
Sustainable Development of Methods for Assessing the Economic
Efficiency of Enterprises under the Conditions of Business
Intellectualization
Denys Vasylychev
a
, Sergiy Tsviliy
b
, Darya Gurova
c
and Olena Halan
d
National University «Zaporizhzhia Polytechnic», Zaporizhzhia, Ukraine
Keywords: Efficiency, Business, Results, Costs, Profit.
Abstract: The content and stages of business efficiency analysis were determined. It is established that for the purpose
of assessing the business management of the enterprise, science and practice have developed economic
indicators that model economic phenomena and are designed to assess the economic performance of an
enterprise or its business activity under the conditions of business intellectualization. It is proved that business
efficiency is measured in one of two ways, reflecting the performance of the enterprise in relation to either
the amount of resources advanced or the amount of their consumption (costs). To assess the efficiency of a
business, a system of indicators is used, it includes both private and generalized indicators of efficiency. The
proposals on the formation of generalizing indicators of economic efficiency at the macro- and micro-level
are considered. When building a model of economic efficiency of business using the resource approach, the
concepts of advanced variable capital and applied variable capital are used. To calculate the economic
efficiency of business using the resource approach, it is necessary to take the ratio of the result, which is
commodity capital in monetary form, and the cost of resources of human and social labor.
1 INTRODUCTION
Assessment of business efficiency of an enterprise is
the final stage of financial and managerial analysis.
Analysis of overall business efficiency is the
prerogative of the highest level of enterprise
management. Efficiency (success) of private
management decisions should be evaluated from the
point of view of overall success of the enterprise, its
long-term survival in the context of the
intellectualization of business.
In modern conditions, in the period of high
competition, the goal of enterprises is to maximize
profits with minimal costs (Rzaev, 2011).
For the purpose of assessing the business
management of an enterprise, science and practice
have developed special tools, which are called
economic indicators. Economic indicators model
economic phenomena. They are designed to measure
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5057-7575
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1720-6238
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3180-0348
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6061-5224
and evaluate the essence of economic characteristics,
economic efficiency of an enterprise's business or its
business activity.
Also, scientific research needs methodological
approaches to the selection of components and
criteria for assessing the economic performance of
enterprises, identifying reserves and opportunities
for their functioning, as well as the use of economic
and mathematical methods for forecasting their
further development.
Thus, the purpose of the article is to investigate
the methods for assessing the economic efficiency of
enterprises under the conditions of business
intellectualization and growth of their profitability.
208
Vasylychev, D., Tsviliy, S., Gurova, D. and Halan, O.
Sustainable Development of Methods for Assessing the Economic Efficiency of Enterprises under the Conditions of Business Intellectualization.
DOI: 10.5220/0011348300003350
In Proceedings of the 5th International Scientific Congress Society of Ambient Intelligence (ISC SAI 2022) - Sustainable Development and Global Climate Change, pages 208-218
ISBN: 978-989-758-600-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2 THEORETICAL BASIS OF
RESEARCH
Intellectualization of economy and business is a
complex system economic category, the methodology
and evaluation of which require both a systematic
approach and a comprehensive approach because of
the need to justify management decisions in the
context of limited resources.
This situation is characterized, first, by the need
for its characterization at different levels of
management − individual, enterprise, sectoral,
regional and national. Secondly, the need for
monitoring and diagnostics not only in statics, but
also in dynamics, in the structural aspect. Thirdly, the
expediency of determining the measure of
effectiveness of the use of unpopular capital as a
realization of intellectual potential. Fourthly, the need
to provide feedback on the effectiveness of public
policy in the business environment. Fifth, the
formation of conclusions about the role of
intellectualization in the process of economic and
business development.
2.1 Stages of Business Efficiency
Analysis
Finding a solution to the problem of improving the
performance of enterprises in the process of
intellectualization of business can be achieved
through the development of methods for analyzing
the effectiveness of enterprise business processes.
Therefore, this actualizes the research in the field of
management of enterprise business intellectualization
on the basis of the development of models for
assessing the economic efficiency of enterprises.
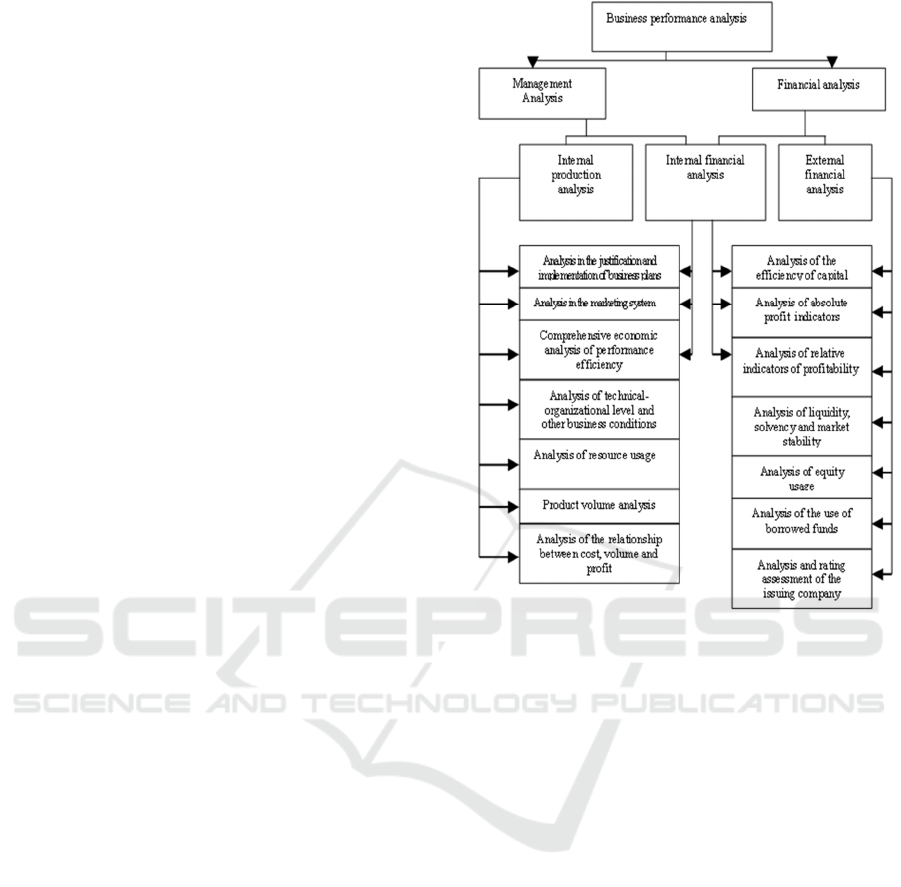
Schematic content of business efficiency analysis is
shown in Figure 1.
