
Impact of COVID-19 on the Welfare of Russian Enterprises
V. V.Osadchii
1a
, A. L. Zolkin
2b
, N. V. Levoshich
3c
, S. I. Tokova
4d
and G. V. Ryabkova
5e
1
International University of Digital Economy and Technology, Moscow, Russia
2
Povolzhskiy State University of Telecommunications and Informatics, Samara, Russia
3
Federal State Budgetary Institution of Higher Education Financial University under the Government
of the Russian Federation, Moscow, Russia
4
Karachay-Circassian State University, Karachaevsk, Russia
5
Moscow Aviation Institute (National Research University), Moscow, Russia
Keywords: Coronavirus, Covid 19, Economy, Crisis, Activity, Income, Budget, Unemployment, Expenses, Market.
Abstract: For people around the world, the situation with the coronavirus COVID-19 has shown that all sectors of the
economy, including the activities of companies, ranging from micro-enterprises to large holdings were not
prepared to such issues. The world economy is in deep crisis. Starting from the first quarter of 2020, there
was a decrease in activity in the economies of most of the market leaders. These include the EEC, USA, Japan,
China. The collapse of the ruble and oil prices, a decrease in revenues to the country's budget, an increase in
the share of unemployment, a decrease in household income, an increase in the share of divorces and suicides,
a drop in the quality of education due to the transition to self-isolation, an increase in mortality due to COVID-
19 disease, have led to uncertainty and destabilization of the situation in the country. Since the beginning of
the coronavirus crisis, there has been a significant decrease not only in jobs, but also in population income.
The self-isolation regime has had a significant impact on the lives of ordinary citizens. The world was not
ready for such shocks. The crisis continues to the present. The article reflects information on the dynamics of
the development of Russian entities during the pandemic, examines and analyzes the consequences of the
impact of coronavirus on the welfare of citizens. The consequences of the impact of the pandemic on various
spheres of an individual's life, provided statistical data and proposed solutions outlined in this article, make it
possible to realize the importance of development of preventive measures in response to similar situations.
The analysis of the expected consequences of the pandemic in the economic sphere of the state is also carried
out, the measures applied by the government in the current situation are considered.
1 INTRODUCTION
Over the last year, COVID-19 has caused more than
1 million deaths and has infected more than 26
million people. World gross domestic product (GDP)
is decreased by 5%.For most of the leading minds of
the country, it has become obvious that COVID-19 is
not just an emergency, but a crisis that grips the
humanitarian, social and economic aspects of the life
of the country in general and of each person in
particular. Despite the timely and general
mobilization of all resources in the fight against the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4092-1862
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5806-9906
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2230-959X
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1349-448X
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1742-3638
virus, the consequences are disappointing: a general
decrease in the standard of living of people, an
increased share of the unemployed, an increase in
prices for goods and services, an increase in the share
of debt on loans to banks. The crisis caused by the
pandemic continues up to date. The consequences of
the impact of the pandemic on various spheres of
human life, as well as the statistical data presented in
this article, make it possible to realize the importance
of development of preventive measures in response to
such situations.
V. Osadchii, V., Zolkin, A., Levoshich, N., Tokova, S. and Ryabkova, G.
Impact of COVID-19 on the Welfare of Russian Enterprises.
DOI: 10.5220/0011119400003439
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Scientific and Practical Conference "COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals" (RTCOV 2021), pages 285-291
ISBN: 978-989-758-617-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
285

2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
The purpose of this study is to review and analyze the
impact of COVID-19 on human well-being.
Objectives:
to consider the consequences of the pandemic
in Russia;
to study the family budget of the population
during pandemic;
to analyze the income of population during
pandemic.
Research hypothesis: it is assumed that if we
analyze the consequences of the impact of COVID-
19 on the well-being of the country's citizens over the
past year and, having made the right conclusions,
direct efforts to develop preventive measures in the
future, then such situations will be minimized.
3 RESEARCH QUESTIONS
In this study, the method of analysis and classification
has been used as a methodological basis for the study.
Internet publications on the impact of COVID-19 on
the welfare of the country's citizens have been used as
a basis for the theoretical study.
