
Quantum Transformation of School Informatics
Serhiy O. Semerikov
1,2,3 a
, Svitlana V. Shokaliuk
1 b
, Liudmyla V. Lehka
1 c
,
Pavlo V. Merzlikin
1 d
and Olena Yu. Tarasova
1 e
1
Kryvyi Rih State Pedagogical University, 54 Gagarin Ave., Kryvyi Rih, 50086, Ukraine
2
Kryvyi Rih National University, 11 Vitalii Matusevych Str., Kryvyi Rih, 50027, Ukraine
3
Institute for Digitalisation of Education of the National Academy of Educational Sciences of Ukraine,
9 M. Berlynskoho Str., Kyiv, 04060, Ukraine
Keywords:
Methods of Teaching Informatics, General Secondary Education, Methods of Teaching Lyceums Students,
Quantum Technologies, Quantum Informatics, Competencies in the Basics of Quantum Informatics.
Abstract:
The study’s objective was to theoretically examine, create, and experimentally test various approaches for in-
structing lyceum students in the fundamentals of quantum informatics. The following was accomplished as a
result of the research assignments: 1) The sources on the issue of teaching quantum informatics in Ukraine and
abroad were examined; 2) The structure and content of the competences in the basics of quantum informatics
for the lyceum students were theoretically grounded and developed (the results of the expert survey and the
European competence framework in the field of quantum technologies were taken into consideration); 3) the
structural and functional model for forming the competences in the basics of quantum informatics were devel-
oped; 4) in the optional course of the same name, it was proposed a methodological framework for teaching
the fundamentals of quantum informatics to lyceum students; and 5) it was also experimentally tested to see
how well the developed methodology worked in developing the students’ competency in the fundamentals of
quantum informatics. Further scientific investigations into the quantum transformation of the school’s infor-
matics are also described.
1 INTRODUCTION
The changes that took place in the methodology of
teaching informatics in schools were caused by the
development of information technology and changes
in society as a result of their influence (Semerikov
et al., 2021). The latter led to the fact that school
informatics together with foreign language became
available at all levels of school education – from pri-
mary school to vocational training at the lyceum. In-
formatics tools are an integrator for all school sub-
jects, and its methods are the basis for the integra-
tion of natural sciences, mathematics and technol-
ogy. This creates a deep understanding of the ser-
vice, subordinate and second-row role of informatics
in the system of school education. The fundamental-
ization of teaching content informatics, in particular –
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0789-0272
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3774-1729
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5768-5475
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0752-411X
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6001-5672
through a quantum transformation of basic knowledge
about information processes and systems, hardware
and software, networks, algorithms and programs will
help to get rid of it.
According to the analytical report of the National
Institute for Strategic Studies (NISS, 2020), Ukraine
is on the sidelines of the development of break-
through technologies, in particular quantum technolo-
gies, which is due, firstly, due to insufficient state bud-
get financing of scientific research on the whole, and
secondly, due to the significant inadequacy of pro-
fessional and qualification workforce to market de-
mands. At the same time, European job search sites
have hundreds of job postings for “quantum software
engineer” and “quantum programmer”.
The analysis of the experience of teaching infor-
matics in Ukraine and the resources on the problems
of research allowed us to identify the contradictions:
• between the importance of quantum informat-
ics for increasing competitiveness and successful
self-fulfillment of graduates of lyceums in the la-
bor market (in particular, in the field of informa-
220
Semerikov, S., Shokaliuk, S., Lehka, L., Merzlikin, P. and Tarasova, O.
Quantum Transformation of School Informatics.
DOI: 10.5220/0012063200003431
In Proceedings of the 2nd Myroslav I. Zhaldak Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology (AET 2021), pages 220-235
ISBN: 978-989-758-662-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

tion technology) and the lack of adequate training
materials in Ukrainian language;
• between the importance of practical experience
with quantum computers and the difficulty of di-
rect access to them;
• between the need to form competences in the ba-
sis of quantum informatics in the lyceums and un-
development of the appropriate methods.
The need to solve the above-mentioned contradic-
tions led to the definition of the study’s aim and for-
mulation of its hypothesis. The aim of the study was
to theoretically analyze, develop and experimentally
test the methods of teaching the basics of quantum in-
formatics to lyceums students. It has been suggested
that the formation of competencies on the basics of
quantum informatics to lyceums students at a high
level is possible by changing some components of the
methodological system of teaching computer science:
content and teaching tools.
2 THEORETICAL
FOUNDATIONS OF TEACHING
THE BASICS OF QUANTUM
INFORMATICS TO LYCEUMS
STUDENTS
2.1 Quantum Informatics as a
Perspective Field of Information
Technology Development
In August 2020, consulting company Gartner pub-
lished yet version of its Hype Cycle of advanced tech-
nologies that will have a significant impact on soci-
ety and business in the next five to ten years. Based
on a review of 1,700 advanced technologies, Panetta
(Panetta, 2021) identifies 5 new trends in their devel-
opment:
• Composite architectures;
• Algorithmic trust;
• Beyond silicon;
• Formative artificial intelligence (AI);
• Digital me.
The Beyond silicon description of the direction
says that Moore’s Law has run out of steam be-
cause it is almost impossible to create transistors
smaller than 1 nm. There are technical difficulties
in manufacturing, so there is a chance to develop
non-silicon technologies – carbon-based transistors
and quantum hardware, including quantum comput-
ers (Panetta, 2021).
At the time when classical computers continue to
develop (processors became multicore, co-processors
appeared to solve photo processing tasks, video cod-
ing, etc.) the pace of quantum technologies develop-
ment is gaining momentum and quantum computers
are becoming a reality. Appearance and development
of quantum equipment, in particular quantum com-
puters, has led to a new field of informatics – quantum
informatics (Lehka and Shokaliuk, 2018).
One should understand that quantum computers
by no means supersede classical ones, but they are
indispensable for certain types of tasks – modeling
complex chemical reactions to develop drugs and sub-
stances with predetermined properties, modeling of
physical quantum systems inaccessible for conven-
tional calculations, quantum calculations of complex
mathematical tasks, quantum long-distance commu-
nication, etc. The solution of these problems is based
on already known quantum algorithms – algorithms
for function balancing (Deutsch-Jozsa and Bernstein-
Vazirani algorithms), algorithm for determining the
totality of functions (Simon’s algorithm), harmonic
analysis algorithms (the quantum Fourier transform
algorithm), cryptoanalysis algorithms (Grover’s and
Shor’s algorithms), quantum teleportation algorithm –
and new (still experimental) algorithms.
In many countries of the world the development of
quantum technologies is supported by legislation and
financed by the government.
Thus, in the U.S., artificial intelligence and quan-
tum technologies have been identified as two strate-
gically important fields for the country’s economic
growth and national security. In 2018, the U.S. gov-
ernment approved legislation for the National Quan-
tum Initiative, which aims to ensure that the U.S.
remains a world leader in quantum informatics and
its technological applications. Funding for National
Quantum Initiative activities for the first five years is
$1.2 billion (NQIA, 2018). Individual commercial re-
search is conducted at the expense of IBM, Microsoft,
Google, Intel and others.
In China, in 2016 the government approved the
National Science and Technology Innovation Plan un-
til 2030 (NSTI, 2016), and in 2017 the construction
of the National Quantum Informatics Laboratory was
launched with initial funding of 7 billion yuan (Chen,
2018). The Chinese tech giant Alibaba is making sig-
nificant investments in its own quantum initiatives, in-
cluding the launch of a quantum calculator service via
a cloud platform (Alibaba, 2018).
Since October 2018, EU countries have launched
project program to support fundamental quantum re-
Quantum Transformation of School Informatics
221

search – “The European Quantum Flagship” (QFlag-
ship), with a minimum duration of 10 years and an ex-
pected budget of 1 billion billion euros (EQF, 2021).
In addition, to protect against cybersecurity threats,
in June 2019, 24 European states participated in the
signing of a declaration on the research, development
and deployment of quantum communication infras-
tructures (EDS, 2019).
The demand for specialists in the field of quantum
technologies becomes urgent. The lack of quantum-
literate specialists hinders the development of the in-
dustry. For example, Hilton (Hilton, 2019), vice pres-
ident of D-Wave, argues that it is necessary to increase
the number of quantum-literate workers, invest in the
training of teenagers, identify capable young people,
develop them in the field of quantum technologies and
create a talent pool of promising workers with knowl-
edge in the quantum field.
