
Take Precautions: A Study on Social Credit System and Venture
Capital Scale
Yuecen Wang
1
, Haozhe Zhou
1
, Yingkai Yin
2
and Yirong Ying
2
1
School of Economics Shanghai University, Shanghai, China
2
Faculty of Geosciences and Environmental, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, China
Keywords: Social Credit System, Credit Investigation System, Venture Capital.
Abstract: The study of social credit system can not only analyze and alleviate the problem of information asymmetry,
but also provide more information about entrepreneurial characteristics for venture investors. This paper
selects Shanghai as a sample and uses the data from 2010 to 2019 to make a regression analysis of the
relationship between social credit system and venture capital scale. The empirical results show that with the
increase of the credit score of a city, the proportion of the venture capital received by the city in the national
venture capital will increase. When the credit ranking of a city declines, the proportion of venture capital
received by the city in the national venture capital will decrease accordingly. Moreover, the rise of the absolute
level of social credit system has a greater impact on the scale of venture capital than the rise of the relative
level.
1 INTRODUCTION
Innovation and entrepreneurship have become a
necessary requirement for transforming the pattern of
economic development and improving the quality of
economic development. ‘The Opinions of The State
Council on promoting high-quality Development of
Innovation and Entrepreneurship and creating an
upgraded version’ clearly points out that venture
capital should fully play its role in supporting
innovation and entrepreneurship. Venture capital
institutions often face obstacles in expanding the
scale of venture capital investment when they invest
in the state of information asymmetry. Therefore, a
deep study of the relationship between the promotion
of social credit system and the expansion of venture
capital scale is of positive guiding significance for
giving full play to the role of credit as a new factor of
production, optimizing the allocation of resources
and improving the efficiency of investment.
This paper selects Shanghai as a sample and uses
the data from 2010 to 2019 to make a regression
analysis of the relationship between social credit
system and venture capital scale. The empirical
results show that with the increase of the credit score
of a city, the proportion of the venture capital
received by the city in the national venture capital
will increase. When the credit ranking of a city
declines, the proportion of venture capital received by
the city in the national venture capital will decrease
accordingly.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
According to modern credit science, credit
investigation is an activity of collecting, sorting out
and saving the credit information of natural persons
according to law, and then providing credit
assessment, credit report and other services to carry
out credit management and provide them to
information users. Some scholars also define credit
reference as tradable carbon credit based on the credit
value used for social welfare or private social
investment (Raji, et al, 2021). Credit bureaus and
registries have become nearly universal. There are
three categories of the social credit investigation
system in China: the banking financial institutions
represented by the Credit investigation Center of the
People's Bank of China; Public institutions
represented by government public credit information
centers; Credit investigation of social institutions
characterized by spontaneous development. The
development of China's social credit investigation
306
Wang, Y., Zhou, H., Yin, Y. and Ying, Y.
Take Precautions: A Study on Social Credit System and Venture Capital Scale.
DOI: 10.5220/0011175200003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 306-312
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
institutions shows obvious government-led
characteristics, and the government has a huge
advantage in promoting the social credit investigation
system.
