
Colour Augmentation for Improved Semi-supervised Semantic
Segmentation
Geoff French
a
and Michal Mackiewicz
b
School of Computing Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, U.K.
Keywords:
Deep Learning, Semantic Segmentation, Semi-supervised Learning, Data Augmentation.
Abstract:
Consistency regularization describes a class of approaches that have yielded state-of-the-art results for semi-
supervised classification. While semi-supervised semantic segmentation proved to be more challenging, re-
cent work has explored the challenges involved in using consistency regularization for segmentation prob-
lems and has presented solutions. In their self-supervised work Chen et al. found that colour augmenta-
tion prevents a classification network from using image colour statistics as a short-cut for self-supervised
learning via instance discrimination. Drawing inspiration from this we find that a similar problem im-
pedes semi-supervised semantic segmentation and offer colour augmentation as a solution, improving semi-
supervised semantic segmentation performance on challenging photographic imagery. Implementation at:
https://github.com/Britefury/cutmix-semisup-seg.
1 INTRODUCTION
State-of-the-art computer vision results ob-
tained using deep neural networks over the last
decade (Krizhevsky et al., 2012; He et al., 2016)
rely on the availability of large training sets con-
sisting of images and corresponding annotations.
Semi-supervised learning offers the possibility of
alleviating the annotation bottleneck that arises from
the manual effort involved in annotation by learning
from un-annotated – or unsupervised – samples in
addition to annotated samples.
Semantic segmentation is the task of classifying
each pixel in an image, often with a view to identify-
ing the type of object under it. While efficient anno-
tation tools (Maninis et al., 2018) can help, producing
pixel-wise ground truth annotation is labour intensive,
making the annotation bottleneck a particularly press-
ing issue for segmentation problems.
The term consistency regularization (Oliver et al.,
2018) refers to a class of approaches that have yielded
state-of-the-art results for semi-supervised classifica-
tion (Laine and Aila, 2017; Tarvainen and Valpola,
2017; Xie et al., 2019; Sohn et al., 2020) over the
last few years. (French et al., 2020) find that plain
geometric augmentation schemes used in prior semi-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2868-2237
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8777-8880
supervised classification approaches frequently fail
when applied to segmenting photographic imagery.
They offer the challenging data distribution of seman-
tic segmentation problems as an explanation and de-
velop a successful approach based on Cutmix (Yun
et al., 2019).
Recent work in self-supervised learning via in-
stance discrimination trains a network for feature ex-
traction without using ground truth labels. As with
consistency regularization the network is encouraged
to yield similar predictions – albeit image embeddings
instead of probability vectors – given stochastically
augmented variants of an unlabelled image. (Chen
et al., 2020a) conducted a rigorous ablation study,
finding that colour augmentation is essential to good
performance. Without it, the network in effect cheats
by using colour statistics as a short-cut for the image
instance discrimination task used to train the network.
Inspired by this, we find that a similar problem can
hinder semi-supervised semantic segmentation. Our
experiments demonstrate the problem by showing that
it is alleviated by the use of colour augmentation.
Other recent approaches – namely Classmix (Ols-
son et al., 2021), DMT (Feng et al., 2021) and
ReCo (Liu et al., 2021) – have significantly improved
on the Cutmix based results of (French et al., 2020).
Our work builds on the Cutmix approach, demonstrat-
ing the effectiveness of colour augmentation. It is not
356
French, G. and Mackiewicz, M.
Colour Augmentation for Improved Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation.
DOI: 10.5220/0010807400003124
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2022) - Volume 4: VISAPP, pages
356-363
ISBN: 978-989-758-555-5; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

our intent to present results competitive with Class-
mix and DMT, thus we acknowledge that our results
are not state of the art.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Semi-supervised Classification
The key idea behind consistency regularization based
semi-supervised classification is clearly illustrated in
the π-model of (Laine and Aila, 2017), in which a
network is trained by minimizing both supervised
and unsupervised loss terms. The supervised loss
term applies traditional cross-entropy loss to super-
vised samples with ground truth annotations. Unsu-
pervised samples are stochastically augmented twice
and the unsupervised loss term encourages the net-
work to predict consistent labels under augmentation.
The Mean Teacher model of (Tarvainen and
Valpola, 2017) uses two networks; a teacher and a
student. The weights of the teacher are an exponen-
tial moving average (EMA) of those of the student.
The student is trained using gradient descent as nor-
mal. The teacher network is used to generate pseudo-
targets for unsupervised samples that the student is
trained to match under stochastic augmentation.
