
Coffee Shop Strategy in using Blockchain to Overcome Supply Chain
Obstacles in Indonesia
Toto Edrinal Sebayang, Dony Saputra, Didiet Gharnaditya, Eufedia Novchelie Budiman and
William Ignatius Ferardi
Management Department, Binus Business School Undergraduate Program, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia
eufedia.budiman@binus.ac.id, william.ferardi@binus.ac.id
Keywords: Coffee Shop, Blockchain, Qualitative, Interview.
Abstract: This study aims to analyze coffee shop strategy in using blockchain to overcome supply chain barriers. The
method used in this research is qualitative with primary data obtained through interviews with 5 informants
of coffee shop owners. Data were analyzed qualitatively with Miles and Huberman approach. The results
show that blockchain technology can affect transparency and data management in overcoming coffee supply
chain barriers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Blockchain is a new digital technology that allows
distributed untrusted parties to conduct financial
transactions without the use of intermediaries such as
banks (Kamilaris et al., 2019). A blockchain (BC) is
a distributed ledger of digital transactions that is
maintained by a network of several computer units
rather than a trusted third party. Individual transaction
data files (blocks) are controlled by software
platforms that allow the data to be sent, processed,
stored, and represented in a human-readable format.
Each block in the original bitcoin configuration has a
header that includes a time stamp, transaction data,
and a link to the preceding block. Every block
generates a hash depending on its contents, which is
then referenced in the heading of the next block.
Every transaction is propagated over the blockchain
protocol’s network of machines and must be validated
by all computer nodes.
The ability of a blockchain to maintain a
consistent view and agreement among participants
(i.e. consensus) is a vital characteristic, even if some
of the members may not be honest. Blockchain
technology is developed based on a distributed ledger
of information. It is made up of numerous blocks,
each with its own address information, as the name
implies. Each block has its own identity and
information (Buterin, 2016). The information from
BC cannot be changed, erased, or updated (Chen et
al., 2019). If any information needs to be changed, a
new block for adding information must be
constructed. Traceability (Dutta et al., 2020) and
auditing at any point in the supply chain (SC) become
efficient and effective as a result of this specific and
unique quality. According to (Hamda and Sastra,
2020), high transmission speed makes the system
very efficient. When compared to the Traditional
Supply Chain (TSC), the BC saves money and
improves quality. Recently, a manufacturing
company began implementing BC in order to boost
Supply Chain (SC) performance.
According to the Indonesian Ministry of
Agriculture (2020), coffee beans have become more
expensive over the last decade. Coffee beans have
become an increasingly important commodity in
Indonesia as a result of increased demand and as a
lifestyle item. With the abundance of coffee beans in
Indonesia, Coffee shops have grown in popularity and
importance, and they have evolved into a new way of
life. Hence, the originality of coffee beans have
become untraceable. With the advancement of
blockchain technology, agricultural products become
easier to trace it back to its origin (Kamilaris et al.,
2019).
The aim of this study is to analyze the importance
and barriers of blockchain technology to trace the
originality of coffee beans.
Sebayang, T., Saputra, D., Gharnaditya, D., Budiman, E. and Ferardi, W.
Coffee Shop Strategy in using Blockchain to Overcome Supply Chain Obstacles in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0011245800003376
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2021), pages 115-118
ISBN: 978-989-758-602-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
115

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
In today’s global market, SCM is critical for lowering
operational costs (Laurence, 2019). Every producer
wants to put their products in the hands of consumers
at the lowest possible price. BC is regarded as a
cutting-edge technology for cost reduction (Moleong,
2010) and quality improvement, and its intricacies
would strengthen the SC. The incorporation of BC in
SCM is elicited by (Muhajirin and Panorama, 2017).
