
Personalized Hip Replacement: State of the Art and New Tools
Proposals
Isabel Moscol
1a
, William Solórzano-Requejo
1,2 b
, Carlos Ojeda
1c
and Ciro Rodríguez
3d
1
Department of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Universidad de Piura, Piura, Peru
2
ETSI Industriales, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid, Spain
3
Department of Software Engineering, Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos, Lima, Peru
crodriguezro@unmsm.edu.pe
Keywords: Hip Arthroplasty, Biomaterials, Short Stems, FEA Software, Artificial Intelligence.
Abstract: Hip replacement is one of the most successful surgical events that progressively more patients require because
of the better life expectancy and increase in the average age of several countries. It further promoted the
improvement of hip prosthesis lifespan in sciences such as materials, mechanics and, recently, computer
science with artificial intelligence (AI). The present investigation aims to make a systematic review of the
progress with recent developments and criteria to get optimal outcomes in the design and selection of hip
implants, emphasizing femoral stem parameters for their relevance to the entire prosthesis performance. New
software tools such as clustering, and a different finite element analysis (FEA) approach are introduced to
speed up customized design processes without sacrificing accuracy. Clustering algorithms delimited the
proximal femur properly according to its anatomical locations. Moreover, Altair SimSolid
®
software proved
satisfactory accuracy compared to NX
®
simulation values despite the complex morphology of the proximal
femur with a maximum deviation of 12.94% and a simulation time of less than 30%.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the main and largest joints in the human body
is the hip. It constituted by the femoral head and the
acetabulum through the articular cartilage, acetabular
labrum and ligaments. Moreover, the femur is the
longest and heaviest bone, receives and
physiologically distributes the gravitational loads of
the body. Different conditions such as walking,
jogging, sitting, among others accentuate the loads, so
it requires high resistance; however, the arrangement
of the hip joint ensures a proper physiological transfer
of loads enabling stability and mobility at the same
time.
Total hip arthroplasty is one of the most
successful surgical procedures (Learmonth et al.,
2007). It has undergone extensive development
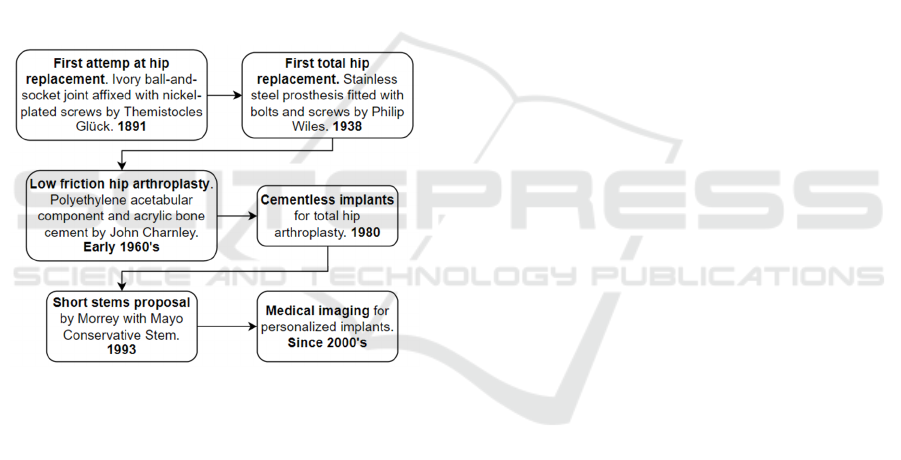
(Figure 1) due to its high demand because
increasingly younger patients require a hip
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8959-9547
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2989-9166
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6163-5382
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2112-1349
replacement, and also, in several countries, the
population is getting older.
This surgical procedure is performed when non-
invasive treatments fail to relieve pain or restore
mobility in the patient's hip. It mainly occurs when
there is a femoral neck fracture, intertrochanteric
fracture, coxarthrosis, or other pathology associated
with the hip joint, often linked to low bone quality or
cartilage degradation. Demand for a primary total hip
replacement among people less than 65 years old was
projected to exceed 52% by 2030 (Kurtz et al., 2010).
In young patients, hip fracture risk appears when
extremely high loads are transferred usually in a short
time due to accidents.
Hip replacement removes the damaged parts of
the femur and acetabulum to replace them with
artificial limbs named hip prosthesis, whose
components are the cup, insert, femoral head, and
stem. The latter has a crucial function in the success
46
Moscol, I., Solórzano-Requejo, W., Ojeda, C. and Rodríguez, C.
Personalized Hip Replacement: State of the Art and New Tools Proposals.
DOI: 10.5220/0010823100003123
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022) - Volume 1: BIODEVICES, pages 46-57
ISBN: 978-989-758-552-4; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
and duration of the implant since it will be in direct or
indirect (through cement) contact with the femoral
cavity, being in charge of proper load transferring to
the proximal femur. The objective is to make this
transfer as close as possible to the natural
biomechanical behaviour by the optimal design and
fixation.
Despite the technological advances, there are still
several postoperative pathologies related to multiple
incompatibilities caused by the external agent.
Corrosion and wear debris, associated with
biomaterial properties, are responsible for osteolysis
inducing bone inflammation and resorption that
eventually lead to periprosthetic loosening of the
implant (Eltit et al., 2019). Moreover, differences in
mechanical properties promote Stress/Strain
Shielding (SS) because of Young's modulus variation
between implant and bone (Table 1), this
phenomenon promotes bone resorption on the
periprosthetic region of the stem.
Figure 1: The temporal sequence of hip prostheses.
In the last two decades, development in
computational tools like CAD/CAE software and AI
have been valuable tools for more accurate and time-
optimized experimentation. Many design and
selection processes could now be automated so that
orthopaedic physicians or biomedical engineers save
time and reduce the number of possible solutions to
evaluate.
These tools can improve surgical outcomes by
ensuring precision in several parameters such as the
positional coordinates and forces to ensure adequate
initial fixation of the implant. Robotic hip surgery
was initiated in the 1980s with the DigiMatch
Robodoc surgical system produced by the company
then called Integrated Surgical Systems
(Subramanian et al., 2019). This system helps
preoperative planning in which patient’s Computed
Tomography (CT) guides the surgeon in the implant
selection and previews the postoperative outcomes.
Nowadays, there’ve been several improvements and
another part of the Robodoc performs the osteotomy
bone cut and inserts the implant minimizing human
error and the risk of bone fracture during the surgery
(Sugano, 2013).
