
Relevance-based Channel Selection for EEG Source Reconstruction: An
Approach to Identify Low-density Channel Subsets
Andres Soler
1
, Eduardo Giraldo
2
, Lars Lundheim
3
and Marta Molinas
1
1
Department of Engineering Cybernetics, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway
2
Department of Electrical Engineering, Universidad Tecnol
´
ogica de Pereira, Pereira, Colombia
3
Department of Electronic Systems, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway
Keywords:
Relevance Channel Selection, Low-density EEG, EEG Signals, Source Reconstruction.
Abstract:
Electroencephalography (EEG) Source Reconstruction is the estimation of the underlying neural activity at
cortical areas. Currently, the most accurate estimations are done by combining the information registered
by high-density sets of electrodes distributed over the scalp, with realistic head models that encode the mor-
phology and conduction properties of different head tissues. However, the use of high-density EEG can be
unpractical due to the large number of electrodes to set up, and it might not be required in all the EEG applica-
tions. In this study, we applied relevance criteria for selecting relevant channels to identify low-density subsets
of electrodes that can be used to reconstruct the neural activity on given brain areas, while maintaining the
reconstruction quality of a high-density system. We compare the performance of the proposed relevance-based
selection with multiple high- and low-density montages based on standard montages and coverage during the
reconstruction process of multiple sources and areas. We assessed several source reconstruction algorithms
and concluded that the localization accuracy and waveform of reconstructed sources with subsets of 6 and 9
relevant channels can be comparable with reconstructions done with a distributed set of 128 channels, and
better than 62 channels distributed in standard 10-10 positions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since the first report of human EEG recordings done
by Hans Berger in 1929 (O’Leary, 1970). The EEG
signals have been considered a window to the hu-
man brain and their analysis as a powerful tool to un-
derstand the multiple brain processes. EEG signals
can be used to estimate the properties of the underly-
ing brain activity, generally its localization and wave-
form, this process is often referred to as source re-
construction (Phillips et al., 1997). The accurate re-
construction of the brain activity requires solving the
forward and inverse problems. Briefly, the forward
problem solution consists of modelling the interaction
between a large population of neurons at the brain
cortex and the electrical field that is recorded. Mul-
tiple methods, like Finite Element Modelling (FEM)
and Boundary Element Modelling (BEM) based on
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) head images al-
low to obtain realistic representations of the brain and
the accurate modelling of source-electrode interaction
(Hallez et al., 2007). In contrast, the inverse problem
solution is the estimation of the brain activity proper-
ties by using the information registered by the elec-
trodes and the forward model solution (Michel and
Brunet, 2019).
The number of electrodes plays a key role in
source reconstruction and it is a well established fact
that a high number of electrodes allows obtaining a
better estimation of the source activity. However,
the EEG electrode distribution was mostly conceived
based on coverage and not based on their contribution
to accuracy. With a wide coverage is possible to attain
a better overview of the brain activity over the entire
head, and compare it between both hemispheres to ob-
tain lateralized information. In 1958, the 10-20 elec-
trode positioning systems was introduced to facilitate
the standardization of EEG recordings and benefit the
comparison of findings in the scientific community
(Jasper, 1958; Ten, 1961). Years afterwards, the 10-
10 electrode positioning system (Chatrian et al., 1985)
was presented as an inherent extension of the 10-20
system, which allowed covering the scalp with more
electrodes. In 2001 this electrode layout was extended
by the introduction of the 10-5 system (five percent
electrode system for high-resolution EEG) (Oosten-
174
Soler, A., Giraldo, E., Lundheim, L. and Molinas, M.
Relevance-based Channel Selection for EEG Source Reconstruction: An Approach to Identify Low-density Channel Subsets.
DOI: 10.5220/0010907100003123
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022) - Volume 2: BIOIMAGING, pages 174-183
ISBN: 978-989-758-552-4; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

veld and Praamstra, 2001), for which an extended
nomenclature and location for up to 345 channels was
proposed. However, the 10-5 electrode positioning
system is not the only scalp distribution to reach hun-
dreds of channels; other electrode distributions like
the radial (BioSemi BV, Amsterdam, Netherlands),
and geodesic (Electrical Geodesics, Inc., USA) allow
recordings with up to 256 channels.
At the time of the introduction of the 10-5 sys-
tem, it was known that the inverse solution required
a higher number of electrodes to obtain more reli-
able reconstructions (Phillips et al., 1997). The num-
ber of channels for source reconstruction has been in-
vestigated in (Song et al., 2015; Sohrabpour et al.,
2015). It has been proven that the use of high-
density EEG systems favors the localization of brain
sources compared to low-density ones. Particularly
in (Sohrabpour et al., 2015) the authors presented a
study with epileptic patients, where it was concluded
that adding electrodes improves the accuracy. How-
ever, continuing to add channels beyond a certain
point did not significantly improve the localization ac-
curacy and which starts plateauing at that point. There
is not a written consensus of what is and what is not
high-density EEG, however, in (Seeck et al., 2017)
it was suggested that high-density EEG can be con-
sidered between 64 to-256 channels. It is generally
accepted that systems with 60 or more electrodes can
be regarded as high-density EEG, while systems with
32 or below might be considered low-density EEG.
Some authors have investigated whether low-
density arrays can accurately localize brain sources,
(Jatoi and Kamel, 2018), where localization errors
around 14 mm were obtained by using Multiple
Sparse Priors (MSP) with a low-density montage
of 7 electrodes. (Soler et al., 2020b) applied pre-
processing with frequency decomposition techniques
to improve source reconstruction with low-density
electrodes arrays of 32, 16, and 8 channels. However,
the aforementioned studies do not provide a rational
criterion for selecting which electrodes will best con-
tribute to accuracy from the considered EEG cover-
age.
In this study, we investigate the use of a data-
driven relevance-based selection criteria for EEG
channels to obtain low-density subsets to be con-
sidered during source reconstruction. Starting from
high-density electrode layouts, we investigate the ef-
fect of reducing electrodes based on coverage, the use
of the standard electrode montages, and our proposal
based on relevance. Finally, we compare the recon-
struction quality in terms of localization accuracy and
correlation of the source activity, and provide a dis-
cussion over the results and the significance of using
low-density electrode arrays in source reconstruction.
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1 Forward Modelling
EEG is an indirect measurement of the post-synaptic
activity that takes place in the cortical areas; thou-
sands of neurons should fire in synchrony to be able
to obtain a measurable electric field at the scalp. It is
because the local field potentials produced by extra-
cellular currents of a large population of neurons
(sources) propagate through different tissues attenu-
ating their strength before reaching the scalp. The
forward modelling is the representation of the rela-
tionship between the source activity and the electrical
potential that can be measured by electrodes at the
scalp. To accurately represent such complex relation-
ships, the forward modelling considers the different
head tissues and the flow of the electrical field across
them.
