
Subsurface Drip Irrigation as a Factor Ensuring Productive and
Ecological Functions of Soils
Nadiya Maksymenko, Olena Gololobova and Oleksiy Shovkun
Department of Environmental Monitoring and Nature Use, Karazin Institute of Environmental Sciences, V. N. Karazin
Kharkiv National University, Svobody sq., 6, 61022, Kharkiv, Ukraine
Keywords: Subsurface Drip Irrigation, The Ecological and Reclamation Condition of the Soil, The Ecological and
Reclamation Monitoring of the Irrigated Soil.
Abstract: Irrigation is a powerful factor influencing soil. Given the accelerated and significant change of ecosystems
under the influence of reclamation load and prevention of degradation processes, soil monitoring using
modern innovative methods becomes especially important. Soil fertility management for irrigated land should
be aimed at developing models of sustainable, environmentally friendly and cost-effective use of natural
resources. It is also essential to preserve and enhance soil productivity and its environmental and social
functions for the long term. This has set high demands for energy efficiency, environmental safety and the
economic feasibility of irrigation technologies, including in urban landscaping. The aim of the study was to
investigate the ecological and reclamation condition of the soil during long-term subsurface drip irrigation of
ornamental grass plot, linden (Tilia cordata Mill.), and white cedar 'Brabant' (Thuja occidentalis 'Brabant').
The experiment was conducted during 2018–2021. Research methods: the assessment was carried out on a
set of diagnostic indicators following the recommendations for the survey of ecological and reclamation
conditions of lands under drip irrigation. The recommendations were developed by the National Scientific
Center “Institute for Soil Science and Agrochemistry Research named after O. N. Sokolovsky”. The results
of the study show that the scoring of diagnostic agrophysical indicators is the most favorable. Subsurface drip
irrigation does not change the content of organic matter; there is no direct dependence of humus content on
irrigation. Subsurface drip irrigation does not change the nutrient status of the soil; the determining influence
of soil genetic characteristics on the content of mineral nutrients is observed. Assessment of diagnostic
indicators for the cation-anion composition of the aqueous soil extract revealed a poor soil condition in terms
of the percentage of Na++K+ from the amount of absorbed alkaline cations. The soil condition in terms of
the content of toxic salts was rated to be close to good. The degree of soil salinization by the Ca/Na ratio was
> 2.5 for both irrigated and natural grass plots. The soil condition in terms of this indicator was rated to be
good. The total pollution rates Zc under subsurface drip irrigation was similar to that for uncontaminated soils.
Assessment of the soil microelement status indicated probable excess of zinc and manganese under the
influence of irrigation. Conclusion. The scoring of the ecological and reclamation condition of the studied
soil according to diagnostic indicators showed the possibility of using subsurface drip irrigation with
compulsory further ecological and reclamation monitoring of the irrigated soil
1 INTRODUCTION
Recognition of the fundamental role of soil in climate
change adaptation and mitigation has made it one of
FAO's top priorities. This should contribute to improving
environmental security and social development,
understanding the importance of maintaining productive
and ecological functions of soils, in particular for the
functioning of terrestrial ecosystems (Baliuk & Drozd,
2017). At the same time, in the context of ecological
reconstruction of the green infrastructure of many
Ukrainian cities, preservation of existing cultivars and
hybrid forms of ornamental plants and introduction of
new ones make actual the introduction of modern
innovative technologies of landscape irrigation, including,
of course, subsurface drip irrigation.
Given the accelerated and significant change of
ecosystems under the influence of reclamation loads and
the need to prevent degradation processes, monitoring of
land in the area of these loads becomes especially
essential, with the obligatory involvement of modern
126
Maksymenko, N., Gololobova, O. and Shovkun, O.
Subsurface Drip Irrigation as a Factor Ensuring Productive and Ecological Functions of Soils.
DOI: 10.5220/0011345200003350
In Proceedings of the 5th International Scientific Congress Society of Ambient Intelligence (ISC SAI 2022) - Sustainable Development and Global Climate Change, pages 126-134
ISBN: 978-989-758-600-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

innovative and methodological approaches. Irrigated land
fertility management should be aimed at developing
models of sustainable, environmentally safe, and cost-
effective use of natural resources (Baliuk & Drozd, 2017,
Baliuk, Kucher & Maksymenko, 2021,), preserving and
increasing productive, environmental and social functions
of soils for the long term, which puts high demands on
energy efficiency, environmental safety, and economic
feasibility of irrigation technologies, including in urban
landscaping (National soil protection program of Ukraine,
2015, Maksymenko et al., 2021).
