
Deep Set Conditioned Latent Representations for Action Recognition
Akash Singh
1
, Tom de Schepper
1
, Kevin Mets
1
, Peter Hellinckx
2
, Jos
´
e Oramas
1
and Steven Latr
´
e
1
1
IDLab, Department of Computer Science, University of Antwerp - imec, Sint-Pietersvliet 7, 2000 Antwerp, Belgium
2
IDLab, Faculty of Applied Engineering, University of Antwerp - imec, Sint-Pietersvliet 7, 2000 Antwerp, Belgium
Keywords:
Action Recognition, Deep Sets, Deep Learning.
Abstract:
In recent years multi-label, multi-class video action recognition has gained significant popularity. While rea-
soning over temporally connected atomic actions is mundane for intelligent species, standard artificial neural
networks (ANN) still struggle to classify them. In the real world, atomic actions often temporally connect to
form more complex composite actions. The challenge lies in recognising composite action of varying dura-
tions while other distinct composite or atomic actions occur in the background. Drawing upon the success of
relational networks, we propose methods that learn to reason over the semantic concept of objects and actions.
We empirically show how ANNs benefit from pretraining, relational inductive biases and unordered set-based
latent representations. In this paper we propose deep set conditioned I3D (SCI3D), a two stream relational
network that employs latent representation of state and visual representation for reasoning over events and ac-
tions. They learn to reason about temporally connected actions in order to identify all of them in the video. The
proposed method achieves an improvement of around 1.49% mAP in atomic action recognition and 17.57%
mAP in composite action recognition, over a I3D-NL baseline, on the CATER dataset.
1 INTRODUCTION
Videos extend the semantic information of images in
the temporal domain like natural language. The se-
ries of temporal and spatial changes in videos are
commonly called events; events temporally connect
in a structured manner to form atomic actions, which
at the same time combine themselves to form com-
posite actions (Girdhar and Ramanan, 2020; Zhu
et al., 2020). For example, in the composite ac-
tion of putting down a glass after drinking
water, drinking and putting down are atomic ac-
tions and after is a temporal connection between
them. Humans understand, recall memories and ob-
jects in an unordered fashion (Holtgraves and Srull,
1990). We can reason about temporally connected ac-
tions also reason about objects, their attributes and
relation between objects involved in actions. Spa-
tial and temporal understanding of events, actions and
objects play an important role in tasks like action
recognition, action prediction, human-object interac-
tion etc. While temporal and spatial reasoning is nat-
ural for intelligent species, standard artificial neural
networks (ANN) do not inherently have this ability.
For complex and human-like spatio-temporal reason-
ing, an ANN not only should comprehend the con-
cept of objects, their relations but also how events
Figure 1: Bounding box shows an example of a change in
spatial relationships between objects. The figure also shows
how Atomic actions temporally relate to form Composite
actions. Composite action of Pick and place (brown)
cone before rotate cylinder is an example of tempo-
ral relation between actions. At any given time multiple
Atomic actions and Composite actions may occur. While
Atomic actions are of fixed length in time, Composite ac-
tions can be of variable duration.
and actions temporally relate as well. For example,
pick and place cone contains temporally related
events where the spatial relation of the cone changes
with respect to the table and other objects. Pick
and place cone before rotate cylinder addi-
tionally contains temporally related actions (Fig.1).
The other major challenge in action recognition
in general, is that actions can take place anywhere
456
Singh, A., de Schepper, T., Mets, K., Hellinckx, P., Oramas, J. and Latré, S.
Deep Set Conditioned Latent Representations for Action Recognition.
DOI: 10.5220/0010838400003124
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2022) - Volume 5: VISAPP, pages
456-466
ISBN: 978-989-758-555-5; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
along the time dimension. Thus, lacking a clear start
and end point. This introduces the requirement of
additional reasoning related to the duration of an ac-
tion, which incurs a high computational cost (Bobick,
1997; Hutchinson and Gadepally, 2020; Shoham,
1987; Zhu et al., 2020). Multi-label and multi-class
action recognition further adds to the challenge as
the method needs to recognise an action while dis-
regarding or taking into consideration multiple other
actions or non-action related elements that may be oc-
curring simultaneously (Hutchinson and Gadepally,
2020). While methods like I3D performs well on
datasets like HMDB51 (Kuehne et al., 2011) and
UCF101 (Soomro et al., 2012), recent studies (Gird-
har and Ramanan, 2020; He et al., 2016) show how
actions are highly co-related to scene bias in the
above-mentioned datasets . For example classifying
playing a given sport based on a playfield always
occurring in the background.
Recent studies (Hu et al., 2018; Santoro et al.,
2017; Shanahan et al., 2020) show that if provided
with additional relational data while training, ANNs
learn to represent and perform better in complex tasks
like object detection and Visual QA as well. Rela-
tional networks further influence other ANN layers
for relational reasoning.
In our study, we take advantage of the above men-
tioned forte of ANNs. We build our work on the
relational network conditioned ResNet50 for action
recognition (Zhang et al., 2019). The ResNet50 was
trained conjointly with relational network for objects
state prediction task (colour, shape, size, position) of
the deep set prediction network (Zhang et al., 2019).
The relational network and ResNet50 were optimised
using mean square error and set loss during the train-
ing of deep set prediction network to output the same
latent representation. Inspired by I3D (Carreira and
Zisserman, 2017), we extend the deep set conditioned
ResNet from 2D to 3D to reason about change in the
state of objects.
We propose SCI3D, a class of methods inspired by
I3D (Carreira and Zisserman, 2017), two-stream net-
work (Simonyan and Zisserman, 2014) and Non-local
neural network (Wang et al., 2018) for action recog-
nition. We explore the change in the states of objects
representations, visual representations and space-time
relation between representations. We refer to the in-
flated 3D ResNet50 as DSPN for rest of the study.
