
The Impact of Carbon Information Disclosure Level on Enterprise
Financing Cost in the New Economy: Research on the Mediating
Effect of Organizational Reputation
Meng Hu
*
and Chen Zhang
Department of Management, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China
*
Corresponding author
Keywords: New Economic Background, Carbon Information Disclosure Level, Financing Cost, Organizational
Reputation.
Abstract: Taking Chinese listed companies that issued social responsibility reports from 2010 to 2019 as research
samples, this paper constructs a carbon information disclosure index system based on the connotation of the
new economic background, and uses Python to mine relevant words to calculate the carbon disclosure score,
empirically tests the impact of carbon information disclosure level on enterprise financing cost, and considers
the impact mechanism of organizational reputation. The results show that the level of carbon information
disclosure is negatively correlated with corporate financing costs, and organizational reputation plays a
intermediary effect in the relationship between carbon information disclosure level and financing costs.
1 INTRODUCTION
At this stage, China's economic development
conditions and environment are undergoing major
changes. From the perspective of development
conditions, China's past advantages in low-cost
factors no longer exist. In order to enhance its
international competitive advantage, in October 2020,
the party proposed to speed up the construction of a
new development pattern with domestic circulation as
the main body and domestic and international double
circulation promoting each other; From the
perspective of development environment, the frequent
occurrence of global extreme climate has caused huge
losses to human production and life. In order to
improve the environment, in March 2021, Premier Li
Keqiang proposed to formulate an action plan for
reaching the peak of carbon emissions by 2030 and do
a solid job in carbon peaking, carbon neutralization
and other work. Therefore, with the changes of
China's economic development conditions and
environment, the new economic background of the
integration of double cycle background and green
low-carbon background came into being. In the
context of the new economy, in order to achieve the
unity of economic and social benefits, enterprises, as
the main participants in the internal and external
economic cycle and the main "perpetrators" of carbon
emissions, need to bear the responsibility of low-
carbon development under the background of internal
and external cycle. Voluntary carbon information
disclosure just provides an opportunity for enterprises
to implement the responsibility of low-carbon
development.
Difficult and expensive financing has always been
a difficult problem perplexing the development of
China's real economy (Zhou, Han, 2020), and the
disclosure of carbon information requires a lot of
costs. With the continuous improvement of investors'
awareness of environmental protection, it is worth
exploring whether enterprises that take the initiative to
disclose carbon can win the public's recognition and
improve their reputation, so as to reduce financing
costs and alleviate financing constraints. At present,
the academic community has not reached a consensus
conclusion on the impact of carbon information
disclosure level on enterprise financing cost. Some
scholars believe that a series of costs such as
measurement, sorting and release will occur in the
process of carbon disclosure, which is easy to lead to
operational risks, so investors demand a higher rate of
return. Moreover, carbon information disclosure will
be understood as a means for enterprises to disguise as
friends of the environment out of "green washing
motivation", so that the financing cost does not
786
Hu, M. and Zhang, C.
The Impact of Carbon Information Disclosure Level on Enterprise Financing Cost in the New Economy: Research on the Mediating Effect of Organizational Reputation.
DOI: 10.5220/0011349400003440
In Proceedings of the Inter national Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 786-794
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

decrease but increases (Lee, Park, Klassen, 2015).
Other scholars believe that carbon information not
only meets the needs of investors for non-financial
information and solves the problem of information
asymmetry, but also helps to show the enterprise's
awareness of environmental responsibility, establish a
good image and improve the recognition (Wen, Zhou,
2017), so as to obtain a lower financing cost. Other
scholars believe that due to the influence of enterprise
life cycle (Ma, Gai, 2019) and environmental
regulatory pressure (Yang, Zhang, et al., 2020), there
is an inverted "U" relationship between carbon
information disclosure level and financing cost.
Therefore, this paper intends to explore the
connotation of the new economy formed by the
integration of internal and external circulation and
green low-carbon, integrate this connotation into the
carbon information disclosure index system, build a
new evaluation system, study the relationship between
enterprise carbon information disclosure and
financing cost, and consider the intermediary role of
organizational reputation, This paper studies whether
enterprises can improve the awareness and level of
carbon disclosure and realize the coordinated
development of enterprises, society and environment
by obtaining lower financing cost.
