
Research on Management Accounting Framework based on Hall
Three-dimensional Structure and DSM
Yanyong Sun
1
, Guang Yu
1
and Ceng Zeng
2a
1
School of Management, Harbin Institute of Technology, Nangang Qu Xi Da Zhi Jie 92 th, Harbin, China
2
School of Accountancy, Shanghai University of Finance and Economics, Yang Puqu Guoding road 777th, China
Keywords: Hall 3D Structure Model, Management Accounting, Enterprise Operation, Design Structure Matrix (DSM).
Abstract: The management accounting framework aims to improve the operation control ability. In view of the lack of
internal relationship between management methods and operation control in the previous research on
management accounting framework systems, this paper puts forward the purpose of this research. We use
Hall's three-dimensional structure model for reference to construct the management accounting framework
based on operation control, and study the characteristics of operation control with the contingency elements
such as organizational structure, control methods, and ability improvement as the logical dimension; Taking
eight tools such as comprehensive budget, performance evaluation and responsibility body as the knowledge
dimension to promote the application of management accounting, the enterprise operation matrix is defined.
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) method is used to study the quantitative correlation between operation control
and management accounting tools, and reveal the quantitative relationship between management accounting
tools. Finally, the case of China Unicom verifies hierarchical characteristics between management accounting
tools.
1 INTRODUCTION
Enterprise operation is a complex system, which is
realized by the exchange of various information as
well as the cooperation of various management
methods. Aiming at improving the quality of
enterprise operational control, the management
accounting framework combines different
management accounting tools based on a certain
logic. Existing research puts forward management
accounting framework including value management,
balanced scorecard, comprehensive budget and
activity-based costing, and so on. However, these
management accounting frameworks lack analysis of
the internal relationship between management
accounting tools and operational control since they
are mainly revolved around a certain management
accounting tool. In the meanwhile, the existing
research ignores the defects of a single management
accounting tool and the correlation among different
management accounting tools since it mainly focuses
on the impact of a single management accounting tool
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2387-4020
on specific operational control. It is necessary to
choose appropriate management accounting tools,
and deeply analyze the correlation between
operational controls and different management
accounting tools and the synergy among management
accounting tools according to organizational
characteristics, so as to ensure that the selected
management accounting toolset can effectively
connect with the enterprise operational control mode.
Therefore, it is of great theoretical and practical
significance to build a management accounting
framework based on operational control for the
application of management accounting tools and the
promotion of enterprise operational control ability.
Using Hall's three-dimensional structure model
for reference, this paper constructed a management
accounting framework based on operational control.
We investigated the characteristics of operational
control (logical dimension) such as organizational
structure, control method, and ability improvement,
management accounting tools (knowledge
dimension) including a comprehensive budget,
performance evaluation, and responsibility body.
Sun, Y., Yu, G. and Zeng, C.
Research on Management Accounting Framework based on Hall Three-dimensional Structure and DSM.
DOI: 10.5220/0011183000003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 415-421
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
415

Based on the framework, we define the operation
matrix. Using the method of DSM matrix, the
quantitative correlation between operation control
and management accounting tools, the quantitative
correlation among management accounting tools
were determined. The case study of China Unicom
validates the central role of comprehensive budgeting
in enterprise operations management. The research
results reveal the significant correlation and
hierarchical features among management accounting
tools. Firstly, management accounting tools are
hierarchical in nature according to the relevance of
operational characteristics, and each hierarchical tool
cooperates with and complements each other and has
hierarchical characteristics. Secondly, the basic
functions of management accounting tools at
different levels are positioned variably with
quantitative intrinsic relationships with each other.
Thirdly, the management accounting practice based
on the operational dimension is the process of deeply
promoting the integration of business and finance.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Existing research puts forward management
accounting framework including value management,
balanced scorecard, comprehensive budget and
activity-based costing, and so on. With the
fundamental goal of continuously creating
shareholder value, Serebryakova put forward a value
management framework (VBM), which determines
specific internal goals, selecting strategy and
organizational design, identifying value drivers,
formulating action plans, and selecting performance
indicators and goals, performance evaluation, as well
as feedback improvement (Serebryakova 2021).
