
Correlation Analysis of Blood Lipid Metabolism Level and Liver
Malignant Tumor under Information System Medical Health Data
Juan Feng
a
and Yong Feng
b
Qingdao West Coast New District People's Hospital, Qingdao, Shandong, China
Keywords: Information System, Medical And Health Data Analysis, Liver Malignant Tumors, Blood Lipid Metabolism.
Abstract: Liver malignant tumor was the fifth most common malignant tumor in the world and the third leading cause
of cancer-related death. To explore the relationship between lipid metabolism level and liver malignant tumor,
in this paper, 142 patients with liver malignant tumors were selected as the experimental group by the method
of obtaining medical and health data through the hospital information system, and 803 health examiners were
selected as the control group with the the same period for visting the hosptical, it gave a correlation analysis
of the blood lipid detection data of the two groups. The performance of liver malignant tumor includes serum
total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, apolipoprotein AI and
apolipoprotein B, which were significantly lower than those of healthy people on physical examination. This
study verify that the blood lipid metabolism level of patients with liver malignant tumors were significantly
lower than that of the normal population with the help of information system medical health data, the blood
lipid metabolism level can be used as an important disease evaluation index for the development of liver
malignant tumors.
1 INTRODUCTION
Blood lipid was the general term for all lipid
components in human blood. Clinical medical tests
mainly detect serum total cholesterol (CHO),
triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein (HDL-
C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL),
apolipoprotein AI (ApoAI), Apolipoprotein B
(ApoB) and other indicators (Adegoke 2020,
Adeyanju 2020). The liver was the largest digestive
organ of the human body and was closely related to
the metabolism of blood lipids in the human body.
Studies have shown that human lipid metabolism
disorders were closely related to the occurrence (Sung
2021, NCD-RisC 2020, Yang 2013) and development
of cardiovascular diseases and tumors (Seko 2013,
Kitahara 2011). At present, the correlation analysis of
blood lipid metabolism level and malignant tumors in
international literature was based on the research and
analysis of small sample size, and there was no
literature to extract medical health data through
informatization to carry out large sample size analysis
(Rimessi 2016, Ahn 2009). In this study, with the help
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7321-7732
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4515-560X
of the hospital’s internal information system, after the
personal medical information was masked, the blood
lipid test data of 803 healthy medical examiners and
142 patients with clearly diagnosed liver malignant
tumors in the same period and the same age group
were collected. Then carry out two sets of correlation
analysis.
In this study, the information system was used to
retrieve the original medical and health data, and the
SPSS statistical software package was used to analyze
the research data. The measurement data was the
average value plus or minus the standard deviation to
indicate the index of abnormal blood lipid
metabolism. Parallel to the analysis of variance, the
abnormal blood lipid metabolism was compared
between the liver malignant tumor group and the
normal physical examination group. The use of
information systems to extract medical and health
data can effectively reduce statistical errors and
improve the accuracy of experimental results.
Through analysis, this study clarified that the
reduction of blood lipid metabolism can be used as an
important indicator of the deterioration of patients
Feng, J. and Feng, Y.
Correlation Analysis of Blood Lipid Metabolism Level and Liver Malignant Tumor under Information System Medical Health Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0011193400003444
In Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare (CAIH 2021), pages 117-122
ISBN: 978-989-758-594-4
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
117

with liver malignant tumors, and provides a reference
for clinicians to observe the development of patients
with liver malignant tumors.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Research Object
142 cases of liver malignant tumor patients treated in
tertiary hospitals from February 2020 to October
2021 were screened with the help of an information
system as the experimental group.
2.2 Standard Constrain
Standard constrain: (1) Diagnosed as liver malignant
tumor by pathological examination; (2) No history of
surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy; (3) The
patient had the result of fasting blood lipid level in the
early morning during hospitalization; (4) The clinical
data of the patient was completed.
