
Machine Learning-based Approach for Stroke Classification using
Electroencephalogram (EEG) Signals
Aktham Sawan
1,2 a
, Mohammed Awad
1 b
and Radwan Qasrawi
2,3 c
1
Department of Computer Systems Engineering, Arab American University, Ramallah, Palestine
2
Department of Computer Science, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, Palestine
3
Department of Computer Engineering, Istinye University, 34010, Istanbul, Turkey
Keywords:
Stroke, Electroencephalogram (EEG), Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), Muse 2, Wearable
Devices, Wavelet Transformation, Fourier Transformation.
Abstract:
In recent years, the health care field has heavily relied on the field of computation. The medical decision
support system DSS, for instance, helps health professionals obtain accurate and reliable readings and diag-
nosis of patients’ vital signs. Nowadays, several medical devices allow capturing brain signals, some of these
devices are wearable, which enhances signal quality and facilitates access to the signals than the traditional
EEG devices. EEG signals are critical for assessing mental health and analyzing brain characteristics as they
are able to detect a wide range of nerve-related diseases, such as stroke. This research seeks to study the
use of machine learning techniques for the medical diagnosis of stroke through EEG signals obtained from
the wearable device ‘MUSE 2.’ Eight ML techniques were used for analysis, the XGboost classifiers outper-
formed other classifiers in identifying strokes with an accuracy rate of 83.89%. The findings proved a 7.89%
improvement on accuracy from the previous study “Predicting stroke severity with a 3-minute recording from
the Muse portable EEG study.
1 INTRODUCTION
Every year, 15 million people worldwide suffer from
a stroke, 5 million die as a result, and another 5 mil-
lion are permanently disabled (Persky et al., 2010).
Significantly improving stroke classification at its
early stages could radically enhance the quality of life
of patients who are unable to be successfully treated
using conventional therapeutic methods. Patients who
are diagnosed with ischemic stroke before the stroke
causes real damage to their brain tissues have a higher
recovery rate, and a lower chance of death given early
treatment by medical professionals or first respon-
dents. Thus, pre-hospital diagnosis of such a condi-
tion, whether at the patient’s home or in the ambu-
lance, could save their life or enhance their life qual-
ity.
For this reason, this study seeks to find a more
efficient and accessible solution directly found either
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2840-6024
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5053-0785
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8758-1420
at the patient’s home or accessible to first responders
on the ambulance. A promising solution to be ex-
plored is the use of electroencephalography (EEG)
wearable devices, and the subsequent employment of
machine learning (ML) approaches for stroke classifi-
cation. We expect the employment of such solution to
achieve greater precision than the traditional methods
(Wilkinson et al., 2020a).
Currently, Computed Tomography (CT) and Mag-
netic resonance imaging (MRI) are used to diag-
nose hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke by providing a
comprehensive analysis of the brain’s anatomy and
pathology. However, findings indicate that strokes
can be accurately diagnosed between 6 to 8 hours
prior to the stroke by using CT. On the other hand,
while MRI imaging is more accurate and may diag-
nose stroke within 30 minutes, it is less available and
may require a longer period of time, even in a major
medical center (Cillessen et al., 1994; Jordan, 2004;
Murri et al., 1998).
Over the last century, the use of non-invasive
structural imaging methods, such as EEG, has grown
from mainly scholarly to more industrial use. Docu-
Sawan, A., Awad, M. and Qasrawi, R.
Machine Learning-based Approach for Stroke Classification using Electroencephalogram (EEG) Signals.
DOI: 10.5220/0010774200003123
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022) - Volume 1: BIODEVICES, pages 111-117
ISBN: 978-989-758-552-4; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
111

mented brain impulses from EEG are translated and
related to the cognitive activity by scientists to ob-
tain a deeper insight into the functioning of the hu-
man brain. Broadly speaking, clinical Nero imag-
ing instruments are most widely used in clinical re-
search, involving high-fidelity accuracy and sophisti-
cated features (Soltanian-Zadeh, 2019).One of these
devices is the MUSE 2 portable device, which mon-
itors EEG signals at a sampling frequency of 256
Hz(Ho et al., 2017).
Through enhancing stroke classification with the
MUSE 2 device by using ML algorithms, this paper
provides the following contributions:
• A novel approach was used to classify the stroke,
which included using the frequency of brain
waves on each electrode and applying it to all fea-
tures through feature selection, which contributed
to improving the accuracy of our model.