Pareek put forward a management framework based
on the principle of the strategic management process,
which takes the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) as the
core and integrates tools such as budget, activity
management, and shareholder value index (Pareek
2021). Ploder focused on the combination of agile
project management and beyond budgeting (Ploder
2020). From the perspectives of economics,
psychology, and sociology, Choi found imply that the
patterns of budget ratcheting could be diverse based
on how local government officials strategically
respond to the dynamics between bargaining power
and the pressure of justifying budgets (Choi 2021).
The existing researches mainly discuss the influence
of specific management accounting tools such as
comprehensive budget, performance evaluation, and
balanced scorecard on specific operational control
when applying the management accounting
framework to operational control. For example,
Cools study the role of budgets in a creative context
(Cools 2017). They find expected creative firms use
their budgets in a more interactive way and
responsive creative firms use their budgets in a rather
diagnostic way. Artz study the effect of performance
measure used on the functional strategic decision.
Lima presents the results of the strategic planning
process and the use of the Balanced Scorecard as a
strategic management system for the Center for
Sustainable Development/Research Group on Energy
Efficiency and Sustainability (Greens), University of
Southern Santa Catarina (Unisul) (Lima 2021).
Malagueño investigate the effect of BSC in SMEs on
their financial performance and innovation outcomes
(Malagueno 2018).
An appropriate management accounting system
depends on the specific environment and
organizational structure design of the organization
itself. In the process of selecting management
accounting tools, enterprises should deeply analyze
the correlation between operational control and
different management accounting tools and the
synergy among management accounting tools
according to organizational characteristics, so as to
ensure that the selected management accounting
toolset can effectively connect with the operational
control mode of enterprises. As a result, it can give
full play to the efficacy of management accounting,
improve the level of enterprise operational control,
and then promote the high-quality development of
enterprises by building a management accounting
framework based on operational control.
3 MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING
TOOLS
The application of management accounting tools in
enterprises is to solve the management problems that
restrict the ability of enterprise value creation.
Therefore, enterprises should not only consider the
internal relationship with enterprise operational
control but also consider the correlation between
management accounting tools when they implement
management accounting tools. For quite a long period
of time, the common topic concerned by both the
practical and academic circles engaged in the
research of management accounting is how to operate
management accounting to better support the
operational control of enterprises; what are the key
elements of an effective management accounting
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
416

framework; what is the relationship among these
factors and enterprise operational control activities;
what is the relationship between the internal elements
of the management accounting framework? Based on
operational control, this paper answers the above
questions in the way of constructing a management
accounting framework.
3.1 Management Accounting
Framework based on Hall's
Three-dimensional Structure
Hall's three-dimensional structure analysis method, a
system engineering methodology put forward by
American system engineering expert Hall in 1969,
can be used to solve the planning, organization, and
management problems of large and complex systems.
Hall's three-dimensional structure divides the whole
system engineering into different stages and steps
closely connected before and after and combines
various professional knowledge and skills needed to
complete these stages and steps. Hence, it formed a
three-dimensional structure composed of the time
dimension, logic dimension, and knowledge
dimension. This paper builds a management
accounting framework based on operational control
by drawing lessons from Hall's three-dimensional
structure analysis method.
Firstly, the time dimension of Hall's three-
dimensional structure represents the whole process of
system engineering activities arranged in time
sequence from beginning to end. The enterprise
operation process is divided into the planning stage,
scheme formulation stage, implementation stage, and
continuous improvement stage. Therefore, this paper
defines the above four stages as time dimensions.
Secondly, the thinking procedure that should be
followed in each stage of the time dimension is
represented by the logical dimension of Hall's three-
dimensional structure. The planning stage and the
programming stage need to be conducted under the
guidance of the organization's strategic objectives. In
this paper, the procedures to be followed in these two
stages are defined as organizational functions. In the
implementation stage, enterprises need to effectively
control the operation process to ensure the effective
implementation of the scheme. In this paper, the
procedures to be followed in the implementation
stage are defined as control activities.
