
Study on Interaction of Dopamine Reward Prediction Error Pathway
and VTA-CA1 Novelty Pathway in VTA Region
Yaoyuan Fan
The White Mountain School, New Hampshire 03574, U.S.A.
Keywords: Dopamine, Reward, Prediction Error, Novelty, VTA, Hippocampus.
Abstract: The function of dopamine neurons (DA) and the dopaminergic pathways in the brain have been studied for
scientists for years. However, people still have questions about how these neural pathways interact with each
other, building “bridges” between different regions of the brain. This paper investigates the mechanism of
dopamine reward prediction error pathway and VTA-hippocampus novelty pathway in VTA Region, and
hypothesized that there may exist some interactions between the RPE pathway and VTA- hippocampus
novelty pathway in the VTA. Behavioral experiments are designed to further investigate the dopamine activity
on VTA and hippocampus when the two pathways work together. The experiments will compare the DA firing
in transgenic mice’s VTA and CA1 regions in the hippocampus when prediction error happens in novel
environments and familiar environments. The results are predicted to show that novelty loop and RPE loop
might interact with each other.
1 INTRODUCTION
Dopamine (DA) is a crucial neurotransmitter in the
brain, and the midbrain DA neurons are well known
not only for regulating emotion, its important
function also include controlling voluntary
movement, creating associations with rewarding
stimuli, attending to salient environmental stimuli,
motivating behavior, and maintenance of working
memory (Bissonette, Roesch 2016). The newest
review in 2021, Dopamine, Prediction Error and
Beyond (Diederen, Fletcher 2021) provided an
overview of the functions of of dopaminergic
pathways in reward learning and evidences that
suggest a crucial role for dopamine in predicting not
only reward, but also general future outcomes.
1.1 Dopaminergic Reward Prediction
Error
Studies have found that there are four functionally
distinct DA projections in the brain (Diederen,
Fletcher 2021), and most of DA neurons are centered
in two small nuclei in VTA and substantia nigra (with
other two subnucleus (Nair-Roberts, Chatelain-
Badie, Benson, White-Cooper, Bolam, Ungless
2008); One of the pathway called mesolimbic
pathway, primarily facilitates reward prediction error
(RPE) signals and transmits DA from VTA to the
nucleus accumbens (NA) in the ventral striatum
(Diederen, Fletcher 2021), and another pathway,
mesocortical pathway, also connect VTA with a few
other regions, including prefrontal cortex (Watabe-
Uchida, Eshel, Uchida 2017).
The importance of DA in signaling reward
prediction error (RPE) has well been proved (Schultz,
Wolfram 2016). Before the conditioned stimulus
training, when no reward was predicted, DA fired
after receiving a reward; when the reward was
predicted, DA fired when the predictive stimulus
occurred; when the predicted reward didn’t occur,
however, DA were silenced. Related experiments
have been done in monkeys and rodents, and datas
have shown that when the animal adapts its behavior
to new situations, the responses of DA neurons may
be particularly important when they are learning
(Schultz, Wolfram 2016, Schultz, et al 1993).
214
Fan, Y.
Study on Interaction of Dopamine Reward Prediction Error Pathway and VTA-CA1 Novelty Pathway in VTA Region.
