
Impact of BOPS and ES on Demand and Profitability: Theoretical
Models and Simulation Analysis
Jinrong Liu and Haitao Sun
School of Economics and Trade, Shanghai Urban Construction Vocational College, Shanghai, China
Keywords: BOPS, ES, Omnichannel, Demand Allocation, Profitability.
Abstract: With the development of information technology and mobile e-commerce, more and more retailers are
beginning to provide consumers with convenient buy online and pickup in store (BOPS) shopping mode.
Online channel often results in high return rates due to lack of product experience, while retailers can increase
consumer perceive value by providing experience services (ES) to increase their purchases. However, the
provision of BOPS and ES will incur certain operating costs. This paper establishes four profit models under
different BOPS opening strategies and ES service offering strategies. Then, the study analyzes and compares
the impacts of BOPS and ES on retailers' demand allocation and profitability. Finally, the simulation test is
carried out by using MATLAB software. The results show that when ES is not provided before or after
opening the BOPS channel, or ES is only provided after opening the BOPS channel, if the inconvenience of
BOPS channel or online return rate is low, the opening of BOPS can reduce the online demand and increase
the total demand and profit; when ES is provided before opening the BOPS channel and ES is not provided
after opening the BOPS channel, the store demand, total demand and total profit will be reduced; when ES is
not provided before opening the BOPS channel and ES is provided after opening the BOPS channel, the total
demand and total profit increase more.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid development of mobile Internet and
O2O e-commerce, online and offline integration is
increasing, and there is an emerging focus on
“omnichannel retailing” that aims to provide
customers with a seamless shopping experience
through all available shopping channels (Bell 2014,
Gallino 2014, Moreno 2014, Brynjolfsson 2013, Hu
2013, Rahman 2013, Rigby 2011). Among all
omnichannel fulfillment initiatives, the BOPS mode
that allows customers to buy online and pick up in
store is regarded as the most important in
omnichannel retailing. For example, Walmart, Best
Buy, Uniqlo, and KFC have all implemented BOPS.
Under the online channel, the customer places an
order online first, and the retailer delivers the goods
to the consumer's home; under the offline store
channel, the customer experience the product directly
in the store, then places the order and picks it up to
home. Different from the first two shopping modes,
in the BOPS mode, consumers first place an order
online and then pick up the goods at the selected
physical store. Therefore, the BOPS omni-channel
mode will bring new traffic and generate new orders
when consumers pick up goods in offline store. Due
to the lack of product experience services, the return
rate of online channel is often high, which brings
great losses to retailers. Especially products that need
to be tried on and highly personalized products, such
as fashion clothing, shoes and hats, cosmetics, etc. To
this end, many retailers are starting to offer the
ultimate experience service to customers in stores to
improve consumers' perceived value of products and
further enhance their purchase willingness and
purchase conversion rates (Liu 2021, Long 2021, Hu
2021, Xu 2021). For example, Uniqlo allows users to
enhance the brand’s awareness and influence while
enhancing the user experience with merchandise
display, personnel training, digital experience tools,
and the final scan code payment. Zara stores enhance
customers’ shopping experience with automated
click-to-carry, self-checkout, and RFID interactive
fitting mirrors. In the “Shoes HOME+” of Red
Dragonfly, the intelligent retail terminal realizes
three-dimensional foot measurement, big data
analysis, product intelligent interaction, and product
Liu, J. and Sun, H.
Impact of BOPS and ES on Demand and Profitability: Theoretical Models and Simulation Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0011359800003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 947-955
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
947

experience and personalized customization to
enhance consumers' multilevel product experience.
However, the opening of the BOPS channel
requires the cooperation and coordination of online
and offline channels, including the connection of
online and offline electronic systems, the increase of
store service personnel and commodity inventory
service capabilities, the distribution of benefits
between different departments, etc. The provision of
ES services also requires a certain amount of
investment in people, money, equipment and
facilities. Both of them will bring certain operating
costs to retailers, and will inevitably have a certain
impact on existing channels, demand and profits.
Therefore, in this paper, we study the impact of BOPS
and ES on the demand allocation and profitability of
brand retailers in the following four situations: 1) ES
is not provided before opening the BOPS channel; 2)
ES is not provided after opening the BOPS channel;
3) ES is provided before opening the BOPS channel;
4) ES is not provided after opening the BOPS
channel, and then make the best choice.
