
The Effect of Procedural Justice, Work Engagement, on Innovative
Work Behavior
Gustiarti Leila, Hamidah and Dede Rahmat Hidayat
Management Science, Universitas Negeri Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Procedural Justice, Work Engagement, Innovative Work Behavior.
Abstract: Government regulation forces companies to focus on innovation as one of the methods to increase work
performance so that they can compete with other companies. At the same time, with the still distant social
hierarchy between the organization and the employees motivates the writers to examine whether procedural
justice affects the innovative work behavior of the employees through the research on the relationship between
procedural justice, work engagement, and innovative work behavior. Research was done on 173 supervisor-
level employees of a nation-owned plantation company located in North Sumatera, Indonesia. Sample was
chosen through simple random sampling method. Structural equation modeling was used to test the
hypothesis. Results showed that procedural justice has a significant positive effect on innovative work
behavior (β=0.242; p=0.000). Procedural justice also indirectly affects innovative work behavior through
work engagement (β = 0.173; p=0.000). Thus, it can be concluded that procedural justice can increase
innovative work behavior both directly and indirectly through the mediation of work engagement. This study
also found that the contribution of procedural justice and work engagement to innovative work behavior is R
2 adjust = 0.28, while the contribution of procedural justice on work engagement is R 2 adjust = 0.20.
Suggestions for further research include strengthening other variables that can also cause increase in
innovative work behavior in this particular company.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to Kanter (1988) and Scott & Bruce
(1994), innovative work behavior can be understood
as a multi-dimensional concept. Employees produce
innovative ideas, look for supports to these ideas from
their colleagues and supervisors, and apply these
ideas in their workplace (De Spiegelaere, Van Gyes
& Van Hootegem, 2014). West & Farr (1990) defined
innovative work behavior as “Every employee’s
behavior that is aimed to the creation, promotion and
application of an idea (in their role, group, or
organization). Based on the works of Kleysen &
Street (2001) and Yuan & Woodman (2010), IWB is
every individual action that is aimed the generation,
processing, and application/implementation of new
ideas regarding methods that include ideas for
products, technology, procedures, or work process
with the aim to increase the effectivity and success of
an organization.
According to De Jong & Den Hartog (2010),
innovative behavior relates to the production of new
ideas and innovative results. Furthermore, innovative
work behavior also refers to the ability to think
differently, reorganize information and knowledge
with other methods, both in order to develop new
products and processes and to realize and spread
them. This concept differs from creativity in that to
show the novelty and radicality of an idea, innovative
behavior encompasses the socio-psychological
process between individuals that concerns more on
the implementation and realization of an idea.
There are many variables that can affect
innovative work behavior of employees. Procedural
justice is one of those variables. Procedural justice
refers to the perception of employees on how open
their organization (leaders) to hear the opinions of its
members on the decision-making process (Zeb,
Abdullah, Othayman & Ali, 2019). Other than that,
procedural justice shows the official standard and
quality of exchanges in the decision-making process.
Decision making process shows the interaction
between decision makers and receivers (Yu, Lee, Han
& Kim, 2019). When an employee feels that they are
involved in a decision-making process, then
according to the social exchange theory, employees
126
Leila, G., Hamidah, . and Rahmat Hidayat, D.
The Effect of Procedural Justice, Work Engagement, on Innovative Work Behavior.
DOI: 10.5220/0011247600003376
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2021), pages 126-131
ISBN: 978-989-758-602-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

will reciprocate with positive behavior in the form of
innovative work behavior.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW AND
HYPOTHESES
2.1 Procedural Justice and Innovative
Work Behavior
Organizational justice, especially procedural justice,
has become an important situational variable in an
organization and employee. Procedural justice
focuses on the decision-making process by giving
employees an opportunity to voice their opinions
(Blader & Tyler, 2003). Procedural justice is a
measure of the extent of uniformity exists in the
decision-making process of an organization and the
opinions of the organization members are mirrored in
the decision-making process. Zeb et al. (2019)
defined procedural justice as the openness of a
method or procedure in the making of a decision or
goals. Tyler (1988) defined that procedural justice
refers to the justice that is felt from the procedure that
is used to make a decision.
The existence of procedural justice increases a
form of cooperative behavior, which is very
important for every technical, economical, and social
progress, including the ability for innovative
behavior. The concept of procedural justice
(Masterson, Lewis, Goldman & Taylor, 2000) relates
to the social exchange pathway. This concept affects
the perception of employees on a strong connection
between them and their work environment.