Enterprises need to make the operation plan to
create value continuously in the stage of continuous
improvement. This paper defines the procedure to be
followed in this stage as capability improvement.
In the end, the knowledge dimension of Hall's
three-dimensional structure represents the
professional knowledge needed to complete these
stages and steps. Management accounting is carried
out around enterprise operational control, and it is a
control system that directly participates in enterprise
operation process management. Management
accounting tools are the concretization of
management accounting concepts and form important
support for the operational control of enterprises.
Therefore, this paper positions management
accounting tools as a knowledge dimension. As
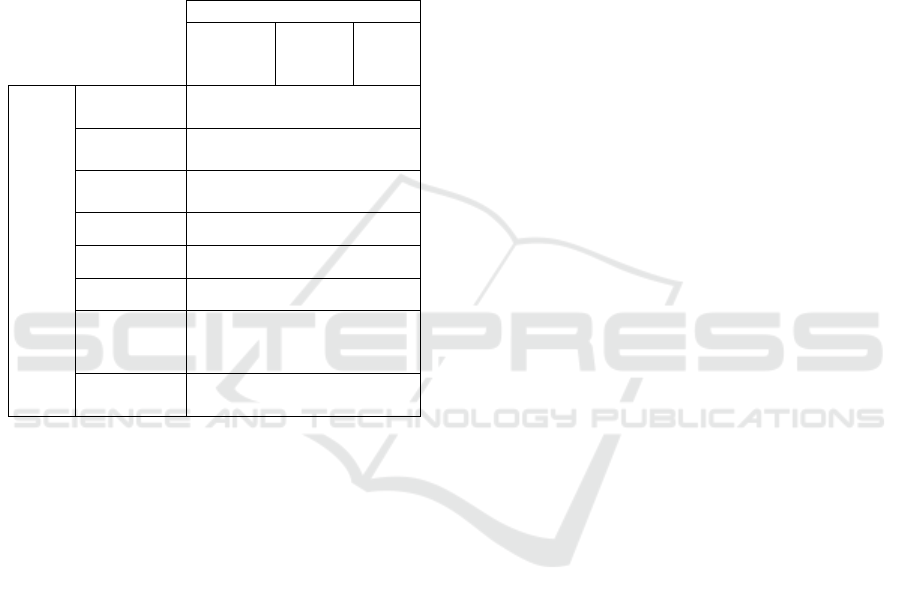
shown in Fig. 1, this paper establishes a management
accounting framework based on operational control
by using Hall's three-dimensional structure model for
reference, and studies the internal relations and
quantitative methods among management accounting
tools based on enterprise operation characteristics.
Figure 1: Management accounting framework model based
on operational control.
3.2 Enterprise Operation Matrix
Usually, based on the changes of the internal and
external environment, enterprises choose the
management accounting tools they need. In fully
competitive industries, enterprises are more willing to
apply management accounting tools to improve
operational efficiency and benefits when the internal
and external environment of enterprises tends to be
complex and changeable, to enhance their
competitiveness.
