
Cancer Detec-Lung Cancer Diagnosis Support System: First Insights
Nelson Faria
1
, Sofia Campelos
2
and Vítor Carvalho
1
1
2Ai - School of Technology, IPCA, Barcelos, Portugal
2
Pathology Laboratory, IPATIMUP - Institute of Pathology and Molecular Immunology, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal
Keywords: Lung Cancer, Digital Pathology, Deep Learning, Convolutional Neural Networks, Whole-Slide Imaging.
Abstract: Lung cancer is the type of cancer that causes most deaths worldwide and as sooner it is discovered as more
possibilities there are for the patient to be treated. An accurate histological classification of tumours is
essential for lung cancer diagnosis and adequate patient management. Whole-slide images (WSI) generated
from tissue samples can be analysed using Deep Learning techniques to assist pathologists. In this study it is
given an overview of the lung cancer exploring the different types of implementations undertaken until the
present. These methods show a two-step implementation in which the tasks consist primarily of the detection
of the tumour and after on the histologic classification of the tumour. To detect the neoplastic cells, the WSI
is split in patches, and then a convolutional neural network is applied to identify and generate a heatmap
highlighting the tumour regions. In the next step, features are extracted from the neoplasic regions and
submitted in a classifier to determine the histologic type of tumour present in each patch. Moreover, in this
paper, it is proposed a possible approach based on the literature review to surpass the limitations found in the
actual models, and with better performance and accuracy, that could be used as an aid in the pathological
diagnosis of the lung cancer.
1 INTRODUCTION
On a global scale, in 2020, lung cancer was the
malignant neoplasia that caused the highest number
of deaths and the second most common in terms of
new cases, appearing more frequently in older people
(Society, 2021; World Health Organization (WHO),
2021). The early detection of the lung cancer is
crucial to reduce the death risk. In the initial
evaluation of a possible lung cancer, several imaging
and surgical procedures are needed such as chest X-
ray, computed tomography (CT), positron emission
tomography (PET), magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI), bronchoscopy, transthoracic needle biopsy
(TNB), fine needle aspiration (FNA),
mediastinoscopy, and endobronchial ultrasound-
guided needle aspiration. The radiologic detection of
a suspected tumour nodule must be followed by a
confirmatory pathologic diagnosis usually made on
small biopsy and cytology samples (Keith, 2020).
When the used methods for diagnosis are in the
radiology scope such as CT, several computer-aided
design (CAD) systems are being tested using a four
steps approach: lung segmentation, nodule detection,
nodule segmentation and nodule diagnosis (El-Baz et
al., 2013). Within the Pathology field, the
microscopic glass slides can be directly observed by
a pathologist on a brightfield microscope, or they can
be scanned to produce digital slides (whole slide
images-WSI). With the evolution of technology, the
computerized image processing has shown that can be
a helper in decision support to histopathological
evaluations but, at the moment, the studies for lung
cancer diagnosis using microscopic images are very
premature (Yu et al., 2016).
This paper aims to carry out a literature review
and it is organized in 4 chapters. In the second
chapter, Literature Review, it starts briefly with the
physiopathology of lung cancer and it is focused on
the lung biopsy since the histopathological
examination is the gold standard for the diagnosis of
cancer (Aeffner et al., 2017). Then, it will be explored
the image processing techniques applied so far to
microscopy images of biopsy tissue samples being
followed by the analysis of the application of artificial
intelligence to the diagnosis of lung cancer. After
that, in chapter three, Proposed Approach, it is
described a strategy to implement a system to
effectively detect and classify the lung cancer in its
two most frequent subtypes. Finally, in chapter 4,
Faria, N., Campelos, S. and Carvalho, V.
Cancer Detec-Lung Cancer Diagnosis Support System: First Insights.
DOI: 10.5220/0010767800003123
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022) - Volume 3: BIOINFORMATICS, pages 81-88
ISBN: 978-989-758-552-4; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
81

Final Remarks, are presented the main conclusions
and described the next project steps.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter is organized in two sections: lung cancer
etiology, classification and detection methodologies,
and artificial intelligence applied to lung cancer.
