
Research on the Impact of Digital Economy on China's Real
Economy: An Empirical Study based on Big Data Analysis of
Household Consumption from 2010 to 2020
Yan Zhang
Xi'an Mingde Institute of Technology, Xi'an, Shanxi, China
Keywords:
Digital Economy, Real Economy, Household Consumption, Var Model.
Abstract:
Digital Economy has become an important engine of China’s economic growth. A large number of
enterprises represented by the Digital Economy, such as Alibaba, bytedance, tencent and Meituan, are rising
rapidly, the decrease of the store, the depression of the large-scale Shopping Mall and the economic
depression have become the important factors that hinder the economic development of our country. Based
on the big data, this paper studies the residents consumption from 2010 to 2020, combs the existing research
results of the academic circles, selects the research variables to construct the Var model, and studies the
relationship between the Digital Economy and the real economy in China, through the Var model, we get
the following conclusion: The moderate growth of the digital economy is beneficial to the promotion of the
consumption level of the residents and the development of the economic aggregate, however, we should pay
attention to and develop the integration of digital economy and real economy to form new industrial
upgrading and innovation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Digital Economy is to take digital as an important
factor of production, through data mining,
processing, screening, processing to produce a new
economic value. At the technical level, including big
data, cloud computing, Internet of things,
blockchain, artificial intelligence, 5g communication
and other emerging technologies, represents the
future direction of technology development. In the
development process of China’s real economy,
domestic demand is the basis of national economic
development, China’s real economy is also an
important indicator of regional economic
development. The current national epidemic, rising
prices, low consumption rate has become an
important factor hindering China’s economic
development. In the development of Digital
Economy, we should consider the sensitivity of
residents’consumption to digital economy in
different periods, so as to better realize the rapid
development of digital economy. At the same time,
China’s real economy also presents a typical dual
characteristics, urban and rural residents in the
consumption concept, consumption structure, there
are obvious differences. Although the contribution
rate of consumption to the total economy is larger
than that of investment and export, there is still a big
gap between China and developed countries.
Whether it is based on the perspective of economic
development, or the perspective of China’s real
economy, this paper is of great significance.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Domestic scholars began to pay attention to the
impact of Digital Economy on China’s economic
development, but mostly from the production
efficiency, resource integration, employment and so
on. Zhou Zhihan and Yang Xi (Zhou, 2021, Yang,
2021) studied the impact of Digital Economy on
industrial productivity, intra-industry resource
integration and social welfare. The results show that
after the introduction of the Digital Economy, the
critical productivity of exports increases, the
changes of the critical productivity of production
and the average productivity of industries are
determined by the critical value of the corresponding
productivity increase index, while the degree of
Zhang, Y.
Research on the Impact of Digital Economy on China’s Real Economy: An Empirical Study based on Big Data Analysis of Household Consumption from 2010 to 2020.
DOI: 10.5220/0011165500003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 145-149
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
145

intra-industry production competition is alleviated,
intensification of intra-industry Export Competition.
Wang Dong, LV Yanfang (Wang and LV , 2021)
mathematical model of the effect of digital
technology on employment in real economy, and a
nonlinear empirical framework was used to test the
effect of digital input on employment in real
economy during 2003-2019. The empirical results
show that narrow-sense digital technology index has
a negative impact on labor employment, but with the
increase of industry output, the negative inhibition
tends to weaken; The effect of generalized digital
technology on the employment of labor force shows
a complicated non-linear trend, which first
suppresses, then promotes, then suppresses, the
cross-product of digital technology and output has a
positive effect on the employment of labor force,
and digital technology has a significant positive
effect on the employment of labor force in low-tech
industries. Thus, while digital technology can induce
unemployment in the real economy through
substitution, when digital technology is deeply
integrated with the real economy, it can lead to the
expansion of industry scale and ultimately promote
employment in the real economy. Liu Shijin (Liu ,
2022) , deputy director of the Economic Committee
of the National Committee of the Chinese People’s
Political Consultative Conference , published an
article in the Beijing Daily: Promoting the effective
integration of the digital economy and the real
economy. In the article, the author talks about the
trend of digital economy, and how to integrate the
real economy with the digital economy is the focus
of attention.
3 VARIABLE SELECTION AND
MODEL INTRODUCTION
3.1 The Selection of a Variable
The digital economy, as an integral part of the
national economy as a whole, will have an important
impact on economic development, and the impact of
the digital economy on the real economy will vary at
different stages of economic development; The aim
of developing the digital economy is to ensure that
our country’s technological development can keep
pace with the global technological progress and
make breakthroughs in new fields. Different types of
digital economy are usually identified according to
the economic cycle, and technical growth rates are
used to reflect changes in the digital economy when
selecting research variables, the following factors
should be considered in the study of Digital
Economy:
(1) the stability and continuity of the
development of digital economy are closely related
to the current information technology, artificial
intelligence technology and blockchain technology.