Irrigation is a powerful factor influencing agro-
ecosystems in general and soils as their main
component in particular. All constituents of the soil as
a whole system are more or less subject to the
transformative effect of irrigation. The
transformation causes the disequilibrium of the
system with the further stabilization at a qualitatively
and quantitatively new level. These changes are as
follows: the transformation of water, air, thermal and
redox regimes; intensification of biological
processes; increase in the mobility and reactivity of
minor and major plant nutrients and toxic pollutants;
increase in the dynamism and variability of some soil
physical parameters (density, hardness, stickiness,
structural properties, permeability, etc.); in some
cases, redistribution of granulometric particles of
different sizes throughout the soil profile; and
quantitative and qualitative changes in the colloidal
part (Baliuk et al., 2018).
The analysis of literature sources indicates a
water-saving effect when applying subsurface drip
irrigation: for example, water consumption has
decreased to 25–50% compared to surface irrigation
(Camp, 1998; Sinobas & Rodríguez, 2012; Camp et
al., 2020). According to USDA-NASS calculations,
the use of subsurface drip irrigation in the United
States in 2006–2016 increased by 89% (Lamm,
2016).
With the long-term use of drip irrigation,
diagnostic agrophysical indicators in moistened areas
have been favorable for plants and soils (Usatova &
Ryabkov, 2018).
The microbial soil coenosis structure was
determined in the Sector of Soil Microbiology in the
National Scientific Center “Institute for Soil Science
and Agrochemistry Research named after O. N.
Sokolovsky”. The results have proved that
microorganisms that take up organic forms of
nitrogen for 0–30 cm soil layer increased their
number from 9.25 to 10.68 million CFU/g under the
influence of subsurface drip irrigation. Organotrophic
microorganisms activation indicates that subsurface
drip irrigation has created conditions contributing to
more active assimilation of nutritious organic
substrate. According to the assessment proposed by
Zvyagintsev, the degree of enrichment of soil with
microorganisms was high without irrigation and very
high with irrigation. The number of microorganisms
assimilating nitrogen of mineral compounds was also
higher under subsurface drip irrigation: 10.29 million
CFU/g versus 7.25 million CFU/g without irrigation.
According to Zvyagintsev, the variant without
irrigation is moderately enriched; with irrigation, it is
highly enriched. Under subsurface drip irrigation, the
number of actinomycetes increased from 5.10 million
CFU/g to 6.68 million CFU/g. This indicates a
favorable trophic regime of soil. According to the
calculation, the oligotrophic index of soil was 0.37
without irrigation and 0.50 with subsurface drip
irrigation. The oligotrophic index indicates that the
studied agricultural method provides a higher content
of easily assimilable nutrients in the soil. Nitrogen
mineralization and immobilization rate characterizes
the intensity of nitrogen mineralization and
assimilation of nitrogen compounds by microbial
coenosis. In both variants, namely in the control
without irrigation and in the variant with subsurface
drip irrigation, the processes of organic matter
synthesis were found to prevail over the processes of
its destruction: in particular, this rate was 0.86 in the
control and 0.95 in the variant with subsurface drip
irrigation (Gololobova, 2020).
About 80% of arable land in Ukraine (over 24
million hectares) has such types of water regime of
soils, which form the dominance of deficient (or
periodically deficient) moisture. This makes the water
regime an extremely important factor. Irrigation is a
cardinal measure of optimization and stabilization.
However, it should be noted that the introduction of
subsurface drip irrigation into the nature management
system is possible according to the monitoring
results, subject to compliance with technological
processes of crop cultivation, environmental
reclamation monitoring (ERM) and its variety – soil
reclamation monitoring (SRM) on irrigated areas
(Recommendations for the survey, 2012).
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The study area is situated within the scientific and
experimental functional zone of the Dendrological
Park of national importance in Kharkiv National
Agrarian University named after V. V. Dokuchaiev
(Fig. 1). A field experiment was established in
autumn 2017 to survey the ecological and reclamation
Subsurface Drip Irrigation as a Factor Ensuring Productive and Ecological Functions of Soils
127

condition of the soil with long-term subsurface drip
irrigation.
Figure 1: Geographic location of study area - Dendrological
Park in Kharkiv National Agrarian University named after
V. V. Dokuchaiev.
The experiment involved experimental sites under
ornamental grass plot, with plantings of small-leaved
linden (Tilia cordata Mill.), white cedar 'Brabant'
(Thuja occidentalis 'Brabant'), and control sites
without irrigation.
The assessment was carried out on a set of
diagnostic indicators according to the
recommendations for the survey of ecological and
reclamation condition of land under drip irrigation
(Recommendations for the survey, 2012). Ecological
and reclamation condition of irrigated land is the land
condition, which is assessed by hydrogeological
(level, hydrochemical composition and
mineralization of groundwater), environmental
engineering (porosity coefficient and degree of
manifestation of exogenous geological processes),
soil reclamation (degree of salinization, alkalinization
and salinity of soils, their water-salt and nutrient
regimes, and irrigation water quality according to
agronomic criteria), ecological-toxicological (the
content of heavy metals and pesticides in the soil and
water pollution) and agronomic criteria (Baliuk &
Drozd, 2017).
