
Can We Use Neural Regularization to Solve Depth Super-resolution?
Milena Gazdieva
1 a
, Oleg Voynov
1 b
, Alexey Artemov
1 c
, Youyi Zheng
2 d
, Luiz Velho
3 e
and Evgeny Burnaev
1 f
1
Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology, Moscow, Russia
2
State Key Lab, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
3
Instituto Nacional de Matem
´
atica Pura e Aplicada, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Keywords:
Depth Super-Resolution, Neural Regularization, 3D Deep Learning.
Abstract:
Depth maps captured with commodity sensors often require super-resolution to be used in applications. In
this work we study a super-resolution approach based on a variational problem statement with Tikhonov
regularization where the regularizer is parametrized with a deep neural network. This approach was previously
applied successfully in photoacoustic tomography. We experimentally show that its application to depth map
super-resolution is difficult, and provide suggestions about the reasons for that.
1 INTRODUCTION
Existing research reveals two major classes of state-
of-the-art approaches to depth super-resolution (SR):
data-driven methods based on deep neural net-
works (Riegler et al., 2016; Hui et al., 2016; Voynov
et al., 2019) and variational optimization-based ap-
proaches (Haefner et al., 2018; Haefner et al.,
2020). Among these, learning-based methods bring
the promise of leveraging powerful data-driven priors
by learning these directly from data, which has proven
to achieve impressive quantitative performance; how-
ever, as deep networks are trained by optimizing their
target functions in an averaged sense, they are likely
to produce imperfect estimates for specific (unseen)
test instances. In contrast, variational approaches
commonly employ sophisticated hand-crafted regu-
larizers and come with theoretical convergence guar-
antees, bounding an error between an estimate and the
true high-resolution depth for individual instances.
Unfortunately, in some instances, the designed regu-
larizer fails to capture image variations present in the
real-world data, leading to suboptimal performance
during variational optimization.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0047-1577
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3666-9166
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5451-7492
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9120-9592
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5489-4909
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8424-0690
Combining advantages offered by these classes of
approaches represents a natural interest; one partic-
ular variant is to incorporate an informative prior or
a distribution statistic learned from a representative
dataset of high-resolution depth images directly into
the optimization formulation, e.g., as a learned reg-
ularizer. In this approach, a pre-trained neural net-
work aims to provide a data-driven loss term during
the optimization of each individual test instance; we
use this approach in this work. The key intuition of it
is to help alleviate the limitations of either learning-
or optimization-based methods by leveraging the data
distribution information summarized by pre-training
on high-resolution depth images but still optimizing
for each individual test instance.
Image-based tasks have successfully integrated
data-driven loss functions (Gatys et al., 2016; John-
son et al., 2016); inspired by this line of research, in
this paper, we consider the question: “Can we use
learned regularizers to improve depth image super-
resolution?” More specifically, we opted to use Net-
work Tikhonov (NETT) (Li et al., 2020) framework,
a theoretically sound regularization approach in the
functional analytic sense offering attractive conver-
gence properties, but adapt it to target specifically
depth images. To this end, we focus on training a
deep convolutional neural network (CNN) to penalize
artifacts found in an input depth image; we further in-
tegrate the norm of feature activations computed in a
pre-trained network as a regularizer into an optimiza-
tion procedure to operate on a per-image basis. To the
582
Gazdieva, M., Voynov, O., Artemov, A., Zheng, Y., Velho, L. and Bur naev, E.
Can We Use Neural Regularization to Solve Depth Super-resolution?.
DOI: 10.5220/0010883500003124
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2022) - Volume 4: VISAPP, pages
582-590
ISBN: 978-989-758-555-5; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

best of our knowledge, we are the first to investigate
data-driven regularizers in the context of depth SR;
we denote this approach DSRNETT.
We systematically study both theoretical require-
ments and empirical behavior of DSRNETT, where
we are able to meet all theoretical claims (e.g., co-
ercivity), obtain pre-trained regularization models,
and perform optimization using a pre-trained net-
work. However, we discover that it is extremely dif-
ficult for the DSRNETT optimization procedure to
reach a good solution; moreover, the respective tar-
get function is found to correlate weakly with com-
monly used quality measures such as per-pixel RMSE
and perceptually-based RMSE
v
(Voynov et al., 2019).
These results hold across multiple appropriate data
augmentation strategies, optimization formulations,
and for networks of varying capacity; together, we
believe they indicate limitations of the NETT-type
frameworks for single-image depth SR tasks.
2 RELATED WORK
Depth Super-resolution. Numerous approaches to
deal with depth super-resolution problem were pro-
posed in recent years. One group of approaches fo-
cuses on application of convolutional neural networks
(CNNs) to depth SR (e.g., (Hui et al., 2016; Voynov
et al., 2019; Song et al., 2020)). For instance, (Hui
et al., 2016) proposes a neural architecture that com-
plements low-resolution depth features with high-
frequency features from high-resolution RGB data,
using a multi-scale fusion strategy. (Voynov et al.,
2019) focus on designing a visual-difference based
loss function, aiming to improve the performance
of existing state-of-the-art depth processing methods.
