
Integrated Geophysical Application to Investigate Groundwater in a
Wind Power Station of Mountainous Area: A Case Study in Xuefeng
Mountain Area of Hunan Province, China
Tianchun Yang
1
, Shixin Dai
2,*
, Zhuochao Chen
1
, Zhui Yang
3
, Zhen Chen
3
and Weiwei Niu
4
1
Resource environment and safety engineering college Hunan university of science and technology Hunan Xiangtan, China
2
Clean Utilization of Coal Resources and Mine Environmental Protection Hunan university of science and technology
Hunan Xiangtan, China
3
Hunan Puqi Geological Exploration Equipment Research Institute Hunan Changsha, China
4
Xiaoxiang College of Hunan university of science and technology Hunan Xiangtan, China
Keywords: Groundwater, Integrated geophysical methods, Three-electrode resistivity, 2D Resistivity, Hydrogeology.
Abstract: Groundwater is an essential source of drinking water in water-deficient regions. The authors mainly discussed
the groundwater exploration of a wind power station in granite mountainous area, and integrated geophysical
methods (i.e. vertical resistivity electrical sounding method with a three-electrode configuration and
frequency selection method of natural electric field) were used to carry out in-site exploration work. Firstly,
the authors carried out three-electrode resistivity sounding profile work, and studied 2D finite element
inversion. The 2D resistivity distribution characteristics and the favorable well position of sounding profiles
had been obtained. On the basis of the resistivity sounding work, the frequency selection method of natural
electric field (FSMNEF) was further developed on the original geophysical profiles. The precise position of
the well was determined by the small volume effect of FSMNEF, and the sounding of FSMNEF was used at
this position to determine the depth of the abnormal body. Subsequent drilling results validate the
effectiveness of geophysical methods, the resistivity anomaly of geo-electrical cross-sections of three-
electrode sounding is very intuitive, and FSMNEF has high accuracy in horizontal positioning and depth
judgment of the aquifer, and is convenient for construction. The application results show that FSMNEF is an
efficient, cost-effective tool for groundwater exploration, the field crews are small, and it has been extremely
useful when coordinated with background hydrogeology or other geophysical methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Groundwater is an important part of freshwater
resources and is the most important source of fresh
water in many parts of the world. The groundwater is
relatively poor in the granite region (Li et al, 2017),
so it is generally believed that the granite area is a
forbidden area for water exploration, and it is very
difficult to look for groundwater yield more than 100
t/d in the granite region. For this reason, some
geologists have carried out related research work on
the occurrence characteristics of groundwater in the
granite region and its exploration problems (Huang et
al, 2005; Mahmoudzadeh et al, 2012; Madhnure et al,
2016; Shi et al, 2016). The groundwater in granite
areas mainly occurs in fault fracture zones, and a
small part of them occur in the weathered layers. In
addition, there is also a small amount of groundwater
in the tectonic fissures or joint fissures. Duan (1999)
believed that the water content of weathered layers
and fault fracture zones in granite areas could be
detected by geophysical methods, therefore, a
combination of shallow seismic refraction method
and vertical electrical sounding method was proposed
and used to obtain better exploration results in
Guangdong, Hainan, Zhejiang Province of China.
Taking the Qingdao area as an example, Zhao (1990)
discussed the problems that should be paid attention
to when searching for groundwater sources in granite
areas. Qiao (1988) studied the types of granite fissure
water and its occurrence characteristics in
Heilongjiang Province and Hulun Buir League region
of China. Cao et al. (2006) carried out water
exploration practice in granite areas by using surface
nuclear magnetic resonance method (NMR).
68
Yang, T., Dai, S., Chen, Z., Yang, Z., Chen, Z. and Niu, W.
Integrated Geophysical Application to Investigate Groundwater in a Wind Power Station of Mountainous Area: A Case Study in Xuefeng Mountain Area of Hunan Province, China.
DOI: 10.5220/0011358200003355
In Proceedings of the 1st International Joint Conference on Energy and Environmental Engineering (CoEEE 2021), pages 68-76
ISBN: 978-989-758-599-9
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

According to a large number of water resources
exploration results in Hebei, Inner Mongolia, it
showed that NMR could detect groundwater within
100 m depth in complex strata containing granite. Li
et al. (2009) used the integrated geophysical methods
such as induced polarization method and audio
frequency geoelectric field method to determine the
spatial distribution characteristics of the water storage
structure in granite area and judge the water content
of the structure, so as to determine the spatial
distribution of groundwater. Their work achieved
satisfactory results (Li et al, 2009).
In the granite area, the lithology of granite is
compact, the porosity is small, the groundwater is
generally deep, the influence of surface is small, and
the water quality is excellent, so it has certain
economic development and utilization value (Dai,
2001). Therefore, exploration and use of groundwater
in granite regions is a difficult but yet a significant
issue. The objective of this paper was to highlight the
utility of resistivity sounding method and the
frequency selection method of natural electric field
(FSMNEF) for the successful exploration of
groundwater in a granite area. According to the
application effect, the experience of groundwater
exploration in the granite area was summarized, and
the effectiveness of the comprehensive method was
illustrated. It is of great guiding significance to the
hydrogeological work, the exploration and utilization
of groundwater resources in granite areas in the
future.