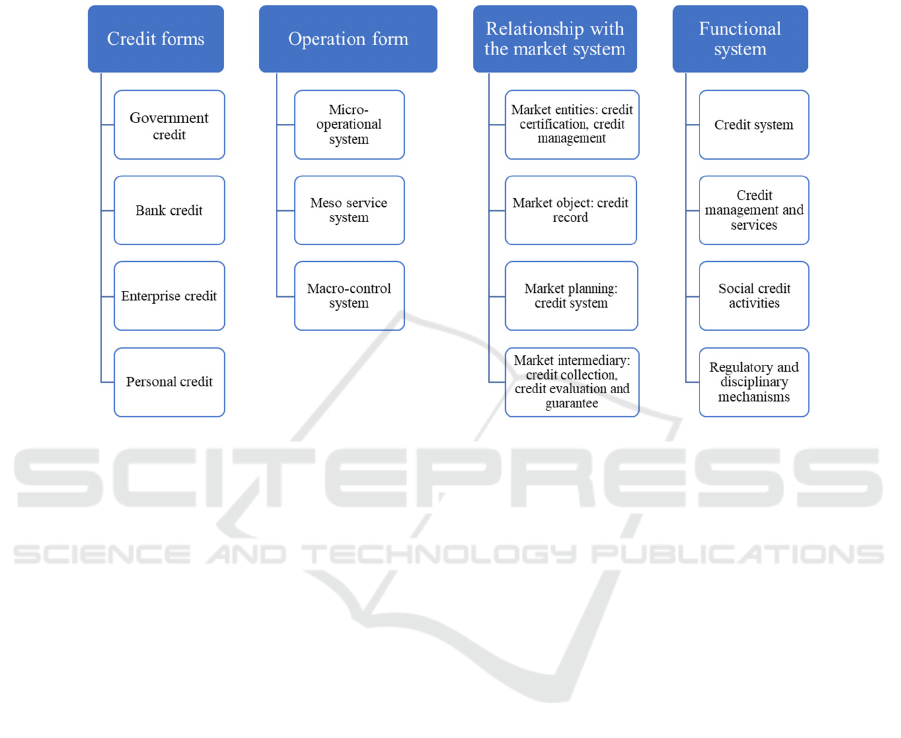
The content of social credit system is extremely
rich and the architecture is also quite complex. The
current viewpoints of scholars are to decompose the
content of social credit system from four angles:
credit form, operation form, relationship with market
system and functional system. The details are shown
in Figure 1.
Figure 1: The content of social credit system divided by four levels.
In short, the social credit system is mainly divided
into three parts: the government, banks, enterprises
and individuals complete their basic credit activities
in the market; the government established a series of
supporting laws and regulations as the founder of the
social credit system; the government also needs to
carry out supervision, regulation and other work to
maintain the operation of the system. Figure 1 shows
that the social credit system is essentially an
extension of the credit investigation system in the
economic and financial field. First, the credit
investigation system is managed by the People's Bank
of China. The social credit system is led by the
National Development and Reform Commission and
the People's Bank of China, with the participation of
many other government departments. Second, the
credit investigation system mainly collects the
negative information of market participants in
lending, guarantee, lease, credit card and other
activities. Social credit system involves participants
in the market credit and public credit field of good
and bad information. Third, credit investigation
system focuses on the economic field; social credit
system covers many fields of social development.
Fourthly, the informatization carrier of credit
investigation system is mainly the Credit
investigation system of the People's Bank of China.
The informatization carrier of social credit system is
the national credit information sharing
platform. Fifth,
from the perspective of the form of credit record
presentation, the credit investigation system is
presented in the form of personal credit investigation
Report; The social credit system is presented in the
form of individual public credit Report and enterprise
legal person public credit Report.
From the perspective of complex system, social
credit system can be divided into three sub-systems:
narrow social credit system, social credit system and
social civilization system. The three sub-systems are
based on two credit data systems. The narrow social
credit system is based on the basic database of
financial credit information. The system mainly acts
in the economic field, and its main tools are credit
investigation system and rating, etc. Its main
objectives are to regulate credit release, rectify and
standardize the order of market economy, realize the
government's market credit supervision, reshape
business ethics, and establish a punishment
mechanism for economic dishonesty.
Social credit system and social civilization system
are based on the national public credit information
sharing platform. The social credit system mainly
acts on the social field, and the main tools are
blacklist system and memorandum of joint
Take Precautions: A Study on Social Credit System and Venture Capital Scale
307

punishment for trust-breaking. Its main goal is to
construct urban credit system, industrial
credit system,
joint punishment for trust-breaking and joint
incentive for trust-breaking, establish market joint
prevention mechanism, and implement credit
education project. The social civilization system
mainly acts in the social field and the
ideological field,
the main tool is the resident credit classification and
blacklist system, the main goal and task is to achieve
the reconstruction of social morality, the construction
of advanced culture and legal society and also the
innovation of social governance.
To sum up, the main content of social credit
system can be summarized as Table 1. The social
credit system is more than what people usually
mention. From the perspective of using tools, it not
only includes the credit investigation system
established by the government in the economic field
and the service system composed of numerous credit
information service agencies in the market, but also
includes the joint punishment memorandum for trust-
breaking, blacklist system, residents' credit rating
system, which can play a role in the field of social
credit and social morality.
