
Management of Modern Enterprise Development: Digital
Competence Formation within the Context of Crisis Management
Matukova Наnna
1a
, Bahashova Natalia
2b
, Matukova-Yaryha Daria
1c
, Korovina Olena
3d
and Oleksandr Olesnevych
2e
1
National Medical University named after O.O. Bohomolets, Kyiv, Ukraine
2
State University Economics of Technology, Kryvyi Rih, Ukraine
3
Kryvorizkyi derzhavnyi pedahohichnyi universytet, Kryvyi Rih, Ukraine
Keywords: Enterprise, Strategy, Crisis Management, Strategic Management, Modern Conditions, Digital Competence.
Abstract: The article suggests financial control principles for crisis management (implementation of the anti-crisis
development strategy) including compliance of the selected strategy with parameters of the internal and
external environment, compliance of the organizational structure with parameters of the internal and external
environment; the optimal structure of property and liabilities; the optimal income-expenses ratio; the optimal
cash inflows-outflows ratio. It is proven that the anti-crisis strategy can only be applicable to a particular
enterprise as there is no universal strategic crisis management. It is ascertained that each enterprise has its
own features of the management structure and a financial mechanism of its provision, so strategy formation
is specific and depends on the enterprise’s position on the market, dynamics of its development and potential,
competitors’ behavior, characteristics of manufactured products (provision of services), the state of the
country's economy, the business environment and many other factors. The necessity and ways of digital
competence formation in the conditions of crisis management are determined.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today, intensification of world globalization
processes and the economic recession have
influenced basic economic factors of the external
environment on activities of national enterprises.
A new paradigm of enterprise development
management is gaining significance. The paradigm is
different from the classical one in recognition of
uncertainty, transition from the wish for stability to
flexibility, provision of long-term efficiency of
activities using not only quantitative, but also
qualitative indicators in the in-depth study of their
causes.
There arises an urgent need to reassess the
structure and the content of the enterprise
development mechanism and adapt its elements to
current economic conditions. Considering this, the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5680-0451
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5242-1224
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7217-8658
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3030-5484
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7076-0679
environmental security problem should be solved by
involving individual industrial enterprises that are to
be considered as an initial stage of green production
which envisages constant recreation of scientific
ideas, information materials, technical means and
engineering solutions to provide a mechanism of
efficient resource use and green production
conditions. Nowadays, it is of primary importance to
develop innovative technological processes that
could provide the foundation for waste-free green
production with high engineering and economic
indices and integrated resource use. Because of some
technical and economic reasons, it is impossible to
transit to waste-free technology immediately. Green
production technologies imply step-by-step transition
to low-waste and then waste-free closed-loop cycles.
Only in this way, the goals of sustainable resource use
Hanna, M., Natalia, B., Daria, M., Olena, K. and Olesnevych, O.
Management of Modern Enterprise Development: Digital Competence Formation within the Context of Crisis Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0011341300003350
In Proceedings of the 5th International Scientific Congress Society of Ambient Intelligence (ISC SAI 2022) - Sustainable Development and Global Climate Change, pages 59-66
ISBN: 978-989-758-600-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
59

and environmental protection can be achieved
(Matukova at al., 2021).
2 MANUSCRIPT PREPARATION
The problems of enterprise development
management are touched upon in scientific works by
such foreign and national researchers as O.L.
Haponenko, Ye.H. Yeliferov, Yu.S. Pohorelov, O.V.
Raievneva, M.R. Tymoshchuk, L.V. Frolova, M.
Hammer and others. Paying tribute to the significant
scientific and practical context of the mentioned
researches into the problem of enterprise
development, some tasks of a conceptual nature
remain unsolved. Today, scholars consider certain
aspects of enterprise development management, but
do not pay sufficient attention to substantiating a
comprehensive system of management (Portiankova
et al., 2020).
