
The Study based on Coordination of Revenue Sharing Contract in
Three-stage Port Supply Chain under Emergencies
Shihao Gong
a
and Zhangchi Sun
b
College of Transportation Engineering, Dalian Maritime University, Linghai Road, Dalian, China
Keywords:
Revenue Sharing Contract, Emergencies, Port Supply Chain, Supply Chain Coordination.
Abstract: On the basis of random market demand, establishing revenue sharing contract can achieve the coordination
of the three-stage port supply chain system. However, the drastic fluctuations of market demand caused by
emergencies will break the coordination of supply chain in stable market, which in turn affects the normal
operation of each node enterprise. This paper gives an emergency optimization strategy for the multimodal
transport service supply chain with the port as the integrator under the emergencies, which makes the
original contract has stronger robustness; and gives the relationship of the profit distribution coefficients
among the subjects when supply chain systems yield the most, and finally verifies the effectiveness of the
improved revenue sharing contract through case analysis.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
Since the global outbreak of COVID-19,
international trade has been hit. Along with the
gradual intensification of trade frictions between
countries, emergencies such as COVID-19 are
unpredictable, short-cycle and of huge influence,
which have led to frequent and dramatic fluctuations
in the market environment, resulting in a global
supply chain crisis. How to achieve coordination
among enterprises at all levels of the supply chain,
enhance their ability to cope with shocks and reduce
losses of supply chain enterprises under the impact of
emergencies has gradually become the focus of
scholars at home and abroad. The port supply chain
in shipping industry is gradually becoming a key link
in the global industrial chain and international trade
chain, providing transportation services for about
70% of global trade and having a major strategic
position in global supply chain network. In the port
supply chain, port enterprises play the role of
integrating multiple information and building a
trading platform. They play a vital role in connecting
road carriers, ocean carriers and port companies as a
whole, and are also responsible for distribution and
coordination of internal revenue within the supply
chain, while directly dealing with shippers externally.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4196-0687
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3388-2444
Therefore, under the impact of emergencies, how to
coordinate the interest conflicts among the three-
stage port supply chain consisting of road carriers,
ocean carriers and port enterprises will become the
key to whether the port supply chain can withstand
risks, maintain efficient and stable operation.
Against the preceding background, this paper
analyzes the response measures of risk and revenue
sharing strategies of port supply chain under
centralized and decentralized decision by using
revenue sharing contract under the disturbance of
emergencies, and explores what response measures
of risk should be taken by the three-stage port supply
chain under different market fluctuations, aiming to
provide theoretical guarantee for port supply chain to
cope with emergencies and port supply
chain security.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
First, the supply chain is a whole composed of multi-
level enterprises. Due to different interests among
enterprises at different levels, it is difficult to
coordinate the interests of the whole supply chain.
How to reasonably divide the interests of the supply
chain so as to maximize the revenue of the supply
chain has been the focus of academic research. For
the distribution of interests within the supply chain,
(Cachon, 2005) first proposed the role of revenue
contribution contract in supply chain coordination,
658
Gong, S. and Sun, Z.
The Study based on Coordination of Revenue Sharing Contract in Three-stage Port Supply Chain under Emergencies.
DOI: 10.5220/0011207700003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 658-668
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

and concluded that revenue sharing contract can give
the optimal revenue allocation proportion and
optimal order quantity for each link in the supply
chain system under a stable market environment,
which proves the effectiveness of revenue sharing
contract. And (Xu, 2010) improved the classical
revenue sharing contract by considering price
elasticity of demand, realized the coordination
between traditional distribution channels and
electronic distribution channels, explored the
conditions for the existence of perfect win-win
coordination between dual-channel supply chains,
and gave a solution method for the contract
parameters. (Niu, 2009) used Stackelberg game
theory to study the game process between retailers
and distributors and the equilibrium effect of revenue
sharing contract on supply chain revenue under
dominant supply chains. The above studies proved
the role of supply chain contract in supply chain
interest distribution, supply quantity optimization,
etc., and proposed various paths to coordinate the
supply chain.
It is worth noting that most of the above studies
are based on normal market models and ignore the
impact of unusual market fluctuations on the supply
chain. Especially under the impact of the COVID-19,
the instability of the supply chain has greatly
increased. In order to cope with the impact of
emergencies, many scholars have conducted research
on the coordination of supply chain based on the
background of abnormal perturbation of market
fluctuations, in order to enhance the ability of supply
chain to cope with risks and resist market
fluctuations, so as to reduce the losses of supply
chain enterprises under the market fluctuations. For
example, (Liu, Liu, 2020). analyzed the coordination
effect of quantity flexibility contract for supply chain
under emergencies based on a two-stage closed loop
supply chain model in the context of contingency
disturbances. (Chen, Liu, 2014) studied the effect of
revenue sharing contract on the coordination of
emergency contingencies based on the perspective of
a three-stage supply chain. (Liu, 2013) demonstrated
that revenue sharing contract can still coordinate the
revenue gap between supply chain links under
complex market fluctuations from a four-stage
supply chain consisting of suppliers, producers,
distributors and retailers, and demonstrated the
robustness of revenue contribution contract.