To obtain accurate and realistic representations of
this relationship, FEM and BEM methods combine
tissue segmented MRI head images and the conduc-
tivity of the head tissues. The measured EEG can be
represented theoretically using the forward equation
in eq. 1. Where M
M
M is the forward model (also know as
lead field matrix) with dimensions n by s (being n the
number of channels and s the number of distributed
sources), y
y
y with dimensions n by t (being t the number
of samples) represents the electrodes measurement of
the electric potential generated by the source activity
in the cortical areas represented by x
x
x, with dimensions
s by t . ε represents the noise usually presented in the
measurements.
y
y
y =M
M
Mx
x
x +ε (1)
2.2 Inverse Modelling
In contrast to the forward problem, the inverse prob-
lem is the estimation of the source activity from the
recorded signals, it is also known as source recon-
struction. In the solution of the inverse problem,
the lead-field matrix M
M
M is known, as it establishes
a set of distributed sources over all the cortical ar-
eas. The inverse solution is the estimation of the con-
tribution of each source to the recorded EEG. The
inverse problem is characterized to be mathemati-
cally ill-posed and ill-conditioned ((H
¨
am
¨
al
¨
ainen and
Ilmoniemi, 1994)). It is because the volume of the in-
formation available in the EEG recording comes from
hundreds of electrodes, in the best cases; a number
Relevance-based Channel Selection for EEG Source Reconstruction: An Approach to Identify Low-density Channel Subsets
175
which is much lower than the number of unknowns,
usually thousands of sources.
Multiple methods based on Tikhonov regulariza-
tion have been applied to overcome these challenges.
Some of the most known and used methods based
on regularization are the minimum norm estima-
tion (MNE) (H
¨
am
¨
al
¨
ainen and Ilmoniemi, 1994), its
weighted version (wMNE) (Iwaki and Ueno, 1998;
Pascual-Marqui, 2002) to compensate for deep activ-
ity, and the standardized low-resolution tomography
(sLORETA), which is characterized by the zero er-
ror localization in absence of noise ((Pascual-Marqui,
2002)). From another perspective, the multiple sig-
nal classification (MUSIC) (Mosher and Leahy, 1998)
algorithm estimates the localization of a source by
identifying the contribution of each source when test-
ing whether its projection (topography) belongs to a
signal-subspace or noise-subspace. This particular
algorithm is useful to identify the number of active
sources and locate them. However, the contribution
is calculated using a localizer function, and it is of-
ten difficult to identify the true active sources due to
the fact that neighbour sources of the true source can
lead to a similar topography and similar value in the
localizer function. Therefore, to avoid this problem
the topography is out-projected and the sources can
be calculated one by one in recursive applied MU-
SIC (RAP-MUSIC). However, the RAP version has
an undesired property of leaving large values in the
localizer function in the vicinity of already located
sources, which produces an overestimation of the
number of sources due to some false positive sources.
This weakness was improved by applying a sequen-
tial dimension reduction of the estimated remaining
signal space at each recursion step in the truncated
RAP-MUSIC (TRAP-MUSIC) (M
¨
akel
¨
a et al., 2018;
Ilmoniemi and Sarvas, 2019). When the localization
of the source is estimated by a MUSIC-based algo-
rithm, the source time-course can be estimated using
Tikhonov regularization, by constraining the solution
to the previous estimated locations.
In this study, we considered five methods for
source reconstruction, wMNE, sLORETA, MUSIC,
TRAP-MUSIC, and Multiple Sparse Priors (MSP).
This method is characterized for offering a low free-
energy solution (Friston et al., 2008) and has been
investigated over low-density EEG settings in (Jatoi
et al., 2014).
We used the ”New York Head Model” as the for-
ward model (Huang et al., 2016). It is a six-layer FEM
model that considered the conductivity of the scalp,
skull, CSF, gray matter, white matter, and air cavi-
ties. The model relates 231 channels with a multiple
number of sources 75K, 10K, 5K, and 2K. The lead
field matrix of 10K sources was used to generate syn-
thetic EEG signals with known ground-truth source
activity (see section 2.3) and the lead field matrix of
5K sources was used for inversion, to prevent the so-
called inverse crime (Colton and Kress, 2019).
2.3 Ground-truth EEG Dataset
A set of three sources with temporal mixing was sim-
ulated at different frequencies. Using the following
equation:
x
i
(t
k
)=e
−
1
2
(
t
k
−c
i
σ
)
2
sin(2π f
i
t
k
) (2)
Each source number i is a Gaussian windowed si-
nusoidal activity and has an associated frequency f
i
,
time center c
i
, a Gaussian window width σ
i
, and a lo-
cation loc
i
in a predefined region of the brain. A sim-
ilar scheme of simulation was used in (Soler et al.,
2020b; Soler et al., 2020a). The parameters for each
source are presented in table 1.