As can be seen from the scheme, which is
presented by A.D. Sheremet, a comprehensive
assessment of the economic efficiency of business is
an integral part of the managerial and financial
analysis (Sheremet, 2011). The article will focus on
the analysis and management of economic efficiency
of enterprise business.
The modern economy is distinguished by two
features:
– complete economic isolation, independence and
responsibility of enterprises as subjects of the market;
– uncertainty of market conditions, as a
consequence of free establishment by the enterprise
of business relations with partners, and free prices and
tariffs for products.
Figure 1: Scheme of the content of business efficiency
analysis (Sheremet, 2011).
Under these conditions, the central task of
management is to minimize business risks on the
basis of the assessment of each decision in terms of
the possibility of extracting economic benefits. This
creates objective prerequisites for increasing the role
of methods for analyzing the economic efficiency of
an enterprise's business. This requires modernization
of the methodology of this analysis, improvement of
methods of enterprise business economic efficiency
management.
For the purpose of assessing the business
management of an enterprise, science and practice
have developed special tools that are called economic
indicators. Economic indicators model economic
phenomena. They are designed to measure and
evaluate the essence of economic characteristics,
economic efficiency of an enterprise's business or its
business activity.
Further we will consider indicators of business
efficiency used in the enterprises of Ukraine.
Economic efficiency penetrates all spheres of
practical human activity, all stages of social
production, is the basis for construction of
quantitative criteria and value of decisions made.
Sustainable Development of Methods for Assessing the Economic Efficiency of Enterprises under the Conditions of Business
Intellectualization
209

2.2 Theory and Methodology of
Performance Evaluation
Currently, the most complete and consistent study of
economic efficiency of business (disclosure of the
subject of analysis) is given in the theory of
comprehensive economic analysis. All sections of
current, prospective and operative analysis are
devoted to efficiency analysis. It evaluates achieved
business efficiency, reveals factors of its change,
unused possibilities and reserves for increase
(Mykytiuk, 2018).
Business efficiency is measured in one of two
ways, reflecting the performance of the enterprise in
relation to either the amount of resources advanced,
or the amount of their consumption (costs) in business
processes.
In the system of economic indicators, some
characterize the effectiveness of a single type of
product (vertical feature of management), others − all
types of products or services (horizontal feature of
management). There are generalized and private
indicators of business efficiency. The first ones
characterize the effectiveness of the use of total labor
costs; the second ones characterize the effectiveness
of the use of individual types of labor costs.
The ratio of the results of labor to the inputs of
live labor reflects a subsystem of indicators of
productivity or output of live labor. The ratio of labor
results to past labor costs (production costs, equity
capital, cost of production funds), which includes the
overwhelming part of total labor costs, represents a
subsystem of indicators characterizing efficiency of
past labor (productivity of funds, productivity of
materials, turnover of current assets). Finally, the
ratio of the results of labor to the total expenditures of
the enterprise is a subsystem of indices characterizing
the efficiency of production of concrete products.
Advantages and disadvantages of methods of
measurement of each of efficiency indicators are
caused by contradictory sides of indicators, which
express the results of business (Babenko, 2010).
The most important indicator of efficiency is the
productivity of live labor. The most obvious
characteristic of productivity of live labor is an
indicator equal to the ratio of the volume of output in
kind, taking into account quality indicators, to the
cost of live labor. Prices have a great influence on the
indicator of the output of live labor, calculated in
value terms by net or net output (Babenko, 2010).
Indicators of return on assets (cost of goods),
material output (cost of materials), the level of
profitability should be distinguished depending on
whether they refer to the output of one type of product
or its entire range. Thus, fixed assets, in some cases,
it is difficult to attribute to the production of a
particular type of product. Among them there are
general-purpose fixed assets. Circulating capital is
not subject to such a division at all. Therefore,
turnover of current assets is determined in relation to
all products.
In the indicators "productivity", "yield of funds",
"productivity of materials", "turnover ratio" the
overall result − the volume of output − is correlated
with a business factor. The listed indicators can be
multidirectional. Each of them characterizes the
efficiency of inputs of live or past labor (Salyha,
2001).