2 TYPES OF HIP PROSTHESES
In 1959, Sir John Charnley proposed the low friction
total hip arthroplasty where a small-diameter socket
restores the total mobility of the joint and eradicates
pain. Despite the good technical skills of the
surgeons, there were still several failure cases. For
that reason, in 1962 Craven suggested the high-
density polyethylene (HMWP) as a material for the
socket that was an excellent complement for
Charnley’s design proposal. (Camacho & Fernandez,
2006)(Wroblewski, 1997). However, the failure rate
of the Charnley prosthesis was higher in young
patients, who are estimated to lead more physical
activity moving their hip around 5 million cycles per
year (Gallart et al., 2018). To recover the entire
mobility and mechanical demands, the cement goes
under high mechanical stresses which, in most cases,
led to its fracture.
Moreover, outcomes of cement fixation are not
the same for patients with good bone quality as in
patients with greater porosity. Better cement-bone
bond is achieved when the patient has a less bone
mass index. (Learmonth et al., 2007)(Cotogno, 2012).
This controversy promoted the introduction of
cementless fixation in 1980, whose target is to
guarantee long-term biological stability through bone
ingrowth on the stem walls, a process known as
osseointegration. It results from direct bone-implant
contact with biocompatible porous coating and
minimal interface micromotion (Nazari-farsani,
2015). Relative displacements are related to surgical
technique, implant geometry and stiffness, bone
quality, daily activities, and patient weight. The
appropriate geometry would enhance
primary/mechanical stability within 3 to 6 months
after surgery and the good engagement of the
prosthesis with the surrounding bone lead to
secondary/biological one due to good
osseointegration (Javed et al., 2013)(Ruben et al.,
2007). The proper implant would have a high rate of
success if the patient’s bone remodelling was also
good, that is why these types of implants are
recommended for young patients.
Personalized Hip Replacement: State of the Art and New Tools Proposals
47

Although cementless fixation showed remarkable
designs continued to be invasive since they occupy
from the proximal region to the upper part of the
femoral diaphysis. It would lead to obstructing the
bloodstream that provides oxygen and nutrients for
bone maintenance. Reducing bone remotion in the
surgical procedure and optimizing the load transfer,
through appropriate implant geometry and material,
would ensure bone preservation and a long prosthesis
lifespan (Gallart et al., 2018).
A study by (Jasty et al., 1993) showed that the
diaphyseal portion of the stem was rendered unusable
when the bone grew proximally. Other studies about
diaphyseal anchorage indicated it is associated with
anomalous load transfer, leading to thigh pain in the
short term and proximal bone loss by SS in the long
term (Amstutz & Duff, 2015). Therefore, the need
arises to shorten the stem length with designs that
span to the metaphyseal region of the proximal femur,
giving rise to the field of short-stem prostheses.
Short stems, also called metaphyseal stems, leave
more bone stock available for being smaller. They
could also preserve bone by distributing loads more
physiologically. Recent studies show less bone
mineral density loss in the proximal region for
patients with this type of stem and a reduced proximal
SS (Sköldenberg et al., 2006). Short stems have been
classified by different authors according to their
geometry and anatomical zones occupied in the
proximal femur, resulting in four main categories:
Type 1: Femoral neck stem.
Type 2: Calcar loading stem.
Type 3: Calcar loading with lateral flare stem.
Type 4: Shortened tapered conventional stem.
Short stems usually have a length between 40 and
135 mm, reaching at most to the superior diaphysis as
in the case of tapered-wedge designs. The best results
according to literature are related to the calcar loading
with lateral flare stems, whose tapered trapezoidal
design achieved adequate fixation and demonstrated
Figure 2: Proximal femur occupied by the Type 3 short stem
DePuy Proxima™ (Santori et al., 2007).
more effective load transfer in the proximal femur
than the other designs (Khanuja et al., 2014)(Kheir et
al., 2020).
Within the category of calcar short stems, load
bearing with lateral flare designs have shown the
highest rate of success. In this category, the DePuy
Proxima™ (DePuy, Leeds, UK) model (Figure 2) is
found standing out with overall survival of 100% for
4.5 years and 97.6% for 7 years according to follow-
up studies made by (Kim et al., 2013) and (Gombár et
al., 2019), respectively.
3 BIOMATERIALS
3.1 Importance and Influence
Biomaterials must meet several requirements that
vary according to whether the prosthesis is cemented
or uncemented. In the first category, usually,
Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) cement will be in
direct contact with the bone while, in the second, stem
walls, normally covered by a porous material, will
enable the stem fixation. Accordingly, biomaterials
will vary depending on their function either in the
body of the components or as a coating or bone
cement. In general, the body/internal component
material must be compatible with mechanical
properties as close as possible to the bone; otherwise,
stresses transmitted to the bone would be reduced to
such an extent that SS occurs. To achieve this, good
mechanical strength, as well as fatigue resistance are
required.
Cemented fixation guarantees primary stability
just after the bone cement has set due to the hardening
properties of the cement which mechanically fixes
and prevents relative mobility at the bone-implant
interface. A homogeneous cement layer with a good
setting improves mechanical fixation, contributing as
well to the physiological transfer of loads and
reducing SS (Cotogno, 2012). The cemented implant
proposed by Sir John Charnley has a probability of
success between 77% and 81% over a range of 25
years after THA, but the failure rate was higher for
young patients. The first problem was related to the
material of the acetabular component, polyethylene
(PE), whose debris infected the bloodstream due to
metallosis (Rieker, 2016)(Hu & Yoon, 2018). This
material was then replaced by high-density
polyethylene (UHMWPE, ultra-high molecular
weight polyethylene). However, the rate of failure
persisted because of incompatibilities between the
bone cement, the active lifestyle, and bone quality of
these patients.
BIODEVICES 2022 - 15th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
48

A study made on 48 patients younger than 30
years with cemented hip implants showed a 10-year
survival of 83% with revision for any reason and 90%
with revision for aseptic loosening as the endpoint
(Busch et al., 2010). A post-study (Schmitz et al.,
2013) with the same population and revision criteria
showed a 15-year survival rate of 75% and 82%,
respectively. However, this option is more
recommended for young people with degenerative
cartilage disease in the hip joint and aseptic loosening
is accompanied sporadically by aggressive bone
destruction, a phenomenon termed cement disease
(Barrack, 2000).
As a result, cementless prostheses were proposed
to take advantage of the good bone quality that
younger patients have. Implant success is highly
correlated to initial stability which is essential to
promote bone ingrowth into the stem coating (Ruben
et al., 2012). The stem coating must enhance
osseointegration and be resistant to wear and
corrosion to minimize the release of particles into the
bloodstream and avoid toxicity. Most of the implants
commonly use a porous coating called
Hydroxyapatite [Ca₁₀(PO₄)6(OH)₂] whose bioactive
interaction accelerates the bone ingrowth process
through a series of reactions between the biomaterial
and the internal fluids of the femur that form a
biologically active carbonate layer, equivalent to the
bone mineral phase (Cotogno, 2012).