The UDA approach of (Xie et al., 2019) adopted
RandAugment (Cubuk et al., 2020); a rich image aug-
mentation scheme that chooses 2 or 3 image opera-
tions to apply from a menu of 14. We note an impor-
tant similarity with Mean Teacher; just as the teacher
network is used to predict a pseudo target, UDA pre-
dicts a pseudo-target for an un-augmented image that
is used as a training target for the same iamge with
RandAugment applied.
The FixMatch approach of (Sohn et al., 2020) re-
fines this approach further. They separate their aug-
mentation scheme into weak – consisting of simple
translations and horizontal flips – and strong that
uses RandAugment. They predict hard pseudo-labels
for weakly augmented unsupervised samples that are
used as training targets for strongly augmented vari-
ants of the same samples.
2.2 Semi-supervised Semantic
Segmentation
(Hung et al., 2018) and (Mittal et al., 2019) adopt
GAN-based adversarial learning, using a discrimina-
tor network that distinguishes real from predicted seg-
mentation maps to guide learning.
(Perone and Cohen-Adad, 2018) and (Li et al.,
2018) are two early applications of consistency regu-
larisation to semantic segmentation. Both come from
the medical imaging community, tackling MRI vol-
ume segmentation and skin lesion segmentation re-
spectively. Both approaches use standard augmenta-
tion to provide perturbation, as in the π-model (Laine
and Aila, 2017) and Mean Teacher (Tarvainen and
Valpola, 2017). (Ji et al., 2019) developed a semi-
supervised over-clustering approach that can be ap-
plied to natural photographic images, where the list
of ground truth classes is highly constrained.
(French et al., 2020) analysed the problem of se-
mantic segmentation, finding that it has a challenging
data distribution to which the cluster assumption does
not apply. They offer this as an explanation as to why
consistency regularization had not been successfully
applied to semantic segmentation of photographic im-
ages. They present an approach that drives the Mean
Teacher (Tarvainen and Valpola, 2017) algorithm us-
ing an augmentation scheme based on Cutmix (Yun
et al., 2019), achieving state of the art results.
2.3 Self-supervised and Unsupervised
Learning
Approaches based on contrastive learning (Henaff,
2020; He et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2020b; Chen et al.,
2020a) train a residual network (He et al., 2016) us-
ing only unlabelled input images. Afterwards the net-
work backbone (consisting of convolutional layers)
is frozen and a linear classifier is trained in a super-
vised fashion using it’s feature representations as in-
puts and ground truth labels as targets. The result-
ing image classifiers – in which only the last linear
layer is trained using ground truth labels – are able
to achieve ImageNet results that are competitive with
those obtained by traditional supervised learning in
which the whole network is trained.
In contrast to prior work (Henaff, 2020) the MoCo
model (He et al., 2020) simplified contrastive learn-
ing using standard augmentation to generate stochas-
tically augmented variants of unlabelled images. The
network is encouraged to predict embeddings that are
more similar for augmented variants of the same input
image than for different images. The augmentation
scheme used is very similar to the standard scheme
used to train residual networks (He et al., 2016) and
by Mean Teacher (Tarvainen and Valpola, 2017) for
their ImageNet results. (Chen et al., 2020a) con-
ducted a rigorous ablation study of the augmentations
used for contrastive learning, assessing the effective-
ness of each augmentation operation. They found
that colour augmentation is essential for good perfor-
Colour Augmentation for Improved Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation
357

mance, as without it the network is able cheat by us-
ing image colour statistics as a short-cut to discrimi-
nate between images, rather than having to focus on
image content. Strong colour augmentation masks
this signal, forcing the network to focus on the image
content, extracting features suitable for accurate im-
age classification and other downstream tasks. Colour
augmentation is also used in the MoCo model (He
et al., 2020).
We note the similarities between recent con-
trastive learning approaches and Information Invari-
ant Clustering of (Ji et al., 2019), who also encourages
consistency under stochastic augmentation.
The recent work of (Liu et al., 2021) adapt con-
trastive learning – typically used for classification –
for semantic segmentation, achieving impressive re-
sults with very few labelled images.
3 APPROACH
We will start by providing a brief overview of semi-
supervised classification and the segmentation, fol-
lowed by our choice of approach and a description
of our addition of colour augmentation.
3.1 Semi-supervised Classification
During training we minimize a loss term L that com-
bines standard supervised cross entropy loss L
sup
with
an unsupervised consistency loss term L
cons
that en-
courages consistent predictions under augmentation.