The research value of this paper lies in: (1) when
constructing the carbon information disclosure
system, innovatively excavate the relevant domestic
and international carbon information disclosed by
enterprises in the social responsibility report by
integrating the connotation of the new economic
background, so as to more comprehensively measure
the level of carbon information disclosure. (2) When
analyzing the relationship between carbon
information disclosure level and financing cost,
consider the intangible asset of organizational
reputation, and enrich the research on the influence
mechanism between carbon information disclosure
level and financing cost from the perspective of
resources
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Theoretical Analysis and Research
Assumptions
2.1.1 Relationship between Carbon
Information Disclosure Level and
Enterprise Financing Cost
According to the stakeholder theory, the stakeholders
of enterprises include shareholders, creditors, the
public and so on. Shareholders, as equity holders,
attach importance to the long-term development of
enterprises. Carbon disclosure can prevent
punishment for failing to comply with carbon
emission requirements, which will affect long-term
development. Therefore, shareholders expect to
reduce risks and require lower return on investment.
As the supplier of funds, creditors can evaluate the
environmental legitimacy and measure the future
repayment ability of enterprises through carbon
information disclosure. When the creditor's loan
collection risk is reduced, the required capital income
also decreases. As product buyers, the public's low-
carbon business information will increase their
positive judgment on high-quality and environmental
protection of products, so as to expand consumer
demand, improve corporate cash flow, reduce
external borrowing, and indirectly reduce financing
costs (Zhou, Zhou, et al, 2018).
H1: the higher the level of carbon information
disclosure, the lower the financing cost of enterprises.
2.1.2 The Relationship Between Carbon
Information Disclosure Level and
Organizational Reputation
Information asymmetry theory holds that there is
information asymmetry between enterprises and
investors. In order to reduce the adverse effects of
information asymmetry before and after the event,
enterprises actively transmit internal information to
the outside world to improve their reputation. On the
one hand, by disclosing relevant information such as
carbon emission reduction strategy, carbon emission
reduction measures and carbon emission reduction
results, enterprises fill the gaps in investors' efforts
and achievements for low-carbon environmental
protection, so as to effectively alleviate information
asymmetry(Mei, Ge, et al, 2020), avoid value
discount and improve enterprise reputation; On the
other hand, the higher the level of carbon information
disclosure, which reflects the higher cultural
conservation and moral standards of the enterprise.
The interest motivation of the management to conceal
bad news is relatively low, and the transparency level
of corporate governance is high, so as to establish a
good image of enterprise integrity and responsibility
and improve the reputation of the enterprise.
Accordingly, hypothesis 2 is put forward.
H2: the higher the level of carbon information
disclosure, the better the reputation of the
organization.
The Impact of Carbon Information Disclosure Level on Enterprise Financing Cost in the New Economy: Research on the Mediating Effect
of Organizational Reputation
787

2.1.3 Mediating Role of Organizational
Reputation
As a reflection of the interactive relationship between
enterprises and investors, carbon information
disclosure actively transmits internal information to
the outside world, affects the enterprise reputation,
and then affects the financing cost. Under the premise
of information asymmetry, the adverse selection of
investors and the moral hazard of managers are not
conducive to the establishment of a good image of
enterprises. The active disclosure of relevant
information is conducive to avoiding value discount
and improving the reputation of enterprises.
According to reputation theory, reputation has asset
attributes and information attributes (Guan, Zhang,
2019). On the one hand, reputation is an important
intangible asset of enterprises, which can help
enterprises obtain commodity premium and cushion
the negative expectation of cost increase. On the other
hand, reputation is the information carrier in the
signal transmission mechanism. A good reputation
can reduce uncertainty and enhance investor
confidence (Li, Tong, et al 2020), reduce the
necessary rate of return required by investors and
reduce the financing cost of enterprises. Accordingly,
this paper puts forward hypothesis 3.
H3: organizational reputation plays an
intermediary role in the process of the impact of
carbon information disclosure level on enterprise
financing cost.
2.2 Research Design
2.2.1 Sample Selection and Data Source
This paper selects listed companies in all A-share
industries in Shanghai and Shenzhen from 2010 to
2019 as the research sample, and further screens and
arranges the samples: (1) eliminate financial listed
companies; (2) Eliminate abnormal data or ST, * ST
listed companies; (3) Excluding the listed companies
with incomplete data, 3270 effective observations
were finally obtained. The financial data of the
company involved in this paper mainly comes from
guotai'an database (CSMAR). The data in the carbon
information disclosure index system mainly comes
from the social responsibility report, and the scores
are collected by text mining. In order to eliminate the
influence of extreme values, this paper winsorize all
variables at 1% and 99% quantiles.