2.2 Teaching Experience of Quantum
Informatics and Popularization of
Quantum Technologies in Ukraine
and the World
In Ukraine all educational programs on quantum in-
formatics were initiated only in universities within the
specialty 104 – Physics and Astronomy (Pinkevych
et al., 2018; NUL-bachelor, 2020; NUL-master,
2021), while in the world the training of correspond-
ing specialists is carried out by different specialties
(QTEdu, 2022).
The European Competence Framework for Quan-
tum Technologies, launched in 2021, provides for
training in quantum informatics, starting from pri-
mary school. Such education should be based on con-
ceptual and intuitive understanding of quantum infor-
matics key essences.
Today, both in Ukraine and abroad, mostly pro-
grams of non-formal education on individual topics of
quantum technologies are offered for students of gen-
eral secondary education institutions. Its are online
schools, master classes, summer camps for children,
etc.
Popular science resources about quantum tech-
nologies for Ukrainian students are offered by
Gnatenko (Gnatenko, 2020a,b). With these electronic
materials (after payment) students can get acquainted
with fundamental concepts of quantum mechanics –
quantum entanglement, quantum beat, quantum par-
allelism, quantum sensing, quantum entanglement,
quantum superposition, tunneling, quantum telepor-
tation, as well as examples of basic tasks of quantum
cryptography.
The Richelieu Lyceum, in cooperation with the
Odesa I. I. Mechnykov National University, of-
fers a series of lectures “Nanoelectronics: Science
and Modernity” (including lectures on quantum ef-
fects) (NSM, 2021), and “Quantum Mechanics” (QM,
2021).
Korshunova and Zavadsky (Korshunova and
Zavadsky, 2018) in their textbook on informatic for
5th grade (section “Information processes and sys-
tems”) gives an overview of quantum computers as a
technology of the future, pointing out the rapid devel-
opment of the quantum industry in the next ten years,
the use of quantum computers to solve certain types of
mathematical problems, emphasizing the use of quan-
tum computers together with conventional computers
(Korshunova and Zavadsky, 2018, p. 28-29).
Since August 2020, the White House Office of
Science and Technology Policy and the National Sci-
ence Foundation have launched an innovative project,
the Q-12 National Education Partnership, which over
the next ten years will bring together industry and sci-
ence educator leaders for large-scale quantum tech-
nology education, ranging from providing classroom
tools for hands-on experience, developing educational
materials, and supporting students on their way to
professional careers in quantum technologies (Q12,
2023). Leading IT companies – IBM, Microsoft, D-
Wave, Google and others – offer joint courses with
universities, as well as educational resources for in-
formal education, based on the use of a cloud ac-
cess to quantum simulators and quantum comput-
ers, tools for creating and executing quantum circuits
and programs, language-independent and language-
independent development environments, etc. (QC-
IBM, 2021; Google, 2022; QDKit-Microsoft, 2023).
A variety of educational resources on quantum
technologies for primary and secondary school stu-
dents and all those interested are offered on the QT-
Edu community portal (QTEduCSA, 2021). The por-
tal is designed to develop an educational ecosystem
in support of the QFlagship project aimed at pop-
ularizing, informing and educating in the field of
quantum technologies. The portal’s collection of re-
sources, structured by education level and target au-
dience, includes educational programs, hyperlinks to
external resources, quantum games, simulators, video
resources, etc., mostly in English, German and Polish
(Ukrainian and Russian resources are not available on
February, 2023).
Experience of European and world practice of
popularization of quantum technologies among high
school students is a good evidence of the possibility
of mastering the basics of quantum technologies, pro-
vided methodical adaptation of educational materials
AET 2021 - Myroslav I. Zhaldak Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
222

to the specifics of the audience perceiving them.
2.3 The Competencies in the Basics of
Quantum Informatics to Lyceums
Students
The key idea of the competency-based approach is
to provide all interested individuals with a diagnostic
tool to measure the level of preparedness of an indi-
vidual to perform certain activities.
Review of the previous results of the world
projects for the selection and determination of the list
of competences in quantum technologies – World-
Skills International professional competitions (fig-
ure 1 and 2), seminar “Key Concepts for Future Quan-
tum Information Science Learners” (NSF, 2020),
Competence Framework for Quantum Technologies
(figure 3) – made it possible to identify competen-
cies in the fundamentals of quantum information sci-
ence of lyceum students as a dynamic combination
of knowledge, skills, abilities, ways of thinking, and
attitudes, other personal qualities in the field of quan-
tum technologies, which determine the ability of an
individual to successfully carry out further profes-
sional and/or educational activities using such tech-
nologies. Competences in quantum informatics ba-
sics of lyceum students include 8 groups of compe-
tences:
1) physical basics of quantum technologies (basic
concepts of quantum physics, cubic dynamics);
2) mathematical basics of quantum informatics (ba-
sics of linear algebra, mathematics of quantum
physics basics, basics of quantum measurement
statistics);
3) software technology (optical technology, labora-
tory technology, experimental control);
4) hardware for quantum computers and sensors
(spin-based devices, neutral atoms and ions, new
types of cubes, equipment for integration, manip-
ulation and counting of cubes, use of hardware
platforms for quantum computing);
5) quantum computing and modelling (quantum
gates, quantum languages, programming tools
and platforms, basic quantum algorithms, quan-
tum error correction, quantum modelling ele-
ments);
6) quantum sensors and metrology (atomic gauges,
sectors of quantum sensors application);
7) quantum communication (quantum cryptography,
quantum networks, quantum communication in-
frastructure and equipment);
8) practical skills and general competences (basics
of classical programming, application of quantum
technologies, general skills/competences).
Considering that quantum information technology
is an interdisciplinary branch of knowledge, the rele-
vant competencies cannot be defined as part of digital
competencies.
3 METHODICAL FOUNDATIONS
OF TEACHING THE BASICS OF
QUANTUM INFORMATICS TO
LYCEUMS STUDENTS
3.1 Special Hardware and Software
Tools for Teaching the Basics of
Quantum Informatics
For the selection of special hardware and soft-
ware tools for teaching quantum informatics to
lyceums students we analyzed services from Mi-
crosoft, QuTech, Amazon and IBM (Lehka and
Shokaliuk, 2021; Lehka et al., 2022a,b).
The greatest number of criteria is satisfied with
IBM Quantum platform, which was turned into the
main instrumental tool for learning the basics of quan-
tum informatics for the course program.
Now IBM provides the greatest opportunities
for free use of quantum computers and simulators
through two services – IBM Quantum Composer and
IBM Quantum Lab.
The first service – IBM Quantum Composer – the
simplest tool for working with quantum algorithms in
the form of quantum circuits.
The second service – IBM Quantum Lab – pro-
vides the possibility to implement quantum algo-
rithms in Python programming language using the
Qiskit library.
3.2 Pedagogical Reasonability and
Content of Teaching the Basics of
Quantum Informatics in Secondary
Schools
The model of the educational process (learning)
within a single educational unit, which reflects the or-
dering (elementary in time and space, in accordance
with the goals of education and training and taking
into account the reverse pedagogy) of the students
(those who learn) in terms of the content of training
Quantum Transformation of School Informatics
223
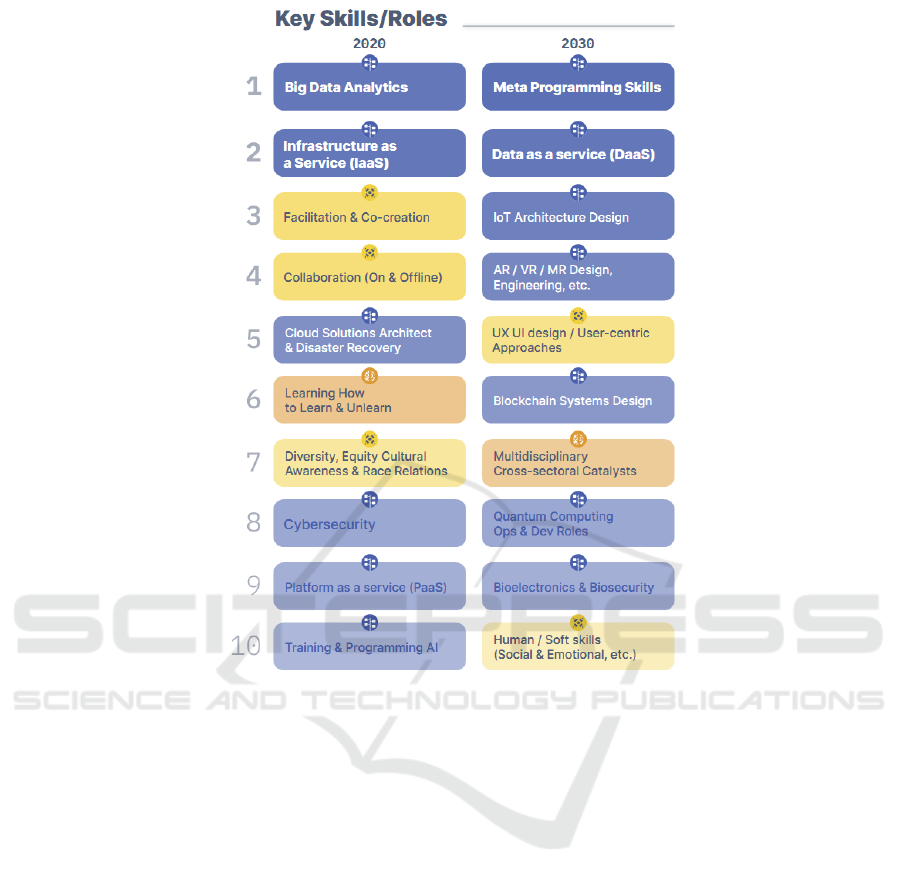
Figure 1: Key skills and roles of the 2020s and 2030s for WorldSkills (WS, 2020, p. 120).