We construct the enterprise operation matrix
based on the above analysis. The logical dimension
refers to the collection of elements controlling
operation activities, which constitutes the ordinate of
enterprise operation matrix, and describes the static
planning and dynamic allocation of organizational
structure, control mode, ability improvement, and
Logical dimension
(Operational control)
Knowledge dimension
(Management
accounting tools)
Continuous improvement
Planning stage
Formulate a scheme
Im
p
lementation
p
hase
Comprehensive budget
Performance appraisal
Responsibility body
…
Organizational function
Control activities
Ability
improvement
function
Time dimension
(Implementation and
improvement)
Research on Management Accounting Framework based on Hall Three-dimensional Structure and DSM
417
other elements realizing business objectives under the
condition of functional division. Knowledge
dimension means the collection of management
accounting tools. The abscissa of enterprise operation
matrix proposed in this paper consists of
comprehensive budget, performance evaluation,
responsibility body, lean cost, supply chain, sales
support, integration of industry and finance, decision
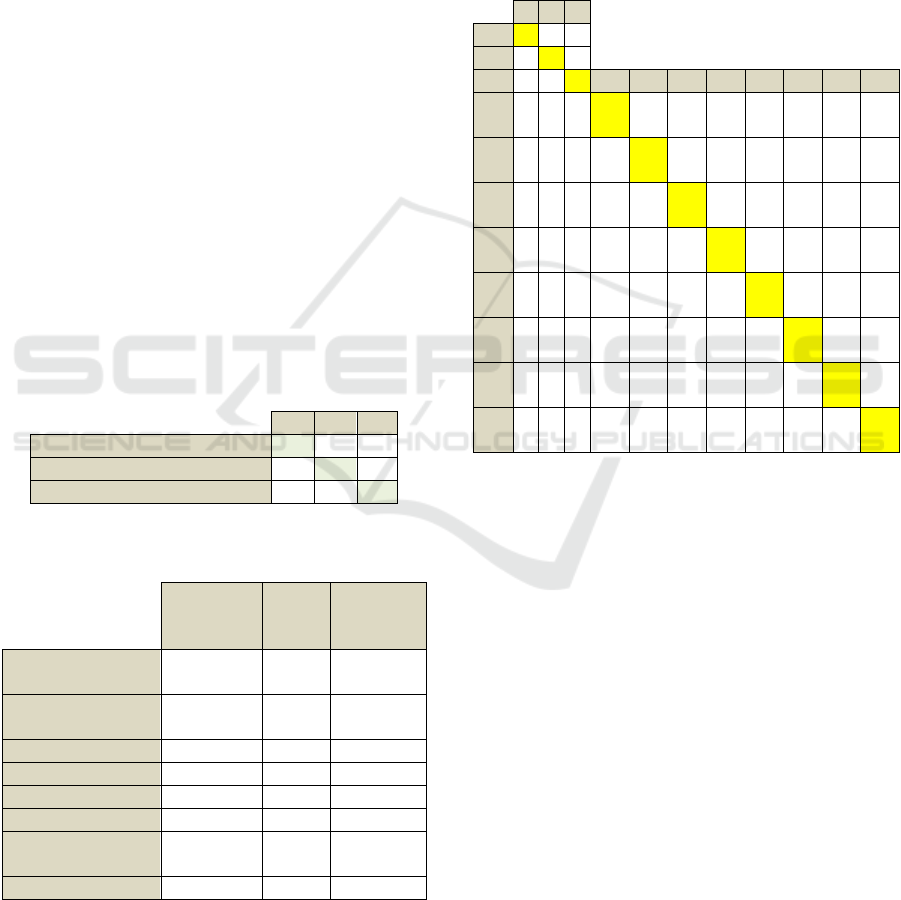
support, and other methods. See Table 1.
Table 1: Operation control dimension and management
accounting tool dimension of enterprise operation matrix.
Operation control
Organizati
onal
function
Control
activities
Ability
improv
ement
Manag
ement
accoun
ting
tools
Comprehensi
ve budget
Performance
a
pp
raisal
Responsibility
b
ody
Lean cost
Supply chain
Sales support
Integration of
industry and
finance
Decision
su
pp
ort
Enterprise operation matrix reflects the internal
logical relationship between operation control
dimension and management accounting tools. The
correlation between the elements of the enterprise
operation matrix is different due to the influence of
the enterprise operating environment. From the
perspective of system engineering, the correlation
and impact of operation matrix elements can be
scientifically quantified and evaluated. Therefore, we
further select the verification method for the
quantitative correlation of enterprise operation matrix
elements. If we can prove that there is an internal
correlation between the constituent elements of the
operation control dimension and management
accounting tools, the internal correlation between
management accounting tools can also be indirectly
proved.
