
Industrial Structure Upgrading and Regional Water Use Intensity
Research on the Driving Effect of Time Dimension Difference
Jiahao Li
a
, Tao Sun
b
and Shengzhe Zhang
c
Business School, Hohai University, Changzhou, 213022, China
Keywords: Water Resources, Industrial Structure Upgrading, Time Dimension, Water Intensity, Yangtze River Economic
Belt.
Abstract: Decomposing the influence of regional water use intensity into industrialization effect, industrial structure
upgrading effect, tertiary industry water-saving technology effect, and domestic water extraction effect from
the time dimension and constructing the LMDI decomposition expansion model of regional water use
intensity time difference. Taking the Yangtze River Economic Belt as an example, the driving channels and
internal influence mechanism of industrial structure upgrading on the time dimension difference of water use
intensity are deeply explored in this article. The study shows that the upgrading of industrial structure is an
important factor that inhibits the water use intensity of the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2000 to 2020,
but its driving effect has changed from negative to positive from 2012 to 2019 to promote the growth of water
use intensity. It is suggested that the urban agglomerations along the economic belt should strengthen policy
support and scientific management, achieve scientific and technological innovation, and vigorously develop
the high-quality water-saving tertiary industry to exert the inhibitory effect of the upgrading of industrial
structure on water use intensity.
1 INTRODUCTION
China's economy is in an important transition period
of rapid development and high-quality development.
The contradiction between water resources allocation
and regional economic development needs has
become a major strategic issue facing the people's
livelihood (E, 2020). In China’s “ 13th Five-Year
Plan ” action plan of dual control of the total amount
and intensity of water resources consumption, it is
pointed out that we should adhere to the priority of
water-saving and systematic governance, “ determine
the demand with water ” and “ adapt to water ”,
control the total amount and intensity of water
resources consumption, comprehensively improve
the utilization efficiency and benefit of water
resources endowment, and help economic growth and
industrial structure transformation and upgrading.
The upgrading of the industrial structure reflects
the change in the proportion of the output value of the
tertiary industry and the output value of the secondary
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1965-3688
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1322-4113
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6517-9150
industry and is a key indicator to measure the level of
servitization in the industrial structure. According to
the data of the National Bureau of Statistics, China’s
economic structure has a significant trend of
upgrading. The proportion of the tertiary industry in
the total output value has risen from 39.88 % in 2000
to 42.73 % in 2020. It is expected that there is still an
upward trend. The output value of the tertiary
industry continues to increase, the contribution rate of
the primary industry is basically stable, the ratio of
the output value of the tertiary industry to the output
value of the secondary industry is still increasing, the
contribution rate of the tertiary industry to social and
economic growth is increasing. To further promote
the development of a water-saving society, it is
important to promote the upgrading of industrial
structure and service transformation, improve the
proportion of service industry in the tertiary industry,
and develop a high-quality tertiary industry. Zhang
Li, J., Sun, T. and Zhang, S.
Industrial Structure Upgrading and Regional Water Use Intensity Research on the Driving Effect of Time Dimension Difference.
DOI: 10.5220/0011171300003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 211-217
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
211

Yu (Zhang, 2020) uses the ratio of tertiary industry
output value to secondary industry output value to
calculate the index of the advanced stage of industry
structure, reflecting the development trend of regional
economic structure. For the operability of the model
decomposition, this paper also uses the ratio of the
output value of the tertiary and secondary industries
to measure the index of the advanced stage of industry
structure.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The existing achievements in China and abroad
mainly focus on the following aspects. ① The time-
dimensional exponential decomposition method. By
using the LMDI-I-Model1 model to decompose the
various effects of the total amount of water resources
utilization in the time dimension, and explore the
influence degree and mechanism of different
economic effects on water resources endowment
(Yao, 2019). ② Multi-method correlation
calculation. By using various deviation coefficients,
combined with the coordination index, the correlation
matching relationship between industrial structure
and water resources utilization is calculated. Most of
the existing studies have studied the influence of
water-saving technology, population size, industrial
structure, and income on the total amount of water use
in the time dimension, and found that the industrial
structure effect has a significant inhibitory effect on
the increase of total water use. Compared with the
total water consumption research, the research on
water intensity is relatively less. Lv Lianghua et al
(Lv, 2021) used the total amount of residential water
consumption index to reflect the water consumption
intensity. Zeng et al (Zeng, 2020) took the water
consumption intensity as the decomposition effect of
the total amount of water consumption and
constructed the LMDI expansion model to indirectly
study the influencing factors of water consumption
intensity. There were few articles directly using the
LMDI model to decompose the water consumption
intensity. Based on the previous studies, this paper
made innovations from this perspective.