and elements of the learning environment of a par-
ticular learning unit, students (those who are taught)
regarding the content of the teaching and elements of
the learning environment for a particular educational
unit is called a normative teaching methods (Bykov,
2008, p. 310).
The real teaching method is based on the norma-
tive one and differs from it. The real teaching meth-
ods take into account the characteristics of the exist-
ing educational environment and mirror the creative
aspect of the educational process participants (e.g.,
specificity of the educational environment of a par-
ticular educational institution, mastery of the teacher,
additional meaningful elements that he or she uses in
the lessons).
The normative teaching method of a certain edu-
cational unit (in our case – basics of quantum infor-
matics as a single subject, elective, integrated course,
etc.) can be presented in the form of a structural-
functional model – a model graphically depicts func-
tional peculiarities of structural elements of a certain
process (in our case – formation of competences in
quantum informatics basics).
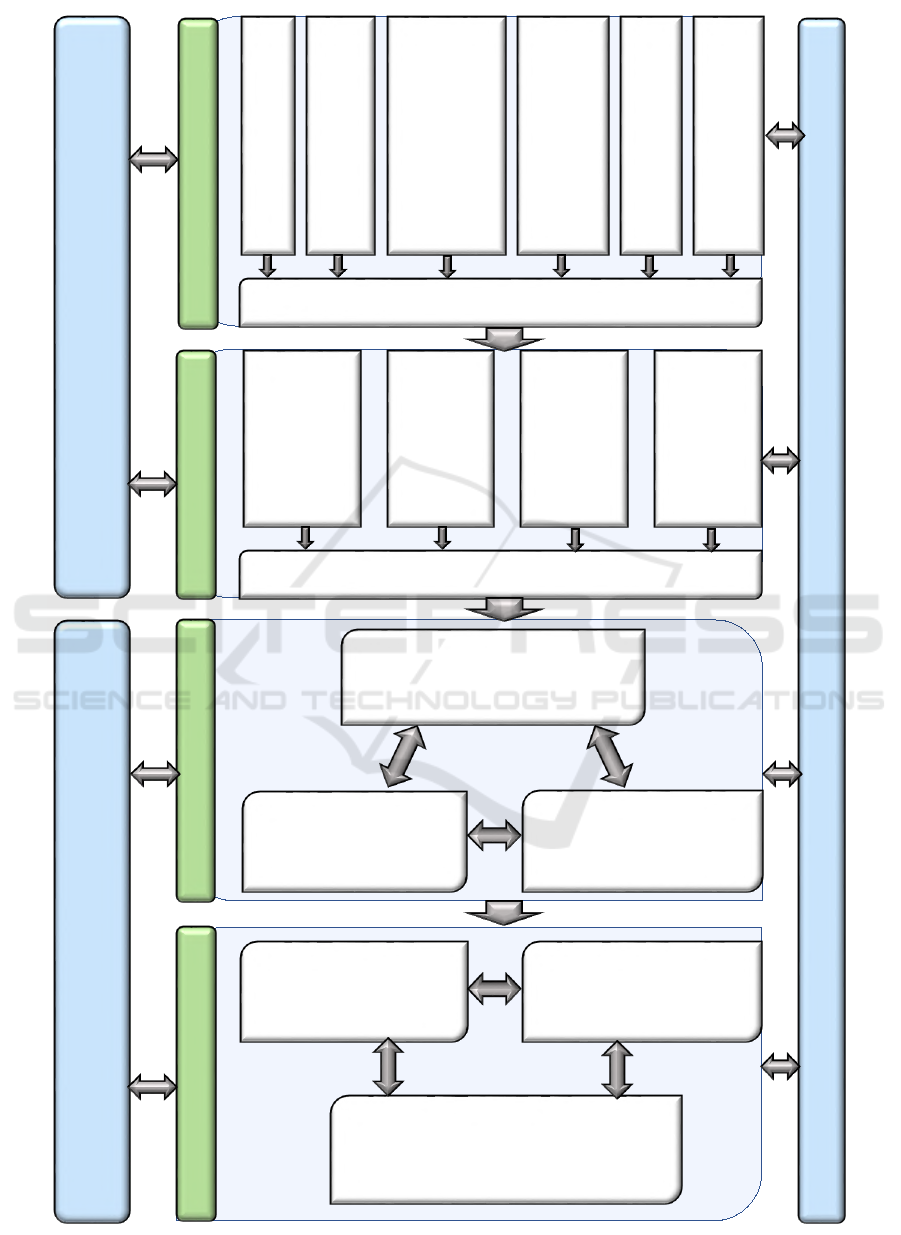
The developed structural-functional model of
competence formation in the basics of quantum in-
formatics (Lehka, 2022, p. 82) includes 4 basic (sys-
tem) blocks – Purpose, Content, Technological and
Productive (figure 4) – and 3 additional blocks en-
suring the interaction of the model’s basic blocks:
general didactic principles of teaching quantum in-
formatics, hardware and software tools for teaching
quantum informatics and methodological approaches
(competence-based, systemic, integrative, personal
and activity-based).
Let us consider the aim and content blocks of the
model.
The aim block of the model includes components
(factors) that determine the pedagogical feasibility of
the educational unit in the educational process (local
or global). Factors of pedagogical feasibility of im-
plementation of quantum informatics basics in the ed-
ucational process of secondary general education in-
stitutions are:
• rapid development of quantum technologies;
• demand of the society for qualified quantum sci-
AET 2021 - Myroslav I. Zhaldak Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
224
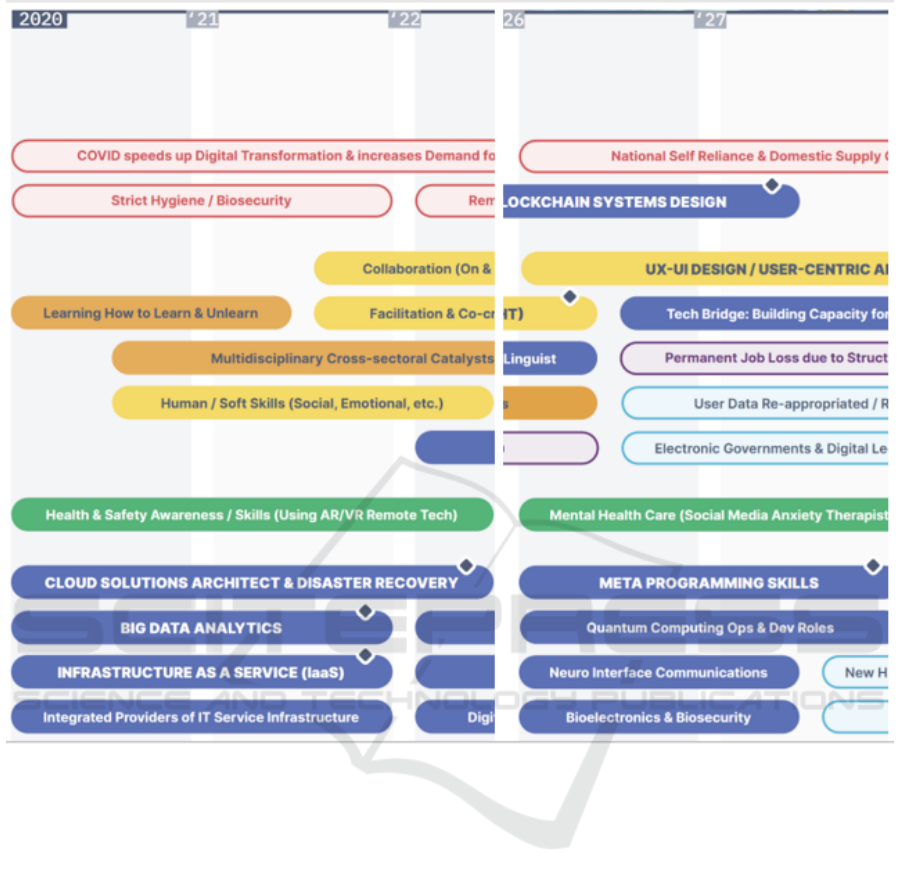
Figure 2: Forecast of the time of mass demand for skills from quantum technologies for WorldSkills (WS, 2020, p. 121).
entists;
• quantum computerization (availability of quan-
tum computers and other quantum equipment);
• free access to quantum computers;
• world experience in “quantum transformation” of
the school informatics;
• pre-professional training in quantum informatics.