(Song et al., 2020) proposes iterative residual learn-
ing based framework with the use of channel atten-
tion, multi-stage fusion and weight sharing strategies
to tackle both synthetic and real-world degradation
processes of depth maps.
Variational approaches represent another group,
dealing with designing and optimizing an appropriate
target function without relying on learning. (Haefner
et al., 2018) propose a variational functional to jointly
solve single-shot depth SR and shape-from-shading
problems, i.e., inferring high-resolution depth from
color variations in the high-resolution RGB image.
(Haefner et al., 2020) modifies the same approach for
multi-shot depth SR using photometric stereo.
We focus on a combined approach; in contrast to
variational approaches, it does not require to construct
a regularizer manually but inherits their good conver-
gence properties. Unlike purely learning-based meth-
ods, it does not rely on training only but optimizes the
solution for individual samples.
Combined Approaches propose learning a regular-
izer and have been drawing attention recently; these
have not been previously applied to depth SR.
One type of combined approaches corresponds
to bilevel optimization, which incorporates learning
into the definition of optimal regularizer parameters
(e.g., (De los Reyes et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2013)).
According to this method, optimal parameters are
derived as empirical risk minimizers for supervised
training dataset. In (De los Reyes et al., 2017) bilevel
optimization approach is applied for total variation
(TV) type regularizers. Bilevel optimization with
richer markov random field (MRF) parametrization of
regularizer is investigated in (Chen et al., 2013) by ap-
plying it to the image restoration tasks.
Data-driven loss functions have been successfully
applied in the context of image-based tasks such as
style transfer (Gatys et al., 2016) and photo super-
resolution (Johnson et al., 2016) (where they are
known as perceptual losses), reconstruction tasks in
computed and photoacoustic tomography (Li et al.,
2020; Obmann et al., 2019; Arridge et al., 2019; Lunz
et al., 2018), or for feature-based knowledge distilla-
tion (see, e.g., (Gou et al., 2021) for a survey).
Two recent combined approaches (Lunz et al.,
2018; Li et al., 2020) focus on neural network
parametrizations of regularizers in application to
computed and photoacoustic tomography reconstruc-
tion respectively. (Lunz et al., 2018) train a regu-
larizer to discriminate ground-truth and (known) im-
perfect solutions. Another combined approach (Li
et al., 2020) trains a regularizer to penalize solutions
with various kinds of artifacts. (Arridge et al., 2019)
gives an overview of more methods aiming to incor-
porate learning into the variational optimization. In
this work, we parametrize the regularizer using a neu-
ral network; more specifically, we follow (Li et al.,
2020) that focuses on theoretical foundations, pro-
vides regularizing properties of their method, and de-
rives respective convergence and convergence rates.
3 NETWORK TIKHONOV
VARIATIONAL FORMULATION
FOR DEPTH
SUPER-RESOLUTION
We start with a brief review of the NETT formulation,
rewriting the mathematical relations for our task. The
goal of depth super-resolution is to
estimate x ∈ D from data y
δ
= F(x) + ε
δ
, (1)
Can We Use Neural Regularization to Solve Depth Super-resolution?
583

where F : D ⊂ X → Y is a (known) downsampling
operator, X, Y denote the spaces of high- and low-
resolution depth images, respectively, and ε
δ
is an un-
known data error, s.t., kε
δ
k 6 δ, δ > 0.
Depth super-resolution as formulated by (1) is an
ill-posed inverse problem and admits many possible
solutions. To favor a particular class of solutions,
Tikhonov regularization rewrites the task in an opti-
mization perspective:
D(F(x),y
δ
) + αR (x) → min
x∈D
, (2)
where D : Y ×Y → [0,∞) is a data fidelity term de-
fined on depth images and R : D → [0,∞) is a regu-
larization term. In this work, we focus on the form of
regularizer term, seeking to learn it from data rather
than design it manually. Our DSRNETT draws inspi-
ration from Network Tikhonov framework (Li et al.,
2020), but is redesigned to target specifically depth
images. Let Φ denote a neural network, which we
view as a composition of affine linear maps V
l
(x) =
A
l
x + b
l
and non-linearities σ
l
where l is a layer in-
dex. Many convolutional architectures such as U-
Net (Ronneberger et al., 2015) admit this form. We
indicate a (trainable) affine part V = (V)
l
in the no-
tion of Φ
V
(·) and formulate our regularizer as
R (x) = ψ(Φ
V
(x)), (3)
where ψ : X → [0,∞) is a scalar function.
To effectively guide optimization in (2), network
parameters V must be learned using the available
training data before any optimization may happen (we
assume that non-linearities σ
l
are not trainable). We
consider the two following pre-training schemes.