2 STUDY AREA AND METHODS
2.1 Study Area
The site of groundwater exploration is located in a
small hilltop area near Baoding mountain, Shuikou
township, Suining county, Hunan province, China.
Datang International Power Generation Co., Ltd. is
building a wind power station here, as shown in figure
1 and figure 2.
Suining county is located in the southwest of Hunan
province. Shuikou township is located in the northwest of
Suining county. This location belongs to the Xuefeng
mountain range, and it is relatively remote and the terrain is
relatively high. The wind power station construction site is
basically located near the top of a small mountain with an
elevation of about 1,100 m in figure 2. The surrounding
mountainous area is lush with vegetation. Its geographical
coordinates are latitude 26°51’42’’N and longitude
110°13’28’’E, as shown on figure 1. The average yearly
minimum temperature is 5.7℃
and January is the coldest
month. The average yearly maximum temperature is
26.7℃ and July is the hottest month. Average annual
rainfall in this region is about 1,320 mm.
From the perspective of regional structure (Figure
3), the working area is located in the central south
section of Xuefengshan uplift belt in the third uplift
of the Neocathaysian. The NE trending folds and
faults are relatively developed, which may be the
local turning position of the Neo-Cathaysian
structure. The NNE trending folds and faults are very
developed, and the associated NW, NNW, NEE and
EW trending faults are also developed, all of them
belong to the tectonic system of Neocathaysian. The
lithology of the study location is Indosinian quartz-
monzonite (γ51) (Figure 3).
During the exploration work of FSMNEF, the
power station facilities have been basically
completed, but they are not yet running. There is no
current in the high-voltage cable in figure 2, and the
temporary power cable is used for the construction of
the power station in the field. The width of the slope
shown in figure 2 is about 120 m, and the power
station covers an area of about 120 m×130 m. In order
to ensure the living needs of 5 to 6 staff members in
the future operation of the power station, it is
necessary to find groundwater in or near the land
acquisition scope of the power station. The owner's
requirement for water quantity is more than 15 t/d.
Prior to geophysical work, engineering geologists
identified two wells locations in the nearby gullies
based on hydrogeological conditions (Figure 1). The
drilling depth of ZK1 is 60 m, 0-4 m is a diluvium, 4-
13 m is a fully weathered or strongly weathered
granite, 13-30 m rock is relatively broken, 30-40 m
rock is relatively complete, and below 40m is
complete granite. The drilling depth of ZK2 is 68 m,
0-5 m is the strong weathered granite, and the rock
fissure of 5-40 m is relatively developed, but the
crack opening angle is not good, and the rock of 40-
68 m is relatively complete. The water yield of ZK1
and ZK2 is about 3 t/d, it cannot meet the demand of
the power station. In order to further find the
groundwater source, the authors use three-electrode
vertical electrical sounding configuration and
FSMNEF for comprehensive exploration.
Integrated Geophysical Application to Investigate Groundwater in a Wind Power Station of Mountainous Area: A Case Study in Xuefeng
Mountain Area of Hunan Province, China
69

Figure 1. Map showing the location of geophysical works in the wind power station.
2.2 Methodology
2.2.1 Three-electrode Electrical Sounding
Method
The conventional vertical electrical sounding method
of the Schlumberger configuration is to increase the
electrode spacing successively at the same sounding
point on the ground, and detect the change of the
apparent resistivity along the vertical direction from
shallow to deep at the sounding point, and infer the
change of vertical geological structure through the
analysis of electric sounding curve or electric
sounding section. The conventional vertical electric
sounding (VES) needs to move current electrode A
and B in opposite directions simultaneously during
exploration. It is time consuming and cost prohibitive.
The difficulty of work increases when the terrain is
undulating and the vegetation is very developed. It
may be also restricted by buildings and venues when
working near a town. At this time, the three-electrode
vertical electrical sounding configuration is more
convenient and applicable.
Figure 2. A field photo of the wind power station.
China
Index map
(not to scale)
ZK2
ZK1
A
A'
B
B'
81/AA'
C'
C
Road
Geophysical
profiles
FSMNEF
sounding statio
n
Legend
Power station
Drilling
position
ZK1
Finall well
location
A
A'
81/AA'
Index map
(not to scale)
N
CoEEE 2021 - International Joint Conference on Energy and Environmental Engineering
70

Figure 3. Regional hydrogeological map of the study location.
The two current electrodes (A, B) and the
potential electrodes (M, N) of the three-electrode
electrical sounding configuration are separated
(Figure 4), which can reduce the electromagnetic
interference. The current electrode B is located at
infinity, the midpoint O of the potential electrodes (M,
N) is the sounding point, and electrodes A, M, N
arranged in a straight line (Xiang et al, 2011). In
practice, it is usually only necessary to move the
current electrode A. Therefore, compared with the
conventional vertical electrical sounding method, the
workload is reduced, and the site adaptability of the
sounding method is improved. The sounding point
spacing on the profiles is 20m, and the instrument is
DDC-5 electric instrument. The on-site work of the
three-electrode VES was completed in April 2016 for
a total of 15 days, and 60 VESs had been completed.