To substantiate the feasibility of introducing the
basics of quantum informatics into educational pro-
grams of secondary general education institutions, To
find out the state of awareness of teachers in the field
of quantum technologies and readiness to teach an
elective course (or a course of their choice) to lyceum
students we have studied the opinion (conducted an
interview) of teachers of informatics in secondary
general education institutions. The survey involved
26 IT teachers who teach chemistry, labor and tech-
nology, and mathematics at the same time.
100% of respondents supported the opinion
that secondary education should provide up-to-date
knowledge and take into account the modern achieve-
ments of the industry when studying the disciplines.
All survey participants indicated that they use moder-
ate technologies when teaching their subject (65.4% –
always, 34.6% – only during distance learning).
96.2% of respondents agree that the educational
material (in particular, quantum informatics) should
be adapted according to the age of the students.
96.2% of the respondents indicated that they
would be pleased with the introduction of new sec-
tions and topics to the discipline curriculum, espe-
cially if sufficient methodological support is avail-
able.
The responses of the respondents indicate that
88.5% would like to take the course “Fundamentals
of Quantum Informatics”, and 38.5% of them noted
that they have encountered a lot of publications on
this topic and were interested in it.
Quantum Transformation of School Informatics
225
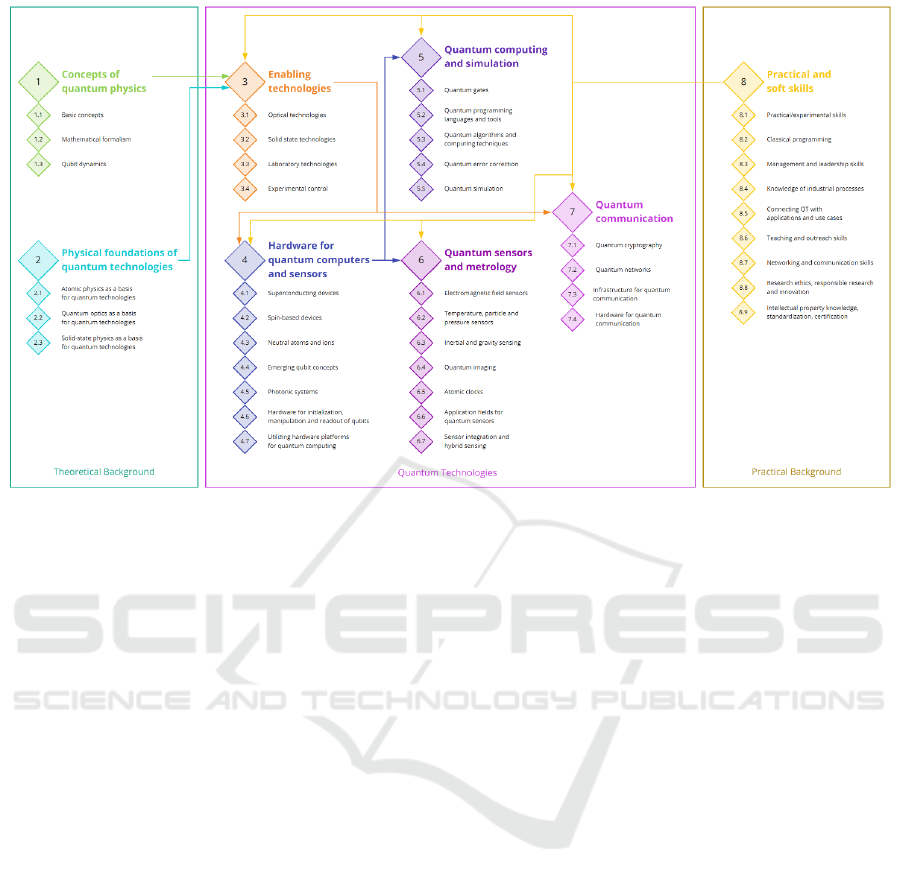
Figure 3: General structure of Competence Framework for Quantum Technologies (Greinert and M
¨
uller, 2021).
61.6% of respondents responded positively to the
question “Would you offer the course “Fundamentals
of Quantum Informatics” for students at your school?
23.1% refused because, in their opinion, this course
would not meet the profile of the educational institu-
tion where they work. Only 3.8% said no.
The survey indicates that teachers follow new
trends in the field and are ready to teach modern and
relevant courses in their institutions. As for the im-
plementation of the basics of quantum informatics for
lyceum students, the teachers expressed their support
for such implementation due to the presence of a cor-
responding course for teachers and methodological
support.
The content block of the model of competence for-
mation in the basics of quantum informatics as a cor-
responding normative teaching methodology reflects
the main content of competence formation in the ba-
sics of quantum informatics.
The content block of the model depicts the main
content of the competence formation in the funda-
mentals of quantum informatics:
• European framework of competences for quantum
technologies (see section 2.3);
• State educational standards;
• content of informatics curriculum;
• expert selection.
Analysis of the development of methodologi-
cal systems of teaching informatics (from 1985 and
up to now, with the consolidation of four stages)
showed that content of teaching school informatics
expanded from algorithms and programming through
the knowledge of information and information and
communication technologies to informatics as a basis
for STEM integration.
In order to clarify the content and recommenda-
tions for teaching the basics of quantum informatics
to lyceums students, to determine the importance of
the European framework of competencies for quan-
tum technologies, an interview was conducted among
those who are interested in the field of quantum tech-
nologies. 36 respondents took part in the survey, some
of them combining several positions, such as univer-
sity teacher and researcher or university teacher and
school teacher.
The analysis of the evaluation results (taking into
account the competence level of the participant of
the expert survey – “have a basic idea” (1), “know
with some components” (2), “deeply know with some
components” (3), “expert” (4)) has allowed to specify
the content of teaching the basics of quantum infor-
matics of the lyceum students and the system of cor-
responding competences (which included, first of all,
those components (knowledge and skills), calculated
parameters of which exceeded the specified threshold
value).
The first group of competencies “Competencies
in the physical foundations of quantum technologies”
includes:
• knowledge of the basic understanding of quantum
AET 2021 - Myroslav I. Zhaldak Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
226
Competency
-based, systemic, integrative, personal and activity
-based methodological approaches
Hardware, general and special software tools
for teaching quantum informatics
General didactic principles of teaching
quantum informatics
The aim: formation competences in the basics of quantum
informatics for lyceum students
The
aim block
The content block
The technology block
The result block
Rapid development of
quantum technologies
Society's need for qualified
specialists in the
quantum
field
Availability of quantum
computers and other
quantum equipment and
free cloud access to
quantum computers
World experience of
"quantum transformation"
of school
informatics
Quantum computerization
Pre-professional training in
computer science
The competence system in the basics of quantum informatics
for lyceum students
European
Competence
Framework for
Quantum
Technologies
State standard of
basic and complete
general education
Content of computer
science
education
Experts' choice
The means of forming
competencies in the basics of
quantum informatics of lyceum
students
The methods of teaching
computer science of
lyceum students
The forms of organizing
lyceum students' training
The means of assessing
learning progress
The means of diagnosing
the formation of competences
in the basics of quantum
informatics of lyceum students
The criteria of assessment, indicators,
levels of competence in the basics of
quantum informatics for lyceum
students
Figure 4: Structural-functional model of competence formation in the basics of quantum informatics.