Exclusion criteria: (1) Combined with abnormal
function of other important systems and organs; (2)
Combined with other types of malignant tumors; (3)
Patients had oral antihypertensive, lipid-lowering,
and hypoglycemic drugs; (4) Pregnant or lactating
women.
In the experimental group, there were 110 males
and 32 females with liver malignant tumors; they
were 43 to 90 years old, with an average age of
(62.04±8.87) years old.
The control group used the information system to
screen out 803 healthy people who came to the
hospital for physical examination during the same
period. Among them, there were 584 males and 219
females; they were 54 to 71 years old, with an average
age of (60.82±4.99) years old.
There was no statistically significant difference in
baseline information between the two groups (all
P>0.05), and they were comparable. All researches
were approved by the hospital ethics committee. The
blood test information of all subjects has been masked
before being extracted from the information system.
All data in this research does not involve personal
privacy.
2.3 Method
In the liver malignant tumor group, 3ml of fasting
peripheral venous blood was taken in the early
morning of hospitalization and delivered to the
laboratory Beckman AU5800 automatic biochemical
analyzer for unified testing. Reference standards for
each test item: total cholesterol: 0-5.17mmol/L,
triglycerides: 0-2.3mmol/L, high-density lipoprotein
cholesterol: 1.29-1.55mmol/L, low-density
lipoprotein cholesterol: 0-3.37 mmol/L,
Apolipoprotein AI: 1.0-1.6g/L, Apolipoprotein B:
0.6-1.1g/L.
2.4 Statistical Analysis
The SPSS statistical software package was used to
analyze the research data. The measurement data was
represented by ⎯x±s parallel analysis of variance or t
test, and the count data was represented by n (%)
parallel X
2
test. P<0.05 indicated that the difference
was statistically significant.
3 RESULT
3.1 Comparison of Baseline Data
Comparison of different genders between the
experimental group and the control group. There were
110 males and 32 females in the experimental group;
584 males and 219 females in the control group
during the same period. The gender difference
between the two groups was not statistically
significant (P>0.05). See Table 1 and Figure 1 for
details.
Table 1. Comparison of the two groups of different genders.
Group Male (%) Female (%)