Figure 4. Three-electrode configuration schemes.
2.2.2 Frequency Selection Method of
Natural Electric Field (FSMNEF)
The FSMNEF is developed by the telluric current
method and the audio-frequency magnetotelluric
method (AMT). It is proposed by Chinese scholars
and a complete set of exploration equipment has been
developed. As far as the surface of the earth is
concerned, the natural electromagnetic field can be
regarded as a plane electromagnetic wave incident
perpendicularly to the surface, and the relationship
between the magnetic field intensity H, the magnetic
induction intensity B, the electric field intensity E, the
electric displacement D, the current density J and the
free charge volume density q are subject to Maxwell's
equations. According to Maxwell's equations, the
skin depth (depth of penetration, investigation depth)
δ of plane electromagnetic wave in passive region can
be estimated as:
f
ρδ
5.503=
(1)
where δ is the depth in meter, ρ is the resistivity value
(
m⋅Ω
) of underground media, and f is the
frequency used in Hz.
When the underground resistivity ρ is constant,
the higher the working frequency f, the shallower the
electromagnetic wave penetration; and conversely,
the smaller the working frequency f, the deeper the
electromagnetic wave penetration. When the
frequency f is constant, the greater the resistivity ρ,
the deeper the electromagnetic wave penetrates, and
the smaller the resistivity ρ, the shallower the
electromagnetic wave penetrates.
The relationship between wave impedance Z
xy
and
the apparent resistivity ρ
S
can be further derived from
Maxwell's equations:
𝜌
=
𝑍
=
𝐸
𝐻
⁄
(2)
where E
x
and H
y
are the orthogonal horizontal electric
field component (mV·km-1) and magnetic field
component (nT) respectively at the surface. Some
scholars believe that H
y
can be ignored in
groundwater exploration and certain specific
directions.
The parallel movement method is adopted in-site
measurement for FSMNEF, namely, the electrodes M
and N move along measuring lines or profiles with 20
m or 10 m electrode spacing, as shown in figure 5(a).
The measuring point spacing is 5 m, and the abnormal
section it is reduced to 2 m. The potential difference
△V of the horizontal component of natural electric
field at different frequencies between two electrodes
is measured, and the midpoint O of M and N is the
recording point. The acquisition instrument used for
FSMNEF is the self-developed MFE-1 natural
electric field frequency selector. The field work was
completed on 26-28 June 2016 for a total of 3 days.
30000
20000
25000
70000
75000
0
2000
4000
m
Study location
Fault
Spring mouth
Drainage
Geological boundary
Granite porphyry vein
Granite fine-grained rock vein
Quartz porphyry
Granite pegmatite vein
Diorite porphyrite
Ordovician slate and sandstone
Cambrian slate
Legend
Cambrian limestone and slate
Indosinian quartz monzonite
1
xy
2-3
O
1
bs
O
1
bs
5
1
5
1
5
1
l
l
l
l
l
5
1
1
xy
2-3
O
1
bs
l
Shujiawan
village
Qiumu
village
Zhushanjiao
village
Yanjing
village
Huangnijing
village
Baoding
mountain
O
M
N
A
B
Integrated Geophysical Application to Investigate Groundwater in a Wind Power Station of Mountainous Area: A Case Study in Xuefeng
Mountain Area of Hunan Province, China
71
(a)
(b)
Figure 5. (a) A schematic diagram of a profile detection configuration; (b) a sounding configuration of FSMNEF
In recent years, vertical electrical sounding of
FSMNEF has been used by some practitioners in
groundwater exploration (Liang, 2016). This
sounding configuration is similar to the conventional
vertical electrical sounding, with the measured
geophysical anomaly point O as the center, and the
electrodes M and N synchronously move outwards
respectively (the distance is usually 5m, and 1m in a
particular case), the exploration depth gradually
increases with the increase of the electrode spacing
MN, see figure 5(b). The sounding of FSMNEF
technique provides information on the vertical
variations in the potential difference of the ground
with depth.
The FSMNEF has been successfully applied to
groundwater exploration and other engineering
geological exploration in limestone areas (Yang at al,
2013), but its field source is very complicated.
According to the authors’ previous research results
(Yang et al, 2016), the authors think that the field
source of FSMNEF comes from the interaction of
alternating electromagnetic fields generated by the
natural factors outside the earth and the alternating
electromagnetic fields produced by human factors on
the earth’s surface. Anthropogenic electromagnetic
fields are generally regarded as interference noise in
the application of AMT, but compared with AMT, the
anthropogenic electromagnetic fields can be regarded
as the far field because the exploration depth of
FSMNEF is usually smaller (generally < 150 m).
Therefore, the horizontal alternating magnetic field
and the horizontal alternating electric field formed by
natural and anthropogenic factors act together on the
underground geological body to form the anomaly of
FSMNEF. Their effect is the same as AMT, satisfying
formula (1), (2).