The primary stability is also related to stem
geometry and materials that likewise influence
biological stability where minimized stress shielding
is required. One of the main factors about implant
material is the stiffness level. Highly stiff implants
induce less micromotion compared to low-stiff ones,
nonetheless, high-stiff materials promote stress
shielding and adverse bone remodelling at the implant
surfaces (Chanda et al., 2020). The long-term stability
of cementless prostheses also depends on the patient's
health, especially bone quality, which influences on
bone remodelling rate in the periprosthetic region.
3.2 New Materials
Several types of materials like ceramics, polymers
and metals have been developed for implants
purposes. They classify based on their interaction
with the surrounding tissue in bio-tolerant, bioactive
and bioresorbable. Metals have shown good quality
outcomes being the most commonly used: stainless
steel (316L), cobalt-based alloys (Co-Cr-Mo) and
titanium-based alloys (Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-5Al-2.5Fe, Ti-
Al-Nb) (Aherwar et al., 2016). Nowadays, titanium is
the most used material in femoral stems manufacture,
it is characterized by low density, highly
biocompatible with good resistance to stress and
corrosion; the latter is since there is a rapid reaction
with oxygen that generates a thin protective layer. Its
alloys, especially Ti-6Al-4V, have shown good
results in reducing SS by having a lower Young's
modulus than other types of alloys; however, this is
approximately 110 GPa, still high compared to
cortical bone (Kunii et al., 2019) producing SS due to
a disproportionate bone remodelling.
Prior biomechanical studies (Kuiper & Huiskes,
1996) concluded that decreasing stem stiffness
reduces stress shielding and avoids severe bone
resorption. Nevertheless, it increases proximal
interface stresses, which may inhibit biological
fixation and cause loosening.
A non-homogeneous Young's modulus material
proposed in (Hanada et al., 2014) is β-Ti33.6Nb4Sn
(TNS) obtained after several cold working and local
heat treatments. It has high strength with Young's
modulus (45 GPa with cold rolling) much lower than
other β-type Titanium alloys: axial stiffness 56%
lower and bending stiffness 53% lower than
Ti6Al4V (Yamako et al., 2017). In studies with TNS,
a low Young’s Modulus in the distal part of the stem
and high fatigue strength (850MPa) in the neck region
were proposed. However, rather low Young's
modulus, although decreasing stiffness, could cause
excessive stresses at the bone-implant interface
inhibiting fixation; additionally in vivo studies must
include adaptative bone remodelling to determine
whether bone changes occur in the surrounding
tissue. Despite that, studies show that bone mineral
density would be 42.6% higher in the Gruen 7 zone
with a TNS stem than Ti-6Al-4V 10 years after
implant placement. Another new option is the Ti21S
alloy (Pellizzari et al., 2020), whose biocompatibility
is like Ti6Al4V, which generates more mechanical
advantages by having Young's modulus of
approximately half, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Mechanical properties of Titanium alloys for hip
prostheses.
Alloy
Young’s
Modulus
(GPa)
Tensile
Strength
(MPa)
Reference
Cortical
Bone
10 - 20 100 - 300
(Cotogno,
2012)
Ti-33.6Nb-
4Sn (TNS)
55 1270
(Yamako et
al., 2014)
Ti-6Al-4V 110 1095
(Facchini et
al., 2011)
β - Ti21S 52 831
(Pellizzari
et al., 2020)
Personalized Hip Replacement: State of the Art and New Tools Proposals
49

Recent studies are evaluating biomechanical
properties obtained with additive manufacturing where
adaptative cell topologies resemble bone local mecha-
nical properties. In (Arabnejad et al., 2017) obtained a
75% reduction in bone loss derived from stress
shielding (8% of bone resorption with the optimized
fully porous implant) compared to a solid implant.
4 PERSONALIZED PROSTHESES
Hip implant longevity is increased by customizing the
prosthesis design. This implies considering the offset,
anteversion, and neck-shaft angle (Figure 3). Before
starting the design and the implant material selection,
it is necessary to know the host bone properties
(Solórzano et al., 2020) and the patient’s health
situation. This way, better performance outcomes and
durability of the hip prostheses can be guaranteed.
Figure 3: Femur parameters considered in a customized
design.
The most noticeable physiological changes are
due to the patient's age because, after a certain age,
bone quality begins a noticeable decline attributed to
metabolic changes in the bone tissue and a decrease
in bone osteocalcin content (Portal-Núñez et al.,
2012). Thus, if the patient is young, the hip joint will
be subjected to higher mechanical loads and is more
likely to undergo revision surgery compared to an
older patient. Therefore, a less invasive stem will be
required. Moreover, the more active bone tissue of
young patients makes them suitable for the use of
cementless prostheses, as it promotes
osseointegration, which accelerates primary stability
and increases implant life by forming a stronger bond
than cemented fixation (Sivasankar et al., 2016).
Another way to customize hip prostheses was
proposed in Milan around 1987 by Cremascoli
(Srinivasan et al., 2012). He suggested the modular
neck to give independence and adaptability according
to physical attributes of the patient's joint, such as
offset, femoral neck anteversion, and neck length.
Modular prosthesis presents two components (stem
and neck separately) coupled by a taper junction with
frictional bonding. The literature reveals no
noticeable variation in the long-term outcomes of
modular and non-modular prostheses; in contrast,
adverse effects such as fretting corrosion and fatigue
probably occur at the junction of modular prostheses
(Kheir et al., 2020)(Schaaff, 2004).
Therefore, monoblock customization of the
implants is recommended. It involves considering
proximal and distal morphologies of the femur for
more accurate stem personalization. In this regard,
CT allows virtual reconstruction of a patient’s femur
(Figure 4). Uncemented prostheses adapted to the
inner part of the femur provide a better fit due to their
optimized volume, which also reduces the weight of
the implant. In this way, the stress distribution and
biomechanics of the joint resemble its natural state
(Katoozian et al., 2001).
Figure 4: Femoral geometry and properties from computed
tomography.
In 2009, (Ojeda, 2009) verified by numerical
simulation the preponderance of customized
prostheses. The study was performed with the
computed tomography (CT) of a 40-year-old woman
from Piura, Peru. Primary stability in a conventional
cementless prosthesis was assessed through micro-
displacements at the femur-stem interface. The
custom design was superior to the CLS Spotorno
®
model, but the relative micromotion in the posterior
lateral proximal zone remained high, ranging from
150 to 200 microns. It is therefore important to
evaluate the lateral zone on the stem design.