The research aims to study and suggest principles
of financial control for crisis management
(implementation of the anti-crisis development
strategy) including compliance of the chosen strategy
with parameters of the internal and external
environment; compliance of the organizational
structure with parameters of the internal and external
environment; the optimal structure of property and
liabilities; the optimal income-expenses ratio; the
optimal cash inflows-outflows ratio, as well as
determination of digital competence formation within
the context of crisis management.
Presentation of main materials and substantiation
of the research results obtained. While managing
enterprise development, its main aim, basic tasks and
principles are formed through implementation of
certain functions. According to the general theory of
management, the process of development
management at an enterprise can be realized through
the following basic functions:
- forecasting (planning) includes defining target
guidelines, setting tasks of operation (tactics) and
development (strategy), determining ways and means
of implementing plans;
– organization and coordination include creation,
coordination of factors and processes of plan
implementation;
– stimulation and intensification involve creation
of personnel’s motives and incentives to perform
coherent and effective actions;
– monitoring implies systematic observation of
activity results, their analysis, adjustment of plans,
ways and means of their implementation
(Pashchenko, 2011).
Development is not a one-time non-recurrent
transformation aimed at achieving the best (and
therefore the primordial) state of a system. It is a
process that does not stop in time, the course of which
does not always occur constantly and continuously
most often going in jumps along with overcoming
crises of various depth and coverage (Vasilenko,
2011).
Management of enterprise development is
basically aimed at providing its effective operation.
Reliability, sustainability, survivability, and
motivation for development are main components of
viability that reflect various aspects of business
activity (Kashuba, 2011).
L.M. Shymanovska-Dianych generalizes
approaches to providing a definition of development
as a philosophical category: development is a process
of self-progression from the lowest level to the
highest one, this resulting in disclosure and
implementation of internal trends, revealing the
essence of phenomena, emergence of something new
and causing changes in various forms of matter
(convenience translation) (Shimanovska-Dianich,
2012.
In managing development of a modern enterprise,
crises should be focused upon. The beginning of a
crisis can be predicted using the theory of cycles and
crises. By studying the change in the enterprise’s life
cycles, it is possible to determine some turning points
approaching and with sufficient probability set timing
of their achievement and depth of shocks
(Prokopyshyn, 2021).
Development of the enterprise involves formation
of its strategy. The concept of strategy is derived from
the ancient Greek word strategia (stratos means army
and ago – the art of the commander) that describes the
most important part of the military art. As for
development of the economic sphere, the concept of
the enterprise strategy first appeared in 1911 at
Harvard University where a course of business policy
began being taught. In the 1960s, there arose a
scientific interest in the concept of strategies.
Today, there are a number of definitions of the
strategy that interpret this concept depending on the
research object and the subject in relation to a
particular situation.
H. Mintzberh distinguishes five definitions of the
strategy: as a plan (a system of consistent actions); as
a position (determining the position of an
organization in the external environment and in
relation to its main competitors); as a smart trick; as a
principle of behaviour; and as a prospect (Porter,
2005).
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
60

The enterprise’s strategy covers long-term, most
fundamental, important instructions, plans, and
intentions of its management regarding production,
income, costs, investments, prices, and social
protection (Melnyk, 2012).
Strategies are formed in three directions:
- the strategy of cost control based on reducing the
enterprise’s own costs compared to those of its
competitors through mandatory control over costs, or
by regulating the size of the enterprise and the volume
of products, due to which its higher performance is
achieved;
- the differentiation strategy, the essence of which
consists in focusing the enterprise’s efforts on several
priorities to have more advantages over other
enterprises; here directions can be different, so there
are many options of the strategy in practice.
- the focusing strategy when the enterprise
purposefully focuses on either a certain group of
consumers, a limited range of products, or a specific
geographical market, a niche in the market most often
being meant here.
As a rule, there are some obstacles hindering
implementation of the formed strategies:
- in most cases, the strategy development process
is not in line with actual strategy implementation; the
strategy is developed considering the enterprise’s
activities for the future, while its implementation
occurs in the current period, so the response to any
changes in the external and internal environment
should be timely;
- a strategy is considered only from the viewpoint
of competition, but not changes in the enterprise’s
activities due to changes in the external environment.