Table 1: The content of social credit system.
Item
Social credit system
Social
credit
system in
narrow
sense
Social credit
system
Social
civilization
system
Field
economic
field
social field
the whole
social
ideology
field
Form
economic
contract
non-standard
commitment
social
public
morality
Tool
credit
reporting
blacklist
system
blacklist
system
State
Start from
2003
Start from
2014
Start from
2016
Objectives and
tasks
Regulation
and
supervision
of credit
distribution
; Rectify
and
standardize
the order of
the market
economy;
Realize the
government
market
credit
supervision
; Reinvent
b
usiness
Construction
of urban
credit
system;
Construction
of industry
credit
system;
Construction
of joint
punishment
and joint
incentive for
trust-
breaking;
Establish
market joint
prevention
Rebuilding
social
morality;
Building
advanced
culture;
Building a
society
ruled by
law;
Innovating
social
governance
Item
Social credit system
Social
credit
system in
narrow
sense
Social credit
system
Social
civilization
system
ethics;
Establish a
punishment
mechanism
for
economic
dishonesty
system;
Implement
honesty
education
project
Data platform
Financial
credit
information
database
National public credit
information sharing
platform
Management
department
People's
Bank of
China
led by the National
Development and Reform
Commission and the
People's Bank of China,
with the participation of
many other government
departments
Main role credit
Social rules
39.58
The advantages of establishing a credit
investigation system can not only reduce the cost of
screening and monitoring (Hauswald, Marquez,
2003), but also increase the credit scale (Bennardo, et
al., 2015). Moreover, it can effectively reduce
adverse selection problems (Libeti, et al., 2017).
However, the potential cost of establishing a credit
investigation system is that it may reduce the
information rent of banks (Scott, et al., 2001) and
reduce the credit supply (Sutherland 2018).
Credit investigation system also has a certain
impact on financing cost in many ways. When
evaluating commercial loan applications, especially
for small and micro enterprises, banks will consider
the credit score of company holders to determine their
loan rate (Kamilah, et al., 2020). There is strong
evidence that enterprises with high credit rating have
lower financing costs. Martinez Peria and Singh
(2014) showed that the credit investigation system
reduced the financing cost of enterprises by 1.3
percentage points. Loan business model influences
the popularization of credit investigation system
(Mishra, et al., 2019, Liberti, et al., 2021).
Nevertheless, by 2020, 88% of economies have had
private credit investigation bureaus or public credit
investigation registries (World Bank 2020).
From the perspective of credit risk, information
sharing can form a reputation constraint mechanism
in repeated games, punishing default behaviors,
increasing default costs, and it can help reduce credit
risk (Bos, et al., 2015). Some scholars have studied
the relationship between credit investigation system
and non-performing loans of banks and found that the
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
308

economic impact of information system reform is
quite large, which reduced the non-performing loan
ratio of banks by nearly 40% (Saibal Ghosh, 2019).
Therefore, bank regulators can consider establishing
a credit investigation system as a macro-prudential
supervision over the growth of non-performing loans
(Wahyoe, et al., 2017).
To sum up, information asymmetry can lead to
adverse selection, moral hazard and credit mismatch
in the credit market. By establishing a credit
investigation system to share credit information,
banks can enhance their ability to select investors
from different risk categories, reduce adverse
selection of borrowers and promote the increase of
credit scale. At the same time, the reputation
constraint mechanism can improve the default cost,
reduce credit risk, and solve the financing difficulties
of small and micro enterprises.
3 MODEL SETTING
3.1 Research Hypothesis
If a social credit system, including the credit
investigation system, has established a shared credit
information collection, and with the continuous
improvement of this system, the availability of
corporate credit information and even more
characteristic information continues to increase, then
adverse selection The problem will be alleviated.
With a relatively complete social credit system, it is
easier for venture investors to screen start-ups and
make investment decisions. This means that the
improvement of the social credit system also means
that the default cost of start-ups will increase, and the
problem of moral hazard will also be alleviated.