Diagnostic soil indicators were determined in the
Laboratory of Instrumental Methods of Soil Research
and the Laboratory of Soil Geoecophysics in the
National Scientific Center “Institute for Soil Science
and Agrochemistry Research named after O. N.
Sokolovsky” according to certified methods (Soil
quality, 2005; Soil quality, 2009; Method of soil
sampling, 2013).
Soil diagnostic indicators were determined by
conventional methods:
- soil density was determined according to
Kachinsky’s method in 0–10 cm, 10–20 cm, 20–30
cm and 30–40 cm soil layers in spring at the
beginning of the growing season;
- macroaggregate analysis was carried out by the
dry sieving method according to Savinov; water
stability of soil aggregates was investigated by wet
sieving method in soil layers of 0–10 cm, 10–20 cm,
20–30 cm, and 30–40 cm;
- content of nitrate and ammonium nitrogen was
determined according to DSTU (State Standards of
Ukraine) 4729:2007 Soil Quality. Determination of
Nitrate and Ammonium Nitrogen in Modification
of NSC ISSAR named for O.N. Sokolovskiy;
- content of mobile compounds of phosphorus
and potassium was determined following DSTU
4114–2002 Soils. Determination of Dynamic
Compounds of Phosphorus and Potassium by the
Modified Method of Machigin;
- cation-anion composition in the soil-water
extract was determined according to DSTU
8346:2015, DSTU 7943:2015, DSTU 7908:2015,
DSTU 7909:2015, DSTU 7944:2015, and DSTU
7945:2015;
- content of mobile fractions of heavy metals in
a buffer ammonium acetate extract (pH 4.8) was
defined using atomic absorption
spectrophotometry, following DSTU 4770.1:2007,
DSTU 4770.2:2007, DSTU 4770.3:2007, DSTU
4770.4:2007, DSTU 4770.5:2007, DSTU
4770.6:2007, DSTU 4770.7:2007, DSTU
4770.8:2007, and DSTU 4770.9:2007.
Scoring of diagnostic indicators of soil was
carried out by the recommendations for the survey of
ecological and reclamation conditions of lands under
drip irrigation (Recommendations for the survey,
2012).
3 RESEARCH RESULTS
Among the physical conditions for the fertility of
medium- and heavy-textured soil, the soil density
andstructural status should be considered the most
important.
Soil density was determined at the experimental
sites according to the Recommendations for the
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
128

survey (2012) before the start of the irrigation period;
the results are presented in Tables 1–2.
The equilibrium density for the soil under the
grass plot had the optimal values after each irrigation
season during 2019–2021 for both 0–15 cm and 15–
30 cm soil layers.
The average values of soil density over the years
of the study were 1.10 g/cm
3
for the 0–15 cm layer
and 1.13 g/cm
3
for the 15–30 cm layer.
The equilibrium soil density recorded at the
beginning of the 2021 growing season showed the
optimal values after three years of subsurface drip
irrigation for white cedar both for all 10 cm soil layers
and for the 0–40 cm layer.
The score of the diagnostic indicator
(Recommendations for the survey, 2012) was
maximally positive both for the control and for the
studied variant (Table 2).
Table 1: Soil density in the experiment with subsurface drip irrigation of the grass plot, g/cm
3
, 2019–2020.
Soil layer, cm 2019 2020 2021
Average over
years
Scored ecological and
reclamation assessment
0–15 1.08 1.11 1.12 1.10 0
15–30 1.12 1.12 1.14 1.13 0
Table 2: Soil density in the experiment with subsurface drip
irrigation of white cedars, May 2021.
Variant
Soil
layer,
c
m
Soil
density,
g
/cm
3
Scored ecological
and reclamation
assessment
Control
0–10 1.08 0
10–20 0.91 0
20–30 1.01 0
30–40 1.01 0
0–40 1.00 0
Subsurface
drip
irrigation
0–10 0.91 0
10–20 0.95 0
20–30 1.06 0
30–40 0.94 0
0–40 0.96 0
Thus, long-term use of subsurface drip irrigation
during 2018–2021 did not result in soil compaction.
In particular, an optimal value of this diagnostic
indicator of the soil agrophysical condition was
recorded both under the grass plot and white cedars.
The absence of soil compaction contributed to the
soft and porous top layer preservation, promoting the
growth and development of both the root system and
the aboveground part of ornamental plants.
In modern sustainable agriculture, the structure of
soil is considered as a kind of regulator of the
processes occurring in it. It is the final result of
natural processes of soil formation and development
and therefore determines the suitability of the soil as
the habitat of the entire agrobiocenosis.