Given the high-level trend of China's economic
transformation and the high-level form of industrial
structure, this paper decomposes the industrial
structure effect into industrialization effect, industrial
structure upgrading effect, tertiary industry water-
saving technology effect and domestic water
extraction effect, and the driving effect of industrial
structure on the temporal difference of water intensity
in the Yangtze River Economic Belt is analyzed in
depth. With the help of LMDI-I-Model1, this paper
constructs the LMDI decomposition and expansion
model of the time dimension of regional water use
intensity and focuses on the driving channels and
internal influencing mechanisms of the industrial
structure, especially the upgrading effect of industrial
structure, on the time dimension difference of water
use intensity. This paper uses the relevant data of the
Yangtze River Economic Belt as an example for
analysis.
3 RESEARCH METHODS
3.1 Calculation of Time-dimensional
Driving Effect
Referring to LMDI-I-Model1, considering various
factors affecting the time-dimensional change of
water use intensity in the Yangtze River Economic
Belt, the LMDI decomposition and expansion model
of time-dimensional difference of water use intensity
is constructed, and the annual and cumulative effects
of industrial structure upgrading on water use
intensity are mainly studied. At the same time, the
difference in the intra-industry contribution rate is
calculated. The variation of water intensity
t-1, t
tot
W
GDP
Δ
from period t–1 to period t is decomposed
into:
t1,t t t-1
tot
t1,t t1,t t1,t t1,t
SG TS WG WT
tt t t
t-1 t-1 t-1 t-1
=
=++
++ +
iii i
iii i
WWW
GDP GDP GDP
WWW W
GDP GDP GDP GDP
SG TS WG WT
ln ln ln ln
SG TS WG WT
ωωω ω
−
−−− −
ΔΔ−Δ
ΔΔΔ+Δ
=
(1)
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
212

Among them, the weight is
tt-1
ii
,
i
WW
GDP GDP
ω
t t-1 t t-1 t t-1
ii i i i i
ttt-1
iii
,
,
WW W W W W
ln ln
GDP GDP GDP GDP GDP GDP
WWW
GDP GDP GDP
−−≠
=
=
(2)
t
i
W
GDP
and
t-1
i
W
GDP
are the water intensity of the i
industry in the t-1 and t period respectively;
t
SG
represents the ratio of regional secondary industry
output to GDP in period t, and
t-1,t
SG
W
GDP
Δ
is the
industrialization effect;
t
TS
represents the ratio of the
tertiary industry output to the secondary industry
output in period t, and
t-1,t
TS
W
GDP
Δ
is industrial structure
upgrading effect;
t
WG
represents the ratio of water
consumption of the tertiary industry to the output
value of the tertiary industry in period t, and
t-1,t
WG
W
GDP
Δ
is the tertiary industry water-saving
technology effect;
t
WT
represents the ratio of total
regional water consumption to tertiary industry water
consumption in period t, and
t-1,t
WT
W
GDP
Δ
is the
domestic water extraction effect.
4 RESEARCH METHODS
4.1 Data Description
The Yangtze River Economic Belt is an important
part of China’s economy, which plays an important
role in promoting the high-quality development of
China’s economy and the transformation and
upgrading of economic structure. At the same time,
the economy of the economic belt is based on water,
and its high-quality development is inseparably
linked to the rational allocation and utilization of
regional water resources. The Yangtze River
Economic Belt covers Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang,
and other 11 provinces and cities, with 21.4 % of the
country's land area accommodating more than 40 %
of the population, contributing more than 40 % of
GDP. The data of total water consumption and the
total industrial output value of each province and city
in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2000 to
2020 are taken from China Statistical Yearbook,
statistical yearbooks of each province and city, and
China Water Resources Bulletin. The total water
consumption is based on the statistics of water
consumption caliber. The total industrial output value
data are all based on the 2000 price as the constant
price (Zhang 2020).
4.2 Driving Effect Analysis of Time
Dimension Difference of Water
Intensity in Yangtze River
Economic Belt
The industrial effect, industrial structure upgrading
effect, tertiary industry water-saving technology
effect, and domestic water extraction effect of water
intensity change in the economic belt from 2000 to
2020 are shown in table Ⅰ, and the sum of each effect
in the same year is recorded as TOT.
Table 1: Decomposition of total water consumption changes in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2000 to 2020.