DOI: 10.5220/0011290600003444
In Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare (CAIH 2021), pages 214-218
ISBN: 978-989-758-594-4
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
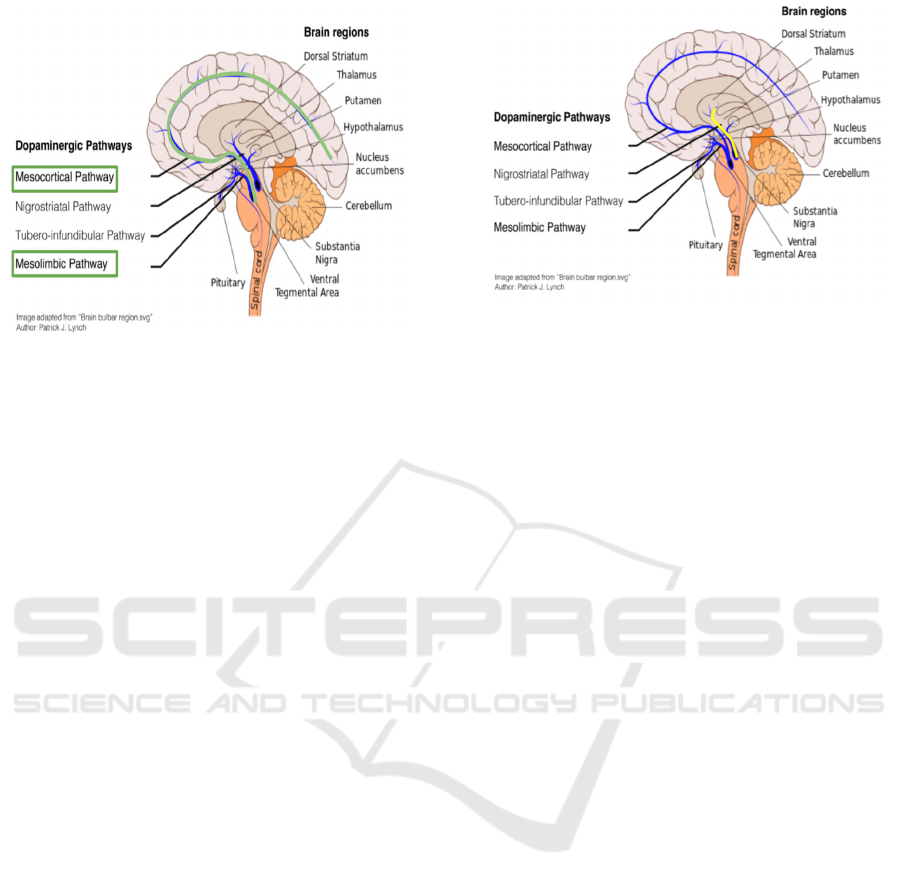
Figure 1: The dopamine reward prediction error pathways
are highlighted with green. Image adapted from Diederen
KMJ, Fletcher PC. Dopamine, Prediction Error and
Beyond. Neuroscientist. 2021 Feb;27(1):30-46. doi:
10.1177/1073858420907591. Epub 2020 Apr 26. PMID:
32338128; PMCID: PMC7804370. Originally adapted
from Patric J. Lynch, “Brain bulbar region.svg”.
1.2 VTA-CA1 Novelty Pathway
Although researchers have found the major four
dopaminergic pathways in the brain (García-García,
Zeighami, Dagher 2017), other studies have found
that there exists another functionally important loop
between the hippocampus and the VTA. Scientists
have found that the exposure to novel stimuli can
evoke investigatory activity and increase NA
dopamine in freely moving rats, and the unilateral
perfusion of the ionotropic glutamate receptor
antagonists kynurenic acid in the ipsilateral but not
the contralateral VTA would block novelty-evoked
elevations in NA dopamine (Legault, Wise 2001).
The loop was further explained by Lisman JE and
Grace AA in 2005 (Lisman, Grace 2005) that there
are two pathways in the VTA- Hippocampus loop
serving different functions. The down-ward loop
carries novelty signals from the hippocampus to the
VTA where it stimulates the novelty dependent firing
of these cells; in the up-ward arm, the DA that is
released enhances LTP in CA1 (Lisman, Grace 2005).
Herein, based on the observations above, a
hypothesis is made: there may exist some interactions
between the RPE pathway and VTA- hippocampus
novelty pathway in the VTA.
Figure 2: The VTA-CA1 novelty pathways are highlighted
with yellow. Image adapted from Diederen KMJ, Fletcher
PC. Dopamine, Prediction Error and Beyond.
Neuroscientist. 2021 Feb;27(1):30-46. doi:
10.1177/1073858420907591. Epub 2020 Apr 26. PMID:
32338128; PMCID: PMC7804370. Originally adapted
from Patric J. Lynch, “Brain bulbar region.svg”.
2 EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH
2.1 Subject
Eighteen transgenic mice in which the mRNA
encoding the CRE enzyme is made only in
dopaminergic neurons (hereafter referred as CRE
mice.)
In order to achieve this, the promoter of the
Tyrosine Hydroxylase is going to be placed at the 5'
end of the DNA coding region of CRE enzyme and
inserted onto the mice chromosomes in the transgenic
mice.