Thus, the enterprise’s strategy consists of planned
actions (the formed strategy) and necessary
amendments in case of unforeseen circumstances
(unplanned strategic decisions). The enterprise
should have a substantiated strategy of actions, yet be
ready to adapt to unexpected circumstances that may
arise in the future.
The purpose of anti-crisis control over the
enterprise’s finances should be based upon principles
of unity of motives, tools and results. From this point
of view, anti-crisis control over the enterprise’s
finance aims to financially enhance long-term
development and existence of the enterprise on the
market. All preventive measures of crisis financial
management can be grouped as follows:
- general measures that enhance the economic
security level of a business entity and ensure stability
of its economic development;
- specific measures as a prompt response to current
threats. The measures are not subject to typification
due to the unique nature of a particular crisis, and
their choice and potential to combine are primarily
associated with the level of professionalism of crisis
managers, their intuition and accumulated
experience.
The crisis management programme should
combine general and specific measures. General
measures that form the enterprise’s protective
reaction and increase its ability to withstand crises
and trends should be developed on a continuous basis
independent of real crisis threats occurring.
Principles of financial management include:
- aim/result-orientation: a crisis programme
cannot be developed without considering hierarchy of
aims of a particular enterprise’s operation;
- reliance on monitoring financial indicators:
building a system of prompt monitoring changes in
key indicators of the enterprise and the environment
to prevent crisis risks;
- predominance of managerial influence:
forecasting crises threats prior to development of
strategic plans in order to consider measures to
prevent serious crisis losses and lost financial
opportunities;
- financial flexibility: maintaining sufficient
solvency of the enterprise by planning future financial
flows through applying a strategic approach to
selecting alternatives for financial resources
allocation and deterring excessive innovations;
- economic feasibility of management:
preliminary assessment of economic feasibility of
implementing a specific measure of crisis financial
management at the enterprise, comparing possible
financial losses and costs of implementing the
corresponding measure;
- compliance of the feedback form: informational
support of implementing anti-crisis methods
(Tkachenko at al., 2018).
Efficiency of implemented measures of the crisis
financial management system of the enterprise is
based on a set of principles that each manager should
follow. Basic principles of financial management are
as follows (Fig. 1).
In addition to the above principles, one can use
general principles of management, namely
systemacy, coherence (integration) of diversity, self-
regulation, self-training, and selectivity.
Foreign scholars identify five groups of key
competences that a specialist should possess:
1) political and social competences;
2) multiculturalism, i.e. the ability to
communicate with different cultures and religions;
3) sociability;
Management of Modern Enterprise Development: Digital Competence Formation within the Context of Crisis Management
61

4) digital competences related to the emergence of
the information society;
5) competences aimed at personal and
professional life-long self-development (Oleshko at
al, 2019).
Figure 1: Principles of financial management (Tkachenko
at al., 2018).
A competence is often seen as a quality, a
characteristic of a person that allows them (or even
gives the right) to solve certain problems, make
decisions, judgments in a particular field. The quality
is based upon knowledge, awareness, and experience
of social and professional activities (Vedernikov at
al., 2018).
The National Qualifications Framework approved
by the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine (Decree #1341
as of November 23, 2011) defines that a competence
is a dynamic combination of knowledge, skills, ways
of thinking, views, values and other personal qualities
that determine a person's ability to socialize
successfully, perform professional and/or further
academic activities (Pro zatverdzhennia Natsionalnoi
ramky kvalifikatsii: Postanova Kabinetu Ministriv
Ukrainy vid 23.11.2011 r. № 1341).
The concept of professional competence covers
some specified skills including the requirement to
perform certain individual tasks, use knowledge and
skills in the workplace as established by requirements
(standards) for this job, the ability to responsibly
perform duties and achieve planned results, etc.
(Matukova, 2014). Summarizing the above, we can
use the formula of the professional competence
suggested by V. Lozovetska (Lozovetska, 2002):
Professional Competence = [(Knowledge+Skills)
+ Emotional intelligence] x Creativity
Thus, in this approach, a professional competence
can be defined as an integral characteristic of a
specialist’s business and personal qualities, which
reflects the level of knowledge, skills, and experience
sufficient to perform professional duties at a certain
level.