3 GEOELECTRICAL
MEASUREMENTS AND
INTERPRETATION
In order to determine the target area for water
exploration, three vertical electrical sounding (VES)
profiles were arranged (Figure 1), sixty VESs were
recorded with the three-electrode configuration in this
study area; 2 of these profiles were selected for
evaluation in this paper. The survey profile AA’ and
the survey profile BB’ are located at the foot and the
half-waist step of the slope in the southwest of the
power station respectively. The survey profile CC’ is
outside the land acquisition scope, the direction is
basically along the road, and it intersects with the
survey profile AA’ and BB’ obliquely.
The measured apparent resistivities were used to
compute electrical resistivity tomograms using
RES2DINV inversion software. This program uses a
finite-element calculation for the forward problem
and solves for subsurface resistivity using an iterative
Gauss-Newton smoothness-constrained least-squares
algorithm (Mcclymont et al, 2011). The 2D inversion
results obtained for the two electrical resistivity
tomography (ERT) profiles of survey profiles AA’
and BB’ are presented in figure. 6. The contour of the
graph is plotted as the logarithm of resistivity in
figure 6.
measuring line
O
moving direction
MN
O
m
V
M
N
H
r
0
980
1000
1020
1040
1060
1080
1100
1120
1
1.6
1.8
2.2
2.4
2.6
3
3.5
4
4.5
5
Resistivity (ohm.m)
( Log10 )
Elevation (m)
120
o
20 60
140 180 220 260 340100 300
Distance along profile AA' (m)
Road
Bamboo
forest
(a)
CoEEE 2021 - International Joint Conference on Energy and Environmental Engineering
72
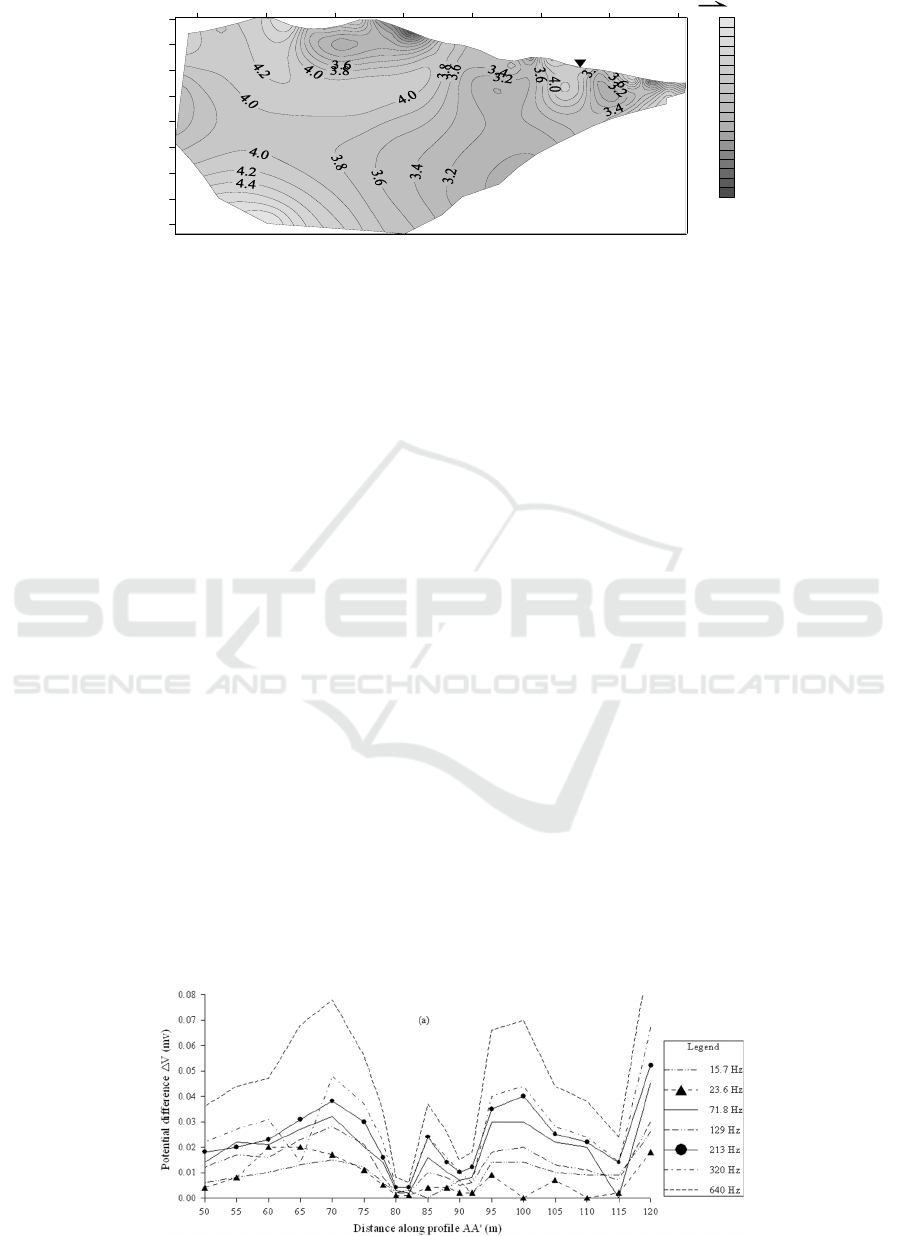
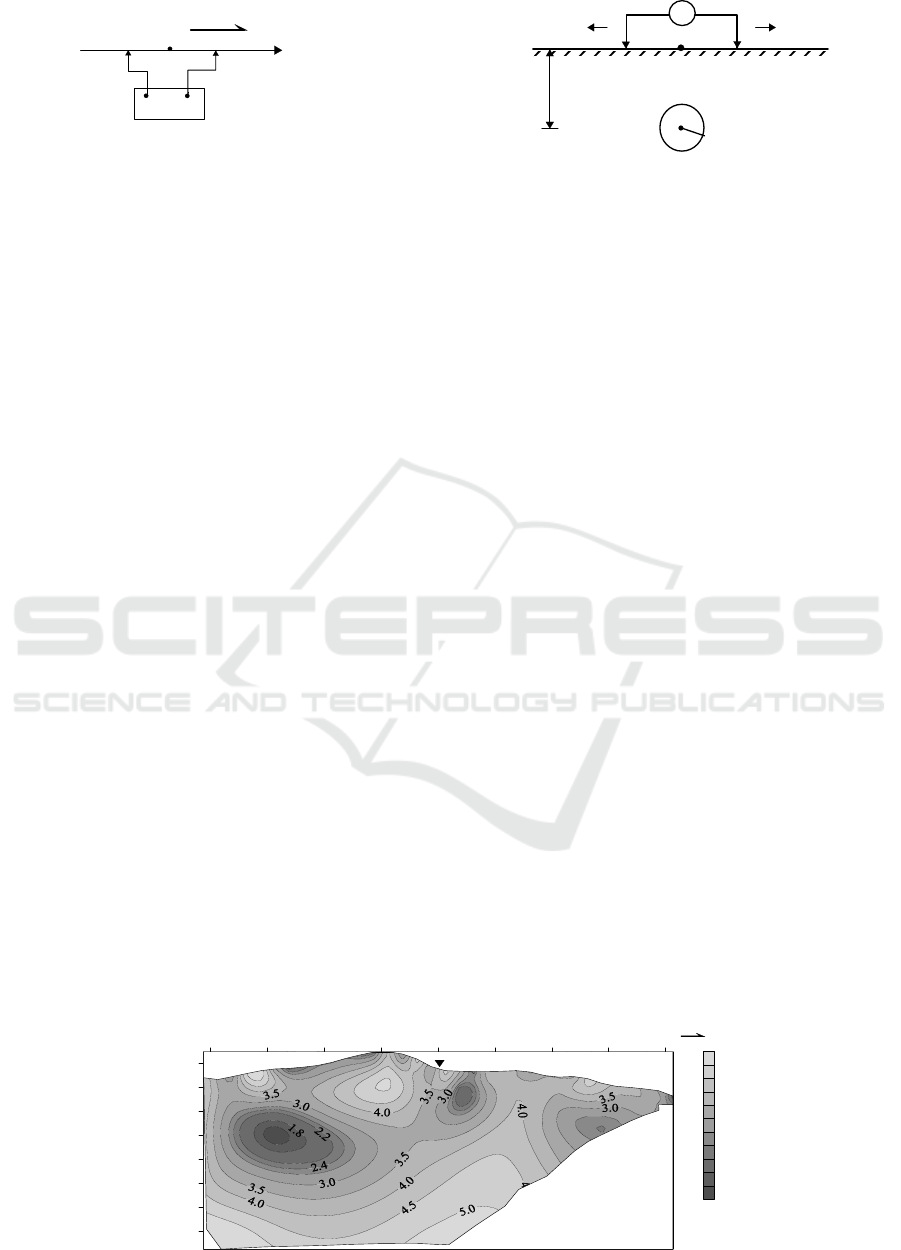