2 DECISION MODEL
2.1 Problem Description
A retailer sells products to customers with three
alternative shopping channels: online channel
(abbreviated as O channel), store channel
(abbreviated as S channel) and BOPS channel.
We have already described similar problems in
our previous paper (Liu 2021, Long 2021, Hu 2021,
Xu 2021), so we won’t repeat them here.
The notations used in our models and their
definitions are shown in Table 1 below.
Table 1: Notations and Definitions.
Figure 1. Notation Figure 2. Definition
p
Unit product price
c
Unit product cost
o
Consumer's shopping cost under O
channel
h
Shopping inconvenient costs under S
channel
l
The inconvenience of BOPS channel
relative to S channel (
01l<<
)
θ
Online return rate (
01
θ
<<
)
s
Customer perceive value of ES
w
A cross-selling net profit from each
unit of store demand or BOPS
demand
e
Cost factor of ES (
01e<<
)
v
Product perceived value
i
U
Consumer utility under
i
channel (
, , i O S and BOPS=
)
ij
U
Consumer utility under
i
channel
in case
j
(
, , i O S and BOPS=
,
1, 2, 3 , 4j =
)
ij
Q
The demand under
i
channel in
case
j
(
, , i O S and BOPS=
,
1, 2, 3, 4j =
)
j
Q
The total demand in case
j
(
1, 2, 3 , 4j =
)
j
Π
The total profit in case
j
(
1, 2, 3 , 4j =
)
According to the problem description and the
notations and their definitions in Table 1, we can
obtain the consumer utility functions under the three
channels of O, S, and BOPS as the following (Liu
2021, Long 2021, Hu 2021, Xu 2021, Chiang 2002,
Chhajed 2003, Hess 2003, Cao 2016, So 2016, Yin
2016):
(1 )( ) (1 )
O
Uvpo
θθ
=− − −+
, (1)
S
Uvphs=− −+
, (2)
(1 )( )
BOPS
Uvpslh
θ
=− −+ −
. (3)
For ease of analysis, we assume that both
v and
h
are uniformly distributed on [0, 1].
2.2 Model Building
2.1.1 Case 1: ES Is Not Provided before
Opening the BOPS Channel
In case 1, the retailer only has two channels of O and
S to sell products, and he does not do any extra ES
efforts in stores, i.e.,
0s =
. Thus, consumer utility
functions are as following:
1
(1 )( ) (1 )
OO
UU vp o
θθ
==− −−+
, (4)
1S
Uvph=− −
. (5)
According to the distribution assumption of
v
and
h
, we can obtain the demand functions under
the two channels of O and S as following (Liu 2021,
Long 2021, Hu 2021, Xu 2021, Chiang 2002,
Chhajed 2003, Hess 2003, Cao 2016, So 2016, Yin
2016):
1
11
= (1 )[1 (1 ) (1 ) ]
12 21
O
Qpo p o
θθ θθ
θθ
++
−− − − −−
−−
,
(6)
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
948

2
1
(1 ) 1 1
(2 2 ) (1 )
2(1 ) 1 2 1
S
o
Qpopo
θθθθ
θθ θ
++ +
=−−+−−
−− −
.
(7)
Then, the total demand is as follows:
2
111
111
= 1 ( )
121
OS
QQ Q p o o
θθ
θθ
++
+=−− +
−−
.
(8)
In this case, because the retailer does not offer any
extra ES efforts, he does not pay the ES cost.
However, customers who come to the store will bring
traffic and generate new orders due to cross-selling.
The retailer obtains a net profit
w from each unit of
S demand (Gao 2017, Su 2017), thus, the total profit
is obtained as follows:
11 1
2
2
() ( )
111
( )[1 ( ) ]
121
(1 ) 1 1
[ (2 2 ) (1 ) ]
2(1 ) 1 2 1
OS
pcQ pcwQ
pc p o o
o
wpopo
θθ
θθ
θθθθ
θθ θ
Π= − + − +
++
=− −− +
−−
++ +
+−−+−−
−− −
.