Due to the fundamental difference between the
service supply chain represented by the port supply
chain and the traditional product supply chain, the
above-mentioned papers still focus on the traditional
product supply chain and lack in-depth exploration of
the service supply chain. At present, in the field of
port supply chain, (Zhang, 2009) analyzed the profit
distribution of port service supply chain by using the
improved Shapley method and proposed a new profit
distribution model from the perspective of
cooperative game. (Wang, 2021) studied the optimal
business strategy under two different decision
scenarios: centralized decision and decentralized
decision, for the port supply chain model under
demand disturbance, and proposed different
transportation strategies for goods with different
characteristics, such as cost-sensitive and time-
sensitive. (Zhao, 2007) studied the longitudinal
alliance structure of the port supply chain and
analyzed the potential benefits from the cooperation
between upstream and downstream port enterprises.
(Lv, 2020) considered the optimization effect of
introducing fourth party logistics on the port supply
chain, and analyzed the competition and coordination
between port integrators and port and shipping
enterprises. He found that the whole supply chain
could achieve the highest yields under centralized
decision, but the members of each link might need to
sacrifice some of their own interests to achieve the
goal of global optimum.
In the above studies on port supply chain,
although they all propose corresponding coordination
mechanisms for the port supply chain model to
ensure the long-term stable operation of the port
supply chain. However, most of the scholars in the
current research are based on the simplified two-
stage supply chain model for supply chain contract
design, ignoring the three-stage supply chain
consisting of road carriers, port enterprises and ocean
carriers in the port supply chain. With the gradual
development of port integration and the increasing
flexibility of transportation services, the “door-to-
door” transportation form represented by multimodal
transport is gradually receiving more and more
attention. Therefore, it is worthwhile to further study
the three-stage port supply chain in the context of
multimodal transport. Meanwhile, most scholars
have focused on traditional product supply chain
research in the study of supply chain coordination for
emergencies, but not on the optimization and
coordination of service supply chain such as logistics
transportation. Currently, the occurrence of frequent
disruptions such as COVID-19 and trade frictions,
the study of service supply chain such as logistics
services has become the focus of global attention.
To sum up, based on the three-stage port supply
chain consisting of road carriers, ports and ocean
carriers and considering both market random
fluctuations and contingency disturbances, this paper
The Study based on Coordination of Revenue Sharing Contract in Three-stage Port Supply Chain under Emergencies
659

constructs a revenue model for each party in the
supply chain and the whole supply chain , and
constructs a revenue sharing contract based on this
model to explore the response strategies of the port
supply chain under contingency disturbances and
uses cases to demonstrate the general application of
the contract.
3 PROBLEM DESCRIPTION AND
CONDITION ASSUMPTIONS
In recent years, with the outbreak of the COVID-19
and the intensification of world trade frictions,
outages and production shutdowns have occurred
from time to time, leading to widespread market
fluctuations, and these emergencies have posed
challenges to the stable operation of the supply chain.
Large fluctuations in market demand can lead to
significant changes in demand for specific
commodities. For example, after the outbreak of
COVID-19, the market demand for medical supplies
such as masks and vaccines increased significantly;
after the China-Australia trade friction intensified,
the volume of coal trade between China and
Australia decreased greatly. At this time, the shipping
industry, as the main carrier of world trade, needs to
adjust to market fluctuations. In the event of demand
expansion and capacity shortage caused by
emergencies, enterprises at all levels of the supply
chain need to improve transportation efficiency,
expand transportation scale and bear the cost of
exigently production increase. And in the case of
sharp decline of market demand caused by
emergencies, there will inevitably be a large amount
of idle capacity in supply chain, resulting in waste
and bringing losses to the supply chain enterprises.
To this end, this paper establishes a three-stage
supply chain consisting of port operators, ocean
carriers and road carriers in the context of sea-land
combined transport. Compared with the traditional
supply chain model, the port supply chain of sea-land
combined transport has the following characteristics:
The information between road carrier and ocean
carrier is symmetrical and independent. Logistics
service as a intangible product without residual
value. The ideal state of the whole supply chain is
that the agreed volume of port operators is equal to
the agreed volume of road carriers and ocean carriers.
In view of the above problems and characteristics,
the following assumptions are proposed in this paper:
Assumption 1: The cost of stocking and retail
price of each service provider do not change, and the
distribution function which market demand subject to
in a stable environment is continuous, differentiable
and derivable.
Assumption 2: The services provided by the port
supply chain are multimodal transport of containers.
Assumption 3: Port service providers, road
carriers, and ocean carriers are risk-neutral and
entirely rational, i.e., each makes decisions according
to the net benefit maximization principle.
Assumption 4: All parties in the supply chain
can accurately predict the demand distribution
function of customers.