Summarizing the main approaches to
understanding the concepts competence and
professional competence, it can be argued that a
professional competence is professional-status
opportunities for a person to exercise state, social and
personal authority in professional activities.
The competence characterizes a person’s
integration into professional activities, their social
and psychological maturity, professional orientation
of their worldview and appropriate value orientations.
In current conditions, with rapid rates of
information technologies development, various
devices are constantly appearing and the number of
Internet users is growing. Researchers indicate
(Oleshko, 2019) that the key technologies impacting
human development will include robotics, artificial
intelligence, the Internet of Things, cloud computing,
big data, three-dimensional printing, digital payment
systems, interoperable technology systems and
platforms. Today, digital technologies are used by the
state, businesses and citizens. They are increasingly
present in various areas of life, so it is important that
all social groups of people are ready to use them
effectively (O kompetencjach cyfrowych w Polsce na
konferencji umiejętności cyfrowe, 2019).
The peculiarities of anti-crisis management in the
digital economy must be taken into account not only
at the stage when the enterprise has already found
itself in a crisis situation, but when building an
integral management system.
Scientists emphasize that total digitization of all
hierarchical levels of the economic system creates a
need for human resources of a new quality.
Consequently, it is necessary to form and develop the
personnel’s digital competence to provide an
opportunity to perform actively in the information
environment and use the latest technological
advances in professional activities.
On 17 January 2018, an updated version of key
competences for lifelong learning was approved
(recommendations 2018/0008 (NLE) of the European
Parliament and the EU Council) (Council
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
62
Recommendation on Key Competences for Lifelong
Learning), which include:
Literacy competence
Language competence
Mathematical competence and competence in
science, technology and engineering
Digital competence
Personal, social and learning competence
Civic competence
Entrepreneurship competence.
Cultural awareness and expression competence
(Kliuchovi kompetentnosti dlia navchannia
vprodovzh zhyttia, 2018).
In order to implement the accelerated scenario of
digital development, which is the most relevant for
Ukraine in terms of challenges, needs and
opportunities, the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine
approved The Concept of Digital Economy and
Society of Ukraine for 2018-2020 (Decree #67-p as
of January 17, 2018), which provides for
implementation of appropriate incentives for
digitalization of the economy, public and social
spheres, awareness of current challenges and tools for
digital infrastructure development, acquisition of
digital competences, identifies critical areas and
projects of digitalization, and stimulates the national
market of digital technology production,
consumption and use (Pro skhvalennia Kontseptsii
rozvytku tsyfrovoi ekonomiky ta suspilstva Ukrainy
na 2018-2020 roky ta zatverdzhennia planu zakhodiv
shchodo yii realizatsii, 2018).