Therefore, this article makes the following
assumptions:
H1: The higher the degree of Changsha’s social
credit system, the larger the scale of venture capital.
3.2 Sample Selection and Data Sources
Considering the representativeness of the sample
cities’ regional geographic location and venture
capital scale, as well as the availability and
completeness of data, this article chooses Changsha
as the analysis object. All the investment events of all
venture capital institutions in the sample cities from
2010 to 2019, the per capita GDP data of the sample
cities from 2010 to 2019, and the proportion of the
output value of the secondary and tertiary industries
in GDP are all taken from the wind database. The City
Business Credit Environment Index (CEI) is mainly
taken from the “CEI Blue Book”. For years with
missing data, the mean value of two consecutive
years is used as an interpolation substitute. In
particular, due to the lack of data in 2014, data of
2013 is the average of previous years, and the 2014’s
is the average of 2013 and 2015.
3.3 Variable Definition and Model
Setting
According to the research purpose and related
literature, this paper chooses the ratio of venture
capital investment to the national total venture capital
investment to measure the scale of entrepreneurship.
This article chooses city’s commercial credit
index as the measure of the level of social credit
system construction. The Urban Commercial Credit
Index is jointly compiled by the Integrity Research
Center of the Chinese Academy of Management
Science and other institutions. It is based on the
theory of social credit system, urban credit system,
and enterprise credit management theory. It provides
financial credit instruments, commercial credit sales,
and enterprise comprehensive evaluation of factors.
Finally get the social credit score of each city and
rank it. The social credit score ranges from 1 to 100.
The higher the score, the higher the construction level
of the city’s social credit system. Existing research
results show that CEI is a reliable indicator to
measure the degree of perfection of the city’s credit
system and the results of its operation. Considering
that the changes in the social credit system may not
have an immediate impact on the decision-making of
venture investors, this article chooses the first-order
lag and second-order lag of CEI as explanatory
variables.
The model established in this paper is as follows:
112 23
y
ttt tt
a b CEI b CEI b Controls
ε
−−
=+ + + +
Where,
y
t
is the explained variable, which
measures the scale of venture capital investment.
1t
CEI
−
and
2t
CEI
−
are explanatory variables, which
measures the degree of perfection of a city's social
credit system.
t
Controls
is control variable. We
choose GDP per capita (ten thousand yuan), the
proportion of secondary industry output
value in GDP,
and the proportion of tertiary industry output value in
GDP to exclude the influence of local economic
development level and industrial structure on venture
capital scale.
All of variable names, symbols and definitions in
model (1) are shown in Table 1.
Take Precautions: A Study on Social Credit System and Venture Capital Scale
309

Table 2: Variable definitions.
Variable types Variable names
Variable
symbols
Variable definitions
explained variable
Scale of venture
investment
y
The permillage of venture capital
amount to the total national venture
ca
p
ital amount
(
‰
)
explanatory
variables
CEI ranking cei_rank
Ranking of urban commercial credit
environment index
CEI score cei_score
Score of urban commercial credit
environment index
first order lag of
CEI score
L1_score First order lag of CEI score
second order lag
of CEI score
L2_score Second order lag of CEI score
first order lag of
CEI rankin
g
L1_rank First order lag of CEI ranking
second order lag
of CEI score
ranking
L2_rank Second order lag of CEI score ranking
control variables
GDP
p
er ca
p
ita
g
d
p_p
c GDP
p
er ca
p
ita
(
ten thousand
y
uan
)
the proportion of
secondary
industr
y
second_pro
The proportion of secondary industry
output value in GDP
the proportion of
tertiar
y
industr
y
tetiary_pro
The proportion of tertiary industry
out
p
ut value in GDP
4 EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS
4.1 Descriptive Statistical Analysis
Table 3: Descriptive statistics of variables.
mean std min max
y 43.51 89.47 0.02 355.45
CEI_score 84.35 2.07 80.09 87.00
CEI_rank 2.11 0.33 2.00 3.00
gdp_pc 11.06 2.52 8.26 15.73
second_pro 33.22 4.86 26.99 41.30
Tertiary_pro 66.32 5.00 58.09 72.74
Among the sample cities selected in this paper,
the average ratio of venture capital investment in
cities to the total amount of national venture capital
investment is 4.351%. The maximum value was
3.55%, and the minimum value was only 0.002%.