2.2 Apparatus
Two square cheese board mazes (One painted yellow
and one painted blue.) The surface of the apparatus
stands 70 cm above the floor, 77.5 cm x 77.5 cm, 3
cm in thickness. A hundred and forty-four food wells
(2.5 cm in diameter, 1.5 cm in depth) are drilled into
the surface of the maze in evenly spaced parallel rows
and columns 2.5 cm apart (10 cm from the edges.) A
start box (20 cm in length, 15 cm in width, 20cm in
height) is placed on the maze surface, centers
perpendicular to the rows of food wells, with the
posterior edge of the box placed along the edge of the
apparatus. There are 3 pieces of walls around the
cheese board mazes (30 cm in height) and are painted
the corresponding color of the cheese board. Figure.
1 shows the sketched design of the apparatus.
Study on Interaction of Dopamine Reward Prediction Error Pathway and VTA-CA1 Novelty Pathway in VTA Region
215

Figure 3: Cheese board mazes. Reproduced from (Gilbert, Kesner 2002). Gilbert, P. E., & Kesner, R. P. (2002). Role of rodent
hippocampus in paired-associate learning involving associations between a stimulus and a spatial location. Behavioral
Neuroscience, 116(1), 63–71. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.116.1.63.
2.3 Experimental Grouping
The 18 CRE mice will be randomly divided into 3
groups, 6 mice for each, marked as control group,
Group A, and Group B. The control group will not
receive any surgery other than inserting electrodes
into VTA and CA1 regions. Group A and Group B
will receive the surgery described in the following
paragraph.
2.4 Surgery
The surgery is designed to control the silencing of
dopaminergic neurons in the VTA-Hippocampus
novelty pathway. ArchT, a high-light sensitivity
optical neural silencer, found by scientists in FCK-
ArchT-GFP lentivirus (Han, Xue et al 2011) is going
to be injected to CA1 regions of the mice in order to
achieve this goal. Since the mRNA encoding the CRE
enzyme is made only in dopaminergic neurons in the
subject, the ArchT gene can only be expressed in DA
neurons in the VTA-hippocampus pathway.
CRE mice in Group A and Group B will take the
surgery. The surgical procedure for virus injection is
adapted from Han, Xue et al., 2011 (Han, Xue et al
2011). Under isoflurane anesthesia, 1 μl FCK-ArchT-
GFP lentivirus is going to be injected through a
craniotomy made in the mouse skull, into the CA1
region in the hippocampus. Virus will be injected at a
rate of 0.1 μl/min for a total of 10 min after which the
injector is left in place for an additional 10 min to
allow for viral diffusion from the tip. Then, an
unilateral optical fiber will be implanted into the
brain, 0.9mm below the brain surface about the
injection site. Two small screws will be anchored at
the anterior and posterior edges of the surgical site
and will be bound with dental glue to secure the
implant in place (Iaccarino, Singer, Martorell,
Rudenko, Gao, Gillingham, Mathys, Seo, Kritskiy,
Abdurrob, Adaikkan, Canter, Rueda, Brown, Boyden,
Tsai 2018). Finally, implant electrodes to detect the
neural activity in CA1 and VTA. After all surgical
procedures, each mouse will be given a 2 weeks
recovery before being tested.
To verify the novelty evoked dopamine firing in
CA1, the mice will be put on the yellow cheese board
apparatus and record the DA firing after the recovery
before training. Because it is a novel environment
for the mice, theoretically there will be dopamine
firing in CA1 in the mice's brain.
2.5 Training
The reward learning is necessary before the PE
experiment, and the training can also make the mice
get familiar with the yellow cheeseboard apparatus.
The conditional training procedure is partially
adapted from Gilbert and Kesner, 2002 (Gilbert,
Kesner 2002). The graphical representation of the
first week and second week training apparatus is
shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. During the first week
of training, each mouse will be given 1 hour per day
to explore the test apparatus (yellow cheese board
maze only) individually. While the mouse is
exploring, 10 pieces of Froot Loop cereal will be
spread out across the surface of the yellow cheese
board. The door to the start box will be open and each
mouse can freely enter the cheese board from the
CAIH 2021 - Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare
216

interior of the box. For the 2nd week of training, a
single, neutral object will be introduced into the
cheese board. It will be placed at the very center of
the cheese board. The object will be used to shape
each mouse to displace an object to receive a food
reward. Once a mouse consistently displaces the
object to receive a food reward, it is ready for the
behavioral experiment later.