L
cons
is modulated by an unsupervised loss weight
hyper-parameter γ, so:
L = L
sup
+ γL
cons
(1)
In a classification scenario L
cons
measures the
squared difference between probability predictions
generated by a neural network f
θ
given stochastically
augmented variants ˆx and ˜x of a sample x:
L
cons
=
f
θ
( ˆx) − f
θ
( ˜x)
2
(2)
The Mean Teacher approach defines L
cons
as the
difference between predictions arising from two net-
works; the student f
θ
trained using gradient descent
as normal and a teacher network g
φ
whose weights
are an exponential moving average of those of the
student. After each gradient descent update of the
student, the weights of the teacher are updated: φ =
βφ +(1 −β)θ where β is the EMA momentum hyper-
parameter. L
cons
is therefore:
L
cons
=
f
θ
( ˆx) − g
φ
( ˜x)
2
(3)
3.2 Semi-supervised Segmentation
Applying standard geometric augmentation –
e.g. affine transformation – in a segmentation
scenario is a little more involved than it is for
classification. For classification one needs to ensure
only that the augmentation or transformation is class
preserving, e.g. it does not alter the classification of
the image.
A geometric transformation t
α
may alter the shape
and position of elements in an image. Given that the
goal of semantic segmentation is to classify the con-
tent under each pixel in an image x resulting in the
segmentation map y, applying a geometric transfor-
mation t
α
to the image such that ˆx = t
α
(x) will result in
a similarly transformed segmentation map ˆy = t
α
(y).
This equivariance must be observed during train-
ing when computing both supervised an unsupervised
loss terms. For our supervised loss term this means
computing the loss given the networks’ predictions
f
θ
(t
α
(x)) given the augmented input image t
α
(x) and
the augmented ground truth t
α
(y). Following (Perone
and Cohen-Adad, 2018) this can be adapted for the
unsupervised loss term in a semi-supervised scenario
by applying the geometric transformation t
α
to the in-
put image prior to passing it to the student network
and to the predicted segmentation from the teacher
network (also illustrated in Figure 1):
L
cons
=
f
θ
(t
α
(x)) − t
α
(g
φ
(x))
2
(4)
3.3 Colour Augmentation for
Segmentation
In their semi-supervised semantic segmentation ap-
proach (French et al., 2020) offer the challenging
data distribution present in semantic segmentation
problems as an explanation as to why consistency
regularization driven by standard augmentation had
yielded few prior successes when applied to photo-
graphic image datasets such as PASCAL VOC (Ev-
eringham et al., 2012). In view of the strong simi-
larity between semi-supervised consistency loss and
the self-supervised loss used in SimCLR (Chen et al.,
2020a) – both encourage consistent predictions under
stochastic augmentation – the ablation study in Sim-
CLR (Chen et al., 2020a) inspires us to offer colour
statistics as an alternative explanation.
The consistency loss term in equation 4 offers the
opportunity for the network to minimize L
cons
using
colour statistics. The application of the transforma-
tion t
α
in both the student and teacher sides will result
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
358
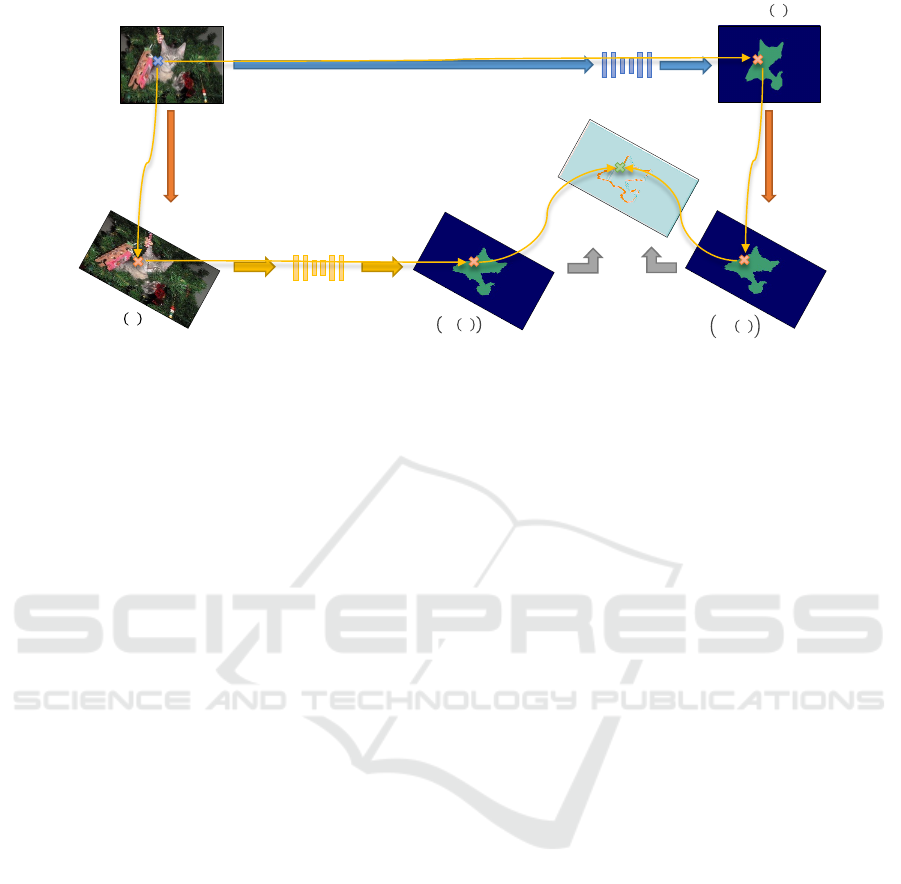
𝑥
Teacher 𝑔
!