The average CEI score of the city was 84.35, and the
standard deviation was 2.07. The CEI scores of
sample cities were higher and the differences were
small. The mean and standard deviation of CEI
rankings were 2.11 and 0.33 respectively. The social
credit scores of selected sample cities are relatively
close, and the difference in ranking is slightly
smaller. The mean value of per capita GDP was
110,600 yuan, and the standard deviation was 2.52,
indicating a small difference. From the perspective of
industrial structure, the average proportion of
secondary industry output value in GDP is 33.22%,
26.99% on minimum, and 41.30% on maximum. The
average proportion of tertiary industry output value in
GDP was 66.32%, 58.09% on minimum and 72.74%
on maximum. The proportion of secondary and
tertiary industries in the sample cities is larger, and
the output value of tertiary industry is relatively
higher.
4.2 Regression Results
The regression results between Shanghai's social
credit system and venture capital scale are shown in
Table 3.
Table 4: Regression results of Shanghai (1).
(1) (2) (3) (4)
y y y y
L1_score 59.21*
(22.28)
44.35
(47.27)
gdp_pc -11.44
(27.03)
-10.34
(72.32)
43.73
(42.82)
15.74
(42.09)
second_pro -1792.95
(929.80)
-1612.16
(2304.28)
-128.60
(1642.48)
-1904.72
(2165.12)
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
310

(1) (2) (3) (4)
tetiary_pro -1757.68
(904.14)
-1588.88
(2223.09)
-160.27
(1587.25)
-1856.36
(2107.10)
L2_score 20.09
(49.39)
-6.88
(39.36)
L1_rank 13.59
(175.31)
L2_rank
cei_score
_cons 171454.11
(90909.89)
153826.84
(218641.06)
15205.98
(157930.46)
186350.09
(211729.29)
Obs. 9 8 8 9
R-squared 0.77 0.82 0.74 0.37
Adj
R-squared
0.54 0.36 0.39 -0.26
F 3.39 1.79 2.10 0.59
Table 5: Regression results of Shanghai (2).
(5) (6) (7)
y
y
y
L1_score 67.97*
(
24.45
)
gdp_pc 38.86
(
15.78
)
-10.89
(
27.43
)
11.48
(
40.49
)
second_p
ro
-67.98
(
840.93
)
-2705.51
(
1353.18
)
-390.65
(
804.03
)
tetiary_pr
o
-82.78
(
821.46
)
-2647.68
(
1317.84
)
-379.53
(
784.65
)
L2_score
L1_rank 193.93
(
140.68
)
-108.91
(
115.77
)
L2_rank 243.22
(94.34)
cei_score -42.61
(
35.30
)
_cons 6560.71
(82644.99)
260279.92
(132001.87)
41807.81
(79779.02)
Obs. 8 9 10
R-
squared
0.96 0.82
0.40
Adj
R-
squared
0.85 0.53
-0.17
F 9.06 2.81 0.56
Standard errors are in parenthesis
*** p<0.01, ** p<0.05, * p<0.1
The econometric analysis of this part is developed
in Model (1). In the case of columns (1) and (6), the
first-order lag term of the city's credit score, as an
explanatory variable, is significant at the level of
10%. At this point, the coefficients of L1_score are
59.21 and 67.966 respectively. This means that when
the urban social credit increases by one point, the
proportion of Shanghai's venture capital investment
in the national venture capital will increase by 5.92%
and 6.80%. In 2019, the proportion of venture capital
investment in Shanghai accounted for 17.18%, and
the CEI score was 85.488, ranking the second in
China. This result indicates that the improvement of
the construction level of urban social credit system
will increase the scale of innovation investment.
5 CONCLUSIONS
5.1 Build a Diversified Credit
Investigation System
We should speed up the construction of diversified
credit investigation system, further establish and
improve the long-term mechanism of credit
information collection and data sharing, break
information barriers, and increase credit information
exchange and sharing among industries. At the same
time, we should accelerate the construction of local
credit investigation platforms with "database +
service platform" as the core, promote information
symmetry between banks and enterprises, improve
the financing efficiency of micro enterprises, and
promote economic development.