To show the effectiveness of our spatiotemporal
relational methods, we chose atomic and composi-
tional action recognition tasks offered by the CATER
dataset (Sec.4.1) (Girdhar and Ramanan, 2020). Un-
like popular dataset, the CATER dataset minimises
scene biases (Girdhar and Ramanan, 2020; Carreira
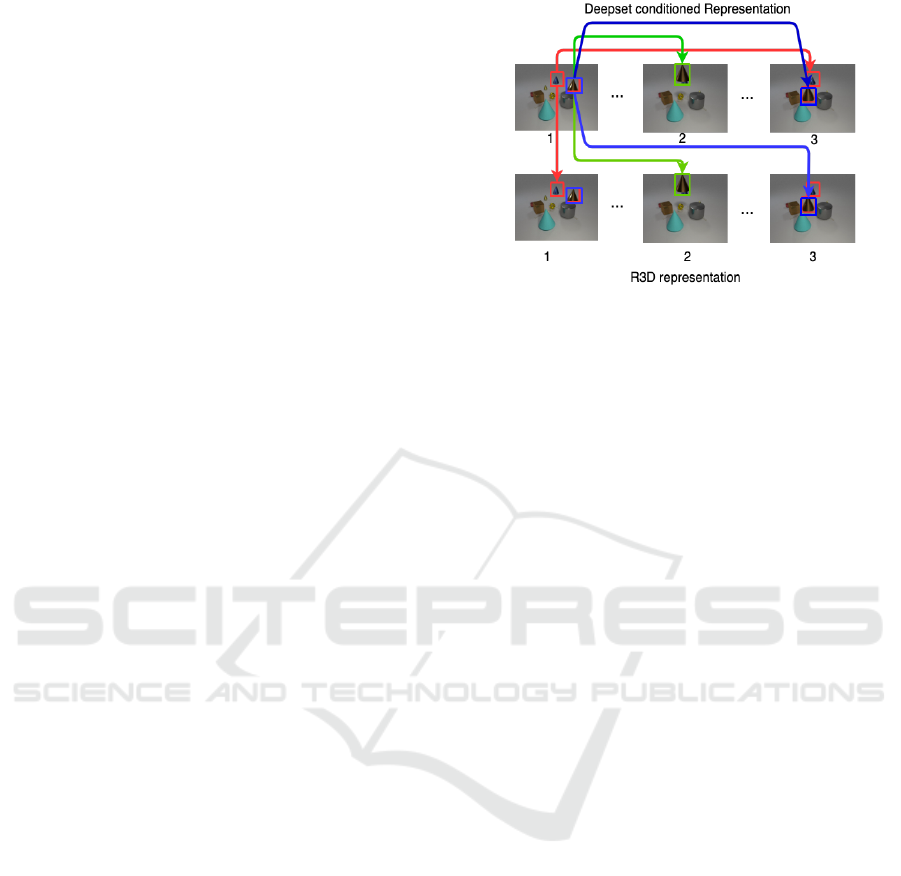
Figure 2: The relational module takes into consideration
space, time, space-time relations between objects. Con-
sidering Deep-set representations on frames labelled 1, 2,
3. Red shows how spatial relation i.e distance or direction
changes between 2 different cones. Green shows the change
of spatial relation i.e position with respect to the table and
other objects but is calculated for the same object it is tem-
poral change. Blue shows the change in spatial and tempo-
ral relations combined. The relational module calculates it
inter and intra stream.
and Zisserman, 2017; Wang et al., 2016). Here
SCI3D outperforms the baseline, i.e. R3D-NL (Wang
et al., 2018), by 1.49% and 17.57% mAP in atomic
and composite action recognition, respectively.
The technical contributions of this work are
• We propose a relational learning formulation over
events, actions that takes in consideration sets of
objects and pixels.
• The proposed methods are capable of generalising
better for actions of variable duration on trimmed
and untrimmed videos.
2 RELATED WORK
The study in the domain of action recognition was
traditionally dominated by handcrafted features (Fer-
nando et al., 2016; Lan et al., 2015; Peng et al.,
2014; Wang et al., 2011; Wang and Schmid, 2013).
However, with better understanding of CNN architec-
tures and of transfer learning, the focus transitioned to
learning the problem in a differential manner. In this
section, we summarize the work with respect to ar-
chitectures based on one-stream and two-stream net-
works. We group multi-stream networks under two-
stream category.
With a focus on a frame to frame prediction,
single-stream networks lack sensitivity to the tem-
poral domain. (Hara et al., 2018; He et al., 2019;
Hutchinson and Gadepally, 2020; Ji et al., 2012; Jiang
et al., 2019; Karpathy et al., 2014a; Taylor et al.,
Deep Set Conditioned Latent Representations for Action Recognition
457
2010; Tran et al., 2015). The idea is to perform im-
age recognition, where features were extracted and
the output of the method was a prediction (Hutchin-
son and Gadepally, 2020). With a lack of temporal
understanding of the data, the single-stream networks
were often coupled with LSTM or with new modules
and blocks (Donahue et al., 2015; Yue-Hei Ng et al.,
2015; Ghadiyaram et al., 2019; Luo and Yuille, 2019;
Tran et al., 2018).
For Temporal domain consideration, the CNN’s
were often coupled with the optical flow to capture
the temporal relationship between the frames. (Horn
and Schunck, 1981; Zhu et al., 2020; Simonyan and
Zisserman, 2014). While with the complement of
temporal data, CNN based approaches come close to
outperforming (UCF 88% vs 87.9% (Soomro et al.,
2012)) or outperformed (HMDB51 59.4% vs 61.1%
(Kuehne et al., 2011)) handcrafted methods, yet they
still needed pre-computation. While methods like
TSN (Wang et al., 2016) try to learn to reason on
the temporal domain, they still lack the capability of
modelling concepts such as objects and their spatial
domain.
Two-stream networks (Simonyan and Zisserman,
2014) still form the cornerstone and inspiration in
the video understanding domain. Methods like Mo-
tionNet (Wu et al., 2020), MARS (Crasto et al.,
2019), D3D (Stroud et al., 2020), Feichetenhofer et al
(Feichtenhofer et al., 2017), Slowfast (Feichtenhofer
et al., 2019), take inspiration from the two-stream net-
works. While two-stream networks and I3D perform
action recognition on datasets like UCF101 (Soomro
et al., 2012) , Sport1M (Karpathy et al., 2014b), THU-
MOS (Jain et al., 2014). They still struggled in situ-
ations where underlying actions are characterised and
relies on spatial and long temporal relations. The
above-mentioned methods focus on convoluting in-
formation in a very local temporal area. The Non-
local neural network (Wang et al., 2018) when com-
bined with I3D, try consolidating long term depen-
dency. Nevertheless, their capabilities have not been
fully utilised. Convolutional neural networks have
been shown to lose this useful temporal informa-
tion down in successive stages of deep neural net-
works (Zhu et al., 2020). The limitation of I3D
in temporal reasoning is more apparent with com-
posite action cases in the dataset like pick place
(brown) cone before rotate cylinder Fig. 1.