4 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The negative consequences of COVID-19 are still felt
in many sectors of the Russian economy, from
industrial companies of various sizes to the agro-
industrial complex. Since the beginning of 2020, the
demand for many types of goods and services has
changed significantly. The purchasing power of the
citizens of the country has significantly decreased. If
we analyze the negative consequences of the
pandemic, then significant “damage” was caused to
meat and milk processing industries, as well as to fish
farms. However, companies that are engaged in crop
production have suffered less due to significant
export volumes. Before the pandemic, demand for
dairy products tended to decline. This was especially
noticeable in premium dairy products. In the minds of
many people, the pandemic was associated with
uncertainty, so many people in our country became
more frugal and thrifty. However, the spring of 2020
has allowed many food companies to increase
production due to increased demand. With the start of
the coronavirus crisis, the prices for imported
vitamins, which were part of the compound feed,
have been increased. And this, in its turn, led to an
increase in prices for all meat and dairy products,
where imported vitamins account for more than 70%.
5 RESULTS
All this ultimately led to a natural increase in prices
for all meat and dairy products.
Since the beginning of the coronavirus crisis, there
has been a significant decrease not only in jobs, but
also in the incomes of the country's population. It
could not but affected the decrease in demand for
products that belong to the expensive segment,
including: fish and various seafood, exotic fruits and
vegetables, cold cuts and flowers. Due to a decrease
in the purchase price for products grown in
greenhouses by retailers, prices for vegetable crops
decreased by 15-20% (see Figure 1).
Changes in demand for products manufactured by
agro-industrial enterprises could be well tracked in
retail chains [6,7].
The category of citizens who purchased products
in premium segment stores such as Land or Azbuka
Vkusa will continue to shop there. However, most of
the citizens with middle or low income have reduced
their consumption of meat and dairy products. In
2020, prices for all main types of products from the
consumer goods basket have been increased as a
result of the weakening of the ruble and falling of the
price for oil.For example, prices for bakery products
increased by 5%, seafood by 4%, dairy products by
5.5%, eggs by 6.5%, and cereals and legumes rose in
price by almost 26%.Thus, a significant increase in
prices has been observed only for legumes and
cereals, while prices for meat products increased by
only 0.7%.
The COVID-19 pandemic has covered the world,
creating unusual conditions that have affected all
areas of human life. These changes have dealt a
devastating blow to production and the field of
entrepreneurship, and therefore the consequences of
the pandemic for the global economy are already
obvious. Russian economic experts are concerned
about the impact of unfavourable factors on the
domestic economic system. According to their
assumptions, as a result of the spread of the pandemic
and the subsequent reduction in production, Russia's
GDP will decline by about 10-20%. Moreover, oil,
which is considered one of the main commodities
supplied by Russia to the world market, has dropped
significantly in price due to the decrease in transport
activity around the world. Experts assume that the
RTCOV 2021 - II International Scientific and Practical Conference " COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals
(RTCOV )
286

Figure 1: Food costs at the start of the pandemic.
average annual rates for this fuel resource will not
exceed $ 25.
It shall be admitted that the coming crisis was
expected. Back in 2014-2015 experts predicted the
onset of a global economic recession due to
overcapitalization of market systems and monopoly
trends in economic structures. This stage of the
economic cycle was considered inevitable, but its
onset came much closer with the advent of the viral
infection COVID-19.
The impact of the pandemic turned out to be so
strong that in the face of the difficulties that arose,
major political conflicts receded into the background,
including the confrontation between China and the
United States, as well as the Brexit process in the UK.
Universal involvement in solving problems caused by
the pandemic has led to a change in course of solving
political, social and economic problems. Due to a new
round in the development of events, other goals, tasks
and issues have emerged that need to be addressed.
Considering the future of Russia in the context of
the impact of the pandemic, experts identify five
possible shock conditions that the country's economy
may undergo.
The first option is the emergence of difficulties in
establishing international relations and contacts with
other states. The reason for this phenomenon may be
the negative consequences of the impact of the
pandemic on the micro- and macroeconomics of the
state.
The second option is associated with a decrease in
oil demand. As one of the main exported products, oil
provides an inflow of funds to Russia. A decrease in
demand for this resource and a general drop in prices
can lead to a weakening of the cash flow directed to
the state budget, which will entail a decline in the
economic system.
The third option is the outflow of funds from
Russia. From the experience of the past decades, it
can be understood that during periods of recession,
funds are transferred from the country to other states
– funds are sent to more developed and promising
systems, or transferred to offshore accounts.
A fourth option is to consider the risk of increased
controls and restrictions that governments may
impose to support overall security. The restrictions
associated with the self-isolation regime generally
reduce the intensity of freight traffic, trade and sales.
The purchasing power and the activity of
entrepreneurs are decreasing. There is a gradual
decline in the incomes of citizens of the country,
which leads to adverse consequences for the
economic system.
Experts say that the fifth option is a decrease in
the level of trust of legal entities and entrepreneurs in
the government and legislative bodies. As a result of
the loss of mutual trust, certainty will be lost, and the
level of protection of entrepreneurship will decrease.