The correlation between the dynamics of output
and the dynamics of results (costs) determines the
nature of economic growth. Business economic
growth can be achieved both extensively and
intensively. The excess of the growth rate of output
over the growth rate of resources or costs indicates
predominantly intensive economic growth.
To assess the efficiency of a business, a system of
indicators is used – profitability of capital, resources
or products. Business activity of an enterprise, in the
financial aspect, manifests itself, first of all, in the rate
of turnover of its funds. The profitability of an
enterprise reflects the degree of profitability of its
business. The analysis of business activity and
profitability lies in the study of levels and dynamics
of various financial ratios of turnover and
profitability, which are relative indicators of
enterprise financial results (Horodynska, 2008).
Thus a system of indicators is used to evaluate
business efficiency. This system should include both
private and generalizing performance indicators. A
generalizing indicator should give an integral
estimation, characterizing efficiency of usage of all
kinds of resources (costs) of enterprise.
None of these economic indicators can be
generalizing, because the result of activity does not
meet the costs. The generalizing indicator should, by
construction, meet the principles of business
efficiency management.
Next, let us consider the proposals available in the
economic literature on the formation of generalized
indicators of economic efficiency at the macro- and
microlevel.
2.3 The Theory of Formation of
Economic Efficiency Indicators at
the Macro Level
The foundations of the formation of the theory of
production efficiency, which characterizes the ratio of
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
210

results and costs, should be attributed to the moment
of analysis of the two factors of goods: consumer
value and value, disclosed by K. Marx (Marx, 1983).
Forming economic laws of time saving and growth of
labor productivity per unit of consumer value K.
Marx notes: "In general, the greater the productive
power of labor, the less labor time required for
production, the less labor mass crystallized in it, the
less its value (Marx, 1983).
The mathematical interpretation of the law of
economy of time, according to K. Marx's theory, can
be represented by expressions:
2
2
1
1
nn
Q
t
Q
t
>
(1)
2
222
1
111
nn
Q
mVc
Q
mVc ++
>
++
(2)
where t
1
/Qn
1
; t
2
/Qn
2
– the time required to
produce a unit of use value Qn
1
, Qn
2
, in the base
period and the new period; с
1
, с
2
– permanent capital
in the base period and the new period;
V
1
, V
2
– variable capital in the base period and the
new period;
m
1
, m
2
– surplus value in the base period and the
new period.
The law of the growth of the productive power of
labor, in fact, is interrelated with the law of economy
of time and can be represented by the expressions:
2
2
1
1
t
Q
t
Q
nn
<
(3)
222
2
1
11
1
mVc
Q
mVc
Q
nn
++
<
++
(4)
The mathematical representation of the laws of
saving time, and the growth of the productive force of
labor makes it possible to determine what constitutes
an indicator of general and comparative economic
efficiency (Marx, 1983).
The theory of efficiency was developed in the 20s
of the twentieth century. It was conditioned by the
solution of the problem of rational use of capital
investments, comparison of options in the
development of projects for the construction of power
plants, railroads, land reclamation facilities. In the
mid-20s of the twentieth century, the problem of
efficiency began to be posed as a problem of
determining the efficiency of capital investments for
individual industries and industry as a whole. Over
time, the problem of efficiency becomes a broader
one, and finally, the debate about it develops into a
dispute about economic efficiency (Salyha, 2001).
The subject of the discussions was the key issues
– the content of the category of efficiency of social
production, criteria and indicators of efficiency at the
level of society and enterprise, ways to measure it,
etc. H. Abezhauz, V. Akulenko, M. Barun, H.
Burshtein, F. Vinnik, R. Holdberg, A. Kalmanovsky,
V. Krasovsky, L. Litoshenko, Yu. Mitlyansky, P.
Maslov, S. Rosentul, J. Rosenfeld, A. Segal, M.
Smith-Falkner, S. Strumilin, Sh. Turetsky, H.
Feldman, N. Shaposhnikov, L. Yushkov, etc. took an
active part in the discussion. However, at that time
economists failed to come to a common position.
Many of their valuable thoughts were not understood
by their contemporaries (Salyha, 2001).
It is not the purpose of this article to review the
development of the theory of economic efficiency.
These issues have already been addressed by some
authors. The task is to identify when for the first time
the authors put forward the idea of determining the
relationship of private indicators of economic
efficiency in a single integral or synthetic indicator.
At the macro level, as a generalizing indicator of
economic efficiency, scientists suggest using the ratio
(Vorst, 1994):
FML
V
Е
in
γ
++
=
(5)
where V – pure product with regard to its
composition and quality;
L
in
– labour input;
М – current costs of material labor;
F – one-time investments in production assets;
γ – the coefficient of reduction to a single
dimension, which allows to sum up the costs and
investments.
This formula conceptually reflects the essence of
the construction of the indicator. But it is impossible
to use it in practice, because it is not clear how to
express the coefficient of conversion. It is not clear
what is the cost-of-living labor is. The formula differs
in its construction from the mathematical expression
of the law of productive labor force. There is no
criterion (threshold standard) of judgment about
efficiency.