Their main focus was on improving the
organization’s performance and cost-effective output
by safeguarding data and transactions, as well as the
dispersed nature and transactions in peer-to-peer
networks
In the case of food production, sustainability
standards and certifications aid organic food and
improve the food life cycle. These kinds of mishaps
result in the development of new industrial and
supply chain technology. The advantages of using BC
are security, irreversibility, dispersedness,
transparency (Musyafak et al., 2020), and accuracy
(Narimawati, 2008). Pagano and Liotine (2020). All
of these requirements will drive the integration of BC
and SCM forward.
From the manufacturer to the end-users via
retailer/supplier, BC helps to ensure transparency,
security, traceability, and cost control. Customers and
end-users are unaware of manufacturing processes,
commodities movement on the production floor, and
the dangers and suffering involved in manufacturing,
transportation, and handling, among other things. The
flow of data assists customers in gaining and
regaining trust.
3 METHODS AND
MEASUREMENT
Qualitative research method is data obtained without
any quantification of data in the form of sentences or
actions, which are then collected and analyzed.
According to Sugiyono (2017) to be able to
understand social reality from the perspective of the
perpetrator, qualitative research methods are used.
In this research, the author uses a descriptive case
study method. Descriptive research is research that
can describe the state of the object in accordance with
current conditions (Sugiyono, 2017). The unit of
analysis in this study is individual coffee producers or
executives who use blockchain technology. The time
horizon used is a Cross Sectional study which is a
study of several cases simultaneously in one time
period (Wijaya and Darmawan, 2017).
The Data Collection method applied in this
research is using semi-structured interviews
consisting
of 5 (five) owners or management teams at coffee
shops that apply blockchain technology. Five
informants have been selected based on their
geographic location, demographics that include both
male and female gender, psychographics, and having
at least two years’ experience using blockchain
technology in their coffee shops for interviews. Data
analysis technique used is inVivo coding with Miles
and Huberman approach. InVivo coding consists of
three steps such as data reduction, data display and
data conclusion. Validity test used is source
Triangulation and membercheck.
4 RESEARCH FINDINGS
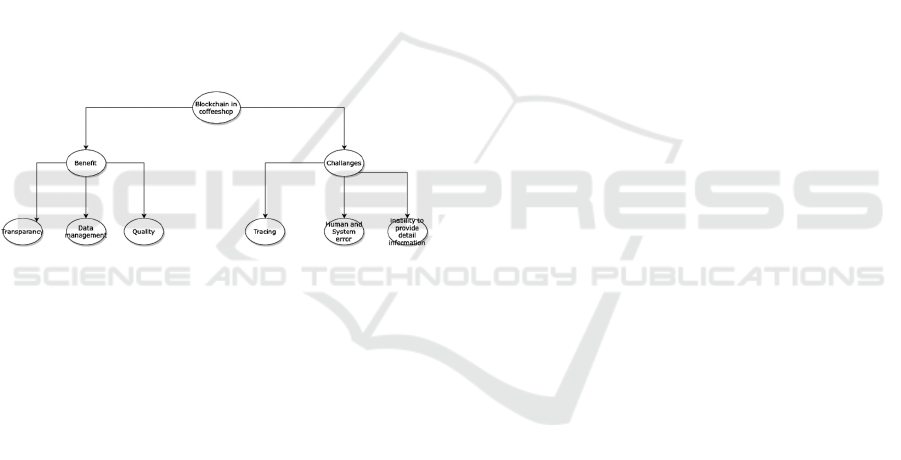
Based on the informant’s interview, it can be
concluded that there are two main findings regarding
the importance of blockchain application and its
challenges. The benefit of applying blockchain for
coffee shop owners is transparency, data
management, and coffee quality as shown by the
transcripts below:
”Yes, the benefit of applying blockchain in our
coffee shop is for transparency from the date of the
process, when is the roasting, what type of process,
and who is doing it, so it is more transparent”
(Informant 1, AS, Head of Marketing Blue Korintji)
”It helps the farmer because the farmer on data
management on updating data based on what he has
today, the farmer harvests. 100 kilos. Yes, he will
report there. 100 kilos costs Rp. 5,000 or Rp. 10,000.”