• Extensive testing was done to put classic and ad-
vanced ML techniques to the test in order to find
a good classifier for the task at hand.
This paper is divided into five sections, one of
which is the current introduction: Section 2 includes
a synopsis of related works. Section 3 discusses
and clarifies the background. Section 4 contains the
methodology. Section 5 contains the results of stroke
classification using the ML classifiers. Finally, Sec-
tion 6 summarizes the work done in this study as well
as the future work.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Several studies have been conducted in the field of
EEG signal analysis for stroke detection using the
Muse 2 portable device. The authors in (Wilkinson
et al., 2020b) showed the use of portable EEG as a
pre-hospital stroke diagnostic process. They used a
portable EEG machine to record data from 25 sub-
jects, 16 had acute ischemic stroke cases and corre-
lated the outcomes with accuracy controls which in-
cluded stroke imitates. In(Gottlibe et al., 2020) ),
the authors examined whether a short recording us-
ing a portable EEG device would differentiate be-
tween control and stroke classes. Data was obtained
from patients with acute ischemic stroke. The mon-
itoring group consisted of balanced volunteers. EEG
recordings were obtained using a handheld brain wave
monitor. The Updated Brain Symmetry Index (pdBSI
) was used to measure the spectral energy similar-
ity between the cerebral sides. Authors in (Djamal
et al., 2020) used a MUSE 2 portable EEG system to
record information for 25 participants, 16 of whom
had sever ischemic stroke cases. The findings indi-
cated an improvement in ischemic stroke-related pa-
tients with serious (p¡0.01).This study will focus on
accurately classifying strokes using an enhanced ma-
chine learning algorithm and MUSE2 to read EEG
signals. Diagnosis will then be provided to the nurs-
ing or ER team.
3 BACKGROUND
3.1 ML Classifier
A variety of machine learning classifiers were used to
conduct the analysis:
• A Random Forest: (RF)classifier is a form of
ensemble classifier that generates numerous de-
cision trees using a random selection of training
variables and data. This classifier has gained pop-
ularity in the field of remote sensing due to the
accuracy of its classifications (Belgiu and Dr
˘
agut¸,
2016).
• eXtreme Gradient Boosting: is a scalable and
efficient implementation of Friedman’s gradient
boosting paradigm. A linear model, a tree, and
a solver learning approach are included in the
software. It offers a variety of objective func-
tions, such as regression, classification, and scor-
ing. The software is meant to be extensible, allow-
ing users to simply create their own goals (Chen
et al., 2015).
• A Decision Tree: is constructed by interactively
partitioning the feature space of the training set.
The objective is to create a set of decision rules
that naturally partition the feature space, resulting
in an effective and resilient hierarchy classifica-
tion model (Myles et al., 2004; Tolles and Meurer,
2016).
• Support-vector Machines: (also known as
support- vector networks) are machine learning
algorithms that teach themselves to solve two-
group classification tasks. The machine gener-
ally follows the schedule: input vectors are non-
linearly transformed to a feature vector of ex-
tremely high dimensions. A linear decision layer
is built in this spatial domain. The unique proper-
ties of the decision surface enable the ML excel-
lent classification accuracy (Cortes and Vapnik,
1995).
• Stochastic Gradient Descent: is a numerical
approach for dealing with large-scale inverse is-
sues. When seen through the perspective of clas-
BIODEVICES 2022 - 15th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
112

sical regularization theory, however, its theoretical
characteristics are primary (Jahn and Jin, 2020).
• A Naive Bayes Classifier: is a basic probabilis-
tic model based on Bayes rule and a high degree
of independence. When unnecessary words are
eliminated from a document, this form of naive
Bayes technique is known as Bernoulli Naive
Bayes (Narayanan et al., 2013).
• The K-nearest Neighbors’: technique is a ma-
chine learning model-based on a non-parametric
classification method. Furthermore, like with
other conventional data mining approaches, it has
computational problems when applied to large
amounts of data (Saadatfar et al., 2020). We di-
rect the reader to the following book for further
information on the mathematical formulations for
some of the classifiers discussed ((Han et al.,
2012)).