Procedural justice also refers to the exchange between
an organization and its employees. Prior researches
show that formal procedure is usually applied by top
management and written on behalf of an organization
that acts as a legal entity (Cropanzano, Prehar &
Chen, 2002). When employees think that the applied
procedure is just, they will reciprocate by forming a
more positive attitude to the organization
(Cropanzano et al., 1997; Masterson et al., 2000).
From empirical studies that were conducted by
Akram (2016) and Kim & Park (2017), procedural
justice shows a significant positive influence both
directly and indirectly on the innovative work
behavior of the employees. When an individual
believes that their organization cares and treat them
justly, their motivation to perform their best on their
work increases, which in turn causes them to be
involved in the creation, development, and
application of ideas related to work.
H1: Procedural justice has a significant positive
influence on the innovative work behavior of the
employees
2.2 Procedural Justice and Innovative
Work Behavior That Is Mediated
by Work Engagement
Many existing literatures emphasize the mediation
role of work engagement in the relation between the
antecedent and consequence in an organization (Kim
et al., 2012). The mediation effects from work
engagement on the relation between procedural
justice and innovative work behavior were examined
by A. Agarwal (2014). The study showed that if an
organization seriously cares about the justice in the
decision-making process, their effort will facilitate
and support the work involvement of employees.
Procedural justice has a definition as the openness of
a method or procedure in the making of a decision or
desirable outcomes (Cropanzano & Ambrose, 2001).
One of the important variables in the procedural
justice theory is process control or voice effect, that
is the act of giving subordinates a chance to express
their wishes, opinions, views, and preferences before
a decision is made. Psychologically speaking, voice
effect gives subordinates the feeling that they are
involved in the making of a decision (Folger, 1987).
The mediation effect of work engagement on the
relation between procedural justice and innovative
work behavior shows that if an organization cares and
is open to their employees’ input, this will make
employees feel involved in the decision-making
process, which ultimately will increase the work
engagement of their employees (A. Agarwal, 2014).
The strengthening of employees’ work engagement,
in turn will increase their willingness to come up with
new ideas for their organization and apply those ideas
to their workplace with the support of their colleagues
or the management. Theoretical framework that refers
to the social exchange theory also supports this
proposition. In the view of the social exchange theory
on meta-analysis (Colquitt et al., 2013), the reciprocal
relationship and the exchange relationship between
employees and their organization (Agarwal, Datta,
Blake-Beard & Bhagarva, 2012) positively influence
employees’ work engagement and in the end increase
the positive behavior of employees (innovative work
behavior).
H2: There exists a significant and positive
influence of procedural justice on innovative attitude
through work engagement.
The Effect of Procedural Justice, Work Engagement, on Innovative Work Behavior
127

Figure 1: Hypothesis model that will be empirically tested
in this study.
3 METHODS
3.1 Research Design and Respondent
This study tests the theoretical model using an
individual data source that is obtained from
supervisor level employees of a nation-owned
plantation company. This study is conducted using
quantitative approach and survey method with
questionnaire that is designed with rating scale. On
the scale of innovative work behavior, all positive
items scores range from 1 (never) to 5 (very often).
On the scale of procedural justice and work
engagement variables, positive items are given scores
ranging from 1 (disagree very strongly) to 5 (agree
very strongly), while negative items are given score 1
(agree very strongly) to 5 (disagree very strongly).
The data gathering technique used is simple
random sampling that is gathered from a population
of 900 supervisor level employees using
questionnaires that are distributed through Google
Form. The results of sample size calculation with the
Slovin formula gives a minimum sample size of 276
respondents. However, the employees that filled the
questionnaires amount to 264 individuals. After
conducting a selection of gathered data, the amount
of data that can be processed statistically is 173,
which consist of 91% males and 9% females, with
work experience ranging from 1 year to more than 30
years.
3.2 Measures
The measure of innovative work behavior is an
adaptation from the scale of innovative work behavior
that is developed by Janssen (2000), which measures
indicators of 1) idea generation, 2) idea promotion,
and 3) idea realization. The number of items before
and after the test are 9 items with Cronbach’s alpha
0.918. The measure of procedural justice that is used
is an adaptation of the scale of procedural justice that
is developed by Reizig, Bratton & Gertz (2007) which
measures indicators of 1) superiors’ respectful
attitude, 2) superiors’ openness, 3) objectivity in
decision making, and 4) fact-based decision making.
The mount of items before testing are 17 and 16 after
testing with Cronbach’s alpha 0.841. The measure of
work engagement that is used is an adaptation of the
work engagement scale that is developed by Shuck et
al. (2016) which measures indicators of: 1) cognitive
engagement, 2) emotional engagement, and 3)
behavioral engagement. The number of items before
testing are 20 and 15 after testing with Cronbach’s
alpha 0.786. The instruments used measure latent
construct with 5 Likert scale answer choices. For
procedural justice and work engagement beginning
from 1 = disagree very strongly to 5 = agree very
strongly. While for innovative work behavior
beginning from 1 = never to 5 = very often.