Liver cancer 110 (77.46) 32 (22.54)
Control 584 (72.73) 219 (27.27)
Chi-square with Yates' correction 1.156
P-value 0.282
CAIH 2021 - Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare
118
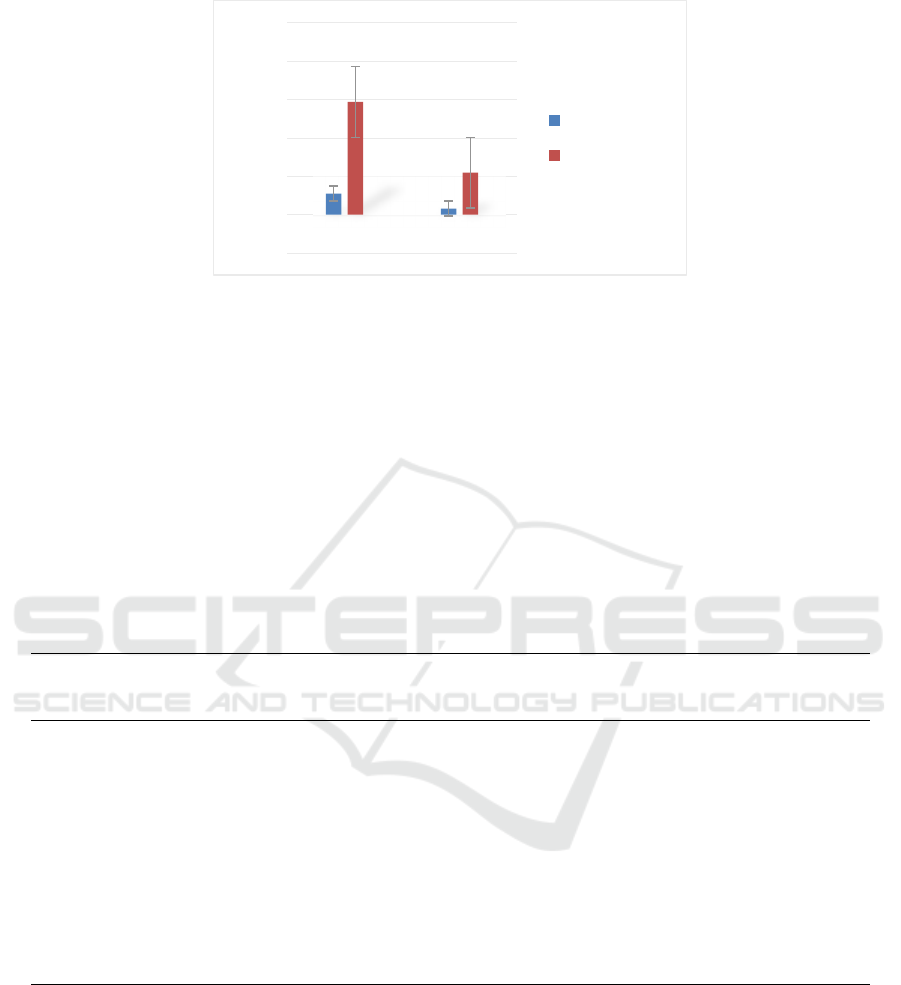
Figure 1: Gender distribution of liver malignant tumor group and healthy population.
3.2 Comparison of Abnormal Blood
Lipid Metabolism of Different
Genders
Serum total cholesterol (CHO) ≥ 5.17mmol/L in the
experimental group was abnormal, with 18 males
(60%) and 12 females (40%); Triglyceride (TG) ≥
2.3mmol/L was abnormal, 5 males (62.5%), 3
females (37.5%); high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C) ≤
1.29mmol/L was abnormal, 81 males (82.65%), 17
cases (17.35%) were female; Low-density lipoprotein
(LDL) ≥ 3.37mmol/L is abnormal, 13 cases were
male (65%), 7 cases were female (35%);
Apolipoprotein AI (ApoAI) ≤ 1.0g/L was reduced, 56
cases were male ( 83.58%), 11 female cases
(16.42%); Apolipoprotein AI (ApoAI) ≥ 1.6g/L was
elevated, 0 males and 4 females (100%);
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) ≤ 0.6g/L was reduced, 28
males (93.33%), 2 cases of female (6.67%)
apolipoprotein B (ApoB) ≥ 1.1g/L were elevated, 23
cases of male (69.70%), 10 cases of female (30%).
The difference between the two groups was
statistically significant (P<0.05). See Table 2.
Table 2: Comparison of abnormal blood lipid metabolism of different sexes in the experimental group.
-------
Male Female
Chi-squ
P-value
Abnormality
(n)
Proportion
(%)
Abnormality
(n)
Proportion
(%)
Cho
18 60% 12 40%
30.00 <0.0001
TG
5 62.5% 3 37.5%
HDL-C
81 82.65% 17 17.35%
LDL
13 65% 7 35%
ApoAI
(
reduction
)
56 83.58% 11 16.42%
ApoAI
(
ascension
)
0 0 4 100%
ApoB
(
reduction
)
28 93.33% 2 6.67%
ApoB
(
ascension
)
23 69.70% 10 30%
3.3 Comparison of the Distribution of
Dyslipidemia between the Two
Groups
Serum total cholesterol (CHO) ≥ 5.17mmol/L was
abnormal, of which 30 cases in the experimental
group were abnormal, accounting for 21.13%; 500
cases in the control group were abnormal, accounting
for 62.27%. The difference between the two groups
was statistically significant (P<0.05).
Triglyceride (TG) ≥ 2.3mmol/L was abnormal, of
which 8 cases in the experimental group were
abnormal, accounting for 5.63%; 154 cases in the
control group were abnormal, accounting for 19.18%.
The difference between the two groups was
statistically significant (P<0.05).