2.1 Lung Cancer: Etiology,
Classification and Detection
Methodologies
According to the WHO, the lung cancer remains the
main cause of deaths in the world and, every year, the
number of deaths is increasing mostly due to smoking
(World Health Organization, 2021). In Portugal, as
globally, this continues to be the biggest cause of
death and the third on the list of new cancer cases with
a number of 5284 cases per year, being responsible
for 20% of deaths by cancer (CUF, 2017; The Global
Cancer Observatory, 2020). Lung cancer is originated
in the lungs but, worryingly, can metastasize to other
organs in the body and normally appears after the fifth
decade (Nasim et al., 2019). The main cause of this
neoplasia is smoking, but other risk factors have been
described such as previous respiratory diseases,
exposure to occupational carcinogens (arsenic,
asbestos, chromium, nickel, and radon), polycyclic
aromatic hydrocarbons, human immunodeficiency,
virus infection, and alcohol consumption (Bade &
Dela Cruz, 2020; Duma et al., 2019).
Most lung cancers are carcinomas, and the most
frequent histological subtypes are adenocarcinoma
(ADC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), large cell
carcinoma (LCC) and small cell lung carcinoma
(SCLC). Historically, carcinomas of the lung were
divided into two large groups: SCLC and NSCLC
because there were no therapeutic implications in a
more specific subdivision. However, the
developments in recent years, such as the discovery
of specific mutations in different subtypes of NSCLC,
make the histological classification of the tumour
subtype essential for therapeutic guidance (Board,
2021; Collins et al., 2007; Duma et al., 2019; Goebel
et al., 2019). Usually, the SCLC is detected in
smokers and represents 12% to 15% of lung cancer
cases. In the SCLC, the tumour has a quicker growth,
it is aggressive and expands earlier to other body parts
(Pulmão, 2017). The NSCLC is responsible for more
than 85% of lung cancer cases and the two more
frequent subtypes are the ADC and SCC. The ADC is
more common in non-smokers and arises from
alveolar cells located in the smaller airway epithelium
(Duma et al., 2019).
The current methodologies to detect the lung
cancer are chest X-ray, computed tomography (CT),
positron emission tomography (PET), magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI), bronchoscopy,
transthoracic needle biopsy (TNB), fine needle
aspiration (FNA), mediastinoscopy, and
endobronchial ultrasound-guided needle aspiration.
However, in more than 50% of the new cases, the
patients are diagnosed when the tumour has already
metastasized to different parts of the body. The
reasons of late detection could be the lack of
symptoms at early-stage, incorrect diagnosis of the
symptoms such as cough and wheezing as well as
limited economic situation to access the detection
methods of last generation. In fact, the detection of
lung cancer in an early stage is extremely important
because as sooner it is detected as greater are the
chances of effective treatment and survival (El-Baz et
al., 2013; Goebel et al., 2019).
The gold standard for lung cancer diagnosis is the
histopathological examination. The material
available for pathological diagnosis (histological or
cytological biopsies) is very scarce and the growing
need for additional studies, such as
immunohistochemistry and molecular studies, makes
the careful management of the available samples
essential for a complete and accurate diagnosis.
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues
from histologic biopsies are processed to originate
glass slides routinely stained by hematoxylin and
eosin (H&E stain) which is the most used stain for
light microscopy, since it is simple to use and
contains the ability to demonstrate a wide range of
both normal and abnormal cell and tissue
components. These glass slides can then be directly