Business development planning will become much
more difficult, since in unstable conditions it is
difficult to make assumptions and forecasts [8,9].
According to statistics from the United Nations
(UN) report "World Economic Situation and
Prospects", as a result of the introduced protective
measures designed to prevent or slow down the
spread of the COVID-19 virus, the global economic
system has decreased by 4.3%. The pandemic-related
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
January February March April May
60,5 60,5
65,4
56,8
58
20,9
20,6
23,8
26
24
Food costs at the start of the pandemic
General expenses Food expenses
Impact of COVID-19 on the Welfare of Russian Enterprises
287

crisis is reported to be greater than any economic
recession in last 90 years.
Crisis situations have already happened in Russia.
For example in 1998 the economy was reduced by
5.3%, in 2009 by 7.8%. In 2020, the decline in
economic activity reached 3.1%. The decline in the
volume of GDP is associated with absolute and
relative factors. In absolute terms, the decline in
production indicators is associated with a decrease in
resource extraction, transportation system,
commercial activities and the service sector. In
relative terms, large losses were incurred by the
catering sector, which decreased by 24%, as well as
by the spheres associated with holding mass events
(cultural and sports segments, which suffered losses
by 11.4%).
The main factor associated with both the risks and
the hopes of the Russian economy is oil, because the
intensity of raising funds depends on the level of its
exports. The government is pinning its hopes on an
increase in oil prices, in particular on Urals products,
but this factor depends on many conditions. Oil can
rise in price only after the full resumption of transport
links between the countries, as well as the return of
production facilities to their previous level of activity
[5].
At the same time, most experts in the field of
economics come to the general opinion that the
pandemic inflicted the least damage on China. This
country was the first to face an exacerbation of the
epidemiological background and quickly overcame it.
In addition, a large number of large industrial
complexes, equipped with the latest technology,
operate in China. In combination with the high
working capacity and the level of responsibility of the
population, China can quickly recover as well as
come to positive results.
In other countries, the situation remains uncertain.
This is also true for Russia, since there is a general
decline in epidemiological safety in our country. At
this stage, accurate forecasting of further events in
Russia is not possible.
6 FINDINGS
The self-isolation regime has had a significant impact
on the life of an ordinary citizen of our vast homeland,
including their daily expenses. None of us faced a
similar situation before and, therefore, for the first
time after the declaration of self-isolation, many
citizens continued to live in the same regime, in the
hope that it would end soon.
On the one hand, the transition to home mode
allowed significant savings on fuel and lubricants and
transportation costs to and from work, payment of
monthly fees for school and kindergartens, and visits
to coffee houses and restaurants. But on the other
hand, there has been an increased expenditure of the
family budget for food. Most of the population began
to purchase food, clothing and other basic necessities
from online stores. Scrolling the ribbon with
beautiful, appetizing pictures encouraged people to
make rash purchases. Therefore, part of the
population continued to live as usual, replacing
visiting food courts with orders via the Internet.
In addition to the increase in food costs, which at
the beginning of the pandemic were fueled by the
artificial rush for the purchase of all cereals, tomatoes
and toilet paper, there have been serious trends in job
cuts due to a decrease in overall demand. In every
second family, there was a 2 times decrease in income
due to a reduction in one of the breadwinners, a
general decrease in income, especially during the
period of illness of one of the family members [10].
Despite the pandemic, it was necessary to pay
monthly fees for previously taken loans. However,
many banks, in order to reduce the risks of economic
damage, have taken measures that allowed citizens to
softly withdraw from credit obligations. The
measures were: reduction of refinancing rates,
issuance of credit loans on favourable terms, debt
restructuring, cancellation of penalties on previously
issued loans.
7 DISCUSSION
The pandemic has made its own adjustments in the
incomes of the population. Many companies were not
ready for such situation, and most of the company
owners did not have a strategy for further
development in the current situation. As a result,
some of the companies that could not promptly react
and adapt to the current situation left the market. Here
is the data on the number of registered and liquidated
companies during the pandemic (see Figure 2).