High-density lipoprotein (HDL-C) ≤ 1.29mmol/L
was abnormal, of which 98 cases in the experimental
group were abnormal, accounting for 69.01%; 190
cases in the control group are abnormal, accounting
110
32
587
219
-200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
Male Female
Liver cancer
Control
Correlation Analysis of Blood Lipid Metabolism Level and Liver Malignant Tumor under Information System Medical Health Data
119

for 23.66%. The difference between the two groups
was statistically significant (P<0.05).
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) ≥ 3.37mmol/L
was abnormal, of which 20 cases in the experimental
group were abnormal, accounting for 14.08%; 207
cases in the control group were abnormal, accounting
for 25.78%. The difference between the two groups
was statistically significant (P<0.05).
Apolipoprotein AI (ApoAI) ≤ 1.0g/L was a
decrease, and apolipoprotein AI (ApoAI) ≥ 1.6g/L
was an increase. The above two conditions were
abnormal. Among them, 67 cases were abnormally
decreased in the experimental group, accounting for
47.18%, 4 cases were abnormally increased,
accounting for 2.82%; 2 cases in the control group
were abnormally decreased, accounting for 0.25%,
and 246 cases were abnormally increased, accounting
for 30.64%. The difference between abnormal
increase and abnormal decrease between the two
groups was statistically significant (P<0.05).
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) ≤ 0.6g/L means a
decrease, and apolipoprotein B (ApoB) ≥ 1.1 g/L
means an increase. Both conditions were abnormal.
Among them, 30 cases in the experimental group
were abnormally decreased, accounting for 21.13%,
33 cases were abnormally increased, accounting for
23.24%; 56 cases in the control group were
abnormally decreased, accounting for 6.97%, and 328
cases were abnormally increased, accounting for
40.85%. The difference between abnormal increase
and abnormal decrease between the two groups was
statistically significant (P<0.05). See Table 3.
Table 3: Comparison of the distribution of dyslipidemia between the two group.
-----
Liver cancer
Control
Chi-square with Yates’
correction
P value
Abnormality
(n)
Proportion
(%)
Abnormality
(n)
Proportion
(%)
Cho 30 21.13 500 62.27 81.25 <0.0001
TG 8 5.63 154 19.18 14.64 <0.0001
HDL-C 98 69.01 190 23.66 115.0 <0.0001
LDL 20 14.08 207 25.78 8.41 <0.005
ApoAI
(reduction)
67 47.18 2 0.25 385.8 <0.0001
A
p
oAI
(
ascension
)
4 2.82 246 30.64 46.57 <0.0001
ApoB(reduction) 30 21.13 56 6.97 27.53 <0.0001
A
p
oB
(
ascension
)
33 23.24 328 40.85 15.11 <0.0001
3.4 Comparison of Blood Lipid
Determination Results between the
Two Groups
Experimental group CHO (4.64±2.52) mmol/L, TG
(1.33±0.64) mmol/L, HDL-C (1.14±0.39) mmol/L,
LDL (2.58±1.64) mmol/L, ApoAI (1.04±0.32) ) g/L,
ApoB (0.92±0.36) g/L metabolic level was lower than
the control group CHO (5.57±1.17) mmol/L, TG
(1.78±1.35) mmol/L, HDL-C (1.53±0.34) mmol /L,
LDL (2.91±0.82) mmol/L, ApoAI (1.48±0.20) g/L,
ApoB (1.02±0.26) g/L, the differences were
statistically significant (all P<0.05).See Table 4,
Figure 2.
Table 4: Comparison of the results of blood lipid determination between the two groups.
Group n Cho TG HDL-C LDL ApoAI ApoB
Liver cancer 142
4.64±2.52 1.33±0.64 1.14±0.39 2.58±1.64 1.04±0.32 0.92±0.36
Control 803
5.57±1.17 1.78±1.35 1.53±0.34 2.91±0.82 1.48±0.20 1.02±0.26
t, value 4.335 6.169 11.18 2.315 15.64 3.044
P value <0.0001 <0.0001 <0.0001 <0.05 <0.0001 <0.0001
CAIH 2021 - Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare
120

Figure 2: Comparison of blood lipid results between the two groups.