The stem is crucial to improving prosthesis
performance because it is subjected to the highest
mechanical stresses and manage the physiological
transfer of loads to the surrounding bone. Firstly,
stem length affects the mechanical stability; hence the
longer, the better. However, this implies greater
invasion of the marrow cavity leaving less bone
available for possible revision surgery. As a
consequence, shorter stems are recommended for
patients younger than 65 years (Cotogno, 2012). The
BIODEVICES 2022 - 15th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
50
custom design of short stems is performed with the
same methodology as conventional stems. However,
load distribution along the femur should be taken into
account, especially in the calcar and lateral regions of
the proximal femur due to its preponderance to the
SS. (Rawal et al., 2011)(Gómez-García et al., 2016).
(Solórzano, 2021) evaluated by FEA personalized
short stems with Ti21S material resulting in a SS of
0.285 and 0.073 for each of two patients; those
prostheses would improve mechanical response and
remodelling of the proximal femur than commercial
hip implants (Yamako et al., 2014)(Yan et al., 2020)
which could produce a SS between 0.61 and 0.93.
5 TECHNOLOGIES
5.1 Statistics and Artificial Intelligence
in Hip Arthroplasty
Initially, statistical methods (Otomaru et al., 2012)
introduced automation to segment the marrow cavity
and ensure prosthesis implantability. They combined
tolerance criteria of experienced surgeons and a map of
distances at the bone-implant interface based on a set
of medical images to create an atlas with the
delimitation of the maximum areas within the channel
cross-section where the stem geometry could be fitted.
Last decade, Artificial Intelligence has been
progressively gaining more space in the healthcare
field. In 2020, (Kang et al., 2020) applied
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) with X-Ray
imaging to build a stem detection model to classify
and cluster different commercial models. The
algorithm could help to collect large-scale stem
information and to make comparisons among
different geometries which in the future would save
time for orthopaedists to identify and make new
selections among commercial prostheses.
Recently, Chitubox
®
, a 3D printing software,
allowed (Bermejillo et al., 2021) to slice CAD models
obtaining a set of white and black pictures that
resemble CT images. That methodology can be used
in the design of femoral stems to acquire information
not only from the stem but also from the medullary
cavity. The slices of the proximal femur (Figure 5)
would be used to train a CNN that predicts femoral
response, like SS. Customization would be done by
evaluating femur response changing the pixel status
of stem portions. Then, after training AI models for
optimization, it could be used with real CT scans to
make personalized stems that restore bone
biomechanics with ideal performance concerning
physiological load transfer.
Figure 5: CT-like slices of a femur with hip replacement
using Chitubox
®
software.
Advanced AI tools are required to make a more
complete description of complex geometries. More-
over, ML-based methodologies may be applicable
when the computational costs of numerical simulation
are unaffordable. Several studies are underway to
improve the performance of AI-based systems to
streamline design processes with adequate accuracy.
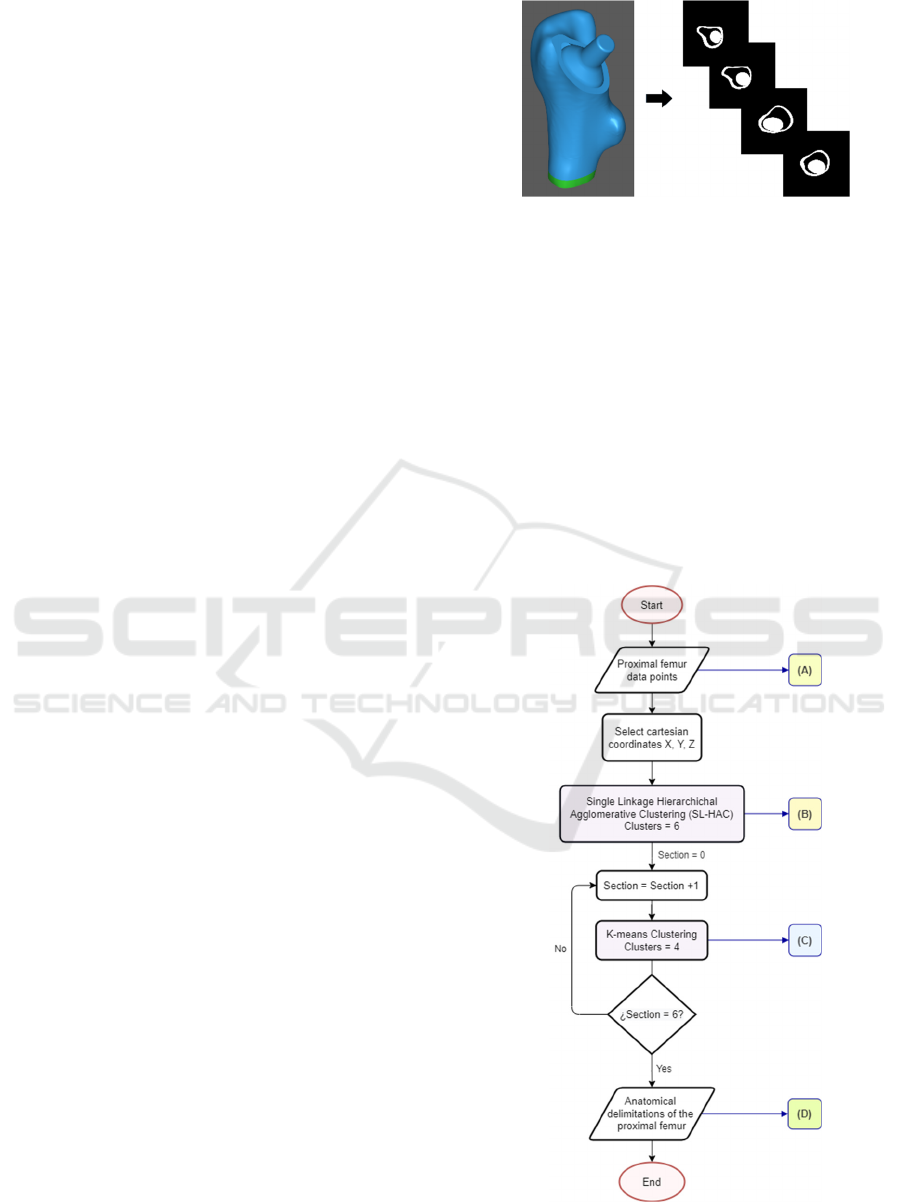
The present investigation proposes clustering
techniques (Figure 6) to make a more accurate and
time-saving assessment of the proximal femur. It
aims to get local information about the physiological
load transfer according to femoral anatomical
locations: lateral, medial, anterior, and posterior.
Figure 6: Flowchart to anatomically demarcate proximal
femur.