The top layer of the soil should be maintained to
have a high level of soil aggregation. Such conditions
improve moisture conservation and enhance the
efficiency of water consumption by plants (Baliuk et
al., 2018).
Table 3 shows the soil structural condition
assessed by the content of air-dry
agronomically
valuable particles with a size of 0.25–10 mm. The
subsurface drip irrigation provided an excellent
structural condition according to the classification
proposed by Dolgov in terms of the content of air-dry
agronomically valuable particles with a size of 0.25–
10 mm (Dolgov et al., 1983).
The average content of air-dry aggregates was
86.24% in the control, whilst it was 88.36% under
subsurface drip irrigation. Thus, subsurface drip
irrigation has maintained excellent soil condition by
this diagnostic soil indicator. The soil structure index
was 6.35 in the control and 8.55 in the studied variant.
It has been demonstrated that the most effective
moisture consumption occurs at the following ratio of
structural fractions: from 20 to 5 mm – 20–25%, from
5 to 0.25 mm – 60–65%, less than 0.25 – up to 15%
(Baliuk et al., 2018).
Subsurface Drip Irrigation as a Factor Ensuring Productive and Ecological Functions of Soils
129

Table 3: The content of air-dry aggregates in dry sieving in the experimental variants with white cedar plantings, May 2021.
Variant Soil layer, cm
Amount of air-dry
aggregates (0,25–10 mm),
%
Soil structure
index
Scored ecological and
reclamation assessment
Control
0–10 87.53 7.02 0
10–20 86.87 6.62 0
20–30 83.60 5.10 0
30–40 86.96 6.67 0
0–40 86.24 6.35 0
Subsurface drip
irrigation
0–10 88.87 7.98 0
10–20 83.14 4.93 0
20–30 93.25 13.81 0
30–40 88.18 7.46 0
0–40 88.36 8.55 0
Therefore, the assessment of the ratio of soil
structural fractions will be relevant in analysing the
soil structural composition. The ratio of structural
fractions in the soil under the white cedar plantings at
the above ranges is presented in Table 4.
Table 4: The ratio of the soil structural fractions at the specified ranges, %, May 2021.
Variant Soil layer, cm <0.25 mm 0.25–5 mm 5–10 mm >10 mm
Control
0–10 6.50 70.97 16.56 5.97
10–20 3.96 72.77 14.1 9.17
20–30 0.99 63.37 20.23 15.41
30–40 2.02 65.62 21.35 11.02
0–40 3.37 68.19 18.06 10.39
Subsurface drip irrigation
0–10 3.90 74.62 14.25 7.24
10–20 2.11 61.61 21.53 14.76
20–30 2.15 73.43 19.82 4.61
30–40 1.35 68.45 19.73 10.47
0–40 2.38 69.53 18.83 9.27
The results show that the ratio of soil structural
fractions at the specified ranges corresponds to the
optimal parameters for the soil structural composition
both in the control and under the subsurface drip
irrigation; in particular, the fraction of 0.25–5 mm is
68.19% in the control and 69.53% in the studied
variant. The established optimal ratio of structural
fractions is a factor improving the moisture balance
and the efficiency of its consumption by plants. The
score of the structural condition is the most favorable.
The results on the number of waterproof
aggregates (7–0.25 mm) in wet sieving are presented
in Table 5.
The results indicate that subsurface drip irrigation
provided the good structural condition of the soil in
terms of the content of waterproof aggregates sized
0.25–7.00 mm, according to Dolgov. The average
values of this indicator for the 0–40 cm soil layer were
51.65% in the control and 54.20% under irrigation.
The score of waterproof aggregates (0.25–7 mm)
content is also the most favorable.
The study of diagnostic agrophysical indicators
therefore showed that subsurface drip irrigation
preserved the soil structure. In this case, the ratio of
structural fractions corresponded to the optimal
parameters, equilibrium density was within optimal
values, and the scoring was the most favorable.