Quantum Transformation of School Informatics
227

physics;
• skill to determine whether qubits are in binded
states;
• skill to represent qubits on a Bloch sphere.
The second group of competencies “Competen-
cies in mathematical foundations of quantum infor-
matics” includes:
• knowledge of the fundamentals of the theory of
complex numbers;
• knowledge of linear algebra fundamentals;
• knowledge of quantum physics mathematical fun-
damentals;
• knowledge of statistical nature of quantum mea-
surements;
• skill to design vectors (matrix-columns, matrix-
rows) of Dirac notation;
• skill to operate with standard bases;
• skill to arrange a vector in a selected basis;
• skill of giving examples of unitary matrices and
performing operations with them.
The third group of competencies “Competencies
in support technologies” includes:
• knowledge of optical technologies;
• knowledge of laboratory technologies;
• knowledge of experimental control;
• skill to separate photon sources.
The fourth group of competences “Competences
in hardware of quantum computers and sensors” in-
cludes:
• knowledge of the structure of spin-based devices
(in particular, quantum dots);
• knowledge of hardware platforms for quantum
computing, methods of their integration with stan-
dard equipment;
• skill to describe types of quantum structures of
quantum computers and explain their general
principles of operation;
• skill to arrange remote access to quantum comput-
ers;
• skill to perform quantum programs on quantum
computers.
The fifth group of competences “Competences in
quantum calculations and modelling” includes:
• knowledge of quantum gates (single-, double- and
multi-qubits);
• knowledge of quantum programming languages,
tools for development of quantum software and
platforms (including graphical ones);
• knowledge of basic quantum algorithms (Shore,
Grover, quantum optimization, quantum phase
evaluation, quantum linear algebra, etc.);
• skill to record quantum gates by means of unitary
matrices;
• skill to separate and use single-cube gates (Pauli
transubstantiation, Adamar gate, phase tensions);
• skill to perform operations using multi-qubit gates
(CNOT, Toffoli and Fredkin gates);
• skill to use quantum gates for writing quantum al-
gorithms;
• skill to use quantum programming languages and
tools;
• skill to implement quantum algorithms (Shore,
Grover etc.);
• skill to work with quantum simulators.
The sixth group of competencies “Competencies
in quantum sensors and metrology” includes the fol-
lowing:
• knowledge of the quantum sensors applications;
• skill to guide examples of quantum sensors appli-
cation in various fields.
The seventh group of competencies “Competen-
cies in quantum communication” includes:
• knowledge of quantum cryptography (quantum
key distribution, secure authentication, digital sig-
natures, use halls);
• knowledge of quantum networks (quantum inter-
net, sensor and dinode networks);
• knowledge of quantum communications infras-
tructure and equipment (fiber optic systems, wire-
less links, satellite systems; quantum random
number generators; quantum memory, interfaces,
switches; repeaters, terminal nodes);
• skill to describe the operating principles and struc-
ture of quantum network equipment;
• skill to give examples of application of quantum
cryptography in various fields.
The eighth group of competences “Practical skills
and general competences” includes
• knowledge of classical (non-quantum) program-
ming basics: programming languages, algo-
rithms, complexity classes, cryptography;
• knowledge of quantum technologies application;
AET 2021 - Myroslav I. Zhaldak Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
228

• skill to implement algorithms of basic complexity
classes (in particular, cryptographic algorithms)
using programming languages;
• skill to give examples of using quantum algo-
rithms to achieve quantum advantages.
3.3 Teaching Methodology the Basics of
Quantum Informatics to Lyceums
Students
Experimental realization of the structural-functional
model of forming competences on quantum informat-
ics basics is carried out within the optional course
“The Basics of Quantum Informatics” for students of
10 (11) grades. The course content is represented
by three subject content lines – “Physical and mathe-
matical foundations of quantum informatics”, “Quan-
tum computing, algorithms and programming” and
“Quantum telecommunication technologies”.
Content line “Physical and mathematical foun-
dations of quantum informatics” reveals fundamen-
tal physical and mathematical aspects of quantum
technique functioning, demonstrates physical realiza-
tion of microscience phenomena described mathemat-
ically.
The conceptual apparatus of the content line
“Physical and mathematical foundations of quantum
informatics” – quantum physics, quantum, photon,
superposition principle, quantum entanglement, tun-
neling, singularity principle, quantum teleportation,
chiral function, interference, diffraction coherence,
decoherence, quantum computer, qubit (quantum bit),
bracket notation, complex numbers, Bloch sphere.
Here are formulations of concepts, which should
be mastered by students in classes on fundamentals of
quantum informatics:
• Quantum physics (quantum mechanics) is a sci-
ence that studies laws of microcosm and describes
phenomena at microparticle level (molecules,
atoms, electrons, photons, etc.).
• A quantum is an indivisible microparticle, a por-
tion of some quantity (energy, light, etc.).
• Photon (quantum of light) is the elementary parti-
cle of which light consists.
• The principle of superposition consists in the abil-
ity of a microparticle to be in different states of the
same set of characteristics at the same time.
• Quantum entanglement – microcosm phe-
nomenon meaning dependence of microparticles
on each other regardless of distance between
them.
• Tunneling – ability of microparticles to pass
through a barrier. A microparticle can undercut
a barrier, “overcome” it or pass through it.
• The singularity principle was formulated by W.
Heisenberg and consists in the fact that it is im-
possible to measure simultaneously coordinates
and momentum of a microparticle with a certain
accuracy.
• Quantum teleportation is an ultra-fast (on aver-
age) transfer of states from one microparticle to
another. Quantum teleportation is not transporta-
tion or any other physical movement of a mi-
croparticle from one place to another.
• Quantum function (state vector) is a quantity,
which completely describes a state of a micropar-
ticle or quantum system as a whole. Quantum
function determines not physical parameters, but
approximate law of microparticle state distribu-
tion.
• Wave interference is a phenomenon that occurs
when two waves arising in the same medium
come in contact with each other.
• Diffraction – the ability of waves to ignore imper-
fections.
• Coherence – coherence of several colival or chiral
processes in time, which occurs when they over-
lap each other.
• Decoherence – incoherence of several colival or
chiral processes in time, which is found when they
are added to each other.
• Quantum computer – computing device, using
quantum superposition and quantum multiplicity
phenomena to transmit and process data.
• Qubit (quantum bit) is the most important element
for data storage in quantum computers. A qubit is
a quantum object with two basic structures, for ex-
ample: electron spin, photon, neutral atom or ion.
Mathematical model of a qubit state is a single
two-dimensional vector.
The competence in the basics of linear algebra in-
cludes understanding not only the concept of vectors
but also matrices, as well as the basic operations over
matrices (addition, matrix multiplication by number,
usual matrix multiplication, tensor matrix multiplica-
tion).
At this stage, students must understand that a vec-
tor can be represented algebraically – in the form of
a linear (vertical or horizontal) table of numbers or
geometrically – in the form of a tensed frame. Vec-
tor column, which represents the state of the cube, is
a certain table of numbers with one column and two
Quantum Transformation of School Informatics
229

rows. Further, it is worth explaining that there can be
several columns and rows of numbers. Such a table
of numbers arranged in rows and columns is a matrix.
The number of rows and columns determines the ma-
trix size. Vector columns or vector rows are separate
(partial) kinds of matrices.
The next step will be to familiarize students with
the actions on matrices. We draw students’ atten-
tion to the fact that matrix multiplication by a number
(scalar) is carried out by multiplying each element of
the matrix by the required number (scalar). Demon-
stration of the application of vector multiplication by
a number and matrix multiplication by a number.
Explanation of the operation of conventional
matrix-to-matrix multiplication begins with matrix-
to-vector multiplication, emphasizing that multiplica-
tion can be applied only to matrices in which the num-
ber of columns of the first matrix and the rows of the
second matrix are identical. The result of multipli-
cation is a dimension matrix equal to the number of
rows of the first matrix and the number of columns
of the second matrix. The elements of the result ma-
trix are the sum of pairwise additions of the elements
of the row of the first matrix to the elements of the
corresponding column of the second matrix. To mul-
tiply a matrix by a vector, each matrix row should be
elementally multiplied by the value of the vector.
In the case of a matrix with three (or more) rows
and columns, the multiplication technique is analo-
gous.
It is advisable to offer students examples of square
matrices and vectors whose elements are exclusively
zeros and ones, both for manual (written) execution
and using the capabilities of a table processor (and/
or a universal computer mathematics system or pro-
gramming language) for self-multiplication.