5.2 Expand the Application Scenarios
of Credit Investigation System
We should strengthen the publicity of credit
investigation system, expand the application
scenarios of credit investigation system, and give full
play to the counter-cyclical adjustment function of
credit investigation system. At the same time, we
should improve risk awareness, integrate internal
corporate customer credit information, strengthen the
connection with judicial and tax platforms, actively
use fintech ways for analysis, and improve risk
prevention capabilities.
However, this paper only selects Shanghai as a
representative city for empirical research, and the
sample is relatively single. In addition, Shanghai, as
an international city, is relatively complete in the
construction of social credit system. However, in
China, there are many small cities that cannot achieve
such an excellent credit investigation system, which
may be slightly different from the conclusion of this
paper. In the future, we can carry out regression
statistics on the data of various counties and cities
across the country to reach a more comprehensive
conclusion.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was supported by National Social
Sciences Founding Project (Grant No.17BJY062).
Take Precautions: A Study on Social Credit System and Venture Capital Scale
311

REFERENCES
Ajwani-Ramchandani, Raji, and Joseph Sarkis. (2021).
Time to Consider Circular and Social Credits
Exchanges? J. Resources, Conservation and Recycling,
vol. 175: 105860, Web.
Andrew Sutherland.(2018). Does Credit Reporting Lead to
a Decline in Relationship Lending? Evidence From
Information Sharing Technology. J. Journal of
Accounting and Economics, vol. 66(1), pp. 123-141.
Bennardo, A., Pagano, M., Piccolo, S. (2015) . Multiple
bank lending, creditor rights, and information sharing.
J. Rev. Financ, vol. 19 (2), pp. 519–570.
Bos J, De Haas R, Millone M. (2015). Show Me Yours and
I'll Show You Mine: Sharing Borrower Information in
a Competitive Credit Market. J. BAFFI CAREFIN
Working Paper 1508, 2015.
Doblas-Madrid, A., Minetti, R. (2013). Sharing information
in the credit market: contract level evidence from US
firms. J. Financ. Econ, vol. 109, pp. 198–223.
Hauswald, R., Marquez, R. (2003). Information technology
and financial services competition. J. Rev. Financ.
Stud, vol. 16 (3), pp. 921–948.
Liberti J M, Sturgess J, Sutherland A.(2021). How
Voluntary Information Sharing Systems Form:
Evidence from a U.S. Commercial Credit Bureau. J.
Journal of Financial Economics, web.
Liberti, José María, and Mitchell A Petersen. (2019).
Information: Hard and Soft. J. The Review of
Corporate Finance Studies, vol. 8.1, pp. 1-41.
Mishra, P., N. Prabhala , and R. G. Rajan . (2019). The
Relationship Dilemma: Organizational Culture and the
Adoption of Credit Scoring Technology in Indian
Banking. J. Social Science Electronic Publishing.
Peria, Ms Martinez , and S. Singh. (2014). The Impact of
Credit Information Sharing Reforms on Firm
Financing?. J. Social Science Electronic Publishing.
Washington DC.
Saibal Ghosh. (2018). Loan Delinquency in Banking
Systems: How Effective Are Credit Reporting
Systems?. J. Research in International Business and
Finance, vol. 47, pp. 220-236.
Scott F, Srinivasan A, Woosley L. (2001). The Effect of
Credit Scoring on Small Business Lending. J. Journal
of Money, Credit and Banking, vol. 33, pp. 813-825.
Wahyoe Soedarmono and Djauhari Sitorus and Amine
Tarazi. (2017). Abnormal loan growth, credit
information sharing and systemic risk in Asian banks.
J. Research in International Business and Finance, vol.
42, pp. 1208-1218.
Williams Kamilah and Brown Leanora. (2021). Does
Information Sharing Matter? Cross-country Evidence
on Foreign Bank Presence. J. Journal of Economics and
Business, vol. 116: 105977, web.
World Bank.(2020). Doing Business 2020: Getting Credit.
World Bank, Washington. DC.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
312