3.2 MUSE EEG
The brain waves are recorded using a standard MUSE
EEG with a sampling frequency of 256 Hz. The
MUSE’s EEG data provides a real-time look into the
human mind. It is easily flexible, and the electrodes
are placed on the brain at the locations TP10, TP9,
AF7, and AF8, according to the 10-20 electrodes
pressure sensor, with the Fpz functioning electrode.
The plastic used in AF8 and AF7 is made of platinum,
whereas the silicone rubber used in the conductor is
utilized in TP9 and TP10. Figure: 1 shows the MUSE
EEG as well as the electrode orientation according to
the 10-20 pressure sensor. The EEG data gathered by
the MUSE 2 offers a real-time glimpse into the hu-
man mind. The device is conveniently flexible while
the electrodes are located on the brain as per the 10-
20 electrodes pressure sensor at the positions TP10,
TP9, AF7, and AF8, with the Fpz working electrode.
Providing a wide range of advantages, such as ver-
satility, complete usability, and low weight, it is mo-
bile and can be paired with any smartphone, tablet, or
computer. The EEG data are collected on a mobile
Figure 1: (a) Device (b) Electrode positions (Liu et al.,
2020).
device using the MUSE 2 display program, transmit-
ted using wired headphones for online processing (Ho
et al., 2017) .
4 METHODOLOGY
4.1 Experimental Setup
Extensive experiments were carried out using eight
different ML algorithms to analyze the frequency of
waves’ techniques and their influence on the final re-
sults. All trials were conducted in the same environ-
ment, on the same computer system (Intel Core(TM)
i7 CPU, 16 GB RAM 1.8GHz (4cores)). The Python
programming language and Oracle SQL were em-
ployed.
4.2 Data Collection Procedure
Each experiment began with a method description to
the subject or their guardian, followed by explicit con-
sent. To ensure a strong connection, the participant’s
head and earlobes were washed with NuPrep, an exfo-
liating gel, and then cleaned with alcohol swabs. Be-
fore and after each session, the Muse-2 was cleaned
with alcohol wipes. EEG recordings were made in
two sessions of three minutes each (eyes open, eyes
closed), with a resting state in between. The patient’s
eyes were open and he was focused on a fixation cross