Year interval SG TS WG WT TOT
2000~2001 20.08 5.19 -96.40 -88.73 -159.86
2001~2002 39.59 -27.50 -163.03 -109.52 -260.45
2002~2003 69.96 -85.39 -272.85 -66.17 -354.46
2003~2004
53.05 -71.46 -165.06 74.19 -109.27
Industrial Structure Upgrading and Regional Water Use Intensity Research on the Driving Effect of Time Dimension Difference
213

2004~2005
35.33 -25.51 -203.26 -47.39 -240.83
2005~2006
44.80 -44.86 -243.89 4.19 -239.76
2006~2007
33.50 -18.45 -264.41 -52.58 -301.94
2007~2008 18.39 -5.04 -217.31 -22.75 -226.71
2008~2009 18.67 -6.60 -203.64 -37.09 -228.66
2009~2010 74.22 -129.44 -183.18 -61.29 -299.69
2010~2011
46.01 -73.85 -230.46 2.58 -255.72
2011~2012
19.10 -20.43 -374.25 101.18 -274.40
2012~2013
6.28 9.34 -152.06 -70.21 -206.65
2013~2014 -0.78 18.86 -175.33 -108.90 -266.14
2014~2015 -22.98 69.69 -119.48 -119.99 -192.75
2015~2016 -23.96 70.49 -153.57 -110.23 -217.27
2016~2017
-13.90 45.09 -173.49 -25.89 -168.19
2017~2018
-18.03 51.93 -135.52 -82.18 -183.80
2018~2019
-6.28 25.00 -162.69 -27.89 -171.87
2019~2020 0.54 -3.04 -110.83 -135.32 -248.65
Integrated value 393.60 -215.98 -3800.71 -983.98 -4607.07
(1) From the data in the table, it can be seen that
from 2000 to 2020, the industrial structure upgrading
effect is an important influencing factor of water use
intensity, which plays an inhibitory role in the
increase of water use intensity in the Yangtze River
Economic Belt, and the cumulative effect value is -
215.98 billion cubic meters / billion. Among them,
from 2000 to 2012, the cumulative utility value of
industrial structure upgrading is -503.34 billion cubic
meters / billion. Since 2001, the industrial structure
upgrading has been playing an inhibitory role in the
increase of water use intensity in the economic belt.
From 2013 to 2019, The driving mechanism of
industrial structure upgrading for water use intensity
in the economic belt has changed from inhibition to
promotion. After 2016, its ability to promote the
increase of water use intensity in the Yangtze River
Economic Belt has been weakened, and it has turned
to inhibition in 2020.
(2) Tertiary industry water-saving technology
effect and domestic water extraction effect focus on
the internal relationship between tertiary industry
water use and the increase or decrease of water
intensity. From 2000 to 2020, the cumulative utility
value of the tertiary industry water-saving technology
effect is -3800.71 billion cubic meters / billion, which
is 17.60 times the total utility of the industrial
structure upgrading effect. The cumulative utility
value of the domestic water extraction effect is -
983.98 billion cubic meters / billion, which is 4.56
times the total utility of the industrial structure
upgrading effect. The utility values of the two are
more than the industrial structure upgrading effect,
and the inhibitory effect on the water intensity is more
obvious. It can be seen that optimizing the industrial
and industrial water use structure, adhering to the
water control strategy of “saving water first”,
increasing the proportion of the output value of the
tertiary industry in the total output value, and the
proportion of the water consumption of the tertiary
industry in the total water consumption is more
conducive to inhibiting the increase of water use