Scheme 1: Train the network to predict an arti-
fact component from the input depth image. In this
scenario, we split a set X
HR
of high-resolution train-
ing images x
i
into two disjoint subsets X
HR
0
∪X
HR
1
and
compute approximations
e
x
i
= F
+
(F(x
i
)) for each x
i
∈
X
HR
1
, using an upsampling operator F
+
(a pseudo-
inverse of F). The network then trains to predict a
residual r
i
= x
i
−
e
x
i
from the input approximation
e
x
i
for images in X
HR
1
, or an exactly zero image for im-
ages in X
HR
0
. A simple regularizer based on this net-
work is a Euclidean norm of the predicted residual:
R (x) = kΦ
V
(x)k
2
2
.
Scheme 2: An alternative approach, which we ex-
perimentally observed to aid convergence, is to train
the model to directly predict ground-truth depth im-
ages given either an input approximation or a ground-
truth image. In this scenario, the network is trained to
output the same image as input x
i
for images in X
HR
0
,
and an ideal x
i
from input approximation
e
x
i
for images
in X
HR
1
. We attribute the advantages of this approach
to the benefit of having inputs of similar scale. A sim-
ilar approach is employed by (Obmann et al., 2019).
We then keep the idea of penalizing images with arti-
facts in the design of regularizer, which is defined as
R (x) = kΦ
V
(x) − xk
2
2
.
NETT is guaranteed to converge to a unique and
stable solution provided that certain analytic condi-
tions hold (Li et al., 2020). We report a detailed anal-
ysis in the context of our task in the Appendix.
4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Toy Examples: GDSR and SimGeo
We start by implementing our approach on sim-
ple synthetic depth images, using the dataset from
(Riegler et al., 2016), that we denote GDSR. It con-
sists of scenes containing randomly placed cubes,
spheres and planes in varying poses and dimensions.
Here and below, we visualize 3D scenes as renderings
of corresponding depth maps, obtaining these using a
simple normals-based method (Voynov et al., 2019).
We train two CNNs to predict residuals in up-
scaled depth images according to Scheme 1 (i.e., the
CNN predicts the artifact part of the training in-
stances): one using the original depth images and an-
other using the noise-augmented depth images, and
perform optimization using the two trained models as
regularizers. To optimize for a final depth image, we
minimize a sum of the squared L
2
-norm data fidelity
term and the squared L
2
-norm of network output:
1
2
kF(x) − yk
2
2
+ αkΦ
V
(x)k
2
2
→ min
x
. (4)
Since the network is trained to output artifact part
of the depth maps for visualization of its performance
we use rendering of sum of network input and net-
work output, which should approximate ground-truth
depth map.
While we are able to train efficient estimators
of residuals using both clean and noise-augmented
images, as shown in Figures 1–2, using the noise
augmentations proves to have a major effect on the
optimization performance (see Figures 3–4). More
specifically, we find that regularizing optimization
in (4) with the network trained on clean synthetic im-
ages leads to a bad solution (see Figures 3 (c)–(d)).
Moreover, we discover that the DSRNETT loss
function correlates poorly with RMSE
d
, the standard
root-mean-squared (RMS) error capturing per-pixel
differences between depth maps, and perceptual mea-
sure RMSE
v
(Voynov et al., 2019), defined as the
RMS difference between renderings capturing visual
differences between 3D surfaces represented as depth
maps. Both RMSE
d
and RMSE
v
represent measures
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
584
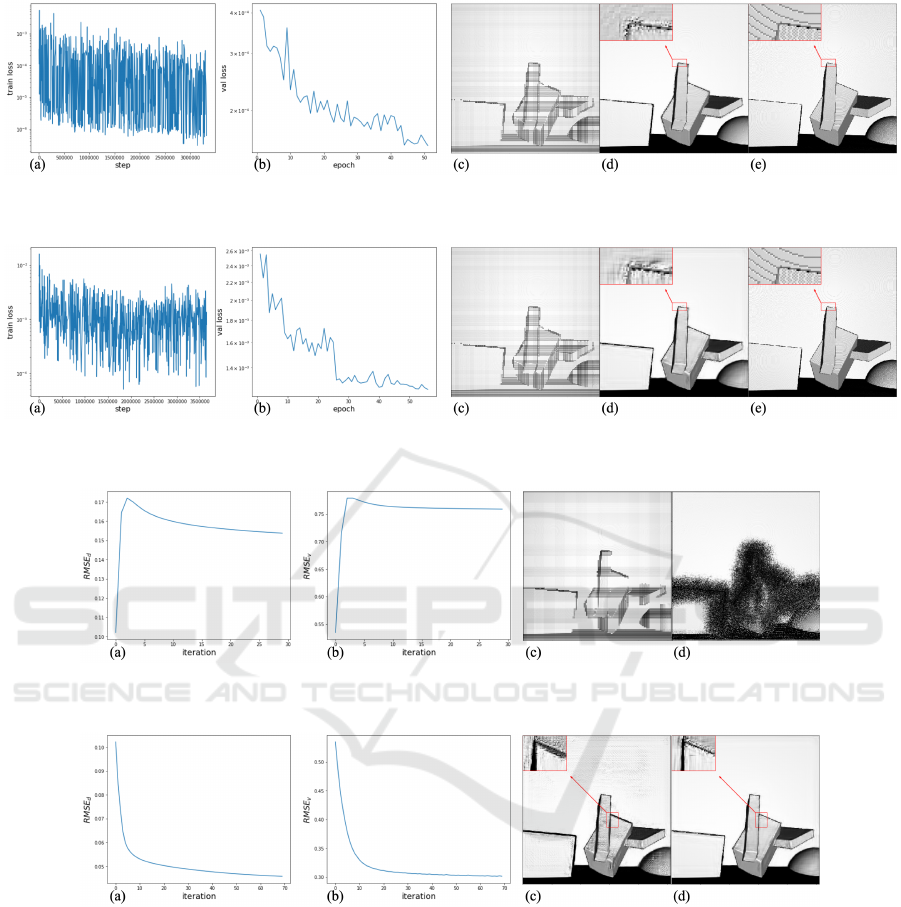
Figure 1: Typical pre-training results using GDSR: (a): train loss dynamics; (b): validation loss dynamics, log-scale; (c):
initial approximation (network input); (d): reconstructed depth image; (e): ground-truth.