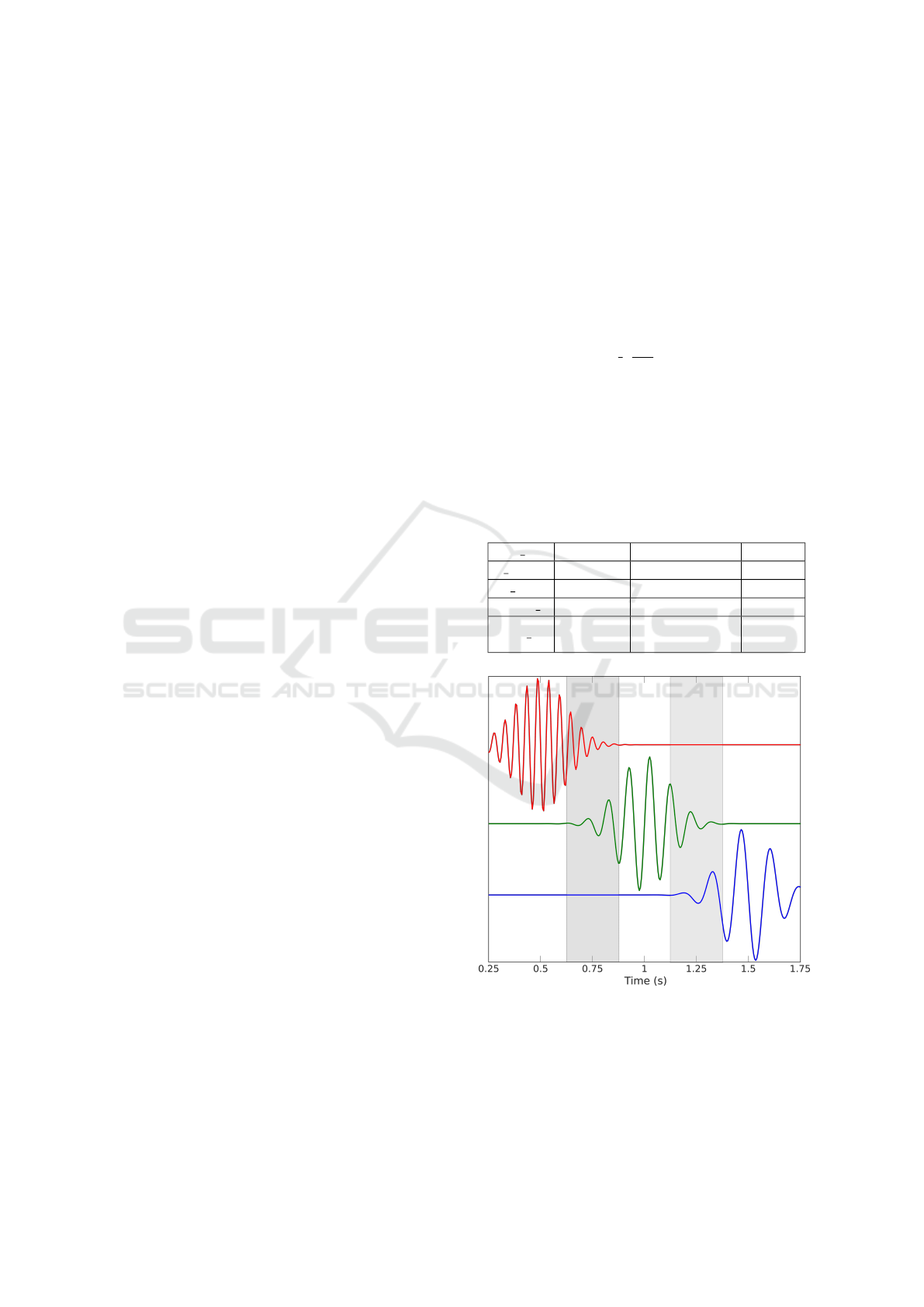
Table 1: Parameters for source simulation.
s i i=1 i=2 i=3
f i (Hz) 19 10 7
c i (s) 0.5 1.0 1.5
sigma i 0.12 0.12 0.12
loc i
Occipital
lobe
Sensory-motor
cortex
Frontal
lobe
Figure 1: Example of the time-courses of simulated source
activity. The light-gray shapes show the time windows
where temporal mixing is present between the sources.
Sources s
1
, s
2
, and s
3
are depicted in red, green, and blue
color, respectively.
Although the sources have a predefined region
of the brain, the final locations of the sources were
BIOIMAGING 2022 - 9th International Conference on Bioimaging
176
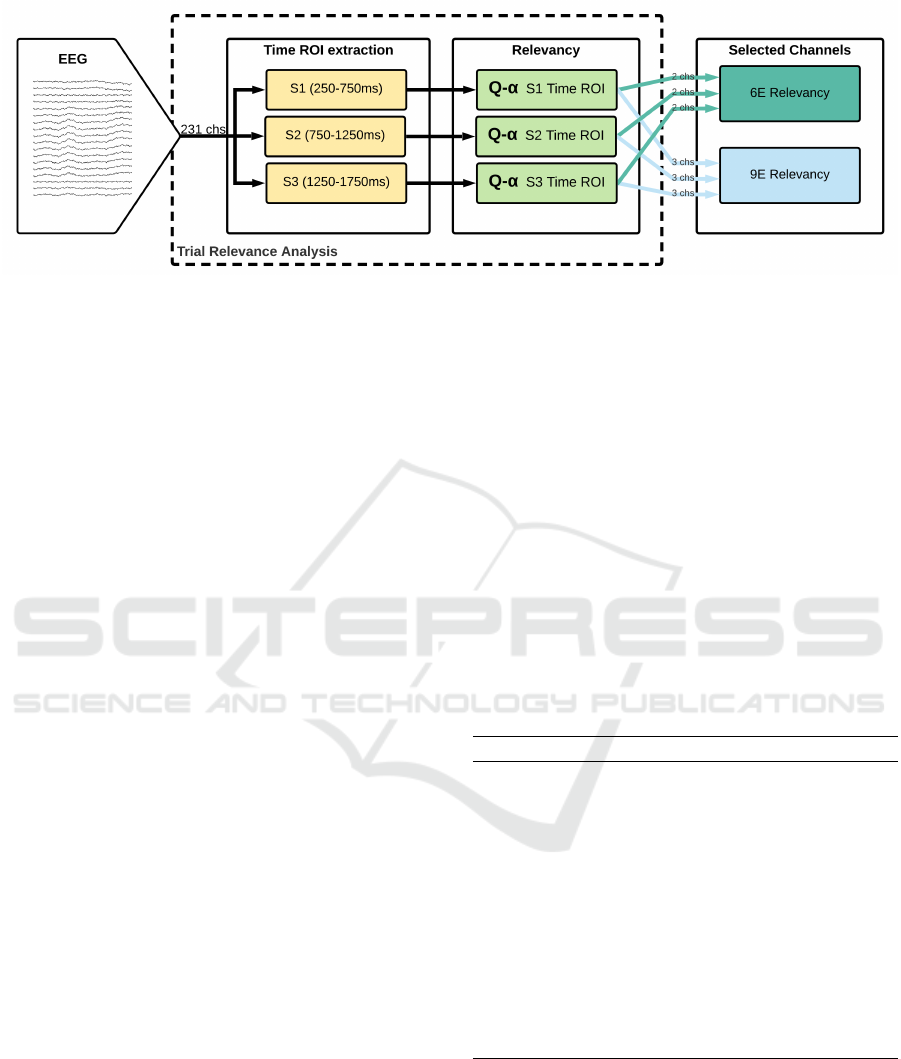
Figure 2: Relevance channel selection procedure for selecting the 6 and 9 most relevant channels per each EEG trial.
randomly selected from a set of twelve locations in
each area, distributed equally for each hemisphere.
The source ground-truth simulation process was re-
peated to obtain 150 trials with different combination
of source locations. The synthetic EEG was obtained
by using the forward equation (eq. 1), a signal-to-
noise ratio (SNR) of 0dB was added to simulate the
level of noise typically found in event related poten-
tials ERPs. An example of the ground-truth activity
can be seen in figure 1
2.4 Relevance based Channel Selection
We applied the relevance analysis proposed by (Wolf
and Shashua, 2005), to select k most relevant EEG
channels to be used for source reconstruction. A time-
ROI is selected for each source, and then for each
time-ROI, the relevance for each channel is calcu-
lated using the Standard Power-Embedded Q-α algo-
rithm. As three sources were simulated, the k =2 and
k =3 most relevant channels per each source time-ROI
were selected, therefore, the total of electrodes per
EEG used during source reconstruction for k =2 and
k =3 were 6 (we refer as Rel −6E) and 9 (we refer as
Rel −9E) respectively. In figure 2 is summarized the
selection process and presented the Time-ROI times
for each source.