2.2.2 Variable Design
a). Explained variable - financing cost. Equity
financing and bond financing are the most common
financing methods.
Therefore, this paper uses their weighted average
capital cost to reflect the financing cost of listed
companies, that is, financing cost = (debt / total
capital) * debt cost * (1-corporate income tax rate) +
(net asset value / total capital) * equity cost.
b). Explanatory variable - carbon information
disclosure level.
In the context of the new economy, green and
low-carbon refers to a sustainable development
concept to alleviate the greenhouse effect and reduce
air pollution; The connotation of internal and external
circulation is: a preliminary consensus has been
reached on the connotation of internal circulation,
that is, considering the national boundary of
economic activities, internal circulation refers to the
cycle formed by domestic production, distribution,
circulation and consumption in reproduction
activities and taking meeting domestic demand as the
starting point and foothold (Liu 2020). The
connotation of external circulation has been
continuously improved with the development of the
times. Under the suppression of current international
trade, external circulation is no longer limited to the
"export-oriented" of raw materials and markets in the
past, but refers to the process in which one or more
links in reproduction activities participate in
international value creation (Lu 2020).
Based on the above connotation, this paper
interprets the corporate social responsibility report
and measures it according to the four dimensions of
low-carbon awareness, emission reduction
management, emission reduction performance and
carbon emission verification. Considering that the
internal and external circulation is mainly divided by
the national boundary of reproduction activities, this
paper uses the method of text analysis to mine the
carbon information related to these four dimensions
at home and abroad, So as to reflect the carbon
information disclosure under the new economic
background. The specific steps are as follows:
first, data acquisition. Crawl the PDF files of the
social responsibility reports of Listed Companies in
Shanghai and Shenzhen stock markets from 2010 to
2019 through Python software on hexun.com;
Secondly, basic keyword extraction. Since the
format and content of the social responsibility report
disclosed by the same enterprise in different years are
basically the same, and the number of enterprises
disclosing the social responsibility report is
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
788

increasing year by year, taking the 2019 social
responsibility report as the sample, referring to the
carbon information disclosure requirements of
domestic and foreign authorities, the basic key
phrases or phrases related to each secondary index are
preliminarily extracted through manual reading;
Thirdly, word segmentation. Jieba library, an
open source tool library of Python language, is used
to segment Chinese words for the sorted basic
keywords, and regular expressions are constructed to
obtain training corpus. The basic keywords are used
to match the corresponding sentences in txt. The
matched sentences are segmented again, and the
mood auxiliary words, connectives, punctuation
marks, numbers and other stop words without clear
meaning are removed, then we use word2vec
algorithm to expand the most similar word, take top5
as the extension word, and add the word to the
existing category, so as to expand the keyword.
Finally, summarize the scores. Use the expanded
keywords to match the responsibility report to obtain
the corresponding score: when the enterprise
discloses domestic relevant carbon information, it is
assigned 1 score, and when it discloses international
relevant carbon information, it is assigned 2 score,
otherwise it is 0 score, and then sum up all scores.
The total score of the index system is 24 points. The
carbon information disclosure level index can be
obtained by dividing the score obtained by each
company by the total score. At the same time, in order
to ensure the reliability of the data results, this paper
uses manual reading to score again to eliminate major
errors.
Table 1: Carbon information disclosure indicator system in the context of the new economy.
First level
indicator
Secondary indicators Indicator meaning Scoring
Low carbon
awareness
Energy saving and
emission reduction
concept
Disclosure of green and low-carbon development
in the corporate spirit and values, and the concept
of becoming a first-class enterprise
1 point is
assigned to
carbon
information
related to the
country, and 2
points are
assigned to
carbon
information
related to the
world.
Emission
reduction
management
Functional
organization
Set up energy-saving and emission-reduction
leading groups, energy-saving committees and
other functional organizations
Management System
Develop and implement management systems
such as energy saving and emission reduction
documents and manuals
Publicity and
education
Adopt management measures such as publicity
and education
Emission
reduction
performance
Economic
performance
Gain economic performance from selling low-
carbon products and obtaining tax incentives
Environmental
performance
Environmental performance such as reduction in
COD emissions
Social performance
Obtained social performance such as the honorary
title of energy saving and emission reduction
Carbon
Assurance
Energy-saving
management system
certification
Through environmental management system or
energy management system
c) Intermediary variable - organizational
reputation. Referring to the practices of Zhen HX and
Wang S (2021), according to the public's evaluation
of corporate reputation, this paper selects 14
corporate reputation evaluation indexes, calculates
the corporate reputation score by factor analysis
method, and then sorts the scores from low to high,
divides them into 10 groups, and assigns them l to 10
in turn.
d) Control variables. At the level of corporate
governance, control the size and age of enterprises.