4 CASE ANALYSIS
The correlation and influence of operational matrix
elements can be scientifically quantified and
evaluated from the perspective of system
engineering. Therefore, the Design Structure Matrix
(DSM) method was selected as the verification
method of quantitative correlation, which is used to
describe the interdependence between different
elements in complex systems (Loureiro 2020). The
enterprise operation matrix composed of operation
control and management accounting tools is a
complex of the correlation of factors such as
products, processes, organizations, and activities.
Therefore, the quantitative research using the DSM
model is suitable for the enterprise operation matrix
model proposed in this paper.
In order to analyze the characteristics of operation
control and management accounting tools, we
introduce the Delphi evaluation method to evaluate
the score of the correlation of the constituent
elements of China Unicom's enterprise operation
matrix quantitatively. Using a valuation scale ranging
from 0 to 5 (0=Unconsidered; 1=Worth a little
consideration; 2=Worth considering; 3=Partly true;
4=Meaningful; 5=Makes sense).
4.1 Quantifying the Impact of
Operational Control on
Management Accounting Tools
The quantitative correlation of the operational control
matrix evaluation is shown in Table 2. The
quantitative correlation between organizational
function α and control activity β is 5, while the
quantitative correlation between control activity β
and organizational function α is 4, indicating that
organizational function α has a greater influence on
control activity β than control activity β has on
organizational function α. Meanwhile, there is another
typical correlation relationship between capability
enhancement ϒ and control activity β. The
quantitative correlation effect of capability
enhancement ϒ on the correlation with control
activity β is 3, while the quantitative correlation effect
of control activity β on capability enhancement ϒ is 1.
It shows that the influence of ability improvement on
control activity β is greater than that of control activity
β on ability improvement. Similarly, the quantitative
correlation effect of organizational function α on
capability enhancement ϒ is 1, while the quantitative
correlation effect of capability enhancement ϒ on
organizational function α is 2. It shows that the
influence of capability enhancement on organizational
function α is greater than that of organizational
function α on capability enhancement.
The quantitative relevance of operational control
activities to the assessment of management
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
418
accounting tools is represented in a domain mapping
matrix, as detailed in Table 3. Among them,
comprehensive budget A, as a tool of strategy
implementation, is affected by the quantitative
correlation of organizational function α, control
activity β, and ability improvement, all of which are
5. Organizational function α is to define the mission
and rules of the organization, control activity β
advances the implementation goals, and capability
enhancement ϒ is to match and invest resources,
indicating that the operational control elements are all
important in influencing the quantitative relevance of
the comprehensive budget, and advancing the
comprehensive budget A is influenced by the
combination of organizational function α, control
activity β, and capability enhancement ϒ. At the same
time, another typical correlation is that the
quantitative correlation of organizational function α,
control activity β, and ability promotion affects
decision support G by 3, 2, and 1 respectively. It
shows that decision support G has a great correlation
with organizational process α, but ϒ is less affected
by ability improvement, and the influence of control
activity β on decision support G is between them.
Other management accounting tools are influenced
by the quantitative relevance of operational control
elements as detailed in Table 3.
Table 2: Operational control dimension matrix DSM.
α β ϒ
Organizational function α α 4 2
Control activity β 5 Β 3
Ability improvement ϒ 1 1 ϒ
Table 3: Management accounting tools and operations
control matrix DMM.
Organization
al function α
Control
activity
β
Ability
improvemen
t ϒ
Comprehensive
budget A
5 5 5
Performance
evaluation B
5 4 3
Responsible body C 5 5 4
Lean cost D 3 4 5
Supply chain E 3 4 3
Sales support F 2 4 3
Integration of industry
and finance G
4 5 2
Decision support H 3 2 1
The multi-domain matrix is an analysis of the
characteristics of the application of management
accounting tools in a business and is reflected as an
intrinsic link between management accounting tools
in a business operations control environment. The
multi-domain matrix constructed by using
operational control dimension DSM (Table 2) and
domain mapping matrix (Table 3) is shown in Table
4, and the quantitative correlation between
management accounting tools is calculated according
to DSM method.