Figure 2: Typical pre-training results using noisy GDSR: (a): train loss dynamics; (b): validation loss dynamics, log-scale;
(c): initial approximation (network input); (d): reconstructed depth image; (e): ground-truth.
Figure 3: Typical optimization results using networks pre-trained on GDSR: (a): RMSE
d
to ground-truth dynamics; (b):
RMSE
v
to ground-truth dynamics; (c): initial approximation; (d): optimization result (30 iterations).
Figure 4: Typical optimization results using networks pre-trained on noisy GDSR: (a): RMSE
d
to ground-truth dynamics;
(b): RMSE
v
to ground-truth dynamics; (c): initial approximation; (d): optimization result (70 iterations).
commonly used in evaluating depth map processing
performance (see inset Figure 5).
Eventually, optimization resulted in only a
marginal improvement for validation samples from
GDSR (see Figures 4 (c)–(d)). We hypothesize that
this stems from a limited capacity in our network, and
seek to increase it in Section 4.2.
Implementation Details. We obtain 128 × 128 high-
resolution training samples by splitting each image
from GDSR dataset into 16 patches. For 50% of
these high-resolution patches, we generate their low-
resolution counterparts, choosing F as a box down-
sampling method with a scaling factor of 4, and ob-
tain approximations
e
x by applying the pseudo-inverse
F
+
as an upsampling operator. In total, we obtained
128K patches for training and 32K for validation.
We employ a U-Net-like architecture (Ron-
neberger et al., 2015). In order to satisfy the co-
ercivity condition for the regularizer term, which is
stated by (Li et al., 2020) to be the most restrictive
one, we replace ReLU activation function in network
architecture with leaky ReLU. We train by optimiz-
ing MSE loss using Adam (Kingma and Ba, 2015)
for ∼70 epochs using a batch size of 2.
Can We Use Neural Regularization to Solve Depth Super-resolution?
585

Figure 5: Pre-training on clean data (a)–(c) leads to op-
timization results where the DSRNETT loss function (4)
does not correlate well with the commonly used RMSE
d
and RMSE
v
measures. Pre-training with noise-augmented
data (d)–(f) yields more predictable optimization dynamics.
Figure 6: Performance of NETT approach in compari-
son to underlying network (CNN) and Bilinear interpola-
tion on samples from SimGeo for a network pre-trained on
GDSR with added noise. For each sample - First row:
depth maps in pseudo-colour; Second row: renderings in
grayscale.
We perform optimization in (4) using the in-
cremental gradient descent algorithm following (Li
et al., 2020). Thus, optimization consisted of two
steps: gradient descent step for data fidelity term with
weight s and gradient descent step for regularizer term
with weight s · α, done with the use of backpropaga-
tion algorithm. We also choose the step weights, fol-
lowing (Li et al., 2020). Yet in contrast, we do not use
a zero image as initial approximation, but start op-
timization from approximation of ground-truth depth
map, derived by upsampling y, since the network is
trained on similar train samples.
To train the network with noisy data, we add
Gaussian noise with variance equal to 0.05 to all pix-
els in input depth images.
Due to the low complexity of the training dataset,
network was pre-trained very well and optimization
did not improve network result for validation sam-
ples from GDSR. On the other hand, for geomet-
rically more complex synthetic scenes from Sim-
Geo (Voynov et al., 2019) dataset network, pre-
trained on GDSR, output poor result and NETT ap-
proach was not working correctly; see Figure 6 for
comparison of approach performance with underly-
ing network and bilinear interpolation on simple and
complex synthetic scenes. According to these sugges-
tions we decided to reimplement NETT with stronger
network architecture, using complex synthetic and
real-world scenes for pre-training.