At the level of company performance, control the
asset liability ratio, return on assets, operating cash
flow and operating income growth rate. Because the
capital return rate and financing cost of enterprises
are different in different industries and years, this
paper introduces industry and year variables to
control. The specific description of variables is
shown in Table
2.
The Impact of Carbon Information Disclosure Level on Enterprise Financing Cost in the New Economy: Research on the Mediating Effect
of Organizational Reputation
789

Table 2: Variable definition table.
Variable Variable name Variable definitions
Explained variable
Financing costs(𝑊𝐴𝐶𝐶)
Financing cost = (debt/total capital) * cost of debt *
(1- corporate income tax rate) + (net asset
value/total capital) * cost of equity
Explanatory variable
Level of carbon information
disclosure(𝐶𝐼𝐷𝐿)
Calculate the score from the carbon information
disclosure indicator system
Intermediary variable
Organizational reputation
(CR)
Build reputation system, calculate scores and assign
values
Control variables
Enterprise size(𝑆𝐼𝑍𝐸)
Natural logarithm of total assets at the end of the
period
Enterprise age(𝐴𝐺𝐸)
Years of listing
The asset
–
liability ratio
(𝐿𝐸𝑉)
Total liabilities at the end of the period/Total assets
at the end of the period
Asset yield(𝑅𝑂𝐴)
Net profit/average total assets
Operating cash flow(𝐶𝐹𝑂)
Net cash flow from operating activities/total assets
at the end of the period
Operating income growth rate
(𝑂𝐼𝐺𝑅)
Business revenue growth this year/previous year
business revenue
Industry(𝐼𝑁𝐷)
virtual variable
Year(𝑌𝐸𝐴𝑅)
virtual variable
2.2.3 Model Design
In order to test the relationship between carbon
information disclosure and enterprise financing cost
and the intermediary role of organizational reputation