The variables used in this paper are shown in
Table 1:
Table 1: Definition of Parameters
,,,
t por
ππ ππ
Profit for the whole supply chain, port
operators, ocean carriers and road
carriers
,,,
tpor
QQ QQ
Optimal transportation volume for the
whole supply chain, port operators,
ocean carriers, and road carriers
,,
p
or
ccc
Unit cost for port operators, ocean
carriers and road carriers
(), ()Fx Gx
Market demand distribution function
after emergencies in a stable market
,
or
θθ
Unit price of ocean carriers and road
carriers
,
or
kk
Benefit coefficient of ocean carriers
and road carriers
,,
p
or
λλλ
Unit opportunity cost for port
operators, ocean carriers and road
carriers following a reduction in
market demand due to emergencies
,,
p
or
μμμ
Unit cost of exigent production
increment for port operators, ocean
carriers and road carriers following an
increase in market demand due to
emergencies
,
tp
pp
Shipper purchase price under
centralized decision and decentralized
decision
Based on the above assumptions, we first develop
a benchmark revenue sharing contract model of
three-stage service supply chain under a stable
market, and further consider how the improved
revenue sharing contract coordinates the entire
system in the event of a sudden increase/decrease in
market demand due to emergencies.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
660
4 THE BENCHMARK REVENUE
SHARING CONTRACT MODEL
OF THREE-STAGE SERVICE
SUPPLY CHAIN
4.1 Model Overview
The port supply chain in the context of multimodal
transport can provide customers with “door-to-door”
entire transport services. Since the whole system has
several independent subjects, the participants in the
supply chain are usually set to make self-interested
and rational decisions, and the goal of their decisions
is often to maximize their own interests. Therefore,
in general, the service volume when the individual
achieves the optimum is often not the optimal
service volume of the whole supply chain.
The supply chain contract model represented by
revenue sharing contract can provide appropriate
incentives for all parties in supply chain to optimize
sales channels to ensure supply chain coordination.
However, the occurrence of emergencies can lead to
changes in contract parameters as well as market
demand, which can result in lower overall revenue
and further lead to supply chain incongruity.
Therefore, we construct the supply chain revenue
sharing contract models respectively under
centralized and decentralized decision to coordinate
the whole supply chain. Further, we consider the
parameter optimization of the revenue sharing
contract model to cope with such perturbations under
the influence of emergencies, and finally, we verify
the effectiveness of our model through case analysis.
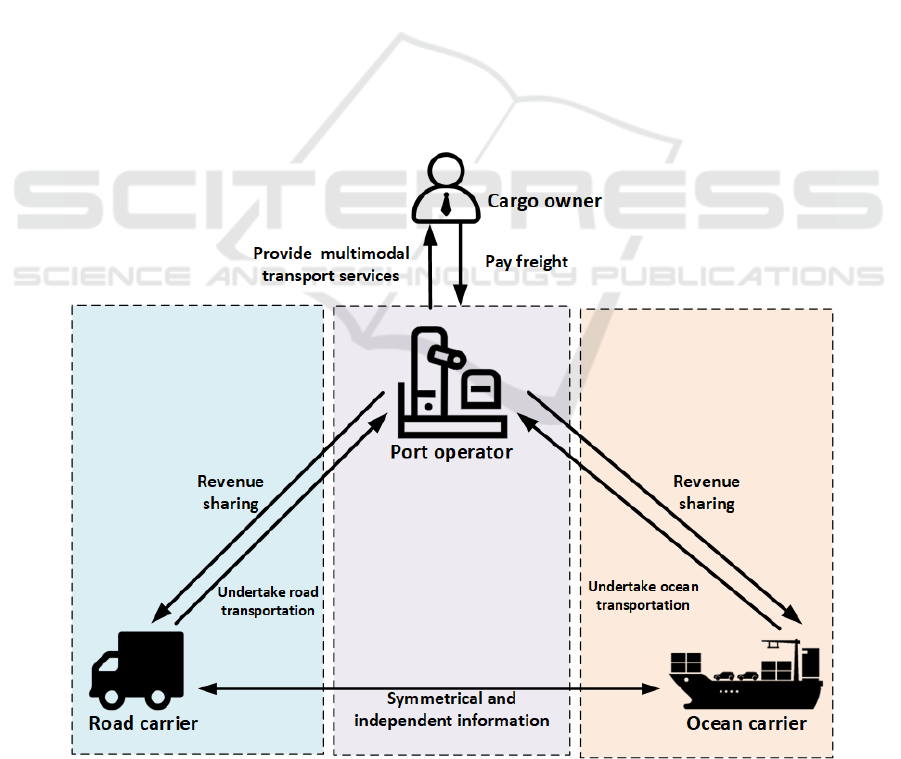
The model in this paper considers a three-stage
service supply chain consisting of port operators,
road carriers, and ocean carriers, whose structure is
shown in Figure1. Under the coordination of revenue
sharing contract, port operators purchase
transportation resources from road and ocean carriers
respectively at below cost to provide multimodal
transport services to customers, and sign carriage
contracts with shippers outside the system as supply
chain integrators, and finally share part of the
revenue to road and ocean carriers through the
earning yields agreed in advance.