The previously mentioned composite action consists
of two atomic actions namely pick place (brown)
cone and rotate cylinder. Furthermore, multi-
ple atomic (Pick place (Blue) cone) and compo-
sitional (Pick and place (brown) cone during
drag (gold) cone) actions can occur simultane-
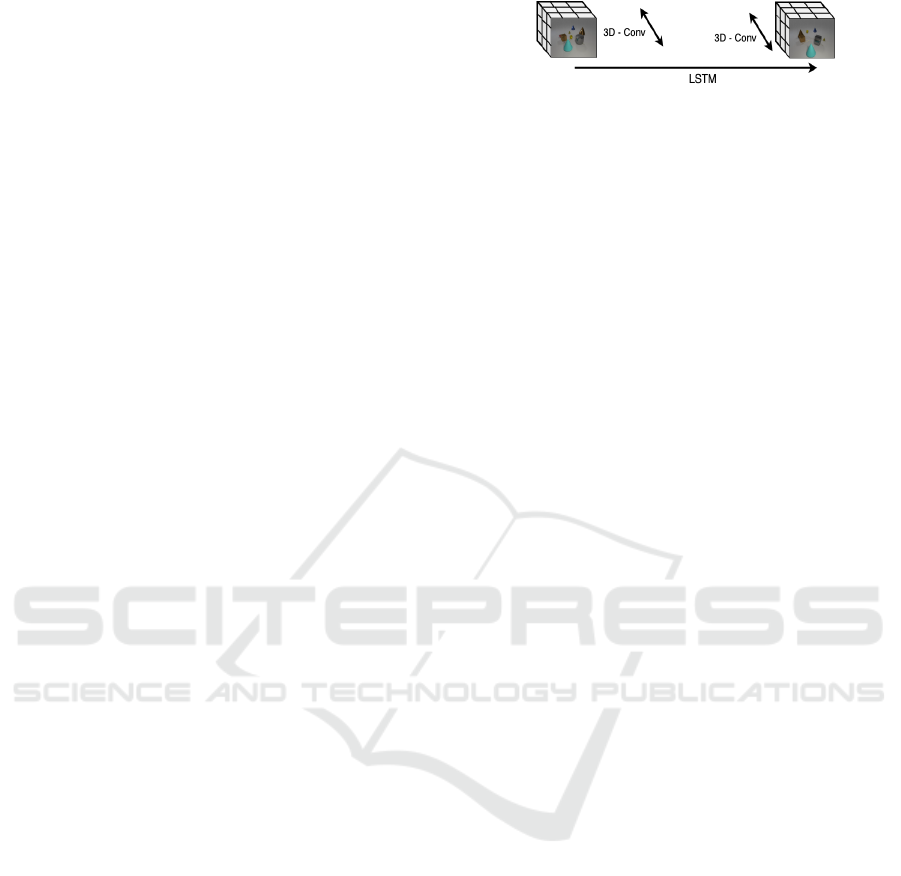
Figure 3: Humans dissect time to reason about the past or
future. 3D convolution reasons on localised temporal do-
main and LSTM reasons on longer temporal domain. The
above figure shows how our method dissects the time to
recognise composite actions of variable temporal length.
ously Fig. 1.
Two-stream networks could be extended to multi-
stream where the other streams can augment the net-
work with more information like audio, optical flow,
or a new convolution working using different hyper-
parameters. In our work we take inspiration from two-
stream network as well.
Recently methods on Transformers (Dosovitskiy
et al., 2020; Vaswani et al., 2017) have gained mo-
mentum thanks to the strong semantic nature of the
transformers (Arnab et al., 2021; Bertasius et al.,
2021). The authors use the self-attention strategy on
patches of image over space, time and space-time, we
focus on the semantic concept of objects and the re-
lational nature of non-local neural networks in space-
time.
3 PROPOSED METHOD
Motivation: 3D convolutions have proven suitable
for the recognition of short duration (1-5 seconds)
actions resembling the atomic actions described in
Task 1. (Sec. 4.1.1) (Carreira and Zisserman, 2017;
Tran et al., 2015; Tran et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2019).
However, 3D CNNs tend to perform poorly when em-
ployed for very long temporally connected action .
To be able to reason over very long temporally
connected actions, i.e composite actions (Sec. 4.1.2),
we draw inspiration from humans and use LSTM and
3D convolution. When reasoning about past or future,
humans tend to divide time in two frames, a coarser
time frame to identify temporal regions of interest and
a finer, more localised, frame to reason about local
space-time details.
Similarly, we bifurcate time in coarse and fine
frames, where 3D CNNs model spatio-temporal de-
tails in a short temporal window and LSTMs ad-
dresses reasoning over long temporally connected ac-
tion components (Fig. 3).
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
458

Figure 4: Proposed SCI3D architecture for action recogni-
tion.
3.1 SCI3D
We define SCI3D as a set-conditioned two-stream net-
work that employs relational networks (Sec. 3.4) to
relate DSPN (Sec. 3.2) and R3D (Sec. 3.3). The
method uses non local as relational network to rea-
son in the space-time domain over the representa-
tions (Fig. 2). The inspiration behind the architec-
ture is to take advantage of the visual representation of
frames and set state of the objects in the frame. Thus,
augment the reasoning of R3D with DSPN (Fig. 7).
Both streams convolute in local space time to influ-
ence each other during training. The other idea that
forms the core of the proposed method is that we want
to extend the spatial relations to temporal connected
events.
With the above mentioned inspiration, we formu-
late SCI3D, where streams are merged using rela-
tional blocks. The standard architecture of the pro-
posed SCI3D is presented in Fig. 4. When not em-
ploying any relational block, we refer the architecture
as SCI3D-NR.
3.2 Set Representation Stream
In theory, the set representation block can be any con-
volutional model that encodes the states of a set of
objects. In practice, we extend the DSPN encoder
of (Zhang et al., 2019) from ResNet34 to ResNet50
and inflate it from 2D to 3D for action recognition
(Sec.4.2).
The ResNet50 was pretrained cojointly with the
relational network to encode the image for state pre-
diction task. The task was to implicitly learn which
object in the image corresponds to which set element
with the associated properties(x, y, z coordinates,
shape, colour, size, material) (Zhang et al., 2019).
The latent representation learned by the ResNet50,
when decoded translates to objects and their proper-
ties. When extending the architecture from 2D to 3D,
we take advantage of convolution operation in tempo-
ral dimension. The operation looks at a series of con-
secutive elements(frames) to detect features, in our
case the change in position as embedded in the latent
space.
3.3 Visual Representation Stream
Visual representations from input frames are encoded
via 3D CNNs along its corresponding pathway .
In practice, we adopt a similar block to I3D (Car-
reira and Zisserman, 2017) which takes advantage of
stacked 3D CNNs and residual connections for spatio-
temporal reasoning. (Carreira and Zisserman, 2017)
inflate the ImageNet pre-trained 2D CNN to 3D by
adopting work from (Wang et al., 2015; Zhu et al.,
2020). This architecture, i.e. I3D, is often referred to
as R3D, when initialised from ResNet (Girdhar and
Ramanan, 2020; He et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2018)
3.4 Relational Block
Relational networks are subsets of neural networks
that embed structure with relational reasoning. The
idea is to capture the explicit or implicit relations em-
bedded in the data. As introduced in (Santoro et al.,
2017) relational network can be expressed as:
RN(O) = f
φ
∑
i, j
g
θ
(o
i
, o
j
)
!