Figure 6. Views of the 2D inversion of the 2D ERT data observed of (a) survey profile AA’ and (b) survey profile BB’.
Three relatively low resistivity anomaly areas
were found on the profile AA’, as shown in figure 6(a).
Among them, the low resistivity anomaly near the
profile of 50-100 m and the elevation of 1060 m is
very obvious. Combined with the local
geomorphology, the anomaly is close to the gully at
25 m of the survey profile. It is inferred that the
abnormal section has large water content, and the
anomaly may be related to the catchment of the gully.
But due to the small area of the catchment on the site,
and the exploration work in the spring, during which
the rain is relative abundant, it is necessary to consider
the influence of rainwater on the anomaly. There is
also a shallow buried relatively low resistivity
anomaly area near the profile of 200 m and the
elevation 1080 m. It is estimated that the buried depth
of the anomaly is less than 30 m. This position is
located in the saddle of the two hilltops, and it can be
inferred that the water content is strong, but it is
outside the land acquisition scope. The bamboo forest
is in the surface area of 290-340 m of survey profile
AA’, where there is an alluvial gully with strong water
content, so it is a relatively low-resistance area. Due to
the influence of surface water in the bamboo forest
gully, and outside the red line of the land acquisition
scope, the bamboo forest area is not an advantageous
well site. The aforementioned borehole ZK1 is located
near the vicinity 300 m of the survey profile AA’, and
the drilling depth of 60 m is basically a dry well, the
lithology buried below 13 m is relatively complete
granite.