Student 𝑓
"
𝐿
#$%&
𝑔
!
𝑥
Augment 𝑡
'
𝑡
'
𝑥
𝑓
"
𝑡
'
𝑥
Augment 𝑡
'
𝑡
'
𝑔
!
𝑥
Figure 1: Illustration of Mean Teacher unsupervised consistency loss driven by standard augmentation for semantic seg-
mentation problems. The path for a pixel on the neck of the cat leading from the input image x is traced by yellows to the
consistency loss map L
cons
(illustrated prior to computing the mean of the square), with the location of the pixel in each image
identified by coloured crosses.
in L
cons
penalising the network for giving inconsistent
class predictions for each individual pixel in the input
image x under geometric augmentation. This is fur-
ther illustrated in Figure 1, in which the yellow arrows
follow a single pixel from the input image x through
both the student and teacher sides of the consistency
loss term. A simple way to minimize L
cons
is to pre-
dict the class of a pixel in the output segmentation
maps using only the corresponding pixel in the input
image, ignoring surrounding context. Thus, we hy-
pothesize that the network effectively learns to cluster
the colour of individual input pixels, rather than using
surrounding context to identify the type of object that
the pixel lies within.
To test our hypothesis we choose a semi-
supervised segmentation approach whose unsuper-
vised component is as similar as possible to the self-
supervised methods that have successfully employed
colour augmentation in prior work. The consistency
loss term used in the Mean Teacher (Tarvainen and
Valpola, 2017) semi-supervised method is very simi-
lar to the self-supervised loss used in the MoCo (He
et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2020b) method; both are
driven by samples that are stochastically augmented
twice and both use two networks, one whose weights
are an EMA of those of the other. We therefore base
our work on the approach and codebase of the semi-
supervised segmentation work of (French et al., 2020)
as it is employs Mean Teacher. It also provides a va-
riety of semi-supervised regularizers: standard aug-
mentation; ICT (Verma et al., 2019); VAT (Miyato
et al., 2017); Cutout and Cutmix that we use to assess
the effectiveness of colour augmentation in combina-
tion with other approaches.
Following (Sohn et al., 2020) we consider colour
augmentation to be a form of strong augmentation,
that is not used when generating pseudo-targets for
unsupervised samples during training. As in (French
et al., 2020) we only apply strong augmentation to the
input images passed to the student network; we do not
apply it to images passed to the teacher.
We acknowledge that (Ji et al., 2019) applied
colour augmentation in an unsupervised semantic
segmentation setting. While their codebase uses a
similar approach as (He et al., 2020) and (Chen et al.,
2020a) they describe it simply as ‘photometric aug-
mentation’ in their paper, giving little hint that it is in
fact key to the success of consistency regularization
based techniques in this problem domain, as we will
show in Section 4.3.
4 EXPERIMENTS
Our experiments follow the same procedure as
(French et al., 2020), using the same network archi-
tectures. We used the same hyper-parameters, with
the exception of the consistency loss weight that we
will discuss in Section 4.3.1.
4.1 Implementation
Our implementation extends that of (French et al.,
2020), allowing colour augmentation to be combined
with standard augmentation, ICT, VAT, Cutout and
Cutmix based regularizers (please see their paper for
full descriptions of their implementation in a seg-
mentation setting). This allows us to assess its ef-
Colour Augmentation for Improved Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation
359

Table 1: Performance (mIoU) on CITYSCAPES validation set, presented as mean ± std-dev computed from 5 runs. Other
work: the results for ’Adversarial’ (Hung et al., 2018) and ’s4GAN’ (Mittal et al., 2019) are taken from (Mittal et al., 2019).