Then students should explain that quantum com-
puting theory uses tensor multiplication of vectors
(matrices), which is used to multiply vectors (matri-
ces) of sufficient size. Students must learn that for
tensor multiplication two steps are necessary:
1) scalar multiplication of each element of the first
matrix by another matrix;
2) to combine the obtained matrices according to the
output positions of these elements.
At first, students can find examples of tensor mul-
tiplication of vectors. As a practical task, students
may be presented with the task of realizing ten-
sor multiplication with the help of a table processor
(or/and a universal system of computer mathematics
or programming language) for two and three vectors.
The following is an application of tensor multiplica-
tion of matrices.
Formation of competence in mathematical foun-
dations of quantum informatics is based on knowl-
edge of statistical nature of quantum measurements.
Microparticle structures described by the Quantum
function have a statistical, i.e., luminescent, nature:
the square of the absolute value (module) of the
Quantum function indicates the luminescence value
of those quantities, on which the Quantum function is
dependent.
Before starting to get acquainted with quantum
gates (actions that can be performed over cubes), it
is necessary to consider the notion of unitary ma-
trix (a special numerical square matrix, elements of
which are real or complex numbers, and the result of
their multiplication by the Hermite-conjugate matrix
is equal to the unity of matrix E), explaining the terms
used in the formula. Namely, the square matrix (ma-
trix in which the number of rows is equal to the num-
ber of columns), the Hermite-conjugate matrix (the
A+ matrix obtained from the A matrix by transposi-
tion and replacement of each element with a complex-
conjugate one), singular matrix (diagonal matrix, di-
agonal elements of which are equal to one), diagonal
matrix (square matrix, posterior diagonal elements of
which are equal to zero). The notion of unitary ma-
trix is suitable to show on two examples – in the first
application, we will use matrix with real-integer ele-
ments, and in the second – matrix with complex nu-
merical elements.
Methods of teaching the content line “Physical
and mathematical foundations of quantum informat-
ics” can be revised, expanded with additional expla-
nations, or shortened, taking into account the training
of scientists in mathematics and physics.
Within the framework of the content line “Quan-
tum computing, algorithmization and programming”
the competences in hardware of quantum comput-
ers and sensors, quantum metrology, competences in
quantum computing and modeling are formed and/or
developed, first of all, Formation of knowledge and
skills to distinguish and use quantum single- and
large-cube gates for recording quantum algorithms,
use platforms for implementation of quantum algo-
rithms in the form of schemes and programs on quan-
tum simulators and real quantum equipment.
It is advisable to start studying this content line by
looking at the structure of a quantum computer and
then move to the issue of providing special conditions
for their functioning:
• temperature control (close to absolute zero);
• insulation against magnetic, electric and thermal
fluctuations, vibrations;
• air dissipation lower than the atmospheric pres-
sure by billions of times.
AET 2021 - Myroslav I. Zhaldak Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
230

Further it is advisable to acquaint students with
hardware platforms for quantum computing, ways
to integrate them with the classical equipment us-
ing quantum simulators and computers of IBM, Mi-
crosoft, Google, Intel, QuTech and others.
We suggest that competence development in re-
mote access to quantum computers should be based
on the IBM Quantum platform, focusing on the
specifics of selecting a simulator or quantum com-
puter in graphical (IBM Quantum Composer) and
software (IBM Quantum Lab) modes.
The skill to perform quantum programs on quan-
tum computers should be formed starting with sim-
ple tasks on using quantum gates to change the
state of a quantum system. And then proceed to
implementation of quantum algorithms (Bernstein-
Vazirani, Deutsch-Jozsa, Grover, Shore).
When introducing the concept of “quantum gates”
(basic logical elements/operations for a quantum
computer), it is important to pay attention of students,
that the understanding of quantum gates is similar to
the understanding of gates (logical elements, opera-
tions) of a classical computer, and therefore it is nec-
essary to use the previous knowledge about logical
operations.
Students must learn that the same logical opera-
tions are performed on qubits in order to change their
state as on classic bits. It is necessary to consider
mathematical representation of each gate (in the form
of unitary matrix) and their graphical representation
and result of quantum scheme application at the same
time.
The interface of the IBM Quantum Composer
chromatically oriented service should be considered
in a mandatory order, focusing on the instrumental
panel of quantum operations, peculiarities of color
categorization of gates by type, adding, setting up
and disconnecting of quantum gates in the Quantum
Scheme Editor area, reviewing changes in the state of
qubits.
One should start from one-qubit quantum gates
as the simplest, and then go to two- and three-qubit
gates. At this stage, students’ attention is necessarily
focused on the result, which is reflected in the form
of the state vector. It is necessary to explain that the
received record of the state of qubits in the twofold
code is read from right to left. In our application, the
result obtained is 01: the zero qubit has a value of 1
and the first one is 0. If there is time, we can ask the
students to use a few more cubes on the diagram one
after another to observe the display of the results.
After familiarization with basic operations on
qubits you can move on to introduction of quantum
algorithms, starting with quantum teleportation algo-
rithm. First students are offered a verbal description
of the algorithm, then a graphical quantum circuit,
and after that a software implementation of the algo-
rithm.
Let us give a verbal description of the quantum
teleportation algorithm, which is described graph-
ically using the IBM Quantum Composer service,
shown in figure 5:
1) by means of the operation NOT we transfer the
zero qubit to state 1, and we leave the first and
second qubits in the primary zero state. It should
be noted that this operation is mandatory for this
example, only to avoid transferring the zero value
of the qubit. Indeed, the zero qubit
2) we put the first qubit into superposition by the gate
H;
3) we rotate the first and second qubits with the
CNOT gates (the first one is control and the sec-
ond one is purpose. If the control (first) qubit is in
state 1, the main (second) qubit is inverted by the
CNOT gate);
4) we will similarly loop the zero and first qubits;
5) convert the zero qubit to superposition (using gate
H);
6) measurement of the zero and the first qubits (Mea-
surement operation). The measurement results are
stored in two classic bits, which are transmitted by
the usual (classic, non-quantum) way of commu-
nication (channel, protocol);
7) on the side where the zero qubit status is transmit-
ted, there is another qubit to which CX and CZ
gates are used (either CX or CZ in turn does not
matter which will be the first), as a result we get
the value of zero qubit in the other qubit;
8) we measure the value of the other qubit.
After creating the algorithm for quantum telepor-
tation in IBM Quantum Composer, students should be
given the task of running this scheme with the help
of a simulator or a quantum computer and analyze
the results. At this point, it is appropriate to encour-
age students to focus on automatically generated code
in a programming language (e.g., Python). Students
should conclude that the resulting code is fully con-
sistent with the structure of the reverse language pro-
gram. It would be useful to make an analogy between
the graphical representation of the gates and their
equivalent – the corresponding command (method) in
programming language and open this scheme with au-
tomatically generated code in IBM Quantum Lab.