in the center of his vision while resting.
4.3 Data Set
In this study, we have used a data set that contains 25
participants, 16 had an acute ischemic stroke, and 9
acted as a control group.
4.4 Data Cleaning and Features
Selection
Preparing the data for the use of these algorithms is
not a trivial task and special care must be taken not to
make labeling errors of the signals. The process starts
removing artifacts from signals by using Fast Fourier
Transform (FFT) and Wavelet transformation. The
features were extracted (shown in equation 1 and 2),
pair-derived Brain Symmetry Index (PDBSI) (shown
in equation 3), and applied based on the Fourier trans-
formation and Wavelet transformation.
DAR =
Deltawave
al phawaves
(1)
Machine Learning-based Approach for Stroke Classification using Electroencephalogram (EEG) Signals
113
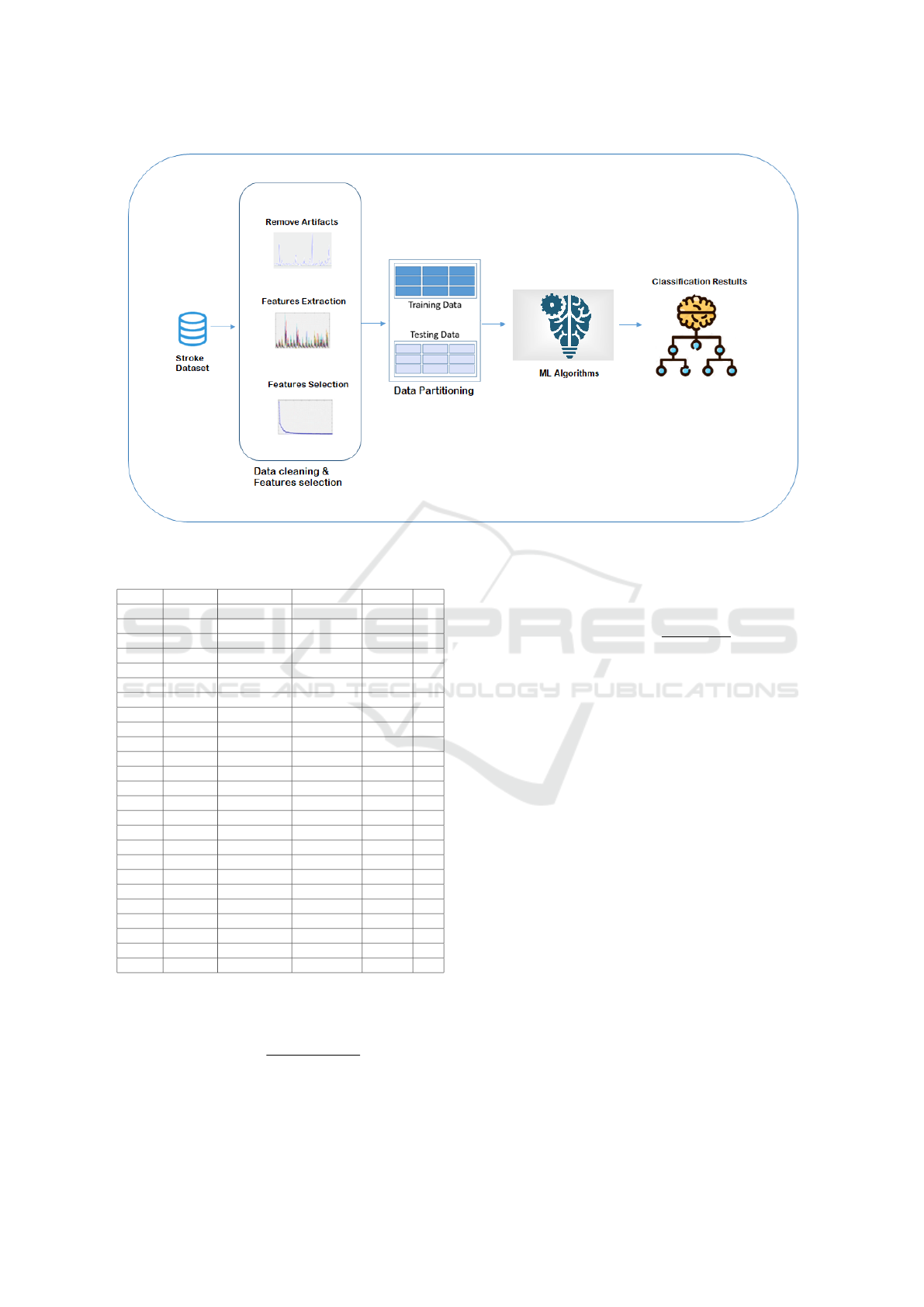
Figure 2: Methodology of this study.
Table 1: Participants information.
Type Severity lateralization Since(Days) Gender Age
Control Control - - M 91
Stroke Small Lef 6 M 87
Stroke Moderate Lef 7 F 61
Stroke Moderate Lef 1 M 65
Stroke Moderate Lef 3 F 83
Stroke Small Right 3 F 19
Stroke Moderate Right 2 F 71
Stroke Moderate Lef 4 M 71
Stroke Small Lef 1 F 86
Stroke Moderate Lef 0 M 85
Stroke Moderate Lef 8 M 37
Stroke Large Right 16 M 87
Control Control - - M 66
Stroke Large Lef 2 F 53
Control Control - - M 53
Stroke Small Lef 3 M 66
Control Control - - F 64
Control Control - - F 81
Stroke Moderate Lef 2 M 75
Control Control - - M 56
Stroke Moderate Lef 0 M 87
Control Control - - M 59
Control Control - - F 48
Stroke Large Right 6 F 72
Control Control - - M 29
DAR was computed as the sum of delta (1–3 Hz) fre-
quency power divided by alpha (8–13 Hz) frequency
power.
DBAT R =
(delta +theta)
(al pha + beta)
(2)
DTABR was determined as the summation of the volt-
age of the delta (1–3 Hz) and theta (4–7 Hz) frequency
divided by the total number of the voltage of the alpha
(8–13 Hz) and beta (14–20 Hz) frequency.
PDBSI =
M
∑
j=1
n
∑
i=1
(Ri j − Li j)
(Ri j + Li j)
(3)
pdBSI is defined as: where Rij and Lij are the spectral
power density of the signals for every electrode pair-
ing (i=1, 2,..., M) for each frequency (j=1, 2,..., N).