(1)
where the input is a set that can be expressed as
an abstract humane concept. It can be pixels, features
(Wang et al., 2018), entities, objects (Santoro et al.,
2017) or frames (Zhou et al., 2018). In our formu-
lation, O is defined by the input video, o
i
, o
j
are the
outputs from the two streams/pathways, whereas f
φ
and g
θ
are functions to relate the outputs.
The relational block reasons about an event or an
action on latent representation of states and of visual
in space-time domain.
We employ the non-local neural networks as a re-
lational block, which given a position they compute
the weighted sum of features to all other positions as
follows:
y
i
=
∑
j∈Ω
ω(x
i
, x
j
)g(x
j
) (2)
Where x
i
represents a feature at position i, y
i
is
the output tensor. ω is similarity function between i
and j, in our case we evaluated dot-product, gaussian
Deep Set Conditioned Latent Representations for Action Recognition
459

and embedded gaussian. g(x
j
) is the pixel represen-
tation at point j. The non-local block performs rela-
tional computations, analogous to relation networks
(Battaglia et al., 2018; Levi and Ullman, 2018; Yin
et al., 2020; Zambaldi et al., 2018). Non local neural
networks can be considered a set to set architecture,
where they expect as input a set of features and out-
put the transformed set of features.
4 EVALUATION
4.1 Dataset
CATER dataset extends the CLEVR dataset (Johnson
et al., 2017), to address the problem of scene bias in
video datasets (Girdhar and Ramanan, 2020; Wang
et al., 2016). We validate our method on the CATER
dataset (Girdhar and Ramanan, 2020) that offers three
tasks that focus on reasoning around cognitive con-
cepts like causal reasoning over long term temporal
structure over events. We target their atomic action
recognition (Sec.4.1.1) and composite action recogni-
tion tasks (Sec.4.1.2). Both multi-label classification
tasks with 14 and 301 classes respectively.
The dataset offers 5000 training videos and 1650
validation videos at 320 × 240 px, where a single
video contains 300 frames, rendered at 24fps. An
atomic action is always constrained to a maximum of
30 frames while a composite action can last anywhere
from 30 to 300 frames.
4.1.1 Task 1: Atomic Action Recognition
It is the primary action recognition task offered
by the CATER dataset (Girdhar and Ramanan,
2020). Events temporally relate to form simple gran-
ular actions like Pick and place cone, rotate
cylinder as shown in Fig.1.
While different actions can share the same events,
we believe it is a simpler of the two considered task
because of the low number of classes (14) as the clas-
sification does not differentiate between object types.
The task can be extended in the future for granular
event-based reasoning by extending actions classes to
include object colour, size etc.
4.1.2 Task 2: Compositional Action Recognition
Real-world actions are mostly compositional in na-
ture. In the composite action recognition task, the
atomic actions can temporally relate in 13 categories
defined in Allen’s temporal algebra (Allen, 1983).
Same as Girdhar and Ramanan (Girdhar and Ra-
manan, 2020) , we consider only 3 categories namely,
before, during and after. Akin to Task 1, multi-
ple composite actions are active at any given mo-
ment in a video. We identify that Task 2 provides
us with the additional challenge that a composite ac-
tion can last for a part or the whole duration of a
video (Fig.1). From Fig.1, an example Pick and
place cone during slide cone may last for the
same time as Task 1, while pick and place cone
before flip cylinder actions lasts for the whole
video. While the model should be capable of adapting
to any temporal window to classify actions, it should
also be capable of identifying other atomic and com-
posite actions.
4.2 Implementation Details
In this section, we define the implementation details
of SCI3D.
DSPN. For the implementation, we extend the back-
bone of (Zhang et al., 2019) from ResNet34 to
ResNet50 to train our DSPN backbone. The 3 × 3
kernel in a residual block of ResNet50 is inflated to
3 × 1 ×1, as discussed by (Feichtenhofer et al., 2016)
and (Wang et al., 2018). As suggested by (Wang et al.,
2018), we also constrain the computation by inflating
only one kernel for every two residual blocks. Apart
from lowering down the number of computations, the
above-mentioned inflation strategy also leads to better
results (Wang et al., 2018).
R3D/R3D-NL. For the implementation, we again fol-
low the inflation details from (Wang et al., 2018).
We initialize the weights with pretrained ResNet50
weights. Similar to the DSPN, the 3 × 3 kernel is in-
flated to 3 × 1 × 1. Otherwise mentioned explicitly,
all other details of the architecture is followed as dis-
cussed in (Wang et al., 2018).
SCI3D. For SCI3D (Fig.4), we employ relational
block (Sec.3.4) to combine DSPN pathway (Sec.3.2)
and R3D pathway (Sec.3.3). For shorter atomic ac-
tion recognition (Sec.4.4), the LSTM component was
redundant in SCI3D (Fig.4), thus we remove it to only
use fully connected layer.
4.3 Training Details
All of the experiments were performed on 2 NVIDIA
V100 GPUs. We adopted baseline LR to 0.0025 ac-
cording to the linear scaling rule (Goyal et al., 2017).
LR, for our methods in Task 1 and Task 2 were 0.015
and 0.0025, respectively. They are reduced by a fac-
tor of 10 at epochs 90 and 100. We use momentum
of 0.9. We fine-tune our method with 32-frame input
clips (Girdhar and Ramanan, 2020). The spatial in-
put size is 224×224 pixels, randomly cropped from a
scaled video whose shorter side is randomly sampled
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
460

Table 1: Comparing the best performing SCI3D variant
with baseline and other standard architectures.
Task Frozen LSTM Achitecture Name mAP (%)
Task 1 latent-FasterRCNN 63.85
Task 1 X Single stream SCI3D 69.21
Task 1 Single stream SCI3D 91.82
Task 1 R3D-NL ((Wang et al., 2018)) 95.28
Task 1 SCI3D-NR 95.95
Task 1 SCI3D 96.77
Task 2 X latent-FasterRCNN 25.45
Task 2 X X Single stream SCI3D 26.32
Task 2 X Single stream SCI3D 69.76
Task 2 X R3D-NL ((Wang et al., 2018)) 52.19
Task 2 X SCI3D-NR 66.71
Task 2 X SCI3D 65.92
in [256, 320] pixels. For our methods on Task 1 and 2,
we train them for 120 and 140 epochs respectively. A
dropout of 0.5 is applied after the global pooling layer
and in LSTMs (Hinton et al., 2012), weight initializa-
tion was adopted from the original work of the non-
local neural networks (Wang et al., 2018; He et al.,
2015).