(2) the development of the digital economy will also
promote and realize the stable and rapid
development of the economy. Whether the digital
economy can promote the development of the real
economy is the focus of our consideration. (3) apart
from the goal of driving economic growth, the
digital economy also has the goal of technological
development and global strategy. The Central Bank
should keep prices stable within the range
acceptable to the residents and avoid irrational price
increases impacting their normal lives, because of
the global impact of the epidemic, the extent of
inflation will also have an important impact on the
development of the Digital Economy, prices will
affect the development of the real economy.
To sum up, according to the existing research
results and the availability of data in the academic
circle, this paper selects the price level (WZ) , the
growth rate of information technology (MN) , and
the resident consumption (CZ) as the research
variables, to explore the relationship between digital
economy and real economy in China.
3.2 Model Introduction
When studying the impact of the digital economy on
residents’ consumption, this paper intends to use the
variable auto-regression model to study the
relationship between them. The expression of the
VAR model is:
11
+=1,2
tt ptpt
yAy Ay t T
ε
−−
=++
(1)
Expand the above formula (1) to:
1
111 1
2
221 2
1
1
,1,2,
tp
tt t
tp
tt t
p
kt p
kt kt kt
y
yy
y
yy
A
AtT
y
yy
ε
ε
ε
−
−
−
−
−
−
=+ +=
(2)
In formula (2) the AP is:
11, 1 ,
1, ,
pkp
P
kp kkp
AA
A
AA
=
(3)
In the Var model, the lag term is included on the
right side of the equation, and the random
perturbation term is independent constant variance.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
146

4 AN EMPIRICAL STUDY ON
THE IMPACT OF DIGITAL
ECONOMY ON REAL
ECONOMY
4.1 ADF Unit Root Test
Before the Empirical Analysis, ADF unit root test
was conducted to determine the validity of the data.
It can be seen from Table 1 that the ADF test value
of variable dlz is-5.93832, p value is 0.0503, the
data of variable nwdlz is stable at 10% level, the
ADF test value of variable DlnMN Is-3.79849, p
value is 0.0112, the data of variable DlnMN is stable
at 5% level The ADF test value of Dlncz
Was-5.37192, P value was 0.0561, which was
significant at 10% level.
Table 1: ADF unit root test.
Variable
ADF test
value
Prob
1%
critical
value at
significan
t level
5%
critical
value at
significan
t level
10%
critical
value
at
signifi
cant
level
Conclu
sion
DlnWZ -5.93832 0.0503
unstable
unstable stable stable
DlnMN -3.79849 0.0112
unstable stable stable stable
DlnCZ -5.37192 0.0561
unstable
unstabl
stable stable
4.2 Construction of Var Model
It is necessary to determine the optimal lag order
before constructing the Var model, and choosing the
appropriate lag time can not only guarantee the
scientificity of the model, but also make the
variables have dynamic characteristics. In this paper,
SC criterion and AIC are used to judge the best lag
order of the model. The test results are shown in
Table 2. Table 2 shows that the AIC and SC values
both reach the minimum when the variable lags the
second order, which shows that the second order is
the best lag order of the model.
Table 2: Test of the order of delay in Var model.
La
g
LogL LR FPE AIC SC
0
65.874
89
NA
9.4843
1*
-9.74932
-11.8474
2
1
89.774
91
148.938
12
5.9383
2
-18.9441
2
-19.9958
8*
2
138.93
135
47.9821
2*
2.0841
1
-19.0842
3*
-20.0945
9*
According to the test result of the lag order of
Var model, the Var model is reconstructed. The
output of the model is as shown in equation (4) .
ln 0.6465 ln ( 1) 0.7089 ln ( 2) 2.0781 ln ( 1)
+1.7842 ln ( 2) 1.8503ln ( 1)+1.6782 ln ( 2) 0.9847
CZ WZ WZ MN
MN CZ CZ
=−×−− ×−+ × −
×−+ − −+
(4)
The regression coefficients of LNWZ (- 1) ,
LNWZ (- 2) and LN (CZ) are both negative, which
shows that the price level has a significant negative
correlation with the resident consumption. The
regression coefficients of LNMN (- 1) and LNMN (-
2) with LN (CZ) are both positive, which shows that
the growth rate of information technology has a
significant positive correlation with residents ’
consumption, it also shows that the moderate
development of digital economy can promote the
consumption of residents. The regression
coefficients of LNCZ (- 1) , LNCZ (- 2) and LN
(CZ) are both positive, which shows that residents’
consumption has a certain path dependence effect
and has a certain consumption inertia in a certain
period of time, the previous consumption habits and
consumption ideas will have an important impact on
the follow-up consumption behavior, it is difficult
for residents to get rid of the solidified consumption
habits in a short time.