A standard MUSE EEG with a sampling frequency of
256 Hz will be used to record the brain waves. The
EEG data from the MUSE gives a real-time view into
the human mind. The electrodes are inserted on the
brain at the sites TP10, TP9, AF7, and AF8, accord-
ing to the 10-20 electrodes pressure sensor, with the
Fpz functional electrode. Platinum is used in the ma-
terial used in AF8 and AF7, whereas silicone rubber
is used in the conductor in TP9 and TP10. We mea-
sured the standard deviations and root mean square
(RMS) of the head movement over time using the on-
board gyroscope and accelerometer to find changes in
movement variability across the X, Y, and Z move-
ment planes. finally In machine learning classifiers,
chosen characteristics from Table 2 are used.
In comparison to (Wilkinson et al., 2020b) , we
utilized the same features and parameters as in this
study, which are listed in table 2, but we added fre-
quency measurements and employed eight machine
learning classifiers instead of simply random forest in
article(Wilkinson et al., 2020b) .
BIODEVICES 2022 - 15th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
114

Table 2: Features from signals.
Age Gyroscope RMS-X plane
Gender Gyroscope RMS-Y plane
DAR-contralateral hemisphere Gyroscope RMS-Z plane
DTABR-contralateral Gyroscope standard deviation-X plane
pdBSI Gyroscope standard deviation-Y plane
Relative beta power Gyroscope standard deviation-Z plane
Relative alpha power Accelerometer RMS-X plane
Relative theta power Accelerometer RMS-Y plane
Relative delta power Accelerometer RMS-Z plane
High frequency pdBSI Accelerometer standard deviation-X plane
Low frequency pdBSI Accelerometer standard deviation-Y plane
PdBSI-frontal electrodes Accelerometer standard deviation-Z plane
Frequency of delta Frequency of alpha
Frequency of beta Frequency of theta
4.5 Data Preparation and Machine
Learning Steps
• Replace the null value with a zero value.
• Using the dummies approach, convert category
variables to binary values.
• Normalize and scale data Normalization refers to
the calculation of measured statistical characteris-
tics in the range of 0 to 1.
• Recursive Feature Elimination RFE is used to
choose features. RFE is a technique for selecting
features.
• For data partitioning, K=10 cross validation was
utilized.
• Eight machine learning classifiers were tested,
with each classifier taking between 3-5 minutes
to compute.
4.6 Classifications Methodology
Following data cleaning, the data preparation phase
was performed. EEG signals have been classified as
0 or 1 depending on whether they are up to normal
or normal respectively. This is done in order to train
the ML algorithm to indicate what class each input
refers to. Machine learning methods are relatively
easy to implement and can be applied to several types
of problems. Figure 2 shows the architecture of the
model following the steps previously outlined.
5 RESULTS
Several common and complex ML classifier tech-
niques were investigated in order to determine which
one performed best for the given dataset. We uti-
lized the Decision Tree (DT), Logistic Regression
(LR), eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGB), Random
Forest (RF), K Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Stochas-
tic Gradient Descent (SGD), Linear Support Vector
Machine Classifier (SVM), and the Bernoulli Naive
Bayes (BNB).
The accuracy, recall, precision, and F-score out-
comes of the dataset are evidenced in Table 4, based
on the confusion matrix, the meaning of these mea-
sures in the following
• Confusion Matrix
Table 3: Confusion Matrix.
Confusion Matrix Prediction No Prediction Yes
Actual No TN FP
Actual Yes FN TP
• FP (False Positives ):- In case that a stroke patient
is predicted but he is actually a normal person.
• FN (False Negatives) :-In case that a normal per-
son is predicted but he is actually a stroke patient.
• TP (True Positive ) :-In case that a stroke patient
is predicted as a stroke patient
• TN (True Negative) :-In case that a normal person
is predicted as a normal person
The classifier classification criteria used for the
rating of classifiers are as follows:
• Accuracy :- Accuracy determines the accuracy of
the classifiers and describes them as the following.
Accuracy =
(T P + T N)
(T P + T N + FP + FN)
(4)
• precision :- The proportion of relevant examples
among the recovered instances.
Precision =
T P
(FP + T P)
(5)
• Recall :-recall is the percentage of relevant in-
stances that were found.
Recall =
T P
(FN + T P)
(6)
• F1-score :- It is defined as the harmonic mean of
recall and precision .