3.3 Hypothesis Statistic
1. The influence of procedural justice on the
innovative work behavior. Ho : βx1y ≤ 0 H1 :
βx1y > 0
2. The influence of procedural justice on the
innovative work behavior through work
engagement. Ho : βx1zy ≤ 0 H1 : βx1zy > 0
4 RESULT
Table 1 is the sample descriptive statistic from the
variables used in this study with 173 respondents. The
table shows the mean value, standard deviation, and
variance of the variables Procedural Justice (PJ),
Work Engagement (ENG), and Innovative Work
Behavior (IWB).
Table 1: Descriptive Statistics of Sample.
N Range Mean
Std.
Dev.
Variance
IWB1 (Y.1) 173 3.00 3.8092 0.68338 0.467
IWB2 (Y.2) 173 3.00 3.7624 0.62248 0.387
IWB3 (Y.3) 173 3.30 3.6081 0.66046 0.436
PJ1 (X
1
.1) 173 1.70 3.9723 0.44018 0.194
PJ2 (X
1
.2) 173 2.20 3.8913 0.49484 0.245
PJ3 (X
1
.3) 173 2.40 3.7855 0.50964 0.260
PJ4 (X
1
.4) 173 2.00 3.8422 0.46781 0.219
ENG1 (Z
2
.1) 173 2.00 4.3434 0.44477 0.198
ENG2 (Z
2
.2) 173 1.70 4.3699 0.46471 0.216
ENG3 (Z
2
.3) 173 2.00 4.2439 0.43178 0.186
Valid N
(listwise)
173
N Range Mean
Std.
Dev.
Variance
ICRI 2021 - International Conference on Recent Innovations
128
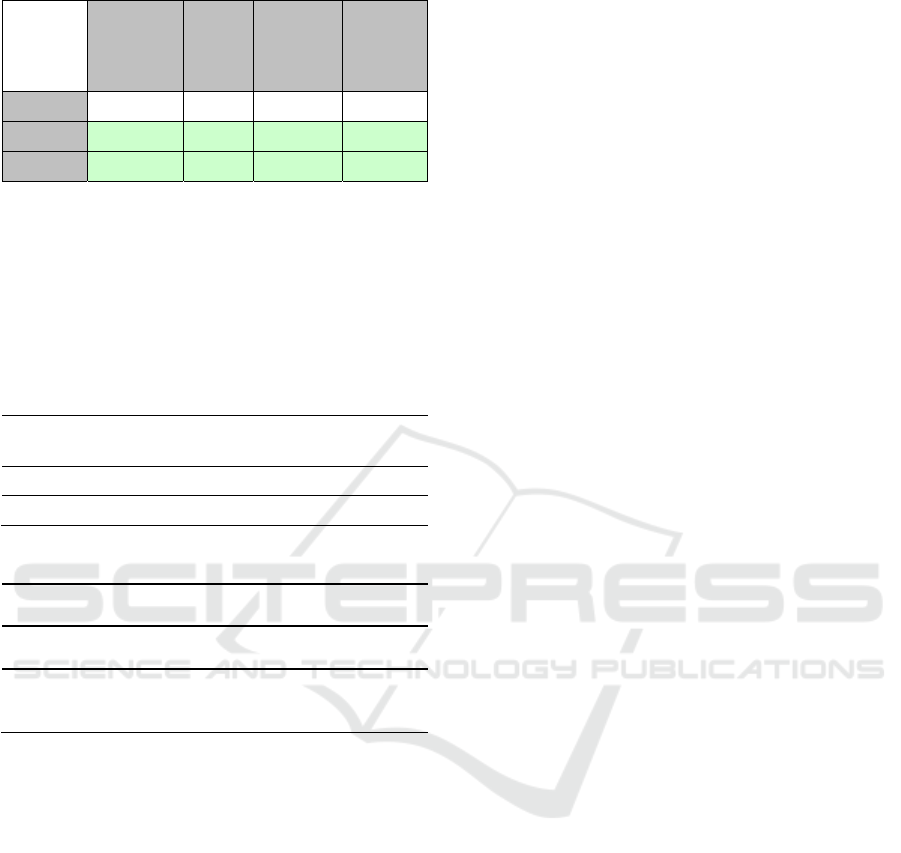
Table 2: Construct Reliability and Validity.