4.3 Robustness Test of Var Model
The robustness of Var model is very important to the
research conclusion. This paper uses unit root test to
test the robustness of Var model. The test result is
shown in figure 1. It can be seen from Fig. 1 that all
the unit roots of Var (- 2) model constructed in this
paper are in a single circle, and the Var model
constructed in this paper is robust by robustness test.
Research on the Impact of Digital Economy on China’s Real Economy: An Empirical Study based on Big Data Analysis of Household
Consumption from 2010 to 2020
147
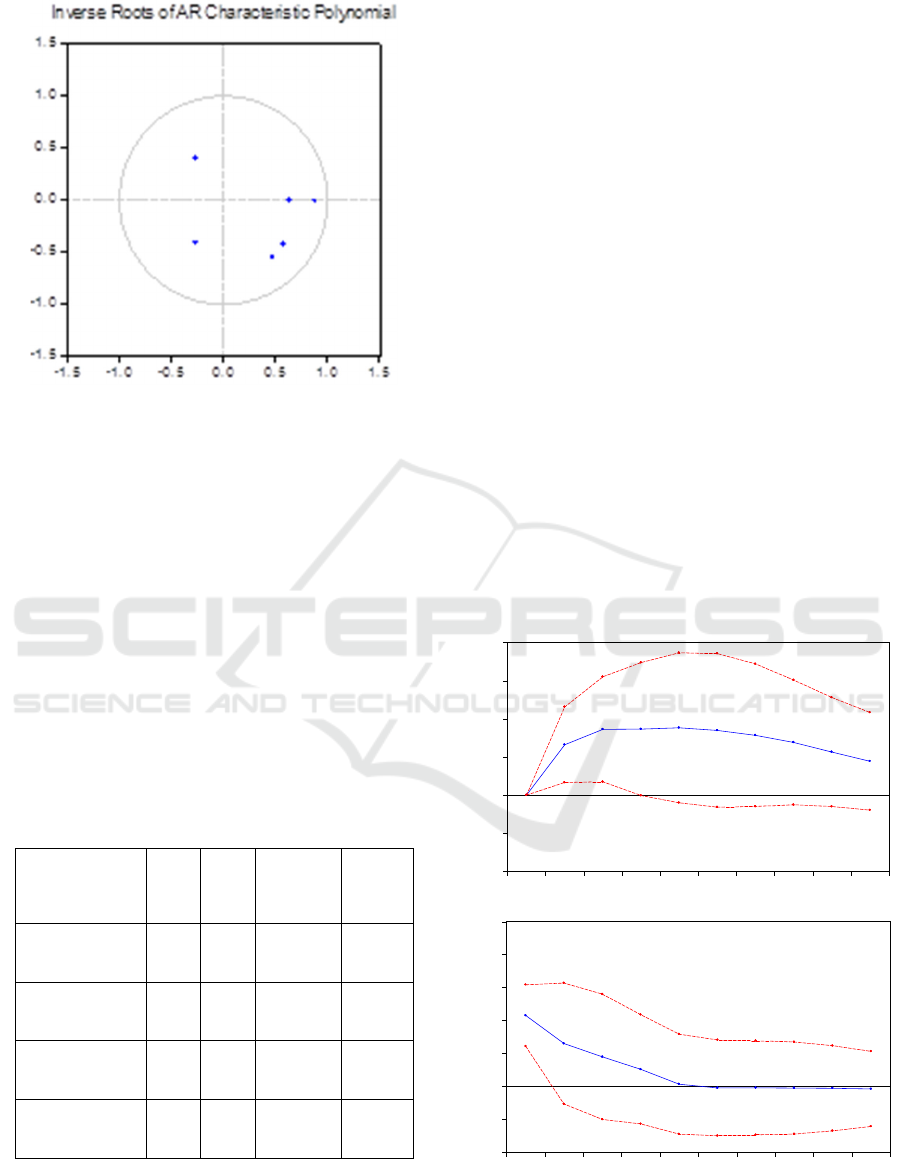
Figure 1: VAR Model Robustness Test Results.
4.4 Percy Grainger’s Causality Test
Granger causality tests were performed on Lnwz,
lnMN and LNCZ. The results are shown in Table 3.
From Table 3, it can be seen that there is a mutual
Granger causality between LNMZ and Lncz, which
shows that the price level and the resident
consumption are Granger causality, and they are
related and influence each other. lnMN is the Percy
Grainger cause of LNCZ, and LNCZ is not the
Percy Grainger cause of Lnmn, which shows that the
growth rate of information technology will affect the
real economy of our country, but the real economy
of our country will not affect the growth rate of
information technology.
Table 3: Percy Grainger’s causality test.