Personalized Hip Replacement: State of the Art and New Tools Proposals
51

The angular association among the proximal
femur planes is based on (Solórzano, 2021) proposal
of an innovative methodology for short stem designs
that guarantees stem implantability by acquiring
information of the medullary cavity and surgery
approach. The first plane corresponds to the
osteotomy plane taken from the CAD model of the
proximal femur of the patient, whose CT scans were
downloaded from an open-access medical image
repository (Raymond, 2019). The second reference is
a horizontal plane located 10mm below the lesser
trochanter. Finally, with equal division of the
osteotomy angle, six planes are obtained as is shown
in Figure 7.
Figure 7: Cortical bone points to be classified.
Through the SL-HAC, bone sections can be
identified without manually labelling each one
(Figure 8). Initially, all samples are individual
clusters, then the algorithm calculates the distance
between the most similar for each pair of clusters to
then combine those who are closer. This division
allows working with points that contain not only
rectangular coordinates but also the local femur
response to mechanical stimuli in stress, strain,
among others values.
Figure 8: Sections generated by the SL-HAC algorithm.
The final clustering shown in Figure 9 is made
automatically by a K-Means algorithm through an
iterative update of the centroids, identified randomly
at the beginning. This ML technique is good at
dealing with data of spherical distribution. Same K-
Means specifications were applied to each of the six
planes in Figure 7.
One of the main benefits of this approach relies on
increasing ML-based models, where speeding up data
acquisition with high accuracy is required. These
delimitations (Figure 10) provide insight into changes
in physiological load distribution and bone
biomechanics as a function of varying load patterns.
SS can also be quantified and analyzed in detail with
this demarcation of the proximal femur.
Figure 9: Zones of one section by K-Means algorithm.
Figure 10: Proximal femur completely delimited according
to the anatomical locations.
Regarding mechanical design, in 2015, (Chanda
et al., 2015) designed an Artificial Neural Network to
relate geometric parameters of the stem to micro-
displacements at the bone-implant interface. They
also included optimization through Genetic
Algorithms (GA) to improve mechanical stability, but
SS is not guaranteed due to its micromotion approach
that doesn’t quantify the loads received by the femur.
In 2017, (Cilla et al., 2017) studied whether the
geometry of a commercial femoral prosthesis could
be effectively optimized to reduce the SS. They
compared Support Vector Machines (SVM) and
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) after combining
them with Pattern Search minimization algorithm
(Table 2). SVM gave better results; however, the
BIODEVICES 2022 - 15th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
52

effectiveness may vary from patient to patient and
depending on the amount of data.
A recent innovation regarding the improvement in
optimization algorithms was raised in 2019, where
(Chatterjee et al., 2019) introduced the concept of the
composite desirability function to solve the problem
of obtaining a single value as output from ANNs. This
function made it possible to consider the
susceptibility to significant stress variations in each
proposed region after the prosthesis was placed. They
also parameterized the patient's bone quality,
quantifying its influence on the same problem.
Table 2: Algorithms for Design Optimization.
Al
g
orithms Hi
g
hli
g
hts
To estimate the femur response to the supported loads
Artificial Neural
Networks (ANN)
Attempts to mimic the human
brain for solving specific tasks
finding
complex associations
among data like a black box.
Support Vector
Machines (SVM)
SVM do not retrain the model to
estimate a new value once it has
already been trained and tested. It
adds the new remark directly and
updates itself.
To find the optimal geometry optimizing a cost function
Genetic
Algorithms (GA)
Stochastic global search method
based on the Darwinian concept of
survival. It uses the principle of
natural selection and genetic
inheritance by evaluating a fitness
score.
Pattern Search
(PS)
Numerical optimization method
that computes objective function
(OF) for the points in a grid. It
explores more than it exploits by
changing iteration with the first
point exceeding the best OF.
5.2 FEA Software
Requirements of large amount of data have also
turned attention to fast simulation software and to
understanding how they work. In conventional
analysis, simulation of a virtual femur could take
from 5 to 15 minutes depending on computer
specifications, the geometric complexity of the model
and boundary conditions as well as the meshing
characteristics.
Around 2018, a meshless software called
SimSolid
®
from Altair Engineering Inc. was
launched. It proposes a new FEA approach where no
discretization in finite elements is done but takes any
type of geometry, whether simple, amorphous or
complex such as the proximal femur and considers it
as a finite element (FE) (Altair, 2019). Furthermore,
this software works with contour functions that
generate the degrees of freedom (DOF) of the
FE/component, unlike the conventional approach
where the number of nodes of the discretized finite
element defines its DOF. In addition, the contour
DOF are not the only ones produced when developing
the external approximations in SimSolid
®
, but also
the internal DOF associated with the volume are
generated automatically. Meshless software performs
adaptive solutions where the number of DOF of the
boundary is automatically assigned to meet the
convergence criteria.
Simulation time is another advantage of meshless
simulation. For femoral analysis, SimSolid
®
takes
from 30 seconds to 1 minute depending on default
solution settings and it could take from 3 to 6 minutes
with increased refinement level. In addition, not using
meshing saves time for model pre-processing,
whereas in conventional FEA simulation the element
size must be defined according to h-method and p-
method through convergence analysis.
The mathematical formulation of the meshless
approach, specifically SimSolid
®
, dates to 1908 when
Ritz proposed an approximate solution to the
boundary value problem with the linear combination
of simple functions (𝑝
). In (1), 𝑎
are factors without
physical representation defined when the energy
function, 𝐹𝑈
,
in (2), is assigned to a
minimum value, 𝑛 is the number of nodes of the FE.
𝑈
ℎ,𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡
𝛴𝑎
𝑖
.𝑝
𝑖
, ∀ 𝑖1,2,3,… ,𝑛
(1)
𝐹𝑈
,
𝐹
𝛴𝑎
.𝑝
min (2)
Equation (3) is satisfied for the FE approximation
to be external of the element. , refers to the pairs
that lie on the element boundary. δ and 𝛾 are
operators,
𝑈 and are approximation functions defined
inside the element. Altogether in (3) guarantees that
the boundary of the limit approximation functions of
𝑈 belong to the Sobolev space which guarantees their
existence only to a certain degree so 𝐹𝑈 provides
finite energy. (SimSolid Corporation, 2015)
𝛿,𝛾𝑈0
(3)
In (4) boundary DOF are also defined, which have
no physical meaning. Their function is to guarantee
that the approximation functions (𝑈) of each FE are
compatible when 𝐵
tends to infinity.
Personalized Hip Replacement: State of the Art and New Tools Proposals
53

𝐵
𝐷𝑂𝐹
𝑔
𝑘
𝛾𝑈𝑑𝛾
𝛾
, ∀ 𝑘1,2,… ,𝑛
(4)
𝛾: the boundary of the finite element.