4.2 Complex Synthetic and Real-world
Scenes: MPI Sintel and Middlebury
To study our approach in a full-scale setting, we use
data collections and network architectures with larger
complexity. More specifically, we use U-MSG-Net, a
U-Net-like version of the MSG-Net architecture (Hui
et al., 2016) that has demonstrated good performance
for depth SR due to the effective use of RGB guid-
ance (see Appendix for more details). For training our
network, we use MPI Sintel (Butler et al., 2012) and
Middlebury 2014 (Scharstein et al., 2014) datasets,
both providing RGB-D images. MPI Sintel contains
complex scenes retrieved from a naturalistic 3D an-
imated short film, while Middlebury 2014 consists
of complex high-quality real images captured with a
structured light system.
Due to the difficulties with optimization conver-
gence, that we discuss further, in addition to training
the network according to Scheme 1 we experimented
with training according to Scheme 2, where the goal
is to predict a reconstructed image given an input ap-
proximation. We observed that Scheme 2 leads to
better convergence in comparison to Scheme 1 and
further provide results for Scheme 2. For optimiza-
tion, we accordingly set the regularizer to R (x) =
kΦ
V
(x) − xk
2
2
, re-using the general framework de-
scribed previously.
We do not explicitly account for the coercivity
condition of the architecture, since (Li et al., 2020)
provides ways to obtain coercivity for an arbitrary ar-
chitecture, e.g., using skip connection between net-
work input and output, as we discuss further.
Data Augmentation. To aid generalization, we study
a number of data augmentation strategies aiming to
expand the training domain, summarized in Table 1.
Training with noisy inputs. We train the network
on input depth images augmented with different vari-
ations of additive random noise (lines 2, 4-6 in the
table).
Training with both noisy inputs and targets. Aim-
ing to increase network robustness, we train the net-
work to predict noisy ground-truth depth from noisy
ground-truth, keeping target noise variance smaller
than that of input noise (line 7).
Training with input in-between approximation and
ground truth. The regularizer R (x) is designed to
push x to ground-truth data manifold, approximated
by Φ
V
(x). Based on the derivation in Appendix, we
hypothesize that, in contrast to this desired behaviour,
the optimization of the regularizer also pushes the out-
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
586

Figure 7: Typical pre-training results using Middlebury 2014 / MPI Sintel (test sample from SimGeo): (a): train loss dynamics;
(b): validation loss dynamics, log-scale; (c): input approximation (network input); (d): reconstructed depth image; (e):
ground-truth image.
Figure 8: Typical optimization results using networks pre-trained on Middlebury 2014 and MPI Sintel: (a): RMSE
d
to
ground-truth dynamics; (b): RMSE
v
to ground-truth dynamics; (c): initial approximation; (d): optimization result (30 itera-
tions).
Figure 9: Typical optimization results using networks pre-trained on noisy Middlebury 2014 and MPI Sintel: (a): RMSE
d
to ground-truth dynamics; (b): RMSE
v
to ground-truth dynamics; (c): initial approximation; (d): optimization result (70
iterations).
Figure 10: Typical optimization results using networks pre-trained on Middlebury 2014 and MPI Sintel augmented using
linear interpolation between GT and approximation: (a): RMSE
d
to ground-truth dynamics; (b): RMSE
v
to ground-truth
dynamics; (c): initial approximation; (d): optimization result (7 iterations).
put of the network in the undesired direction. To pre-
vent that, we additionally train the network on the
samples, where the input is the result of one step of
optimization with small regularizer step size s · α =
0.001. We also try a simpler strategy to train on ran-
dom linear interpolation between the approximation
and the ground truth as the input.
Additionally, in the experiments with MPI Sin-
tel and Middlebury 2014 we randomly rotate the
patches by 90
◦
. We briefly review the results of these
experiments below.
Similarly to results in Section 4.1, training without
data augmentations results in optimization hitting a
bad solution (see Figure 8). Network trained on noisy
data tends to produce over-smooth depth maps (see
Figure 9). Using noisy data with gradually decreas-
Can We Use Neural Regularization to Solve Depth Super-resolution?
587

Table 1: Summary of conducted experiments. Mid./Sint. correspond to Middlebury 2014/MPI Sintel.
Pre-training Net Scheme Input augmentation Optimization Result Opt. RMSE
d
RMSE
v
GDSR U-Net 1 — GDSR Noisy X X X
GDSR U-Net 1 Gaussian noise with σ = 0.05 GDSR OK X X X
Mid./Sint. U-MSG-Net 2 — SimGeo Noisy X 7 7
Mid./Sint. U-MSG-Net 2 σ = 0.03 SimGeo Over-smoothed X X X
Mid./Sint. U-MSG-Net 2 σ = 0.03, scaled by 0.7 every 10-th epoch SimGeo Over-smoothed X X X
Mid./Sint. U-MSG-Net 2 Additional input samples (+): GT with gaussian noise with σ = MSE(GT,approximation) SimGeo Same as input X X 7
Mid./Sint. U-MSG-Net 2 + GT with noise ε, and target with noise ε/10 SimGeo Same as input X X 7
Mid./Sint. U-MSG-Net 2 + random linear interpolation between GT and approximation SimGeo Noisy 7 7 7
Mid./Sint. U-MSG-Net 2 + with the result after one step of optimization SimGeo Same as input X 7 7
ing noise variance similarly leads to over-smoothed
network outputs and optimization result. Expand-
ing training data with intermediate optimization re-
sults did not alleviate difficulties with optimization
convergence. Moreover, in some instances, this re-
sulted in well trained network, but exploding opti-
mization, yielding extremely noisy results (see Figure
10). Training using noisy targets again led to over-
smoothed network outputs and aggravated artefacts in
optimization results.