(9)
2.1.2 Case 2: ES Is Not Provided after
Opening the BOPS Channel
In case 2, the retailer has three channels of O, S, and
BOPS to sell products, but he does not offer any extra
ES efforts in stores, i.e.,
0s =
. Thus, consumer
utility functions are obtained as following:
2
(1 )( ) (1 )
OO
UU vp o
θθ
==− −−+
,
(10)
2S
Uvph=− −
, (11)
2
(1 )( )
BOPS
Uvplh
θ
=− − −
. (12)
Similar to Case 1, the demand functions under the
three channels of O, S, and BOPS, and the total
demand function can be obtained as following:
2
2
11 (1)(1)
=(1 )(1 ) [1 ]
12
O
l
Qpo o p o
ll
θθθ θ
θθ
++ −+
−− − − −−
−
,(13)
2
2
(1 ) (1 )(1 )
=[22 ]
2
(1 )(1 )
[1 ]
2
S
ol
Qpo
ll
l
po
l
θθ
θ
θθ
θ
+−+
−−
−+
+−−
,
(14)
22
2
(1 ) 1 1
()
21
BOPS
ol
Q
ll
θ
θθ
+−
=−
−
, (15)
22
222 2
1(1)
1
12(1)
O S BOPS
o
QQ Q Q p o
l
θθ
θθ
++
=++ =−− +
−−
.
(16)
In this case, because the retailer does not offer any
extra ES, he does not pay the ES cost. However,
whether customers who go to the store to try on and
place an order through S channel, or customers who
pick-up the goods through BOPS channel, they will
bring traffic to the store and generate new orders and
a net profit
w . Thus, we obtain the retailer’s profit
function as follows:
22 2 2
22
2
() ( ) ( )
1(1) (1)
( )[1 ] [
12(1) 2
111
(2 2 ) (1 ) ]
12
O S BOPS
pcQ pcwQ pcwQ
oo
pc p o w
ll
l
po p o
l
θθ θ
θθ
θθ θ
θθ
Π= − + − + + − +
++ +
=− −− + +
−−
+−+
−− + −−
−
.
(17)
2.1.3 Case 3: ES Is Provided before Opening
the BOPS Channel
In case 3, the retailer only has two channels of O and
S to sell products, but he does some extra ES effort in
stores, i.e.,
0s ≠
. Thus, consumer utility functions
are as following:
3
(1 )( ) (1 )
OO
UU vp o
θθ
==− −−+
(18)
3S
Uvphs=− −+
. (19)
Similar to Case 1, the demand functions under the
two channels of O and S, and the total demand
function can be obtained as following:
3
11
= (1 )[1 (1 ) (1 ) ]
1221
O
Qpos p o
θθ θθ
θθ
++
−− −− − −−
−−
,
(20)
2
3
1111
(1 )[ (1 ) (1 ) ] ( )
12 2121
S
Qposp o os
θθ θθ θ
θθθ
+++
=−− + − +− + +
−−−
, (21)
2
333
111
= 1 ( )
121
OS
QQ Q p o os
θθ
θθ
++
+=−− + +
−−
,
(22)
33 3
2
2
() ( )
111
=( ) [1 ( ) ] ( )
121
1111
{(1 )[ (1 ) (1 ) ] ( ) }
12 2121
OS
pcQ pceswQ
pc p o os wes
pos p o os
θθ
θθ
θθ θθ θ
θθθ
Π= − + − − +
++
−−− + ++−
−−
+++
−− + − +− + +
−−−
.
(23)
In this case, the retailer provides ES to customers
of S channel, and customers who go to the store to try
on and place an order through S channel will bring
traffic to the store and generate new orders and a net
profit
w . Thus, we obtain the total profit function as
Eq. (23).
Impact of BOPS and ES on Demand and Profitability: Theoretical Models and Simulation Analysis
949

2.1.4 Case 4: ES Is Provided after Opening
the BOPS Channel
In case 4, the retailer sells products through three
channels of O, S, and BOPS, and he does some extra
ES effort in stores. Consumer utility functions are
obtained as following:
4
(1 )( ) (1 )
OO
UU vp o
θθ
==− −−+
,
(24)
4S
Uvphs=− −+
, (25)
4
(1 )( )
BOPS BOPS
UU vpslh
θ
==−−+−
.