(Informant 2, S, CEO Kopi Alam Kerinci)
”In terms of quality, it has a significant impact
both before and after we use blockchain because we
can detect the coffee, we want based on what we
want” (Informant 3, PA, CEO Noka Coffee)
The challenges that come from applying
blockchain for coffee shop owners are carrying out
supply chain activities such as tracing which is the
perpetrator of supply chain activities prior to using
blockchain, the number of human and system errors
that occur because data collected is not structured
properly prior to using blockchain technology, and
the inability to provide detail information as shown
by the transcripts below:
”We don’t just sell it randomly; the challenge is to
trace the supply chain, although there’s a barcode
ICRI 2021 - International Conference on Recent Innovations
116
from Kerinci to here.” (Informant 2, S, CEO Kopi
Alam Kerinci).
”Without the application of blockchain
technology, if we did it manually, there could be a
human and system error because it’s not neatly
arranged.” We are now reserving a batch, and once it
is clear, we will separate it into storage. We can now
more easily assess the quality of the coffee beans.”
(Informant 3, PA, CEO Noka Coffee).
”Assisting farmers and every farmer’s difficulty
to provide detail information, imagine if President
Obama drank the coffee and then gave 5 stars, right
after the QR code came out, oh, he would conclude
that apparently this coffee belongs to Mr. A.
However, if President Obama would drink the same
coffee from me again next week, and the coffee is not
good and give it a one star, Obama would know that
the coffee is not good, which would make me feel as
an inferior farmer and thinking, wow, I did something
wrong yesterday. If it’s not delicious, then if it’s not
good, it means the farmer made a mistake in the
process.” ” (Informant 3, S, CEO Noka Coffee)
Figure 1: Model findings.
5 CONCLUSION
The driving criteria of BC were explored in this
research in order to apply it with the SC and make it
more resilient and sustainable. Several conclusions
can be drawn based on the findings of a qualitative
study using semi-structured interview and
documentation techniques to examine the impact of
blockchain technology on supply chain management
which has an impact on coffee producers and coffee
commodities in Indonesia such as:
• The function of applying blockchain in coffee
shops is used as a tool to facilitate monitoring in
supply chain activities, ensuring that all
activities, including data management and the
provision of high-quality coffee beans, go off
without a hitch. Hence, to attract customers,
coffee shops are adopting blockchain as a
marketing branding technique.
• The importance of applying blockchain is
transparency, data management, and coffee
quality are three elements influenced by
blockchain in reducing supply chain hurdles.
• Coffee shops face challenges in carrying out
supply chain activities such as tracing which is
the perpetrator of supply chain activities prior to
using blockchain, the number of human errors
that occur because data collected is not
structured properly prior to using blockchain
technology, and the inability to provide
information. Coffee beans of the highest grade
in conformity with consumer expectations.
REFERENCES
Ayoub, H. F., & Abdallah, A. B. (2019). The effect of
supply chain agility on export performance. Journal of
Manufacturing Technology Management.
Belu, M. G. (2019). Application of Blockchain in
International Trade: An Overview. The Romanian
Economic Journal.
Buterin, V. (2016). The Business Blockchain. John Wiley
& Sons, Inc.
Chen, J., LV, Z., & Song, H. (2019). Design of personnel
big data management system based on blockchain.
Future Generation Computer Systems 101. Dobrovnik,
M., Herold, D. M., Fürst, E., & Kummer, S. (2018).
Blockchain for and in Logistics: What to Adopt and
Where to Start. Logistics.
Dutta, P., Choi, T.-M., Somani, S., & Butala, R. (2020).
Blockchain technology in supply chain operations:
Applications, challenges, and research opportunities.
Transportation Research Part E.