The results for DMT (Feng et al., 2021) and Classmix (Olsson et al., 2021) are from their respective works. Bold results in
blue colour indicate results from other works that beat our best results. Our best results are in bold. The baseline results use
plain supervised learning using only samples from the labelled subset.
Fraction labelled ∼1/30 1/8 1/4 All
(# labelled) (100) (372) (744) (2975)
Results from other recent work, ImageNet pre-trained DeepLab v2 network
Baseline — 56.2% 60.2% 66.0%
Adversarial — 57.1% 60.5% 66.2%
s4GAN — 59.3% 61.9% 65.8%
DMT 54.80% 63.06% — 68.16%
Classmix 54.07% 61.35% 63.63% —
Results from (French et al., 2020) and our results, ImageNet pre-trained DeepLab v2 network
Baseline 44.41% ± 1.11 55.25% ± 0.66 60.57% ± 1.13 67.53%± 0.35
Cutout 47.21% ± 1.74 57.72% ± 0.83 61.96% ± 0.99 67.47% ± 0.68
+ colour aug. (ours) 48.28% ± 1.98 58.30% ± 0.73 62.59% ± 0.60 67.93% ± 0.36
CutMix 51.20% ± 2.29 60.34% ± 1.24 63.87% ± 0.71 67.68% ± 0.37
+ colour aug. (ours) 51.98% ± 2.77 61.08% ± 0.71 64.61% ± 0.57 68.11% ± 0.55
fect on a variety of regularizers across three datasets;
CITYSCAPES, PASCAL VOC 2012 and the ISIC Skin
Lesion segmentation dataset (Codella et al., 2018).
We apply colour augmentation to unsupervised
images as part of the strong augmentation scheme
used on images sent to the student network (see Sec-
tion 3.3). This is performed prior to any adversarial
(VAT) or mix-based (ICT or CutMix) unsupervised
regularizer. Our colour augmentation scheme con-
sists of randomly adjusting the brightness, contrast,
saturation and hue of an image with 80% probability
(we use ColorJitter from the torchvision (Chin-
tala et al., 2017) package), followed by converting to
grayscale with 20% probability.
4.2 Cityscapes
CITYSCAPES is a photograpic image dataset of urban
scenery captured from the perspective of a car. Its’
training set consists of 2975 images.
Our CITYSCAPES results are presented in Ta-
ble 1 as mean intersection-over-union (mIoU) per-
centages, where higher is better. The addition of
colour augmentation results in a slight improvement
to the CutOut and CutMix results across the board.
4.3 Augmented Pascal VOC 2012
PASCAL VOC (Everingham et al., 2012) is a pho-
tographic image dataset consisting of various indoor
and outdoor scenes. It consists of only 1464 training
images, and thus we follow the lead of (Hung et al.,
2018) and augment it using SEMANTIC BOUND-
ARIES(Hariharan et al., 2011), resulting in 10582
training images.
Our PASCAL VOC 2012 experiments evalu-
ate regularizers based on standard augmentation,
ICT (Verma et al., 2019) and VAT (Miyato et al.,
2017), Cutout and Cutmix as in (French et al., 2020).
Our results are presented in Table 2.
4.3.1 Consistency Loss Weight
We note that the effects of colour augmentation re-
sulted in different optimal values for γ (consistency
loss weight) than were used by (French et al., 2020).
When using standard geometric augmentation they
found that a value of 0.003 was optimal, yielding a
very slight improvement over the supervised baseline.
Increasing γ caused performance to drop below that
of the supervised baseline. We note that at 0.003, the
consistency loss term would have little effect on train-
ing at all. When using colour augmentation, we were
able to use a value of 1 for γ; the same as that used for
the more successful Cutout and CutMix regularizers.
This strongly suggests that without colour augmenta-
tion, a low value must be used for γ to suppress the
effect of the pixel colour clustering short-cut hypoth-
esized in Section 3.3.
We were also able to use a value of 1 – instead of
0.01 – for the ICT (Verma et al., 2019) based regu-
larizer when using colour augmentation. For VAT we
continue to use a weight of 0.1; we attribute this lower
loss weight to the use of KL-divergence in VAT rather
than mean squared error for the consistency loss.
Being able to use a single value for the consistency
loss weight for all regularizers simplifies the use of
our approach in practical applications.
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
360

Table 2: Performance (mIoU) on augmented PASCAL VOC validation set, using same splits as (Mittal et al., 2019). Other
work: the results for ’Adversarial’ (Hung et al., 2018) and ’s4GAN’ (Mittal et al., 2019) are taken from (Mittal et al., 2019).