Implementation Details. We construct training
dataset similar to the one proposed in (Hui et al.,
2016) for training MSG-Net but appropriate for use
within DSRNETT. We split all images into patches
of size 64 × 64. For all patches we calculate inten-
sity, corresponding to RGB component. For half of
the patches we generate low-resolution depth using
box downsampling method with a scaling factor of
4, and obtain approximations using a bilinear upsam-
pling method instead of pseudo-inverse of box down-
sampling, since the former produces patches that are
more relevant for training MSG-Net. Finally, follow-
ing our Scheme 2, we train the model using the high-
frequency (HF) components of intensity and depth of
generated patches as inputs, and HF components of
ground-truth depth and intensity as targets. For sim-
plicity we further omit the fact that model is trained
on HF components and its inputs and outputs con-
tain not only depth, but also intensity part, since it
is not changed during training or optimization. In to-
tal, training was performed on 75K patches with 15K
patches used for validation. We train by optimizing
MSE loss using Adam for ∼120 epochs with a batch
size of 128.
We experimentally set minimum noise variance to
0.03. In experiment with noisy targets for network
inputs we added Gaussian noise with variance σ =
0.001; each target variance of noise was defined as
MSE(σ,0), divided by 10.
Ensuring Coercivity of Regularizer. According to
remark in (Obmann et al., 2019) in order to ensure
coercivity of regularizer in experiments with U-MSG-
Net, we employed skip-connection between network
input and output and define regularizer as R (x) =
kΦ
V
(x)−xk
2
+kxk
2
. We have checked, that such reg-
ularizer design does not help to solve optimization
issues and concluded, that optimization convergence
to undesired local minimum was not lead by possible
regularizer non-coercivity.
5 DISCUSSION
In this work, we performed an adaptation of
NETT (Li et al., 2020), an approach to image process-
ing leveraging data-driven regularizers, for the depth
super-resolution (SR) task. We have validated that
our formulation of depth SR meets all theoretical re-
quirements of NETT, including the restrictive coer-
civity condition. Furthermore, we were able to train
an efficient residual estimator deep network in all ex-
perimental cases. Unexpectedly, we have discovered
subsequent optimization to converge to the bad min-
imum in most experiments despite multiple efforts
to increase network stability by varying the training
dataset, applying data augmentations, selecting dif-
ferent models, or considering various formulations of
the optimization task.
Our results raise questions regarding the use of
learned regularizers in the context of depth SR (or
image-based tasks), which may represent promising
future research directions. More specifically,
1. What is the required form of the regularization
term that would allow effective optimization?
2. What are the characteristic features of image-
based tasks that might prevent optimization meth-
ods such as (Li et al., 2020) from converging to
good solutions?
3. What is the “right” training procedure for the reg-
ularizer?
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Ministry of Science and
Higher Education grant No. 075-10-2021-068. We
acknowledge the usage of Skoltech CDISE supercom-
puter Zhores (Zacharov et al., 2019) for obtaining the
presented results.
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
588

REFERENCES
Arridge, S., Maass, P.,
¨
Oktem, O., and Sch
¨
onlieb, C.-B.
(2019). Solving inverse problems using data-driven
models. Acta Numerica, 28:1–174.
Butler, D. J., Wulff, J., Stanley, G. B., and Black, M. J.
(2012). A naturalistic open source movie for optical
flow evaluation. In Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Per-
ona, P., Sato, Y., and Schmid, C., editors, Computer
Vision – ECCV 2012, volume 7577 of LNCS, pages
611–625, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin Heidel-
berg.
Chen, Y., Pock, T., Ranftl, R., and Bischof, H. (2013). Re-
visiting loss-specific training of filter-based mrfs for
image restoration. In Weickert, J., Hein, M., and
Schiele, B., editors, German Conference on Pattern
Recognition, volume 8142 of LNCS, pages 271–281,
Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer.
De los Reyes, J. C., Sch
¨
onlieb, C.-B., and Valkonen, T.
(2017). Bilevel parameter learning for higher-order
total variation regularisation models. Journal of Math-
ematical Imaging and Vision, 57(1):1–25.
Gatys, L., Ecker, A., and Bethge, M. (2016). A neural algo-
rithm of artistic style. Journal of Vision, 16(12):326–
326.
Gou, J., Yu, B., Maybank, S. J., and Tao, D. (2021). Knowl-
edge distillation: A survey. International Journal of
Computer Vision, 129(6):1789–1819.