4 DISCUSSION
Serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density
lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, apolipoprotein
AI, and apolipoprotein B were the main components
of human blood lipids, and they were also key test
indicators in clinical laboratories. The relevant test
data was easy to obtain and easy Perform dynamic
assessments. These indicators participate in signal
transduction, inflammation, vascular factor
regulation and other activities in the human body, and
participate in the formation of cell membranes.
Abnormal blood lipid metabolism was not only
related to human cardiovascular and cerebrovascular
diseases, but also closely related to the occurrence
and development of tumors.
In the experimental group, 60% of men in the
experimental group had abnormal serum cholesterol
metabolism, 62.5% of triglyceride metabolism,
82.65% of high-density lipoprotein metabolism, and
65% of low-density lipoprotein metabolism, the
abnormal decrease in apolipoprotein AI accounted for
83.58%, and the abnormal decrease in apolipoprotein
B accounted for 93.33%. The abnormal metabolism
of the above indicators accounted for higher
proportions than women. The reason may be that the
severity of liver damage in male patients with liver
malignant tumors is generally higher than that in
female patients, and the proportion of liver damage
and alcohol consumption in male patients was higher
than that in female patients. The specific reasons still
need to be confirmed by further experiments, and
there was no relevant literature report at home and
abroad.
The metabolic level of the experimental group
(CHO (4.64±2.52) mmol/L, TG (1.33±0.64) mmol/L,
HDL-C (1.14±0.39) mmol/L, LDL (2.58±1.64)
mmol/L, ApoAI (1.04±0.32) g/ L, ApoB (0.92±0.36)
g/L) was lower than that of the control group. Lipids
were an important part of the cell membrane. When
cells become cancerous, the lipids on the cell
membrane will be destroyed. Abnormalities will
occur during the normal absorption, synthesis, and
metabolism of lipids, resulting in a decrease in blood
lipid metabolism. The reduction of blood lipid
metabolism will further induce the normal
construction of the body's cell membrane, leading to
the continuous development of the body's tumor cells.
L
i
ve
r c
a
n
ce
r
g
r
o
u
p
C
on
tr
ol
g
rou
p
0
5
10
15
20
25
Cho(mmoL/L)
t
,
=4.335
P<0.0001
L
iver
cancer gr
oup
C
ontro
l gr
ou
p
0
5
10
15
20
TG(mmoL/L
)
t
,
=2.345
P<0.05
L
ive
r
can
c
er
g
r
o
up
C
o
ntr
ol
grou
p
0
1
2
3
4
HDL-C(mmoL/L)
t
,
=11.18
P<0.0001
L
i
ver
can
cer
g
r
oup
C
ontro
l g
rou
p
0
5
10
15
LDL-C(mmoL/L)
t
,
=11.18
P<0.0001
L
iver c
a
n
c
e
r g
r
oup
C
ontrol
grou
p
0
1
2
3
ApoA1(g/L)
t
,
=15.64
P<0.0001
L
i
ver
c
an
ce
r g
r
ou
p
C
ontrol g
r
ou
p
0
1
2
3
4
ApoB(g/L)
t
,
=3.044
P<0.005
Correlation Analysis of Blood Lipid Metabolism Level and Liver Malignant Tumor under Information System Medical Health Data
121

On the other hand, the liver parenchyma of patients
with liver malignant tumors has been severely
damaged. With liver damage, the liver will have more
and more serious effects on the metabolism of blood
lipids, and its ability to convert into lipids will
gradually weaken. Serum total cholesterol,
triglycerides, high-density lipoproteins, low-density
lipoproteins, apolipoproteins AI, apolipoprotein B
and other indicators will gradually decrease
compared with the normal physical examination
population.