Original
hypothesis H0
Lag
peri
od
F
test
valu
e
Confiden
ce
Probabilit
y
Conclu
sion
LnWZ is not
lnCZ’s Percy
Grainger reason
2 2.72
13
0.002 Refuse
H0
lnCZ is not
lnWZ’s Percy
Grainger reason
2 3.16
53
0.025 Refuse
H0
lnMN is not
lnCZ’s Percy
Grainger reason
2 2.20
93
0.037 Refuse
H0
lnCZ is not
lnMN’s Percy
Grainger reason
2 3.14
03
0.026 Accept
H0
4.5 Impulse Response Test
In the Var model, the impulse response is mainly to
examine the impact of one variable’s change on
another. This paper analyzes the impact of it growth
rate and price level on China’s real economy, the
result is shown in figure 2, where the red line shows
the change trajectory of the variable after the
pressure is applied, and the Blue Line shows the
deviation region of plus or minus twice the standard
deviation. As can be seen from figure 2, the impact
of the growth rate of information technology on
China’s real economy shows an obvious upward
trend in the first and second periods, reaching the
peak in the third period, and showing a clear
downward trend after the third period, this shows
that the appropriate growth of information
technology is conducive to improving the level of
consumption of residents, but the digital economy
after a large-scale people’s lives, and form habits,
such as online shopping is not conducive to China’s
real economy. The impact of the price level on
China’s real economy shows an obvious downward
trend from the first to the sixth period, and the
change tends to be stable after the sixth period,
which shows that the rise of the price level is not
conducive to the promotion of China’s real
economy, this is also in line with the basic economic
law.
-.10
-.05
.00
.05
.10
.15
.20
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Response of lnMN to lnCZ
-.08
-.04
.00
.04
.08
.12
.16
.20
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Response of lnWZ to lnCZ
Figure 2: Impulse response of price level and information
technology growth rate to China’s real economy.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
148

5 CONCLUSIONS AND
RECOMMENDATIONS
Based on the time series data from 2010 to 2020,
this paper sorts out the existing research results in
the academic circle, selects research variables to
construct the Var model, and studies the relationship
between digital economy and China’s real economy,
the following conclusions are obtained by Var
Model: (1) the growth rate of digital economy and
the regression coefficient of real economy in China
are positive, showing a positive correlation between
them. The impulse response analysis found that in
the first and second periods, there was an obvious
upward trend, reaching the peak in the third period,
and after the third period, there was an obvious
downward trend. This shows that the moderate
growth of the digital economy is beneficial to the
promotion of the consumption level of the residents,
we will promote the development of our overall
economic output. The excessive growth of digital
economy is not conducive to the promotion of China
’s real economy. Attention must be paid to the
integrated development of digital economy and real
economy to form new industrial upgrading and
innovation. (2) the regression coefficient between
price level and real economy is negative, which
shows that there is a significant negative correlation
between them. The impulse response shows that
there is an obvious downward trend from the first to
the sixth period, and the change tends to be stable
after the sixth period, which indicates that the rising
of price level is not good for the promotion of
China’s real economy.
According to the above analysis, we can put
forward countermeasures and suggestions to
improve China’s real economy. First, adjust the
digital economy according to the actual economic
situation. From the results of Var model, we can see
that in different stages of economic development,
the impact of digital economy on China’s real
economy is different. Second, external factors have
been affected by the global epidemic since 2020,
and the real economy has been severely impacted,
and with the rapid development of information
technologies such as big data, artificial intelligence,
blockchain, and the meta-universe, the real economy
and the digital economy have both grown and
grown, but the digital economy is a part of the total
economy, how to integrate the real economy and the
digital economy, to upgrade industries and innovate,
is one of the trends in the future. Third, stabilizing
the price level is the first priority. Price level will
have an important impact on China ’ s real
economy, and there is a significant negative
correlation between the two. Price is a key factor
affecting the national economy and the people’s
livelihood, and also has a very important impact on
social stability and harmony. The important aim of
the implementation of the digital economy is to
stabilize the economic development and promote the
promotion of the national income level and the
consumption level. In the implementation of the
digital economy, we should proceed from the basic
goal and promote the improvement of the real
economy of our country, we will ensure steady and
orderly economic development.
REFERENCES
Lau sai-kam. Promoting the effective integration of digital
economy and real economy. Beijing Daily, 2022-1-10.
Wang Dong and Lu Yanfang. A study on the nonlinear
effect of digital technology on employment in real
economy. Modern Management Science, 2021(12):
110-120.
Zhou Zhihan, Yang Xi. Industrial effect of Digital
Economy: A theoretical analysis based on data factor.
Contemporary Finance and Economics, 2021(12):
101-114.
Research on the Impact of Digital Economy on China’s Real Economy: An Empirical Study based on Big Data Analysis of Household
Consumption from 2010 to 2020
149