Table 4: Operational control and management accounting
tool MDM.
α β ϒ
α α 4 2
β 5 β 3
ϒ 1 1 ϒ A B C D E F G H
A 5 5 5 A
32
5
37
5
31
5
26
5
23
5
29
5
16
5
B 5 4 3
34
0
B
31
8
27
1
22
7
20
4
25
1
13
7
C 5 5 4
39
0
31
6
C
30
8
25
8
22
9
28
6
16
0
D 3 4 5
30
0
24
7
28
2
D
19
7
17
2
22
1
12
7
E 3 4 3
28
0
22
9
26
2
21
9
E
16
0
20
3
11
7
F 2 4 3
25
0
20
7
23
4
19
3
16
1
F
17
9
10
7
G 4 5 2
34
0
27
6
31
7
26
8
22
2
19
5
G
14
0
H 3 2 1
18
0
14
3
16
8
14
5
12
1
11
0
13
3
H
4.2 Quantifying the Correlation
between Management Accounting
Tools
The management accounting tool DSM is derived
from the multi-domain matrix MDM (Table 4) by
optimizing the ranking according to the correlation
value and increasing the color scale, as shown in
Table 5. Firstly, the quantitative relevance of
comprehensive budgets to other management
accounting tools is at the top of the list. It can be seen
that the strategic position and function of
comprehensive budget have quantitatively verified
the position of the comprehensive budget as the core
tool of enterprise management and control. Secondly,
the quantitative correlation among comprehensive
budget, responsibility body, and performance
evaluation is above 316, which also shows that these
three management accounting tools together
constitute the key elements to enhance the operational
capability of enterprises. Thirdly, among the impacts
on the comprehensive budget, the quantitative
Research on Management Accounting Framework based on Hall Three-dimensional Structure and DSM
419
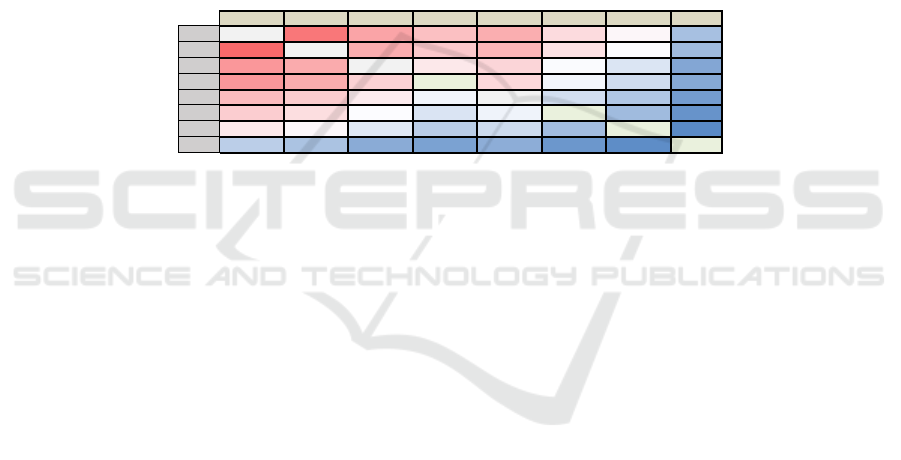
relevance of the responsibility body 390 ranks first,
the quantitative relevance of the performance
evaluation system 340, while the quantitative
relevance of the business-financial integration 340,
the quantitative relevance of the lean cost 300, the
quantitative relevance of the supply chain 280, the
quantitative relevance of the sales support 250, and
the quantitative relevance of the decision support
180, indicating that the responsible body is the core
element to achieve the budget decomposition.