F1 − score =
2(precision ∗ Recall)
(precision + Recall)
(7)
Among all comparable algorithms for the (Wilkin-
son et al., 2020b) dataset, the XGB Classifier proved
the best accuracy (0.8389), while Random Forest ob-
tained the highest Precision score (0.868). The SGD
Classifier, on the other hand, obtained the lowest per-
formance accuracy (0.6184) and precision (0.6863);
moreover, XG- B Classifier outperforms (Wilkinson
et al., 2020b) (0.76) by 0.7389, as shown in Figure 3.
Machine Learning-based Approach for Stroke Classification using Electroencephalogram (EEG) Signals
115

Table 4: Results of ML algorithms centered.
Classifier Accurecy Precision Recall F1
BernoulliNB 0.6826 0.7014 0.7259 0.7131
DecisionTreeClassifier 0.7597 0.7836 0.7682 0.7726
KNeighborsClassifier 0.8107 0.8262 0.8196 0.8226
LinearSVC 0.6742 0.6902 0.6267 0.6489
LogisticRegression 0.7069 0.7407 0.6964 0.7172
RandomForestClassifier 0.8374 0.868 0.8261 0.8465
SGDClassifier 0.6184 0.6863 0.5641 0.7211
(Wilkinson et al., 2020b) 0.76 – – –
XGBClassifier 0.8389 0.8518 0.8473 0.8493
Figure 3: Accuracy of all ML algorithms based in Table 4.
As demonstrated in Figure 4, the Random Forest
Classifier in the (Wilkinson et al., 2020b) dataset has
the best Precision for all datasets (0.868), while the
SGD Classifier has the lowest Precision (0.6863).
Figure 4: Precision based on reported results in Table 4.
Based on the above findings and discussion, it
is reasonable to infer that the proposed approach
will provide adequate performance for categorizing
strokes when compared to the results of the xx
(Wilkinson et al., 2020b) study.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
Given the precision accuracy found in the XGB and
Random Forest classifiers, we expect that the current
findings will enable health professionals and health
respondents to timely classify strokes using EEG
signals in the early stages. Furthermore, this arti-
cle describes the main guidelines for running exper-
iments on the (Wilkinson et al., 2020b) dataset for
stroke classification. This research studied the effi-
cacy of several ML classifiers (XGBoost, KNN, NB,
DT, SVM, LR,RF, and SGC) for classifying strokes
and thus allowing for the provision of timely and
early treatment. The experimental results showed
that the XGboost classifier had a maximum accuracy
of around 83.89 %, compared to (Wilkinson et al.,
2020b) 76%. The given study will be applied to hy-
brid ML algorithms in the future to improve accuracy.
The suggested model will allow the computer to iden-
tify patterns and anomalies in the EEG data, as well as
possible future possibilities for decision support sys-
tems (DSS).
7 DISCUSSION
These findings suggest that the Muse EEG device can
identify strokey. At some frequencies, brain symme-
try changes between stroke patients and healthy con-
trols. Furthermore, DAR and DTABR are elevated in
moderate and severe strokes, indicating a slowdown
of brain activity. Furthermore, the Muse installation
took around 5 minutes and was accepted even by pa-
tients with severe impairments, making this system
suitable to be used in an ambulance in the future. In
an emergency medicine context, the qEEG measure-
ments employed, including pdBSI and slowing mea-
sures, may be promptly determined. Its interpreta-
tion might be simplified further, for as in a program
that processes and analyzes EEG data from a proba-
ble stroke patient. The quick set-up time, along with
simple qEEG measurements, makes this approach a
potential tool for discriminating strokes from stroke
mimics and detecting those strokes linked with LVO
that require priority triage to complete stroke cen-
ters with percutaneous thrombectomy capabilities.In
comparison to (Wilkinson et al., 2020b), we utilized
the same features and parameters as in this study,
which are listed in table 2, but we added frequency
measurements and employed eight machine learning
classifiers instead of simply random forest in article
(Wilkinson et al., 2020b).
BIODEVICES 2022 - 15th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
116

REFERENCES
Belgiu, M. and Dr
˘
agut¸, L. (2016). Random forest in remote
sensing: A review of applications and future direc-
tions. ISPRS journal of photogrammetry and remote
sensing, 114:24–31.