The features of anti-crisis management of an
enterprise in the context of digitalization are
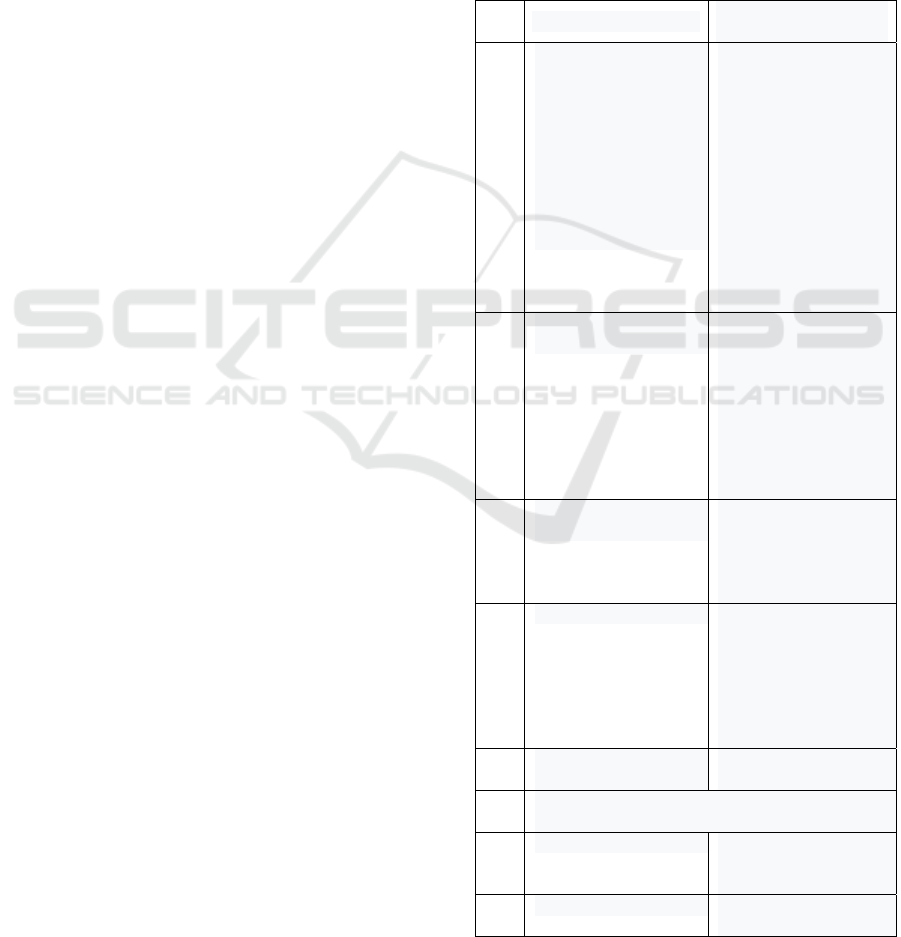
summarized in Table 1 (Butrova, 2021).
The transition to the digital economy also imposes
new requirements on the head of the enterprise, on his
professional competencies in the field of
management, personnel management, and IT
technologies.
The issue of creating a corporate culture based on
effective interaction at all management levels and
readiness for change is also important.
According to the Concept, development of
Ukraine's digital economy consists in creating market
incentives, motivations, demand and forming needs
for using digital technologies, products and services
among Ukrainian industries, life activity areas,
business and society to ensure their efficiency,
competitiveness and national development, high-tech
production and well-being of population.
The digital economy can evolve through
developing the national market of production, use and
consumption of information, communication and
digital technologies. Digital development involves a
set of tasks that will positively influence the
economy, business, society and life of the country as
a whole.
Introduction of digital jobs concept is also among
digitalization areas in the Concept. Digital workplace
is the virtual equivalent of the physical one, which
requires proper organization, use and management, as
it should guarantee increased efficiency of employees
and create more favourable working conditions for
them (Matukova at al., 2021).
Table 1: Features of anti-crisis management of an enterprise
in modern conditions of digitalization.
№ Feature
Impact on anti-crisis
management processes
1 The possibility of
using automated
control systems for
collecting, processing
and analyzing big data
in real time, as well as
generating new models
and algorithms of
behavior using
artificial intelligence
Efficiency of data
provision, incl. already
calculated financial and
economic ratios and
other indicators
necessary for making
managerial decisions.
Using the capabilities
of artificial intelligence
to generate new models
and algorithms for the
system's response to
certain values, markers
2 Digital ecosystem:
internal and external
Efficiency of
interaction with
government agencies,
customers, suppliers.