Cronbach's
Alpha
rho_A
Composite
Reliability
Average
Variance
Extracted
(AVE)
PJ (X1) 0.841 0.857 0.893 0.677
ENG (Z) 0.786 0.788 0.575 0.700
IWB (Y) 0.859 0.861 0.914 0.779
Table 2 shows that all variables have the
Cronbach’s alpha and composite reliability values
above 0.7. This shows that the instrument used can be
deemed reliable. The average variance extracted
values of each variable are above 0,5 showing that
those indicators represent their latent variables. Thus,
the instrument can be deemed valid.
Table 3: Significant value of direct and indirect influence.
Variable Path
coefficient
P Values Conclusion
PJ->IWB 0.242 0.008 H1: Ho rejected
PJ->ENG -> Y 0.041 0.089 H2: Ho rejected
Table 4: Determinant coefficient values.
Endo
g
en variable R
2
adjusted
Work Engagement (Z) 0,20
Innovative Work
Behavior
(
Y
)
0,28
4.1 Hypothesis Testing
The results of hypothesis testing with PLS-SEM
shows that H0 is rejected on the direct influence of
procedural justice on innovative work behavior
(β=0.242, p = 0.008). This means that there exists a
significant positive influence of procedural justice on
innovative work behavior. This agrees with the
proposed research hypothesis. Results also shows that
H0 is rejected on the indirect influence of procedural
justice on innovative work behavior through work
engagement (β=0.173, p= 0,000). This means that
there is a significant influence of procedural justice
on innovative work behavior which is mediated
through work engagement. This also agrees with the
proposed hypothesis.
The determinant coefficient values on work
engagement variable R 2 adjusted = 0.20 which
means that the procedural justice variable contributes
20% to the engagement variable. While the
determinant coefficient on the innovative work
behavior variable R 2 adjusted = 0.28 which means
that the contribution of procedural justice and work
engagement variable on the innovative work behavior
is 28%.
5 DISCUSSION
The results of statistic testing on the direct influence
of procedural justice on the innovative work behavior
gives the path coefficient value β = 0.242 (p=0.008),
which indicates a significant result. This indicates
that the procedural justice which is precepted by
employees of the company affects innovative work
behavior.
Procedural justice is the openness in decision
making of the company management to its members.
To be more exact, procedural justice is employees’
perception on how open an organization is and to
what extent it applies reasonable procedures and
shows willingness in listening to the opinions of its
members in the decision-making process.
Prior studies have found that there is a significant
and insignificant influence between procedural
justice with innovative work behavior. Research
(Akram, Taher & Feng, 2016) shows that a form of
organizational justice has a strong positive influence
on the innovative work behavior of employees in
China, especially procedural justice on innovative
work behavior has a correlation of (r= 0.627, n= 235,
p< 0.00), which indicates that procedural justice has
a significant correlation to the innovative work
behavior. In line with this, Kim & Park (2017)
discovers that procedural justice directly influences
engagement positively. The same result is also shown
by studies done by Nazir et al. (2019) that shows that
procedural justice especially can motivate the
innovative behavior of employees. Study by Ismail
(2020) also indicates that there is a significant
relationship between procedural justice on innovative
work behavior. Research on the effect of
organizational justice on engagement (Ohiorenoya &
Eguavoen, 2019) shows that three dimensions of
distributive, interactional, and procedural have
influences on employees’ engagement.
Statistic testing results of indirect influence of
procedural justice on innovative work behavior
through engagement gives path coefficient value β =
0.173 (p=0.000). This shows a significant result,
which means there is an influence between procedural
justice on innovative work behavior through work
engagement.
The Effect of Procedural Justice, Work Engagement, on Innovative Work Behavior
129

The goal of this study is to show the mediation
ability of engagement in the relationship between
procedural justice with innovative work behavior.
Previous studies have examined the direct effect of
procedural justice on engagement (Akram, Taher &
Geng, 2016; S. Nazir, Shafi, Atif, Qun & Abdullah,
2019; A. Agarwal, 2014; Streicher et al., 2012;
Ismail, 2020) which show that procedural justice
positively influences innovative work behavior. The
results of the indirect effect of procedural justice on
innovative work behavior by W. Kim & Park (2017)
show that there exists a significant relationship
between procedural justice and innovative work
behavior that is mediated by engagement.
The determinant coefficient values of procedural
justice to innovative work behavior and the
relationship between procedural justice and work
engagement to innovative work behavior are 20% and
28% respectively. These values are relatively weak.
This indicates that there needs to be strengthening of
other variables in addition to the aforementioned
variables in order to increase work engagement and
innovative behavior in this company.