Figure 4: A graphical representation of the first week
training apparatus.
Figure 5: A graphical representation of the second week
training apparatus.
2.6 Behavioral Experiment 1
Blue cheese board will be used in this experiment, as
a novel environment.
For the CRE mice in Group B, their dopamine
firing in VTA and CA1 will be tested as each of them
enters the apparatus from the start box.
For the CRE mice in the control group and Group
A, each of them will go through the following PE
experiment. A single, neutral object (same as which
in the training) will be introduced into the very center
of the testing apparatus. A froot loop will be placed in
the food well under the object, and the mouse will be
placed in the start box. The dopamine firing in the
VTA and CA1 region will be recorded once the
mouse exits the start box. Once the mouse displaces
the object and gets the food reward, it will be moved
into the start box again. The object will be replaced at
the center, and the froot loop under the object will be
removed this time. Let the mouse restart, and record
its DA firing in VTA and CA1 once it exits the start
box.
2.7 Behavioral Experiment 2
Yellow cheese board apparatus will be used in this
experiment. For the CRE mice in Group A and Group
B, their VTA-Hippocampus novelty pathway will be
silenced using an optogenetic method.
2.7.1 Optical Stimulation Procedure
The optical stimulation procedure is well described in
(Iaccarino, Singer, Martorell, Rudenko, Gao,
Gillingham, Mathys, Seo, Kritskiy, Abdurrob,
Adaikkan, Canter, Rueda, Brown, Boyden, Tsai
2018). A 200 mW, 4,793nm DPSS laser will be
connected to a patch cord with a fibre
channel/physical contact connector at each end.
During the experiment, 1mW (measured from the end
of the fibre) of optical stimulation will be delivered
for 1h.
In order to verify the effect of the optogenetic
method of silencing of DA neurons in CA1, each
mice will be given an optical stimulation for an hour
on the optical implantation site. Then, they will be
introduced to a novel environment, and record their
dopamine firing in CA1. If there’s no potentiation
recorded in CA1, then the VTA-Hippocampus
novelty pathway is silenced.
After the VTA-Hippocampus novelty pathway is
completely silenced, the control group, Group A, and
Group B will go through the same procedure
described in the PE experiment in Behavior
Experiment 1.
3 ANALYSIS AND PREDICTED
OUTCOME
Based on my hypothesis that there may exist some
interactions between the RPE pathway and VTA-
hippocampus novelty pathway in the VTA, combined
with the background knowledge of PE and the two
pathways, I made the following analysis and
inference.
1. In the Behavioral Experiment 1, since the blue
cheese board apparatus is a novel environment for the
mice, there will be a large number of novelty-evoked
dopamine firing in the CA1 region in all three groups
of CRE mice as they enter the apparatus. In the
Behavioral Experiment 2, however, there will be no
Study on Interaction of Dopamine Reward Prediction Error Pathway and VTA-CA1 Novelty Pathway in VTA Region
217

novelty-evoked dopamine firing in CA1 for Group A
and Group B since the VTA-Hippocampus novelty
loop has been silenced. Since the mice have been
trained in the yellow cheese board before, it is a less
novel environment for the mice. Therefore, there will
be less novelty-evoke dopamine firing for the control
group in the Behavioral Experiment 2 than in the
Behavioral Experiment 1.
2. In the Behavioral Experiment 1, the novelty-
evoked dopamine firing might change the reward
prediction error dopamine responses in VTA. By
comparing the dopamine firing data of Group A in
Behavioral Experiment 1 and 2, the interaction of
dopaminergic RPE pathway and VTA-hippocampus
novelty pathway can be specified.
3. It is possible that the novelty-evoked DA
release in CRE mice in Behavioral Experiment 1 goes
through the up-ward arm of VTA-hippocampus loop
(Lisman, Grace 2005) enhances LTP in CA1, and the
interaction between the dopaminergic RPE pathway
and VTA-hippocampus pathway sends RPE signal to
the hippocampus, hence reinforcing the RPE
learning.