Figure 1: The framework of port three-level service supply chain.
The Study based on Coordination of Revenue Sharing Contract in Three-stage Port Supply Chain under Emergencies
661

To establish a benchmark three-stage service
supply chain, we let the demand of shippers in the
market D be an obeying random variable of F(x), and
the unit stocking cost of the three parties, namely,
port operators, road carriers and ocean carriers, be
,,
p
ro
ccc
.
4.2 The Revenue Sharing Contract
Model under Centralized Decision
Under centralized decision, the supply chain parties
jointly aim at maximizing the profit of the system,
and let the overall profit of the supply chain be
t
π
,
the agreed volume jointly decided by supply chain
participants under the centralized decision be
t
Q
and
the unit charge to shippers be
t
p
. When the market
volume is D, the final actual volume of the port
supply chain is
{
}
min ,
t
D
Q
.
The unit cost of the port supply chain consists of
the unit cost of each party together, i.e.
tpro
cccc=++
.After the supply chain participants
reach an agreed volume, each participant prepares
resources for stocking according to the determined
agreed volume, and the overall stocking cost is
()
++
p
rot
cccQ
. Thus, the profit of the port supply
chain under centralized decision is shown as follows:
{
}
()
min ,
tt t prot
pDQcccQ
π
=−++
(1)
The expected profit function is:
()
()
0
() ()
t
t
Q
tt t prot
Q
E
pxfxdxQfxdxcccQ
π
∞
=+−++
(2)
.. 0
t
stQ >
The first derivative of the expected profit for the
whole supply chain with respect to the agreed
volume
t
Q
is:
[]
()
()
1()
t
ttpro
t
E
p
FQ c c c
Q
π
∂
=− −++
∂
The second derivative of the expected
profit
()
t
E
π
with respect to the agreed volume
t
Q
is:
()
()
2
2
t
tt
t
E
pf Q
Q
π
∂
=−
∂
Because of
()
2
2
0
t
t
E
Q
π
∂
<
∂
,
()
t
E
π
is convex function,
and the agreed volume of the whole port supply
chain is determined by
()
t
t
E
Q
π
∂
∂
.
Let
()
0
t
t
E
Q
π
∂
=
∂
,then
()
*
1
p
ro
t
t
ccc
FQ
p
++
=−
, i.e.:
*1
1
p
ro
t
t
ccc
QF
p
−
++
=−
Therefore, under the centralized decision, the
optimal agreed volume of the whole supply chain is
shown in the above equation.
4.3 The Revenue Sharing Contract
Model under Decentralized
Decision
Since port operators, as the integrators of the supply
chain, dominate the game process in the port supply
chain, in order to match the agreed volumes of each
party under the decentralized decision with the
agreed volumes under the centralized decision, i.e., to
achieve supply chain coordination, we adopt a
revenue sharing contract to allocate the revenue of
each party in the supply chain. The road carrier and
ocean carrier determine the respective optimal agreed
volumes
**
,
ro
QQ under a given revenue sharing
contract
(,),(, )
rr oo
kk
θθ
,
,
ro
θθ
are the unit
prices of transport services purchased by the port
from the road carrier and ocean carrier, and
,
ro
kk
are the proportion of revenue allocated by the port to
two parties. Further, the port operator determines his
own optimal agreed volume
*
p
Q based on his
expected revenue function and
(,),(, )
rr oo
kk
θθ
.
Under the revenue sharing contract, the revenue
functions of the road and ocean carriers are as
follows:
()
{
}
() {}
min ,
min ,
rrrrrp r
ooooop o
cQ kp DQ
cQ kp DQ
πθ
πθ
=− +
=− +
(3)
Expected profit function is:
()
()
0
0
( ) () ()
() () ()
r
r
o
o
Q
rrrrrp r
Q
Q
ooooop o
Q
E
cQ kp xfxdx Qfxdx
E
cQ kp xfxdx Qfxdx
πθ
πθ
∞
∞
=− + +
=− + +
(4)
.. , 0
ro
stQ Q >
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
662

Calculate the first derivative and the second
derivative of
()
r
E
π
, and results are as follows:
()
[]
2
2
()
1()
()
()
r
rr rp r
r
r
rp r
r
E
ckp FQ
Q
E
kp f Q
Q
π
θ
π
∂
=−+ −
∂
∂
=−
∂
Because of
2
2
()
0
r
r
E
Q
π
∂
<
∂
, and
()
r
E
π
is
convex function, its optimal agreed volume
*
r
Q can
be determined by
()
r
r
E
Q
π
∂
∂
.