We assume a broader definition of actions, that
considers the actions of both animate and inanimate
actors (Hutchinson and Gadepally, 2020). Thus, we
define an action as temporally connected events or
other actions that can be of any length in time when
weaved. Action recognition is the classification of
such actions.
Considering the variable duration and the broader
definition of actions, the experiments with the pro-
posed methods present the empirical results (Table.1)
supporting how the cognitive concept of objects aids
with action recognition.
4.4 Experiments: Task 1
An action of the atomic action recognition task can
be expressed as, temporally connected events located
in a local neighbourhood. 3D CNN are well suited
for simpler action recognition tasks defined in a lo-
cal neighbourhood. They lie in the centre for all the
baselines and the proposed methods.
We approach the task as a multi-label classifica-
tion problem (Girdhar and Ramanan, 2020). We eval-
uate the performance of all the methods with mean
average precision (mAP).
Baselines: For the task, we employ R3D-NL (Car-
reira and Zisserman, 2017; Wang et al., 2018) and
latent-FasterRCNN (Ren et al., 2015) as baselines.
On the one hand, R3D-NL provides a bottom-up
visual representation. On the other hand, latent-
FasterRCNN aims at exploiting a semantic-level rep-
resentations learned from isolated objects in the
dataset.
We consider R3D-NL baseline as discussed by
(Girdhar and Ramanan, 2020). To establish the latent-
Figure 5: The architecture for single stream methods. The
architecture forms the foundation for R3D-NL, SCI3D.
Figure 6: Validation during training on task 1, the plot illus-
trates the effectiveness of weight initialization.
FasterRCNN (Ren et al., 2015) baseline, we train
the method with ResNet50 as the backbone for ob-
ject detection on the CLEVR dataset. We extract the
backbone of FasterRCNN and inflate the ResNet50
to R3D as discussed in Sec. 4.2. The choice of es-
tablishing latent-FasterRCNN was influenced by OP-
Net(Shamsian et al., 2020). By reason, the latent
representation of FasterRCNN are similar to DSPN,
they both identify objects but in theory, they differ.
While FasterRCNN’s goal is object detection, DSPN
extends object detection to also model the state of the
objects.
We also consider the single-stream variants of
SCI3D. In these variants, SCI3D only has a sin-
gle pathway which is initialised with a DSPN (see
Fig. 5). We investigate the usefulness of the set con-
ditioned latent representations with respect to latent-
FasterRCNN baseline by freezing the SCI3D. We
present the results in Table 1.
Results. The first observation done throughout the
execution of this experiment was that given the rel-
atively short duration of the atomic actions involved
in Task 1, the LSTM component was redundant. For
this reason, it was removed from the archiecture when
conducting experiments related to Task 1.
Regarding the single-stream baselines, the frozen
SCI3D outperforms the latent-FasterRCNN backbone
by 5.36% mAP with only FC trainable weights. The
fact that SCI3D outperforms the pre-trained latent-
FasterRCNN, leads us to conclude that reasoning
about set-level properties (beyond that of individual
objects as done by latent-FasterRCNN) leads to the
Deep Set Conditioned Latent Representations for Action Recognition
461

Figure 7: Validation during training plot comparing differ-
ent methods on task 1.
better results (Fig.6). Thus, supporting the benefits of
the proposed conditioning on deep set-level represen-
tations . Yet, from Table 1 it is clear that these single-
stream are unable to outperform the state-of-the-art
R3D-NL.
The last observation from above changes when
we look at the proposed two-stream SCI3D. We no-
tice that while the non-relational SCI3D-NR vari-
ant is on part with the R3D-NL baseline (mAP
around 95.28%), its relational variant outperforms it
by around 1.5% mAP (Fig.7).
We attribute the higher performance of R3D-NL
compared to single stream SCI3D to the fact that Task
1 (Sec.4.1.1) is an event-centric task, where events
last only for a fraction of an action. Suggesting that
methods need to take in account the minor change in
pixels. The non-local configuration in the R3D-NL
variant proposed by (Girdhar and Ramanan, 2020) is
better suited to detect the change in transformations.
Moreover, the reduced difference between SCI3D
(96.77% mAP) and SCI3D-NR (95.95% mAP) on
Task 1 further strengthens our belief about the focus
on very local events and pixels in Task 1.
4.5 Experiments: Task 2
Task 2 extends the atomic action recognition task
where 2 atomic actions temporally connect to form a
composite action. Task 2 (Sec. 4.1.2) is inherently dif-
ferent from Task 1, an action commenced at frame=0
can last till the end of the video. The methods in
Task 2 need to reason for a flexible temporal range.
They also need to take into account other atomic
actions and composite actions occurring simultane-
ously. Thus we employ the original proposed archi-
tecture of the SCI3D and SCI3D-NR (Fig.4). We also
extend the single-stream SCI3D (Fig.5) variants from
Task 1 (Sec. 4.4) with 2 layer LSTM. The LSTMs in
the architecture assists in longer variable length tem-
poral reasoning.
Figure 8: Validation during training plot comparing differ-
ent methods on task 2.
We approach the problem as multi-label classifi-
cation, an use mAP as performance metric.
Baselines: we follow (Girdhar and Ramanan, 2020)
where R3D-NL is extended using 2 layer LSTM with
512 hidden units. A similar extension was applied to
the latent-FasterRCNN baseline.
Results. At first sight the absolute performance val-
ues on this task are relatively lower compared to those
on Task 1. This clearly indicated the increased com-
plexity of this task.
We notice that the single-stream SCI3D achieves
69.76% mAP on the task, outperforming the R3D-NL
baseline by 17.57% mAP (Fig.8).
It is noticeable from training Fig. 8 that single
stream SCI3D trains faster and more efficiently.
SCI3D and SCI3D-NR achieve 65.92% and
66.71% mAP (Table1). They outperform baseline by
13.73% and 14.52% mAP respectively.
Single stream SCI3D outperforms SCI3D and
SCI3D-NR by 3.84% and 3.05% mAP respectively.
As discussed previously, the R3D block when com-
bined with the DSPN using the relational block in
SCI3D promotes the focus on local events and shorter
actions. (Wu et al., 2019) empirically show, the re-
lational block performs the best when combined with
longer temporal representations.
4.6 Ablation Study
To fully understand the contribution of each build-
ing block, we conduct ablation studies (Table 2) by
adding and deleting components.