4 CONCLUSIONS
A method determining the connection between the
dopamine reward prediction error pathway and the
VTA-CA1 novelty pathway by simulating the
experiment of prediction error with and without
novelty was established in this research. It can help
us further explore the interaction between different
regions of the brain, including the interaction
between VTA and hippocampus-CA1, PFC and VTA.
If the hypothesis is true, then we might inferred that
people can use novel environment to reinforce RPE
learning, that is, making learning more productive.
REFERENCES
Bissonette GB, Roesch MR. Development and function of
the midbrain dopamine system: what we know and
what we need to. Genes Brain Behav. 2016
Jan;15(1):62-73. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12257. Epub 2015
Nov 8. PMID: 26548362; PMCID: PMC5266527.
Diederen KMJ, Fletcher PC. Dopamine, Prediction Error
and Beyond. Neuroscientist. 2021 Feb;27(1):30-46.
doi: 10.1177/1073858420907591. Epub 2020 Apr 26.
PMID: 32338128; PMCID: PMC7804370.
García-García I, Zeighami Y, Dagher A. Reward Prediction
Errors in Drug Addiction and Parkinson's
Disease: from Neurophysiology to Neuroimaging. Curr
Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2017 Jun;17(6):46. doi:
10.1007/s11910-017-0755-9. PMID: 28417291.
Gilbert, P. E., & Kesner, R. P. (2002). Role of rodent
hippocampus in paired-associate learning involving
associations between a stimulus and a spatial location.
Behavioral Neuroscience, 116(1), 63–71.
doi:10.1037/0735-7044.116.1.63
Han, Xue et al. “A high-light sensitivity optical neural
silencer: development and application to optogenetic
control of non-human primate cortex.” Frontiers in
systems neuroscience vol. 5 18. 13 Apr. 2011,
doi:10.3389/fnsys.2011.00018
Iaccarino HF, Singer AC, Martorell AJ, Rudenko A, Gao F,
Gillingham TZ, Mathys H, Seo J, Kritskiy O, Abdurrob
F, Adaikkan C, Canter RG, Rueda R, Brown EN,
Boyden ES, Tsai LH. Gamma frequency entrainment
attenuates amyloid load and modifies microglia.
Nature. 2016 Dec 7;540(7632):230-235. doi:
10.1038/nature20587. Erratum in: Nature. 2018 Oct;
562(7725): E1. PMID: 27929004; PMCID:
PMC5656389.
Legault M, Wise RA. Novelty-evoked elevations of nucleus
accumbens dopamine: dependence on impulse
flow from the ventral subiculum and glutamatergic
neurotransmission in the ventral tegmental area.
Eur J Neurosci. 2001 Feb;13(4):819-28. doi:
10.1046/j.0953-816x.2000.01448.x. PMID: 11207817.
Lisman JE, Grace AA. The hippocampal-VTA loop:
controlling the entry of information into long-term
memory. Neuron. 2005 Jun 2;46(5):703-13. doi:
10.1016/j.neuron.2005.05.002. PMID: 15924857.
Nair-Roberts RG, Chatelain-Badie SD, Benson E, White-
Cooper H, Bolam JP, Ungless MA. Stereological
estimates of dopaminergic, GABAergic and
glutamatergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area,
substantia nigra and retrorubral field in the rat.
Neuroscience. 2008 Apr 9;152(4):1024-31. doi:
10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.046. Epub 2008 Feb 7.
PMID: 18355970; PMCID: PMC2575227.
Schultz, W et al. “Responses of monkey dopamine neurons
to reward and conditioned stimuli during successive
steps of learning a delayed response task.” The Journal
of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for
Neuroscience vol. 13,3 (1993): 900-13.
doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-03-00900.1993
Schultz, Wolfram. "Dopamine reward prediction error
coding." Dialogues in clinical neuroscience 18.1
(2016): 23.
Watabe-Uchida M, Eshel N, Uchida N. Neural Circuitry of
Reward Prediction Error. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2017 Jul
25; 40:373-394. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-072116-
031109. Epub 2017 Apr 24. PMID: 28441114; PMCID:
PMC6721851.
CAIH 2021 - Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare
218