By using the Standard Power-Embedded Q-α al-
gorithm, it is calculated a relevance indicator associ-
ated with each channel, this indicator is represented
by α
α
α ∈R(0, 1), where the values closer to 1 represent
the most relevant channels. (Wolf and Shashua, 2005)
presented the algorithm for feature selection, being
relevance directly related to the clustering quality of
features. Here, applied to EEG channel selection, the
relevance measures the ability of the channels to cap-
ture the underlying neural activity in the time-ROI.
Here the algorithm is presented in the context of EEG
channel selection. Consider the pre-processed EEG
as y
y
y
T
1
, ..., y
y
y
T
n
, such that each row is centered around
zero and its L2 norm ∣∣y
y
y
i
∣∣=1. For notation, the term
P
T
stands for the transpose of matrix P. Consider A
A
A
α
to be the affinity matrix of the inner-product between
data points weighted by α
α
α as A
A
A
α
=
∑
n
i=1
α
α
α
i
y
y
y
i
y
y
y
T
i
. Also
consider Q
Q
Q as an orthonormal t by k matrix, whose
columns are the k eigenvectors of A
A
A associated with
the highest eigenvalues. To find the channel relevance
α is calculated by solving the optimization problem
presented below:
maxtrace
Q
Q
Q,α
α
α
(Q
Q
Q
T
A
A
A
T
α
A
A
A
α
Q
Q
Q)
subject to α
α
α
T
α
α
α =1
(3)
which can be solved by applying the Power-
Embedded Q-α algorithm (algorithm 1) adapted for
EEG channel relevance. The number of r iterations
was set to r =10 according to the number of iterations
suggested in (Wolf and Shashua, 2005).
Algorithm 1: Power-Embedded Q-α algorithm.
1: procedure Q-α(y)
2: Q
0
← random orthonormal q by k matrix
3: r ← 1
4: while r ≤ 10 do
5: G
i, j
← (y
y
y
T
i
y
y
y
j
)y
y
y
T
i
Q
Q
Q
r−1
Q
Q
Q
T
r−1
y
y
y
j
6: α
α
α ← the largest eigenvector of G
7: A
A
A
α
←
∑
n
i=1
α
α
α
i
y
y
y
i
y
y
y
T
i
8: Z ← A
A
A
α
Q
Q
Q
r−1
9: Q
Q
Q
r
R ← QR decomposition of Z
10: r ← r + 1
11: end while
12: return α
α
α
13: end procedure
2.5 Standard-based and
Coverage-based Channel
Distributions
The New York Head forward model in (Huang et al.,
2016) considers 231 electrodes positions, of which
161 are located in the scalp according to the 10-5
Relevance-based Channel Selection for EEG Source Reconstruction: An Approach to Identify Low-density Channel Subsets
177

Figure 3: Standard-based (top row) and coverage-based (middle and bottom rows) electrode Layouts. The selected electrodes
for each layout are marked with a red circle over the 161 electrodes available in the New York Head.
system, and 70 electrodes distributed between neck
and face. To compare the performance of source re-
construction using relevance-based channel selection,
we selected multiple layouts based on coverage and
standard systems. One of the selected electrode dis-
tribution is based on the 161 scalp electrodes of the
BIOIMAGING 2022 - 9th International Conference on Bioimaging
178
model, we refer to it as HD−161E. Two subsets of 19
and 62 electrodes were considered based on the 10-20
and 10-10 standard electrode distribution, we refer to
them as LD −19E(10 −20) and HD −62E(10 −10),
respectively. Four more subsets of electrodes were
selected based on coverage criteria, one lays in the
category of high-density with 128 channels, it is re-
ferred as HD −128E; the other three are considered
low-density, with channel numbers of 32, 16, and 8,
they were selected trying to keep an equal coverage of
the head, they are referred as LD−32E, LD−16E, and
LD −8E. The Figure 3. shows the different standard-
based and coverage-based layouts.
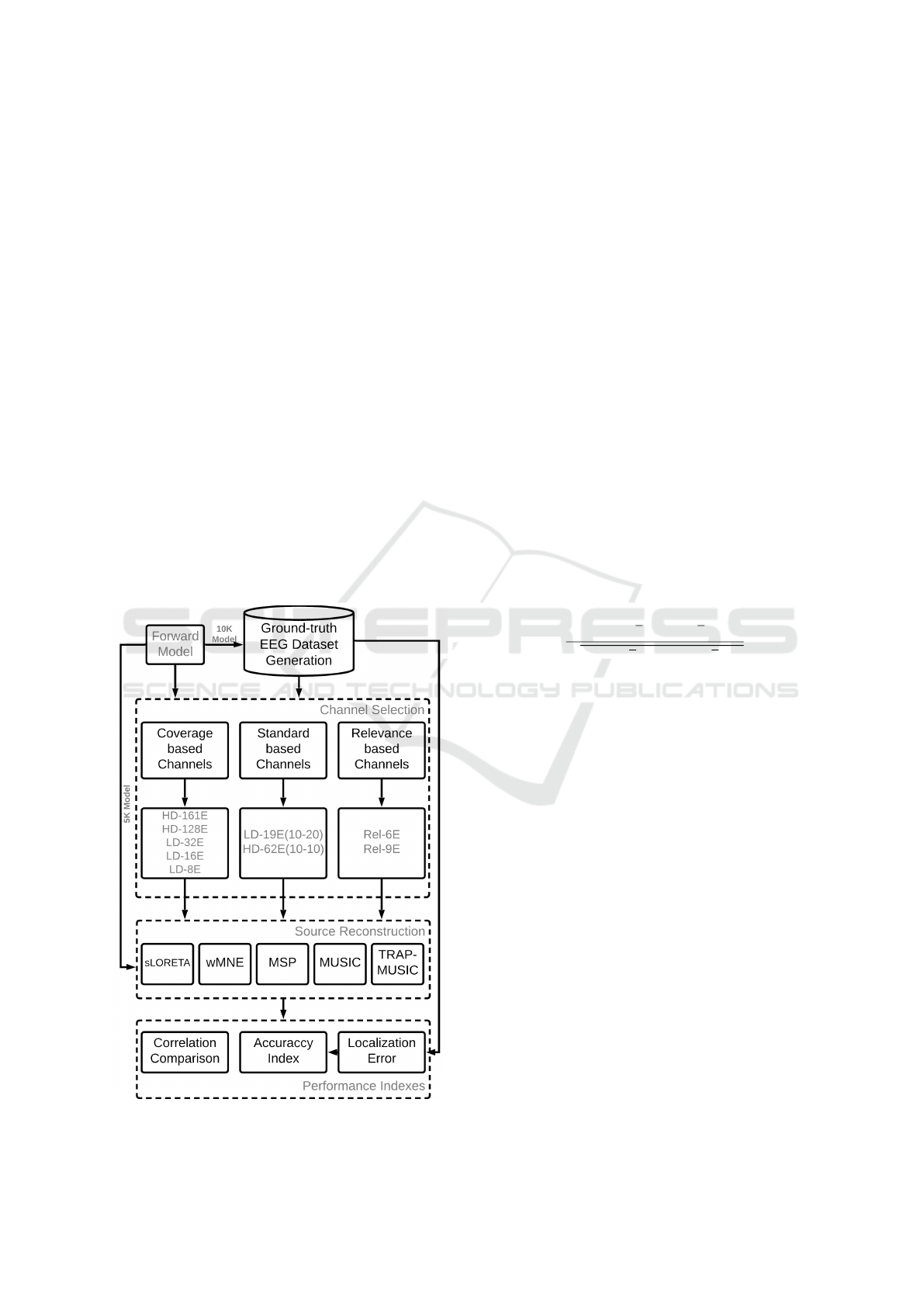
2.6 Evaluation Procedure
The evaluation procedure is presented in figure 4.