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
130
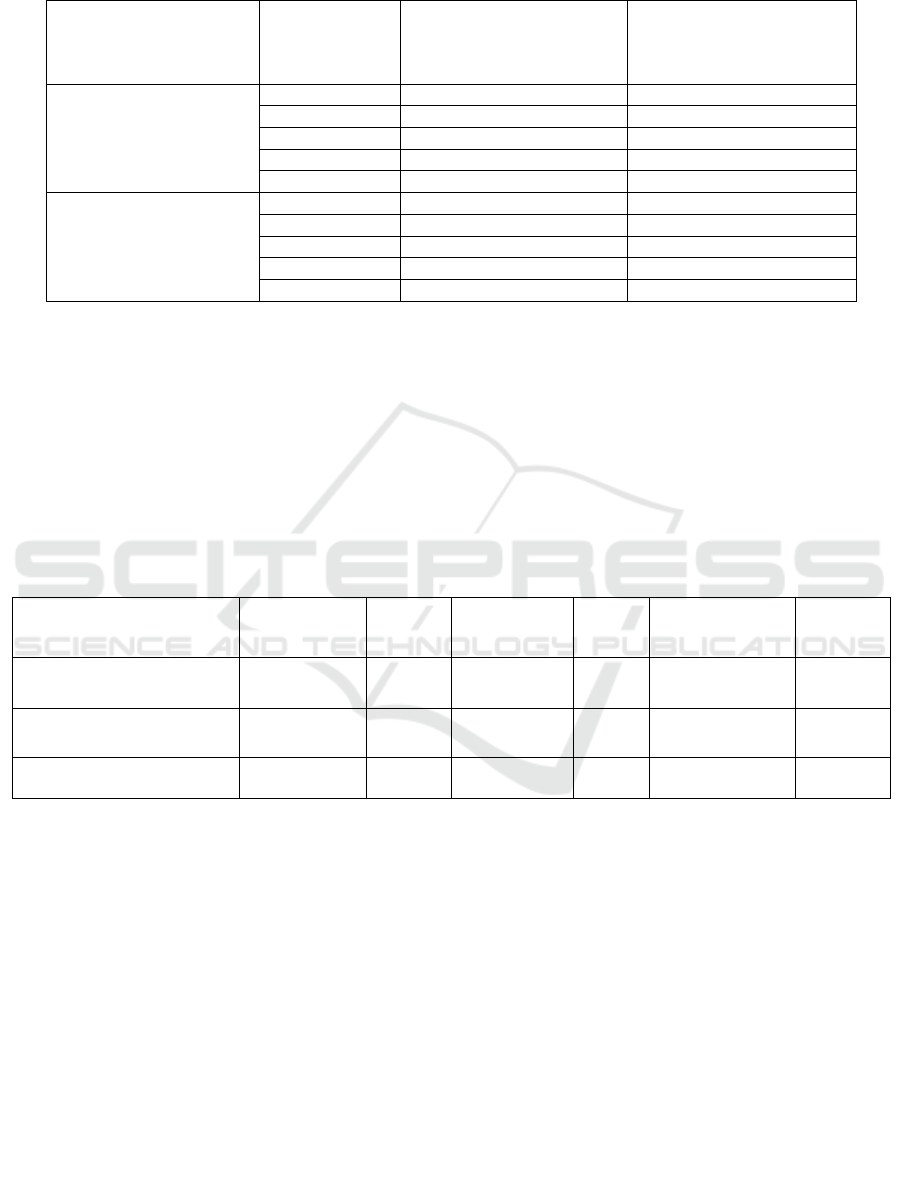
Table 5: Content of waterproof aggregates (0.25–7.00 mm) according to the experimental variants with white cedar plantings,
May 2021.
Variant Soil layer, cm
Content of waterproof
aggregates (0.25–7.00 mm),
%
Scored ecological and
reclamation assessment
Control
0
–
10 42.00
10
–
20 49.52
20
–
30 57.88
30
–
40 57.22 0
0
–
40 51.65
Subsurface drip irrigation
0
–
10 47.54
10
–
20 56.56
20
–
30 62.76
30
–
40 49.94 0
0
–
40 54.20
The soil indicators describing the soil nutrient
status are presented in Table 6.
The content of mineral nitrogen according to the
grouping of soils by this indicator is very low for both
irrigated and natural grass plots, amounting to 9.78
and 13.59 mg/kg, respectively.
In the variant with subsurface drip irrigation of
white cedar, the mineral nitrogen content is medium
and makes 18.14 mg/kg.
The results indicated good phosphate status for
the grass plot with subsurface drip irrigation, as well
as for the control site of natural grass plot.
In the soil under the white cedars, the availability
of labile phosphorus forms was very high, accounting
for 88.7 mg/kg. The availability of labile potassium
forms was high for control and irrigated sites (187.21
and 187.18 mg/kg, respectively).
Table 6: Diagnostic indicators for soil nutrient status under subsurface drip irrigation and their scoring, 0–30 cm soil layer,
2019–2020.
Variant
Р
2
О
5
content,
mg/kg
Score
К
2
О content,
mg/kg
Score
Mineral nitrogen
content, mg/kg
Score
Grass plot with subsurface
drip irrigation
54.05 0 269.51 0 13.59 5
White cedars, subsurface
drip irrigation
88.70 0 187.18 0 18.14 2
Control 53.47 0 187.21 0 9.78 5
Thus, the determining influence of soil genetic
characteristics on mineral nutrient contents was
observed. Poor nitrogen status was due to the natural
characteristics of the soil and the peculiarities of
nitrogen uptake by ornamental plants. It is obvious
that the studied soil requires the application of
nitrogen fertilizers on the grass plot to maximize the
potential of the ornamental plants, in particular not
only at the beginning of the growing season but also
after each mowing. As for the nitrogen status of the
soil under the white cedars, small amounts of nitrogen
fertilizers should be applied once during the period of
active needle growth.