between carbon information disclosure and financing
cost, this paper constructs the following three
regression models with reference to the intermediary
effect analysis method of Wen Zhonglin et al. (2005).
𝑊𝐴𝐶𝐶
,
=𝛼
+𝛼
𝐶𝐼𝐷𝐿
,
+𝛼
𝑆𝐼𝑍𝐸
,
+𝛼
𝐴𝐺𝐸
,
+
𝛼
𝐿𝐸𝑉
,
+𝛼
𝑅𝑂𝐴
,
+𝛼
𝐶𝐹𝑂
,
+𝛼
𝑂𝐼𝐺𝑅
,
+
∑
𝐼𝑁𝐷 +
∑
𝑌𝐸𝐴𝑅 + 𝛼
,
(1)
𝐶𝑅
,
=𝛽
+𝛽
𝐶𝐼𝐷𝐿
,
+𝛽
𝑆𝐼𝑍𝐸
,
+𝛽
𝐴𝐺𝐸
,
+
𝛽
𝐿𝐸𝑉
,
+𝛽
𝑅𝑂𝐴
,
+𝛽
𝐶𝐹𝑂
,
+𝛽
𝑂𝐼𝐺𝑅
,
+
∑
𝐼𝑁𝐷 +
∑
𝑌𝐸𝐴𝑅 + 𝛽
,
(2)
𝑊𝐴𝐶𝐶
,
=𝛾
+𝛾
𝐶𝐼𝐷𝐿
,
+𝛾
𝐶𝑅
,
+𝛾
𝑆𝐼𝑍𝐸
,
+
𝛾
𝐴𝐺𝐸
,
+𝛾
𝐿𝐸𝑉
,
+𝛾
𝑅𝑂𝐴
,
+𝛾
𝐶𝐹𝑂
,
+𝛾
𝑂𝐼𝐺𝑅
,
+
∑
𝐼𝑁𝐷 +
∑
𝑌𝐸𝐴𝑅 + 𝛾
,
(3)
3 RESULTS& DISCUSSION
3.1 Descriptive Statistics
Table 3 shows the descriptive statistical results of the
main variables. The average value of financing cost
is 0.093, the minimum value is 0.018 and the
maximum value is 0.640, indicating that there are
great differences in financing costs among different
sample enterprises. The average carbon information
disclosure level is 0.227, indicating that the carbon
information disclosure level of the sample enterprises
is generally low, and the minimum value is 0 and the
maximum value is 0.375, indicating that there are
great differences in the carbon information disclosure
level among the sample enterprises. The average
values of domestic carbon information disclosure
level and international carbon information disclosure
level are 0.151 and 0.076 respectively, indicating that
the domestic carbon information disclosure level of
the sample enterprises is higher than the international
carbon information disclosure level. The median of
organizational reputation are 5, indicating that the
sample enterprises have good reputation.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
790
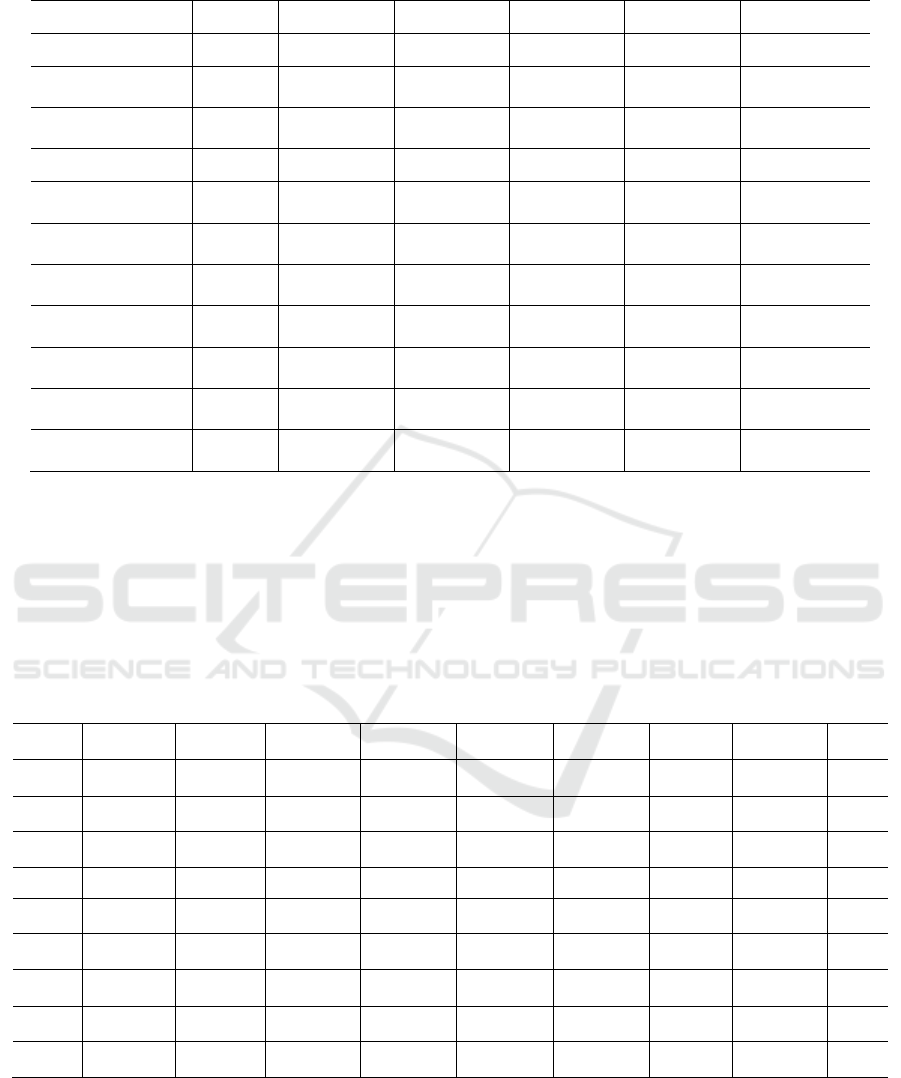
Table 3: Descriptive statistics of main variables.
𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒
N Mean SD Min Median Max
𝑊𝐴𝐶𝐶
3270 0.093 0.074 0.018 0.079 0.640
𝐶𝐼𝐷𝐿
3270 0.227 0.082 0 0.250 0.375
𝐷𝐶𝐼𝐷𝐿
3270 0.151 0.061 0 0.167 0.250
𝑁𝐶𝐼𝐷𝐿
3270 0.076 0.044 0 0.083 0.167
CR 3270 5.468 2.873 1 5.000 10
𝑆𝐼𝑍𝐸
3270 23.266 1.407 20.555 23.147 27.028
𝐴𝐺𝐸
3270 13.069 6.359 1 14 26
𝐿𝐸𝑉
3270 0.487 0.196 0.063 0.502 0.857
CFO 3270 0.058 0.068 -0.131 0.057 0.250
𝑅𝑂𝐴
3270 0.059 0.048 0.002 0.046 0.236
𝑂𝐼𝐺𝑅
3270 0.182 0.289 -0.351 0.128 1.573
3.2 Correlation Analysis
Table 4 shows the Pearson correlation analysis results
between the main variables. The level of carbon
information disclosure is significantly negatively
correlated with the financing cost at the level of 5%,
and the correlation coefficient is -0.044, which
preliminarily verifies the hypothesis H1. There is a
significant correlation between organizational
reputation and carbon information disclosure level,
and there is also a significant correlation between
most control variables and financing cost. The
absolute values of correlation coefficients among
variables are less than 0.8, indicating that there is no
collinearity problem among variables.
Table 4: Correlation analysis results between variables.
𝑊𝐴𝐶𝐶 𝐶𝐼𝐷𝐿
CR
𝑆𝐼𝑍𝐸 𝐴𝐺𝐸 𝐿𝐸𝑉 𝐶𝐹𝑂 𝑅𝑂𝐴 𝑂𝐼𝐺𝑅
𝑊𝐴𝐶𝐶
1
𝐶𝐼𝐷𝐿
-0.044** 1
CR -0.032* 0.051* 1
𝑆𝐼𝑍𝐸
-0.058*** 0.037** 0.758*** 1
𝐴𝐺𝐸
0.023 -0.008 0.102*** 0.298*** 1
𝐿𝐸𝑉
-0.141*** -0.022 0.333*** 0.592*** 0.242*** 1
𝐶𝐹𝑂
0.100*** -0.000 0.172*** -0.044** -0.021 -0.247*** 1
𝑅𝑂𝐴
0.158*** -0.027 0.148*** -0.247*** -0.154*** -0.471*** 0.465*** 1
𝑂𝐼𝐺𝑅
-0.028 -0.014 0.042** 0.005 -0.071*** 0.095*** -0.018 0.155*** 1
Note: ***, **, * indicate significant at the level of 1%, 5%, and 10%, respectively. The t value is in parentheses.
The Impact of Carbon Information Disclosure Level on Enterprise Financing Cost in the New Economy: Research on the Mediating Effect
of Organizational Reputation
791
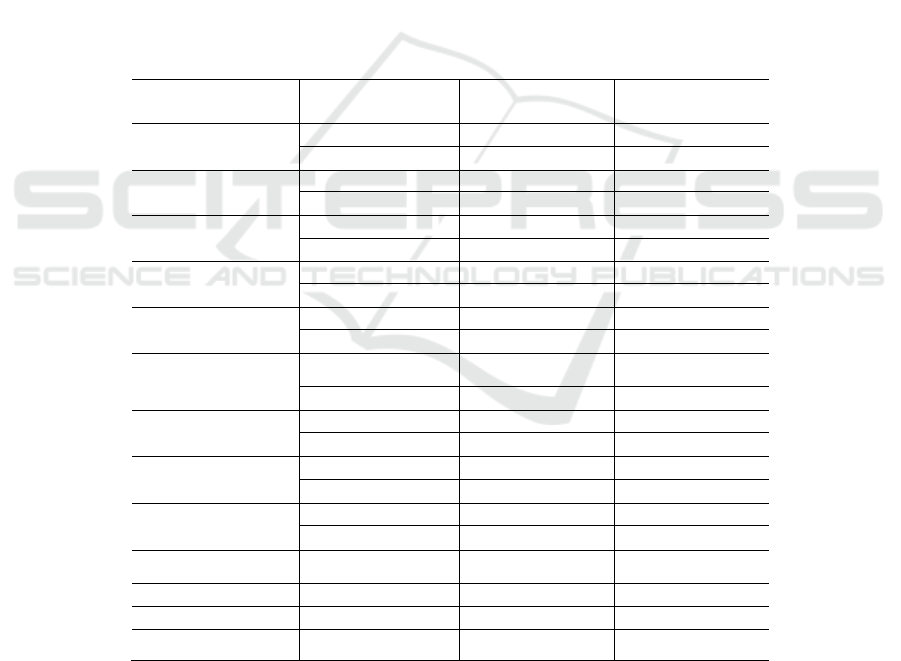
3.3 Multiple Linear Regression
Analysis
Column 2 of table 5 reports the empirical results of
the impact of carbon information disclosure level on
corporate financing costs. It can be seen that the
regression coefficient of carbon information
disclosure level in model (1) is significantly negative
at the level of 1%, which supports hypothesis 1, that
is, the higher the carbon information disclosure level,
the lower the financing cost, indicating that under the
new economic background, the high-level carbon
information disclosure formed by disclosing
enterprises' participation in domestic and
international carbon governance can reduce the
financing cost of companies.