Hamda, D., & Sastra, A. A. (2020). A To Z Memulai Dan
Mengelola Usaha Kedai Kopi . Jakarta: PT AgroMedia
Pustaka.
Ikhawana, A. (2018). Supply chain management of coffee
commodities. MATEC. Web Conference.
Irawan. (2021). Mantap! Noka Coffee Luncurkan Kopi
Berbasis Teknologi
Blockchain. Diambil kembali dari Saibumi: https://www.
saibumi.com/artikel-103771-mantap-noka-coffee-lunc
urkan-kopi-berbasis-teknologi- blockchain.html
Kamilaris, A., Fonts, A., & X. Prenafeta-Boldύ, F. (2019).
The rise of blockchain technology in agriculture and
food supply chains. Trends in Food Science &
Technology.
Kelompok Tani. (2018). Profil Alko Alam Kerinci.
Diambil kembali dari Kopi Alam Kerinci:
https://kopialamkerinci.com/profil-alko-coffee-kerinci/
Laurence, T. (2019). Blockchain for dummies. John Wiley
& Sons, Inc.
Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). An Expanded
Sourcebook: Qualitative Data Analysis. London: Sage
Publications.
Moleong, L. (2010). Metodologi penelitian kualitatif.
Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya.
Moleong, L. (2016). Metodologi Penelitian Kualitatif Edisi
Coffee Shop Strategy in using Blockchain to Overcome Supply Chain Obstacles in Indonesia
117

Revisi. Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya.
Muhajirin, & Panorama, M. (2017). Pendekatan praktis:
metode penelitian kualitatif dan kuantitatif.
Yogyakarta: Idea Press.
Musyafak, A., Susanti, A. A., Putra, R. K., & Widaningsih,
R. (2020). Outlook Kopi. Pusat Data dan Sistem
Informasi Pertanian Seketariat Jenderal - Kementrian
Pertanian.
Narimawati, U. (2008). Metodologi Penelitian Kualitatif
dan Kuantitatif, Teori dan applikasi. Bandung: Agung
Media.
Pagano, A. M., & Liotine, M. (2020). Technology in Supply
Chain Management and Logistics Current Practice and
Future Applications. Elsevier.
Panggabean, E. (2019). Buku Pintar Kopi. Jakarta: PT
AgroMedia Pustaka. Ramachandra, M. (2010). Web-
Based Supply Chain Management and Digital Signal
Processing: Methods for Effective Information
Administration and
Transmission. IGI Global.
Sakaran, U., & Bougie, R. (2017). Metode Penelitian untuk
Bisnis: Pendekatan Pengembangan-Keahlian. Jakarta
Selatan: Salemba empat.
Sugiyono. (2013). Metodelogi Penelitian Kuantitatif,
Kualitatif Dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sugiyono. (2015). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif Kualitatif
dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sugiyono. (2017). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif,
Kualitatif, dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta, CV.
Sugiyono. (2018). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif,
Kualitatif, dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Thiruchelvam, V., Mughisha, A. S., Shahpasand, M., &
Bamiah, M. (2018).
Blockchain-based Technology in the Coffee Supply Chain
Trade: Case of Burundi Coffee. Journal of
Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer
Engineering.
Wijaya, D. A., & Darmawan, O. (2017). Blockchain Dari
Bitcoin Untuk Dunia. Jasakom.
Yadav, S., & Singh, S. P. (2020). Blockchain critical
success factors for sustainable supply chain. Resources,
Conservation & Recycling.
Kamilaris, A., Fonts, A., & Prenafeta-Boldύ, F. X. (2019).
The rise of blockchain technology in agriculture and
food supply chains. Trends in Food Science &
Technology, 91, 640-652.
Yadav, S., & Singh, S. P. (2020). Blockchain critical
success factors for sustainable supply chain. Resources,
Conservation and Recycling, 152, 104505.
ICRI 2021 - International Conference on Recent Innovations
118