Compared with the traditional small number of
medical samples, the data comparison results were
more accurate in the liver malignant tumor patient
population and the same period. In this study, with the
support of informatized medical health data, the
correlation analysis between blood lipid metabolism
and liver malignancies was carried out to provide a
more accurate reference for the treatment and
prognosis of liver cancer patients.
5 CONCLUSIONS
It was an important method to analyze the correlation
between blood lipid and tumor by using health data
measurement. In this paper, a large number of
measurement data were collected through
information system, and the correlation analysis
between abnormal lipid metabolism and liver
malignant tumor was carried out by chi-square test. It
selected the performance index as an evaluation
criterion including the metabolism of serum total
cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein,
low-density lipoprotein, apolipoprotein AI, and
apolipoprotein B in patients with liver malignant
tumors. Studies have found that the performance
index was much lower than that of the normal
population. Studies have shown that there were
statistically significant differences in the distribution
of abnormal blood lipid metabolism in patients with
liver malignant tumors in different genders and
different age groups. This study can assist clinicians
to more quickly and accurately assess the
development of liver malignant tumors, and provide
a reference for the treatment of liver malignant
tumors in the future.
With the rapid development of artificial
intelligence and medical health data analysis
technology, the application of information systems in
the medical field has become more and more in-
depth. In the next step, we will further use the
information system to extract a large number of
experimental data to carry out clinical research and
analysis, and promote the deep integration of
"medical and industrial" fields.
REFERENCES
Adegoke TE, Sabinari IW, Usman TO, Abdulkareem TO,
Michael OS, Adeyanju OA, Dibia C, Omotoye OO,
Oyabambi AO, Olatunji LA. Allopurinol and valproic
acid improve cardiac triglyceride and Na+-K+-ATPase
activity independent of circulating aldosterone in
female rats with glucose intolerance. Arch Physiol
Biochem. 2020,23:1-7.
Adeyanju OA, Falodun TO, Michael OS, Soetan OA,
Oyewole AL, Agbana RD. Spironolactone reversed
hepato-ovarian triglyceride accumulation caused by
letrozole-induced polycystic ovarian syndrome: tissue
uric acid-a familiar foe. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch
Pharmacol. 2020,393(6):1055-1066.
Ahn J, Lim U, Weinstein SJ, Schatzkin A, Hayes RB,
Virtamo J, Albanes D. Prediagnostic total and high-
density lipoprotein cholesterol and risk of cancer.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009,18(11):2814-
2821.
Kitahara CM, Berrington de González A, Freedman ND,
Huxley R, Mok Y, Jee SH, Samet JM. Total cholesterol
and cancer risk in a large prospective study in Korea. J
Clin Oncol. 2011,29(12):1592-1598.
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC).
Repositioning of the global epicentre of non-optimal
cholesterol. Nature. 2020,582(7810):73-77.
Rimessi A, Previati M, Nigro F, Wieckowski MR, Pinton P.
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and
inflammation: Molecular mechanisms, diseases and
promising therapies. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
2016,81(Pt B):281-293.
Seko Y, Akuta N, Suzuki F, Kawamura Y, Sezaki H, Suzuki
Y, Hosaka T, Kobayashi M, Kobayashi M, Saitoh S,
Arase Y, Ikeda K, Kumada H. Amino acid substitutions
in the hepatitis C Virus core region and lipid
metabolism are associated with hepatocarcinogenesis in
nonresponders to interferon plus ribavirin combination
therapy. Intervirology. 2013,56(1):13-21.
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram
I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality
Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer
J Clin. 2021,71(3):209-249.
Xilin Yang, Ying Wang, Andrea O Y Luk, Wing Yee So,
Ronald C W Ma, Alice P S Kong, Gang Xu, Juliana C
N Chan. Enhancers and attenuators of risk associations
of chronic hepatitis B virus infection with
hepatocellular carcinoma in type 2 diabetes. Endocr
Relat Cancer. 2013,20(2):161-71.
CAIH 2021 - Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare
122