(26)
Similar to Case 2 and Case 3, the demand and
profit functions can be obtained as following:
4
1(1)(1)
=(1 )[1 ]
1
1(1)(1)
[ (1 ) (1 ) ]
2
1(1)(1)
[1 ]
O
os
Qpo
l
os
pos
l
lo s
ps
l
θθθ
θ
θθ
θθ
θθ
θ
+++−
−− −
−
++−
−−+++−
−+ +−
−+−
,(27)
4
(1 ) (1 ) (1 )[(1 ) (1 ) ]
={1 }
2
1(1)(1)
[ (1 ) (1 ) ]
2
1(1)(1)
[1 ]
S
os los
Qps
ll
os
pos
l
lo s
ps
l
θθ θθ
θ
θθ
θθ
θθ
θ
++− − ++−
−−+
++−
+−+++−
−+ +−
−+−
,
(28)
4
(1 ) (1 )
2
(1 )[(1 ) (1 ) ] (1 )
{ }
1
BOPS
os
Q
l
lo s o
s
l
θθ
θθ θ
θθ
++−
=
−++− +
−−
−
,(29)
444 4
=
1(1)(1)1
1 ( )
121
OSBOPS
QQ Q Q
os
po os
l
θθθθ
θθ
++
+++−+
=− − + +
−−
.
(30)
44 4 4
=( ) ( ) ( )
1(1)(1)1
= ( )[1 ( )]
121
(1 ) (1 ) 1
( ){ (2 2 )
21
1(1)(1)
[ (1 ) (1 ) ]
2
1
[1
O S BOPS
pcQ pceswQ pceswQ
os
pc p o os
l
os
wes ps o
l
os
pos
l
l
ps
θθθθ
θθ
θθ θ
θ
θθ
θθ
θ
Π − +−−+ +−−+
+++−+
−−− + +
−−
++− +
+− − +−
−
++−
+−+++−
−
−+−
(1 ) (1 )
]}
os
l
θθ
++−
.
(31)
3 IMPACT OF BOPS AND ES ON
DEMAND ALLOCATION AND
PROFITABILITY
In this section, we analyze the impact of BOPS and
ES on demand allocation and profitability in four
scenarios.
3.1 No ES is Provided before and after
Opening the BOPS Channel
In this scenario, by comparing the corresponding
demand and profit functions (6) ~ (9) and (13) ~ (17),
the following proposition 1 can be easily obtained.
Proposition 1. If ES is not provided, BOPS
channel has the following effects on the retailer.
(i) The total demand increases by
22
2
(1 ) (1 )
2(1 )
ol
l
θθ
θ
+−−
−
, its demand from the online
channel decreases by
22 2
22
(1 ) (1 )
2(1 )
ol
l
θθ
θθ
+−−
−
, and its
demand from the store channel decreases by
22
(1 ) (1 )
2(1 )
ol
l
θθ
θθ
+−−
−
.
(ii) The total profit increases by
22
2
(1)(1)[(1)( )]
2(1 )
ollwpcwl
l
θθθ θ
θθ
+−−−−+−+
−
.
Furthermore, if
2
3
()[4(3)(1)]
(1 )(1 )[ (1 3 ) (1 ) ]
lpcl
w
ll
θθθ
θθθ
−−−−
>
−− −−−
and
(1 )(3 ) / 4l
θθ
<− − , the increases in total demand
and total profit are negatively correlated with
l
and
positively correlated with
o . The increases in total
profit and total demand are positively correlated with
θ
, and vice versa. These values are both independent
of
s
.
Proposition 1(i) shows the impact of BOPS on the
demand allocations when ES is not offered before and
after opening the BOPS channel. Actually, some
customers will switch from O channel to BOPS
channel to avoid the costs of shipping and waiting
time, and some customers will switch from S channel
to BOPS channel to reduce the inconvenient costs of
finding goods among shelves and waiting for
checkout, thereby reducing the demand from both O
channel and S channel. In addition, this new BOPS
channel can generate new demand that was not
previously available. As a result, the retailer’s total
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
950

demand increases. Proposition 1(ii) shows the
conditions under which the retailer benefits from
opening BOPS channel due to cross-selling.
3.2 No ES is Provided before Opening
the BOPS Channel and ES is
Provided after Opening the BOPS
Channel
In this scenario, by comparing the demand and profit
functions (6) ~ (9) and (27) ~ (31), the following
proposition 2 can be easily obtained.