A special function of soil humus is that it
contributes to the formation of close to optimal soil
properties, even at unfavorable chemical composition
(Baliuk et al., 2018). Subsurface drip irrigation did
not change the content of organic matter: in
particular, the content values were 2.06 and 2.33% for
the control and irrigated grass plots, respectively.
According to the grouping of soils by humus content,
it is assessed as medium (Fateev & Samokhvalova,
2012b). Such humus content is a characteristic natural
feature of the studied soil, i. e. there was no direct
dependence of the humus content on irrigation during
the observation period.
Diagnostic indicators of the cation-anion
composition in soil-water extract for the grass plot
with subsurface drip irrigation and the control
(without irrigation) in the 0–40 cm soil layer are
presented in Table 7, as well as their scoring. The
degree of soil salinity by the Ca/Na ratio has a value
Subsurface Drip Irrigation as a Factor Ensuring Productive and Ecological Functions of Soils
131

above 2.5 for both irrigated and natural grass plots.
That is, the subsurface drip irrigation did not
cause a noticeable transformation in the qualitative
composition of water-soluble salts towards the
narrowing of the calcium-to-sodium ratio. The
condition of the soil on this indicator was rated to be
good.
Table 7: Scoring of diagnostic indicators for the cation-anion composition in soil-water extract when using subsurface drip
irrigation, 2020.
Variant
pH aqueous
Score
∗
Ca/Na
Score
∗
HCO
–Ca
, mEq/100 g
Score
∗
Na
+
K
,%oftot
a
absorbed cations
Score
∗
Content of toxic
salts, mEq/100 g
Score
∗
Grass plot with
subsurface drip
irrigation
8.18
2
3.18
0
0.45
0
16.00
10
0.35
5
Control
(natural grass
plot without
irri
g
ation
)
8.24
2
3.48
0
0.51
1
15.79
10
0.37
5
*According to Recommendations for the survey (2012).
By the content of toxic salts, the soil condition
was rated to be intermediate between satisfactory and
good (close to good) in both cases.
Secondary soil alkalinity was estimated by the
percentage of Na
+
+ K
+
of the amount of absorbed
alkaline cations. According to this indicator, the
condition was unsatisfactory both for the control site
and for the studied agricultural practice.
The speed and extent of the detected process are
determined by the quality of irrigation water (the
content of alkaline salts of sodium and potassium in
an equivalent ratio exceeds the content of calcium,
magnesium, and iron salts), the initial properties of
the soil, including the carbonates content and calcium
ions activity, and condition of the irrigated land. For
the soil with shallow carbonates (40–50 cm), the
effective environmental and economic practice would
be deep reclamation plowing, which is an alternative
to gypsum treatment (Baliuk et al., 2018).
The alkaline reaction of the soil solution was
preferred by the white cedars: the plants developed
well and rapidly, the annual growth of the studied
Thuja occidentalis was 25–30 cm.
The content of heavy metals in the 0–30 cm soil
layer in the experimental variants is presented in
Table 8.
Table 8: Content of heavy metals in the experimental variants, 0–30 cm soil layer, 2020, mg/kg.
Variant Cu Fe Mn Ni Co Pb Cr Zn Cd Z
C
Scor
e
White
cedars with
subsurface
drip
irrigation
0.09 2.07 13.95 0.14 0.02 0.61 0.66 0.68 0.12 2.11
0
Grass plot
with
subsurface
drip
irri
g
ation
0.24 2.86 8.92 0.14 0.11 2.29 0.49 0.70 0.08 4.54
0
Control 0.26 0.86 5.80 1.30 0.13 2.61 0.40 0.17 0.06 4.59
0
Threshold
limit value*
3.0 - - 4.0 5.0 6.0 6.0 23.0 0.7
Background
value*
min 0.01 0.02 0.89 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.04 0.01 0. 02
max 2.91 32.16 59.47 2.2 1.08 5.3 2.82 4.28 1.12
mean 0.36 3.22 14.9 0.94 0.2 0.62 0.5 0.38 0.15
*According to Fateev and Samokhvalova (2012b)
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
132

The results indicate that heavy metals content in
the soil in none of the variants exceeded the threshold
limit value (Fateev & Samokhvalova, 2012a).
The calculations of the total pollution rates Z
C
(Gutsulyak, 2001), which are presented in Table 8,
indicate that subsurface drip irrigation does not cause
soil contamination with heavy metals; the soil of the
experimental site, according to the polyelement
contamination indicators, belongs to the
uncontaminated (Z
C
< 16) (Gutsulyak, 2001). The
expected scoring is presented in Table 8.