The study of the efficiency of social production
would be incomplete without considering production
functions that characterize the dependence of output
on production factors (Vasyl’yva, 2021). The first
version of such functions is the Cobb-Douglas
production function, which considers the dependence
of output on only two factors − capital and labor:
Sustainable Development of Methods for Assessing the Economic Efficiency of Enterprises under the Conditions of Business
Intellectualization
211

,
βα
LKAV ⋅⋅=
(6)
where V – production volume;
К – production funds;
L – labor force;
А,
α
,
β
– parameters of the function;
А – coefficient of proportionality or scale;
α
,
β
– coefficients of output elasticity by capital and
labor, which characterize the increase in output per
1% increase in the corresponding factor of
production.
This expression was improved by a number of
researchers, including economists A. Solow, E.
Denison, A.I. Anchishkin, S.M. Veshnev, P.F.
Pochkin, Y.L. Shtern, O.O. Vasyl’yva who proposed
to consider in the form of special coefficients such
factors as qualification of workers, technical level of
production, etc. As a result, the Cobb-Douglas
function acquired the following generalized form
(Holovenko, 2016):
,
Rt
eLKAV ⋅⋅⋅=
βα
(7)
where: e
Rt
– a factor that denies the impact of
qualitative changes in production, including
technological progress.
Expressed in terms of the average annual growth
rate, the function is transformed and has the following
form:
I
о
=
α
I
к
+
β
I
ch
+ R
(8)
where: I
о
, I
к
, I
ch
– the growth rates of production,
production funds and labor force, respectively;
R – a complex index of growth of the total
economic efficiency of all production factors
(Holovenko, 2016).
According to the authors of this article, if we use
the Cobb-Douglas production function, business
efficiency can be expressed by the ratio of output (in
value terms) to costs:
1==
βα
L
AK
V
E
(9)
The above considered mathematical models of the
formation of economic efficiency indicator at the
macro level.
2.4 The Theory of Economic Efficiency
Indicators at the Micro Level
In theory and practice, the level of profitability of
business processes is preferred as a generalizing one
(Kudrenko, 2014). This statement is controversial for
a variety of reasons. Firstly, profit is not the result
only of the turnover of production assets. Secondly,
this indicator (numerator) can increase due to the
growth of prices, while other efficiency indicators can
worsen. As a consequence, productivity of funds,
material productivity, and productivity of live labor
will decrease. Thirdly, during the period during which
profits will be made, current assets will make many
turns, and fixed assets will serve only a part of their
service life. Fourth, the authors of this article believe
that for purposes of measuring the business
performance of an enterprise, fixed assets and current
assets cannot be added up, despite the fact that these
components are measured in cost units.
Thus, in order to evaluate the performance of an
enterprise, Ohon C.H. proposes to introduce the
coefficient of active costs, defined as the ratio of
active costs to the cost of production (Ohon, 1996). In
this case, active costs are understood as labor costs,
the cost of introducing new technologies. Such an
indicator has the right to exist. However, it cannot be
classified as a generalizing indicator. It does not
reflect the overall performance of the enterprise and
the resources (costs) to obtain them.
Of scientific interest is the proposal of some authors
to use the following ratio as a generalizing one
(Salyha, 2007:
ОСОf
zpА
СС
PII
Е
+
++
=
(10)
where I
А
– amortization charges;
I
ZP
– labor costs;
P – balance sheet profit of the enterprise;
С
Оf
– average annual value of fixed assets,
С
ОС
– average annual value of current assets of the
enterprise.
As a justification of this indicator the authors note
that in this formula "depreciation charges represent
the degree of use of fixed assets, while wages and
profits represent the degree of use of current assets"
(Salyha, 2007).
It is difficult to fully agree with the proposals of
some authors for various reasons, namely:
having taken the economic efficiency
indicator as a ratio of results to costs as the basis for
formation, the authors substituted results for costs,
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
212

including depreciation, labor costs and profits. For
example, the ratio of depreciation to the cost of fixed
assets is an indicator that characterizes the rate of
depreciation, i. e. the number of turns of fixed assets
per year;
the authors' notion that wages and profits
characterize the degree of use of current assets is
controversial. After all, current assets are designed to
ensure the circulation of material costs, remuneration
of labor, and participate in the formation of profits.
But profit is not a consequence of turnover of current
assets only;
fixed assets and current assets are for all the
costs of living and public labor, necessary for the
production of products;
costs do not include intangible assets as an
element of resources;
according to L.N. Drahun the most
generalized assessment of production efficiency is
given by the coefficient of the marginal level of net
profit. It is determined by the ratio of net profit to the
volume of commodity production. To solve the
problems of intrafarm operational analysis offer the
indicator of the specific reduced costs, determined
from the ratio of the annual costs to the volume of
marketable products. Reduced annual costs are
calculated as the sum of production costs and the
amount of fixed assets, current assets and labor,
expressed with the coefficients of conversion. These
coefficients are determined by the ratio of the value
of taxes (VAT, profit tax, land tax, excise tax, etc.) to
the cost of fixed assets, current assets and payroll with
social charges, respectively (Drahun, 2000).
This proposal is controversial for the following
reasons. First, there is no criterion for judging the
effectiveness of the decision. Secondly, the
coefficient of the marginal level of net profit
(profitability of marketable output) is a private
indicator, if only for the reason that profit is not the
result (consequence) of marketable output (reason).
Third, the authors lose sight of the fact that the annual
cost should express the cost of labor and capital labor
on output. Fourthly, they overlook the fact that
circulating capital ensures the turnover of material
costs, sales of products and labor remuneration. In
other words, current assets contain part of the cost-of-
living labor. Therefore, there is double counting in the
assessment of labor resources.