We limit the study of SCI3D and baselines to 3D
ResNet50 backbones because it is one of the most
popular backbones in action recognition (Carreira and
Zisserman, 2017; Feichtenhofer et al., 2019; Wang
et al., 2018). Adding more fully connected (FC) lay-
ers over frozen single stream SCI3D did not improve
model performance significantly. With 2 FCs of 2048
and 512 units each, we observed an increase of mAP
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
462
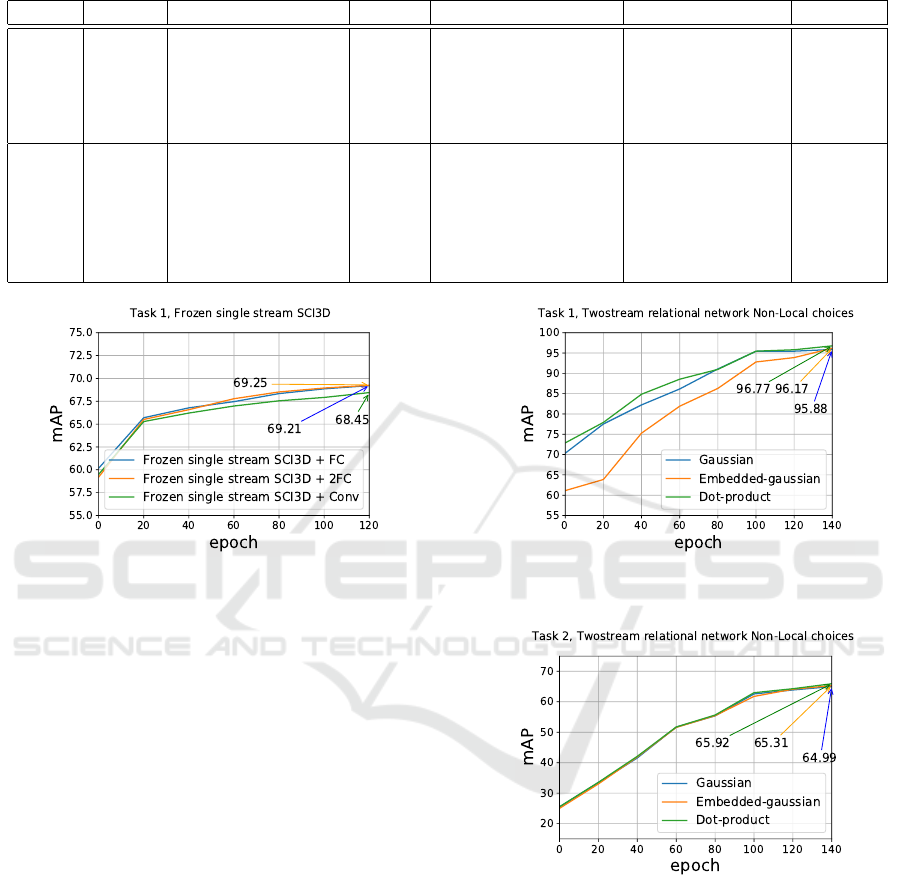
Table 2: Ablation study to understand the advantage of different building blocks, methods and their impact on respective task.
Conv refers to a single convolution of kernel 3, stride 1 and padding 0.
Task Frozen Relational block LSTM Architecture block mAP(%)
Task 1 X - - Single stream SCI3D 2 FC 69.25
Task 1 X - - Single stream SCI3D 1 Conv 68.45
Task 1 - - X Single stream SCI3D 256 LSTM 91.79
Task 1 - Embedded gaussian - SCI3D - 96.17
Task 1 - Gaussian - SCI3D - 95.88
Task 2 - Embedded gaussian - SCI3D - 65.31
Task 2 - Gaussian - SCI3D - 64.99
Task 2 - - X SCI3D FC + 512 LSTM 31.11
Task 2 - X - SCI3D 512 LSTM 53.71
Task 2 - - X SCI3D-NR 1FC + 512 LSTM 32.35
Task 2 - - X SCI3D 512 LSTM 55.68
Figure 9: Validation during training plot when frozen one
stream SCI3D combined with different blocks.
of 0.04%. While adding a convolutional block with a
FC we saw a drop in mAP of 0.8%. Adding more FC
or convolutional layers provides little to no gain. Us-
ing 2 LSTM layers with 256 hidden units with single
stream SCI3D logs 91.79% mAP on Task 1.
Addition of an additional convolutional block
or an FC over SCI3D-NR architecture on Task 1
(Sec. 4.2), did not show any major impact. The choice
of the non-local strategy for the SCI3D architecture
makes a little difference for Task 1, as shown in vali-
dation during training plots in Fig. 10. While for Task
2 there is little to no difference, see Fig. 11. We ob-
serve that adding an FC layer between LSTMs and
the relational block flattens all temporal information
and leads to under-performance. Under this setting,
the SCI3D achieves an mAP of 31.11% on Task 2.
5 DISCUSSION
Action recognition from the visual appearance alone
is challenging in the CATER dataset. The dataset
offers untrimmed videos, which poses an additional
challenge as the methods needs to classify an ac-
tion while disregarding other actions. The study
Figure 10: Ablation study of different strategies of non-
local block for Task 1.
Figure 11: Ablation study of different strategies of non-
local block for Task 2.
achieve an improvement of 17.57% mAP over the
baseline R3D-NL on untrimmed videos by employing
the deep-set conditioned latent representation. The la-
tent representation embed the set of objects and at-
tributes like shape, colour and x, y, z coordinates.
Though the study does not provide any results sup-
porting the advantages of explicitly using the set of
objects, it lays the foundation for it. The SCI3D net-
work under performs in Task 2 (Sec. 4.1.2) because it
is constrained by branch focused on localised events
and actions. However, (Wu et al., 2019), show non-
Deep Set Conditioned Latent Representations for Action Recognition
463

local relation block performs the best when supple-
mented with features supporting longer temporal re-
lation. Yet, besides this, the results show that the
single-stream variant of SCI3D, which only relies on
set-based representations leads the performance by a
significant margin. This further strengthens the poten-
tial gains that can be achieved by shifting reasoning
from individual entities to sets. The current study can
also be translated to real-world scenarios, by mod-
elling hands as discussed by (Girdhar and Ramanan,
2020). It can also be adopted for real-world videos
by adopting latent representations trained on natural
images from (Rezatofighi et al., 2017).
6 CONCLUSION
The study focuses on untrimmed action recognition
but it generalises to recognise trimmed composite ac-
tion as well. We empirically show the advantages
of deep set conditioned representations and relational
networks. When the deep network is initialized with
the representations and equipped with relational rea-
soning, they outperform benchmarks. The proposed
method, SCI3D outperforms the previous methods by
17.57% mAP. Based on the outcome and discussion
of this work (Hu et al., 2018), we believe set of objects
and relational networks are promising components for
the automatic understanding of natural videos. While
we limit our work to tasks in the CATER dataset, we
believe the methods can be extended to explanatory
and predictive causal reasoning tasks like why hap-
pened and what is about to happen.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This research received funding from the Flemish
Government under the “Onderzoeksprogramma Arti-
fici
¨
ele Intelligentie (AI) Vlaanderen” programme.