Column 3 of table 5 reports the empirical results
of the impact of carbon information disclosure level
on organizational reputation. It can be seen that the
regression coefficient of carbon information
disclosure level in model (2) is significantly positive
at the level of 1%, which supports hypothesis 2, that
is, the higher the level of carbon information
disclosure, the better the organizational reputation,
indicating that the active disclosure of enterprises'
efforts for carbon emission reduction at home and
abroad is conducive to improving the level of carbon
information disclosure and winning a good
organizational reputation.
Column 4 of table 5 reports the empirical results
of the intermediary role of organizational reputation.
It can be seen that in model (3), the regression
coefficient of carbon information disclosure level
CIDL is significantly negative at the level of 1%, and
the regression coefficient of organizational reputation
Cr is significantly negative at the level of 5%,
indicating that organizational reputation plays an
intermediary role in the relationship between carbon
information disclosure level and financing cost.
Table 5: regression results of the relationship between carbon information disclosure level and financing cost.
𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒
Model (1)
WACC
Model (2)
CR
Model (3)
WACC
𝐶𝐼𝐷𝐿
-0.052*** 1.167*** -0.050***
(-3.291) (3.585) (-3.126)
CR
-0.002**
(-2.555)
𝑆𝐼𝑍𝐸
0.001 1.746*** 0.005**
(0.653) (63.554) (2.344)
𝐴𝐺𝐸
0.001*** -0.046*** 0.001***
(3.339) (-9.687) (2.861)
𝐿𝐸𝑉
-0.040*** 0.451** -0.039***
(-3.859) (2.123) (-3.764)
𝐶𝐹𝑂
0.042* 1.031** 0.044*
(1.799) (2.168) (1.897)
𝑅𝑂𝐴
0.135*** 20.205*** 0.180***
(3.657) (26.721) (4.402)
𝑂𝐼𝐺𝑅
-0.000 -0.287*** -0.001
(-0.055) (-2.998) (-0.190)
𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
0.032 -36.400*** -0.049
(0.916) (-51.406) (-1.042)
IND Yes Yes Yes
YEAR Yes Yes Yes
𝑁
3270 3270 3270
2
R
0.072 0.742 0.073
Note: ***, **, * indicate significant at the level of 1%, 5%, and 10%, respectively. The t value is in parentheses.
3.4 Robustness Test
In order to test the robustness of the empirical results,
this paper uses the practice of Wu XB et al. (Wu, et
al, 2017) and adopts "debt financing cost * asset
liability ratio + equity financing cost * (1-asset
liability ratio)" (ACOC) as an alternative variable of
financing cost (WACC). After testing, the empirical
results are basically consistent with the previous text,
indicating that it is robust.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
792

Table 6: Robustness test.
𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒
Model (1)
ACOC
Model (2)
CR
Model (3)
ACOC
𝐶𝐼𝐷𝐿
-0.050*** 1.167*** -0.048***
(-2.895) (3.585) (-2.749)
CR
-0.002**
(-2.243)
𝑆𝐼𝑍𝐸
0.001 1.746*** 0.005**
(0.816) (63.554) (2.220)
𝐴𝐺𝐸
0.001*** -0.046*** 0.001***
(4.056) (-9.687) (3.621)
𝐿𝐸𝑉
-0.033*** 0.451** -0.032***
(-2.872) (2.123) (-2.788)
𝐶𝐹𝑂
0.062** 1.031** 0.064**
(2.436) (2.168) (2.522)
𝑅𝑂𝐴
0.129*** 20.205*** 0.171***
(3.189) (26.721) (3.844)
𝑂𝐼𝐺𝑅
-0.003 -0.287*** -0.004
(-0.665) (-2.998) (-0.783)
𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
0.018 -36.400*** -0.059
(0.478) (-51.406) (-1.157)
IND Yes Yes Yes
YEAR Yes Yes Yes
𝑁 3270 3270 3270
2
R
0.059 0.742 0.060
Note: ***, **, * indicate significant at the level of 1%, 5%, and 10%, respectively. The t value is in parentheses.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In order to explore whether corporate carbon
disclosure can reduce financing costs, this paper
analyzes the mechanism based on stakeholder theory,
information asymmetry theory, signal transmission
theory and reputation theory, excavates domestic and
international carbon information from the four
dimensions of low-carbon awareness, emission
reduction management, emission reduction
performance and carbon emission assurance, and
constructs the evaluation system of carbon
information disclosure level, Taking the listed
companies that issued social responsibility reports
from 2010 to 2019 as a sample, this paper discusses
the impact of carbon disclosure level on corporate
financing cost, and studies the intermediary role of
organizational reputation in the relationship between
carbon information disclosure level and financing
cost. Research findings:(1) The level of carbon
information disclosure of listed companies needs to
be improved. The disclosure content is not perfect.