intensity.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
214
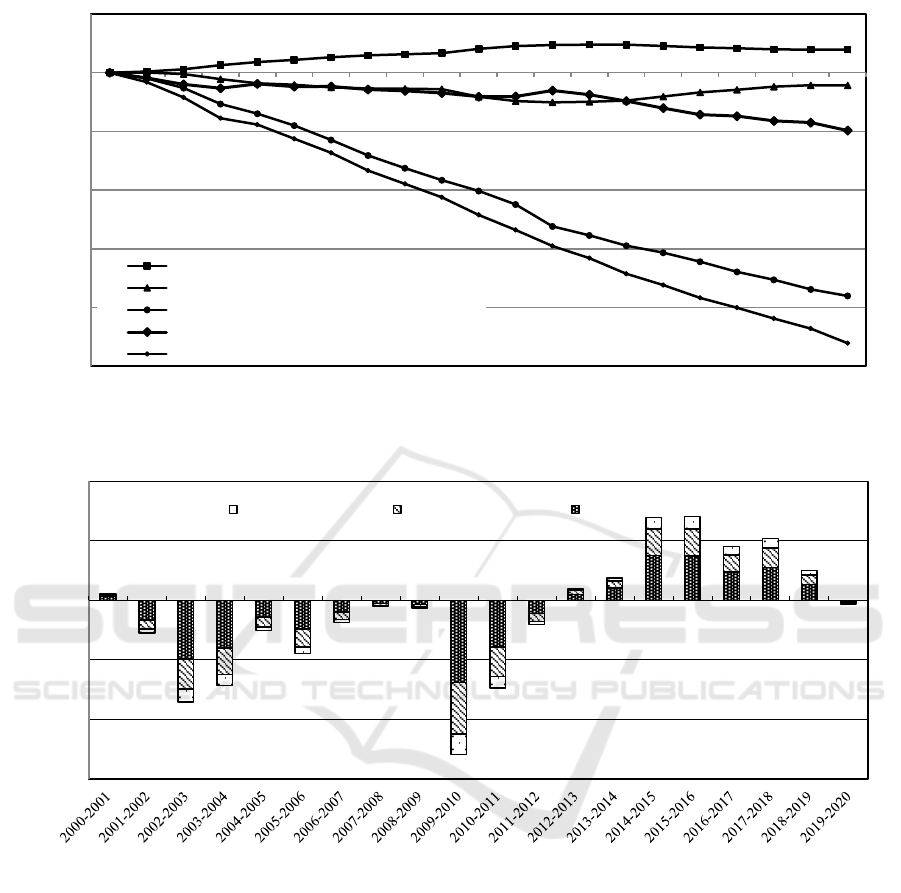
Figure 1: Cumulative effect of water intensity change in economic belt from 2000 to 2020.
Figure 2: The differences of industrial structure upgrading within the economic belt from 2000 to 2020.
(3) The industrialization effect reflects the
industrial development and industrialization level of
the Yangtze River Economic Belt, as well as the
demand of the secondary industry for water
resources, which plays a catalytic role in increasing
the water consumption intensity of the economic belt.
From 2000 to 2020, the total utility of
industrialization effect is 393.60 billion cubic meters
/ billion. The industrialization effect value from 2000
to 2013 is positive, which drives the increase of water
intensity. From 2014 to 2019, the industrialization
effect value is negative, which inhibits the increase of
water intensity. In 2020, the industrialization effect
turns to promote the increase of water intensity. The
use of water resources is an important issue in the
process of industrialization. Reasonable distribution
of industrial structure can weaken the driving effect
of industrialization on the increase of water use
intensity in the economic belt to a certain extent.
However, compared with the utility values of
industrial structure upgrading effect, tertiary industry
water-saving technology effect, and domestic water
extraction effect, it is found that only focusing on
industrial structure and relying on industrial structure
-5 000
-4 000
-3 000
-2 000
-1 000
0
1 000
2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
Cumulative effect
(billion cubic meters / billion yuan)
Year
industrialization effect
industrial structure upgrading effect
tertiary industry water-saving technology effect
domestic water extraction effect
total effect
-150
-100
-50
0
50
100
Effect
(billion cubic meters / billion yuan)
Year interval
Tertiary Industry Secondary Industry Primary Industry
Industrial Structure Upgrading and Regional Water Use Intensity Research on the Driving Effect of Time Dimension Difference
215

adjustment to regulate water use intensity has great
limitations.
(4) Studying the effect of industrial structure
upgrading within the industry, as shown in Figure 3,
2012 is a significant node. From 2000 to 2012, the
cumulative contribution values of the output value of
the first, second, and third industries to the upgrading
effect of industrial structure is -276.16 billion cubic
meters / billion, -161.68 billion cubic meters / billion,
and -655.50 billion cubic meters / billion respectively,
which played an inhibitory role; from 2012 to 2019,
the cumulative contribution value of the output value
of the first, second and third industries to the
upgrading effect of the industrial structure was
154.74 billion cubic meters / billion, 92.25 billion
cubic meters / billion and 43.42 billion cubic meters /
billion respectively, which played a promoting role;
since 2019, it has turned to inhibition. With the rising
contribution rate of the tertiary industry, the utility
value of industrial structure upgrading has been
effectively increased, and the water intensity of the
economic belt has been inhibited from 2000 to 2012.