observed on a brightfield microscope, or they can be
scanned to produce digital slides, and a morphologic
diagnose will be made by the pathologist. Additional
special techniques are frequently used, such as
immunohistochemistry, for a more accurate diagnosis
on the specific subtypes (Kleczek et al., 2020). The
capacity to extract a high-resolution digital scan from
a microscopic slide has become known as digital
pathology which are named as WSI (Hanna et al.,
2020). The acquired images can be in two dimensions
or z-stacks, and each one may contain up to forty
gigabytes of uncompressed data (Bankhead et al.,
2017). From WSI, it is possible to count, measure
sizes and density of the present objects, and apply
algorithms of image processing to detect lesions or
cancer (Bioscience, 2017). An example of a WSI is
BIOINFORMATICS 2022 - 13th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
82
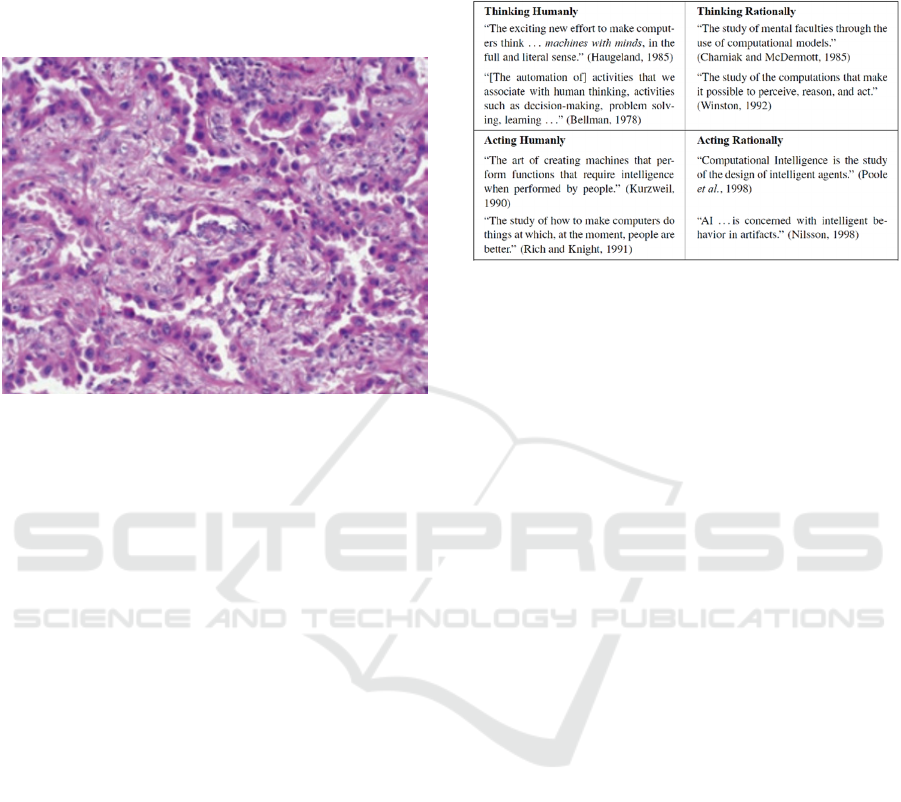
shown in figure 1 (adapted from (Pavlisko & Roggli,
2020)).
2.2 Artificial Intelligence Applied to
Lung Cancer
Figure 1: Demonstration of a WSI of an adenocarcinoma
stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) [original
magnification ×200] (adapted from (Pavlisko & Roggli,
2020)).
Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques are
increasing its presence in our daily lives, whether in
the autonomous driving, processing large amounts of
data in real-time, personalized advertisements,
detecting fraud and diseases such as breast cancer
(Helm et al., 2020).
Over the years, several definitions have emerged
to describe the term AI. The different definitions can
be organized into four perspectives: “Thinking
Humanly”, “Thinking Rationally”, “Acting
Humanly” and “Acting Rationally” (Figure 2).
"Thinking Humanly" states that a system understands
how humans think, however, obtaining one correct
answer from an algorithm does not guarantee that it is
simulating human thinking as there is great difficulty
in defining the model of the human thinking.
“Thinking Rationally” intends to solve problems and
create models of thought processes but it has
obstacles such as the difficulty in defining informal
knowledge using logical notation and the difference
between solving a theoretical and practical problem.
The idea of "Acting Humanly" is to find an
operational way to define intelligence and ensure a
human-level performance in all cognitive tasks,
however, it has as constraints the inability to learn or
deal with new situations and be focused on the
behavior. “Acting Rationally” maximizes the
expectation of reaching the desired goals based on the
available information and the rational behavior
involves taking the correct decision with an implicit
rational decision (Russell & Norvig, 2021).
Figure 2: Definitions of AI to the four categories (Russell
& Norvig, 2021).
AI encompasses Machine Learning (ML) and
Deep Learning (DL) which are composed of AI
algorithms that are implemented in systems to make
predictions, rankings based on input data, image
analysis, and decision making (Greenfield, 2019;
Russell & Norvig, 2021).
In the Medicine field, with the increase amount of
data generated by clinical systems and computational
capacity, the use of artificial intelligence is being
enhanced with the aim of benefiting patients and
physicians by making diagnosis simpler (Greenfield,
2019). Specifically, for cancer detection, the most
common field of AI used is the DL, which consists in
deep neural networks that have several layers that are
refined as the system responds to a specific type of
problem. Like the human brain, they create
"neuronal" connections from "dendritic" connections
at various levels of hierarchical data (Helm et al.,
2020). Nowadays, the most used type of network to
perform image data analysis, such as tumor detection
in the pathology images of breast cancer, is the
convolutional neural network (CNN) (D. Wang et al.,
2016).