We would like to thank MMaction2 contribu-
tors and community (Contributors, 2020) for tremen-
dously helpful documentation and code. We also
thank Weights and biases (Biewald, 2020) for free
academic account to log and visualize the training.
REFERENCES
Allen, J. F. (1983). Maintaining knowledge about temporal
intervals. Communications of the ACM, 26(11):832–
843.
Arnab, A., Dehghani, M., Heigold, G., Sun, C., Lu
ˇ
ci
´
c, M.,
and Schmid, C. (2021). Vivit: A video vision trans-
former. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.15691.
Battaglia, P. W., Hamrick, J. B., Bapst, V., Sanchez-
Gonzalez, A., Zambaldi, V., Malinowski, M., Tac-
chetti, A., Raposo, D., Santoro, A., Faulkner, R., et al.
(2018). Relational inductive biases, deep learning, and
graph networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.01261.
Bertasius, G., Wang, H., and Torresani, L. (2021). Is space-
time attention all you need for video understanding?
arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.05095.
Biewald, L. (2020). Experiment tracking with weights and
biases. Software available from wandb.com.
Bobick, A. F. (1997). Movement, activity and action: the
role of knowledge in the perception of motion. Philo-
sophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London.
Series B: Biological Sciences, 352(1358):1257–1265.
Carreira, J. and Zisserman, A. (2017). Quo vadis, action
recognition? a new model and the kinetics dataset.
In proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 6299–6308.
Contributors, M. (2020). Openmmlab’s next generation
video understanding toolbox and benchmark.
Crasto, N., Weinzaepfel, P., Alahari, K., and Schmid, C.
(2019). Mars: Motion-augmented rgb stream for ac-
tion recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recog-
nition, pages 7882–7891.
Donahue, J., Anne Hendricks, L., Guadarrama, S.,
Rohrbach, M., Venugopalan, S., Saenko, K., and Dar-
rell, T. (2015). Long-term recurrent convolutional net-
works for visual recognition and description. In Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision
and pattern recognition, pages 2625–2634.
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn,
D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer,
M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., et al. (2020). An image is
worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recogni-
tion at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929.
Feichtenhofer, C., Fan, H., Malik, J., and He, K. (2019).
Slowfast networks for video recognition. In Proceed-
ings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on
computer vision, pages 6202–6211.
Feichtenhofer, C., Pinz, A., and Wildes, R. P. (2016). Spa-
tiotemporal residual networks for video action recog-
nition. corr abs/1611.02155 (2016). arXiv preprint
arXiv:1611.02155.
Feichtenhofer, C., Pinz, A., and Wildes, R. P. (2017).
Spatiotemporal multiplier networks for video action
recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 4768–
4777.
Fernando, B., Gavves, E., Oramas M., J., Ghodrati, A., and
Tuytelaars, T. (2016). Modeling video evolution for
action recognition. In TPAMI.
Ghadiyaram, D., Tran, D., and Mahajan, D. (2019). Large-
scale weakly-supervised pre-training for video action
recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Con-
ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
pages 12046–12055.
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
464

Girdhar, R. and Ramanan, D. (2020). CATER: A diagnos-
tic dataset for Compositional Actions and TEmporal
Reasoning. arXiv:1910.04744 [cs].
Goyal, P., Doll
´
ar, P., Girshick, R., Noordhuis, P.,
Wesolowski, L., Kyrola, A., Tulloch, A., Jia, Y.,
and He, K. (2017). Accurate, large minibatch
sgd: Training imagenet in 1 hour. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1706.02677.
Hara, K., Kataoka, H., and Satoh, Y. (2018). Can spa-
tiotemporal 3d cnns retrace the history of 2d cnns and
imagenet? In Proceedings of the IEEE conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages
6546–6555.
He, D., Zhou, Z., Gan, C., Li, F., Liu, X., Li, Y., Wang, L.,
and Wen, S. (2019). Stnet: Local and global spatial-
temporal modeling for action recognition. In Proceed-
ings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
volume 33, pages 8401–8408.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2015). Delv-
ing deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level per-
formance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings
of the IEEE international conference on computer vi-
sion, pages 1026–1034.
He, Y., Shirakabe, S., Satoh, Y., and Kataoka, H. (2016).
Human action recognition without human. In Hua,
G. and J
´
egou, H., editors, Computer Vision – ECCV
2016 Workshops, pages 11–17, Cham. Springer Inter-
national Publishing.
Hinton, G. E., Srivastava, N., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I.,
and Salakhutdinov, R. R. (2012). Improving neural
networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature de-
tectors. arXiv preprint arXiv:1207.0580.
Holtgraves, T. and Srull, T. K. (1990). Ordered and un-
ordered retrieval strategies in person memory. Journal
of Experimental Social Psychology, 26(1):63–81.
Horn, B. K. and Schunck, B. G. (1981). Determining optical
flow. Artificial intelligence, 17(1-3):185–203.
Hu, H., Gu, J., Zhang, Z., Dai, J., and Wei, Y.
(2018). Relation Networks for Object Detection.
arXiv:1711.11575 [cs].
Hutchinson, M. and Gadepally, V. (2020). Video Action
Understanding: A Tutorial. arXiv:2010.06647 [cs].
Jain, M., van Gemert, J., Snoek, C. G., et al. (2014). Univer-
sity of amsterdam at thumos challenge 2014. ECCV
THUMOS Challenge, 2014.
Ji, S., Xu, W., Yang, M., and Yu, K. (2012). 3d convolu-
tional neural networks for human action recognition.
IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine
intelligence, 35(1):221–231.
Jiang, B., Wang, M., Gan, W., Wu, W., and Yan, J. (2019).
Stm: Spatiotemporal and motion encoding for action
recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Interna-
tional Conference on Computer Vision, pages 2000–
2009.
Johnson, J., Hariharan, B., van der Maaten, L., Fei-Fei, L.,
Lawrence Zitnick, C., and Girshick, R. (2017). Clevr:
A diagnostic dataset for compositional language and
elementary visual reasoning. In Proceedings of the
IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition (CVPR).
Karpathy, A., Toderici, G., Shetty, S., Leung, T., Suk-
thankar, R., and Fei-Fei, L. (2014a). Large-scale video
classification with convolutional neural networks. In
Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vi-
sion and Pattern Recognition, pages 1725–1732.