Since 2012, the state has implemented the most
stringent water resources management system,
strengthened the red line management of water
resources development and utilization control, and
strictly implemented the total amount of water
control. The use of regional water resources has been
strictly planned and managed, and the construction of
a water-saving society has been comprehensively
promoted, which effectively improves the water use
efficiency of the three major industries. Therefore,
while focusing on the industrial structure, we should
pay more attention to the optimization and upgrading
of the industry itself (Zhang 2020). Combined with
the driving mechanism of the water-saving
technology effect of the tertiary industry and the
extraction effect of domestic water on water intensity,
we should improve the internal proportion of the
tertiary industry and develop a more water-saving and
high-quality tertiary industry to inhibit the increase of
water intensity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND POLICY
RECOMMENDATIONS
5.1 Conclusion
In this paper, the LMDI decomposition expansion
model of the time dimension difference of water
intensity is constructed to explore the specific
mechanism affecting the internal water intensity of
the Yangtze River Economic Belt. The effect of water
intensity is divided into industrial effect, industrial
structure upgrading effect, tertiary industry water-
saving technology effect, and domestic water
extraction effect. Through data integration and
empirical analysis, it is found that the upgrading of
industrial structure is an important restraining factor
for water use intensity from 2000 to 2020, but its
driving effect changed from negative to positive in
2012-2019 promoting the growth of water use
intensity. In terms of the other three effects, the
tertiary industry water-saving technology effect and
domestic water extraction effect are the primary and
secondary factors that inhibit the growth of water use
intensity in each province and city of the economic
belt, while the industrialization effect generally
promotes the increase of water use intensity.
5.2 Policy Recommendations
5.2.1 Optimizing the Inter-Industry
Structure and Developing a
Higher-quality Tertiary Industry
Provinces and cities should pay attention to the
relationship between the upgrading of industrial
structure and the water use intensity, adhere to the
priority of water-saving strategy (Ma 2014), “
determine the demand with water ” and “ adjust to
water ”, continuously increase the proportion of
industries and services which have high water use
efficiency, continuously improve the industrial
quality and the intensity of knowledge economy of
the tertiary industry in each province and city, and
vigorously support the development of water-saving
industries, so as to achieve effective control of water
use intensity.
5.2.2 Focus on Technology and Promote the
Continuous Development of a
Water-saving Society
Strengthen the strength of science and technology,
strengthen the foundation of science and technology,
strengthen the implementation of policies such as the
national water-saving action plan, improve the
process flow, vigorously develop water-saving
technology, optimize the water use capacity of high
water consumption industries such as steel and
petrochemical, and cultivate water-saving
enterprises. Speed up the transformation of
theoretical results to the actual, promote the
production and industrialization of water-saving
technology, and build a water-saving society.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
216

5.2.3 Strengthening the Effective Guidance
and Scientific Management of the
Government
The governments along the Yangtze River Economic
Belt should make differentiated policies according to
their different natural conditions and different
economic development levels. Optimize the pricing
mechanism and use mechanism of water resources,
formulate incentive mechanism and punishment
mechanism of water use in enterprises, and promote
the recycling and sustainable development of water
resources utilization.
REFERENCES
Hailiang Ma, Jia Xu, Pucha Wang. (2014) Water Resources
Utilization in the Process of Urbanization in China[J].
Resource Science.
Jingping E. (2020). Insisting on water-saving priority to
build happy rivers and lakes[N]. China Water
Conservancy News.
Lianghua Lv, Beilei Jiang, Leihua Geng, Haibin Zhang, Su
Pang. (2021) Construction of water intensity index
system of Xiongan New Area based on total water
consumption control[J/OL]. Water Resources
Protection.
Lina Zhang, Yiwen Cao, Qinghua Pang, Chenjun Zhang,
Changfeng Shi. (2020) Research on the driving effect
of industrial structure upgrading on the spatial-temporal
difference of regional water consumption [J]. Soft
Science.
Longqin Yao, Hengquan Zhang, Chenjun Zhang, Wanli
Zhang. (2019) Driving effects of spatial differences of
water consumption based on LMDI model construction
and data description[J]. Cluster Computing.
Peng Zeng, Ying Ya. (2020) Analysis and prediction of
influencing factors of water use intensity change in
Hunan Province in recent years [J]. Rural Economy and
Science.
Wei Zhang, Xuan Tang, Guanlei Yang, Donglan Zha.
(2020) Decomposition of CO 2 emission intensity in
Chinese MIs through a development mode extended
LMDI method combined with a production-theoretical
approach[J]. Science of the Total Environment.
Yu Zhang. (2021) The overall and regional test of the
impact of residents’ consumption capacity on China’ s
industrial structure upgrading [J]. Research on
Commercial Economy.
Industrial Structure Upgrading and Regional Water Use Intensity Research on the Driving Effect of Time Dimension Difference
217