It starts with the generation of the ground-truth
EEG dataset (section 2.3). The 150 trials are pro-
cessed separately, for each EEG, the channels are
selected according to the three criteria: coverage-
based, standard-based, and relevance-based. The se-
lected channels are considered during inverse solu-
tion and processed with the five source reconstruc-
tion algorithms. The algorithms wMNE, sLORETA,
Figure 4: Summary of the evaluation procedure.
and MSP provide localization and time-course of the
sources, while MUSIC and TRAP-MUSIC provided
only source localization, however, they can be com-
plemented with Tikhonov regularization constrained
to the estimated locations to estimate the time-course
activity.
After estimating the brain activity, the localization
error for each of the three sources is calculated by us-
ing the euclidean distance (equation 4) between the
ground-truth P
x
and the estimated P
ˆx
location. Then,
the localization error is averaged between the three
sources to provide a single value for the error of lo-
calization.
LocE =∣∣P
x
−P
ˆx
∣∣
2
(4)
The number of trials in which the localization er-
ror with relevance selection was equal or lower than
with coverage or with standard-based layouts is pro-
posed to measure at what extend of trials, the rel-
evance selection produced equal or better accuracy
compared to the other criteria. We refer to it as the
Accuracy Comparison index.
The time course of the sources reconstructed with
Rel −6E, Rel −9E are extracted and compared with
the time courses reconstructed with the denser elec-
trode layout HD −161E. To compare them, we used
the Pearson Correlation Coefficient:
r =
∑
(x
1i
−x
1i
)(x
2 j
−x
2 j
)
√
∑
(x
1i
−x
1i
)
2
∑
(x
2 j
−x
2 j
)
2
(5)
where i and j are the location of the sources with the
highest amplitudes of two different reconstructions,
and x
1i
and x
2 j
are the time courses.
3 RESULTS
The mean and standard deviation of the localization
error for the 150 trials is shown in figure 5. The elec-
trode layouts in the x-axis were organized according
to the number of electrodes they consider, excepting
the Rel −6E and Rel −9E that were located first on the
left side. The best accuracy was obtained when using
the highest number of electrodes with the HD−161E
layout when considering all the scalp electrodes of
the forward model. In contrast, the worst accuracy
was obtained when using the LD−8E layout. A trend
can be seen in the localization error, as the number of
electrodes is being reduced, the localization accuracy
decreases. However, the trend is abruptly interrupted
when considering the results of the channels selected
with the relevance criteria.
The localization error of the relevance selec-
tion Rel −6E and Rel −9E are comparable to the
HD −128E test. Particularly the methods wMNE,
Relevance-based Channel Selection for EEG Source Reconstruction: An Approach to Identify Low-density Channel Subsets
179
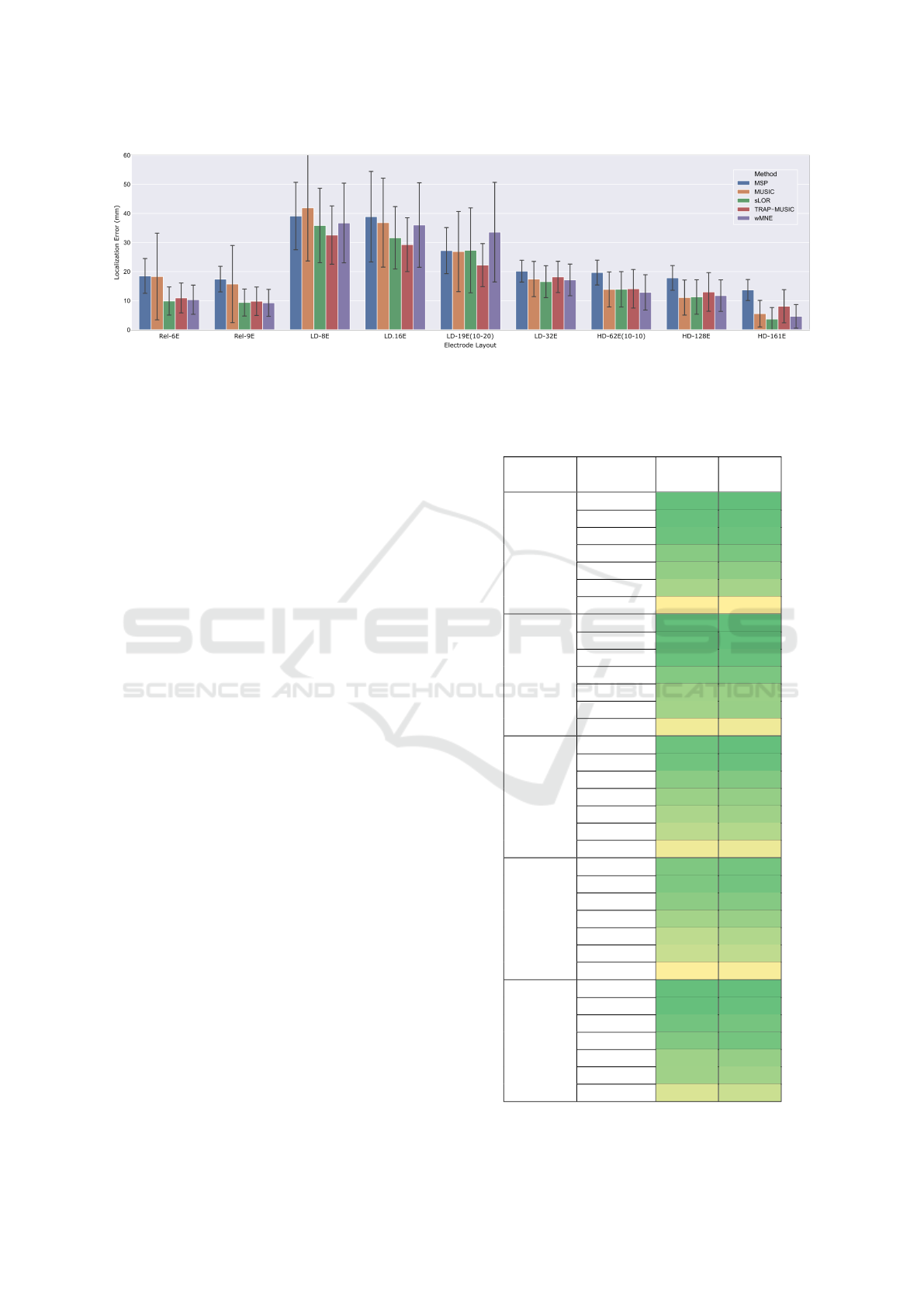
Figure 5: Localization error of the multiple electrode layouts combined with each of the source reconstruction algorithms.