Karpathy, A., Toderici, G., Shetty, S., Leung, T., Suk-
thankar, R., and Fei-Fei, L. (2014b). Large-scale
video classification with convolutional neural net-
works. In CVPR.
Kuehne, H., Jhuang, H., Garrote, E., Poggio, T., and Serre,
T. (2011). HMDB: a large video database for human
motion recognition. In Proceedings of the Interna-
tional Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).
Lan, Z., Lin, M., Li, X., Hauptmann, A. G., and Raj, B.
(2015). Beyond gaussian pyramid: Multi-skip fea-
ture stacking for action recognition. In Proceedings
of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pat-
tern recognition, pages 204–212.
Levi, H. and Ullman, S. (2018). Efficient coarse-to-fine
non-local module for the detection of small objects.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.12152.
Luo, C. and Yuille, A. L. (2019). Grouped spatial-temporal
aggregation for efficient action recognition. In Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference
on Computer Vision, pages 5512–5521.
Peng, X., Zou, C., Qiao, Y., and Peng, Q. (2014). Ac-
tion recognition with stacked fisher vectors. In Euro-
pean Conference on Computer Vision, pages 581–595.
Springer.
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., and Sun, J. (2015). Faster
r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region
proposal networks. Advances in neural information
processing systems, 28:91–99.
Rezatofighi, S. H., BG, V. K., Milan, A., Abbasnejad, E.,
Dick, A., and Reid, I. (2017). Deepsetnet: Predicting
sets with deep neural networks. In 2017 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pages
5257–5266. IEEE.
Santoro, A., Raposo, D., Barrett, D. G. T., Malinowski, M.,
Pascanu, R., Battaglia, P., and Lillicrap, T. (2017). A
simple neural network module for relational reason-
ing. arXiv:1706.01427 [cs].
Shamsian, A., Kleinfeld, O., Globerson, A., and Chechik,
G. (2020). Learning object permanence from video.
In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages
35–50. Springer.
Shanahan, M., Nikiforou, K., Creswell, A., Kaplanis,
C., Barrett, D., and Garnelo, M. (2020). An
Explicitly Relational Neural Network Architecture.
arXiv:1905.10307 [cs, stat].
Shoham, Y. (1987). Reasoning about change: time and
causation from the standpoint of artificial intelligence.
PhD thesis, Yale University.
Simonyan, K. and Zisserman, A. (2014). Two-stream con-
volutional networks for action recognition in videos.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1406.2199.
Soomro, K., Zamir, A. R., and Shah, M. (2012). Ucf101:
A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in
the wild. arXiv preprint arXiv:1212.0402.
Deep Set Conditioned Latent Representations for Action Recognition
465

Stroud, J., Ross, D., Sun, C., Deng, J., and Sukthankar, R.
(2020). D3d: Distilled 3d networks for video action
recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Win-
ter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision,
pages 625–634.
Taylor, G. W., Fergus, R., LeCun, Y., and Bregler, C.
(2010). Convolutional learning of spatio-temporal
features. In European conference on computer vision,
pages 140–153. Springer.
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., and Paluri,
M. (2015). Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d
convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE
international conference on computer vision, pages
4489–4497.
Tran, D., Ray, J., Shou, Z., Chang, S.-F., and Paluri, M.
(2017). Convnet architecture search for spatiotempo-
ral feature learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.05038.
Tran, D., Wang, H., Torresani, L., Ray, J., LeCun, Y., and
Paluri, M. (2018). A closer look at spatiotemporal
convolutions for action recognition. In Proceedings of
the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, pages 6450–6459.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones,
L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, Ł., and Polosukhin, I.
(2017). Attention is all you need. In Advances in
neural information processing systems, pages 5998–
6008.
Wang, H., Kl
¨
aser, A., Schmid, C., and Cheng-Lin, L.
(2011). Action Recognition by Dense Trajectories. In
CVPR 2011 - IEEE Conference on Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition, pages 3169–3176, Colorado
Springs, United States. IEEE.
Wang, H. and Schmid, C. (2013). Action recognition with
improved trajectories. In 2013 IEEE International
Conference on Computer Vision, pages 3551–3558.
Wang, L., Xiong, Y., Wang, Z., and Qiao, Y. (2015). To-
wards good practices for very deep two-stream con-
vnets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.02159.
Wang, L., Xiong, Y., Wang, Z., Qiao, Y., Lin, D., Tang, X.,
and Van Gool, L. (2016). Temporal segment networks:
Towards good practices for deep action recognition. In
European conference on computer vision, pages 20–
36. Springer.
Wang, X., Girshick, R., Gupta, A., and He, K. (2018). Non-
local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE
conference on computer vision and pattern recogni-
tion, pages 7794–7803.
Wu, C.-Y., Feichtenhofer, C., Fan, H., He, K., Krahenbuhl,
P., and Girshick, R. (2019). Long-term feature banks
for detailed video understanding. In Proceedings of
the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, pages 284–293.
Wu, P., Chen, S., and Metaxas, D. N. (2020). Motion-
net: Joint perception and motion prediction for au-
tonomous driving based on bird’s eye view maps. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 11385–
11395.
Yin, M., Yao, Z., Cao, Y., Li, X., Zhang, Z., Lin, S., and Hu,
H. (2020). Disentangled non-local neural networks.
In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages
191–207. Springer.
Yue-Hei Ng, J., Hausknecht, M., Vijayanarasimhan, S.,
Vinyals, O., Monga, R., and Toderici, G. (2015). Be-
yond short snippets: Deep networks for video classi-
fication. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 4694–
4702.
Zambaldi, V., Raposo, D., Santoro, A., Bapst, V., Li, Y.,
Babuschkin, I., Tuyls, K., Reichert, D., Lillicrap, T.,
Lockhart, E., et al. (2018). Relational deep reinforce-
ment learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.01830.
Zhang, Y., Hare, J., and Prugel-Bennett, A. (2019). Deep set
prediction networks. In Wallach, H., Larochelle, H.,
Beygelzimer, A., d'Alch
´
e-Buc, F., Fox, E., and Gar-
nett, R., editors, Advances in Neural Information Pro-
cessing Systems, volume 32. Curran Associates, Inc.
Zhou, B., Andonian, A., Oliva, A., and Torralba, A. (2018).
Temporal relational reasoning in videos. In Proceed-
ings of the European Conference on Computer Vision
(ECCV), pages 803–818.
Zhu, Y., Li, X., Liu, C., Zolfaghari, M., Xiong, Y., Wu,
C., Zhang, Z., Tighe, J., Manmatha, R., and Li, M.
(2020). A Comprehensive Study of Deep Video Ac-
tion Recognition. arXiv:2012.06567 [cs].
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
466