Most companies tend to disclose domestic carbon
information and lack international carbon
information; The disclosure methods are not unified,
the disclosure process is not standardized, and the
comparability of carbon information is poor. (2)
Improving the level of carbon information disclosure
is conducive to improving the reputation of the
organization, so as to reduce the financing cost. A
The Impact of Carbon Information Disclosure Level on Enterprise Financing Cost in the New Economy: Research on the Mediating Effect
of Organizational Reputation
793

high level of carbon information disclosure can
reflect the environmental responsibility
consciousness and environmental risk management
level of listed companies, establish a good image,
improve corporate social reputation and reduce
corporate financing costs.
In order to improve the carbon information
disclosure level of Chinese enterprises, we should
pay attention to the following points:(1) The
government should speed up the construction of
carbon information disclosure regulations and
enhance the level of carbon information disclosure of
enterprises. Refine carbon information disclosure
requirements or separately issue carbon information
disclosure standards to clearly specify the content of
carbon information disclosure; Establish an official
platform for carbon information disclosure, conduct
disclosure at a unified time and place, and standardize
the disclosure process. (2) Listed companies should
improve the level of carbon information disclosure
and give full play to the financing cost advantage it
brings to enterprises. In terms of disclosure content,
we should seriously follow the relevant guidelines at
home and abroad to achieve domestic and
international standards; In terms of disclosure
methods, a separate social responsibility report is
published on the enterprise's official website to
establish a good corporate image and enhance the
organization's reputation, so as to reduce the
financing cost.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was financially supported by The National
Natural Science Foundation of China (71971071).
REFERENCES
Guan KL., Zhang R., (2019) Corporate reputation and
earnings management: effective contract view or rent-
seeking view [J] Accounting research, (01): 59-64.
Lee S Y., Park Y S., Klassen R D . (2015) Market responses
to firms' voluntary climate change information
disclosure and carbon communication[J]. Corporate
Social Responsibility & Environmental Management,
22(1):1-12.
Li XD., Tong X., et al., (2020) Reputation mechanism,
social trust and shared economic development -- an
analysis based on the sample data of 70 cities in China
[J] Business research, (11): 35-42.
Liu ZB. (2020) Seeking the new logic of reshaping chinese
economic cycle in domestic and foreign [J].
Exploration and Free Views, (07):42-49+157-158.
Lu JY. (2020) Analyzing the “DualCirculation”
development pattern from the perspective of value
creation [J]. Contemporary Economic Management,
42(12): 8-15.
Ma W., Gai YX. (2019) Corporate life cycle, carbon
information. disclosure and financing constraints:
empirical evidence based on heavy pollution
industries[J]. Journal of Industrial Technological
Economics, 303(01):109-116.
Mei XH., Ge Y., et al., (2020) Research on the impact
mechanism of environmental legitimacy pressure on
enterprise carbon information disclosure [J] Soft
science ,34 (08): 78-83.
Wen SB., Zhou LL. (2017) The influencing mechanism of
carbon disclosure on financial performance--“inverted
u-shaped” moderating role of media governance [J].
Management Review, 29(11): 183-195.
Yang J., Zhang M., et al. (2020) Carbon information
disclosure, environmental regulatory pressure and debt
financing costs——empirical data from chinese a-share
listed companies in the high carbon industry[J]. Journal
of Nanjing University of Technology (Social Science
Edition), 19 (06):86-98+112.
Zhou B., Han L. (2020) Land Finance, endogenous money
and corporate financing cost--evidence from the data of
chinese listed companies[J] Journal of Shanxi
University of Finance and Economics, 42(12):53-67.
Zhou, ZF., Zhou, H., et al., (2018) Carbon disclosure,
financial transparency, and agency cost: Evidence from
Chinese manufacturing listed companies. [J]Emerging
Markets Finance & Trade, 54(12):2669-2686.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
794