𝑔
: simple functions on the boundary of the FE.
In (3), 𝑈 is the function to be approximated in the
element like stresses or displacements in structural
analysis. When it comes to external analysis, the 𝑈
function from (5) and (6) not only incorporates the
element but also considers its boundary.
𝑈
ℎ
𝑈
𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡
𝑈
𝑏𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟
𝑦
(5)
𝑈
ℎ
𝛴𝑎
𝑖
𝑈
𝑝
𝑖
𝛴
𝑔
𝑘
𝛾𝑈𝑑𝛾
𝛾
𝑝
𝑘
(6)
In equation (6),
𝑎
: internal DOF of the element.
𝑝
: basis functions within the internal DOF.
𝑝
: basis functions of the boundary DOF.
Literature shows that SimSolid
®
presents a
deviation concerning other numerical simulation
software lower than 1% in the high-stress
concentration elements, reaching values lower than
5% in all cases (skew plate, plate with hole, U-shaped
notch) with the maximum precision setting. reducing
variation from 29.3% to 2.8% compared to the default
configuration (Symington, 2020). The only study
found with human geometry (Rivera et al., 2020)
evaluated a mandible reconstructed from a CT scan
getting 2-7% of deviation when compared with other
FEA software.
Figure 11: Maximum principal stresses of the intact femur
under ISO load with NX
®
and SimSolid
®
.
Figure 11 shows simulation results with the
following boundary conditions: rigid fixation at the
bottom, adherence of cortical and trabecular bone
contact surfaces and a 2300N force established by the
International Standardization Organization (ISO)
under the ISO 7206-4 standard.
Maximum Principal Stress is suggested for
analyzing stress distribution in bones (Solórzano et
al., 2020)(Jung & Kim, 2014)(Schileo et al., 2008).
Likewise, Von Misses stress was considered due to its
previous use as a reference to compare the accuracy
of SimSolid
®
(Symington, 2020) even in a
biomechanical study on the mandibular structure
(Rivera et al., 2020). Von Misses stresses are also
used to assess the implant fracture risk that in the
proximal femur customization approach could have
relatively complex geometries.
Table 3: Results comparison between both software.
NX
®
SimSolid
®
Deviation
Maximum Principal Stress
Maximum 35.270 30.706 12.94%
Minimum -12.796 -11.525 9.93%
Von Misses Stress
Maximum 30.482 30.740 0.85%
Minimum 0.033 0.036 9.09%
The maximum deviation was 12.94% and the rest
were less than 10%, which is acceptable if we deal
with a complex morphology such as a femur (Table
3). Von Misses stress ranges from 1-9%
approximately which is close to (Rivera et al., 2020)
study whose results ranged from 1-7% compared to
the Inventor
®
software. In any case, the trade-off for
obtaining precise solutions in a short time offered by
SimSolid
®
is a good alternative if you are looking to
generate a large amount of data with CAE software.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Ti21S is a good alternative to Ti-6Al-4V, currently
used in most stems. Although both materials are
biocompatible due to their titanium content,
aluminium in small quantities could produce toxicity
effects when its debris enter the patient’s
bloodstream. The most notorious difference between
both materials is Young's modulus, since the lower its
value, the better, because it will more closely
resemble the mechanical properties of the patient's
cortical bone, producing a better load transfer and
distribution. In this regard, Ti21S would be more
likely to increase the implant’s lifespan.
Currently, there is a growing demand for data in a
short time for orthopaedic implants where the
likelihood of successful outcomes and for a patient to
acquire medical complications or pathologies
(pneumonia, urinary tract infection, etc.) are
BIODEVICES 2022 - 15th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
54

influenced by the preoperative time. Therefore, more
research should be done on computational tools such
as SimSolid
®
, which with a validated good accuracy
could help to speed up the data acquisition process.
Likewise, it can be complemented with ML-based
models to extract local information from the femur
and improve the process of prosthetic design
customization.
Due to the complex morphology of the proximal
femur, it is reasonable that deviations in results from
simulations are greater than in the literature reviewed
about SimSolid
®
, where common geometries, such as
bars, cylinders, or spheres, were analysed.
Furthermore, since these are approximate solutions,
there will always be a simulation error, even between
different FEA software working with conventional
finite elements.
Although recently there has been extensive
research on the design of short stem prostheses,
studies on conventional cemented stems should not be
neglected since they present better fixation in older
adults and accelerate postoperative recovery. In
addition, conventional prostheses are usually used in
revision surgery, where short anterior stems help
guarantee success, leaving sufficient good-quality
bone stock improving the fixation of the new implant.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was funded by CONCYTEC-
PROCIENCIA under the financial scheme "Becas de
Mentorías María Reiche 2021-01" [Contract N°E053-
2021-PROCIENCIA].
The authors express their gratitude to the
Biomechanics Group of the Universidad de Piura for
all their support in the development of this research.
The authors acknowledge the support of reviewers
and their relevant questions, which led to a more
detailed and consistent paper.
REFERENCES
Aherwar, A., Singh, A. K., & Patnaik, A. (2016). Cobalt
based alloy: A better choice biomaterial for hip
implants. Trends Biomaterials and Artificial Organs,
30(1), 50–55.
Altair. (2019). Simulation-Driven Design: Solving the
Geometry Problem.
Amstutz, H. C., & Duff, M. J. Le. (2015). Hip resurfacing:
history, current status, and future. Wichtig Publishing,
25(4), 330–338. https://doi.org/10.5301/hipint.50
00268
Arabnejad, S., Johnston, B., Tanzer, M., & Pasini, D.
(2017). Fully porous 3D printed titanium femoral stem
to reduce stress-shielding following total hip
arthroplasty. Journal of Orthopaedic Research, 35(8),
1774–1783. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.23445
Barrack, R. L. (2000). Early failure of modern cemented
stems. Journal of Arthroplasty, 15(8), 1036–1050.
https://doi.org/10.1054/arth.2000.16498
Bermejillo, M., Franco-Martínez, F., & Díaz, A. (2021).
Artificial intelligence aided design of tissue
engineering scaffolds employing virtual tomography
and 3D Convolutional Neural Networks. Materials,
14(5278). https://doi.org/https:// doi.org/10.3390/
ma14185278
Busch, V., Klarenbeek, R., Slooff, T., Schreurs, B. W., &
Gardeniers, J. (2010). Cemented hip designs are a
reasonable option in young patients. Clinical
Orthopaedics and Related Research, 468(12), 3214–
3220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1355-z
Camacho, J., & Fernandez, J. (2006). Sir John Charnley
(1911-1982). Sociedad Mexicana de Ortopedia, AC,
20.