Proposition 2. If no ES is provided before opening
the BOPS channel and ES is provided after opening
the BOPS channel, BOPS has the following effects
on the retailer.
(i) The total demand increases by
23 2 22
2
(1 ) 2 (1 ) (1 ) (1 ) (1 )
2(1 )
sos o l
l
θθθθθ
θ
−+ − ++ + −−
−
,
its demand from the online channel decreases by
22 2 2 2 2
22
(1 ) [ (1 ) (1 ) 2 (1 )
2(1 )
]lo s s A
l
θθ θ θ
θθ
−− + + −
−
+−
, and its demand from the store channel decreases by
2(1 )
B
l
θθ
−
, when
3222
22
(1 )[ (1 ) 2 (1 )] (1 )
(1 )[ 2 (1 ) ] [ (1 ) 2 (1 )]
oo s s
l
spsoos
θθ θ θ
θθ θ θ
−+ −+−
<
−−++ −
+
++
.
Furthermore, the increase in total demand is
negatively correlated with
l
and positively
correlated with
o and
s
. If
222
2
1)[4 (1)( )(
4(1 )
]oos
o
l
θθ
θ
−−
<
−−
+
, the increase in total
demand is negatively correlated with
θ
, and vice
versa, where
22
(1 )(1 ) (1 ) (1 )Ao l o l p
θθθθ
=+ −− ++ −
,
22
2
(1 )[ (1 ) 2 (1 )]
(1 )[ (1 ) 2 (1 ) ]
Bo l o s
s
ssllp
θθ θ
θθ θ
=−− + + −
+− − −− −
.
(ii) The total profit increases by
2
22
2(1)
lEC
l
lD
θθ
+
−
−
if and only if
(
)
()
2
4/2lD D CE E<− −
, where
22
()(1)( )Cwes osos
θθθ
=− − ++−
,
2
[( )(2 ) ( ) ]( ) (1 )wes pc oso sD
θθθθθ
−−−− +=+−−
22
22
(1 ) [ 2 (1 ) ( )
2 (1 ) (1 ) [( ) (1 )]]
Eoweosop
ws w p o w
s
pc
θθ θθθ
θθθθ
−+−+++−
++ − − − − −
=
+
.
Proposition 2(i) shows the impact of BOPS on the
demand allocations when ES is not offered before
opening the BOPS channel and ES is offered after
opening the BOPS channel. Similar to Proposition 1,
the total demand increases. Proposition 2(ii) shows
the condition for the increase in total profit after
opening the BOPS channel.
3.3 ES is Provided before Opening the
BOPS Channel and no ES is
Provided after Opening the BOPS
Channel
In this scenario, by comparing the demand and profit
functions (13) ~ (17) and (20) ~ (23), the following
proposition 3 can be easily obtained.
Proposition 3. If ES is provided before opening
the BOPS channel and no ES is provided after
opening the BOPS channel, BOPS has the following
effects on the retailer.
(i) If
2
2
2
(1 )
[(1 ) (1
)
]
(1
)
l
os
o
θ
θθ
θ
−
>
++ −
+
, then the total
demand is reduced by
2222 2
2
(1 ) (1 ) (1 ) 2 (1 )
2(1 )
ls o l los
l
θθθ θ
θ
−− + −−+ −
−
. If
22 2 2 2 2
2
2
222
2(1) (1)(1)(1 )(
]
1)
2]
[[
(1 1
]8
)/[ () 2 (1 )
osl slp l
sl l
θθ θ θ θθ
θθ θ θ
−−+−+−
−−
−
−+
>
−
, the online channel demand is reduced by
22 2 22 2 2
22
(1 ) (1 ) 2 (1 ) 2 (1 )(1 )
2(1)
olosl slp
l
θθθθθ θ
θθ
+−−+ −− −−
−
, and the store channel demand is reduced by
22
(2 2 )(1 ) (1 ) (1 )
2(1 )
ls p s o l
l
θθθθ
θθ
−+ −+ + −−
−
.
Furthermore, the reduction in total demand is
positively correlated with
l
and
s
. Only when
l
is greater than a certain threshold, the reduction in
total demand is positively correlated with
o
and
θ
.