According to the gradation provided by
Medvedev, chemical degradation of soils is absent if
zinc content < 11 mg/kg, copper content < 1.5 mg/kg,
cobalt content < 2.5 mg/kg, lead content < 3.0 mg/kg,
and cadmium content does not exceed three times the
background content (Medvedev, 2012).
The comparison indicates no probability of
chemical degradation of the soil for any of these
chemical elements.
The resistance of plants to biotic and abiotic
factors is determined both at the cellular level and by
the processes that take place under the harmonious
influence of all plant organs. Micronutrients play an
essential role in that regard as cofactors of various
enzymes, which have their specific action in redox
processes; in some cases, there is their
interchangeability. Bobko, Vlasyuk, Peive, Shkolnik,
Gedz, Toma, and others drew attention to the positive
effect of micronutrients on the resistance of plants to
adverse conditions and, in particular, to drought, due
to changes in the chemistry of the plant body (Baliuk
et al., 2018).
The microelement status of the soil in the
experimental sites was assessed using the grouping of
soils by the content of labile forms of micronutrients
extracted with acetate-ammonium buffer (pH 4.8),
mg/kg of soil (Fateev & Samokhvalova, 2012b). The
results showed that the availability of micronutrients
in the soil from the experimental site with subsurface
drip irrigation of white cedars was as follows: high
for Mn, very low for Cu and Co, and very high for Zn.
In the soil from the experimental site with subsurface
drip irrigation of the grass plot, the availability of
micronutrients was as follows: medium for Mn and
Co; very low for Cu, and very high for Zn. In the
control site, the micronutrients content was low for
Mn and Cu and medium for Zn and Co.
The assessment provides an opportunity to predict
possible changes in soil conditions in the context of
determining the lack or excess of micronutrients.
Irrigated soil will be characterized by a high content
of zinc and manganese, and in the future, they are
likely to be in excess. At the same time, subsurface
drip irrigation does not contribute to the accumulation
of labile forms of copper and cobalt.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The presented findings of the 2019–2021 study
allowed us to draw the following preliminary
conclusions.
1. The equilibrium soil density showed the
optimal values at the beginning of the growing season
in 2020–2021 for all soil layers: 1.08–1.16 g/cm
3
for
grass plot and 0.91–1.08 g/cm
3
for white cedar
plantings.
2. The use of subsurface drip irrigation provided
an excellent structural condition in terms of air-dry
agronomically valuable particles with a size of 0.25–
10 mm; the ratio of structural fractions corresponded
to the optimal parameters. The average content of air-
dry aggregates was 86.24% in the control, whilst it
was 88.36% under subsurface drip irrigation. The soil
structure index was 6.35 in the control and 8.55 in the
studied variant.
3. Subsurface drip irrigation provided good
structural condition of the soil in terms of the content
of waterproof aggregates sized 0.25–7.00 mm. The
average values of this indicator for the 0–40 cm soil
layer were 51.65% in the control and 54.20% under
irrigation. The score of diagnostic agrophysical
indicators is the most favorable.
4. Subsurface drip irrigation did not change the
content of organic matter: in particular, the content
values were 2.06 and 2.33% for the control and
irrigated grass plots, respectively. This humus content
value was a characteristic natural feature of the
studied soil, i. e. there was no direct dependence of
the humus content on irrigation during the
observation period.
5. Subsurface drip irrigation did not change the
soil nutrient status, namely the content of mineral
nitrogen, labile phosphorus and potassium; the
scoring was the same for both the irrigated and the
control sites. No direct dependence of nutrient
content on irrigation was observed. There was the
determining influence of soil genetic characteristics
on the content of mineral nutrients. Poor nitrogen
status was due to the natural characteristics of the soil
and the peculiarities of nitrogen uptake in ornamental
plants. The studied soil requires the application of
nitrogen fertilizers on the grass plot to improve
fertility, in particular not only at the beginning of the
growing season but also after each mowing. As for
the nitrogen status of the soil under the white cedar,
the application of small amounts of nitrogen
Subsurface Drip Irrigation as a Factor Ensuring Productive and Ecological Functions of Soils
133

fertilizers once during the period of active needle
growth is relevant.
6. Assessment of diagnostic indicators for the
cation-anion composition of the aqueous soil extract
revealed a poor soil condition in terms of the
percentage of Na
+
+K
+
from the amount of absorbed
alkaline cations in both variants. By the content of
toxic salts, the soil condition was rated to be
intermediate between satisfactory and good (close to
good) in both cases. The degree of soil salinization by
the Ca/Na ratio was more than 2.5 for both irrigated
and natural grass plots. The soil condition in terms of
this indicator was rated to be good.