sLORETA, and TRAP-MUSIC, for the relevance
cases offer a slightly better localization error mean
with similar standard deviation as with the HD −
128E. Here it is remarkable that for the same meth-
ods, Rel −9E kept the mean localization error below
10mm, result that was achieved only with all the elec-
trodes HD −161 case. The case of the MSP method
presents a similar behavior with Rel −9E compared to
HD−128E, and the MSP accuracy with Rel −9E was
slightly lower than with HD −128E. In contrast, the
MUSIC method was highly affected by the reduction
in the number of electrodes. It is a generalized effect
for this particular algorithm, regardless of whether the
channels were selected with relevance or not; as the
number of electrodes is reduced the standard devia-
tion increases.
Table 2. offers the accuracy comparison indexes
when considering the percentage of trials that ob-
tained equal or better localization error with rele-
vance criteria Rel −6E and Rel −9E, than the other
layouts based on standard and coverage criteria. It
is remarkable that for methods sLOR, wMNE, and
TRAP-MUSIC, Rel −9E obtained an index between
61% and 68% when comparing with HD −128E and
between 67% and 73% when comparing with HD −
62E(10 −10), especially considering that Rel −9E
has 119 and 51 fewer channels than HD −128E, and
HD−62E respectively. In the case of Rel −6E the re-
sults are also noticeable, it uses 122 fewer channels
than HD−128E and 55 less than HD −62E(10−10),
and it obtained indexes between 59% and 64% when
comparing with HD −128E and between 63% and
71% when comparing with HD −62E(10−10).
To compare the reconstructed time courses of the
estimated source activity, we computed the Pearson
correlation coefficient between the reconstructions
using Rel −6E and Rel −9E and the denser electrode
layouts of HD −161E and HD −128E. The compari-
son was done for the reconstructions with the methods
that obtained the lowest localization error, sLORETA,
and wMNE. The results of the comparison between
Table 2: Accuracy Comparison Index, percentage of trials
that obtained equal or better localization error when com-
paring the relevance criteria Rel − 6E and Rel − 9E with
other electrode configurations.
Methods
Channel
Layout
Rel-6E Rel-9E
LD-8E 0,96 0,97
LD-16E 0,95 0,95
LD-19E 0,91 0,92
LD-32E 0,77 0,85
HD-62E 0,71 0,73
HD-128E 0,59 0,61
sLOR
HD-161E 0,11 0,11
LD-8E 0,97 0,97
LD-16E 0,95 0,97
LD-19E 0,93 0,94
LD-32E 0,79 0,84
HD-62E 0,63 0,67
HD-128E 0,62 0,68
WMN
HD-161E 0,19 0,21
LD-8E 0,91 0,97
LD-16E 0,90 0,94
LD-19E 0,75 0,80
LD-32E 0,67 0,70
HD-62E 0,57 0,64
HD-128E 0,49 0,53
MSP
HD-161E 0,21 0,22
LD-8E 0,82 0,88
LD-16E 0,83 0,89
LD-19E 0,75 0,79
LD-32E 0,62 0,68
HD-62E 0,47 0,55
HD-128E 0,42 0,47
MUSIC
HD-161E 0,13 0,15
LD-8E 0,96 0,97
LD-16E 0,96 0,95
LD-19E 0,89 0,87
LD-32E 0,81 0,88
HD-62E 0,65 0,69
HD-128E 0,64 0,63
TRAP-
MUSIC
HD-161E 0,32 0,41
BIOIMAGING 2022 - 9th International Conference on Bioimaging
180
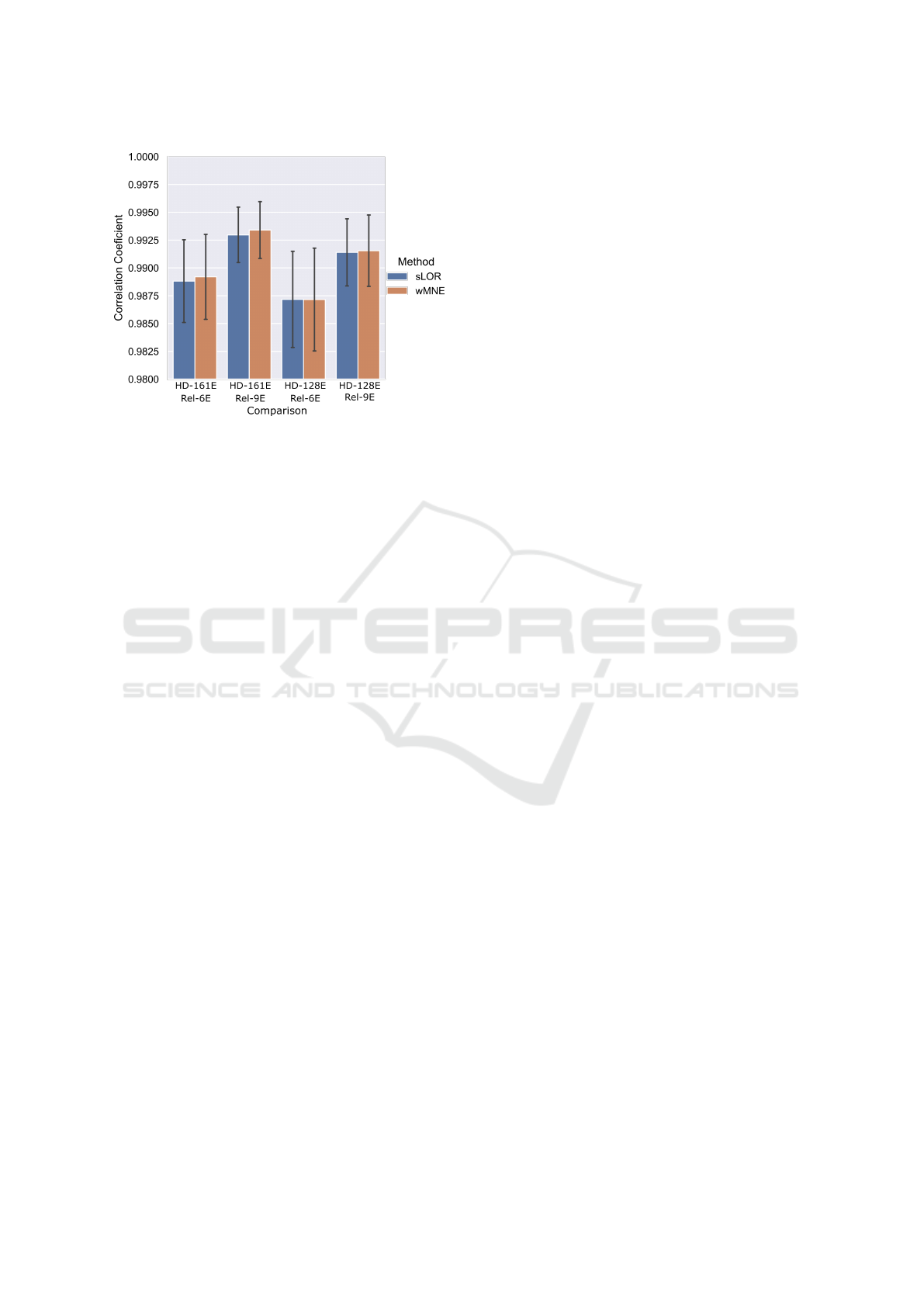
Figure 6: Source time courses correlation coefficient be-
tween high-density layouts and relevance based channel se-
lection.