(ii) The retailer’s profit is reduced by
222 2
22
(1 )
2(1 )
ow Fl Gl
l
θθ
θθ
−−+
−
, if
22 22
4(1)
2
FF Gow
l
G
θθ
−− −
>
, where
22
(1 )(1 ) [ (2 ) ( ) ]Fo w pc
θθ θ θ
=−+ −−−
,
22
2
(1 ) [( )(1 ) ( ) ]
2 (1 )[( ) (1 )(1 )]
Go wes pc
os p c e p H
θθθ θ
θθ θ
=+ − −−−
−−−−−−−
,
222
(1 ) [( ) 2(1 )( ) (1 ) ]Hs pcws pwes es e p
θθ θ
= − −+ +− −− − −
.
Impact of BOPS and ES on Demand and Profitability: Theoretical Models and Simulation Analysis
951

Proposition 3(i) shows that total demand is
usually reduced, except for a few cases where the
inconvenience of the BOPS channel is extremely low.
Moreover, store channel demand is reduced, and the
online channel demand is reduced under some
conditions. Furthermore, the higher the
l
or
s
, the
more the total demand is reduced. When
l
is
greater than a certain threshold, the higher the
o
or
θ
, the more the total demand is reduced. Proposition
3(ii) shows that the total profit is reduced when the
inconvenience of the BOPS channel exceeds a certain
threshold.
3.4 ES is Provided before and after
Opening the BOPS Channel
In this scenario, by comparing the demand and profit
functions (27) ~ (31) and (20) ~ (23), the following
proposition 4 can be easily obtained.
Proposition 4. If ES is provided before and after
opening the BOPS channel, BOPS has the following
effects on the retailer.
(i) The total demand increases by
2
2
(1 )( )
2(1 )
losos
l
θθθ
θ
−− + + −
−
, its demand from the
online channel decreases by
22
22
()(1)
2(1)
oso s l
l
θθ θ
θθ
++ − −−
−
, and its demand from
the store channel decreases by
2
(1 )( )
2(1 )
losos
l
θθθ
θθ
−− + + −
−
. Furthermore, the
increase in total demand is negatively correlated with
l
and positively correlated with
o
and
s
. If
22
)
4
(3 4 (1 )
l
o
o
s
θθ θ
−+ −
<
−
, the increase in total
demand is negatively correlated with
θ
, and vice
versa.
(ii) If and only if
()(1)
()(1)()
wes
l
wes pc
θ
θθ
−−
<
−−−−
,
the total profit increases by
2
22
(1 )( ) [( )(1 )(1 ) ( )]
2(1 )
lososwesl lpc
l
θθθ θθ
θθ
−− + + − − − − + −
−
, where
( )(1 ) (1 )[( ) ( )(1 )]Jwes l pc wes
θθ θ θ
=− −++ − −− −
.
Proposition 4(i) shows the impact of BOPS on the
demand allocations when ES is offered before and
after opening the BOPS channel. Similar to
Proposition 1, the total demand increases. Proposition
4(ii) shows that the total profit increases after opening
the BOPS channel when the inconvenience of the
BOPS channel within a certain threshold.
Therefore, if ES is provided, the retailer’s
profitability under the three channels of O, S, and
BOPS channel is better than that under the two
channels of O and S when the BOPS channel is
convenient or the online return rate is not very high.
4 COMPARISON AND
SIMULATION ANALYSIS
In this section, we set 0.6p = and
0.3c =
with
different values of
l
, o and
θ
, the value range of
l
is set to [0.3, 0.9], the value range of
θ
is set to
[0.1, 05]. In addition,
0.04o =
indicates that the
shopping costs of the online channel is low, and
0.12o =
, indicates that the shopping costs of the
online channel is high. The comparison and
simulation analysis of the impact of opening the
BOPS channel on demand and profit in the four
scenarios are shown in Fig. 1 to Fig. 4 by using
MATLAB software.
From Fig. 1, we can get the following conclusion
1.
Conclusion 1. When ES is not provided before or
after opening the BOPS channel, or ES is only
provided after opening the BOPS channel, the online
demand will be reduced because
21
0
O
QΔ<
,
41
0
O
QΔ<
,
43
0
O
QΔ<
. Moreover, regardless of
whether ES is provided after opening the BOPS
channel, when ES is not provided before opening the
BOPS channel, the online demand will be reduced
more because
41 43OO
QQΔ<Δ
,
21 23OO
QQΔ<Δ
.