Fourthly, the financial integration to comprehensive
budgeting is relatively large and must be considered
in the process of implementing the management
accounting framework. Fifthly, the quantitative
relevance of lean cost, supply chain, and sales support
to other management accounting tools is at the
medium level, which is related to the fact that they
are operation-oriented management accounting tools
and the management attributes supporting the
operation level. Sixthly, the quantitative correlations
among lean cost, supply chain, and sales support are
less than their quantitative correlations among
comprehensive budget, performance evaluation, and
accountability body, indicating significant
hierarchical nature of quantitative correlations among
management accounting tools. Seventhly, the
quantitative relevance of decision support to various
management accounting tools is weak, which is
related to the fact that decision support is based on the
information integration attribute of various
management accounting tools, and also related to the
fact that decision support is the management attribute
supporting the management of enterprises.
Table 5: Management accounting tool DSM.
A C B G D E F H
A A 375 325 295 315 265 235 165
C 390 C 316 286 308 258 229 160
B 340 318 B 251 271 227 204 137
G 340 317 276 H 268 222 195 140
D 300 282 247 221 D 197 172 127
E 280 262 229 203 219 E 160 117
F 250 234 207 179 193 161 F 107
H 180 168 143 133 145 121 110 G
To sum up, DSM is used to prove that there is a
quantitative correlation between the operation control
elements of the case enterprise and the management
accounting tools, as well as in the management
accounting tools, so as to demonstrate the
effectiveness of the enterprise operation matrix.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In order to overcome the defects of the former
management framework system lacking quantitative
research on the internal relationship between
management methods and operation control. Firstly,
this paper uses Hall's three-dimensional structure
model to construct a management accounting
framework based on operational control. Secondly,
taking the contingency elements such as
organizational structure, control methods, and ability
improvement as the logical dimension, this paper
studies the characteristics of enterprise operation
control, takes eight tools such as comprehensive
budget, performance evaluation, and responsibility
body as the knowledge dimension to promote the
application of management accounting and defines
the enterprise operation matrix accordingly. Finally,
a case study is conducted to verify the core role of
comprehensive budget in enterprise operation
management, and it constitutes the key method
affecting enterprise operation ability together with
responsibility body and performance evaluation. The
results reveal that there are significant correlations
and hierarchical characteristics among management
accounting tools.
REFERENCES
C. Ploder, T. Dilger, P. Schttle. (2020). Agile Project
Budgeting-Teaching the Combination of Agile Project
Management and Beyond Budgeting Basics. J.
Edulearn. 7,1145.
G. B. Loureiro, J. Ferreira, P. Messerschmidt. (2020).
Design structure network (DSN): a method to make
explicit the product design specification process for
mass customization. J. Research in Engineering
Design. 31(2), 197-220.
M. Cools, K. Stouthuysen, A. Van den Abbeele. (2017).
Management Control for Stimulating Different Types
of Creativity: The Role of Budgets. J. Journal of
Management Accounting Research. 29(3): 1-21.
M. Lima, G. Mazon, B. Castro, S. L. Bocasanta, José
Baltazar Salgueirinho Osório de Andrade Guerra.
(2021). The book, Strategic Planning for a Sustainable
Development Centre Using the Balanced Scorecard.
Cham: Springer International Publishing.
R. Malagueno, E. Lopez-Valeiras, J. Gomez-Conde.
(2018). Balanced Scorecard in SMEs: Effects on
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
420

Innovation and Financial Performance. J. Small
Business Economics. 51(1), 221-244.
S. K. Pareek, S. Mukherjee. (2021). Balanced Scorecard
and Its Application Through Strategic Management
Perspective in Real Estate Industry. J. Advances in
Smart Grid and Renewable Energy. 1,69-77.
T. Serebryakova, O. Gordeeva, O. Kurtaeva, A. Anisimov.
(2021). Theoretical framework of accounting and
analysis for value-based management. J. SHS Web of
Conferences. 94(5):01034.
Y. S. Choi, M. O. Kim, H. R. Jung, H. Cho. (2021).
Bargaining power and budget ratcheting: Evidence
from South Korean local governments. J. Management
Accounting Research. 53(3/4), 100767.
Research on Management Accounting Framework based on Hall Three-dimensional Structure and DSM
421