All this could not but affect the income of the
population. Many company owners sent their staff to
work remotely, someone found a way out to layoffs
or send them on indefinite leave without pay.As a
result of a decrease in demand for goods and services,
the establishment of restrictions on movement,
interruptions in the supply of necessary raw materials,
all this led to a decrease in production volumes, which
RTCOV 2021 - II International Scientific and Practical Conference " COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals
(RTCOV )
288
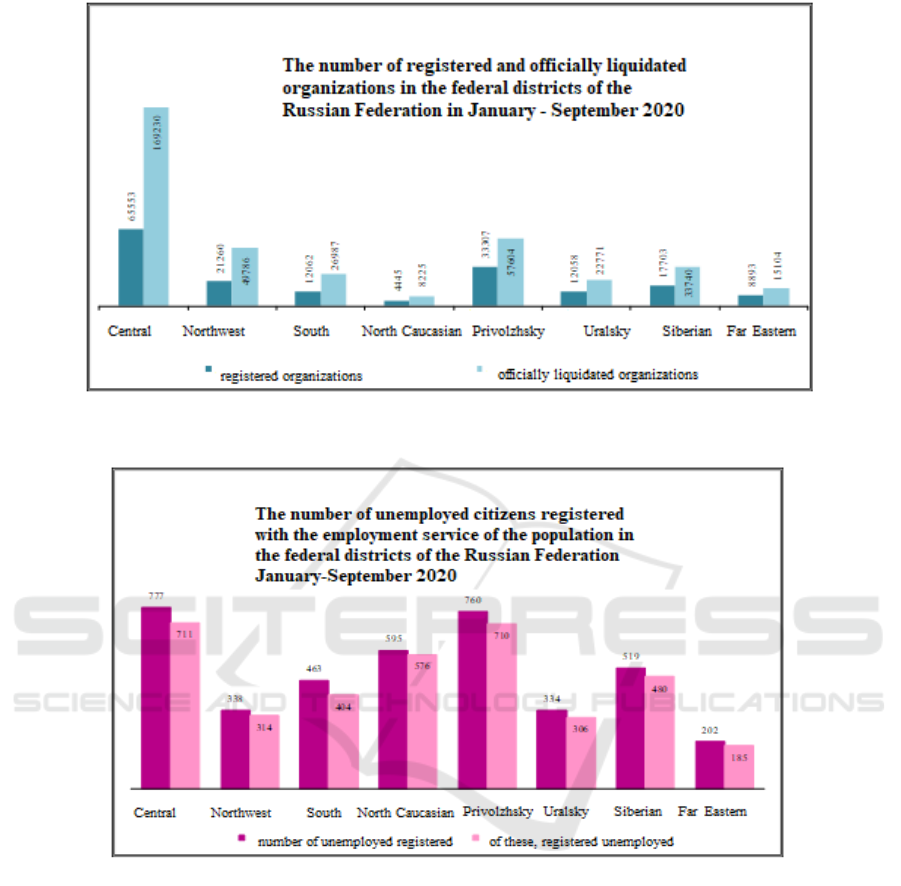
Figure 2: The number of registered and officially liquidated organizations in the federal districts of the Russian Federation in
January-September 2020.
Figure 3: The number of unemployed citizens registered with the employment service of the population in the federal districts
of the Russian Federation at the end of September 2020, thousand people.
also negatively affected the income of the self-
employed and small enterprises [11] (see Figure 3).
If we analyze the situation in the Central Federal
District, then by the end of the 3rd quarter of 2020
there were almost 941,000 people in active search, in
other words it is an unemployed category of citizens.
More than 711,000 people were registered in the
employment services.
But due to the state policy to support the
population and business during the pandemic, the
income of the population did not fall below the level
of the consumer basket (see Figure 4).Among the
measures of state support, the following can be
distinguished:
● increased unemployment benefits;
● increasing benefits for caring for children of
different ages;
● various subsidies, preferential lending
programs, deferrals.
And if we consider the situation with payroll in the
Central Federal District, then in the period from the
beginning of 2020 to the 3rd quarter of 2020, the
nominal wages of company employees amounted to
62,600 rubles, which exceeded the indicators of 2019
by 6% [12].