the aforementioned sets of channels are presented in
figure 6. It can be seen that the correlation in all
the cases was more than 98% and particularly for
the comparisons with Rel −9E, the correlation values
were higher than 99%.
To offer an overview of the relevance-based se-
lected channels we computed the number of times that
the channels were repeatedly chosen by the two rel-
evance criteria. The number of repetitions for each
channel is shown in figure 7. For relevance analysis,
the 231 channels positions of the forward model were
considered, including 70 locations in face and neck,
however, none of the selected channels were in those
areas. It is important to note that the selected chan-
nels across trials were distributed between both hemi-
spheres, in which a particular position in the right
hemisphere and its equivalent at the left hemisphere
obtained similar repetition values. The small differ-
ences can be explained by the location of the simu-
lated sources which were selected randomly from a
pre-set of sources for each brain area, equally dis-
tributed between both hemispheres.
4 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
With the introduction of relevance criteria for channel
selection, a subset of selected channels, with a sparser
number far from high-density EEG, can reconstruct a
set of sources in the brain with comparable quality as
a high-density number of channels. The reconstruc-
tion quality obtained with relevance channel selection
can be comparable to using a set of 128 channels, and
better than 62 channels in terms of the localization
error. Moreover, in terms of the time-courses simi-
larity, the high level of correlation obtained between
the reconstruction with the relevant channels and the
densest coverage-based layouts supports the hypothe-
sis that relevance-based channel selection criteria can
be comparable with high-density to reconstruct a par-
ticular brain activity.
The aim of this work is not to discourage the use
of high-density EEG systems, it is rather to offer an
alternative technique to select and reduce the number
of electrodes for source reconstruction while keeping
the quality. In situations where for practical reasons
high-density systems are not applicable or affordable,
low-density EEG solutions designed with relevance
criteria will favour portability and reduce the volume
of data while achieving the same quality as the high
density solutions. These traits will enable the devel-
opment of much needed EEG tools for medical di-
agnosis and non-medical applications. The results of
this research suggest the application of this analysis
in cases in which apriori known areas of the brain are
going to be monitored and it is not possible or diffi-
cult to constantly measure with a high-density system.
For example, in Brain-computer interfaces (BCI) sys-
tems based on source reconstructed activity (Edelman
et al., 2016; Lindgren, 2017) or Mobile Brain Imag-
ing (MoBI) applications in which the recordings are
taken out of the lab (Gramann et al., 2011; Lau-Zhu
et al., 2019).
It is important to consider that the selected elec-
trodes based on relevance criteria are relevant on the
basis of the particular source activity in which the
analysis is applied. It must not be miss-interpreted
that a selected set of electrodes can be used for map-
ping all the cortical regions. In such cases, to estimate
a generalized activity over the brain, high-density is
proven to be effective regardless of the area of the
brain activity.
It is important to note that multiple channels that
were repeatedly selected were located in positions
out of standards 10-10, and 10-20, which supports
the idea that multiple locations in non-standard posi-
tions contribute to improving the reconstruction qual-
ity, unfortunately, these positions are generally avail-
able only in denser layouts and EEG caps. However,
the use of head models including intermediate posi-
tions can be combined with the physical adjustment
of the positions of the electrodes of a system to the
relevant selected ones, in order to monitor a particu-
lar brain activity.
The proposed relevance-based channel selection
for source reconstruction remains to be verified over
real signals, further studies on multiple recording
paradigms and analysis of different brain activity re-
Relevance-based Channel Selection for EEG Source Reconstruction: An Approach to Identify Low-density Channel Subsets
181

Figure 7: Channel repetition for relevance-based selection.
sponses should be done in order to validate the pro-
posed selection over a more realistic scenario. How-
ever, the presented framework for source and EEG
simulation in this study simulates signals with simi-
larities to ERPs as can be seen in figure 1. In addition,
considering that the level of noise added to the signals
had equal power than the signal, the trial data simu-
lated here can be regarded as having a similar SNR to
typical ERP signals.
In this study, we introduced the concept of rele-
vance for channel selection applied in specific time
windows (time-ROI) in which the underlying activity
was registered by the EEG recordings and compared
the performance of multiple high-density electrode
arrays, standard montages, and low-density versions
based on coverage criterion. We can conclude that the
localization accuracy and waveform of reconstructed
sources with subsets of Rel −6E and Rel −9E rel-
evant channels are comparable with reconstructions
done with coverage-based distributed sets of HD −
128 channels, and better than 62E(10 −10) channel
layout for a particular brain activity.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
AS and EG conceived and designed the experiments.
AS performed the experiments. AF, LL, MM dis-
cussed and selected the source reconstruction algo-
rithms. All the authors analyzed the data, discussed
teh results and wrote and refined the mansucript.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was supported by the Enabling technology
program of Biotechnology of Norwegian University
of Science and Technology NTNU, project ”David
and Goliath: single-channel EEG unravels its power
through adaptive signal analysis”.