After acquiring knowledge about the basic quan-
tum gates, creating a quantum teleportation circuit,
Quantum Transformation of School Informatics
231
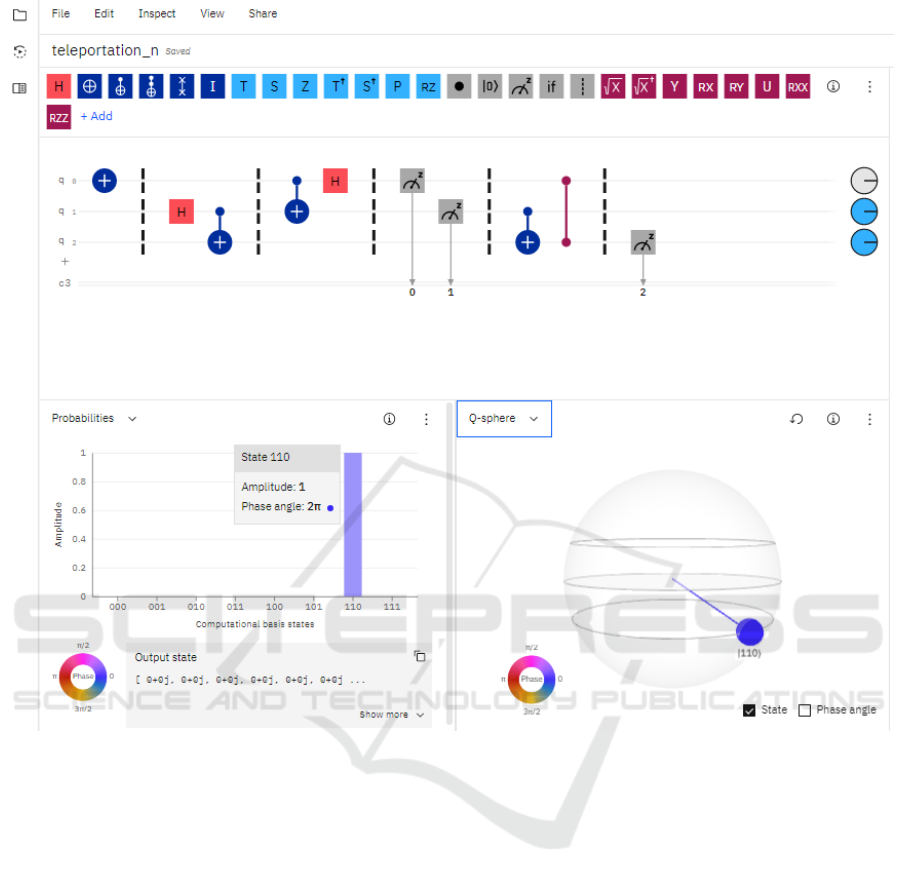
Figure 5: Quantum teleportation algorithm in IBM Quantum Composer
the students are ready to proceed to the next stage
of learning the basics of quantum informatics – to
implement quantum algorithms in programming lan-
guage, within the framework of which the forma-
tion of knowledge and skills to distinguish and use
quantum one-, two- and three-cube gates for the im-
plementation of quantum algorithms in programming
language (Python), use online programming services,
which support Python work with Qiskit module, for
the implementation of quantum algorithms on quan-
tum simulators and real quantum equipment.
The basic foundation for the teaching methodol-
ogy of this section is the knowledge of the basics of
classical (non-quantum) programming and the ability
to implement basic classical algorithms in program-
ming language.
This is a dedicated platform for working with
quantum algorithms (IBM Quantum) that provides
their implementation in Python language. Therefore,
it is methodologically appropriate to repeat the basics
of structural programming in Python.
Despite the lack of experience of students in the
implementation of Python programs with the help of
Jupyter Notebook, it is obvious, that before starting to
implement quantum algorithms using the IBM Quan-
tum Lab server it is necessary to familiarize students
with the peculiarities of their writing and launching,
for example, using the online service Google Colab
(https://colab.research.google.com/).
After implementing and launching the application
programs by means of the online service Google Co-
lab, it is advisable for the students to propose the au-
tomatically generated code for the implementation of
the quantum teleportation algorithm in IBM Quantum
Lab. It is necessary to ask the students: What is sim-
ilar in the interface of Google Colab and IBM Quan-
tum Lab online services? We make a joint conclusion
about the uniqueness of these environments and pro-
ceed to consider the features of the connection to the
quantum simulators and computers in IBM Quantum
AET 2021 - Myroslav I. Zhaldak Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
232

Lab on the requested code fragments.
It should be noted that after completing the con-
tent line “Quantum calculations, algorithmization and
programming” students will be able not only to learn
about the most popular algorithms of quantum pro-
gramming and try to learn how to implement them on
real quantum equipment, but also to improve compe-
tence in the basics of programming in Python.
Within the framework of the content line “Quan-
tum telecommunication technologies” the formation
of competencies in security technologies (optical
technologies, laboratory and experimental control
technologies, photon sources) and quantum commu-
nication technologies (quantum cryptography, quan-
tum networks, quantum communication infrastruc-
ture and equipment).
Formation of competences from the enabling tech-
nologies can be carried out in the form of short self-
prepared student reports on the topics suggested by
the teacher, or in the form of watching short popular
science stories that reflect the current state of devel-
opment of the field.
It is important for students to know about the
limitation of quantum communications. The teacher
states that the main limitations of quantum cryptog-
raphy are the speed of key distribution and the dis-
tance between the transmitter and the receiver. This
problem is trying to be solved by modern physicists
who have proposed new protocols, new optical cir-
cuits, new methods of quantum-state measurements.
It is also necessary to tell the students that an im-
portant task of quantum communication channel qual-
ity is to reduce the number of errors (the critical error
rate is 11%). Students should know that the greater
the distance over which a quantum key is transmitted,
the greater the attenuation of the signal in the fiber
optic lines, while the noise remains. Because of this,
it is not possible to transmit information for hundreds
of kilometers in real fiber optic lines.
It will be useful to remember the previously dis-
cussed phenomenon of decoherence (disintegration of
quantum state due to interaction of quantum system
with ambient environment). The teacher can describe
that photons after transmission through many kilome-
ters of real fiber optic lines in most cases cease to
be quantum entangled (connected) and transform into
usual, not interconnected, quanta of light. Therefore,
in order to produce efficient fiber optic line it is nec-
essary to ensure preservation of quantum entangle-
ment when the signal is weakened and when it passes
through an amplifier. Fibre optic cables laid at the
bottom of the oceans contain a number of special am-
plifiers based on optical warehouse of rare-earth ele-
ment houses, and these amplifiers make high quality
transmission of information possible.
It is worthwhile to find some examples of quantum
cryptography application spheres that would motivate
further study. It is worthwhile to make an example
that today world’s bank data centers have encryptors
that use symmetric keys. They are additionally com-
plemented by quantum distribution systems for keys,
which are changed not monthly (in the classical ap-
proach), but every second. On the one hand, this
mechanism is not good for the disposable notebook,
but on the other hand, it gives tremendous advantage.
You can ask students to use any search engine to
find information about the use of quantum technolo-
gies in the field of finance, for example, for the last
six months. If a sufficient number of students work,
the task can be refined by geographical location (on
certain continents, in certain countries, etc.).
It will be interesting for students to learn that
quantum cryptography can also be used for dis-
tributed data storage. It is possible to distribute in-
formation in several data centers and constantly move
it by means of quantum-secured channels. Thus, even
if someone gains access to some of these data centers,
he or she does not receive all of the necessary infor-
mation. This will also work if some of the data centers
are disconnected: a light user will be able, by authen-
ticating to the network of data centers, to restore all
relevant information.
We also inform the students that quantum keys
will be useful for securing authentication tasks,
which, in essence, is a check “friend-or-foe”. In this
case, the combination of hash function technologies
and a one-time notepad allows you to check if, for
example, the data for the online speech system came
from the control center or from someone else. This
is very important, because in five or seven years the
work of quantum computer is a reality. At the same
time on the streets will appear a large number of
driverless cars, which are not just a few, but will be
millions. And all of them will need to receive control
signals and update the firmware in a trusted manner,
not interacting with people for thousands of years.
This means that they will have to receive quantum
keys and use them afterwards in the process of flight.
Prospects of quantum cryptography can be de-
scribed by the application of China, which has already
established a national quantum network that connects
Beijing, Shanghai, Hefei and Jinan.
The main technological problem nowadays is
whether the humanity will be able to produce a high-
quality quantum repeater in the nearest ten years?
This question can be discussed by the scientists by
dividing them into supporters and opponents of this
idea.
Quantum Transformation of School Informatics
233

4 EXPERIMENTAL TESTING OF
METHODS FOR TEACHING
THE BASICS OF QUANTUM
INFORMATICS TO LYCEUMS
STUDENTS
Forty-five students from three schools in the city of
Kryvyi Rih (Ukraine) took part in the experiment. In
order to evaluate the level of competence in the fun-
damentals of quantum informatics the entrance exam-
ination and post-assessment test were conducted.
Positive dynamics of changes in the level of com-
petence was noted in each group of competencies,
which confirmed the study hypothesis.
As a result of the experiment the ways of intro-
duction of quantum informatics basics into the educa-
tional process of lyceums were determined:
1. choice module “The Basics of Quantum Informat-
ics” (17 hours);
2. cross-curricular study of quantum informatics
basics in physics, mathematics and informatics
courses (17 hours);
3. integrated course “The Basics of Quantum Infor-
matics” (35 hours).
Regardless of the choice of experimental model of
propaedeutic study of quantum informatics, the main
goal of its implementation is to develop the compo-
nents of computer literacy and information culture
through the acquisition of basic theoretical knowledge
and practical skills to manage quantum computers as
a new generation of computers.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Quantum transformation of school informatics course
should be carried out due to the perspective of
quantum technologies and the demand for quantum-
literate specialists.
The competences of quantum informatics basics
of lyceums students is a natural integration of some
interdisciplinary physical and mathematical compe-
tences and new subject-specific informatics compe-
tences.