In addition, the opening of the BOPS channel
does not necessarily reduce the online channel
demand due to the lack of ES. As noted in Fig. 1 (a)
and (b), the higher the shopping costs of the online
channel, the more the online channel demand is
reduced.
(a)
0.04o =
(low)
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
952

(b)
0.12o =
(high)
Figure 1: Ccomparison of changes in the online channel
demand Δ𝑄
.
From Fig. 2, the following conclusion 2 can be
obtained.
Conclusion 2. The store demand is definitely
reduced in the scenario where ES is provided before
opening the BOPS channel and no ES is provided
after opening the BOPS channel because
23
0
S
QΔ<
.
(a)
0.04o =
(low)
(b)
0.12o =
(high)
Figure 2: Comparison of changes in the store channel
demand Δ𝑄
.
(a)
0.04o =
(low)
(b)
0.12o =
(high)
Figure 3: Comparison of changes in the total demand Δ𝑄.
Fig. 2 demonstrates that when the inconvenience
of the BOPS channel and the online return rate is not
very high, if ES is provided before opening the BOPS
channel, and regardless of whether ES is provided
after opening the BOPS channel, the store channel
demand will be reduced because
23 43 21 41
0
SSSS
QQQQΔ<Δ<Δ<Δ<
. In addition,
the higher the shopping costs of the online channel,
the more the store channel demand is reduced.
As noted in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4, we can get the
following conclusion 3.
Conclusion 3. After opening the BOPS channel,
when the inconvenience of the BOPS channel and the
online return rate is not high, the increases in the total
demand and total profit in the second scenario are the
largest followed by the fourth scenario because
23 21 43 41
0QQQQΔ < <Δ <Δ <Δ
,
23 21 43 41
0ΔΠ < < ΔΠ < ΔΠ < ΔΠ
.
In addition, regardless of whether ES is provided
before opening the BOPS channel, providing ES after
opening the BOPS channel can increase total demand
and total profit more. It reflects the significant role of
ES. Furthermore, comparing (a) and (b) in Fig. 3 and
Fig. 4, we observe that when the BOPS channel is
more convenient and the online return rate is lower or
the shopping costs of online channel is higher, the
opening of the BOPS channel is more profitable.
Impact of BOPS and ES on Demand and Profitability: Theoretical Models and Simulation Analysis
953
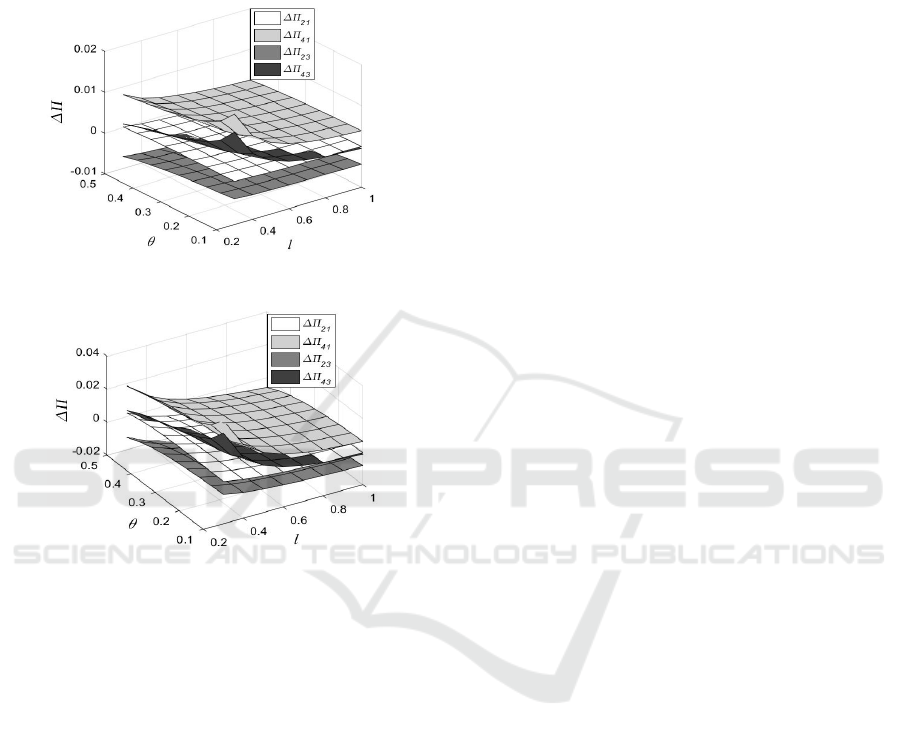
The third scenario is the most special of the four
scenarios. This scenario demonstrates that in the
current new retail era, ES has become increasingly
important and is an inevitable trend to provide
customers with the ultimate experience service to
enhance their competitive advantage.