Compared with survey profile AA’, there is no
very obvious low resistivity anomaly area on profile
BB’, as shown in figure 6(b). The profile BB’ passes
through the middle step of the slope in figure 2. Except
for the bamboo forest area, the measuring point
elevation of the survey profile is generally larger than
that of the survey profile AA’. The measuring points
near the slope are closer to the hilltop (Figure 2), and
the water content in the slope decreases, which leads
to the increase in the resistivity and the relatively low
resistivity anomaly is not very obvious, but there are 3
relatively low value anomalies (Figure 6(b)). Firstly,
there is a shallow low-apparent resistivity anomaly
near the profile of 100 m and the elevation of 1120 m.
It is located in the depression area of two hills in the
middle of slope step in figure 2. It is presumed that the
water content is strong below this position, and the
anomaly has a certain correlation with the position
anomaly near the profile AA’ of 200 m in figure 6(a),
because both anomalies are located in the depressed
area of the slope. There is a relatively low resistance
trend near the profile of 200 m, this anomaly is located
at the side of the road and at the saddle of the two hills.
The 260-300 m section of profile BB’ is located in the
bamboo forest, where there is an alluvial valley. There
is a small amount of water in the shallow covering
strata, but there is not necessarily groundwater in the
deep because the borehole ZK1 on the previous survey
profile AA’ has been verified.
1
2
2.6
3.2
3.8
4.4
5
Road
Bamboo
forest
Resistivity (ohm.m)
(Log10)
980
1000
1020
1040
1060
1080
1100
1120
1140
El eva ti on (m)
120
o
Distance along profile BB' (m)
300
260220180140100
6020
(b)
Integrated Geophysical Application to Investigate Groundwater in a Wind Power Station of Mountainous Area: A Case Study in Xuefeng
Mountain Area of Hunan Province, China
73

Figure 7. Results of FSMNEF on (a) survey profile AA’ and (b) survey profile BB’.
According to the results of three-electrode
electrical sounding, the resistivity anomaly near the
50-100 m section of survey profile AA’ and the
buried depth of about 40 m is the favorable position
for water prospecting.
Figure 7(a) and figure 7(b) show the partial
detection results of FSMNEF on survey profile AA’
and BB’, respectively, and the data next to the curve
in the figure represents different detection
frequencies. After 115 m of profile AA’ and 90 m of
profile BB’, the curve increases obviously. It is
caused by the interference of the cable used for
temporary construction on the ground. Therefore, the
data results which are interfered after 115 m of profile
AA’ and 90 m of profile BB’ are omitted here and not
drawn out. According to the results of FSMNEF,
there are two obvious low potential anomalies in
profile AA’, namely near 81m and 91 m. The two
anomalies were observed carefully in the field work,
that is, the measuring point spacing was reduced from
5 m to 2 m. The reliability of the anomaly is
determined. The anomaly of 81 m is more obvious
than the anomaly of 91 m, and the relative amplitude
of the anomaly is larger, and the synchronization of
the detection results at different frequency is better,
as shown in figure 7(a). In addition, the reliability of
the low potential anomaly at 115 m of the survey
profile AA’ is affected by the interference of the
nearby power supply.
The anomalies of FSMNEF on survey profile BB’
mainly appear near the profile of 45 m and 70 m, and
relative amplitude of the anomaly at 70 m is more
obvious and the anomaly is more reliable. According
to the position relationship between the survey profile
AA’ and BB’, it is presumed that the anomaly at 70
m of the profile BB’ is associated with the anomaly at
81 m of profile AA’. The survey profile CC’ is
roughly parallel to the construction road up to the
mountain (Figure 1), and there is a high-voltage
power supply line along the road, so the FSMNEF is
not performed on the profile.
According to the results of FSMNEF method and
vertical resistivity sounding, the position of the
FSMNEF anomaly at 81 m is overlapping with that of
resistivity sounding anomaly of 50~100 m on profile
AA’, which further determines the reliability of
FSMNEF anomaly at 81m, and the point of 81m is
finally determined as well location. For this reason,
the vertical electrical sounding of FSMNEF is further
carried out at this site (ie, point 81/AA’), and the
sounding curves are shown in figure 8. It same as
those shown in figure 7, the data next to the curve in
the figure represents different detection frequencies.