Impact of COVID-19 on the Welfare of Russian Enterprises
289
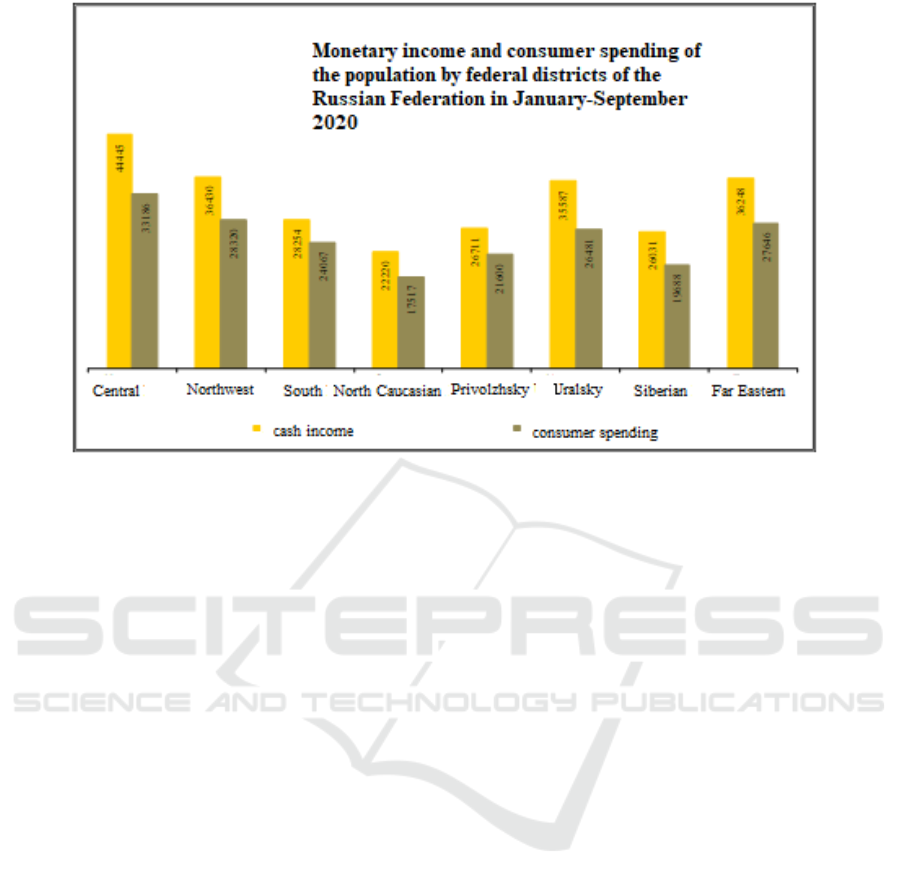
Figure 4: Average monthly wages of employees of organizations by federal districts of the Russian Federation in January-
September 2020, rubles.
8 CONCLUSION
Thus, in our opinion, such situations in the world
should force the governments of all countries to
reconsider the issues of state support for the
healthcare sector and other leading sectors of the
economy in order to carry out timely respond and take
appropriate measures, as well as strive to reduce the
number of unemployed in any area.
The behaviour of a person as a consumer of goods
and services cannot be changed in the short time. For
this reason, that part of the citizens who were able to
adapt to the current conditions, competently approach
the distribution of the family budget and spending,
use the current situation for their own benefit, will be
able not only to survive this difficult period with
dignity, but also to find new ways out, thereby
increasing their income. The consequences of the
pandemic will be felt for some time in every country.
As preventive measures, it is necessary to develop
such steps that will be aimed at covering of all
segments of the country's population. The more
economically stable the state is, the easier it will be to
go through such situations. The coronavirus crisis has
become a turning point for the entire world, forcing
great minds to think wider and deeper.
REFERENCES
Belaya, A. A., 2020. Analytics. Regime of not-high alert.
Which problems of agrarian entities are identified by
coronavirus, https://www.agroinvestor.ru/.
Levshukova, O. A., 2020. Possible consequences of
COVID-19 pandemic that would make an impact on
Russian economy. Liberal arts and Scientific studies,
29(3): 191-194.
Maksimova, E. V., Ryabtsev, A., Sazonova, O., 2020.
Impact of coronavirus on Russian economy. Scientific
and analytical journal “Innovations and investments”,
4: 283-286.
Shchurina, S.V., 2020. Support measures for small and
medium-sized businesses in priority sectors of the
Russian economy in 2020. Economy. Taxes. Law, 1: 60-
71.
Zolkin, A. L., Aygumov, T.G., Pakhomova, A.I., Bobkov,
V.V., 2021. Research of modern opportunities for
obtaining the grant support for innovative projects
financing. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and
Environmental Science. Krasnoyarsk Science and
Technology City Hall.
Delfani, F., Samanipour, H., Beiki, H., Yumashev, A.,
Akhmetshin, E., 2020. A robust fuzzy optimisation for
a multi-objective pharmaceutical supply chain network
design problem considering reliability and delivery
time. International Journal of Systems Science:
Operations and Logistics, pages 1-25.
Kruntyaeva, E. D., 2020. Consequences of COVID-19
pandemic for Russian economy. Young scientist,
35(325): 44-46.
RTCOV 2021 - II International Scientific and Practical Conference " COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals
(RTCOV )
290

Lachinina, T. A., Chirkov, M.A. and Chistyakov, M.S.,
2020. On the development of health care management
in the post-coronavirus era in variations of
epidemiological uncertainty. Philosophy of the
economy, 6: 201-207.
Impact of COVID-19 on the Welfare of Russian Enterprises
291