Let
()
0
r
r
E
Q
π
∂
=
∂
, then
()1
rr
r
rp
c
FQ
kp
θ
−
=+
, i.e.:
*1
(1 )
rr
r
rp
c
QF
kp
θ
−
−
=+
Calculate the first derivative and the second
derivative of
()
o
E
π
, and results are as follows:
()
[]
2
2
()
1()
()
()
o
oo op o
o
o
op o
o
E
ckp FQ
Q
E
kp fQ
Q
π
θ
π
∂
=−+ −
∂
∂
=−
∂
Because of
2
2
()
0
o
o
E
Q
π
∂
<
∂
, and
()
r
E
π
is
convex function, its optimal agreed volume
*
r
Q can
be determined by
()
o
o
E
Q
π
∂
∂
.
Let
()
0
o
o
E
Q
π
∂
=
∂
, then
()1
oo
o
op
c
FQ
kp
θ
−
=+
, i.e.:
*1
(1 )
oo
o
op
c
QF
kp
θ
−
−
=+
The port operator, as the supply chain integrator,
is the actual leader of this service supply chain. The
port operator purchases transportation services from
road carriers and ocean carriers respectively and then
allocates the profits received from the customer to
the carriers for supply chain coordination, so its
profit function can be expressed as:
()
{
}
()
1min,
p
rop p prop
kkp DQ c Q
πθθ
=−− − ++
(5)
Its expected profit function is:
()
()
0
() 1 () ()
p
p
Q
prop p prop
Q
E
kkp xfxdx Qfxdx c Q
πθθ
∞
=−− + − + +
.. 0
p
stQ >
(6)
Calculate the first derivative and the second
derivative of
p
Q with respect to ()
p
E
π
, and the
results are as follows:
()
()
()
2
2
()
11()
()
1()
π
θθ
π
∂
=−− − − ++
∂
∂
=− − −
∂
p
rop p pro
p
p
rop p
p
E
kkp FQ c
Q
E
kkpfQ
Q
Because of
2
2
()
0
p
p
E
Q
π
∂
<
∂
, and ()
p
E
π
is
convex function, its optimal agreed volume
*
p
Q can
be determined by
()
p
p
E
Q
π
∂
∂
.
Let
()
0
p
p
E
Q
π
∂
=
∂
, then
()
()1
1
pro
p
rop
c
FQ
kkp
θθ
++
=−
−−
, i.e.:
()
*1
1
1
pro
p
rop
c
QF
kkp
θθ
−
++
=−
−−
In summary, the respective optimal agreed
volumes for road carriers, ocean carriers and port
operators under decentralized decision are shown
above.
4.4 Coordination of Centralized
Decision and Decentralized
Decision
For the three-level port supply chain who provides
the service of transport, the key to achieve overall
coordinating is that the decided volume of each party
should be equal, the same as the optimal volume of
the centralized decision.
Proposition 1. When the market remains stable,
the revenue sharing contract enables the supply chain
to be coordinated, which means that the optimal
volume of each party of the decentralized decision
should equal with that of the centralized decision.
The proof as follows:
The Study based on Coordination of Revenue Sharing Contract in Three-stage Port Supply Chain under Emergencies
663

let
**
p
t
QQ=
,
then
()
1
pro pro
rop t
cccc
kkp p
θθ
++ ++
=
−−
.Considering
that the port, as an integrator, receives the quotation
of the cargo owner in our model, so
p
t
pp=
, the
constraints on the port in our overall coordination are
as follows:
1
pro
ro
pro
c
kk
ccc
θθ
++
−−=
++
(7)
let
****
,
rtot
QQQQ==
,then
()
rrrrop
ckccc
θ
=− ++
(8)
()
ooorop
ckccc
θ
=− ++
(9)
put the above three equations into the profit
function of port operator, road carrier and marine
carrier respectively:
()
{
}
()
()
1min,1
prot t roprot
kkp DQ kkcccQ
π
=− − −− − ++
(10)
{
}
()
min ,
rrt t rprot
kp DQ k c c c Q
π
=−++
(11)
{
}
()
min ,
oot t oprot
kp DQ k c c c Q
π
=−++
(12)
Compare the result with the overall profit
function of the supply chain of centralized
decision
p
π
, and we can find:
()
1
prot
kk
ππ
=−−
(13)
rrt
k
ππ
= (14)
oot
k
ππ
= (15)
In this case, we can figure out that the profit
function of each part of decentralized decision and
the overall profit function of centralized decision are
affine. Therefore, when the market reaches a plateau,
the revenue sharing coefficient can maintain its
coordination by adjusting the supply chain.
Proposition 2. The road carriers and ocean
carriers are the independent information-sharing
carriers in the supply chain, and their revenue
contract coefficients satisfy the following
relationship when the supply chain is coordinated:
()()
or r ro o
kckc
θθ
−= − (16)
Let
**
ro
QQ= , then
11
oo
rr
rp op
c
c
kp kp
θ
θ
−
−
+=+
.