REFERENCES
(1961). The ten twenty electrode system: International fed-
eration of societies for electroencephalography and
BIOIMAGING 2022 - 9th International Conference on Bioimaging
182

clinical neurophysiology. American Journal of EEG
Technology, 1(1):13–19.
Chatrian, G. E., Lettich, E., and Nelson, P. L. (1985).
Ten percent electrode system for topographic studies
of spontaneous and evoked eeg activities. American
Journal of EEG Technology, 25(2):83–92.
Colton, D. and Kress, R. (2019). Inverse Acoustic and Elec-
tromagnetic Scattering Theory. Springer, 4 edition.
Edelman, B. J., Baxter, B., and He, B. (2016). Eeg source
imaging enhances the decoding of complex right-hand
motor imagery tasks. IEEE Transactions on Biomedi-
cal Engineering, 63:4–14.
Friston, K., Harrison, L., Daunizeau, J., Kiebel, S., Phillips,
C., Trujillo-Barreto, N., Henson, R., Flandin, G., and
Mattout, J. (2008). Multiple sparse priors for the
M/EEG inverse problem. NeuroImage, 39(3):1104–
1120.
Gramann, K., Gwin, J. T., Ferris, D. P., Oie, K., Jung, T.-P.,
Lin, C.-T., Liao, L.-D., and Makeig, S. (2011). Cogni-
tion in action: imaging brain/body dynamics in mobile
humans. 22(6):593–608.
Hallez, H., Vanrumste, B., Grech, R., Muscat, J., De Clercq,
W., Vergult, A., D’Asseler, Y., Camilleri, K. P., Fabri,
S. G., Van Huffel, S., and Lemahieu, I. (2007). Re-
view on solving the forward problem in EEG source
analysis. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabili-
tation, 4.
H
¨
am
¨
al
¨
ainen, M. S. and Ilmoniemi, R. J. (1994). Interpret-
ing magnetic fields of the brain: minimum norm esti-
mates. Medical & Biological Engineering & Comput-
ing, 32(1):35–42.
Huang, Y., Parra, L. C., and Haufe, S. (2016). The new
york head—a precise standardized volume conduc-
tor model for eeg source localization and tes target-
ing. NeuroImage, 140:150 – 162. Transcranial electric
stimulation (tES) and Neuroimaging.
Ilmoniemi, R. J. and Sarvas, J. (2019). Brain Signals:
Physics and Mathematics of MEG and EEG. The MIT
Press.
Iwaki, S. and Ueno, S. (1998). Weighted minimum-norm
source estimation of magnetoencephalography utiliz-
ing the temporal information of the measured data.
Journal of Applied Physics, 83(11):6441.
Jasper, H. (1958). Ten-Twenty Electrode System of the In-
ternational Federation. Electroencephalography and
Clinical Neurophysiology, 10:371–375.
Jatoi, M. A. and Kamel, N. (2018). Brain source localiza-
tion using reduced eeg sensors. Signal, Image and
Video Processing, 12(8):1447–1454.
Jatoi, M. A., Kamel, N., Malik, A. S., Faye, I., and Be-
gum, T. (2014). A survey of methods used for source
localization using eeg signals. Biomedical Signal Pro-
cessing and Control, 11:42 – 52.
Lau-Zhu, A., Lau, M. P., and McLoughlin, G. (2019). Mo-
bile EEG in research on neurodevelopmental disor-
ders: Opportunities and challenges. Developmental
Cognitive Neuroscience, 36:100635.
Lindgren, J. T. (2017). As above, so below? Towards un-
derstanding inverse models in BCI. Journal of Neural
Engineering, 15(1):012001.
M
¨
akel
¨
a, N., Stenroos, M., Sarvas, J., and Ilmoniemi, R. J.
(2018). Truncated RAP-MUSIC (TRAP-MUSIC) for
MEG and EEG source localization. NeuroImage,
167:73–83.
Michel, C. M. and Brunet, D. (2019). EEG source imaging:
A practical review of the analysis steps. Frontiers in
Neurology, 10(APR):325.
Mosher, J. C. and Leahy, R. M. (1998). Recursive MU-
SIC: A framework for EEG and MEG source localiza-
tion. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,
45(11):1342–1354.
O’Leary, J. (1970). Hans berger on the electroencephalo-
gram of man. the fourteen original reports on the hu-
man electroencephalogram. translated from the ger-
man and edited by pierre gloor. Science, 168:562–563.
Oostenveld, R. and Praamstra, P. (2001). The five
percent electrode system for high-resolution EEG
and ERP measurements. Clinical Neurophysiology,
112(4):713–719.
Pascual-Marqui, R. D. (2002). Standardized low-resolution
brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA): Tech-
nical details. Methods and Findings in Experimental
and Clinical Pharmacology, 24(SUPPL. D):5–12.
Phillips, J. W., Leahy, R. M., Mosher, J. C., and Timsari,
B. (1997). Imaging neural activity using MEG and
EEG. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology
Magazine, 16(3):34–42.
Seeck, M., Koessler, L., Bast, T., Leijten, F., Michel, C.,
Baumgartner, C., He, B., and Beniczky, S. (2017). The
standardized EEG electrode array of the IFCN.
Sohrabpour, A., Lu, Y., Kankirawatana, P., Blount, J., Kim,
H., and He, B. (2015). Effect of EEG electrode num-
ber on epileptic source localization in pediatric pa-
tients. Clinical Neurophysiology, 126(3):472–480.
Soler, A., Giraldo, E., and Molinas, M. (2020a). Low-
density EEG for Source Activity Reconstruction us-
ing Partial Brain Models. In Proceedings of the
13th International Joint Conference on Biomedical
Engineering Systems and Technologies, pages 54–63.
SCITEPRESS - Science and Technology Publications.
Soler, A., Mu
˜
noz-Guti
´
errez, P. A., Bueno-L
´
opez, M., Gi-
raldo, E., and Molinas, M. (2020b). Low-Density
EEG for Neural Activity Reconstruction Using Mul-
tivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition. Frontiers in
Neuroscience, 14:175.
Song, J., Davey, C., Poulsen, C., Luu, P., Turovets, S., An-
derson, E., Li, K., and Tucker, D. (2015). EEG source
localization: Sensor density and head surface cover-
age. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 256:9–21.
Wolf, L. and Shashua, A. (2005). Feature Selection for
Unsupervised and Supervised Inference: The Emer-
gence of Sparsity in a Weight-Based Approach * Am-
non Shashua. Journal of Machine Learning Research,
6:1855–1887.
Relevance-based Channel Selection for EEG Source Reconstruction: An Approach to Identify Low-density Channel Subsets
183