The early detection of lung cancer plays an
important role since it can determine the survival of
the patient. The application of an artificial
intelligence methodology in the diagnosis process can
help the pathologist to reduce the time detecting and
classifying the tumour, obtain more accurate results,
making possible to move faster to the final diagnosis.
Usually, the process to diagnose lung cancer is
performed in two parts: Detection and Classification.
In figure 3 is shown the process used by Wang and
his team to detect and classify the lung cancer (Xi
Wang et al., 2020). The studies mentioned next had
Cancer Detec-Lung Cancer Diagnosis Support System: First Insights
83
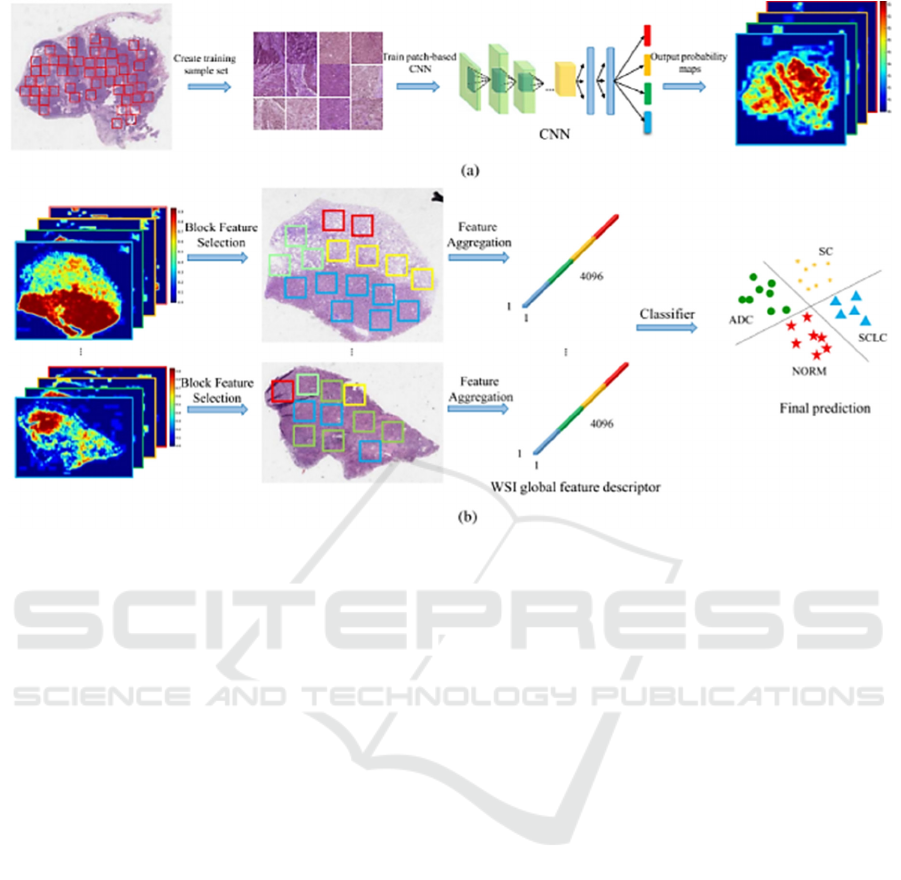
Figure 3: The process for the lung cancer detection. “(a) Discriminative patch prediction. A patch-based CNN is used to find
discriminative regions. (b) Context-aware feature selection and aggregation. By imposing spatial constraint, features from
discriminative blocks are selected and aggregated for the WSI classification” (Xi Wang et al., 2020).
as main task the detection of the tumour present in the
evaluated sample and determinate if it is malignant or
non-malignant.
After a pathologist has manually labelled the
Regions of Interest (ROI), Wang et al. developed a
CNN model to analyse ADC WSIs. To train and test,
they extracted 267 images from the National Lung
Screening Trial (NLST) dataset and 457 images from
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset. This
model segments the haematoxylin and eosin (H&E)
images, by classifying each pixel as nucleus centroid,
non-nucleus, or nucleus boundary. The authors
applied a sliding window in patches of 300 by 300
pixels in the WSI, generating a heatmap to detect the
tumour regions. Spatial distribution in the tumour
microenvironment, nuclear morphology and textural
features were extracted and used as predictors in a
recurrent prediction model (S. Wang et al., 2019;
Xiangxue Wang et al., 2017). This approach
facilitates the detection of the tumour and the study of
its distribution, shape, and boundary features (S.