The above equation can be obtained after
simplification. At this time, the optimal volume of
the three parties in the three-stage chain of the port is
equal to the optimal volume of the system, from
which it can be obtained that under the coordination
of the revenue sharing contract, the optimal volume
of the participating parties are the same, and their
profit functions are affine to the overall income
function of the supply chain, and the supply chain
reaches coordination.
Proposition 3. The pricing of ocean carriers and
road carriers are negatively correlated with their
revenue sharing coefficients respectively when the
decentralized decision parties adopt the optimal
volume under a centralized agreement, as evidenced
by the following:
According to Proposition 1, if supply chain
coordination is to be achieved under the revenue
sharing contract, the optimal agreed volume for road
carriers and ocean carriers is:
()
*1
1
1
pro
p
rop
c
QF
kkp
θθ
−
++
=−
−−
(17)
As can be seen from the equation, under the
decentralized decision, if the supply chain is required
to achieve coordination, both road carriers and ocean
carriers should use this optimal agreed volume, at
this time,
** *
por
QQQ== , the optimal supply of
transportation services for the road carrier under
decentralized decision is:
*1
(1 )
rr
r
rp
c
QF
kp
θ
−
−
=+
(18)
If the road carrier is still required to maintain the
original optimal volume at this time, i.e.
**
rp
QQ= .
The relationship between its revenue sharing
coefficient
r
k
and the price of transport services
provided to the port operator
r
θ
can be obtained as:
1
orro
rr
or p por
kcck
k
cc c c
θ
θθ
−−
=+
++ ++
(19)
.. 1
o
st k <
It can be obtained from the above formula, there
is a negative correlation between
r
k
and
r
θ
, which
demonstrates that when the port operator increases
the revenue-sharing coefficient, the carrier will
correspondingly reduce the unit price of its transport
services in order to increase the freight volume to
gain more revenue. As a result, when supply chain
reaches equilibrium, the revenue-sharing contract can
regulate the overall pricing of the supply chain.
Integrators can adjust the overall price by adjusting
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
664

the revenue-sharing coefficient in order to adapt to
the normal fluctuations and changes of the market.
5 OPTIMIZATION OF REVENUE
SHARING CONTRACT
COORDINATION FOR THE
THREE-STAGE PORT SUPPLY
CHAIN UNDER THE
DISTURBANCE OF
EMERGENCIES
5.1 The Effect of Emergencies to
Three-stage Port Supply Chain
Now considering the effect of benchmark revenue
sharing contract on supply chain coordination when
emergencies lead to drastic fluctuations in market
demand, causing the distribution function of market
demand subject to change from
()Fx
to
()Gx
.
Proposition 4. Supply chain coordination cannot
be achieved if the benchmark revenue sharing
contract is still adopted in the presence of large
fluctuations in market demand under emergencies, as
evidenced by the following:
When
*
QQ>
, due to emergencies resulting in a
sharp increase in demand for cargo transportation of
the shipper, the supply chain parties need to provide
the exigent transportation capacity, the amount is
()
*
QQ− ,the unit incremental cost of exigent
production increment of port operators, road carriers
and ocean carriers are
,,
pro
μμμ
. At this time the
profit function of three parties becomes as:
()
()
()
**
1
proppro p
kkpQc Q QQ
πθθμ
=−− − ++ − −
(20)
()
()
**
rrr rp r
cQ kpQ QQ
πθ μ
=− + − −
(21)
()
()
**
ooo op o
cQ kpQ QQ
πθ μ
=− + − −
(22)
Taking the road carrier as an example, at this
point, substituting the revenue sharing ratio of the
road carrier in a stable market state into its profit
function, we can get
()
**
1
rr r
rt
rr r
c
QpQ QQ
kk k
θ
μ
π
−
=+−−
. Now
the profit function of the road carrier is not affine to
the whole supply chain’s profit function
t
π
, so the
supply chain cannot be coordinated according to the
original revenue sharing coefficient.
When
*
QQ<
,as a result of emergencies that
lead to a sharp drop in the transportation demand for
the cargo of the shipper, all parties in the supply
chain still prepare their goods in accordance with the
optimal volume
*
Q in a stable market, therefore
there will be surplus capacity
()
*
QQ− cannot be
sold, the respective increased unit opportunity cost
for port operators, road carriers and ocean carriers are
,,
pro
λλλ
. At this point the profit functions of the
three parties become as:
()
()
()
**
1
propprop
kkpQc Q QQ
πθθλ
=−− − + + − −
(23)
()
()
**
rrr rp r
cQ kpQ Q Q
πθ λ
=− + − −
(24)
()
()
**
ooo op o
cQ kpQ Q Q
πθ λ
=− + − −
(25)
By the same token, the profit function of each
party in the supply chain is not affine to the profit
function of the whole supply chain, and the supply
chain cannot be coordinated as well.
5.2 Optimizing Revenue Sharing
Contract Coordination
In order to enable the three-stage port service supply
chain to coordinate by using the revenue sharing
contract even under the disturbance of emergencies,
we improve the original revenue
sharing contract, i.e.,
the cost of exigent production increment borne by
each supply chain entity is allocated according to its
benefit coefficient in the whole.