Chanda, S., Gupta, S., & Pratihar, D. K. (2015). A
combined neural network and genetic algorithm based
approach for optimally designed femoral implant
having improved primary stability. Applied Soft
Computing Journal, 38, 296–307. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.asoc.2015.10.020
Chanda, S., Mukherjee, K., Gupta, S., & Pratihar, D. K.
(2020). A comparative assessment of two designs of hip
stem using rule-based simulation of combined
osseointegration and remodelling. Proceedings of the
Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of
Engineering in Medicine, 234(1), 118–128.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0954411919890998
Chatterjee, S., Dey, S., Majumder, S., RoyChowdhury, A.,
& Datta, S. (2019). Computational intelligence based
design of implant for varying bone conditions.
International Journal for Numerical Methods in
Biomedical Engineering, 35(6), 1–17.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cnm.3191
Cilla, M., Borgiani, E., Martínez, J., Duda, G. N., & Checa,
S. (2017). Machine learning techniques for the
optimization of joint replacements: Application to a
short-stem hip implant. PLoS ONE, 12
(9), 1–16.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183755
Cotogno, G. (2012). Total hip arthroplasty: State of the art,
prospects and challenges (Issue July). Joint Research
Centre of the European Commission. https://doi.org/
10.2788/31286
Eltit, F., Wang, Q., & Wang, R. (2019). Mechanisms of
Adverse Local Tissue Reactions to Hip Implants. Front.
Bioeng. Biotechnol, 7, 176. https://doi.org/
10.3389/fbioe.2019.00176
Facchini, L., Magalini, E., Robotti, P., Molinari, A., Höges,
S., & Wissenbach, K. (2011). Ductility of a Ti-6Al-4V
alloy produced by selective laser melting of prealloyed
powders. Rapid Prototyping Journal. https://doi.org/
10.1108/13552541011083371
Personalized Hip Replacement: State of the Art and New Tools Proposals
55

Gallart, X., Riba, J., Bori, G., Mu, E., & Combalia, A.
(2018). Hip prostheses in young adults . Surface
prostheses and short-stem prostheses. Revista Española
de Cirugía Ortopédica y Traumatología, 62(2), 142–
152.
Gombár, C., Janositz, G., Friebert, G., & Sisák, K. (2019).
The DePuy Proxima
TM
short stem for total hip
arthroplasty – Excellent outcome at a minimum of 7
years. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery, 27(2), 1–6.
https://doi.org/10.1177/2309499019838668
Gómez-García, F., Fernández-Fairen, M., & Espinosa-
mendoza, R. (2016). A proposal for the study of
cementless short-stem hip prostheses. Acta Ortopédica
Mexicana, 30(4), 204–215.
Hanada, S., Masahashi, N., Jung, T., & Yamada, N. (2014).
Fabrication of a high-performance hip prosthetic stem
using β Ti–33 . 6Nb–4Sn. Journal of the Mechanical
Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 30, 140–149.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2013.11.002
Hu, C. Y., & Yoon, T. R. (2018). Recent updates for
biomaterials used in total hip arthroplasty. Biomaterials
Research, 22(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40824-
018-0144-8
Jasty, M., Krushell, R., Zalenski, E., Connor, D. O.,
Sedlacek, R., & Harris, W. (1993). The contribution of
the nonporous distal stem to the stability of proximally
porous-coated canine femoral components. 8(1), 33–
41.
Javed, F., Ahmed, H., Crespi, R., & Romanos, G. (2013).
Role of primary stability for successful
osseointegration of dental implants: Factors of
influence and evaluation. Interventional Medicine and
Applied Science, 5(4), 162–167. https://doi.org/
10.1556/IMAS.5.2013.4.3
Jung, J. M., & Kim, C. S. (2014). Analysis of stress
distribution around total hip stems custom-designed for
the standardized Asian femur configuration.
Biotechnology and Biotechnological Equipment, 28(3),
525–532.
https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2014.928450
Kang, Y. J., Yoo, J. Il, Cha, Y. H., Park, C. H., & Kim, J.
T. (2020). Machine learning–based identification of hip
arthroplasty designs. Journal of Orthopaedic
Translation, 21, 13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.jot.2019.11.004
Katoozian, H., Devy, D. T., Arshi, A., & Saadati, U. (2001).
Material optimization of femoral component of total hip
prosthesis using fiber reinforced polymeric composites.
Medical Engineering & Physics, 4533(October), 0–9.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S1350-4533(01)00079-0
Khanuja, H. S., Banerjee, S., Orth, M. S., Glasg, M., Jain,
D., & Orth, M. S. (2014). Short Bone-Conserving
Stems in Cementless Hip Arthroplasty. Bone & Joint
Surgery, 96-A, 1742–1752.
Kheir, M. M., Drayer, N. J., & Chen, A. F. (2020). An
Update on Cementless Femoral Fixation in Total Hip
Arthroplasty. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery
, 1646–
1661.
Kim, Y., Park, J., & Kim, J. (2013). Is Diaphyseal Stem
Fixation Necessary for Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty
in Patients with Osteoporotic Bone (Class C Bone)?
Journal of Arthroplasty, 28(1), 139-146.e1.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2012.04.002
Kuiper, J. H., & Huiskes, R. (1996). Friction and stem
stiffness affect dynamic interface motion in Total Hip
Replacement. Journal of Orthopaedic Research, 14,
36–43.
Kunii, T., Mori, Y., Tanaka, H., Kogure, A., Kamimura, M.,
Mori, N., Hanada, S., Masahashi, N., & Itoi, E. (2019).
Improved Osseointegration of a TiNbSn Alloy with a
Low Young’s Modulus Treated with Anodic Oxidation.
Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/
10.1038/s41598-019-50581-7
Kurtz, S. M., Ms, E. L., Ong, K., Ma, K. Z., Kelly, M., &
Bozic, K. J. (2010). Future young patient demand for
primary and revision joint replacement: National
projections from 2010 to 2030. Clinical Orthopaedics
and Related Research, 2009, 2606–2612.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-0834-6
Learmonth, I. D., Young, C., & Rorabeck, C. (2007). The
operation of the century: total hip replacement. Lancet,
370(9597), 1508–1519. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-
6736(07)60457-7
Nazari-farsani, S. (2015). Precision and Accuracy of
Marker-Based and Model-Based Radiostereometric
Analyses in Determination of Three-Dimensional
Micromotion of a Novel Hip Stem (Issue December).
Åbo Akademi University.
Ojeda, C. (2009). Estudio de la influencia de estabilidad
primaria en el diseño de vástagos de prótesis femorales
personalizadas: aplicación aplicación a paciente
específico. In Tesis doctoral, Universidad Politécnica
de Madrid.