Chen, T., He, T., Benesty, M., Khotilovich, V., Tang, Y.,
Cho, H., et al. (2015). Xgboost: extreme gradient
boosting. R package version 0.4-2, 1(4).
Cillessen, J., Van Huffelen, A., Kappelle, L., Algra, A.,
and Van Gijn, J. (1994). Electroencephalography im-
proves the prediction of functional outcome in the
acute stage of cerebral ischemia. Stroke, 25(10):1968–
1972.
Cortes, C. and Vapnik, V. (1995). Support-vector networks.
Machine learning, 20(3):273–297.
Djamal, E. C., Ramadhan, R. I., Mandasari, M. I., and
Djajasasmita, D. (2020). Identification of post-stroke
eeg signal using wavelet and convolutional neural net-
works. Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Infor-
matics, 9(5):1890–1898.
Gottlibe, M., Rosen, O., Weller, B., Mahagney, A., Omar,
N., Khuri, A., Srugo, I., and Genizi, J. (2020).
Stroke identification using a portable eeg device–a pi-
lot study. Neurophysiologie Clinique, 50(1):21–25.
Han, J., Kamber, M., and Pei, J. (2012). Data Mining: Con-
cepts and Techniques.
Ho, K. C., Speier, W., El-Saden, S., and Arnold, C. W.
(2017). Classifying acute ischemic stroke onset time
using deep imaging features. In AMIA Annual Sympo-
sium Proceedings, volume 2017, page 892. American
Medical Informatics Association.
Jahn, T. and Jin, B. (2020). On the discrepancy princi-
ple for stochastic gradient descent. Inverse Problems,
36(9):095009.
Jordan, K. G. (2004). Emergency eeg and continuous eeg
monitoring in acute ischemic stroke. Journal of clini-
cal neurophysiology, 21(5):341–352.
Liu, R., Xu, M., Zhang, Y., Peli, E., and Hwang, A. D.
(2020). A pilot study on electroencephalogram-based
evaluation of visually induced motion sickness. Jour-
nal of Imaging Science and Technology, 64(2):20501–
1.
Murri, L., Gori, S., Massetani, R., Bonanni, E., Marcella,
F., and Milani, S. (1998). Evaluation of acute is-
chemic stroke using quantitative eeg: a comparison
with conventional eeg and ct scan. Neurophysiologie
Clinique/Clinical Neurophysiology, 28(3):249–257.
Myles, A. J., Feudale, R. N., Liu, Y., Woody, N. A., and
Brown, S. D. (2004). An introduction to decision tree
modeling. Journal of Chemometrics: A Journal of the
Chemometrics Society, 18(6):275–285.
Narayanan, V., Arora, I., and Bhatia, A. (2013). Fast and
accurate sentiment classification using an enhanced
naive bayes model. In International Conference on In-
telligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning,
pages 194–201. Springer.
Persky, R. W., Turtzo, L. C., and McCullough, L. D. (2010).
Stroke in women: disparities and outcomes. Current
cardiology reports, 12(1):6–13.
Saadatfar, H., Khosravi, S., Joloudari, J. H., Mosavi, A., and
Shamshirband, S. (2020). A new k-nearest neighbors
classifier for big data based on efficient data pruning.
Mathematics, 8(2):286.
Soltanian-Zadeh, H. (2019). Multimodal analysis in
biomedicine. In Big Data in Multimodal Medical
Imaging, pages 193–203. Chapman and Hall/CRC.
Tolles, J. and Meurer, W. (2016). Logistic regression:
Relating patient characteristics to outcomes. JAMA,
316:533.
Wilkinson, C. M., Burrell, J. I., Kuziek, J. W.,
Thirunavukkarasu, S., Buck, B. H., and Mathewson,
K. E. (2020a). Application of the muse portable eeg
system to aid in rapid diagnosis of stroke. medRxiv.
Wilkinson, C. M., Burrell, J. I., Kuziek, J. W.,
Thirunavukkarasu, S., Buck, B. H., and Mathewson,
K. E. (2020b). Predicting stroke severity with a 3-min
recording from the muse portable eeg system for rapid
diagnosis of stroke. Scientific Reports, 10(1):1–11.
Machine Learning-based Approach for Stroke Classification using Electroencephalogram (EEG) Signals
117