Wang et al., 2018). The result of the classification
accuracy obtained in the testing set was 89.8%.
Li and team divided the WSI with objective
magnifications of 20 times into 256-pixel-by-256-
pixel portions, cropping them with a stride of 196
pixels, to ensure sufficient overlapping between
adjacent patches. Then, they compared the
performance between different CNNs, being them
AlexNet (Krizhevsky et al., 2017), VGG (Chatfield et
al., 2014), ResNet (He et al., 2016) and SqueezeNet
(Iandola et al., 2016). To test the CNNs, they applied
two different training schemas, which were training
from scratch and pre-trained networks. They recruited
33 lung patients to test the efficiency of their method,
having as result a better accuracy using AlexNet in
training from scratch strategy (97%) and the ResNet
in pre-trained networks (93%). However, the number
of samples used is lower than the used by Wang and
this is a point to take into account (Li et al., 2018).
According to the study of Yu and team, they
followed the same steps as the authors above, that is,
divided the WSI into tiles with 1000 by 1000 pixels,
with a 50% overlap to avoid crop losses, evaluating
the AlexNet (Krizhevsky et al., 2017), GoogLeNet
(Szegedy et al., 2015), VGG (Chatfield et al., 2014)
and ResNet (He et al., 2016) networks that were fine-
tuned from pretrained ImageNet classification
models (Yu et al., 2020). They processed WSIs of
ADC and SCC from TCGA, resulting in an accuracy
of 93.5%. (Yu et al., 2020). Also, Coundray trained a
CNN where the 1635 slides (ADC, non-malignant
and SCC) extracted from the TCGA dataset were tiled
by non-overlapping 512 x 512 pixels patches,
BIOINFORMATICS 2022 - 13th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
84

resulting in a accuracy of 87% for the biopsies
(Coudray et al., 2018).
One relevant limitation for the implementations
done by most of the authors is that they required a
pathologist to do annotations in the patches in order
to get a better result. To overcome this constraint,
Chen and team created a technique to train standard
CNNs with WSIs as inputs, that is, without dividing
the input image or feature maps into patches.
Although, the authors pointed as a limitation the used
memory in the host to process images larger than
20,000 x 20,000 pixels. To address this problem, they
suggested first use a magnification of x4 to locate
important regions and then x40 images of those
regions for the final image recognition task (Chen et
al., 2021). The result of accuracy for ADC and SCC
WSIs is nearly 93%.
When the heatmaps are already generated from
the WSI, it is possible to extract features like
distribution, shape, and boundary features to be
analysed and classified by applying morphological
operations as erosion and dilation (S. Wang et al.,
2018). To those extracted features, it is possible to use
models on them to classify the lung cancer type such
as an ADC, non-malignant or small cell lung cancer.
In the study of Wang and team, they selected the
features that were significantly associated with
survival outcomes and used an univariate Cox
proportional hazard model with a penalty to avoid
overfitting (S. Wang et al., 2018). As aim to classify
the types of the tumour, Yu and colleagues applied
Naive Bayes classifiers (Friedman et al., 1997),
Support Vector Machines (SVM) with Gaussian,
linear, and polynomial kernels (Cortes & Vapnik,
1995), bagging, random forest with conditional
inference trees (Strobl et al., 2008) and Breiman’s
random forest (Liaw & Wiener, 2002). These
algorithms received as input the extracted features
from whole-slide histopathology images of ADC and
SCC received from TCGA and give as output the
predicted diagnosis groups in which SVM with
Gaussian kernel, random forest utilizing conditional
inference trees, and Breiman’s random forest were
the best algorithms obtained an approximate accuracy
of 85% (Yu et al., 2016).
3 PROPOSED APPROACH
After reviewing the literature, it was possible to
identify the limitation of the majority of different
models that are the need of a pathologist to label the
WSIs or the patches. One of the main goals of this
work is to identify and locate the presence of
carcinoma on each sample in order to help the
pathologist saving time and proceed faster to the
following required techniques needed for final
diagnosis.