7. The results indicate no probability of chemical
soil degradation for any chemical element. The total
pollution rates Zc in both white cedar sites and the
grass plot were similar to that for uncontaminated
soils.
8. The assessment of the microelement status of
the soil enables forecasting of possible changes in soil
status in the context of determining the lack or excess
of micronutrients. The content of zinc and manganese
may increase due to the irrigation, and their excess is
likely to continue. At the same time, subsurface drip
irrigation does not contribute to the accumulation of
labile forms of copper and cobalt.
9. Score assessment of the ecological and
reclamation condition of the studied soil by
diagnostic indicators revealed subsurface drip
irrigation utility with compulsory further ecological
and reclamation monitoring of the irrigated soils.
REFERENCES
Baliuk, S. A. & Drozd, O. M. (Eds.). (2017). Assessment of
ecosystem services of saline soils under the influence of
land reclamation (Guidelines). Kharkiv: FOP Brovin
O.V.
Baliuk S.A. , Kucher A.V. & Maksymenko N.V. 2021,
Soil resources of Ukraine: state, problems and strategy
of sustainable management. Ukrainian Geographical
Journal. № 2: 03-11.
Baliuk, S. A., Medvedev, V.V., & Nosko, B.S. (Eds.).
(2018). Adaptation of agro-technologies to climate
change: Soil and agrochemical aspects. Kharkiv:
Stylna Typografiya.
TruCamp, C. R. (1998). Subsurface drip irrigation: A
review. Transactions of the ASAE, 41(5), 1353.
Camp, C. R., Lamm, F. R., Evans, R. G., & Phene, C. J.
(2000, November). Subsurface drip irrigation – Past,
present and future. In Proc. Fourth Decennial Nat’l
Irrigation Symp., Nov (pp. 14–16).
Dolgov, S.I., Bakhtin, P.U., & Rastvorova, O.G. (1983).
Soil physics. Leningrad.
Fateev, A.I. & Samokhvalova, V.L. (2012a). Detoxification
of heavy metals in the soil system. Guidelines. Kharkiv:
KP Miskdruk.
Fateev, A.I. & Samokhvalova, V.L. (Eds.). (2012b).
Diagnosis of the state of chemical elements of the soil-
plant system. Kharkiv: KP Miskdruk.
Gololobova, O.O. (2020). Assessment of ecological status
of the soil under subsurface drip irrigation using
microbiological indicators. In Ecology, environmental
protection and sustainable use of nature: Education –
Science – Production – 2020. Proceedings of the XXIII
International Scientific and Practical Conference,
December 17-18, 2020 (pp. 30–31). Kharkiv.
Gutsulyak, V.M. (2001). Landscape-geochemical ecology.
Chernivtsi: Ruta.
Lamm, F. R. (2016). Cotton, tomato, corn, and onion
production with subsurface drip irrigation: A
review. Transactions of the ASABE, 59(1), 263–278.
Maksymenko, N. V, Burchenko S. V., Utkina K. B. &
Buhakova M. V. (2021) Influence of green
infrastructure objects for quality of surface runoff
(on the example of green roofs in Kharkiv). Visnyk of
V. N. Karazin Kharkiv National University, series
“Geology. Geography. Ecology”, 55, 275-285.
Medvedev, V.V. (2012). Soil monitoring in Ukraine.
Concept. Outcomes. Tasks. Kharkiv: KP Gorodskaya
Tipografiya.
Method of soil sampling in perennial crop plantations
under drip irrigation. Recommendations. (2013).
Kharkiv: KP Miskdruk
National soil protection program of Ukraine. (2015).
Kharkiv: Smugasta Typografiya.
Recommendations for the survey of ecological and
reclamation condition of lands under drip irrigation.
(2012). Kharkiv: NNC ISSAR.
Sinobas, L. R., & Rodríguez, M. G. (2012). A review of
subsurface drip irrigation and its management. In Water
Quality, Soil and Managing Irrigation of Crops (pp.
171–194).
Soil quality. Sampling. DSTU 4287-2004. (2005). Kyiv:
Derzhspozhivstandart Ukrayiny.
Soil quality. Determination of the content of labile
compounds of manganese (zinc, cadmium, iron, cobalt,
copper, nickel, chromium, and lead) in the soil in a
buffer ammonium acetate extract with a pH of 4.8 by
atomic absorption spectrophotometry. DSTU 4770.1-
9:2007. (2009). Kyiv: Derzhspozhivstandart Ukrayiny
Usatova, L.G., & Ryabkov, S.V. (2018). Spatial
heterogeneity of soil properties in fruit plantations
under drip irrigation. In Agrochemistry and Soil
Science. Special issue. Volume 2. Amelioration,
reclamation, soil protection, humus status, soil biology,
organic farming (pp. 60–63). Kharkiv: PP Styl-Izdat
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
134