R.M. Petukhov's proposal for assessing the
efficiency (Petukhov, 1987):
)(
bОСofn
BB
КССЕI
V
C
V
Е
++⋅+
==
(11)
where Е – coefficient of economic efficiency of
production;
V
B
– annual gross output, calculated in
comparable wholesale prices;
С – total reduced costs;
I – annual production costs of the given
production unit;
Е
n
– normative coefficient of economic efficiency
of capital investments;
С
Оf
– average annual cost of fixed production
assets;
С
ОС
– current assets;
К – economic evaluation of human resources.
Here К
b
is interpreted as the cost of professional
training, as investment in the training of personnel.
R.M. Petukhov believes that the proposed
indicator can be used to compare the economic
efficiency of businesses in different sectors of the
economy.
Let us give a critical assessment of this proposal.
Essentially, the indicator reflects the ratio of the
volume of gross output and the costs, which are
necessary for the output. Consequently, the criterion
for choosing the option should be the condition in
which the numerator exceeds the denominator, i.e. the
indicator is greater than or equal to one. But such a
condition should be observed at every enterprise
when business results exceed the present annual
costs. If this condition is not met, the enterprise is
operating at a loss. This conclusion leads to the
following conclusion: firstly, this indicator is not
suitable for comparing the economic efficiency of
businesses. Secondly, the normative indicator of
economic efficiency of investments is absent in the
statistical and financial statements of the enterprise.
Thirdly, the author overlooked the fact that the
product Еn(С
Оf
+ С
ОС
+ К
b
) is a normative profit,
expressed as a share of investment. Fourth,
investments in personnel are already accounted for
partly in current assets, so there is double counting in
the estimation of costs. Fifth, the author's attempt to
present the given annual costs as a resource-cost
approach to assessing the economic efficiency of a
business is inappropriate. This is a cost approach.
Only part of the cost of live labor in the form of
normative profit is expressed as a share of resources.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Analysis of methods for measuring the economic
performance makes it possible to draw the following
conclusions:
Sustainable Development of Methods for Assessing the Economic Efficiency of Enterprises under the Conditions of Business
Intellectualization
213

1 In the economic literature, to assess economic
efficiency, a system of particular indicators is used,
which characterize the performance of the enterprise
either the amount of resources advanced, or the
amount of their consumption (costs).
2 In foreign sources there are general
suggestions for the calculation of the generalizing
indicator, reflecting the economy of the enterprise,
which is defined as the ratio of the volume of output
to the volume of consumed resources. For enterprises
in Ukraine economists recommend using the level of
profitability of products or sales as a generalizing
indicator.
3 Economic indicators have different names.
For example, the profitability of sales has names:
profitability of turnover, commercial margin,
profitability ratio. In this regard, the authors believe
that it is necessary to create a state standard on
economic terminology.
4 Employees, to ensure the long-term survival
of the enterprise, are interested in business efficiency
not only in terms of increasing income per unit cost
due to internal factors, but also the influence of
external factors. Thus, business efficiency is an
economic category that depends on internal and
external variables.
5 Since profit is the result of living labor with
the help of means of labor and objects of labor, the
question of determining the impact of each cost value
(each resource) on the amount of profit received is
considered relevant.
6 In assessing the business efficiency of an
enterprise, scientists have not considered all options.
The indicators proposed in the economic literature are
private. In them, the entire result is transferred to one
of the factors of production or not all costs are taken
into account. The result is not the consequence, and
the costs are the cause.
7 There are no or insufficiently substantiated
threshold values of the considered indicators. The
dynamics of changes in the calculated indicators
indicates the improvement (deterioration) of the
indicator. In the absence of a standard,
recommendations to improve the efficiency of the
business of the enterprise can be developed with the
help of expert evaluations.
8 A certain difficulty for practice is a set of
private indicators, to a certain extent duplicating
information. In our opinion, it is necessary to allocate:
a generalizing indicator; the main private indicators;
additional private indicators of economic efficiency
of business enterprise.
9 One of the disadvantages, which does not
allow to comprehensively and accurately measure the
effectiveness of the business of the enterprise is the
lack of a generalizing or integral indicator. It would
make it possible to measure the level or increase in
efficiency at the macro- and micro-level. A wide set
of individual indicators, because of their different
orientation, allows to give an unambiguous
assessment of the level or increase in business
efficiency.
10 In a set of indicators there is no logical
consistency, unity, interrelation, interdependence,
consistency.
11 In the economic literature there is no
distinction between the categories of "economic
efficiency" and "economic efficiency of business".
To build a model of economic efficiency of
business through the resource approach, the authors
of the article use the concepts - advanced variable
capital and applied variable capital. The advanced
variable capital (capitalized wages) is understood as
a part of current assets, which is in circulation and is
spent on wages and unified social tax (UST). In
essence it is a salary for one its turnover. Under the
applied variable capital we understand annual
expenses on a labor payment with UST.
There is a relationship between the categories in
question. Annual labor costs with UST are equal to
the product of variable capital (capitalized wages and
salaries) by the number of turns it will make during
the year. Consequently, the amount of variable capital
(capitalized wages) can be found from the ratio:
,
п
I
С
zp
zp
=
(12)
where С
zp
– variable capital (capitalized wages
and salaries), UAH;
I
zp
– annual labor costs with UST, UAH/year;
n – the number of revolutions of variable capital
per year.