The results for DMT (Feng et al., 2021) and Classmix (Olsson et al., 2021) are from their respective works. Bold results in
blue colour indicate results from other works that beat our best results. Our best results are in bold. The baseline results use
plain supervised learning using only samples from the labelled subset.
Fraction labelled 1/100 1/50 1/20 1/8 All
(# labelled) (106) (212) (529) (1323) (10582)
Results from other work with ImageNet pretrained DeepLab v2
Baseline – 48.3% 56.8% 62.0% 70.7%
Adversarial – 49.2% 59.1% 64.3% 71.4%
s4GAN+MLMT – 60.4% 62.9% 67.3% 73.2%
DMT 63.04% 67.15% 69.92% 72.70% 74.75%
Classmix 54.18% 66.15% 67.77% 72.00% —
Results from (French et al., 2020) + ours, ImageNet pre-trained DeepLab v2 network
Baseline 33.09% 43.15% 52.05% 60.56% 72.59%
Std. aug. 32.40% 42.81% 53.37% 60.66% 72.24%
+ colour aug. (ours) 46.42% 49.97% 57.17% 65.88% 73.21%
VAT 38.81% 48.55% 58.50% 62.93% 72.18%
+ colour aug. (ours) 40.05% 49.52% 57.60% 63.05% 72.29%
ICT 35.82% 46.28% 53.17% 59.63% 71.50%
+ colour aug. (ours) 49.14% 57.52% 64.06% 66.68% 72.91%
Cutout 48.73% 58.26% 64.37% 66.79% 72.03%
+ colour aug. (ours) 52.43% 60.15% 65.78% 67.71% 73.20%
CutMix 53.79% 64.81% 66.48% 67.60% 72.54%
+ colour aug. (ours) 53.19% 65.19% 67.65% 69.08% 73.29%
(French et al., 2020) + ours, ImageNet pre-trained DeepLab v3+ network
Baseline 37.95% 48.35% 59.19% 66.58% 76.70%
CutMix 59.52% 67.05% 69.57% 72.45% 76.73%
+ colour aug. (ours) 60.02% 66.84% 71.62% 72.96% 77.67%
(French et al., 2020) + ours, ImageNet pre-trained DenseNet-161 based Dense U-net
Baseline 29.22% 39.92% 50.31% 60.65% 72.30%
CutMix 54.19% 63.81% 66.57% 66.78% 72.02%
+ colour aug. (ours) 53.04% 62.67% 63.91% 67.63% 74.16%
(French et al., 2020) + ours, ImageNet pre-trained ResNet-101 based PSPNet
Baseline 36.69% 46.96% 59.02% 66.67% 77.59%
CutMix 67.20% 68.80% 73.33% 74.11% 77.42%
+ colour aug. (ours) 66.83% 72.30% 74.64% 75.40% 78.67%
Table 3: Performance on ISIC 2017 skin lesion segmentation validation set, measured using the Jaccard index (IoU for lesion
class). Presented as mean ± std-dev computed from 5 runs. All baseline and semi-supervised results use 50 supervised
samples. The fully supervised result (’Fully sup.’) uses all 2000.
Baseline Std. aug. VAT ICT Cutout CutMix Fully sup.
(50) (2000)
Results from (Li et al., 2018) with ImageNet pre-trained DenseUNet-161
72.85% 75.31% – – – – 79.60%
Our results: Same ImageNet pre-trained DenseUNet-161
67.64% 71.40% 69.09% 65.45% 68.76% 74.57% 78.61%
± 1.83 ± 2.34 ± 1.38 ± 3.50 ± 4.30 ± 1.03 ± 0.36
+ colour augmentation
73.61% 61.94% 50.93% 73.70% 74.51%
± 2.40 ± 6.72 ± 7.16 ± 2.59 ± 1.95
Colour Augmentation for Improved Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation
361

4.4 ISIC 2017 Skin Lesion
Segmentation
The ISIC skin lesion segmentation dataset (Codella
et al., 2018) consists of dermoscopy images focused
on lesions set against skin. It has 2000 images in its
training set and is a two-class (skin and lesion) seg-
mentation problem, featuring far less variation than
CITYSCAPES and PASCAL. Our results are presented
in Table 3.
While colour augmentation improved the perfor-
mance of all regularizers on the PASCAL dataset when
using the DeepLab v2 architecture, the results for
ISIC 2017 are less clear cut. It harms the performance
of VAT and ICT, although we note that we increased
the consistency loss weight of ICT to match the value
used for PASCAL. It yields a noticeable improve-
ment when using standard augmentation and Cutout.