Following the authors approach and as shown in
figure 4, this work will split the process in two phases:
Figure 4: Diagram of the proposed approach to detect and classify the Lung Cancer according to a given WSI.
Cancer Detec-Lung Cancer Diagnosis Support System: First Insights
85

1) Image Processing and Tumours Detection, and 2)
Classification of the Lung Cancer type. For the Image
Processing step it will be used a pretrained neural
network such as ResNet since it will facilitate the
detection and the generation of the heatmap for an
image. Since the technology is evolving, the WSI will
be segmented in patches of 512 by 512 pixels. Then,
features like shape, color and perimeter will be
extracted from the highlighted regions and analyzed
by a SVM algorithm. In order to train, test and
validate the implementation, data sets of
histopathological images without or with few
annotations from repositories like Digital Pathology
Association (DIGITAL PATHOLOGY
ASSOCIATION, 2020) and Genomic Data
Commons Data Portal (GDC, n.d.) will be used.
4 FINAL REMARKS
In this paper, studies applied to histopathological
images using artificial intelligence were reviewed and
it was observed the implementation of deep learning
neural networks that are giving satisfactory results for
the tumour detection and lung cancer type
classification tasks. However, one limitation is that
there are no annotated datasets with size and breadth
of scenarios large enough to be able to develop
algorithms with such high performance that they can
be validated for clinical use. Also, this paper proposes
a high-level approach based on the available studies,
but with the aim of assisting the pathologist in the first
morphological approach to the lesion in order to
optimize the diagnostic process. In this proposed
implementation, the WSI is transformed into patches
and a neural network is applied to the generated
heatmap that contains all the tumour regions
highlighted. After that, features are extracted to a
classifier that, according to the feature’s information,
will indicate to the pathologist the presence of lung
carcinoma and its subtype. Further steps will include,
among others, a deep analysis of the AI
methodologies applied and the development of
algorithms to evaluate the presence/non presence of
tumour in the analysed images.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank to the National Lung
Screening Trial, The Cancer Genome Atlas and the
Genomic Data Commons Data Portal for the lung
cancer datasets availability and to FCT – Fundação
para a Ciência e Tecnologia and FCT/MCTES in the
scope of the project UIDB/05549/2020 for funding.
REFERENCES
Aeffner, F., Wilson, K., Martin, N. T., Black, J. C.,
Hendriks, C. L. L., Bolon, B., Rudmann, D. G.,
Gianani, R., Koegler, S. R., Krueger, J., & Young, G.
D. (2017). The gold standard paradox in digital image
analysis: Manual versus automated scoring as ground
truth. In Archives of Pathology and Laboratory
Medicine (Vol. 141, Issue 9, pp. 1267–1275). College
of American Pathologists. https://doi.org/
10.5858/arpa.2016-0386-RA
Bade, B. C., & Dela Cruz, C. S. (2020). Lung Cancer 2020:
Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. In Clinics in
Chest Medicine (Vol. 41, Issue 1, pp. 1–24). W.B.
Saunders. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ccm.2019.10.001
Bankhead, P., Loughrey, M. B., Fernández, J. A.,
Dombrowski, Y., McArt, D. G., Dunne, P. D.,
McQuaid, S., Gray, R. T., Murray, L. J., Coleman, H.
G., James, J. A., Salto-Tellez, M., & Hamilton, P. W.
(2017). QuPath: Open source software for digital
pathology image analysis. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1–7.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17204-5
Bioscience, M. (2017). Whole Slide Imaging | MBF
Bioscience. Bioscience, Whole Slide Imaging | MBF.
https://www.mbfbioscience.com/whole-slide-imaging
Board, W.C. of T.E. (2021). THORACIC TUMOURS (W.
H. Organization (ed.); 5th ed., Vol. 5). World Health
Organization.
Chatfield, K., Simonyan, K., Vedaldi, A., & Zisserman, A.
(2014). Return of the Devil in the Details: Delving Deep
into Convolutional Nets. BMVC 2014 - Proceedings of
the British Machine Vision Conference 2014. http://
arxiv.org/abs/1405.3531
Chen, C. L., Chen, C.C., Yu, W. H., Chen, S.H., Chang, Y.
C., Hsu, T. I., Hsiao, M., Yeh, C. Y., & Chen, C.Y.