The sum of labor costs and profits is the newly
created value due to live labor. Live labor, as noted
above, can be expressed in terms of the number of
workers or in monetary terms (in resource terms as
the sum of variable capital and capitalized profit, or
in cost terms as the sum of annual labor costs and
annual profit).
The relationship of live labor in the resource
approach is supposed to be expressed as:
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
214
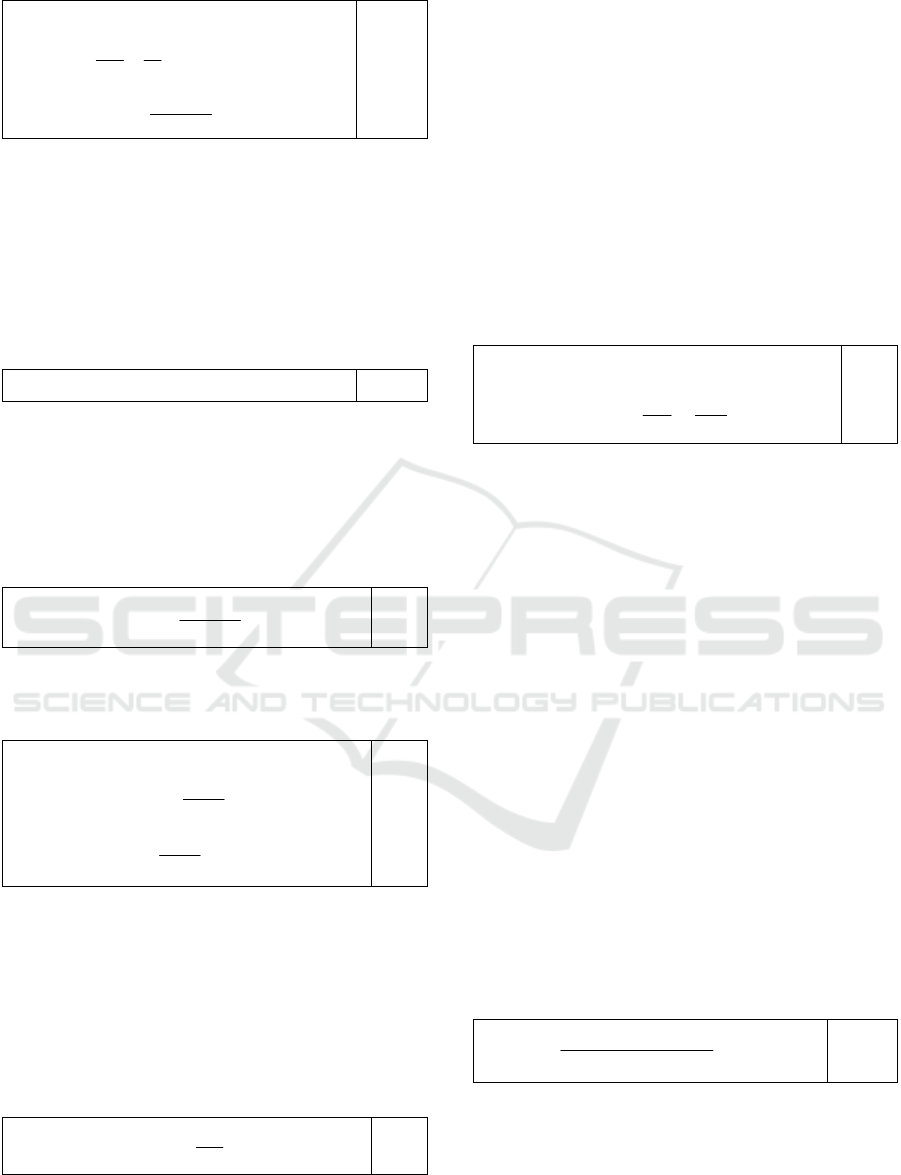
.
;
;
пCh
PI
К
ChК
п
P
п
I
ChКСС
zp
ch
ch
zp
chпzp
⋅
+
=
⋅=+
⋅=+
(13)
(14)
(15)
Consequently, the coefficient of the living labor
inputs Kch is equal to the sum of types of created
value per one worker and per one turn of capitalized
wages (variable capital) and profits.
For clarity, let us present the relationship of living
labor costs in the resource and cost form,
understanding that the cost-of-living labor is a newly
created value, i.e.:
,ChКPI
chzp
⋅
′
=+
(16)
where I
zp
, P – respectively, annual labor costs and
profits, UAH;
К
ch
′
– the coefficient of resource and current costs
of live labor, UAH/year person;
Ch – number of employees, pers.
From here we find:
.
Ch
PI
К
zp
ch
+
=
′
(17)
There is a correlation between the coefficient of
the input of live labor in the resource and cost form:
.
;
;
ch
ch
ch
ch
chch
К
К
п
п
К
К
пКК
′
=
′
=
⋅=
′
(18)
(19)
(20)
Next, we determine the capitalized material costs.
Capitalized tangible costs are the advanced part of
current assets, which is in a turnover and is spent on
material and other costs. The annual sum of material
and other costs in business costs is the applied
capitalized material costs. The applied costs are equal
to the product of the advanced part by the number of
turnovers for the year, i.e.:
,
п
I
С
m
m
=
(21)
where С
m
– capitalized material costs, UAH;
I
m
– annual material and other costs, UAH/year;
n – number of turnovers of capitalized material costs
per year.