Additional advantage
over “traditional”
companies not
involved in the digital
ecosyste
m
3 "The paradox of
profitability"
Growth of
capitalization of digital
companies against the
background of their un
p
rofitableness
4 High rate of change The need to accelerate
management decisions
and predict the
dynamics of
development of the
macro- and
microenvironment
5 The dynamism of the
macro environment
The need to take into
account risks
6 Possibility to reduce costs through the use of
di
g
ital technolo
g
ies
6.1. Remote work Possibility to reduce
office maintenance
costs
6.2. Using digital twins Possibility to reduce
costs for real tests by
Management of Modern Enterprise Development: Digital Competence Formation within the Context of Crisis Management
63

using digital twins
(study of technical
characteristics, such as
strength, reliability,
functionality, etc.) with
the ability to design at
a given cost
6.3. Digital sharing
platforms
Possibility to reduce
the cost of maintaining
fixed assets
Public administration is a separate area of
digitalization in the Concept covering synergetic
potential of social, mobile, and cloud technologies,
data analysis technologies, the Internet of Things
which individually and together can lead to
transformational changes in public administration
and make the public sector efficient, reactive and
valuable (Diadin, 2019).
The Concept of Development of Digital Economy
and Society of Ukraine states that implementation of
initiatives to digitize public institutions should
consider the following technological concepts: the
digital workplace of civil servants, multichannel
information supply and involvement of citizens, open
data, the Internet of Things, digital government
platforms, and blockchain.
In addition, the Concept indicates that Ukraine’s
public administration with the growing number of
tasks, initiatives, projects and simultaneous cost
optimization should be based on technological and
digital forms of providing its smooth and effective
operation. All digitalization measures can cause
transformational changes in public administration,
make the public sector efficient and the country's
economy developed.
They should form timely anti-crisis programmes
of enterprises of all forms of ownership, create the
personnel’s motivational demand for mastering
digital competences and form the need for using
digital technologies to make business and individuals
competitive on the economic market.
The anti-crisis strategy can include the following
structural blocks:
- situational actions of financial orientation to
adapt to new conditions that will form the most likely
of possible and/or expected future critical events;
- mandatory actions to ensure and improve
security of the production and economic system; they
are reflected in the enterprise’s strategic plan and
focused on increasing business profitability, reducing
or eliminating financial pressure of expected adverse
events. Anti-crisis measures of the programme
include prevention of increasing unprofitable
potential by eliminating low-income industries,
aligning with the basic potential of support and
service potential, as well as strengthening quality of
identifying and implementing synergies and
developing key competences;
- mandatory operational actions to overcome
bottlenecks to increase profitability, as well as
specific measures to intensify financial inflows and
firmly regulate financial outflows of assets to
maintain ongoing solvency;
- measures to strengthen control over
implementing anti-crisis decisions to ensure the
planned set of actions and measures. National
enterprises usually have underdeveloped or
centralized services involved in developing anti-crisis
measures, elaborating, implementing and monitoring
financial plans, conducting systematic assessment of
the enterprise financial condition.
In current conditions of the COVID-19 pandemic,
the need to adapt to new economic conditions forces
us to look for ways to use available production
capacity. Simulation can be used to choose the
strategy of enterprise development by reproducing
events that occur simultaneously or sequentially in
simulation time (Kompanets at al., 2021).
The main task of developing a simulation model
is to choose an optimal strategy for enterprise
development and determine the maximum profit that
should be expected from implementation of the
strategy with limited investment, which is the subject
of our further research.
3 CONCLUSIONS
The proposed principles of financial management are
aimed at providing crisis management
(implementation of the anti-crisis development
strategy): compliance of the chosen strategy with
parameters of the internal and external environment;
compliance of the organizational structure with
parameters of the internal and external environment;
the optimal structure of assets and liabilities; the
optimal income-expenses ratio; the optimal cash
inflows-outflows ratio.
In most cases, a crisis arises at the managerial
stage starting with errors in management,
disorganization, non-optimized business processes,
etc.
The anti-crisis strategy can be applicable only to
a particular enterprise as there is no universal
strategic crisis management.
Each enterprise on the market has its own
characteristics of the management structure and the
financial support mechanism, so strategy formation is
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
64

specific and depends on the enterprise’s position on
the market, dynamics of its development and
potential, behaviour of competitors, characteristics of
products (services), the country’s economy, the
business environment and many other factors.
The formation of a new digital technological
paradigm leads to the emergence of new features that
affect the processes of anti-crisis management.