Colour augmentation increases the variance of the ac-
curacy when using CutMix, making it slightly less
reliable. We hypothesized the the hue jittering com-
ponent of the colour augmentation may harm perfor-
mance in this benchmark as colour is a useful queue
in lesion segmentation, so we tried disabling it when
using ICT and VAT. This did not however improve
colour augmentation results.
4.5 Comparison with Other Work
While we have demonstrated that colour augmenta-
tion can improve semi-supervised segmentation per-
formance when using a simple consistency regulariza-
tion based approach, we acknowledge that our results
do not match those of the recent Classmix (Olsson
et al., 2021), DMT (Feng et al., 2021) and ReCo (Liu
et al., 2021) approaches that use more recent semi-
supervised regularizers.
We also note that (Liu et al., 2021) focused on sit-
uations in which a very small number of labelled sam-
ples were used. As their work did not feature experi-
ments with a comparable number of labelled samples
to our own, we were unable to directly compare their
results with ours in Tables 1 and 2.
5 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
As observed by (French et al., 2020) prior work
in the field of semi-supervised image classification
attributed the success of consistency regularization
based approaches to the smoothness assumption (Luo
et al., 2018) or cluster assumption (Chapelle and Zien,
2005; Sajjadi et al., 2016; Shu et al., 2018; Verma
et al., 2019). Their analysis of the data distribution
of semantic segmentation showed that the cluster as-
sumption does not apply. Their successful application
of an adapted CutMix regularizer to semi-supervised
semantic segmentation demonstrated that the cluster
assumption is in fact not a pre-requisite for successful
semi-supervised learning. In view of this, they of-
fered the explanation that the variety of augmentation
used need to provide perturbations to samples that are
sufficiently varied in order to constrain the orienta-
tion of the decision boundary in the absence of the
low density regions required by the cluster assump-
tion. CutMix succeeds due to offering more variety
than standard geometric augmentation.
Our results indicate a more nuanced explanation.
The positive results obtained from adding colour aug-
mentation to standard geometric augmentation, com-
bined with being able to use a consistent value of 1 for
the consistency loss weight for all regularizers shows
that it is in fact the pixel colour clustering short-
cut that was hampering the effectiveness of standard
geometric augmentation by itself, rather than a lack
of variation. The fact that CutMix without colour
augmentation comfortably out-performs standard ge-
ometric augmentation with colour augmentation does
however show that CutMix adds useful variety that
enables more effective semi-supervised learning.
The story presented by the ISIC 2017 results is
less positive however. The augmentation used to drive
the consistency loss term in a semi-supervised learn-
ing scenario must be class preserving. Modifying an
unsupervised sample such that its class changes will
cause the consistency loss term to encourage consis-
tent predictions across the decision boundary, harm-
ing the performance of the classifier (see the toy 2D
examples in (French et al., 2020) for a more thor-
ough exploration of this). In light of this, practitioners
should carefully consider whether colour augmenta-
tion could alter the ground truth class of a sample.
We offer this as an explanation of the inconsistent ef-
fect of colour augmentation on the ISIC 2017 dataset
in which the colour of lesions is an important signal.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was funded under the European Union
Horizon 2020 SMARTFISH project, grant agreement
no. 773521. The computation required by this work
was performed on the University of East Anglia HPC
Cluster.
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
362

REFERENCES
Chapelle, O. and Zien, A. (2005). Semi-supervised classifi-
cation by low density separation. In AISTATS 2005.
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., and Hinton, G.
(2020a). A simple framework for contrastive learning
of visual representations. In ICML 2020.
Chen, X., Fan, H., Girshick, R., and He, K. (2020b). Im-
proved baselines with momentum contrastive learn-
ing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.04297.
Chintala, S. et al. (2017). Pytorch.
Codella, N. C., Gutman, D., Celebi, M. E., Helba, B.,
Marchetti, M. A., Dusza, S. W., Kalloo, A., Liopy-
ris, K., Mishra, N., Kittler, H., et al. (2018). Skin
lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: A chal-
lenge at the 2017 international symposium on biomed-
ical imaging (isbi), hosted by the international skin
imaging collaboration (isic). In ISBI 2018.
Cubuk, E. D., Zoph, B., Shlens, J., and Le, Q. (2020).
Randaugment: Practical automated data augmentation
with a reduced search space. In NeurIPS 2020.
Everingham, M., Van Gool, L., Williams, C. K. I.,
Winn, J., and Zisserman, A. (2012). The
PASCAL Visual Object Classes Challenge
2012 (VOC2012) Results. http://www.pascal-
network.org/challenges/VOC/voc2012/workshop/index.html.