The normative methods of teaching the basics
of quantum informatics to lyceum students is the
structural-functional model of forming the corre-
sponding competences.
Teaching the basics of quantum informatics to 10
(11) grades on the IBM Quantum platform can be car-
ried out with the author’s optional course materials.
This study does not cover all aspects of the prob-
lem of quantum transformation of informatics educa-
tion. Subsequent scientific searches for its solution
are appropriate in the following directions: 1) devel-
opment of partial methods of competence formation
in the field of quantum technologies in accordance
with the European framework; 2) integrated teaching
of quantum physics and informatics to students of sci-
entific lyceums; 3) use of immersive medium for de-
velopment of virtual manipulatives of quantum tech-
nologies; 4) teaching method development of the ba-
sics of quantum technologies to professional schools
students.
REFERENCES
Alibaba (2018). Quantum laboratory. https://damo.alibaba.
com/labs/quantum.
Bykov, V. Y. (2008). Modeli orhanizatsiinykh system vid-
krytoi osvity [Models of the open education organiza-
tional systems]. Atika, Kyiv. https://lib.iitta.gov.ua/
845/.
Chen, S. (2018). China building world’s biggest quantum
research facility. https://tinyurl.com/fftfa49a.
EDS (2019). Austria, Bulgaria, Denmark and Romania join
initiative to explore quantum communication for Eu-
rope. https://tinyurl.com/3xb2s3rc.
EQF (2021). Quantum Flagship. https://qt.eu/.
Gnatenko, K. (2020a). Kvantovi kompiutery: sohodennia
ta maibutnie [Quantum computers: the present and
the future]. Kolosok, (5):2–7. https://tinyurl.com/
yckuhxz3.
Gnatenko, K. (2020b). Neimovirne u kvantovomu sviti [The
unbelievable in a quantum world]. Kolosok, (4). https:
//tinyurl.com/sdvyzubw.
Google (2022). Educational resources. https://quantumai.
google/education.
Greinert, F. and M
¨
uller, R. (2021). Competence
Framework for Quantum Technology. Ver-
sion 1.0. https://qt.eu/app/uploads/2019/02/
Competence Framework for QT 1.0 May2021.pdf.
Hilton, J. (2019). Building The Quantum Work-
force Of The Future. https://www.forbes.
com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2019/06/19/
building-the-quantum-workforce-of-the-future.
Korshunova, O. and Zavadsky, I. (2018). Informatika
[Computer science]. Osvita, Kyiv.
Lehka, L. V. (2022). Metodyka navchannia osnov kvan-
tovoi informatyky uchniv litseiv [Methods of teach-
ing the basics of quantum informatics to lyceums stu-
dents]. The dissertation submitted for scientific degree
of doctor of philosophy) on specialty 014 secondary
education (informatics), Kryvyi Rih State Pedagogical
University. http://elibrary.kdpu.edu.ua/xmlui/handle/
123456789/7042.
Lehka, L. V., Bielinskyi, A. O., Shokaliuk, S. V., Soloviev,
V. N., Merzlykin, P. V., and Bohunenko, Y. Y. (2022a).
AET 2021 - Myroslav I. Zhaldak Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
234

Prospects of Quantum Informatics and the Study of
Its Basics in the School Course. In Semerikov,
S., Osadchyi, V., and Kuzminska, O., editors, Pro-
ceedings of the 1st Symposium on Advances in Ed-
ucational Technology - Vol. 1: AET, pages 233–
240. INSTICC, SciTePress. https://doi.org/10.5220/
0010922900003364.
Lehka, L. V. and Shokaliuk, S. V. (2018). Quantum pro-
gramming is a promising direction of IT develop-
ment. CEUR Workshop Proceedings, 2292:76–82.
http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2292/paper07.pdf.
Lehka, L. V. and Shokaliuk, S. V. (2021). Hardware and
software tools for teaching the basics of quantum in-
formatics to lyceums students. Educational Dimen-
sion, 4:102–121. https://doi.org/10.31812/educdim.
v56i4.4440.
Lehka, L. V., Shokaliuk, S. V., and Osadchyi, V. V. (2022b).
Hardware and software tools for teaching the basics of
quantum informatics to students of specialized (high)
schools. CTE Workshop Proceedings, 9:228–244.
https://doi.org/10.55056/cte.117.
NISS (2020). Analytical report to the annual Presidential
Address to the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine “On the
internal and external situation of Ukraine”. https://
niss.gov.ua/en/node/3797.
NQIA (2018). National Quantum Initiative Act.
https://www.congress.gov/bill/115th-congress/
house-bill/6227/text.
NSF (2020). Key concepts for future qis learn-
ers. https://files.webservices.illinois.edu/9156/
keyconceptsforfutureqislearners5-20.pdf.
NSM (2021). Nanoelektronika: nauka i sovremen-
nost [Nanoelectronics: science and moder-
nity]. https://youtube.com/playlist?list=
PLuKEIL5ZUv-Wt4DutmgVmddaHQPSpj6uX.
NSTI (2016). Gu
´
ow
`
uyu
`
an gu
¯
any
´
u y
`
ınf
¯
a “sh
´
ıs
¯
anw
ˇ
u” gu
´
oji
¯
a
k
¯
ej
`
ı chu
`
angx
¯
ın gu
¯
ıhu
`
a de t
¯
ongzh
¯
ı gu
´
o f
¯
a (2016) 43
h
`
ao [Circular of the state council on printing and dis-
tributing the national science and technology innova-
tion plan for the “13th five-year plan” guo fa [2016]
no. 43]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2016-08/
08/content 5098072.htm.
NUL-bachelor (2020). Osvitno-profesiina prohrama
bakalavra “kvantovi kompiutery ta kvantove prohra-
muvannia” [Quantum computers and quantum
programming. Educational and professional pro-
gram]. https://physics.lnu.edu.ua/wp-content/
uploads/OP bak kvant komp 2020.pdf.
NUL-master (2021). Osvitno-profesiina prohrama
mahistra “kvantovi kompiutery ta kvantove prohra-
muvannia” [Quantum computers and quantum
programming. Educational and professional pro-
gram]. https://physics.lnu.edu.ua/wp-content/
uploads/OP mag kvant comp 1.9 2021.pdf.
Panetta, K. (2021). 5 Trends Drive the Gartner Hype Cycle
for Emerging Technologies, 2020. https://tinyurl.com/
abp7aktd.
Pinkevych, I. P., Dmytruk, I. M., Yeshchenko, O. A.,
and Kravchenko, V. M. (2018). Osvitno-naukova
prohrama “kvantovi kompiutery, obchyslennia ta
informatsiia” na zdobuttia osvitnoho stupeniu:
mahistr za spetsialnistiu 104 “fizyka ta astronomiia”
[Quantum computers, calculations, information.
Educational and scientific program for obtaining a
master’s degree, specialty 104 “Physics and Astron-
omy”]. https://www.phys.univ.kiev.ua/wp-content/
uploads/2021/05/onp magistry kvant komp obch
inf last 03 12 2018.pdf.
Q12 (2023). About - National Q-12 Education Partnership.
https://q12education.org/about.
QC-IBM (2021). Educators program - IBM Quan-
tum. https://quantum-computing.ibm.com/programs/
educators.
QDKit-Microsoft (2023). Q# and the quantum de-
velopment kit. https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/
resources/development-kit/quantum-computing.
QM (2021). Kvantova mekhanika [Quantum me-
chanics]. https://youtube.com/playlist?list=
PLuKEIL5ZUv-WlkkZQb0DPPTmmgQLl6 By.
QTEdu (2022). Programs, Courses and Trainings - QTEdu.
https://qtedu.eu/programs-courses-and-trainings/
higher-education.
QTEduCSA (2021). Qt educational initiatives
in primary and secondary schools and pub-
lic outreach. https://drive.google.com/file/d/
14mt X2xA5smT3 kYZSiXqdWpevRlLY6W/view.
Semerikov, S. O., Teplytskyi, I. O., Soloviev, V. N., Hama-
niuk, V. A., Ponomareva, N. S., Kolgatin, O. H., Kol-
gatina, L. S., Byelyavtseva, T. V., Amelina, S. M., and
Tarasenko, R. O. (2021). Methodic quest: Reinventing
the system. Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
1840(1):012036. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/
1840/1/012036.
WS (2020). Future Skills for the 2020s. https:
//api.worldskills.org/resources/download/12832/
14248/15165?l=en.
Quantum Transformation of School Informatics
235