Many of them open up new opportunities for the
enterprise and increase the likelihood of a faster
overcoming of crisis phenomena, however, if we are
talking about a manufacturing enterprise that, due to
certain reasons, is not able to flexibly adapt to new
requirements and market challenges, it is necessary to
build an integral system, the key components of
which are presented in the study.
At the same time, it should be noted that today
much depends on the professionalism of the leader
himself, his experience and creativity in approach to
crisis management, professional outlook, leadership
qualities and so-called soft skills, openness to new
tools and management mechanisms, as well as
corporate loyalty and professionalism of the team.
In current conditions of the COVID-19 pandemic,
we should adapt to new economic conditions and look
for ways to intensify available production capacity,
which is the subject of our further research.
REFERENCES
Matukova, H., Khrapkina, V., Bahashova, N., Matukova-
Yaryha D., and Mamanazarov, M. (2021),
“Environmental Management in Condition of Stable
Development and Efficient Use of Resources”,
ISCSEES 2020 IOP, Conf. Series: Earth and
Environmental Science, Ivano-Frankivsk, Ukraine,
January 2020, IOP Publishing. DOI:10.1088/1755-
1315/628/1/012020
Portiankova, N.L., Diatlova, V.V., and Nersesov, V.R.
(2020), “Strategic development of enterprises in the
sphere of telecommunications based on the project
approach”, Zb. nauk. prats za materialamy kruhloho
stolu [Collection of research works from the round-
table materials], Aktualni problemy ekonomiky ta
upravlinnia: zovnishnoekonomichni, innovatsiini ta
finansovi aspekty [Current problems of economics and
management: foreign economic, innovative and
financial aspects], Mariupol, Ukraine, 29 May 2020,
pp. 74–83.
Pashchenko, O.P. (2011), “Strategic management of
enterprise development”, Visnyk Khmelnytskoho
natsionalnoho universytetu, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 99–103.
Vasilenko, V.A. (2011), “Organizational-cyclic and
structural-functional models of organizational
development”, Kultura narodov Prychernomoria, vol.
232, pp. 100–107.
Kashuba, Ya.M. (2011), “Choice of methods and
approaches of strategic management of business
development”, Ekonomika ta derzhava, vol. 9, pp. 16-
17.
Shimanovska-Dianich, L.M. (2012), Upravlinnia
rozvytkom personalu orhanizatsii: teoriia i praktyka
[Management of organization personnel development:
theory and practice], PUET, Poltava, Ukraine.
Prokopyshyn, O.S. (2021), “The system of anti-crisis
management as a basis for prevention of crisis
phenomena at enterprises”, Investytsii: praktyka ta
dosvid, vol. 9, pp. 40-45.
Porter, M.E. (2005), Konkurentsyia [Competitiveness],
Vyliams, Moscow, Russia.
Melnyk, L.G. (2012) Ekonomika pidpryiemstva:
pidruchnyk [Enterprise economy], Universietskaya
kniga, Sumy, Ukraine.
Tkachenko, S.O., and Speros, Dzh. N. (2018), “The concept
of anti-crisis management of enterprise finance”,
Zbirka dopovidei na Mizhnarodnii nauk.-prakt. konf.
[Conference Proceedings of the International Scientific
and Practical Conference], Suchasni problemy
pravovoho, ekonomichnoho ta sotsialnoho rozvytku
derzhavy [Modern problems of legal, economic and
social development of the state], Kharkiv, Ukraine, 30
November 2018, pp. 279‒281.
Oleshko, A.A., and Usatenko, A.O. (2019), “Formuvannia
ta rozvytok tsyfrovoi kompetentnosti personalu”
[Formation and development of personnel’s digital
competence], URL:
http://www.investplan.com.ua/pdf/23_2019/5.pdf
Vedernikov, M.D., Chernushkina, O.O., and Mantur-
Chubata, O.S. (2018), “Suchasni tekhnolohii
upravlinnia personalom: kompetentsiinyi pidkhid”
[Modern technologies of personnel management; the
competence approach].