Feng, Z., Zhou, Q., Gu, Q., Tan, X., Cheng, G., Lu, X., Shi,
J., and Ma, L. (2021). Dmt: Dynamic mutual training
for semi-supervised learning. CoRR, abs/2004.08514.
French, G., Laine, S., Aila, T., Mackiewicz, M., and Fin-
layson, G. (2020). Semi-supervised semantic segmen-
tation needs strong, varied perturbations. In BMVC
2020.
Hariharan, B., Arbel
´
aez, P., Bourdev, L., Maji, S., and Ma-
lik, J. (2011). Semantic contours from inverse detec-
tors. In ICCV 2011.
He, K., Fan, H., Wu, Y., Xie, S., and Girshick, R. (2020).
Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual represen-
tation learning. In CVPR 2020.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2016). Deep resid-
ual learning for image recognition. In CVPR 2016.
Henaff, O. (2020). Data-efficient image recognition with
contrastive predictive coding. In ICML 2020.
Hung, W.-C., Tsai, Y.-H., Liou, Y.-T., Lin, Y.-Y., and
Yang, M.-H. (2018). Adversarial learning for
semi-supervised semantic segmentation. CoRR,
abs/1802.07934.
Ji, X., Henriques, J. F., and Vedaldi, A. (2019). Invariant
information clustering for unsupervised image classi-
fication and segmentation. In ICCV 2019.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2012). Im-
ageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neu-
ral Networks. In NIPS 2012.
Laine, S. and Aila, T. (2017). Temporal ensembling for
semi-supervised learning. In ICLR 2017.
Li, X., Yu, L., Chen, H., Fu, C.-W., and Heng, P.-A.
(2018). Semi-supervised skin lesion segmentation via
transformation consistent self-ensembling model. In
BMVC 2018.
Liu, S., Zhi, S., Johns, E., and Davison, A. J. (2021). Boot-
strapping semantic segmentation with regional con-
trast. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.04465.
Luo, Y., Zhu, J., Li, M., Ren, Y., and Zhang, B.
(2018). Smooth neighbors on teacher graphs for semi-
supervised learning. In CVPR 2018.
Maninis, K.-K., Caelles, S., Pont-Tuset, J., and Van Gool,
L. (2018). Deep extreme cut: From extreme points to
object segmentation. In CVPR 2018.
Mittal, S., Tatarchenko, M., and Brox, T. (2019). Semi-
supervised semantic segmentation with high-and low-
level consistency. PAMI 2019.
Miyato, T., Maeda, S.-i., Koyama, M., and Ishii, S. (2017).
Virtual adversarial training: a regularization method
for supervised and semi-supervised learning. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1704.03976.
Oliver, A., Odena, A., Raffel, C., Cubuk, E. D., and Good-
fellow, I. J. (2018). Realistic evaluation of semi-
supervised learning algorithms. In ICLR 2018.
Olsson, V., Tranheden, W., Pinto, J., and Svensson, L.
(2021). Classmix: Segmentation-based data augmen-
tation for semi-supervised learning. In WCACV 2021.
Perone, C. S. and Cohen-Adad, J. (2018). Deep semi-
supervised segmentation with weight-averaged con-
sistency targets. In Deep Learning in Medical Image
Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Deci-
sion Support.
Sajjadi, M., Javanmardi, M., and Tasdizen, T. (2016). Mu-
tual exclusivity loss for semi-supervised deep learn-
ing. In ICIP 2016.
Shu, R., Bui, H., Narui, H., and Ermon, S. (2018). A DIRT-t
approach to unsupervised domain adaptation. In ICLR
2018.
Sohn, K., Berthelot, D., Carlini, N., Zhang, Z., Zhang, H.,
Raffel, C. A., Cubuk, E. D., Kurakin, A., and Li, C.-
L. (2020). Fixmatch: Simplifying semi-supervised
learning with consistency and confidence. In NeurIPS
2020.
Tarvainen, A. and Valpola, H. (2017). Mean teachers are
better role models: Weight-averaged consistency tar-
gets improve semi-supervised deep learning results. In
NIPS 2017.
Verma, V., Lamb, A., Kannala, J., Bengio, Y., and Lopez-
Paz, D. (2019). Interpolation consistency training for
semi-supervised learning. CoRR, abs/1903.03825.
Xie, Q., Dai, Z., Hovy, E., Luong, M.-T., and Le, Q. V.
(2019). Unsupervised data augmentation. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1904.12848.
Yun, S., Han, D., Oh, S. J., Chun, S., Choe, J., and Yoo,
Y. (2019). Cutmix: Regularization strategy to train
strong classifiers with localizable features. In ICCV
2019.
Colour Augmentation for Improved Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation
363