6 IMPLICATION
The determinant coefficient values of procedural
justice to innovative work behavior and the
relationship between procedural justice and work
engagement to innovative work behavior are 20% and
28% respectively. These values are relatively weak.
This indicates that there needs to be strengthening of
other variables in addition to the aforementioned
variables in order to increase work engagement and
innovative behavior in this company.
7 CONCLUSION
This study applies social exchange theory that states
that when employees feel that they are treated well by
the management through effort such as involving
them in decision making process, then they will
reciprocate by showing innovative work behavior.
Thus, companies are expected to maintain positive
attitude (such as procedural justice) so that innovative
work behavior can be maintained. Determination
testing results show that the contribution of
procedural justice to engagement is 20%, while the
contribution of procedural justice and work
engagement to the innovative work behavior is 28%.
These are relatively weak and show that there needs
to be additional measures taken by strengthening
other variables that can increase innovative work
behavior in this company.
REFERENCES
A. Agarwal, U. (2014). Linking justice, trust and innovative
work behaviour to work engagement. Personnel
Review, 43(1), 41–73. https://doi.org/10.1108/pr-02-
2012-0019
Agarwal, U. A., Datta, S., Blake-Beard, S., & Bhargava, S.
(2012). Linking LMX, innovative work behaviour and
turnover intentions: The mediating role of work
engagement. Career Development International, 17(3),
208–230. https://doi.org/10.1108/13620431211241063
Akram, T., Taher, M. J., & Feng, Y. X. (2016). The Effects
of Organizational Justice on the Innovative Work
Behavior of Employees : An Empirical Study from
China. Journal of Creativity and Business Innovation, 2.
Blader, S. L., & Tyler, T. R. (2003). What constitutes
fairness in work settings ? A four-component model of
procedural justice. Human Resources Management
Review, 13, 107–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1053-
4822(02)00101-8
Colquitt, J. A., Scott, B. A., Rodell, J. B., Long, D. M.,
William, C., Zapata, C. P., & Wesson, M. J. (2013).
Justice at the Millennium, a Decade Later : A Meta-
Analytic Test of Social Exchange and Affect-Based
Perspectives. 98(2), 199–236. https://doi.org/10.1037/
a0031757
Cropanzano, R., Prehar, C. A., & Chen, P. Y. (2002). Using
Social Exchange Theory to Distinguish Procedural
From Interactional Justice. Group and Organization
Management, 27(3), 324–351. https://doi.org/10.1177/
1059601102027003002
Folger, R. (1987). Distributive and Procedural Justice in the
Workplace. Social Justice Research, 1(2).
Ismail, U. (2020). Moderating / Mediating Effects Of Hrm
Practices In Organizational Justice On Innovative Work
Behaviour Among Hotel Industry Of Pakistan : Case
Study Of Karachi. (February).
Janssen, O. (2000). Job demands, perceptions of effort-
reward fairness nd innovative work behavior. Journal of
Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 287–
302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.01.018
Masterson, S. S., Lewis, K., Goldman, B. M., & Taylor, M.
S. (2000). Integrating Justice And Social Exchange :
The Differing Effects Of Fair Procedures And
Treatment On Work Relationships. Academy of
Management Journal, 43(4), 738–749.
Nazir, S., Shafi, A., Atif, M. M., Qun, W., & Abdullah,
S. M. (2019). How organization justice and
perceived organizational support facilitate employees ’
innovative behavior at work. Employee Relations:
The International Journal, 41(6), 1288–1311.
https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-01-2017-0007
Ohiorenoya, J. O., & Eguavoen, E. O. (2019). Influence
of Organizational Justice on Employee Engagement
ICRI 2021 - International Conference on Recent Innovations
130

in Tertiary Institutions in Edo State, Nigeria.
European Scientific Journal ESJ, 15(28), 56–75.
https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2019.v15n28p56
Tyler, T. R. (1988). What is Procedural Justice?: Criteria
Used by Citizens to Assess the Fairness of Legal
Procedures. Law & Society Review, 22(1).
Yu, J., Lee, A., Han, H., & Kim, H. R. (2019).
Organizational Justice and Performance of Hotel
enterprises: Impact of Job Embeddedness. Journal of
Quality Assurance in Hospitality and Tourism, 00(00),
1–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/1528008X.2019.1663571
Zeb, A., Abdullah, N. H., Othayman, M. Bin, & Ali, M.
(2019). The Role of LMX in Explaining Relationships
between Organizational Justice and Job Performance.
Journal of Competitiveness, 11(2), 144–160.
https://doi.org/10.7441/joc.2019.02.10
The Effect of Procedural Justice, Work Engagement, on Innovative Work Behavior
131