URL:http://nbuv.gov.ua/UJRN/Nvuumevcg201819%2
81%2911
Pro zatverdzhennia Natsionalnoi ramky kvalifikatsii:
Postanova Kabinetu Ministriv Ukrainy vid 23.11.2011
r. № 1341 [On approving the National framework of
qualifications: Decree of the Cabinet of Ministers of
Ukraine as of Nov. 23, 2011 #1341] URL:
https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/1341-2011-
%D0%BF
Matukova, A.Y. (2014), “Sovershenstvovanye systemы
upravlenyia personalom: sozdanye modely
neobkhodymыkh kompetentsyi” [Improvement of the
personnel management system: creation of the required
competences model] Strategii si politici de
management in economia contemporana (editia a III-a),
28-29 martie, 2014/com org: Turcanu Gheorghe [et al.],
Chisinau, ASEM, рр. 127-131.
Lozovetska V.T. (2002), “Teoretyko-metodolohichni
osnovy profesiinoho navchannia molodshoho
spetsialista silskohospodarskoho profiliu” [Theoretical
and methodological principles of vocational training of
Management of Modern Enterprise Development: Digital Competence Formation within the Context of Crisis Management
65

agricultural junior specialist]. Candidate’s thesis, Kyiv,
Ukraine.
Oleshko, A.A., and Horokhovets. Ye.V. (2019)
Informatsiino-komunikatsiini tekhnolohii ta liudskyi
rozvytok [Information and communication
technologies and human development]
URL:http://www.investplan.com.ua/pdf/16_2019/4.pd
f
O kompetencjach cyfrowych w Polsce na konferencji
umiejętności cyfrowe 2019. Pl. NASK.
URL:https://www.nask.pl/pl/aktualnosci/3603,O-
kompetencjach-cyfrowych-w-Polsce-na- konferencji-
Umiejetnosci-cyfrowe-2019pl.html
Butrova, E.V. (2021), “Osobenosti antikrizisnogo
upravleniya predpriyatiem v usloviyah tsifrovizatsii”,
Ekonomika, predprinimatelstvo i pravo, vol. 11, 3.
Council Recommendation on Key Competences for
Lifelong Learning. European Commission. URL:
https://ec.europa.eu/education/education-in-the-
eu/council-recommendation-on- key-competences-for-
lifelong-learning_en
Kliuchovi kompetentnosti dlia navchannia vprodovzh
zhyttia 2018 – Tsyfrova kompetentnist [Key
competences for lifelong leraning 2018. Digital
competence] URL:
http://dystosvita.blogspot.com/2018/01/2018.html
Pro skhvalennia Kontseptsii rozvytku tsyfrovoi ekonomiky
ta suspilstva Ukrainy na 2018-2020 roky ta
zatverdzhennia planu zakhodiv shchodo yii realizatsii:
Rozporiadzhennia Kabinetu Ministriv Ukrainy vid
17.01.2018 r. № 67-r. [On approving The Concept of
Digital Economy and Society of Ukraine for 2018-2020
and establishing the plan for its implementation (Decree
#67-p as of January 17, 2018)] URL:
https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/67-2018-
%D1%80
Matukova, H.I., Bahashova, N.V., and Matukova-Yaryha,
D.H. (2021), Antykryzovyi menedzhment: alhorytm
pidvyshchennia konkurentospromozhnosti
pidpryiemstva [Crisis management: the algorithm of
improving the enterprise’s competitiveness], Efektyvna
ekonomika [Effective economy] URL:
http://www.economy.nayka.com.ua/?op=1&z=9525
(дата звернення: 07.12.2021). DOI: 10.32702/2307-
2105-2021.11.6
Diadin, A.S. (2019), “Scenario technique in the system of
anti-crisis financial management of the enterprise”,
Sotsialna ekonomika, vol. 57, pp. 18–24.
Kompanets, K.A., Litvyshko, L.O., and Artemchuk, V.O.
(2021), “Features of innovative strategic enterprise
management during the COVID-19 pandemic”, Intelekt
XXI, vol. 1, pp. 82–86.
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
66