The relationship between capitalized material
costs and wages (variable capital) is due to three
circumstances. First, the amount constitutes
circulating capital. Second, the ratio of capitalized
tangible costs to variable capital is equal to the ratio
of tangible costs to labor costs. Third, the number of
revolutions that advance material costs and labor
costs are the same. This is due to the fact that the
circulation of all elements of current assets occurs
simultaneously.
In mathematical interpretation it is offered to
represent these dependences as:
,
;
.
.
п
I
п
I
С
ССС
zp
m
ко
zpmко
+=
+=
(22)
(23)
where С
о.к
– circulating assets.
It is necessary to draw a distinction between the
categories of " circulating capital " and "current
assets". It is necessary to define these theoretical
concepts more clearly. circulating capital, according
to K. Marx, is a part of fixed capital spent on the
objects of labor (capitalized material costs) and
variable capital spent to pay the labor force
(capitalized wages) (Marx, 1983).
Circulating capital of enterprises, in principle, is
also spent to finance material costs and labor
remuneration, but its composition is designated by a
different principle. Circulating capital includes:
current assets (production inventories, work in
progress) and circulation funds (inventories of
finished goods, shipped products, cash on settlement
accounts and in cash of the enterprise, accounts
receivable).
Economic efficiency of monetary capital turnover
Ек is proposed to be determined by the ratio of capital
received with the newly created value to the cost of
capital spent on the purchase of means of production
and labor:
(
)
()
.1
1
.
.
п
сооf
псооf
к
СС
СС
Е
ρ
ρ
+=
+
+⋅+
=
(24)
where
ρ
п
– profitability of products, fractions of
units.
Thus, the economic efficiency of the circulation
of monetary capital is a value proportional to the ratio
of the volume of products sold to the business costs.
Capitalized profit, which is the amount of money in
Sustainable Development of Methods for Assessing the Economic Efficiency of Enterprises under the Conditions of Business
Intellectualization
215

circulation, is the source of payments at the expense
of business profits.
The criterion for choosing the best business
solution should be the condition that ensures a profit
not lower than the norm, i.e.:
,1
.inк
Е
ρ
+≥
(25)
where ρ
n.i
– normative product profitability,
which is the ratio of normative profit to business
costs, fractions of units.
To calculate the economic efficiency of business
using the resource approach, it is necessary to take the
ratio of the result, which is commodity capital in
monetary form, and the cost of resources of living and
public labor. In other words, both the numerator and
the denominator of the formula are proposed to be
expressed in resource form.
A number of questions arise here:
1. Can commodity capital be expressed in natural
form?
2 How can it be represented in monetary form?
3 When can commodity capital be represented in
kind?
4 Are we making a methodological mistake by
representing commodity capital received in a year,
but expressing expenditures as resources? What does
this mistake lead to?
5 What is the criterion for choosing the best
business solution?
To answer these questions, let us again turn to the
turnover of monetary capital. At the second stage of
monetary capital turnover there is a connection of
means of labor, objects of labor and labor force
(living labor), productive capital turns into
commodity capital, into production, which includes
added value. Newly produced commodity capital, by
its properties and external form, differs from the
goods purchased for the production of products, with
greater value.
Consequently, commodity capital can be
represented both in kind (if one type of product is
produced) and in money terms. Since in practice the
volume of output is measured only for a certain
period, let us represent commodity capital by the ratio
of the annual volume of output to the number of turns
of commodity (monetary) capital for the year.
This means that commodity capital is the volume
of output (in kind or in money terms) for one turn of
monetary capital.
In other words, the annual volume of output is
equal to the product of commodity capital and the
number of turns of commodity capital per year. Here
we assume that all output (commodity capital) will be
sold.
Thus, commodity capital can be represented both
in physical and monetary terms. It should be
presented in physical terms when we are talking about
the economic efficiency of the production of one type
of product. If we are talking about the economic
efficiency of the business of an enterprise which
produces a nomenclature of products, only a
monetary representation of the result is appropriate.
Based on the above, the indicator of economic
efficiency of business using the resource approach is
proposed to be expressed by the ratio:
,1=
⋅++
=
ChКСС
Т
Е
chmоf
(26)
where Е – indicator of the economic efficiency of
the enterprise;
Т – commodity capital, UAH;
С
оf
– average annual value of fixed assets and
intangible assets, UAH;
С
m
– capitalized material and other costs, UAH;
К
ch
– the coefficient of resource and current costs
of live labor, UAH/year person;
Ch – average annual number of personnel, person.
The criterion of choice is the condition Е=1,
assuming that the commodity capital is equal in value
to the resources spent.
Let us represent this dependence using economic
indicators, reflected in statistical reporting and used
in practice, assuming that one type of product is
produced:
.1
0
..
0
≥
++
⋅
=
п
P
СC
n
Q
v
Е
n
соfо
(27)
where v – unit price, UAH/unit;
Q – the annual volume of marketable products
(commodity capital), units/year;
п
0
– number of revolutions performed by cash
capital per year;
С
о.с
– annual average balance of current assets,
UAH;
P
n
– annual volume of profit (normative profit),
UAH/year.
By performing conversions in the formula, we
obtain:
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
216

()
;1
0
≥
+
−⋅
=
осоf
n
СС
п
PQv
Е
(28)
.
0
п
СС
PQv
Е
осоf
n
≥
+
−⋅
=
(29)
The proposed mathematical models make it
possible to:
– identify the relationship between private
economic indicators of the use of certain types of
resources;
– to calculate the amount of money (money
supply) that is in circulation of the enterprise;
– to calculate the turnover rate of financial
resources for the year.
