on the table, it is found that the SES
measurement tool forms 3 factors, namely agentic
engagement, behavioral & emotional engagement,
and cognitive engagement. However, this result is
different from the theory proposed by Reeve & Tseng
(2011) which states that SES consists of 4 factors, so
the researcher performs the EFA test again by
bringing up 4 factors. The results of this analysis
show that the SES which consists of 4 factors is able
to explain 62.078% of the total variance of SES.
However, the results of the eigenvalues of three
factors have a value above 1 and one factor has a
value of 0.900. The results of loading factors from
this analysis can be seen in the following table:
Table 2: SES loading factor results with 4 factors.
No
item
Factors
1 2 3 4
i1 .190 .247 .667 .108
i2 .108 .052 .825 .069
i3 .146 .083 .839 .085
i4 .342 .224 .661 -.061
i5 .229 .079 .741 .146
i6 .185 .795 .115 .099
i7 .210 .737 .134 .178
i8 .269 .791 .108 .085
i9 .424 .686 .127 .099
I10 .194 .611 .162 -.307
i11 .429 .565 .170 .312
i12 .341 .539 .149 .426
i13 .513 .541 .165 .367
i14 .239 .189 .226 .787
i15 .725 .274 .183 .088
i16 .729 .234 .150 .017
i17 .759 .192 .238 .019
i18 .642 .183 .272 .056
i19 .627 .140 .247 .170
i20 .618 .296 .025 .089
i21 .691 .209 .154 .141
i22 .596 .257 .162 .144
Based on the table, it is found that SES forms 4
factors with items 1-5 forming the AE factor, items 6-
10 forming the BE factor, items 11-14 forming the EE
factor, and items 15-22 forming the CE factor, so
these results are in accordance with the theory
submitted by Reeve & Tseng (2011).
4 DISCUSSION
The results of this study found that the SES reliability
value was 0.927. The results of the EFA test show that
the Indonesian version of SES is formed by 3 factors
which explain the SES of 57,986%. Then it could also
form 4 factors that could explain the SES of 62.078%.
In this study the Indonesian version of SES was
adapted from SES made by Reeve & Tseng (2011)
which states that SES consists of 4 factors, if we refer
to the EFA results where 3 factors have an
eiugenvalue value above 1 then one more factor has
an eigenvalue of 0.900. So that we can conclude that
there is a possibility that the Indonesian version of
SES is a multi-dimensional measuring tool that can
be used as 3 factors. Research conducted by Fredricks
& McColskey (2012) states that student engagement
is a multidimensional construct consisting of 3 factors.
The Indonesian version of SES can also be used
as 4 factors according to the basic theory. Research
conducted by Veiga (2016) on students in Portugal
also found that SES consists of 4 factors, namely
agentic engagement, behavioral engagement,
emotional engagement, and cognitive engagement.
Based on the results of the study, the Indonesian
version of SES allows it to be used by using 3 or 4
factors. However, for even stronger proof, the
researcher suggests conducting tests using
confirmatory factor analysis to test the theoretical
model whether the Indonesian version of SES is fit
with a 3-factor or 4-factor model.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The results showed that the Indonesian version of
SES has a reliability coefficient of 0.927. The EFA
results show that SES consists of 3 factors that can
explain 57,986% of SES, and form 4 factors that can
explain SES of 62.078%. So based on these results it
is possible that SES can be used with 3 factors or 4
factors. However, for further research, the researcher
suggests conducting a confirmatory factor analysis
test to ensure the correct theoretical model to explain
the theoretical construct of SES.
Exploratory Factor Analysis of the Indonesian Version of Student Engagement Scale
75

REFERENCES
Appleton, J. J., Christenson, S. L., Kim, D., & Reschly, A.
L. (2006). Measuring cognitive and psychological
engagement: Validation of the Student Engagement
Instrument. Journal of School Psychology, 44(5), 427–
445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2006.04.002
Beaton, D. E., Bombardier, C., Guillemin, F., & Ferraz, M.
B. (2000). Guidelines for the Process of Cross-Cultural
Adaptation of Self-Report Measures. Spine, 25(24),
3186–3191. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-
200012150-00014
Fredricks, J. A., & McColskey, W. (2012). The
Measurement of Student Engagement: A Comparative
Analysis of Various Methods and Student Self-report
Instruments. In Handbook of Research on Student
Engagement (pp. 763–782). Springer US.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-2018-7_37
Handelsman, M. M., Briggs, W. L., Sullivan, N., & Towler,
A. (2005). A Measure of College Student Course
Engagement. The Journal of Educational Research,
98(3), 184–192.
https://doi.org/10.3200/JOER.98.3.184-192
Klem, A. M., & Connell, J. P. (2004). Relationships Matter:
Linking Teacher Support to Student Engagement and
Achievement. Journal of School Health, 74(7), 262–
273. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1746-
1561.2004.tb08283.x
Reeve, J., & Tseng, C.-M. (2011). Agency as a fourth aspect
of students’ engagement during learning activities.
Contemporary Educational Psychology, 36(4), 257–
267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2011.05.002
Skinner, E. a, Kindermann, T. A., Connell, J. P., &
Wellborn, J. G. (2009). Engagement and disaffection as
organizational constructs in the dynamics of
motivational development. Handbook of Motivation in
School, 503, 223–246.
Veiga, F. H. (2016). Assessing Student Engagement in
School: Development and Validation of a Four-
dimensional Scale. Procedia - Social and Behavioral
Sciences, 217, 813–819.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.02.153
Wang, M.-T., & Holcombe, R. (2010). Adolescents’
Perceptions of School Environment, Engagement, and
Academic Achievement in Middle School. American
Educational Research Journal, 47(3), 633–662.
https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831209361209
Icometh 2021 - International Conference of Mental Health
76