Haefner, B., Peng, S., Verma, A., Qu
´
eau, Y., and Cremers,
D. (2020). Photometric depth super-resolution. IEEE
Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intel-
ligence, 42(10):2453–2464.
Haefner, B., Qu
´
eau, Y., M
¨
ollenhoff, T., and Cremers,
D. (2018). Fight ill-posedness with ill-posedness:
Single-shot variational depth super-resolution from
shading. In 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 164–174.
Hui, T.-W., Loy, C. C., and Tang, X. (2016). Depth map
super-resolution by deep multi-scale guidance. In
Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., and Welling, M., ed-
itors, European Conference on Computer Vision –
ECCV 2016, volume 9907 of LNCS, pages 353–369,
Cham. Springer International Publishing.
Johnson, J., Alahi, A., and Fei-Fei, L. (2016). Perceptual
losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution.
In European conference on computer vision, pages
694–711. Springer.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2015). Adam: A method for
stochastic optimization. In ICLR (Poster).
Li, H., Schwab, J., Antholzer, S., and Haltmeier, M. (2020).
NETT: Solving inverse problems with deep neural
networks. Inverse Problems, 36(6):065005.
Lunz, S.,
¨
Oktem, O., and Sch
¨
onlieb, C.-B. (2018). Adver-
sarial regularizers in inverse problems. In Proceedings
of the 32nd International Conference on Neural In-
formation Processing Systems, NIPS’18, pages 8516–
8525, Red Hook, NY, USA. Curran Associates Inc.
Obmann, D., Nguyen, L., Schwab, J., and Haltmeier, M.
(2019). Sparse l
q
-regularization of inverse problems
using deep learning. arXiv:1908.03006 .
Riegler, G., Ferstl, D., R
¨
uther, M., and Bischof, H. (2016).
A deep primal dual for guided depth super-resolution.
In British Machine Vision Conference, United King-
dom. The British Machine Vision Association.
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., and Brox, T. (2015). U-
net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image
segmentation. In Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells,
W. M., and Frangi, A. F., editors, Medical Image Com-
puting and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI
2015, volume 9351 of LNCS, pages 234–241, Cham.
Springer International Publishing.
Scharstein, D., Hirschm
¨
uller, H., Kitajima, Y., Krathwohl,
G., Ne
ˇ
si
´
c, N., Wang, X., and Westling, P. (2014).
High-resolution stereo datasets with subpixel-accurate
ground truth. In Jiang, X., Hornegger, J., and Koch,
R., editors, German Conference on Pattern Recog-
nition, volume 8753 of LNCS, pages 31–42, Cham.
Springer International Publishing.
Song, X., Dai, Y., Zhou, D., Liu, L., Li, W., Li, H., and
Yang, R. (2020). Channel attention based iterative
residual learning for depth map super-resolution. In
2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pages 5630–5639.
Voynov, O., Artemov, A., Egiazarian, V., Notchenko, A.,
Bobrovskikh, G., Zorin, D., and Burnaev, E. (2019).
Perceptual deep depth super-resolution. In Proceed-
ings of the IEEE International Conference on Com-
puter Vision, pages 5653–5663.
Zacharov, I., Arslanov, R., Gunin, M., Stefonishin,
D., Bykov, A., Pavlov, S., Panarin, O., Mal-
iutin, A., Rykovanov, S., and Fedorov, M. (2019).
“zhores”—petaflops supercomputer for data-driven
modeling, machine learning and artificial intelligence
installed in skolkovo institute of science and technol-
ogy. Open Engineering, 9(1):512–520.
APPENDIX
Network Tikhonov Regularization
Assumptions
(Li et al., 2020) prove well-posedness and conver-
gence of NETT regularization, provided that cer-
tain assumptions on regularizer and data fidelity term
hold.
We have tried to ensure fulfillment of this condi-
tions in our work. Conditions on data fidelity term are
not restrictive and hold for squared L
2
-norm distance,
while the conditions on regularizer term include:
1. Regularizer R (x) = ψ(Φ
V
(x)) is weakly lower
semicontinuous, which is guaranteed by condi-
tions:
• Linear operators A
l
are bounded;
• Non-linearities σ
l
are weakly continuous;
Can We Use Neural Regularization to Solve Depth Super-resolution?
589
• Scalar functional ψ is weakly lower-
semicontinuous;
2. R (x) is coercive, i.e. lim
kxk→∞
R (x) = 0.
U-Net-type and U-MSG-Net architectures in-
clude convolution operations and batch normaliza-
tions, that are bounded linear operations, and max
pooling, leaky ReLU and upsampling operations, that
are weakly continuous and coercive non-linearities.
We use squared L
2
-norm distance as weakly lower
semi-continuous scalar functional ψ. We note that the
number of parameters in the U-Net model is close to
7M, while in the U-MSG-Net it is around 700K.