The FSMNEF sounding is similar to the conventional
vertical electrical sounding of the Schlumberger
configuration, but there are no current electrodes (AB)
at this time. The potential electrodes (MN) are
symmetrical with respect to the sounding point O and
spacing of MN gradually increases, and potential
differences △V of different frequencies are measured
at different electrode spacing (Liang et al, 2016). It
can be seen from the sounding curves of figure 8 that
the FSMNEF sounding curves of 15.7 Hz, 23.6 Hz,
71.8 Hz and 129 Hz have relatively low potential
anomalies around MN=20 m. According to the
experience of, there is an approximately equal
relationship between the electrode spacing MN and
the detection depth H is, that is MN/H≈1 (Liang et al,
2016). Therefore, it is assumed that the buried depth
of the aquifer is about 20 m.
CoEEE 2021 - International Joint Conference on Energy and Environmental Engineering
74
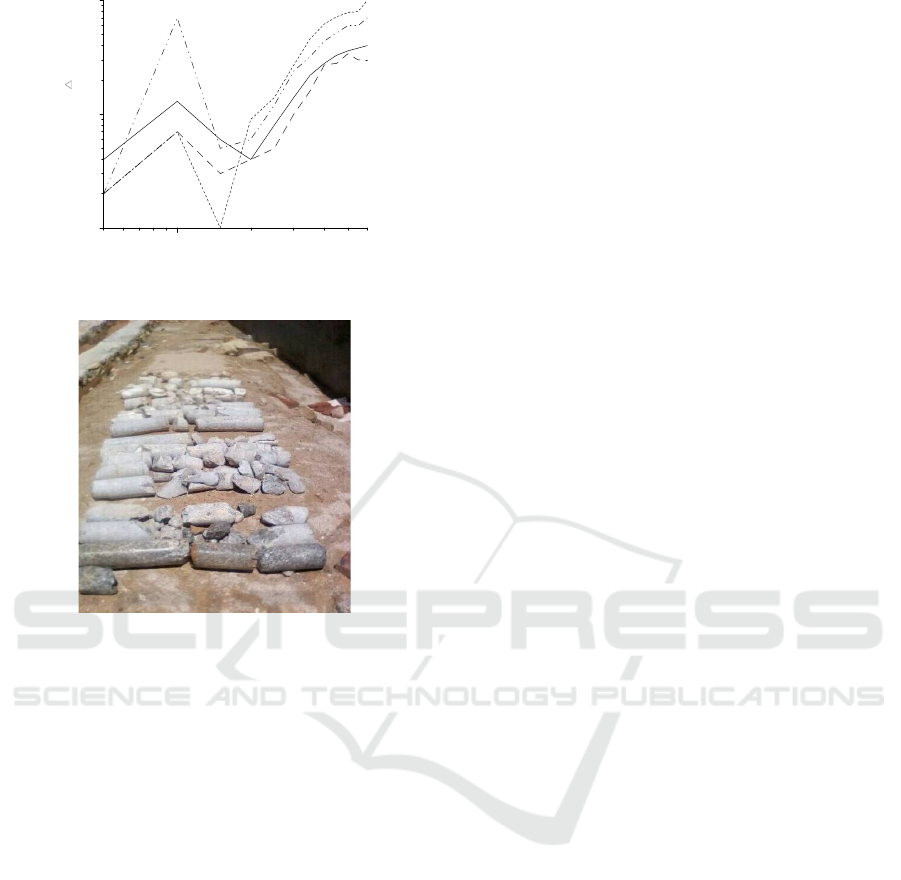
Figure 8. Sounding curves of FSMNEF at 81/AA’.
Figure 9. Drilling cores for 28m depth.
Figure 9 shows the core after drilling at point
81/AA’, in which there are water-bearing fractures at
23-26.5 m segment, and the core is relatively
fragmented and incomplete. The pumping test result
shows that the water output of the well is about 30 t/d,
and the final drilling depth of the well is only 30 m
because the water requirement (>15 t/d) is satisfied.
It can be seen that the ratio of electrode spacing MN
(=20 m) of low potential anomaly reflected by
FSMNEF sounding curves to the average buried
depth H (=24.75 m) of water-bearing fractures is
about 0.8.
4 CONCLUSIONS
According to the effect of groundwater prospecting
practice in this granite area, the use of integrated
geophysical technologies is an effective method for
groundwater exploration in granite areas. As far as
exploration results are concerned, the profile of three-
electrode electrical sounding can delineate the range
of low-resistivity anomalies and draw an intuitive
geoelectrical cross-section of the survey profile. The
horizontal volumetric effect of FSMNEF is small, and
the horizontal position of the water-bearing structure
can be determined accurately and meticulously,
which is convenient for accurate positioning of well
position.
From the exploration results of FSMNEF
sounding method, it has similar exploration effects as
the conventional direct current sounding of the
Schlumberger configuration, that is, the exploration
depth increases with the increase of potential
electrodes spacing (MN). The authors believe that
this is due to the existence of stray current in the
ground. This is also a question worthy of further study
in the future.
From the in-situ work, the conventional resistivity
method is more troublesome, the workload is large,
the volume effect is strong, the topography effect is
serious, and curves are distorted. But FSMNE
overcomes the defects of conventional geophysical
prospecting methods which are complex and
cumbersome in the in-situ work, and FSMNE has the
advantage of cost effective, rapid and quick survey
time, strong site adaptability and less ambiguity
interpretations of results when compared to other
geophysical survey methods, it has a good prospect of
development and application. At the same time,
FSMNE is an electromagnetic method which is
susceptible to the artificial electromagnetic
interference in the field. This is a problem that needs
pay attention to it.