Otomaru, I., Nakamoto, M., Kagiyama, Y., Takao, M.,
Sugano, N., Tomiyama, N., Tada, Y., & Sato, Y.
(2012). Automated preoperative planning of femoral
stem in total hip arthroplasty from 3D CT data: Atlas-
based approach and comparative study. Medical Image
Analysis, 16(2), 415–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.media.2011.10.005
Pellizzari, M., Jam, A., Tschon, M., Fini, M., Lora, C., &
Benedetti, M. (2020). A 3D-Printed Ultra-Low
Young’s Modulus β -Ti Alloy for Biomedical
Applications. Materials, 1–16.
Portal-Núñez, S., Lozano, D., De la Fuente, M., & Esbrit,
P. (2012). Fisiopatología del envejecimiento óseo.
Revista Española de Geriatría y Gerontología, 47(3),
125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regg.2011.09.003
Rawal, B. R., Ribeiro, R., Malhotra, R., & Bhatnagar, N.
(2011). Design and manufacture of short stemless
femoral hip implant based on CT images. Journal of
Medicine on Science, 11(8), 296–301.
Raymond, D. (2019, June 28).
FemurFracture - Lower
Extremity CTs. Embodi3D.Com. https://www.embodi
3d.com/files/file/25956-femurfracture/
Rieker, C. B. (2016). Tribology of total hip arthroplasty
prostheses. EFORT Open Reviews, 1(2), 52–57.
https://doi.org/10.1302/2058-5241.1.000004
Rivera, A. F., Castro, F. De, Moreno, A., & Rubio, J. C.
(2020). Assessment of the Highest Stress Concentration
BIODEVICES 2022 - 15th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
56

Area Generated on the Mandibular Structure Using
Meshless Finite Elements Analysis. Bioengineering, 1–
11.
Ruben, R. B., Fernandes, P. R., & Folgado, J. (2012). On
the optimal shape of hip implants. Journal of
Biomechanics, 45(2), 239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.jbiomech.2011.10.038
Ruben, R. B., Folgado, J., & Fernandes, P. R. (2007). A
Three-Dimensional Model for Shape Optimization of
Hip Prostheses Using a Three-dimensional shape
optimization of hip prostheses using a multicriteria
formulation. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg,
September. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-006-0072-4
Santori, F. S., Learmonth, I., Grifka, J., Valverde, C., &
Kim, Y. H. (2007). DePuy PROXIMA Hip - Surgical
Technique.
Schaaff, P. (2004). The role of fretting damage in total hip
arthroplasty with modular design hip joints - evaluation
of retrieval studies and experimental simulation
methods. Journal of Applied Biomaterials &
Biomechanics, 2, 121–135.
Schileo, E., Taddei, F., Cristofolini, L., & Viceconti, M.
(2008). Subject-specific finite element models
implementing a maximum principal strain criterion are
able to estimate failure risk and fracture location on
human femurs tested in vitro. Journal of Biomechanics,
41(2), 356–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.20
07.09.009
Schmitz, M. W., Busch, V. J., Gardeniers, J. W., Hendriks,
J. C., Veth, R. P., & Schreurs, B. W. (2013). Long-term
results of cemented total hip arthroplasty in patients
younger than 30 years and the outcome of subsequent
revisions. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 14.
https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-14-37
SimSolid Corporation. (2015). SimSolid Technology
Overview (pp. 1–33).
Sivasankar, D. M., Arunkumar, S., Bakkiyaraj, V.,
Muruganandam, A., & Sathishkumar, S. (2016). A
Review on Total Hip Replacement. International
Research Journal In Advanced Engineering and
Technology (IRJAET), 2(April), 589–642.
https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.13686.80969
Sköldenberg, O. G., Bodén, H. S. G., Salemyr, M. O. F.,
Ahl, T. E., & Adolphson, P. Y. (2006). Periprosthetic
proximal bone loss after uncemented hip arthroplasty is
related to stem size DXA measurements in 138 patients
followed for 2 – 7 years. Acta Orthopaedica, 77(3),
386–392. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453670610046307
Solórzano, W. (2021). Innovación en el diseño
personalizado de vástagos femorales cortos.
Universidad de Piura.
Solórzano, W., Ojeda, C., & Lantada, A. D. (2020).
Biomechanical study of proximal femur for designing
stems for total hip replacement. Applied Sciences
(Switzerland), 10(12), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/
APP10124208
Srinivasan, A., Jung, E., & Levine, B. R. (2012).
Modularity of the Femoral Component in Total Hip
Arthroplasty. Journal of the American Academy of
Orthopaedic Surgeons
, 20, 214–222.
Subramanian, P., Wainwright, T. W., Bahadori, S., &
Middleton, R. G. (2019). A review of the evolution of
robotic-assisted total hip arthroplasty. HIP
International, 29(3), 232–238. https://doi.org/10.1177/
1120700019828286
Sugano, N. (2013). Computer-assisted orthopaedic surgery
and robotic surgery in total hip arthroplasty. Clinics in
Orthopedic Surgery, 5(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/
10.4055/cios.2013.5.1.1
Symington, I. (2020). Designer Oriented Software - Is it
Accurate? The International Magazine for Engineering
Designers & Analysts from NAFEMS, The
Electromagnetics Issue, 32–44.
Wroblewski, B. M. (1997). Wear of the high-density
polyethylene socket in total hip arthroplasty and its role
in endosteal captation. Proceedings of the Institution of
Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering
in Medicine, 211(1), 109–118. https://doi.org/
10.1243/0954411971534737
Yamako, G., Chosa, E., Totoribe, K., Hanada, S.,
Masahashi, N., Yamada, N., & Itoi, E. (2014). In-vitro
biomechanical evaluation of stress shielding and initial
stability of a low-modulus hip stem made of Beta type
Ti-33.6Nb-4Sn alloy. Medical Engineering and
Physics, 36(12), 1665–1671. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.medengphy.2014.09.002
Yamako, G., Janssen, D., Hanada, S., Anijs, T., Ochiai, K.,
Totoribe, K., Chosa, E., & Verdonschot, N. (2017).
Improving stress shielding following total hip
arthroplasty by using a femoral stem made of β type Ti-
33.6Nb-4Sn with a Young’s modulus gradation.
Journal of Biomechanics, 63, 135–143.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2017.08.017
Yan, S. G., Chevalier, Y., Liu, F., Hua, X., Schreiner, A.,
Jansson, V., & Schmidutz, F. (2020). Metaphyseal
anchoring short stem hip arthroplasty provides a more
physiological load transfer: a comparative finite
element analysis study. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery
and Research, 15(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/
s13018-020-02027-4
Personalized Hip Replacement: State of the Art and New Tools Proposals
57