Several ways to obtain coercivity of the regular-
izer are discussed in (Li et al., 2020). One way is to
ensure layer-wise coercivity, i.e. use coercive non-
linearities σ
l
and linear operators A
l
, satisfying the
inequality:
∃c
l
∈ [0,∞)∀x ∈ X : kxk ≤ c
l
kA
l
xk. (5)
We relied on this approach in experiments with U-
Net-type architecture. Since U-MSG-Net contains
non-coercive parametric ReLU non-linearities, we
used another way to obtain network coercivity by ex-
ploiting skip connection between network input and
output, see ”Ensuring coercivity of regularizer” in
Section 4.2.
Specifically, fulfillment of presented conditions
guarantee existence of a solution, stability and con-
vergence for optimization problem (2). Stability of
the method corresponds to continuous dependence of
the solutions x of optimization problem (2) on input
y. Convergence of the method states, that while noise
level δ
k
in inputs y
δ
k
decreases to zero, sequence x
k
of corresponding solutions weakly converges to the
R (·)-minimizing solution x
+
of F(x) = y
0
, if it is
unique.
Experiments
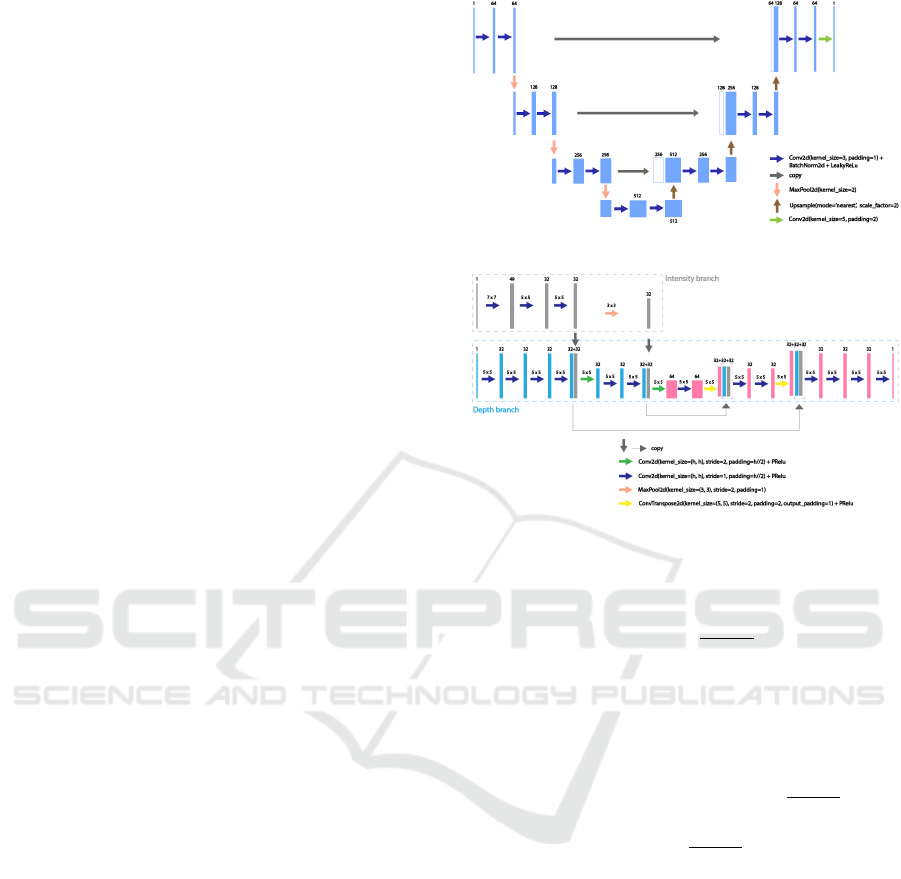
Figures 11 and 12 represent architectures of networks,
used in experiments in Sections 4.1 and 4.2 respec-
tively.
Training on Intermediate Optimization
Results as Input
In our experiments we use approximation
e
x, i.e.
upsampled low-resolution version of ground-truth
depth, as optimization initial approximation. We sup-
pose, that optimization approximation is not signifi-
cantly changed after the first data fidelity gradient de-
scent step and treat
e
x as its result.
Figure 11: U-Net-type architecture.
Figure 12: U-MSG-Net architecture.
Then after the regularizer gradient descent step we
obtain approximation x
1
:
x
1
=
e
x − s · α ·
dR (x)
x
|
x=
e
x
(6)
If network is trained to predict ground-truth depth
given both
e
x or x
1
, then regularizer gradient descent
step would not move optimization approximation to
the direction of x
1
:
kΦ
V
(x
1
) − x
1
k
2
= kΦ
V
(
e
x) −
e
x + s · α ·
dR (x)
x
|
x=
e
x
k
2
≥ kΦ
V
(
e
x) −
e
xk
2
+ ks · α ·
dR (x)
x
|
x=
e
x
k
2
≥ kΦ
V
(
e
x) −
e
xk
2
.
Thus, we come to idea to add optimization first step
approximation for small s · α = 0.001 to the training
samples.
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
590