In addition, the FSMNE sounding is a new
sounding method put forward by Chinese researchers
in practical application recently, and it has achieved
good results in practice (Liang et al, 2016). However,
the inversion of data is still in the stage of empirical
interpretation, and the theoretical research of this
method needs to be further studied.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was substantially supported by the
National Key R&D Program of China(Grant No.
2018YFC0807801), National Key R&D Program of
China(Grant No. 2018YFB0605503), National
Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant No.
51804112), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan
Province of China(Grant No. 2018JJ3169), Hunan
Provincial Department of Education funded scientific
research project (16K031).
10
0.001
0.010
0.100
71.8 Hz
23.6 Hz
15.7 Hz
Electrode spacing MN (m)
129 Hz
20
30
40 50
60
5
Potential difference V (mv)
Integrated Geophysical Application to Investigate Groundwater in a Wind Power Station of Mountainous Area: A Case Study in Xuefeng
Mountain Area of Hunan Province, China
75

REFERENCES
Cao, G.Q., Zhou, Z.H. (2006). Application of the surface
nuclear magnetic resonance method to detecting
groundwater in granite regions (in Chinese with English
abstract). Hydrogeol Eng Geol, 33(2):108-113.
Dai, S.B. (2001). Forming mechanism of trace elements in
the ground water from granite area (in Chinese with
English abstract). J Henan Univ (Nat Sci), 31(2):83-86.
Duan, J.S. (1999). Combination of shallow refraction
seismic survey with electrical sounding method used
for water research in the granite-covered area (in
Chinese). Geol Prospect, 35(3): 46-48.
Huang D.S. (2005). Occurrence characteristics of granite
crevice-water and key to discover water (in Chinese
with English abstract). Cons Util Miner Resour+,
25(4):51-54.
Li,, G.Z., Wang, X. (2009). Application effect of water
prospecting in granite region by comprehensive
geophysical methods (in Chinese with English
abstract). Site Invest Sci Technol, 27(4), 55-57.
Li, J., Pang, Z.H., Kong, Y.L., Lin, F.L., Wang, Y.L.,
Wang, G.J., Lv, L.H. (2017). An integrated
magnetotelluric and gamma exploration of groundwater
in fractured granite for small-scale freshwater supply: a
case study from the Boshan region, Shandong Province,
China. Environ Earth Sci. 76(4):1-12.
Liang, J., Wei, Q.F., Hong, J., Zheng, S.Y., Qin, Y.C., Yan,
F.S., Feng, Y.X. (2016). Application of self-potential
method to explore water in karst area (in Chinese with
English abstract). Geotech Invest Surv, 44(2):68-78.
Madhnure, P., Peddi, N.R., Allani, D.R. (2016). An
integrated hydrogeological study to support sustainable
development and management of groundwater
resources: a case study from the Precambrian
Crystalline Province, India. Hydrogeol J, 24(2):475-
487.
Mahmoudzadeh, M.R., Francés, A.P., Lubczynski, M.,
Lambot, S. (2012). Using ground penetrating radar to
investigate the water table depth in weathered granites
– Sardon case study, Spain. J Appl Geophys, 79(1):17-
26.
Mcclymont, A.F., Roy, J.W., Hayashi, M., Bentley, L.R.,
Maurer, H., Langston, G. (2011). Investigating
groundwater flow paths within proglacial moraine
using multiple geophysical methods. J Hydrol, 399(1-
2):57-69.
Qiao, X.X. (1988). Types and occurrence characteristics of
granite fractured water in Hulun Buir and Heilongjiang
province (in Chinese). Site Invest Sci Technol, 6(4):5-
8.
Shi, Y.F., Li, X., Pei, M.R., Wang C.M. (2016). Experiment
on solute transport in fracture of granite rock (in
Chinese with English abstract). J Water Res Water Eng,
27(2):222-226.
Xiang, Q.A., Yang, T.C. (2011). The application of IP
sounding method to IP anomaly appraisal in Liling gold
deposit, Hunan province (in Chinese with English
abstract). Gold Sci Technol, 19(5):1-6.
Yang, T.C., Zhang, H. (2013). A study of the anomaly
genesis for the frequency selection method in a natural
electric field of a karst body (in Chinese with English
abstract). Hydrogeol Eng Geol, 40(5):22-28.
Yang, T.C., Zhang, Q., Wang, Q.R., Fu, G.H., Liao, J.P.
(2016). Study on the anomaly genesis of the frequency
selection method for a sphere under natural
electromagnetic field (in Chinese with English
abstract). J Hunan Univ Sci Technol (Nat Sci Ed),
31(2):58-65.
Zhao, G.T. (1990). Criterions in the survey of ground water
source at granite area (in Chinese with English
abstract). Trans Oceanol Limnol, 12(4):31-36.
CoEEE 2021 - International Joint Conference on Energy and Environmental Engineering
76