(a)
0.04o =
(low)
(b)
0.12o =
(high)
Figure 4: Comparison of changes in the total profit ΔΠ.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we present four models to study the
impact of BOPS and ES on demand allocation and
profitability. We find that whether a retailer provides
ES and whether a retailer opens the BOPS channel
depends on the number of stores and product
characteristics of the retailer. The number of physical
stores determines the convenience of the BOPS
channel, the product characteristics determine the
customer's demand for the experience service and the
return rate. Therefore, for daily necessary products,
due to the low online return rate and the high shipping
cost, regardless of whether ES is provided, it is
advisable to open the BOPS channel to increase store
traffic and generate new demand; For fast fashion
clothing, shoes and hats and consumer electronics,
due to the high demand for ES, it is advisable to
provide ES to increase customer purchases regardless
of whether the BOPS channel is open. In the above
two cases, it is more profitable to open the BOPS
channel when the number of stores is large. However,
if the number of stores is small (that is, the delivery
is not convenient), the product lacks features or the
update is slow, then the opening of the BOPS channel
or providing ES will reduce the total demand and total
profit.
This study offers several essential insights for
retailers in omnichannel retailing and helps them
develop successful omnichannel strategies. The
store's ultimate experience service not only increases
the purchase of the store channel and BOPS channel
but also directly and indirectly reduces the total return
rate. Therefore, regardless of whether BOPS is
opened, we recommend retailers to provide ES in the
new retail era centered on consumer experience.
BOPS is a popular fulfillment option among
customers. However, not all products are suitable for
store pick-up, such as large furniture, large appliances
and fresh goods. Therefore, selecting an item suitable
for in store and making corresponding inventory
decisions may be another interesting research
question in the future.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is partially supported by the Philosophy
and Social Science Program of Shanghai (Grant No.
2020BGL014) and Fundamental Research Funds for
the Central Universities, China (Grant No. CUSF-
DHD-2018048).
REFERENCES
D.R. Bell, S. Gallino, and A. Moreno, How to win in an
omnichannel world. 56th ed., vol. 1, MIT Sloan
Manage. Rev. 2014, pp. 45-53.
D. Rigby, The future of shopping. 89th ed., vol. 12, Harvard
Busi. Rev. 2011, pp. 65-76.
E. Brynjolfsson, Y.J. Hu, M.S. Rahman, Competing in the
age of omnichannel retailing. 54th ed., vol. 4, MIT
Sloan Manage. Rev. 2013, pp. 23-29.
F. Gao and X. Su, Omnichannel retail operations with buy-
online-and-pickup-in-store, 63th ed., vol. 8, Manage.
Sci. 2017, pp. 2478–2492.
J. Liu, G. Long, Y. Hu, and H. Xu, Impact of BOPS on
Demand Allocation and Profitability in Omnichannel
E-commerce Retailing with Consideration of
Experience Service, DOI:10.1109/ ECIT52743. 2021.
00016, pp. 40–45.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
954

J. Cao, K. C. So, and S. Yin, Impact of an“online-to-
store”channel on demand allocation, pricing and
profitability, 248th ed., vol. 1, Euro. J. Opera. Res.
2016, pp. 234–245.
W. Y. K. Chiang, D. Chhajed, and J. D. Hess, Direct
marketing, indirect profits: A strategic analysis of dual-
channel supply-chain design. 49th ed., vol. 1, Manage.
Sci. 2003, pp. 1–20.
Impact of BOPS and ES on Demand and Profitability: Theoretical Models and Simulation Analysis
955