(2021). An annotation-free whole-slide training
approach to pathological classification of lung cancer
types using deep learning. Nature Communications,
12(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-
21467-y
Collins, L. G., Haines, C., Perkel, R., & Enck, R. E. (2007).
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis and Management. http://
familydoctor.org/161.xml.
Cortes, C., & Vapnik, V. (1995). Support-vector networks.
Machine Learning, 20(3), 273–297. https://
doi.org/10.1007/bf00994018
Coudray, N., Ocampo, P. S., Sakellaropoulos, T., Narula,
N., Snuderl, M., Fenyö, D., Moreira, A. L., Razavian,
N., & Tsirigos, A. (2018). Classification and mutation
prediction from non–small cell lung cancer
histopathology images using deep learning. Nature
Medicine, 24(10), 1559–1567. https://doi.org/
10.1038/s4 1591-018-0177-5
CUF. (2017). Cancro do pulmão| CUF. https://www
.cuf.pt/saude-a-z/cancro-do-pulmao (in Portuguese)
BIOINFORMATICS 2022 - 13th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
86

DIGITAL PATHOLOGY ASSOCIATION. (2020). Whole
Slide Imaging Repository. https://digitalpatholo
gyassociation.org/whole-slide-i maging-repository
Duma, N., Santana-Davila, R., & Molina, J. R. (2019).
Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Epidemiology,
Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Mayo Clinic
Proceedings, 94(8), 1623–1640. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.may ocp.2019.01.013
El-Baz, A., Beache, G. M., Gimel’Farb, G., Suzuki, K.,
Okada, K., Elnakib, A., Soliman, A., & Abdollahi, B.
(2013). Computer-aided diagnosis systems for lung
cancer: Challenges and methodologies. In International
Journal of Biomedical Imaging (Vol. 2013). https://doi.
org/10.1155/2013/942353
Friedman, N., Geiger, D., & Goldszmidt, M. (1997).
Bayesian Network Classifiers. Machine Learning,
29(2–3), 131–163. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:100746
5528199
GDC. (n.d.). Retrieved July 10, 2021, from
https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/
Goebel, C., Louden, C. L., McKenna, R., Onugha, O.,
Wachtel, A., & Long, T. (2019). Diagnosis of Non-
small Cell Lung Cancer for Early Stage Asymptomatic
Patients. Cancer Genomics and Proteomics, 16(4),
229–244. https://doi.org/10. 21873/cgp.20128
Greenfield, D. (2019). Artificial Intelligence in Medicine:
Applications, implications, and limitations - Science in
the News. https://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2019/
artificial-intelligence-in-medicine-applications-implica
tions-and-limitations/?web=1&wdLOR=c5DCD23 86-
04EB-463E-86FD-48BACB362747
Hanna, M. G., Parwani, A., & Sirintrapun, S. J. (2020).
Whole Slide Imaging: Technology and Applications. In
Advances in Anatomic Pathology (Vol. 27, Issue 4, pp.
251–259). Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. https://
doi.org/10.1097/PAP.0000000000000273
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual
learning for image recognition. Proceedings of the
IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition, 2016-Decem, 770–778. https://
doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Helm, J. M., Swiergosz, A. M., Haeberle, H. S., Karnuta, J.
M., Schaffer, J. L., Krebs, V. E., Spitzer, A. I., &
Ramkumar, P. N. (2020). Machine Learning and
Artificial Intelligence: Definitions, Applications, and
Future Directions. In Current Reviews in
Musculoskeletal Medicine (Vol. 13, Issue 1, pp. 69–76).
Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-020-09600-8
Iandola, F. N., Han, S., Moskewicz, M. W., Ashraf, K.,
Dally, W. J., & Keutzer, K. (2016). SqueezeNet:
AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and
<0.5MB model size. http://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07360
Keith, R. L. (2020). Lung Carcinoma.
https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/pulmona
ry-disorders/tumors-of-the-lungs/lung-carcinoma
Kleczek, P., Jaworek-Korjakowska, J., & Gorgon, M.
(2020). A novel method for tissue segmentation in high-
resolution H&E-stained histopathological whole-slide
images. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics
,
79, 101686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag
.2019.101686
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Hinton, G. E. (2017).
ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural
networks. Communications of the ACM, 60(6), 84–90.
https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
Li, Z., Hu, Z., Xu, J., Tan, T., Chen, H., Duan, Z., Liu, P.,
Tang, J., Cai, G., Ouyang, Q., Tang, Y., Litjens, G., &
Li, Q. (2018). Computer-aided diagnosis of lung
carcinoma using deep learning - a pilot study.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1803.05471
Liaw, A., & Wiener, M. (2002). Classification and
Regression by randomForest. R News, 2(3), 18–22.
http://www.stat.berkeley.edu/
Nasim, F., Sabath, B. F., & Eapen, G. A. (2019). Lung
Cancer. In Medical Clinics of North America (Vol. 103,
Issue 3, pp. 463–473). W.B. Saunders. https://
doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2018.12.006
Pavlisko, E. N., & Roggli, V. L. (2020). Lung cancer:
Clinical findings, pathology, and exposure assessment.
In Occupational Cancers (pp. 205–226). Springer
International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-
3-030-30766-0_10
Pulmão, F. P. do. (2017). Que tipo de tumor é?
https://www.fundacaoportuguesadopulmao.org/apoio-
ao-doente/cancro-do-pulmao/que-tipo-de-tumor-e/?sba
ck#462
Russell, S., & Norvig, P. (2021). Artificial intelligence: a
modern approach (4 (Ed.)).
Society, A. C. (2021). Key Statistics for Lung Cancer.
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/about/key-
statistics.html
Strobl, C., Boulesteix, A. L., Kneib, T., Augustin, T., &
Zeileis, A. (2008). Conditional variable importance for
random forests. BMC Bioinformatics, 9(1), 1–11.
https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-307
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S.,
Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Vanhoucke, V., & Rabinovich,
A. (2015). Going deeper with convolutions. Proceedings
of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, 07-12-June, 1–9.
https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594
The Global Cancer Observatory. (2020). Portugal Source:
Globocan Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence by
cancer site.
Wang, D., Khosla, A., Gargeya, R., Irshad, H., Beck, A. H.,
& Israel, B. (2016). Deep Learning for Identifying
Metastatic Breast Cancer. https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.
05718v1
Wang, S., Chen, A., Yang, L., Cai, L., Xie, Y., Fujimoto, J.,
Gazdar, A., & Xiao, G. (2018). Comprehensive analysis
of lung cancer pathology images to discover tumor
shape and boundary features that predict survival
outcome. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 1–9. https://
doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27707-4
Wang, S., Wang, T., Yang, L., Yang, D. M., Fujimoto, J.,
Yi, F., Luo, X., Yang, Y., Yao, B., Lin, S. Y., Moran,
C., Kalhor, N., Weissferdt, A., Minna, J., Xie, Y.,
Wistuba, I. I., Mao, Y., & Xiao, G. (2019). ConvPath:
A software tool for lung adenocarcinoma digital
Cancer Detec-Lung Cancer Diagnosis Support System: First Insights
87

pathological image analysis aided by a convolutional
neural network. EBioMedicine, 50, 103–110. https://
doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.10.033
Wang, Xi, Chen, H., Gan, C., Lin, H., Dou, Q., Tsougenis,
E., Huang, Q., Cai, M., & Heng, P. A. (2020). Weakly
Supervised Deep Learning for Whole Slide Lung
Cancer Image Analysis. IEEE Transactions on
Cybernetics, 50(9), 3950–3962. https://doi.org/
10.1109/TCYB.2019.2935141
Wang, Xiangxue, Janowczyk, A., Zhou, Y., Thawani, R.,
Fu, P., Schalper, K., Velcheti, V., & Madabhushi, A.
(2017). Prediction of recurrence in early stage non-
small cell lung cancer using computer extracted nuclear
features from digital H&E images. Scientific Reports,
7(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13773-7
World Health Organization. (2021). Cancer. https://
www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer
Yu, K. H., Wang, F., Berry, G. J., Ré, C., Altman, R. B.,
Snyder, M., & Kohane, I. S. (2020). Classifying non-
small cell lung cancer types and transcriptomic
subtypes using convolutional neural networks. Journal
of the American Medical Informatics Association,
27(5), 757–769. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocz230
Yu, K. H., Zhang, C., Berry, G. J., Altman, R. B., Ré, C.,
Rubin, D. L., & Snyder, M. (2016). Predicting non-
small cell lung cancer prognosis by fully automated
microscopic pathology image features. Nature
Communications, 7(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/
ncomms12474
BIOINFORMATICS 2022 - 13th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
88