Proposition 5. In the case of emergencies
perturbation resulting in an increase in market size,
the cost of exigent production increment is allocated
according to the benchmark revenue sharing
coefficient, at which point the adjusted revenue
sharing contract still can make supply chain back to
the coordinated situation, as evidenced by the
following:
Assuming that the emergencies make the market
demand expectations increased to
Q
, let the optimal
volume obtained by adopting revenue sharing
contract coordination under the stable operation of
the market is
*
Q
, then the revenue functions for
each of the decision parties are shown as:
()
()
()
()
()
'*
*
1
1
proppro
ro p r o
kkpQc Q
kk QQ
πθθ
μμμ
=−− − ++
−− − + + −
(26)
The Study based on Coordination of Revenue Sharing Contract in Three-stage Port Supply Chain under Emergencies
665

()
()
()
'* *
rrr rp rpro
cQ kpQk QQ
πθ μμμ
=− + − ++ −
(27)
()
()
()
'* *
ooo op opro
cQ kpQk QQ
πθ μμμ
=− + − ++ −
(28)
Now respectively substitute the revenue sharing
ratio between each subject and the whole
()
1,,
roro
kkkk−− into
'''
,,
p
ro
πππ
, we can find
that the profit functions of road carriers, ocean
carriers and port operators are still affine to the
revenue function of the whole supply chain, i.e. the
port supply chain is re-coordinated. In the three-stage
port service supply chain, the company that receives
more shared revenue also needs to bear greater costs
accordingly to achieve the overall coordination of
supply chain.
Similarly, when the market demand is reduced by
emergencies, the newly increased opportunity costs
of all parties in the supply chain are distributed
according to the benchmark revenue sharing
coefficient. The adjusted revenue sharing contract
can also make the income function of all parties
involved in decision-making form an affine
relationship with the overall income function, that is,
the supply chain can achieve coordination again.
In that case, the current market demand is the
optimal transportation service provision for the
whole supply chain. Thus, through revenue sharing
contract, it is possible to optimize and adapt to
specific volumes. This enables enterprises in the
supply chain to have a strong risk response
capability, which greatly enhances the overall
earnings of the supply chain and realizes the risk
sharing of the supply chain.
6 CASE ANALYSIS
Assuming that the market demand
D
satisfies the
uniform distribution of
[
]
30,60 ,
5, 6, 4, 5
2, 0.2, 0.3, 48
pro r
or o p
ccc
kk p
θ
θ
====
== = =
Under the above conditions, coordination
between carriers is achieved when satisfying
**
ro
QQ= , the relationship between the revenue
sharing contract coefficients
()
, k
θ
for road and
ocean carriers is shown in Figure 2:
Carrier Price
Figure 2: Relationship between carrier yield sharing
coefficient
and price .
It can also be seen from the figure that there is a
negative correlation between the price of each carrier
and its yield coefficient.
Under decentralized decision, when the revenue
sharing coefficient, unit cost and unit price of each
carrier and port operator are respectively unknown,
the relationship between the optimal agreed volume
of carriers and each coefficient is shown as:
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
Yield Coefficient
-5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Road Carrier
Ocean Carrier
Figure 3: Relationship between carrier yield sharing
coefficient
and optimal volume.
The figure shows that the optimal agreed volume
of road carriers and ocean carriers are positively
related to their respective yield sharing coefficient.
Through the case analysis, we compare the yield
sharing coefficient of road carriers and ocean carriers
separately with the optimal agreed volumes and their
own selling prices, and visualize how the revenue
sharing coefficient coordinate the whole
supply chain.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
666

7 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we only considered the contingency
response of the three-stage port service supply chain
when the market price is stable. We first propose the
use of revenue sharing contract for the stable market
to achieve coordination among the participants of
the three-stage port supply chain so as to maximize
the overall revenue of the supply chain. Further, we
consider the impact of emergencies on the
transportation demand of cargo owners in
the market,
where the disturbance of such emergencies can make
the originally coordinated supply chain no longer
coordinated. For this reason, we adjust the existing
revenue sharing contract model so that each entity
shares the cost of the whole supply chain in
proportion to the revenue coefficient, and in this
case, the improved revenue sharing contract can
restore the system to coordination after the
perturbation.
The study concludes that when the disturbance of
transportation cost and market demand caused by
emergencies is small, the transportation plan does not
need to be adjusted and the supply chain system has
the ability to recover itself; however, when the
disturbance of emergencies is large enough to
influence the transportation cost, the original revenue
sharing contract cannot achieve the purpose of risk
sharing and the revenue sharing coefficient of each
entity need to be adjusted in time. The improved
revenue sharing contract can enable the supply chain
companies to share the risk to cope with emergencies
and maximize the overall revenue.