Thus, if the annual volume of sales or other
measures (net production, profit) is used as a result,
and as costs the resources being advanced, one of the
basic principles of construction of a generalizing
indicator of economic efficiency of enterprise
business is violated – matching costs and results
(costs cause, results – consequence).
The proposed models for calculating economic
efficiency under conditions of business
intensification make it possible to: identify the
relationship between private economic indicators of
the use of certain types of resources; calculate the
amount of money that is in circulation of the
enterprise; calculate the rate of capital turnover for
the year.
4 CONCLUSIONS
As a result of the research, it was found that for the
purpose of assessing the business management of the
enterprise, science and practice have developed
economic indicators that model economic
phenomena and are designed to assess economic
efficiency in terms of business enterprise or its
business activity.
It is proved that business efficiency is measured
in one of two ways, reflecting the performance of the
enterprise in relation to either the amount of resources
advanced, or the amount of their consumption (costs)
in business processes. To assess the efficiency of a
business, a system of indicators is used, which
includes both private and generalized indicators of
efficiency. The proposals available in the economic
literature on the formation of generalizing indicators
of economic efficiency at the macro- and micro-level
were considered. The task was to identify when the
authors first put forward the idea of determining the
relationship of private indicators of economic
efficiency in a single integral or synthetic indicator.
The ratio of the results of labor to the inputs of
live labor reflects a subsystem of indicators of
productivity or output of live labor. The ratio of labor
results to past labor costs (production costs, equity
capital, cost of production funds), which includes the
overwhelming part of total labor costs, represents a
subsystem of indicators characterizing efficiency of
past labor (productivity of funds, productivity of
materials, turnover of current assets). The ratio of
labor results to the total expenditures of the enterprise
serves as a subsystem of indicators characterizing the
efficiency of production of specific products.
When constructing a model of economic
efficiency of business with the use of the resource
approach, the concepts of advanced variable capital
and applied variable capital are used. The advanced
variable capital (capitalized wages and salaries) is
understood as a part of circulating assets, which is
spent on wages and unified social contribution (UST).
To calculate the economic efficiency of business
using the resource approach, it is necessary to take the
ratio of the result, which is commodity capital in
monetary form, and the cost of resources of living and
public labor.
The proposed models for calculating the
economic efficiency of business under the conditions
of business intellectualization make it possible to:
identify the relationship between private economic
indicators of the use of certain types of resources;
calculate the amount of money that is in circulation of
the enterprise; calculate the turnover rate of financial
resources for the year.
REFERENCES
Babenko, A.H., Vasylychev, D.V., Bolduyeva, O.V.,
Trifonov H.F., 2010. Productivity Management.
Zaporizhzhia: ZTSNTEL.
Chutis, A.V., 1999. Financial position of the enterprise
(assessment, analysis, planning). Sumy: Publishing
house "University book".
Drahun, L.N., Redina, N.I., Zayats, E.I., 2000. Project on
Production Efficiency Management System Creation:
Goal Formulation, Criteria Selection. In Ekonomics:
Problems of Theory and Practice. № 22.
Holovenko, I.P., 2016. Theoretical and methodological
approaches to the assessment of economic efficiency of
functioning of enterprises. In Global and National
Problems of Economics. № 11.
Sustainable Development of Methods for Assessing the Economic Efficiency of Enterprises under the Conditions of Business
Intellectualization
217

Horodynska, D., 2008. Economical stability of an
enterprise. In Actual problems of economics. № 10(42).
Kudrenko, N., 2014. Theoretical and methodological
approaches to the assessment of economic efficiency of
functioning of enterprises. In Ekonomics. № 24.
Marx, K., 1983. Capital. Vol. 1-3. Moscow: Politizdat.
Mykytiuk, V.M., Palamarchuk, T.M., Rusak, O.P., 2018.
Fundamentals of Economical Analysis. Zhytomyr:
Ruta.
Ohon, C.H. 1996. Financial Methods of Regulation of
Economy. In Finansy Ukrainy. № 1.
Petukhov, R.M., 1987. Economic results of intensification
of industrial production, methods and indicators of their
evaluation. In Proceedings of the Academy of Sciences
of the USSR. Ser. Economic. № 4
Polyak, H.B., Akodis, I.A., Kraeva, T.A., 1997. Financial
Management. Moscow: Finance, UNITI.
Rzaev, G., 2011. Economic growth and steel development:
signs and results of the level of competitiveness of
enterprises. In Bulletin of Khmelnitsky National
University. Series "Economical Sciences". № 3.
Salyha, S.Y., Kostanyan, G.A., Vasylychev, D.V., 2001.
Management of Efficiency of Economic Entities.
Zaporizhzhia: The private company "Pavel".
Salyha, S.Y., Nusinov, V.Y., Semenov, G.A., 2007.
Efficiency of use of current assets of enterprises. Krivoi
Roh: Publishing house.
Sheremet, A.D., 2011. Theory of economic analysis.
Moscow: INFRA-M.
Vasyl’yeva, O., 2021. Assessment of factors of sustainable
development of the agricultural sector using the Cobb-
Douglas production function. In Baltic Journal of
Economic Studies, Vol. 7.
Vorst, J., Reventlow, P., 1994. Economics of the firm.
Moscow: Vysshaya shkola.
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
218