In this paper, we only consider the applying and
improving of revenue sharing contract and enable it
to effectively coordinate the supply chain system
under emergencies under the situation where the the
information is complete, the data such as cost
structure and profit function of each supply chain
node enterprise is available, and the demand
distribution faced by retailers can be predicted, and
the risk is neutral.
Further in-depth research is needed to address the
complex situation of incomplete information of the
supply chain system and different risk attitudes of the
node companies.
REFERENCES
Chen Wentao, Liu Lang. Revenue-sharing contracts for
three- stage supply chain coordination for
extraordinary emergencies, Journal of Catastrophology
2014, 29(04): 23-28.
Du Shaofu, Du Chan, Liang Liang, Liu Tianzhuo. Supply
chain contracts and coordination that considers equity
concerns, Journal of Management Science, 2010, 13
(11): 41-48.
Gérard P. Cachon,Martin A. Lariviere. Supply Chain
Coordination with Revenue-Sharing Contracts:
Strengths and Limitations. Management Science,
2005, 51(1)
Liu Chongguang, Liu Lang. Price stochastic closed-loop
supply chain under the condition of emergency
quantity flexibility contract. Journal of Beijing
institute of technology (social science edition), 2020,
22 (02): 50 -59, DOI: 10.15918 / j.j bitss1009-
3370.2020.7955.
Li Zhifang, Liu Wei, Cheng Guoping. Research on supply
chain profit distribution strategy based on stackelberg
game. Logistics Technology, 2008(05):91-92.
Lu Yongming. Port coordination mechanism of supply
chain benefit-sharing contract. Journal of Shanghai
maritime university, 2017, 38 (01): 52-56. DOI:
10.13340 / j.j smu 2017.01.011.
Liu Qiusheng, Hu Xiaoyue, Hou Yunzhang. Research on
four-stage supply chain coordination under emergency
based on revenue sharing contract. Science and
technology management research, 2013, 33(12): 228-
233.
Liu Chongguang, Liu Lang. An emergency quantitative
elastic contract for closed-loop supply chain under
stochastic price. Transactions of Beijing Institute of
Technology (Social Science Edition), 2020,22(02):50-
59.DOI:10.15918/j. jbitss1009-3370.2020.7955.
Lu Jing, Qiao Yu, Xu Peng.4PL Port Supply Chain
Enterprises competition and cooperation and interest
coordination strategy, Journal of Dalian Maritime
University, 2020, 46(02): 49-58.
DOI:10.16411/j.cnki.issn1006-7736.2020.02.007.
Niu Chunyang. Research on Emergency Management of
Supply Chain under Revenue Sharing Contract. Xidian
University,2009.
Pang Qinghua, Zhang Yue, Hu Yulu, Chen Huamin. A
demand - dependent price–sharing contract for three -
stage supply chain under emergency, Journal of
Systems Management. 2015, 24(06): 887-896.
Peng Haiyan, Chen Weijiong, Liang Chengji. Study on the
contingency strategy of three-stage supply chain under
joint contract. Journal of Central China Normal
University (Natural Science edition), 2017, 51(01):40
-46.DOI: 10.19603/j.cnki.1000-1190.2017.01.007.
Pang Qinghua. Study on coordination of three-stage
supply chain response to emergencies under revenue
sharing Contract, Chinese Management Science, 2010,
18(04): 101-106. DOI: 10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-
207x.2010.04.009.
Wang Jiahao, Chen Zigen, Xin Congying, Yang Ang.
Coordination strategy of port logistics service supply
chain considering demand disturbance, Journal of
Dalian Maritime University .2021.1-9
Wang Yonglong, Fu Heng, Fang Xin, Jian Ming. Supply
chain coordination strategy under emergent output,
The Study based on Coordination of Revenue Sharing Contract in Three-stage Port Supply Chain under Emergencies
667

Chinese Management Science, 2019,27(07):137-
146.DOI: 10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003207x.2019.07.013.
Xu Guangye, Dan Bin, Xiao Jian. Research on Dual-
channel Supply Chain Coordination Based on
Improved Revenue Sharing Contract. Chinese
Management Science, 2010, 18(06): 59-64.
DOI:10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2010.06.008.
Yang Bofeng. Research on port supply chain coordination
based on revenue Sharing contract under multimodal
transport, Southwest Jiaotong University.2018.
Ye Fei, Li Yina, Hu Xiaoling. A study on sharing revenue
contract of supply chain technology Innovation under
uncertain demand. Research on Science
andTechnology Management. 2005(03): 81-83.
Zhou Xianxian. Research on coordination of secondary
slogistics service supply chain based on joint contract.
Bohai University,2019.
Zhang Zhiyong, Zheng Chenghua, Song Xuefeng. Benefit
distribution analysis of port logistics service supply
chain based on improved Shapley value. Industrial
technical economy. 2009, 28(06):113-115.
Zhao Gang. Research on Rizhao Port Supply Chain
management based on vertical strategic alliance.
Hohai University, 2007
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
668
